从零解析Qwen3 MoE源码:大模型混合专家系统实现原理详解!
本文深入解析阿里Qwen3 MoE模型的源码实现,从Qwen3MoeForCausalLM到Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock,详细剖析了混合专家系统的工作机制。文章重点介绍了MoE模型中的门控机制(router)和多个专家(experts)的实现,解释了token如何被路由到不同专家进行处理,以及如何通过top-k选择和权重分配实现高效计算。通过源码分析,读者可清晰了解MoE模型相比传
一、背景
温馨提示:一定按文章顺序读,跳读不一定理解,如果有解读不对的地方也欢迎指正,谢谢!!!
废话不多说,咱们开始吧!
源码剖解
剖解Qwen3MoeForCausalLM源码
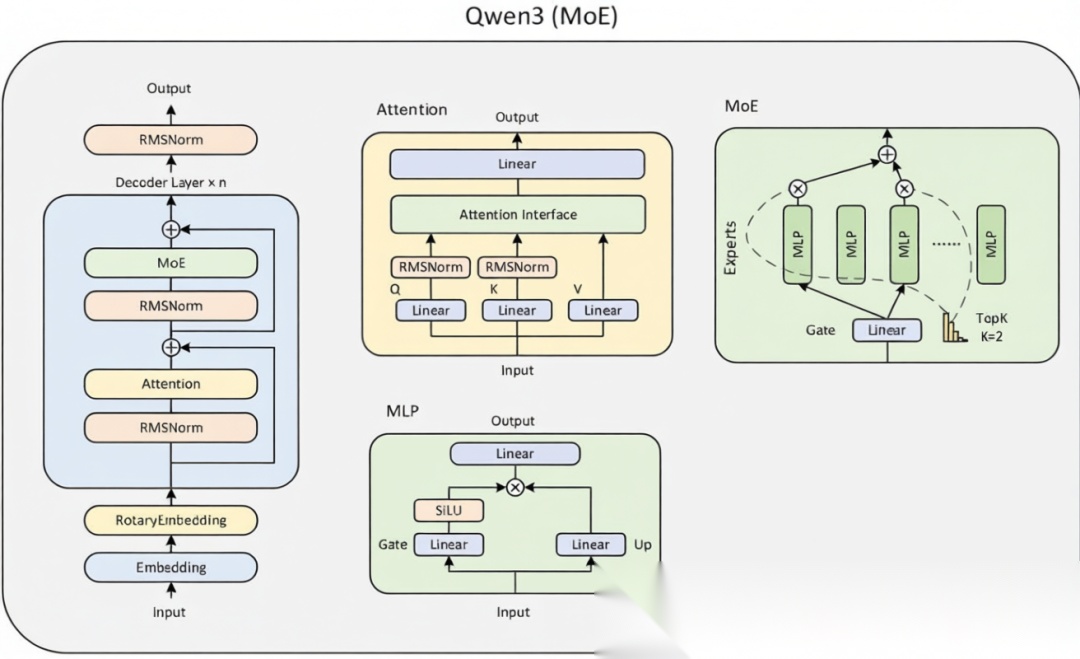
现在我们来看下阿里开源的Qwen3MoE模型怎么实现的?下图是Qwen3MoE开源的代码结构:
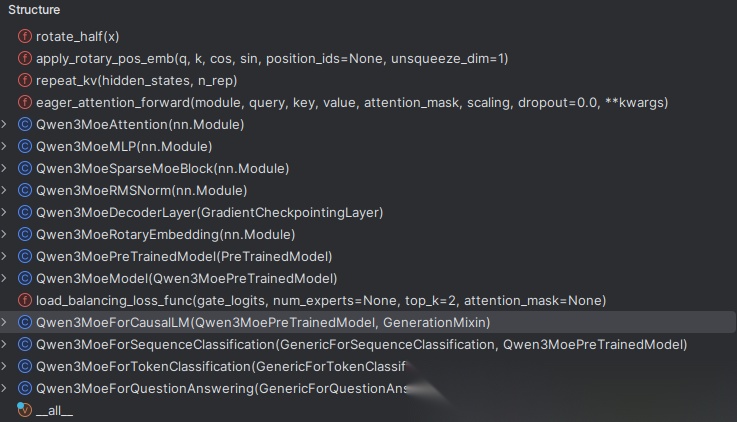
结构图中包含了Attention、MLP、RMSNorm、Trained等模块,我们从则Qwen3MoeForCausalLM类开始一步步解析整个过程,下面为其代码片段,为了更好的理解,整理成一个图,方便理解。
class Qwen3MoeForCausalLM(Qwen3MoePreTrainedModel, GenerationMixin):
_tied_weights_keys = ["lm_head.weight"]
_tp_plan = {"lm_head": "colwise_rep"}
_pp_plan = {"lm_head": (["hidden_states"], ["logits"])}
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
self.model = Qwen3MoeModel(config)
self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False)
self.router_aux_loss_coef = config.router_aux_loss_coef
self.num_experts = config.num_experts
self.num_experts_per_tok = config.num_experts_per_tok
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
@can_return_tuple
@auto_docstring
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_router_logits: Optional[bool] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
logits_to_keep: Union[int, torch.Tensor] = 0,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
) -> MoeCausalLMOutputWithPast:
output_router_logits = (
output_router_logits if output_router_logits is not None else self.config.output_router_logits
)
# decoder outputs consists of (dec_features, layer_state, dec_hidden, dec_attn)
outputs: MoeModelOutputWithPast = self.model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_router_logits=output_router_logits,
cache_position=cache_position,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
# Only compute necessary logits, and do not upcast them to float if we are not computing the loss
slice_indices = slice(-logits_to_keep, None) if isinstance(logits_to_keep, int) else logits_to_keep
logits = self.lm_head(hidden_states[:, slice_indices, :])
loss = None
if labels is not None:
loss = self.loss_function(logits, labels, self.vocab_size, **kwargs)
aux_loss = None
if output_router_logits:
aux_loss = load_balancing_loss_func(
outputs.router_logits,
self.num_experts,
self.num_experts_per_tok,
attention_mask,
)
if labels is not None:
loss += self.router_aux_loss_coef * aux_loss.to(loss.device) # make sure to reside in the same device
return MoeCausalLMOutputWithPast(
loss=loss,
aux_loss=aux_loss,
logits=logits,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values,
hidden_states=outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=outputs.attentions,
router_logits=outputs.router_logits,
)

从上面可以知道以下几个信息:
1、Qwen3MoeForCausalLM继承MixtralForCausalLM
2、创建了Qwen3MoeModel实例
3、config.num_experts需要传入Moe专家数,阿里的Qwen3为:128个experts
4、lm_head输出logits
注意: 因果模型和分类模型主要是因为lm_head的不同,因为分类模型主要是看num_labels的一个概率分布score,而因果模型是看词表的概率分布的最后一行概率值来推断下一词。
# Qwen3MoeForCausalLM
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False)
# Qwen3MoeForSequenceClassification
self.score = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.num_labels, bias=False)
如果你也想通过学大模型技术去帮助就业和转行,可以扫描下方链接👇👇
大模型重磅福利:入门进阶全套104G学习资源包免费分享!

二、剖解Qwen3MoeModel类
如果看了之前我写的手搓Qwen3的文章,这个类是不是很熟悉?大模型的基本所有的代码都是一个模子,难是难在数据、算力、创新。
class Qwen3MoeModel(Qwen3MoePreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3MoeConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id
self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size
self.embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, self.padding_idx)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
)
self.norm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.rotary_emb = Qwen3MoeRotaryEmbedding(config=config)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
@check_model_inputs
@auto_docstring
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
) -> MoeModelOutputWithPast:
if (input_ids is None) ^ (inputs_embeds is not None):
raise ValueError("You must specify exactly one of input_ids or inputs_embeds")
if use_cache and past_key_values is None:
past_key_values = DynamicCache(config=self.config)
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.embed_tokens(input_ids)
if cache_position is None:
past_seen_tokens = past_key_values.get_seq_length() if past_key_values is not None else 0
cache_position = torch.arange(
past_seen_tokens, past_seen_tokens + inputs_embeds.shape[1], device=inputs_embeds.device
)
if position_ids is None:
position_ids = cache_position.unsqueeze(0)
mask_function = create_causal_mask if self.config.sliding_window is None else create_sliding_window_causal_mask
causal_mask = mask_function(
config=self.config,
input_embeds=inputs_embeds,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
cache_position=cache_position,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
# create position embeddings to be shared across the decoder layers
position_embeddings = self.rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids)
for decoder_layer in self.layers[: self.config.num_hidden_layers]:
hidden_states = decoder_layer(
hidden_states,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
attention_mask=causal_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
use_cache=use_cache,
cache_position=cache_position,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = self.norm(hidden_states)
return MoeModelOutputWithPast( # only diff with Mistral is the output type, we need MoE
last_hidden_state=hidden_states,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
)
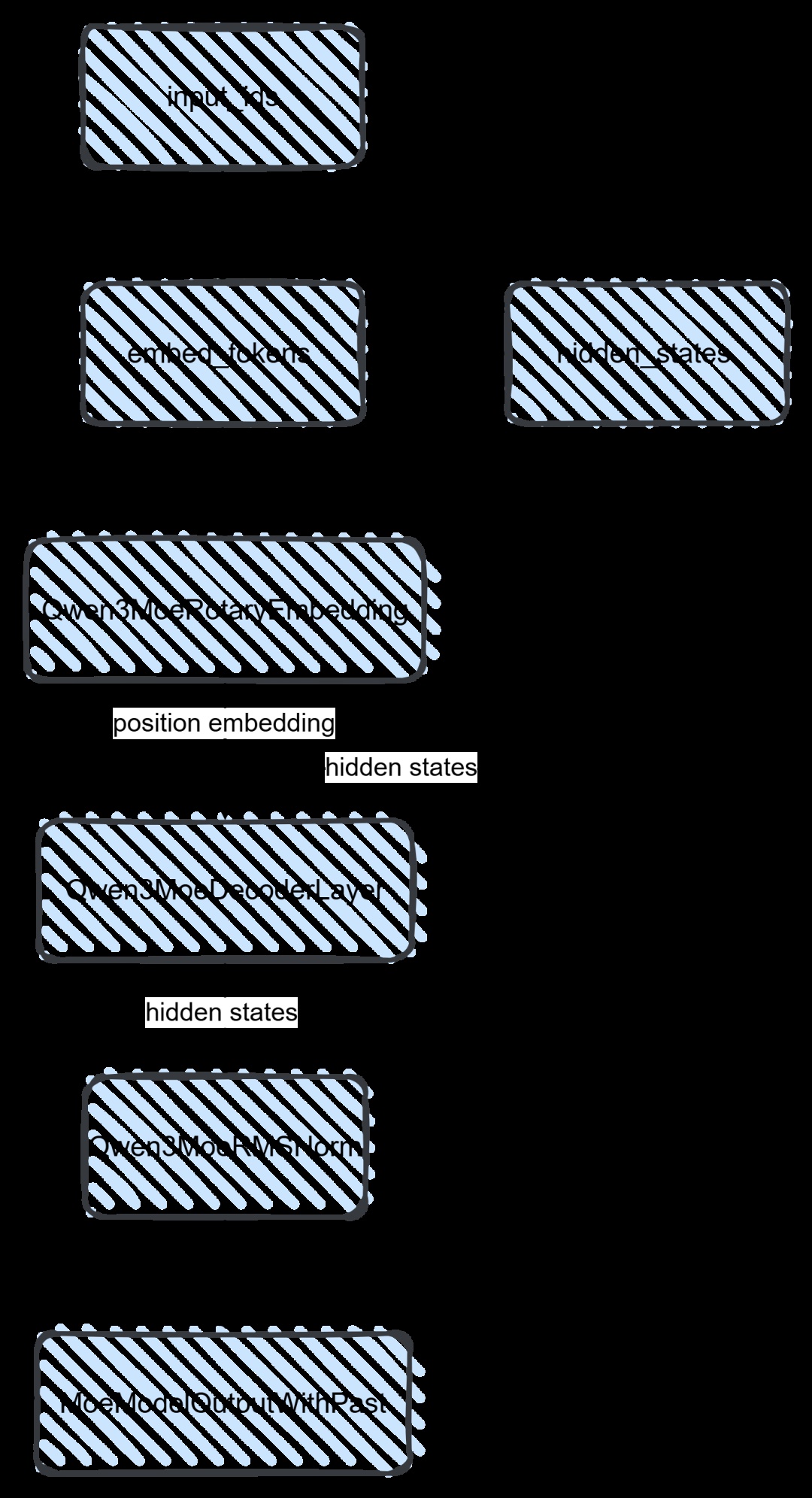
这里也大概总结一下:
第一步:input_ids通过nn.Embedding完成了embedding的过程,从而hidden_states也就有了;
第二步:需要位置编码,所以通过rotary_emb得到了position_embeddings(注意:这里只是拿到旋转频率:inverse frequencies)
第三步: hidden_states和position_embeddings就是transformer的输入,因此可以给到transformer模块,既Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer;
第四步: 从结构图可以看到,transformer之后就是rmsnorm对参数进行归一化。
注意:Qwen系列都是Decoder模型,因此,Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer就是一个解码模块,里面就是transformer结构。
三、解剖Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer
class Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer(GradientCheckpointingLayer):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3MoeConfig, layer_idx: int):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.self_attn = Qwen3MoeAttention(config, layer_idx)
if (layer_idx not in config.mlp_only_layers) and (
config.num_experts > 0 and (layer_idx + 1) % config.decoder_sparse_step == 0
):
self.mlp = Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock(config)
else:
self.mlp = Qwen3MoeMLP(config, intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size)
self.input_layernorm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.post_attention_layernorm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
@deprecate_kwarg("past_key_value", new_name="past_key_values", version="4.58")
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
position_embeddings: tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
# Self Attention
hidden_states, _ = self.self_attn(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
cache_position=cache_position,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
# Fully Connected
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
# For the MoE layers, we need to unpack
if isinstance(hidden_states, tuple):
hidden_states, _ = hidden_states
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
return hidden_states
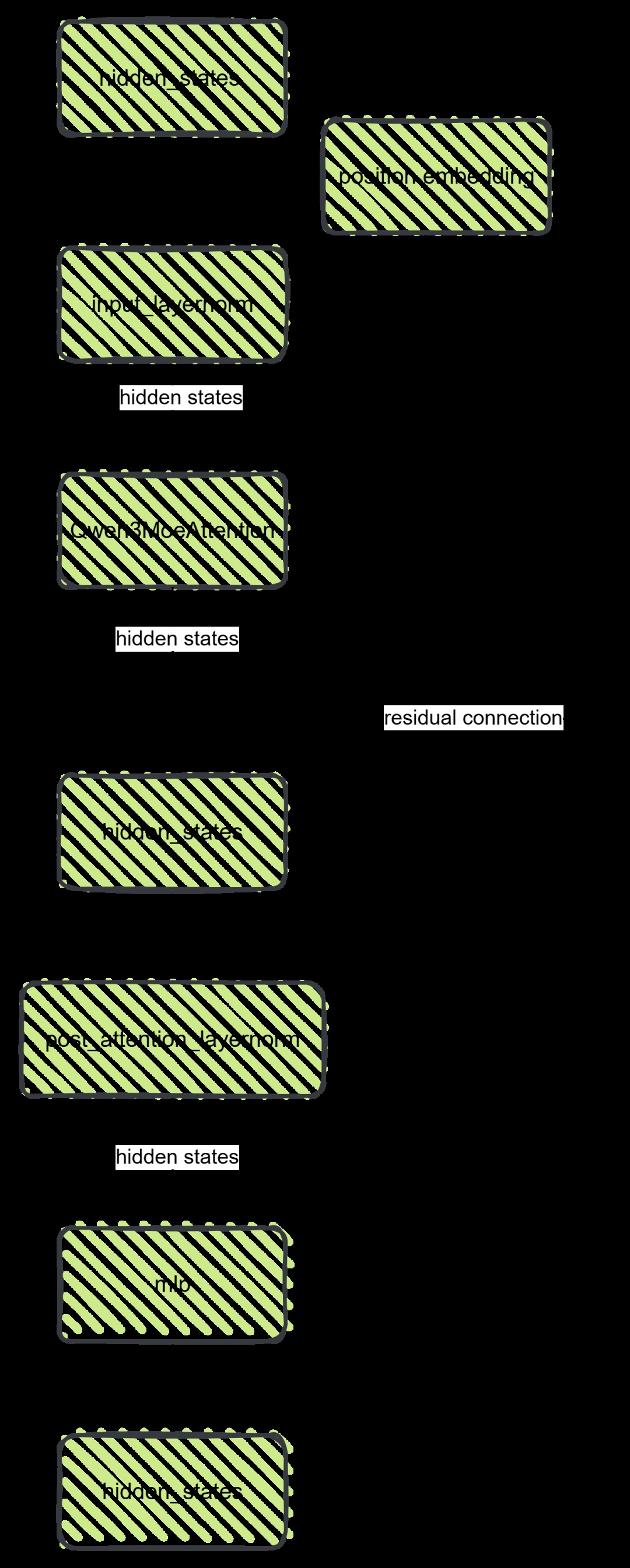
这个类是解码的核心,里面包括attention、mlp、residual connetion,大体的执行流程为:
第一步:输入的hidden states经过一层输入的layer norm归一化;
第二步:利用归一化的hidden states和position embedding给到moe attention模块,得到新的hidden states;
第三步:这里会有一次残差连接;
第四步:之后再进行一次norm,传输给mlp(多层感知:3个线性层组成) ;
第五步:再进行一次残差连接,得到新的hidden states。
注意:核心是经历了moe attention、两次残差连接、以及mlp。
四、解剖Qwen3MoeAttention
class Qwen3MoeAttention(nn.Module):
"""Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper"""
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3MoeConfig, layer_idx: int):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.layer_idx = layer_idx
self.head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads)
self.num_key_value_groups = config.num_attention_heads // config.num_key_value_heads
self.scaling = self.head_dim**-0.5
self.attention_dropout = config.attention_dropout
self.is_causal = True
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(
config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, config.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.q_norm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(self.head_dim, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) # unlike olmo, only on the head dim!
self.k_norm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(self.head_dim, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) # thus post q_norm does not need reshape
self.sliding_window = getattr(config, "sliding_window", None)
@deprecate_kwarg("past_key_value", new_name="past_key_values", version="4.58")
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
position_embeddings: tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor],
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
input_shape = hidden_states.shape[:-1]
hidden_shape = (*input_shape, -1, self.head_dim)
query_states = self.q_norm(self.q_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)
key_states = self.k_norm(self.k_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape).transpose(1, 2)
cos, sin = position_embeddings
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
if past_key_values is not None:
# sin and cos are specific to RoPE models; cache_position needed for the static cache
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}
key_states, value_states = past_key_values.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
attention_interface: Callable = eager_attention_forward
if self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":
attention_interface = ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS[self.config._attn_implementation]
attn_output, attn_weights = attention_interface(
self,
query_states,
key_states,
value_states,
attention_mask,
dropout=0.0 if not self.training else self.attention_dropout,
scaling=self.scaling,
sliding_window=self.sliding_window, # diff with Llama
**kwargs,
)
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(*input_shape, -1).contiguous()
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, attn_weights
这里是attention的核心,主要也是讲解attention的一个计算过程,总结如下:
第一步:拿到hidden states,通过norm和linear之后得到query_states、key_states、value states;
第二步:利用position embedding计算cos,sin值,并结合query_states、key_states进行旋转位置编码计算,得到新的query_states、key_states (注意:这里进行旋转编码只针对query_states、key_states,并没有针对value_states);
第三步:利用eager_attention_forward进行attention计算,从而得到attn_output, attn_weights;
注意: attention实现方式有多种,如flash_attention_2、eager、sdpa等。
解剖eager_attention_forward
其实这部分就是一个attention的计算过程,代码如下:
def eager_attention_forward(
module: nn.Module,
query: torch.Tensor,
key: torch.Tensor,
value: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor],
scaling: float,
dropout: float = 0.0,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
):
key_states = repeat_kv(key, module.num_key_value_groups)
value_states = repeat_kv(value, module.num_key_value_groups)
attn_weights = torch.matmul(query, key_states.transpose(2, 3)) * scaling
if attention_mask is not None:
causal_mask = attention_mask[:, :, :, : key_states.shape[-2]]
attn_weights = attn_weights + causal_mask
attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32).to(query.dtype)
attn_weights = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=dropout, training=module.training)
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value_states)
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
return attn_output, attn_weights

这里就不再讲解attention的计算过程了,可以根据图自己理解。
Qwen3的Moe藏在哪里?
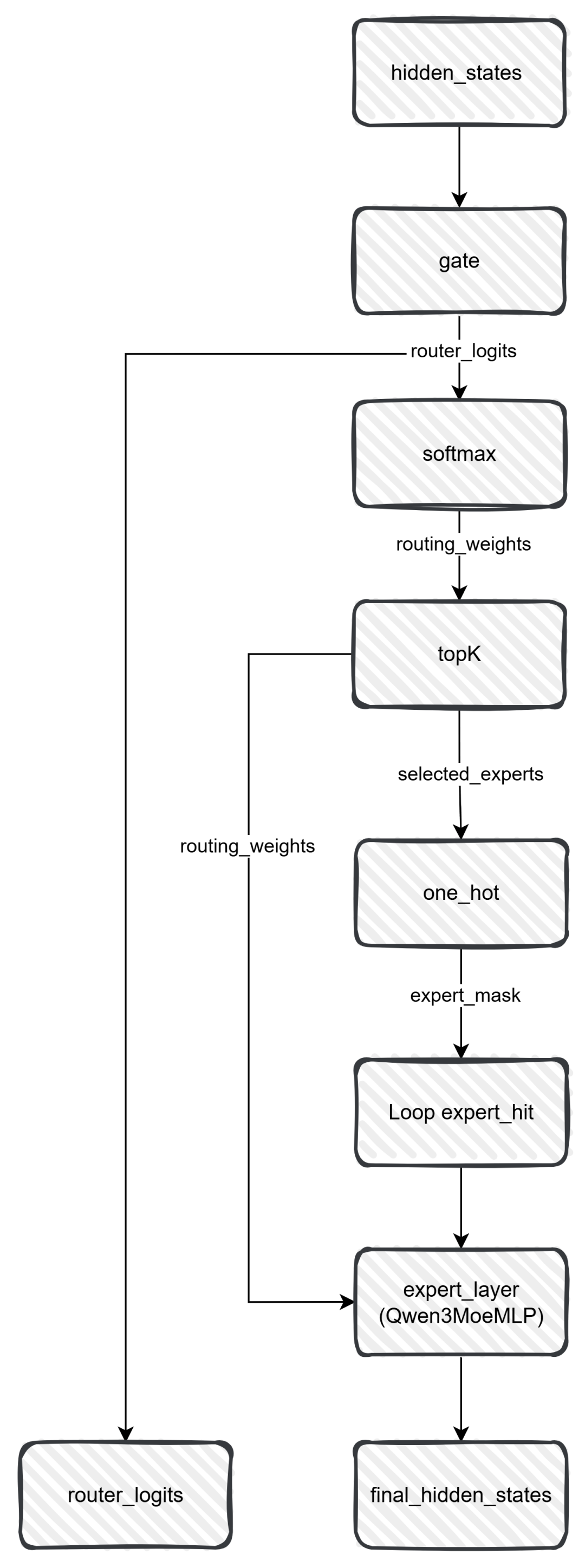
讲了这么久的流程和代码,那Qwen3的moe究竟藏在哪里呢?看了之前的文章就知道,moe层主要的改变是FNN层,多了一个门控和若干个专家。我们来看下这一部分代码和下面的流程图,就一目了然了:
class Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.num_experts = config.num_experts
self.top_k = config.num_experts_per_tok
self.norm_topk_prob = config.norm_topk_prob
# gating
self.gate = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_experts, bias=False)
self.experts = nn.ModuleList(
[Qwen3MoeMLP(config, intermediate_size=config.moe_intermediate_size) for _ in range(self.num_experts)]
)
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
""" """
batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_dim = hidden_states.shape
hidden_states = hidden_states.view(-1, hidden_dim)
# router_logits: (batch * sequence_length, n_experts)
router_logits = self.gate(hidden_states)
routing_weights = F.softmax(router_logits, dim=1, dtype=torch.float)
routing_weights, selected_experts = torch.topk(routing_weights, self.top_k, dim=-1)
if self.norm_topk_prob: # only diff with mixtral sparse moe block!
routing_weights /= routing_weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
# we cast back to the input dtype
routing_weights = routing_weights.to(hidden_states.dtype)
final_hidden_states = torch.zeros(
(batch_size * sequence_length, hidden_dim), dtype=hidden_states.dtype, device=hidden_states.device
)
# One hot encode the selected experts to create an expert mask
# this will be used to easily index which expert is going to be sollicitated
expert_mask = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(selected_experts, num_classes=self.num_experts).permute(2, 1, 0)
# Loop over all available experts in the model and perform the computation on each expert
expert_hit = torch.greater(expert_mask.sum(dim=(-1, -2)), 0).nonzero()
for expert_idx in expert_hit:
expert_layer = self.experts[expert_idx]
idx, top_x = torch.where(expert_mask[expert_idx].squeeze(0))
# Index the correct hidden states and compute the expert hidden state for
# the current expert. We need to make sure to multiply the output hidden
# states by `routing_weights` on the corresponding tokens (top-1 and top-2)
current_state = hidden_states[None, top_x].reshape(-1, hidden_dim)
current_hidden_states = expert_layer(current_state) * routing_weights[top_x, idx, None]
# However `index_add_` only support torch tensors for indexing so we'll use
# the `top_x` tensor here.
final_hidden_states.index_add_(0, top_x, current_hidden_states.to(hidden_states.dtype))
final_hidden_states = final_hidden_states.reshape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_dim)
return final_hidden_states, router_logits
这部分代码是Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer类中的mlp,这个mlp其实就是我们熟知的多层感知机,既Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock。
从初始化就能看到一个gate和多个experts。所以你如果写了一个Dense model,其实把原有的mlp改成这个moe mlp即可,也是一个新的moe模型。
五、AI大模型从0到精通全套学习大礼包
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
只要你是真心想学AI大模型,我这份资料就可以无偿共享给你学习。大模型行业确实也需要更多的有志之士加入进来,我也真心希望帮助大家学好这门技术,如果日后有什么学习上的问题,欢迎找我交流,有技术上面的问题,我是很愿意去帮助大家的!
如果你也想通过学大模型技术去帮助就业和转行,可以扫描下方链接👇👇
大模型重磅福利:入门进阶全套104G学习资源包免费分享!

01.从入门到精通的全套视频教程
包含提示词工程、RAG、Agent等技术点
02.AI大模型学习路线图(还有视频解说)
全过程AI大模型学习路线

03.学习电子书籍和技术文档
市面上的大模型书籍确实太多了,这些是我精选出来的

04.大模型面试题目详解


05.这些资料真的有用吗?
这份资料由我和鲁为民博士共同整理,鲁为民博士先后获得了北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士学位,在包括IEEE Transactions等学术期刊和诸多国际会议上发表了超过50篇学术论文、取得了多项美国和中国发明专利,同时还斩获了吴文俊人工智能科学技术奖。目前我正在和鲁博士共同进行人工智能的研究。
所有的视频由智泊AI老师录制,且资料与智泊AI共享,相互补充。这份学习大礼包应该算是现在最全面的大模型学习资料了。
资料内容涵盖了从入门到进阶的各类视频教程和实战项目,无论你是小白还是有些技术基础的,这份资料都绝对能帮助你提升薪资待遇,转行大模型岗位。


智泊AI始终秉持着“让每个人平等享受到优质教育资源”的育人理念,通过动态追踪大模型开发、数据标注伦理等前沿技术趋势,构建起"前沿课程+智能实训+精准就业"的高效培养体系。
课堂上不光教理论,还带着学员做了十多个真实项目。学员要亲自上手搞数据清洗、模型调优这些硬核操作,把课本知识变成真本事!

如果说你是以下人群中的其中一类,都可以来智泊AI学习人工智能,找到高薪工作,一次小小的“投资”换来的是终身受益!
应届毕业生:无工作经验但想要系统学习AI大模型技术,期待通过实战项目掌握核心技术。
零基础转型:非技术背景但关注AI应用场景,计划通过低代码工具实现“AI+行业”跨界。
业务赋能 突破瓶颈:传统开发者(Java/前端等)学习Transformer架构与LangChain框架,向AI全栈工程师转型。
👉获取方式:
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以保存图片到wx扫描二v码免费领取【保证100%免费】🆓
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献141条内容
已为社区贡献141条内容






所有评论(0)