AgenticAI与AI编程完全指南
本文介绍了AgenticAI(智能体AI)的基础概念与编程实践。AgenticAI是具有自主性、目标导向和交互能力的AI系统,能够感知环境、制定计划并执行任务。文章从基础概念入手,详细讲解了AgenticAI的核心组件(感知、决策、执行、学习模块)和Python实现方法,包括环境搭建、基础模型使用以及任务导向型代理的构建。 在高级功能部分,重点探讨了记忆系统、上下文管理和工具集成等技术,并通过个人
·
第一部分:AgenticAI基础概念
1.1 什么是AgenticAI?
AgenticAI(智能体AI)是指具有自主性、目标导向和交互能力的AI系统。与传统AI模型不同,AgenticAI能够感知环境、制定计划、执行行动并从中学习,实现复杂的多步骤任务。
python
# 基础AgenticAI类示例
class BasicAIAgent:
def __init__(self, name, capabilities):
self.name = name
self.capabilities = capabilities # 代理具备的能力
self.memory = [] # 记忆存储
self.goals = [] # 目标列表
def perceive(self, environment):
"""感知环境信息"""
observations = []
for sensor in self.capabilities.get('sensors', []):
observation = sensor.observe(environment)
observations.append(observation)
return observations
def plan(self, observations, goals):
"""基于观察和目标制定计划"""
plan = []
# 简单的规划逻辑
for goal in goals:
if self._is_achievable(goal, observations):
steps = self._generate_steps(goal, observations)
plan.extend(steps)
return plan
def act(self, plan, environment):
"""执行计划中的行动"""
results = []
for action in plan:
result = action.execute(environment)
results.append(result)
self.memory.append({
'action': action,
'result': result,
'timestamp': time.time()
})
return results
def learn(self):
"""从经验中学习"""
recent_experiences = self.memory[-10:] # 最近10条经验
for experience in recent_experiences:
if experience['result']['success']:
# 强化成功的行为模式
self._reinforce_successful_pattern(experience)
else:
# 调整失败的行为
self._adjust_failed_behavior(experience)
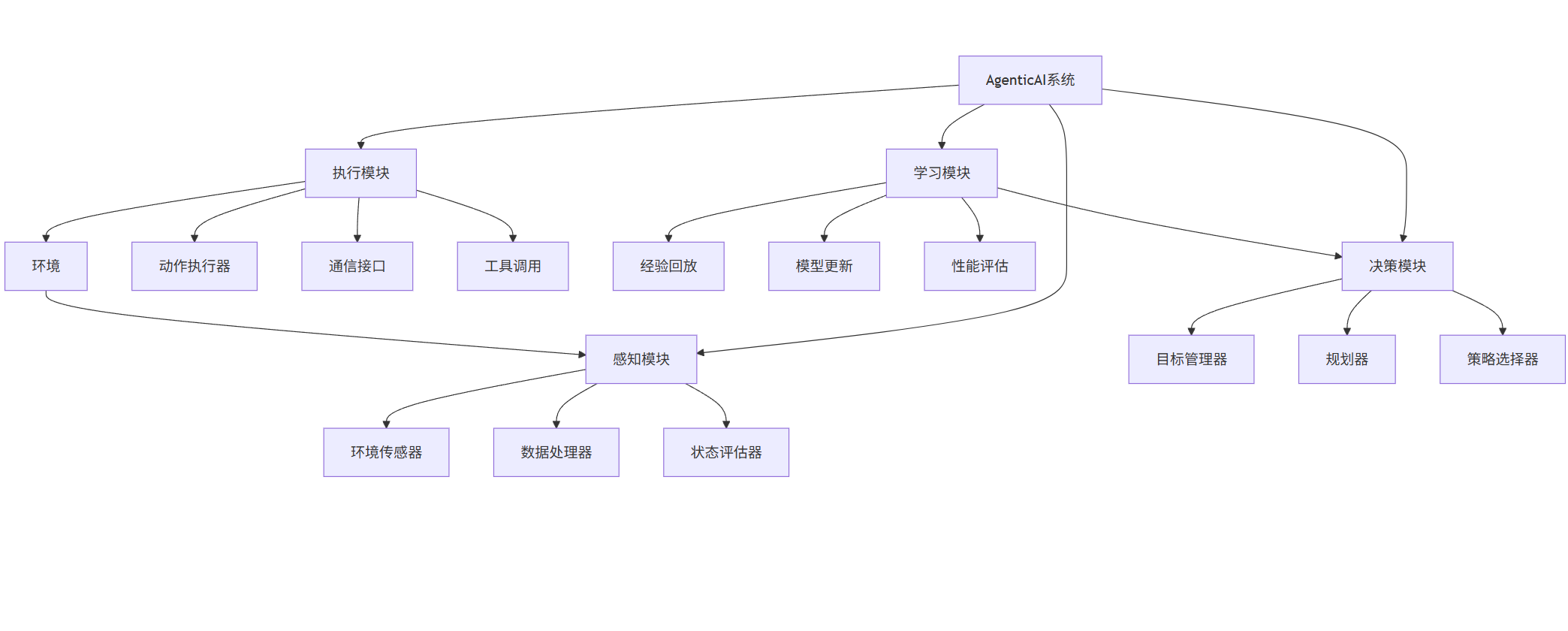
1.2 AgenticAI的核心组件
graph TD
A[AgenticAI系统] --> B[感知模块]
A --> C[决策模块]
A --> D[执行模块]
A --> E[学习模块]
B --> B1[环境传感器]
B --> B2[数据处理器]
B --> B3[状态评估器]
C --> C1[目标管理器]
C --> C2[规划器]
C --> C3[策略选择器]
D --> D1[动作执行器]
D --> D2[通信接口]
D --> D3[工具调用]
E --> E1[经验回放]
E --> E2[模型更新]
E --> E3[性能评估]
F[环境] --> B
D --> F
E --> C
第二部分:AI编程基础
2.1 Python AI开发环境搭建
python
# requirements.txt 示例
"""
torch>=2.0.0
transformers>=4.30.0
langchain>=0.0.200
openai>=1.0.0
numpy>=1.24.0
pandas>=1.5.0
matplotlib>=3.7.0
seaborn>=0.12.0
scikit-learn>=1.2.0
jupyter>=1.0.0
"""
# 环境配置脚本
import subprocess
import sys
def setup_ai_environment():
"""设置AI开发环境"""
packages = [
"torch", "transformers", "langchain", "openai",
"numpy", "pandas", "matplotlib", "seaborn",
"scikit-learn", "jupyter"
]
for package in packages:
try:
subprocess.check_call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", package])
print(f"✓ 成功安装 {package}")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
print(f"✗ 安装 {package} 失败")
# 验证安装
try:
import torch
import transformers
print("✓ AI环境配置完成!")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"✗ 环境配置失败: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
setup_ai_environment()
2.2 基础AI模型使用
python
import torch
from transformers import pipeline, AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class BasicAIModels:
def __init__(self):
self.models = {}
self.tokenizers = {}
def load_text_generation_model(self, model_name="gpt2"):
"""加载文本生成模型"""
print(f"正在加载模型: {model_name}")
self.tokenizers['text_gen'] = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.models['text_gen'] = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
# 添加padding token如果不存在
if self.tokenizers['text_gen'].pad_token is None:
self.tokenizers['text_gen'].pad_token = self.tokenizers['text_gen'].eos_token
print(f"✓ 模型 {model_name} 加载完成")
def generate_text(self, prompt, max_length=100, temperature=0.7):
"""生成文本"""
if 'text_gen' not in self.models:
self.load_text_generation_model()
inputs = self.tokenizers['text_gen'](prompt, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self.models['text_gen'].generate(
inputs.input_ids,
max_length=max_length,
temperature=temperature,
do_sample=True,
pad_token_id=self.tokenizers['text_gen'].eos_token_id
)
generated_text = self.tokenizers['text_gen'].decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
return generated_text
def load_sentiment_analysis(self):
"""加载情感分析模型"""
self.models['sentiment'] = pipeline(
"sentiment-analysis",
model="distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
)
def analyze_sentiment(self, text):
"""分析文本情感"""
if 'sentiment' not in self.models:
self.load_sentiment_analysis()
result = self.models['sentiment'](text)
return result
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
ai_models = BasicAIModels()
# 文本生成示例
prompt = "人工智能的未来发展"
generated_text = ai_models.generate_text(prompt, max_length=150)
print("生成的文本:", generated_text)
# 情感分析示例
sentiment = ai_models.analyze_sentiment("I love this amazing technology!")
print("情感分析结果:", sentiment)
第三部分:构建智能代理系统
3.1 任务导向型代理
python
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Callable
import json
import time
class TaskOrientedAgent:
def __init__(self, name: str, tools: List[Callable] = None):
self.name = name
self.tools = tools or []
self.task_history = []
self.current_goal = None
self.state = "idle"
def add_tool(self, tool: Callable, description: str):
"""添加工具到代理"""
self.tools.append({
'function': tool,
'description': description,
'name': tool.__name__
})
def set_goal(self, goal: str):
"""设置当前目标"""
self.current_goal = goal
self.state = "planning"
self.task_history.append({
'timestamp': time.time(),
'type': 'goal_set',
'goal': goal
})
def plan_execution(self) -> List[Dict]:
"""制定执行计划"""
print(f"{self.name} 正在为目标制定计划: {self.current_goal}")
# 简单的基于规则的规划
plan = []
goal_lower = self.current_goal.lower()
if "计算" in goal_lower or "calculate" in goal_lower:
plan.append({
'action': 'calculate',
'tool': 'calculator_tool',
'parameters': {'expression': self._extract_expression(goal_lower)}
})
elif "搜索" in goal_lower or "search" in goal_lower:
plan.append({
'action': 'search',
'tool': 'search_tool',
'parameters': {'query': self._extract_query(goal_lower)}
})
elif "总结" in goal_lower or "summarize" in goal_lower:
plan.append({
'action': 'summarize',
'tool': 'summary_tool',
'parameters': {'text': self._extract_text(goal_lower)}
})
else:
# 默认行动
plan.append({
'action': 'general_processing',
'tool': 'general_tool',
'parameters': {'input': self.current_goal}
})
return plan
def execute_plan(self, plan: List[Dict]) -> Any:
"""执行计划"""
self.state = "executing"
results = []
for step in plan:
print(f"执行步骤: {step['action']}")
# 查找对应的工具
tool_info = next(
(t for t in self.tools if t['name'] == step['tool']),
None
)
if tool_info:
try:
result = tool_info['function'](**step['parameters'])
results.append({
'step': step['action'],
'result': result,
'status': 'success'
})
except Exception as e:
results.append({
'step': step['action'],
'result': str(e),
'status': 'failed'
})
else:
results.append({
'step': step['action'],
'result': f"工具 {step['tool']} 未找到",
'status': 'failed'
})
self.state = "completed"
return results
def _extract_expression(self, text: str) -> str:
"""从文本中提取数学表达式"""
# 简单的提取逻辑
import re
numbers = re.findall(r'\d+\.?\d*', text)
operators = re.findall(r'[+\-*/]', text)
return ' '.join(numbers + operators)
def _extract_query(self, text: str) -> str:
"""从文本中提取搜索查询"""
# 移除搜索相关关键词
query = text.replace('搜索', '').replace('search', '').strip()
return query
def _extract_text(self, text: str) -> str:
"""从文本中提取需要总结的内容"""
# 在实际应用中,这里会有更复杂的逻辑
return text
# 工具函数示例
def calculator_tool(expression: str) -> float:
"""计算工具"""
try:
result = eval(expression)
return f"计算结果: {expression} = {result}"
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
def search_tool(query: str) -> str:
"""搜索工具(模拟)"""
return f"搜索 '{query}' 的结果: 这是模拟的搜索结果"
def summary_tool(text: str) -> str:
"""总结工具"""
words = text.split()
if len(words) > 10:
summary = ' '.join(words[:10]) + "..."
else:
summary = text
return f"总结: {summary}"
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建代理
agent = TaskOrientedAgent("任务助手")
# 添加工具
agent.add_tool(calculator_tool, "执行数学计算")
agent.add_tool(search_tool, "搜索信息")
agent.add_tool(summary_tool, "文本总结")
# 设置目标并执行
agent.set_goal("计算 25 + 38 的结果")
plan = agent.plan_execution()
results = agent.execute_plan(plan)
print("执行结果:")
for result in results:
print(f"- {result['step']}: {result['result']} (状态: {result['status']})")
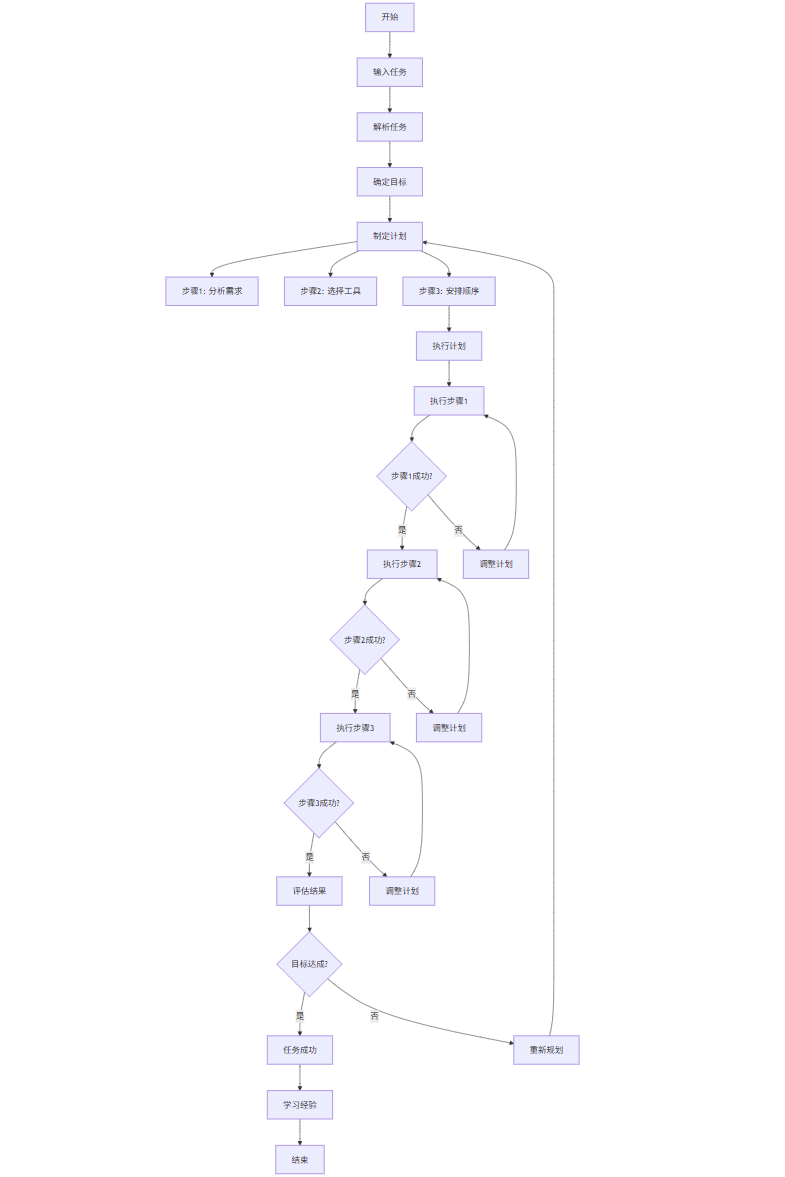
3.2 多步骤任务处理流程图
flowchart TD
Start[开始] --> Input[输入任务]
Input --> Parse[解析任务]
Parse --> Goal[确定目标]
Goal --> Plan[制定计划]
Plan --> PlanStep1[步骤1: 分析需求]
Plan --> PlanStep2[步骤2: 选择工具]
Plan --> PlanStep3[步骤3: 安排顺序]
PlanStep3 --> Execute[执行计划]
Execute --> Step1[执行步骤1]
Step1 --> Check1{步骤1成功?}
Check1 -->|是| Step2[执行步骤2]
Check1 -->|否| Adjust1[调整计划]
Adjust1 --> Step1
Step2 --> Check2{步骤2成功?}
Check2 -->|是| Step3[执行步骤3]
Check2 -->|否| Adjust2[调整计划]
Adjust2 --> Step2
Step3 --> Check3{步骤3成功?}
Check3 -->|是| Evaluate[评估结果]
Check3 -->|否| Adjust3[调整计划]
Adjust3 --> Step3
Evaluate --> FinalCheck{目标达成?}
FinalCheck -->|是| Success[任务成功]
FinalCheck -->|否| Replan[重新规划]
Replan --> Plan
Success --> Learn[学习经验]
Learn --> End[结束]
第四部分:高级AgenticAI功能
4.1 记忆与上下文管理
python
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from collections import defaultdict
import pickle
class MemorySystem:
def __init__(self, max_memories=1000):
self.memories = []
self.max_memories = max_memories
self.memory_vectors = {} # 用于相似性搜索的向量存储
self.importance_weights = defaultdict(float)
def add_memory(self, content: str, memory_type: str = "general",
importance: float = 0.5, metadata: dict = None):
"""添加记忆"""
memory = {
'id': len(self.memories),
'content': content,
'type': memory_type,
'timestamp': datetime.now(),
'importance': importance,
'last_accessed': datetime.now(),
'access_count': 0,
'metadata': metadata or {}
}
self.memories.append(memory)
# 维护记忆数量限制
if len(self.memories) > self.max_memories:
self._prune_memories()
# 更新重要性权重
self._update_importance(memory_type, importance)
def retrieve_relevant_memories(self, query: str, n_results: int = 5):
"""检索相关记忆"""
# 简单的基于关键词的检索(实际应用中会使用嵌入向量)
query_lower = query.lower()
relevant_memories = []
for memory in self.memories:
content_lower = memory['content'].lower()
# 计算简单相关性分数
score = 0
for word in query_lower.split():
if word in content_lower:
score += 1
# 考虑记忆的重要性和新鲜度
recency = self._calculate_recency(memory['timestamp'])
importance_score = memory['importance']
final_score = score + importance_score + recency
if final_score > 0:
relevant_memories.append((memory, final_score))
# 按分数排序并返回前n个结果
relevant_memories.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return [mem for mem, score in relevant_memories[:n_results]]
def _calculate_recency(self, timestamp):
"""计算新鲜度分数"""
time_diff = datetime.now() - timestamp
hours_diff = time_diff.total_seconds() / 3600
# 指数衰减的新鲜度分数
recency = np.exp(-hours_diff / 24) # 24小时衰减因子
return recency
def _prune_memories(self):
"""修剪记忆,移除不重要的"""
if len(self.memories) <= self.max_memories:
return
# 计算每个记忆的综合分数
memory_scores = []
for memory in self.memories:
recency = self._calculate_recency(memory['timestamp'])
score = memory['importance'] + recency + (memory['access_count'] * 0.1)
memory_scores.append((memory, score))
# 按分数排序,移除分数最低的
memory_scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
memories_to_remove = memory_scores[:len(self.memories) - self.max_memories]
for memory, _ in memories_to_remove:
self.memories.remove(memory)
def _update_importance(self, memory_type: str, importance: float):
"""更新记忆类型的重要性权重"""
self.importance_weights[memory_type] = (
0.9 * self.importance_weights[memory_type] + 0.1 * importance
)
def save_memories(self, filepath: str):
"""保存记忆到文件"""
with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump({
'memories': self.memories,
'importance_weights': dict(self.importance_weights)
}, f)
def load_memories(self, filepath: str):
"""从文件加载记忆"""
try:
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
data = pickle.load(f)
self.memories = data['memories']
self.importance_weights = defaultdict(float, data['importance_weights'])
except FileNotFoundError:
print("记忆文件不存在,创建新的记忆系统")
# 增强的代理类,包含记忆系统
class AdvancedAIAgent(TaskOrientedAgent):
def __init__(self, name: str, tools: List[Callable] = None):
super().__init__(name, tools)
self.memory_system = MemorySystem()
self.conversation_context = []
self.max_context_length = 10
def process_with_memory(self, user_input: str) -> str:
"""使用记忆处理用户输入"""
# 检索相关记忆
relevant_memories = self.memory_system.retrieve_relevant_memories(user_input)
# 添加上下文
self.conversation_context.append({
'role': 'user',
'content': user_input,
'timestamp': datetime.now()
})
# 构建增强的提示
enhanced_prompt = self._build_enhanced_prompt(user_input, relevant_memories)
# 处理请求(这里简化处理,实际会调用AI模型)
response = self._generate_response(enhanced_prompt)
# 保存到记忆
self.memory_system.add_memory(
content=f"用户: {user_input} - 助手: {response}",
memory_type="conversation",
importance=0.7,
metadata={'interaction_type': 'conversation'}
)
# 更新上下文
self.conversation_context.append({
'role': 'assistant',
'content': response,
'timestamp': datetime.now()
})
# 维护上下文长度
if len(self.conversation_context) > self.max_context_length * 2:
self.conversation_context = self.conversation_context[-self.max_context_length * 2:]
return response
def _build_enhanced_prompt(self, user_input: str, relevant_memories: list) -> str:
"""构建增强的提示"""
prompt = "基于以下信息和上下文回答用户问题:\n\n"
# 添加上下文
if self.conversation_context:
prompt += "最近的对话上下文:\n"
for msg in self.conversation_context[-self.max_context_length:]:
role = "用户" if msg['role'] == 'user' else "助手"
prompt += f"{role}: {msg['content']}\n"
prompt += "\n"
# 添加相关记忆
if relevant_memories:
prompt += "相关记忆:\n"
for memory in relevant_memories:
prompt += f"- {memory['content']}\n"
prompt += "\n"
prompt += f"当前问题: {user_input}\n\n回答:"
return prompt
def _generate_response(self, prompt: str) -> str:
"""生成响应(简化版本)"""
# 在实际应用中,这里会调用语言模型
# 这里使用简单的规则作为示例
if "你好" in prompt or "hello" in prompt.lower():
return "你好!我是你的AI助手,有什么我可以帮助你的吗?"
elif "计算" in prompt:
# 提取并执行计算
import re
numbers = re.findall(r'\d+', prompt)
if len(numbers) >= 2:
return f"计算结果: {numbers[0]} + {numbers[1]} = {int(numbers[0]) + int(numbers[1])}"
elif "天气" in prompt:
return "我目前无法获取实时天气信息,但建议你查看当地的天气预报应用。"
return "我理解了你的问题,但我需要更多信息来提供准确的回答。你能详细说明一下吗?"
4.2 工具使用与API集成
python
import requests
import json
class ToolIntegrationSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.available_tools = {}
self.api_keys = {}
def register_tool(self, tool_name: str, tool_function: Callable, description: str):
"""注册工具"""
self.available_tools[tool_name] = {
'function': tool_function,
'description': description,
'parameters': self._extract_parameters(tool_function)
}
def register_api(self, api_name: str, base_url: str, api_key: str = None):
"""注册API"""
self.api_keys[api_name] = {
'base_url': base_url,
'api_key': api_key
}
def execute_tool(self, tool_name: str, **kwargs):
"""执行工具"""
if tool_name not in self.available_tools:
return f"错误: 工具 '{tool_name}' 未找到"
try:
tool = self.available_tools[tool_name]
result = tool['function'](**kwargs)
return result
except Exception as e:
return f"执行工具时出错: {e}"
def call_api(self, api_name: str, endpoint: str, method: str = "GET", data: dict = None):
"""调用API"""
if api_name not in self.api_keys:
return f"错误: API '{api_name}' 未注册"
api_info = self.api_keys[api_name]
url = f"{api_info['base_url']}/{endpoint}"
headers = {}
# 添加API密钥(如果存在)
if api_info['api_key']:
headers['Authorization'] = f"Bearer {api_info['api_key']}"
try:
if method.upper() == "GET":
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, params=data)
elif method.upper() == "POST":
headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json'
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
else:
return f"不支持的HTTP方法: {method}"
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()
else:
return f"API调用失败: {response.status_code} - {response.text}"
except requests.RequestException as e:
return f"API请求错误: {e}"
def _extract_parameters(self, func: Callable) -> list:
"""提取函数参数信息"""
import inspect
sig = inspect.signature(func)
parameters = []
for name, param in sig.parameters.items():
param_info = {
'name': name,
'type': str(param.annotation) if param.annotation != inspect.Parameter.empty else 'any',
'required': param.default == inspect.Parameter.empty
}
parameters.append(param_info)
return parameters
def list_tools(self) -> dict:
"""列出所有可用工具"""
return {
name: {
'description': tool['description'],
'parameters': tool['parameters']
}
for name, tool in self.available_tools.items()
}
# 示例工具函数
def web_search_tool(query: str, max_results: int = 5) -> str:
"""网页搜索工具(模拟)"""
# 在实际应用中,这里会调用真实的搜索API
return f"搜索 '{query}' 的模拟结果: 找到了 {max_results} 条相关信息"
def calculator_tool(expression: str) -> float:
"""高级计算工具"""
try:
# 安全地评估数学表达式
allowed_chars = set('0123456789+-*/.() ')
if all(c in allowed_chars for c in expression):
result = eval(expression)
return f"计算结果: {expression} = {result}"
else:
return "错误: 表达式包含不安全字符"
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
def weather_tool(city: str) -> str:
"""天气查询工具(模拟)"""
# 模拟天气数据
weather_data = {
"北京": "晴, 25°C",
"上海": "多云, 23°C",
"广州": "雨, 28°C",
"深圳": "阴, 26°C"
}
if city in weather_data:
return f"{city}的天气: {weather_data[city]}"
else:
return f"未找到{city}的天气信息"
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
tool_system = ToolIntegrationSystem()
# 注册工具
tool_system.register_tool(
"web_search",
web_search_tool,
"执行网页搜索"
)
tool_system.register_tool(
"calculator",
calculator_tool,
"执行数学计算"
)
tool_system.register_tool(
"weather",
weather_tool,
"查询天气信息"
)
# 测试工具
print("=== 工具测试 ===")
print(tool_system.execute_tool("web_search", query="人工智能", max_results=3))
print(tool_system.execute_tool("calculator", expression="(15 + 23) * 2"))
print(tool_system.execute_tool("weather", city="北京"))
print("\n=== 可用工具列表 ===")
tools = tool_system.list_tools()
for tool_name, tool_info in tools.items():
print(f"- {tool_name}: {tool_info['description']}")
第五部分:实际应用案例
5.1 个人学习助手
python
class PersonalLearningAssistant(AdvancedAIAgent):
def __init__(self, name: str):
super().__init__(name)
self.learning_goals = []
self.study_sessions = []
self.knowledge_base = {}
# 初始化学习相关工具
self._initialize_learning_tools()
def _initialize_learning_tools(self):
"""初始化学习工具"""
self.add_tool(self.create_study_plan, "制定学习计划")
self.add_tool(self.quiz_me, "生成测验题目")
self.add_tool(self.summarize_content, "总结学习内容")
self.add_tool(self.track_progress, "跟踪学习进度")
def set_learning_goal(self, goal: str, deadline: str = None):
"""设置学习目标"""
learning_goal = {
'goal': goal,
'deadline': deadline,
'created_at': datetime.now(),
'progress': 0.0,
'sub_tasks': []
}
self.learning_goals.append(learning_goal)
self.memory_system.add_memory(
content=f"设置了学习目标: {goal}",
memory_type="learning_goal",
importance=0.9
)
return f"已设置学习目标: {goal}"
def create_study_plan(self, goal: str, hours_per_week: int = 10, weeks: int = 4):
"""制定学习计划"""
total_hours = hours_per_week * weeks
plan = {
'goal': goal,
'total_hours': total_hours,
'weekly_hours': hours_per_week,
'duration_weeks': weeks,
'weekly_topics': [],
'resources': []
}
# 生成每周学习主题(简化版本)
topics = self._generate_learning_topics(goal, weeks)
plan['weekly_topics'] = topics
# 推荐学习资源
resources = self._recommend_resources(goal)
plan['resources'] = resources
self.memory_system.add_memory(
content=f"为目标 '{goal}' 创建了学习计划,总计 {total_hours} 小时",
memory_type="study_plan",
importance=0.8,
metadata={'plan_details': plan}
)
return plan
def quiz_me(self, topic: str, difficulty: str = "medium", num_questions: int = 5):
"""生成测验题目"""
# 在实际应用中,这里会调用AI模型生成题目
questions = []
question_templates = {
"easy": [
f"什么是{topic}的基本概念?",
f"{topic}的主要应用领域有哪些?",
f"列举三个与{topic}相关的关键词"
],
"medium": [
f"解释{topic}的核心原理",
f"比较{topic}与传统方法的区别",
f"分析{topic}的优势和局限性"
],
"hard": [
f"详细描述{topic}的实现机制",
f"讨论{topic}在未来发展中的挑战",
f"提出改进{topic}的创新思路"
]
}
templates = question_templates.get(difficulty, question_templates["medium"])
for i in range(min(num_questions, len(templates))):
questions.append({
'id': i + 1,
'question': templates[i],
'type': 'open_ended'
})
quiz_session = {
'topic': topic,
'difficulty': difficulty,
'questions': questions,
'timestamp': datetime.now()
}
return quiz_session
def summarize_content(self, content: str, max_length: int = 200):
"""总结学习内容"""
# 简化版的总结功能
sentences = content.split('。')
if len(sentences) > 3:
summary = '。'.join(sentences[:3]) + '。'
else:
summary = content
if len(summary) > max_length:
summary = summary[:max_length] + '...'
return {
'original_length': len(content),
'summary_length': len(summary),
'summary': summary,
'reduction_ratio': f"{((len(content) - len(summary)) / len(content)) * 100:.1f}%"
}
def track_progress(self, goal: str = None):
"""跟踪学习进度"""
if goal:
# 跟踪特定目标进度
target_goal = next((g for g in self.learning_goals if g['goal'] == goal), None)
if target_goal:
return {
'goal': goal,
'progress': f"{target_goal['progress'] * 100}%",
'days_since_start': (datetime.now() - target_goal['created_at']).days
}
else:
return f"未找到目标: {goal}"
else:
# 跟踪所有目标进度
progress_report = {
'total_goals': len(self.learning_goals),
'goals': []
}
for goal in self.learning_goals:
progress_report['goals'].append({
'goal': goal['goal'],
'progress': f"{goal['progress'] * 100}%",
'days_active': (datetime.now() - goal['created_at']).days
})
return progress_report
def _generate_learning_topics(self, goal: str, weeks: int):
"""生成学习主题"""
# 简化版本,实际应用中会使用更智能的方法
base_topics = [
"基础概念和术语",
"核心原理和机制",
"实际应用案例",
"高级特性和技巧",
"最佳实践和模式",
"常见问题和解决方案",
"进阶学习和资源"
]
topics = []
for i in range(weeks):
if i < len(base_topics):
topics.append(f"第{i+1}周: {base_topics[i]}")
else:
topics.append(f"第{i+1}周: {goal} 进阶学习")
return topics
def _recommend_resources(self, goal: str):
"""推荐学习资源"""
# 模拟资源推荐
resource_categories = {
"编程": ["官方文档", "在线教程", "视频课程", "实践项目"],
"数学": ["教科书", "练习册", "在线课程", "解题指南"],
"语言": ["教科书", "听力材料", "口语练习", "语法指南"]
}
# 简单的分类逻辑
if any(keyword in goal.lower() for keyword in ['编程', '代码', '开发']):
category = "编程"
elif any(keyword in goal.lower() for keyword in ['数学', '计算', '统计']):
category = "数学"
elif any(keyword in goal.lower() for keyword in ['英语', '语言', '口语']):
category = "语言"
else:
category = "通用"
if category in resource_categories:
return resource_categories[category]
else:
return ["在线课程", "实践项目", "参考书籍", "社区论坛"]
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
assistant = PersonalLearningAssistant("学习助手")
print("=== 个人学习助手演示 ===")
# 设置学习目标
goal = "Python人工智能编程"
print(assistant.set_learning_goal(goal, "2024-12-31"))
# 创建学习计划
plan = assistant.create_study_plan(goal, hours_per_week=8, weeks=6)
print("\n=== 学习计划 ===")
print(f"目标: {plan['goal']}")
print(f"总时长: {plan['total_hours']} 小时")
print("每周主题:")
for topic in plan['weekly_topics']:
print(f" - {topic}")
# 生成测验
quiz = assistant.quiz_me("机器学习", difficulty="medium", num_questions=3)
print("\n=== 测验题目 ===")
for question in quiz['questions']:
print(f"{question['id']}. {question['question']}")
# 总结内容
content = "人工智能是计算机科学的一个分支,旨在创造能够执行通常需要人类智能的任务的机器。这些任务包括学习、推理、问题解决、感知和语言理解。人工智能可以分为弱人工智能和强人工智能,弱人工智能专注于特定任务,而强人工智能则具有通用的人类级智能。"
summary = assistant.summarize_content(content)
print("\n=== 内容总结 ===")
print(f"总结: {summary['summary']}")
print(f"长度减少: {summary['reduction_ratio']}")
# 跟踪进度
progress = assistant.track_progress()
print("\n=== 学习进度 ===")
print(f"总目标数: {progress['total_goals']}")
for goal_progress in progress['goals']:
print(f"- {goal_progress['goal']}: {goal_progress['progress']} 完成")
5.2 系统架构图
graph TB subgraph UserInterfaceLayer["用户界面层"] A[Web界面] B[移动应用] C[API接口] D[命令行工具] end subgraph ApplicationServiceLayer["应用服务层"] E[学习助手服务] F[任务管理服务] G[记忆管理服务] H[工具执行服务] end subgraph AICoreLayer["AI核心层"] I[语言理解模块] J[规划决策模块] K[对话管理模块] L[学习优化模块] end subgraph DataStorageLayer["数据存储层"] M[用户数据] N[记忆存储] O[知识库] P[学习记录] end subgraph ExternalServiceLayer["外部服务层"] Q[AI模型API] R[工具API] S[知识图谱] T[云存储] end A --> E B --> E C --> E D --> E E --> F E --> G E --> H F --> J G --> I H --> J I --> Q J --> Q K --> Q E --> M E --> N E --> O E --> P H --> R E --> S G --> T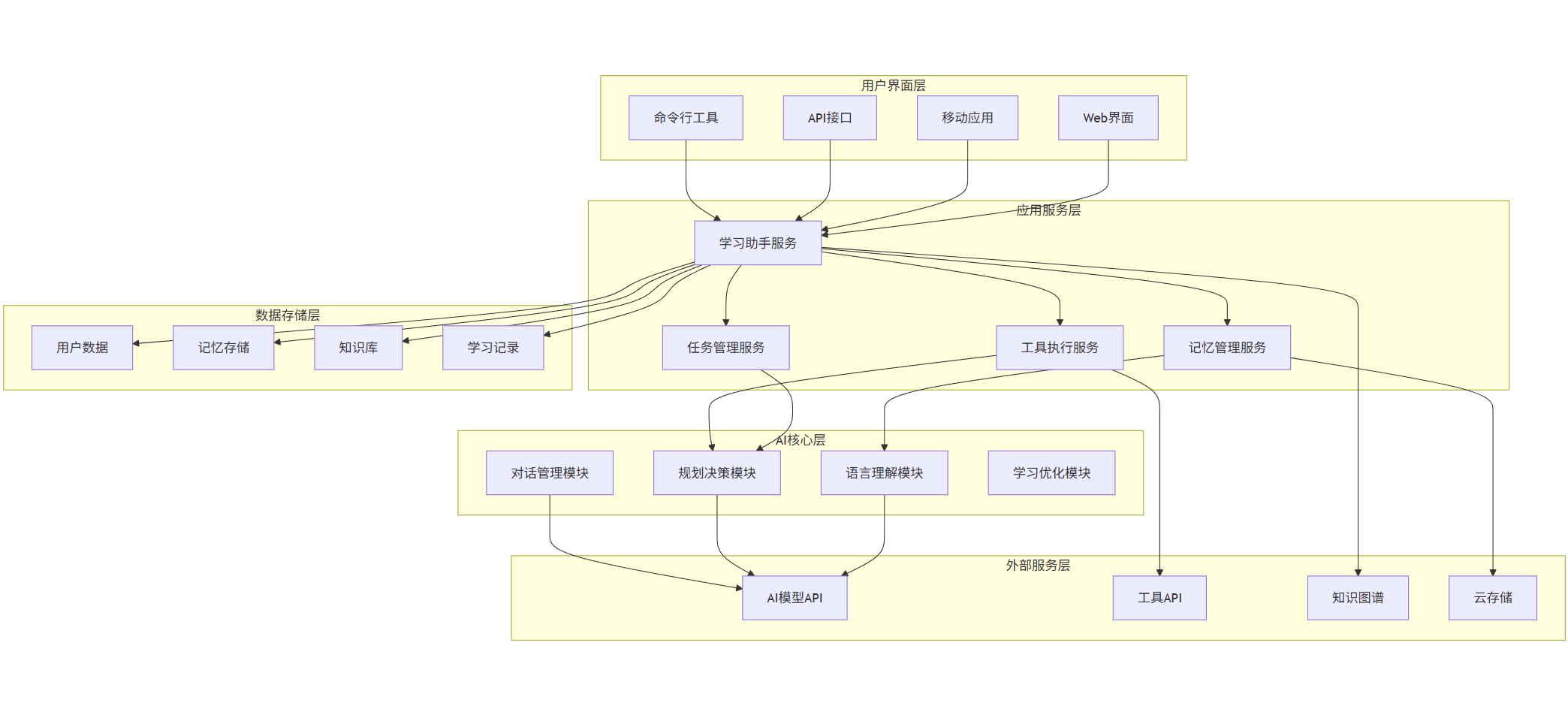
第六部分:性能优化与最佳实践
6.1 性能监控与优化
python
import time
import psutil
import logging
from functools import wraps
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, List, Any
@dataclass
class PerformanceMetrics:
response_time: float
memory_usage: float
cpu_usage: float
success: bool
timestamp: float
class PerformanceMonitor:
def __init__(self):
self.metrics: List[PerformanceMetrics] = []
self.logger = logging.getLogger('PerformanceMonitor')
def monitor_performance(self, func):
"""性能监控装饰器"""
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
start_memory = psutil.Process().memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
start_cpu = psutil.cpu_percent()
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
success = True
except Exception as e:
result = None
success = False
self.logger.error(f"函数 {func.__name__} 执行失败: {e}")
end_time = time.time()
end_memory = psutil.Process().memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
end_cpu = psutil.cpu_percent()
metrics = PerformanceMetrics(
response_time=end_time - start_time,
memory_usage=end_memory - start_memory,
cpu_usage=end_cpu - start_cpu,
success=success,
timestamp=time.time()
)
self.metrics.append(metrics)
self._check_performance_thresholds(metrics, func.__name__)
return result
return wrapper
def _check_performance_thresholds(self, metrics: PerformanceMetrics, func_name: str):
"""检查性能阈值"""
warnings = []
if metrics.response_time > 5.0: # 5秒阈值
warnings.append(f"响应时间过长: {metrics.response_time:.2f}秒")
if metrics.memory_usage > 100: # 100MB阈值
warnings.append(f"内存使用过多: {metrics.memory_usage:.2f}MB")
if metrics.cpu_usage > 50: # 50%阈值
warnings.append(f"CPU使用率过高: {metrics.cpu_usage:.2f}%")
if warnings:
warning_msg = f"性能警告 [{func_name}]: " + "; ".join(warnings)
self.logger.warning(warning_msg)
def get_performance_report(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取性能报告"""
if not self.metrics:
return {"error": "没有可用的性能数据"}
successful_metrics = [m for m in self.metrics if m.success]
if not successful_metrics:
return {"error": "没有成功的执行记录"}
return {
"total_executions": len(self.metrics),
"success_rate": len(successful_metrics) / len(self.metrics),
"avg_response_time": sum(m.response_time for m in successful_metrics) / len(successful_metrics),
"max_response_time": max(m.response_time for m in successful_metrics),
"avg_memory_usage": sum(m.memory_usage for m in successful_metrics) / len(successful_metrics),
"total_monitoring_duration": self.metrics[-1].timestamp - self.metrics[0].timestamp
}
# 优化的代理类
class OptimizedAIAgent(AdvancedAIAgent):
def __init__(self, name: str):
super().__init__(name)
self.performance_monitor = PerformanceMonitor()
self.cache = {}
self.request_timeout = 30
@PerformanceMonitor.monitor_performance
def process_with_memory_optimized(self, user_input: str) -> str:
"""优化的记忆处理"""
# 检查缓存
cache_key = f"response_{hash(user_input)}"
if cache_key in self.cache:
return self.cache[cache_key]
# 原有的处理逻辑
response = super().process_with_memory(user_input)
# 缓存结果
self.cache[cache_key] = response
return response
def clear_cache(self):
"""清空缓存"""
self.cache.clear()
def optimize_memory_usage(self):
"""优化内存使用"""
# 清理旧的记忆
current_time = time.time()
self.memory_system.memories = [
memory for memory in self.memory_system.memories
if current_time - memory['timestamp'].timestamp() < 30 * 24 * 3600 # 保留30天内的记忆
]
# 限制记忆数量
if len(self.memory_system.memories) > 500:
self.memory_system.memories = self.memory_system.memories[-500:]
# 清理缓存
if len(self.cache) > 100:
# 保留最近使用的100个缓存项
self.cache = dict(list(self.cache.items())[-100:])
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 设置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
agent = OptimizedAIAgent("优化助手")
# 测试性能监控
test_inputs = [
"你好,请介绍一下人工智能",
"计算 123 * 456 的结果",
"什么是机器学习",
"Python编程的最佳实践",
"如何学习深度学习"
]
print("=== 性能测试 ===")
for i, input_text in enumerate(test_inputs, 1):
print(f"处理请求 {i}: {input_text}")
response = agent.process_with_memory_optimized(input_text)
print(f"响应: {response[:50]}...")
print("-" * 50)
# 获取性能报告
report = agent.performance_monitor.get_performance_report()
print("\n=== 性能报告 ===")
for key, value in report.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
# 优化内存使用
agent.optimize_memory_usage()
print("\n✓ 内存优化完成")
6.2 错误处理与容错机制
python
class RobustAIAgent(OptimizedAIAgent):
def __init__(self, name: str):
super().__init__(name)
self.error_count = 0
self.max_errors = 10
self.recovery_actions = []
self.fallback_responses = [
"我遇到了一些技术问题,请稍后再试。",
"系统正在维护中,请稍后联系。",
"我目前无法处理这个请求,你可以尝试重新表述问题。",
"服务暂时不可用,正在努力修复中。"
]
def safe_process_request(self, user_input: str) -> str:
"""安全处理请求,包含错误恢复"""
try:
# 检查错误计数
if self.error_count >= self.max_errors:
return "系统检测到过多错误,已进入安全模式。请稍后重试。"
response = self.process_with_memory_optimized(user_input)
self.error_count = 0 # 重置错误计数
return response
except Exception as e:
self.error_count += 1
self.log_error(e, user_input)
# 执行恢复动作
self.execute_recovery_actions()
# 返回降级响应
return self.get_fallback_response()
def log_error(self, error: Exception, user_input: str):
"""记录错误"""
error_info = {
'timestamp': datetime.now(),
'error_type': type(error).__name__,
'error_message': str(error),
'user_input': user_input,
'error_count': self.error_count
}
# 在实际应用中,这里会记录到日志文件或数据库
print(f"错误记录: {error_info}")
# 添加到记忆系统用于学习
self.memory_system.add_memory(
content=f"系统错误: {error} - 输入: {user_input}",
memory_type="error",
importance=0.6,
metadata=error_info
)
def add_recovery_action(self, action: Callable, description: str):
"""添加恢复动作"""
self.recovery_actions.append({
'action': action,
'description': description
})
def execute_recovery_actions(self):
"""执行恢复动作"""
print(f"执行恢复动作 (错误计数: {self.error_count})")
for recovery in self.recovery_actions:
try:
recovery['action']()
print(f"✓ 执行恢复: {recovery['description']}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"✗ 恢复动作失败: {e}")
def get_fallback_response(self) -> str:
"""获取降级响应"""
import random
return random.choice(self.fallback_responses)
def health_check(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""健康检查"""
return {
'status': 'healthy' if self.error_count < 5 else 'degraded',
'error_count': self.error_count,
'memory_usage_mb': psutil.Process().memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024,
'cache_size': len(self.cache),
'memory_count': len(self.memory_system.memories),
'uptime': time.time() - getattr(self, '_start_time', time.time())
}
# 恢复动作示例
def clear_cache_recovery():
"""清理缓存恢复动作"""
# 这个函数会被添加到恢复动作中
pass
def restart_components_recovery():
"""重启组件恢复动作"""
# 这个函数会被添加到恢复动作中
pass
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
robust_agent = RobustAIAgent("健壮助手")
# 添加恢复动作
robust_agent.add_recovery_action(
clear_cache_recovery,
"清理缓存"
)
robust_agent.add_recovery_action(
robust_agent.optimize_memory_usage,
"优化内存使用"
)
print("=== 健壮性测试 ===")
# 测试正常请求
response = robust_agent.safe_process_request("你好")
print(f"正常响应: {response}")
# 健康检查
health = robust_agent.health_check()
print(f"健康状态: {health}")
总结
本教程详细介绍了AgenticAI和AI编程的各个方面,从基础概念到高级应用,涵盖了:
-
AgenticAI基础:智能代理的核心概念和基本架构
-
AI编程环境:Python AI开发环境的搭建和基础模型使用
-
智能代理系统:任务导向型代理的设计和实现
-
高级功能:记忆系统、工具集成、API调用
-
实际应用:个人学习助手的完整实现
-
性能优化:监控、优化和容错机制
通过详细讲解和丰富的代码示例,你应该已经掌握了构建智能AI代理系统的核心技能。这些知识可以应用于各种实际场景,如个人助手、客服系统、教育工具等。
记住,AI代理开发是一个不断迭代的过程,持续学习新的技术和方法,结合实际需求进行创新,才能构建出真正有用的AI系统。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献33条内容
已为社区贡献33条内容







所有评论(0)