Python 网络爬虫从入门到实战:全网最详细技术解析
网络爬虫(Web Crawler)是一种按照一定规则,自动抓取万维网信息的程序或脚本。它就像互联网上的 "蜘蛛",通过链接关系从一个网页爬到另一个网页,采集需要的数据。
一、引言:揭开网络爬虫的神秘面纱
1.1 什么是网络爬虫?
网络爬虫(Web Crawler)是一种按照一定规则,自动抓取万维网信息的程序或脚本。它就像互联网上的 "蜘蛛",通过链接关系从一个网页爬到另一个网页,采集需要的数据。
应用场景:
数据采集与分析(市场调研、竞品分析)
搜索引擎(百度、谷歌的网页抓取)
学术研究(文献数据获取)
电商比价(商品价格监控)
1.2 爬虫技术栈全景图
|
技术分类 |
核心工具 |
官方文档链接 |
|
数据获取 |
requests、aiohttp、Scrapy |
|
|
数据解析 |
BeautifulSoup、lxml、PyQuery |
|
|
反爬处理 |
Selenium、Playwright、代理 IP |
|
|
数据存储 |
MongoDB、MySQL、CSV |
1.3爬虫的基本概念
1.3.1网络爬虫(Web Crawler):
本质是模拟浏览器行为,通过 HTTP/HTTPS 协议向服务器发送请求,获取网页内容并解析数据的程序。
1.3.2爬虫的工作流程:
发送请求:向目标网站服务器发送 HTTP 请求
接收响应:获取服务器返回的 HTML/JSON 等格式的页面内容
解析数据:从响应内容中提取所需信息
存储数据:将提取的数据保存到本地(数据库、文件等)
1.4 HTTP 协议与网络请求基础
1.4.1常见 HTTP 请求方法:
◦ GET:获取资源(最常用的爬虫请求方式)
◦ POST:提交数据到服务器
◦ HEAD:获取响应头信息
1.4.2 重要 HTTP 响应状态码:
◦ 200 OK:请求成功,返回页面内容
◦ 403 Forbidden:禁止访问(常见反爬机制)
◦ 404 Not Found:页面不存在
◦ 500 Internal Server Error:服务器错误
1.4.3请求头(Headers)的关键字段:
◦ User-Agent:标识浏览器信息(爬虫需模拟真实浏览器 UA)
◦ Cookie:存储会话信息,用于保持登录状态
◦ Referer:标识请求来源页面
二、环境搭建:工欲善其事必先利其器
2.1 安装 Python 环境
推荐使用 Python 3.8 + 版本,通过官网下载安装包:Python 官方下载地址
安装完成后,在命令行验证:
|
python --version # 输出类似:Python 3.9.7 |
2.2 安装核心爬虫库
|
# 基础库 pip install requests beautifulsoup4 lxml # 进阶库 pip install scrapy selenium playwright # 数据存储 pip install pymongo pandas |
2.3 开发工具推荐
PyCharm:专业 Python IDE,支持调试和代码补全
VS Code:轻量级编辑器,安装 Python 插件后体验极佳
Charles/Fiddler:抓包工具,分析网络请求流程
2.4 Python 爬虫常用库与工具
2.4.1 网络请求库:requests
requests是 Python 中最常用的 HTTP 请求库,支持丰富的请求参数和自定义设置:
没有安装requests库的可以在终端安装:
代码:
import requests
# 发送GET请求
response = requests.get("https://example.com",
headers={
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36",
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml"
})
# 检查响应状态
if response.status_code == 200:
# 获取文本内容(自动解码)
html_content = response.text
# 获取二进制内容(用于图片、文件下载)
binary_content = response.content
else:
print(f"请求失败,状态码:{response.status_code}")2.4.2 解析库:BeautifulSoup 与 lxml
2.4.2_1 BeautifulSoup:简单易用的 HTML 解析器
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 解析HTML内容
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, 'html.parser')
# 通过标签名查找元素
title = soup.title.text
# 通过类名查找元素
articles = soup.find_all('div', class_='article-item')
# 通过CSS选择器查找元素
links = soup.select('a.read-more')2.4.2_2 lxml:高效的 XML/HTML 解析器(性能优于 BeautifulSoup)
from lxml import etree
# 解析HTML
html_tree = etree.HTML(html_content)
# 使用XPath表达式提取数据
title = html_tree.xpath('//title/text()')[0]
article_titles = html_tree.xpath('//div[@class="article-item"]/h3/a/text()')
article_links = html_tree.xpath('//div[@class="article-item"]/h3/a/@href')2.4.3 正则表达式:re 模块
正则表达式适用于复杂文本模式的匹配,常用于提取非结构化数据:
import re
# 提取所有URL
urls = re.findall(r'https?://[^\s/$.?#].[^\s]*', html_content)
# 提取邮箱地址
emails = re.findall(r'[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}', html_content)
# 提取电话号码(示例:中国大陆手机号)
phones = re.findall(r'1[3-9]\d{9}', html_content)2.4.4 异步爬虫:aiohttp 与 asyncio
对于高并发爬取场景,异步编程可大幅提升效率:
import asyncio
import aiohttp
async def fetch(url, session):
try:
async with session.get(url, timeout=10) as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.text()
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求出错:{url}, 错误:{e}")
return None
async def main(urls):
async with aiohttp.ClientSession(headers={
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36"
}) as session:
tasks = [fetch(url, session) for url in urls]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
return results
# 调用示例
urls = ["https://example.com/page1", "https://example.com/page2", ...]
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
htmls = loop.run_until_complete(main(urls))三、基础爬虫开发:从 requests 到数据解析
3.1入门程序:
3.1.1 首先清华镜像网址安装selenium库:
pip install selenium -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.baidu.com/'
driver.get(url) # 打开百度首页
driver.maximize_window() # 将浏览器最大化
# 找到搜索框元素,搜索框的 id 为"kw"
search_box = driver.find_element(By.ID, "kw")
# 在搜索框中输入查询内容
search_box.send_keys("csdn博客")
# 模拟点击搜索按钮,搜索按钮的 id 为"su"
search_button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "su")
search_button.click()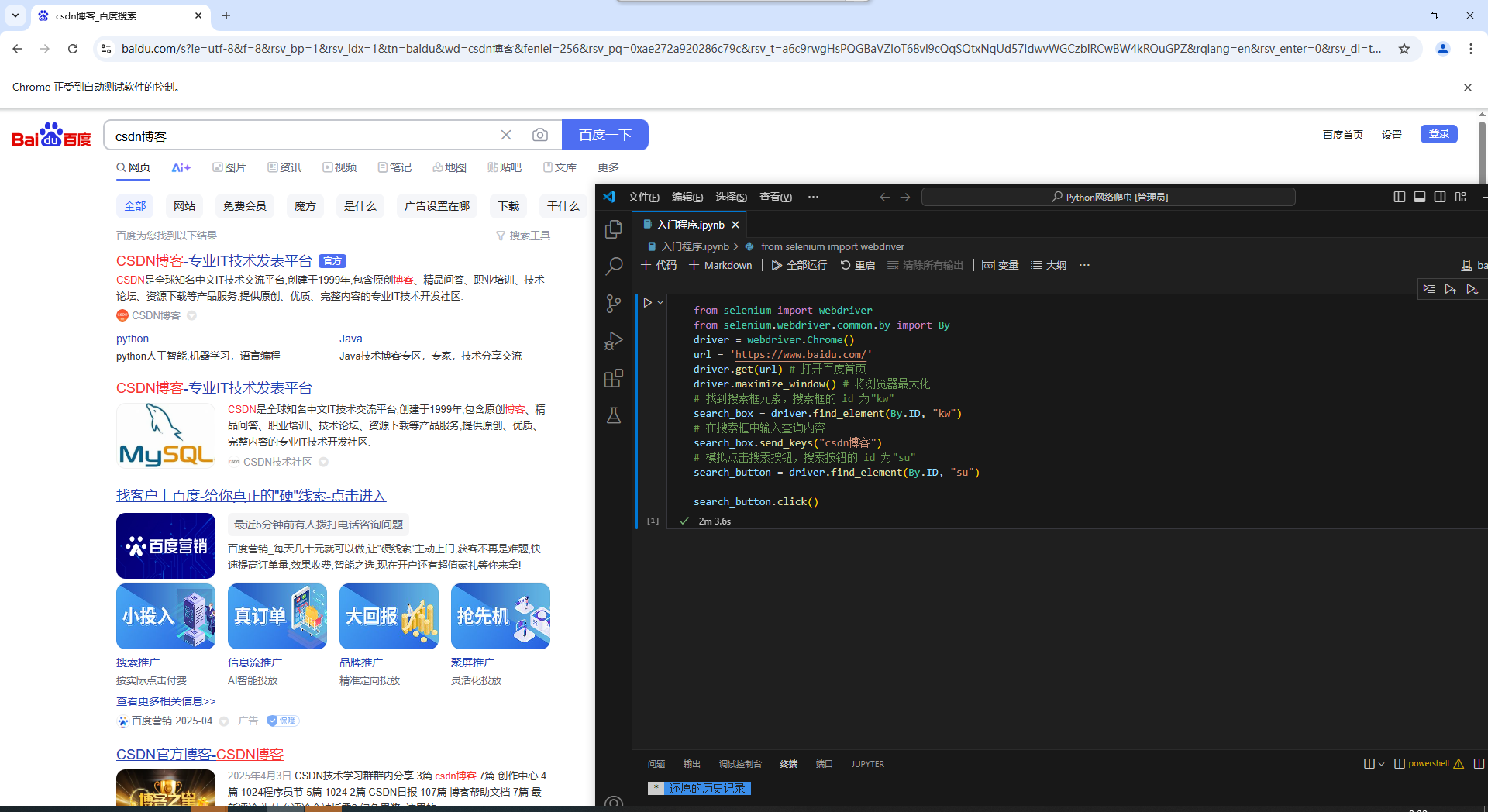
3.2 发送 HTTP 请求(以豆瓣电影 Top250 为例)
3.2.1 分析目标网站
豆瓣电影 Top250 页面结构特点:
- 分页 URL 规律:
https://movie.douban.com/top250?start=25&filter=(start 参数控制页码,每次增加 25) - 电影信息包含在
class="grid_view"的ol标签下的li元素中 - 需提取字段:电影名称、评分、导演、主演、上映时间、简介
完整爬虫代码
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
import random
import csv
import os
# 配置请求头(模拟浏览器)
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36",
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Language": "zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8",
"Connection": "keep-alive"
}
# 存储数据的列表
movies_data = []
def get_movie_info(url):
"""获取单页电影信息"""
try:
# 发送请求,添加随机延迟避免频繁请求
time.sleep(random.uniform(1, 3))
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status() # 抛出HTTP错误
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding # 自动检测编码
# 解析HTML
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
movie_list = soup.find('ol', class_='grid_view').find_all('li')
for movie in movie_list:
# 提取电影信息
movie_info = {}
movie_info['rank'] = movie.find('em').text # 排名
movie_info['title'] = movie.find('span', class_='title').text # 标题
# 处理可能存在的副标题
subtitle = movie.find('span', class_='other')
movie_info['title'] += subtitle.text if subtitle else ""
# 提取导演、主演等信息
info_div = movie.find('div', class_='bd')
movie_info['info'] = info_div.p.text.strip() # 导演、主演、年份等信息
# 提取评分
movie_info['rating'] = movie.find('span', class_='rating_num').text
# 提取评价人数
movie_info['votes'] = movie.find('span', class_='pl').text.strip('人评价')
# 提取简介
quote = movie.find('span', class_='inq')
movie_info['quote'] = quote.text if quote else "暂无简介"
movies_data.append(movie_info)
print(f"已获取:{movie_info['title']}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取页面{url}出错:{e}")
def main():
"""主函数:爬取所有页面并保存数据"""
base_url = "https://movie.douban.com/top250"
# 创建存储目录
if not os.path.exists("douban_movies"):
os.makedirs("douban_movies")
# 爬取10页数据(Top250)
for start in range(0, 250, 25):
page_url = f"{base_url}?start={start}&filter="
print(f"正在爬取页面:{page_url}")
get_movie_info(page_url)
# 保存数据到CSV文件
csv_file = os.path.join("douban_movies", "douban_top250.csv")
with open(csv_file, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8-sig') as f:
fieldnames = ['rank', 'title', 'info', 'rating', 'votes', 'quote']
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(movies_data)
print(f"爬取完成!共获取{len(movies_data)}条电影信息,已保存至{csv_file}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()|
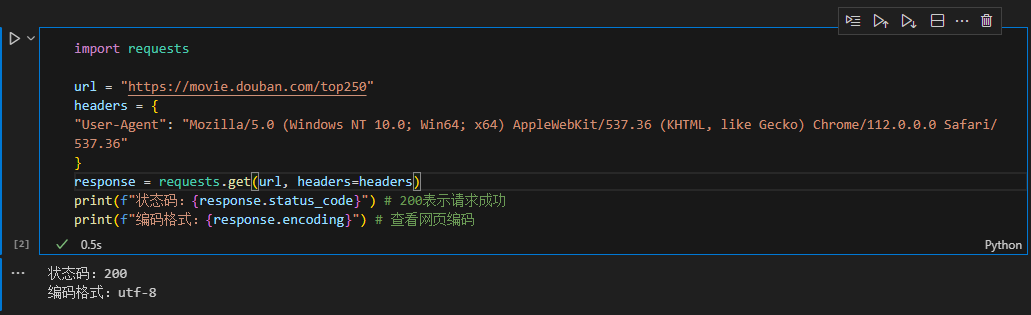
import requests url = "https://movie.douban.com/top250" headers = { "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/112.0.0.0 Safari/537.36" } response = requests.get(url, headers=headers) print(f"状态码:{response.status_code}") # 200表示请求成功 print(f"编码格式:{response.encoding}") # 查看网页编码 |
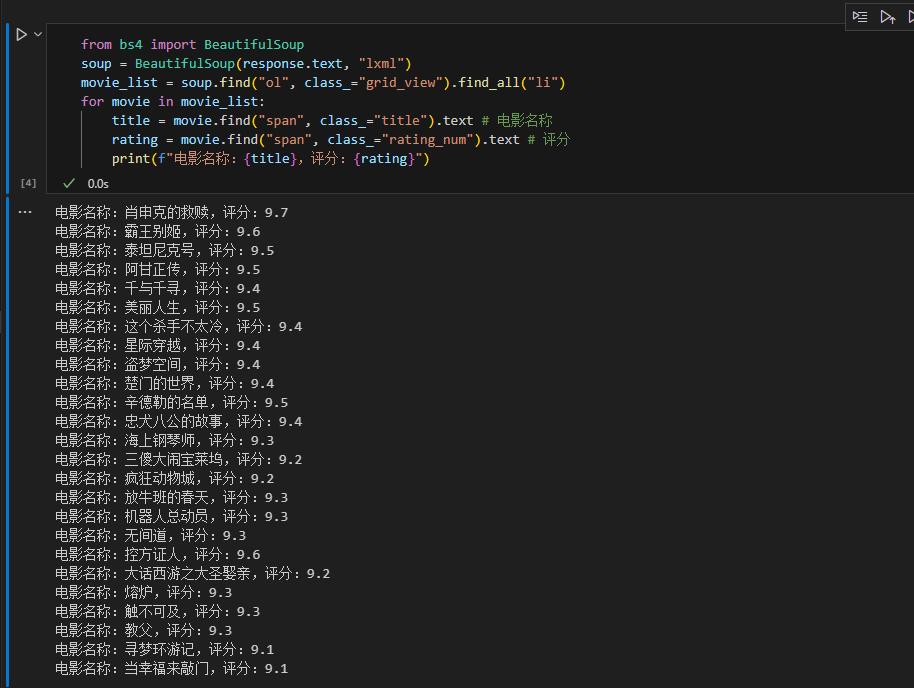
3.3解析 HTML 内容(使用 BeautifulSoup)
|
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "lxml") movie_list = soup.find("ol", class_="grid_view").find_all("li") for movie in movie_list: title = movie.find("span", class_="title").text # 电影名称 rating = movie.find("span", class_="rating_num").text # 评分 print(f"电影名称:{title},评分:{rating}") |
3.4 提取数据的三种方式对比
|
解析方式 |
优点 |
缺点 |
适用场景 |
|
BeautifulSoup |
简单易用,支持多种解析器 |
速度较慢 |
快速原型开发 |
|
lxml |
解析速度快,支持 XPath |
学习成本较高 |
大规模数据解析 |
|
正则表达式 |
灵活性强 |
复杂网页难以维护 |
特定模式匹配 |
四、反爬机制应对:爬虫与网站的攻防博弈
4.1 基础反爬手段破解
(1)User-Agent 伪装(设置随机请求头)
|
# 随机User-Agent生成器(使用fake_useragent库) from fake_useragent import UserAgent ua = UserAgent() headers = {"User-Agent": ua.random} |
(2)IP 代理池搭建(使用代理IP)
|
# 示例:使用代理IP发送请求 proxies = { "http": "http://proxy.example.com:8080", "https": "https://proxy.example.com:8080" } response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies) |
重要注意事项
-
遵守robots.txt协议
-
设置合理的请求间隔(time.sleep)
-
避免对目标网站造成过大压力
-
注意法律合规性
4.2 JavaScript 渲染页面处理
当遇到动态加载数据(如滚动加载、AJAX 请求)时,需要使用浏览器自动化工具:
|
# Selenium+Chrome示例 from selenium import webdriver driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.get("https://example.com/dynamic-page") # 等待页面加载 driver.implicitly_wait(10) html = driver.page_source driver.quit() |
4.3 Cookies 处理与登录态保持
|
# 使用Session对象保持会话 session = requests.Session() login_url = "https://example.com/login" session.post(login_url, data=login_data, headers=headers) # 登录后访问需要权限的页面 response = session.get(protected_url, headers=headers) |
五、实战案例
5.1:爬取豆瓣电影短评(单页为例)
5.1.1 需求分析
抓取指定博主的所有博客文章,获取以下信息:
用户名、点赞数量、评论时间、爬取IP地、评论内容
5.1.2代码实现过程
1、爬取数据并生成bs对象
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import pandas as pd
url = 'https://movie.douban.com/subject/30181250/comments?status=P'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html_str = response.text
print(html_str) 打印结果:
2、开发者工具中分析网页结构,定位短评数据在html中的位置
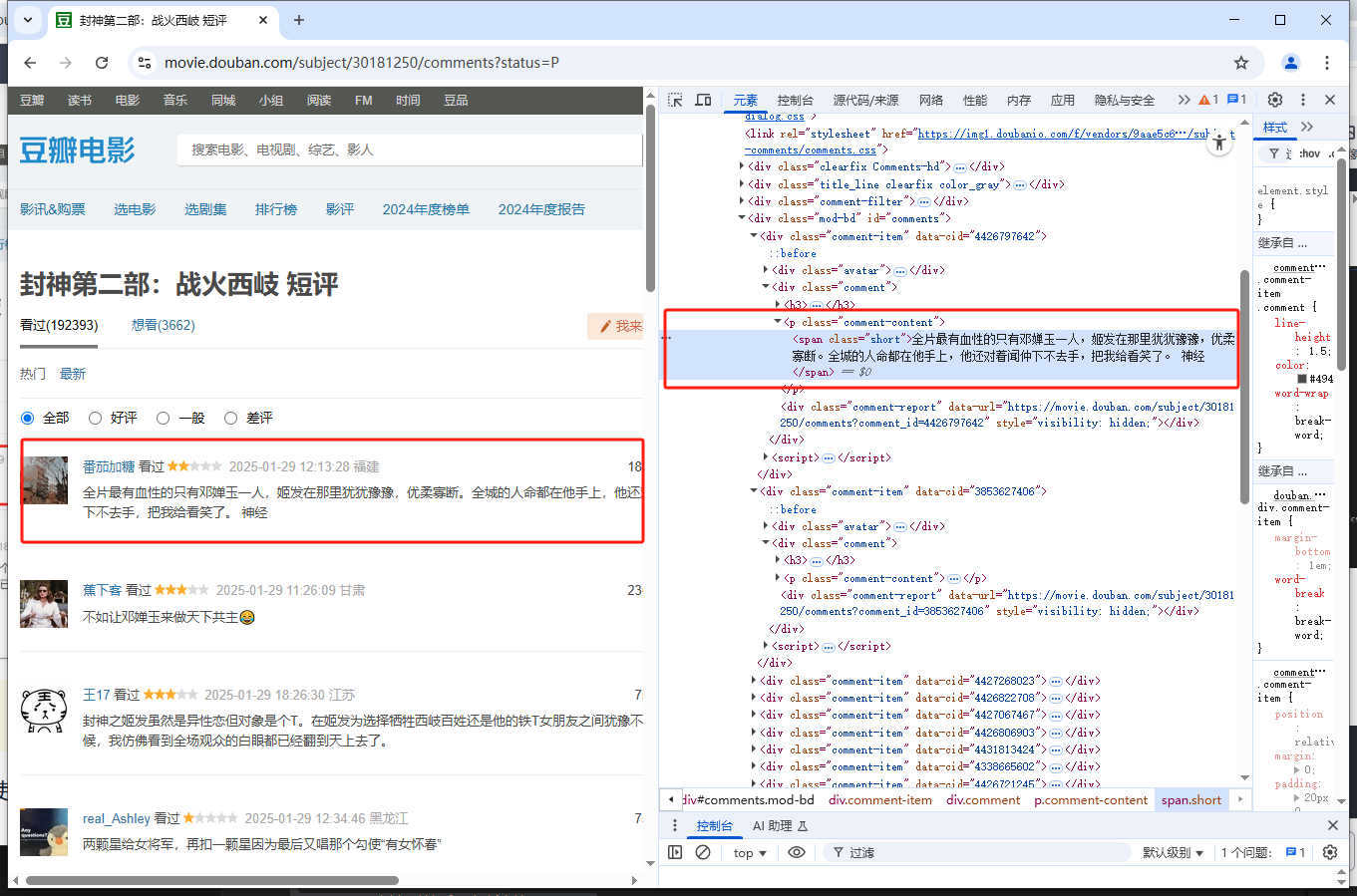
3、爬取用户名
#3、爬取用户名
list_name = [a.string for a in soup.select('.comment-info a')]
print(len(list_name))
print(list_name)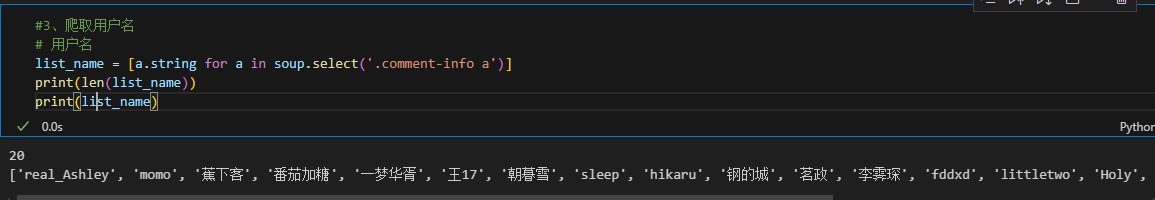
4、爬取点赞数量
# 点赞
list_votes = [span.string.strip() for span in soup.select('.votes')]
len(list_votes)
print(list_votes)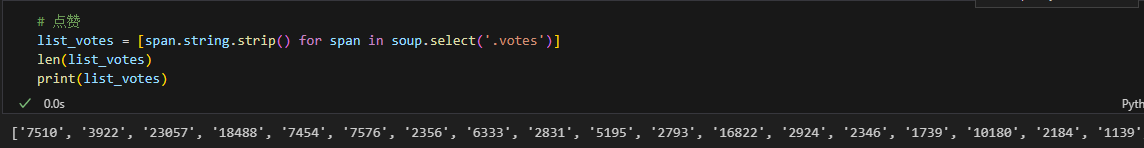
5、爬取评论时间
# 时间
list_time = [span.string.strip() for span in soup.select('.comment-time')]
len(list_time)
print(list_time)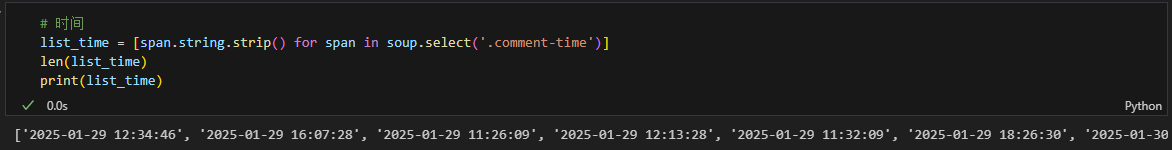
6、 爬取IP地
#爬取IP地
# ip地
list_location = [span.string.strip() for span in soup.select('.comment-location')]
len(list_location)
print(list_location)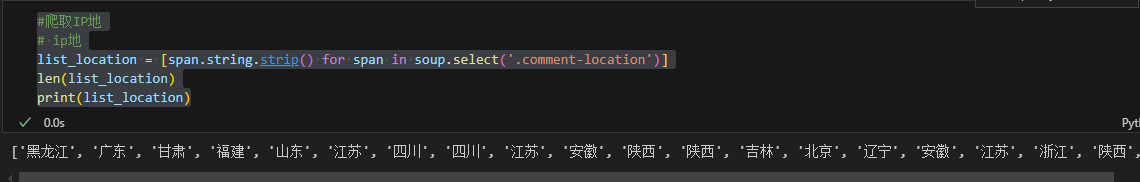
7、 爬取评论内容
#爬取评论内容
list_content = [i.string.strip() for i in soup.select('.comment-content .short')]
print(len(list_content))
print(list_content)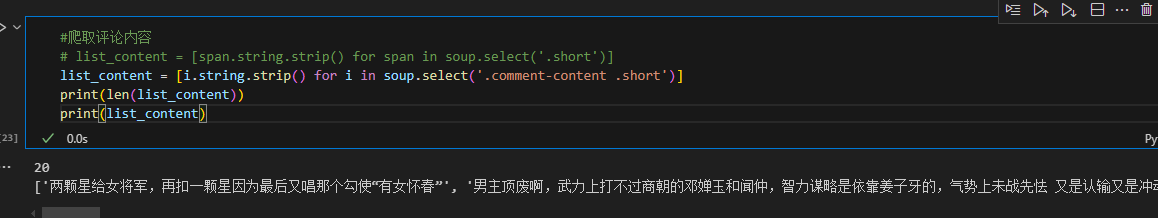 8、 生成表格对象
8、 生成表格对象
# 生成表格对象
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'用户名': list_name,
'时间': list_time,
'ip地': list_location,
'点赞数': list_votes,
'短评内容': list_content
})
df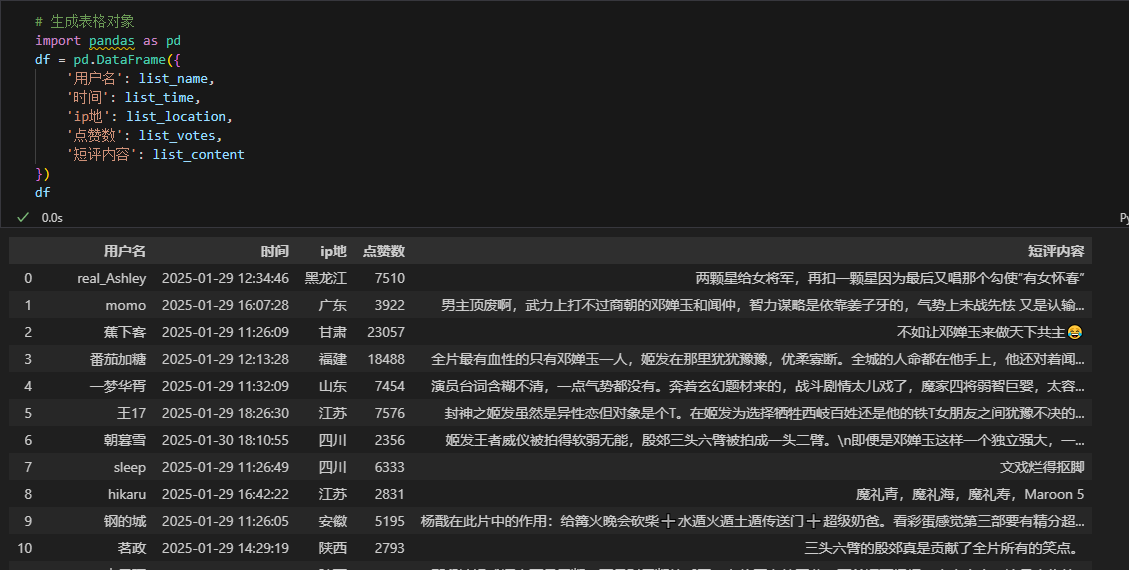
9、数据存储
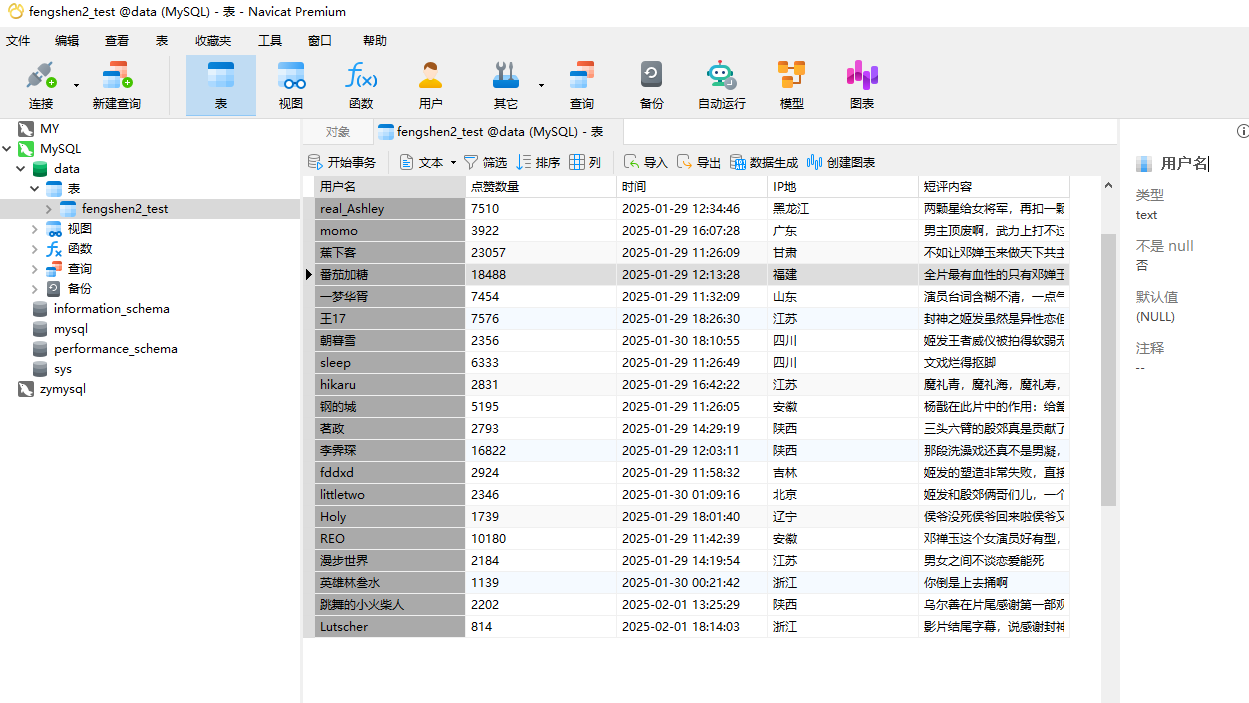
# 存储到MySQL
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456(密码)@localhost:3306/data(数据库名)')
df.to_sql('currency1', engine, index=False, if_exists='replace')
print("数据存储成功")
5.1.3 爬取豆瓣电影短评完整代码(封装函数:包含翻页爬取)
import time
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 爬取单页数据函数
def get_one_page(url,database,table):
'''
url: 某电影的豆瓣短评页面url
table_name: mysql数据库中存储爬取到的数据的表的名称
'''
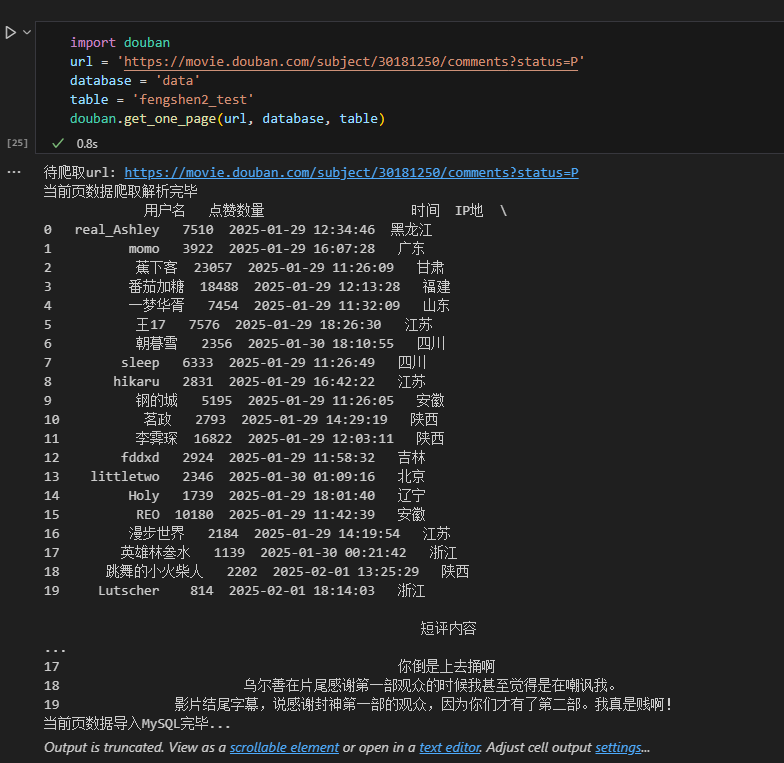
print('待爬取url:', url)
# 爬取数据,并生成bs对象
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html_str = response.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
# 数据解析
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
list_name = [a.string for a in soup.select('.comment-info a')]
list_time = [span.string.strip() for span in soup.select('.comment-time')]
list_location = [span.string.strip() for span in soup.select('.comment-location')]
list_votes = [span.string.strip() for span in soup.select('.votes')]
list_content = [i.string.strip() for i in soup.select('.comment-content .short')]
# print(len(list_name))
# print(len(list_time))
# print(len(list_location))
# print(len(list_votes))
# print(len(list_content))
df = pd.DataFrame({
'用户名': list_name,
'点赞数量': list_votes,
'时间': list_time,
'IP地': list_location,
'短评内容': list_content
})
print('当前页数据爬取解析完毕\n', df)
#数据储存
engine = create_engine(f'mysql+pymysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/{database}')
df.to_sql(table, engine, index=False, if_exists='append')
print('当前页数据导入MySQL完毕...')
# 爬取多页数据
def get_more_page(url, database, table, max_page):
'''
url: 某电影的豆瓣短评首页url\n
database: 数据保存的mysql数据库名\n
table: 数据保存的mysql表名\n
max_page: 你要爬取的总页数
'''
# 爬取首页数据
get_one_page(url, database, table)
# 再爬第2页到第max_page页
for i in range(2, max_page + 1):
url_new = url[:url.find('?')+1] + f'start={20*(i-1)}&limit=20&status=P&sort=new_score'
get_one_page(url_new, database, table)
if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'https://movie.douban.com/subject/30181250/comments?status=P'
# database = 'hjw'
# table = 'fengshen2'
# get_one_page(url,database,table)
get_more_page(url,'hjw','fengshen2',5)5.4.3运行结果展示
六、进阶技巧:分布式爬虫与效率优化
6.1 异步爬虫(aiohttp 实现)
|
import aiohttp import asyncio async def fetch(session, url): async with session.get(url) as response: return await response.text() async def main(urls): async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: tasks = [fetch(session, url) for url in urls] results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) return results if __name__ == "__main__": urls = ["https://example.com/page1", "https://example.com/page2", ...] # 100个URL asyncio.run(main(urls)) |
6.2 Scrapy 框架使用
|
# items.py定义数据结构 import scrapy class BlogItem(scrapy.Item): title = scrapy.Field() link = scrapy.Field() read_count = scrapy.Field() # spider文件 class CsdnSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = "csdn_spider" start_urls = ["https://blog.csdn.net/your_username?page=1"]
def parse(self, response): for article in response.css("div.article-item-box"): yield { "title": article.css("h4 a::text").get(), "link": response.urljoin(article.css("h4 a::attr(href)").get()), "read_count": article.css("div.article-bar-bottom span:nth-child(1)::text").get() } # 处理分页 next_page = response.css("a.next-page::attr(href)").get() if next_page: yield response.follow(next_page, self.parse) |
6.3 分布式爬虫架构
推荐使用Scrapy-Redis实现分布式爬取,架构图如下:
七、合规与伦理:做有道德的爬虫工程师
7.1 法律风险提示
遵守网站的robots.txt协议(如https://example.com/robots.txt)
避免抓取用户隐私数据(手机号、身份证号等)
控制请求频率,防止影响网站正常运行
7.2 文明爬虫规范
添加请求间隔(time.sleep(1))
尊重网站版权,不滥用爬取数据
遇到反爬措施时,优先通过合法渠道获取数据
八、总结与展望:爬虫技术的未来
8.1 核心知识回顾
网络爬虫的基本原理与技术栈
从 requests 到 Scrapy 的开发进阶
反爬机制的应对策略
实战案例的完整开发流程
8.2 技术发展趋势
AI 驱动爬虫:结合 NLP 识别动态内容
无代码爬虫工具:降低技术门槛
区块链反爬:数据加密技术的新挑战
8.3 学习路线和资源推荐
学习路线推荐:HTML/CSS基础 → 2. HTTP协议 → 3. 正则表达式 → 4. Scrapy框架
推荐资源:
官方文档:永远的第一手资料
技术博客:CSDN 爬虫专栏
相关专栏推荐 ➡️ Python爬虫进阶技巧
开源项目:Awesome Crawlers
源码获取 ➡️ GitHub仓库地址
如果您在实践过程中遇到问题,欢迎在评论区留言交流!让我们一起探索数据世界的无限可能~
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)