每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 10 - MCP通信过程追踪与调试技能训练(一)
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 10 - MCP通信过程追踪与调试技能训练(一)!如果文章对你有帮助,还请给个三连好评,感谢感谢!
·
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP 40天学习计划 - 第10天
朋友们,我又来啦!今天我们要化身智能世界的"福尔摩斯",学会追踪MCP系统中每一个数据包的蛛丝马迹。就像给病人做检查需要各种仪器一样,我们调试MCP也需要掌握各种"诊断工具"。不过别担心,我会用最接地气的方式,让你从调试小白变成排错大师!
MCP通信过程追踪与调试技能训练(第一部分)
一、MCP调试的重要性与基本概念
想象一下,MCP系统就像一个繁忙的快递网络,消息像包裹一样在客户端和服务端之间飞来飞去。当包裹出现延误、丢失或者损坏时,我们就需要像快递公司的客服一样,追踪每个包裹的轨迹,找出问题到底出在哪里。
调试技能等级对照表
| 等级 | 技能描述 | 掌握工具 | 解决问题类型 | 比喻说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新手村 | 会看错误信息,能重启解决 | 基础日志查看 | 简单连接问题 | 像会换灯泡的普通人 |
| 青铜段 | 能分析日志,定位基本问题 | Claude Desktop调试 | 配置和权限问题 | 像会修水龙头的居民 |
| 白银段 | 能追踪消息流,分析通信过程 | 消息追踪、JSON解析 | 通信协议问题 | 像会修电路的电工 |
| 黄金段 | 能结合多种工具,快速定位 | 多工具组合使用 | 复杂系统性问题 | 像经验丰富的维修师傅 |
| 钻石段 | 能预测问题,主动优化系统 | 性能分析、预警系统 | 性能和稳定性问题 | 像系统架构师 |
二、Claude Desktop调试模式启用指南
Claude Desktop的调试模式就像给汽车装上了行车记录仪,能够记录下所有重要的"行车数据"。让我们一步步来启用这个强大的调试功能。
调试模式配置步骤表
| 步骤 | 操作内容 | 配置文件位置 | 关键参数 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 找到配置文件 | ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json (macOS) |
- | Windows路径不同 |
| 2 | 备份原配置 | 复制配置文件 | - | 防止配置错误无法恢复 |
| 3 | 启用调试日志 | 添加调试参数 | "debugLogging": true |
重启Claude Desktop生效 |
| 4 | 设置日志级别 | 配置详细程度 | "logLevel": "debug" |
debug > info > warn > error |
| 5 | 验证配置 | 检查日志输出 | 查看Console应用 | macOS系统控制台 |
Claude Desktop调试配置实现
import json
import os
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Dict, Any
class ClaudeDesktopDebugConfig:
"""Claude Desktop调试配置管理器,就像汽车的诊断仪"""
def __init__(self):
self.config_paths = {
"darwin": "~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json", # macOS
"win32": "~/AppData/Roaming/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json", # Windows
"linux": "~/.config/claude/claude_desktop_config.json" # Linux
}
self.current_config = {}
self.backup_path = ""
def get_config_path(self) -> str:
"""获取当前系统的配置文件路径"""
import platform
system = platform.system().lower()
if system == "darwin":
return os.path.expanduser(self.config_paths["darwin"])
elif system == "windows":
return os.path.expanduser(self.config_paths["win32"])
else:
return os.path.expanduser(self.config_paths["linux"])
def backup_config(self) -> bool:
"""备份原始配置,就像给重要文件做备份"""
config_path = self.get_config_path()
if not os.path.exists(config_path):
print("⚠️ 配置文件不存在,可能需要先运行Claude Desktop")
return False
# 创建备份文件名
from datetime import datetime
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
self.backup_path = f"{config_path}.backup_{timestamp}"
try:
import shutil
shutil.copy2(config_path, self.backup_path)
print(f"✅ 配置备份成功: {self.backup_path}")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 备份失败: {str(e)}")
return False
def load_current_config(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""加载当前配置"""
config_path = self.get_config_path()
try:
if os.path.exists(config_path):
with open(config_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.current_config = json.load(f)
print("✅ 当前配置加载成功")
else:
self.current_config = {}
print("⚠️ 配置文件不存在,将创建新配置")
return self.current_config
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 配置加载失败: {str(e)}")
return {}
def enable_debug_logging(self, log_level: str = "debug") -> bool:
"""启用调试日志,就像给汽车装上诊断仪"""
# 可用的日志级别
valid_levels = ["error", "warn", "info", "debug"]
if log_level not in valid_levels:
print(f"❌ 无效的日志级别: {log_level}")
print(f" 可用级别: {', '.join(valid_levels)}")
return False
# 首先备份配置
if not self.backup_config():
return False
# 加载当前配置
config = self.load_current_config()
# 添加调试配置
debug_config = {
"debugLogging": True,
"logLevel": log_level,
"enableConsoleLogging": True,
"mcpLogLevel": log_level, # MCP特定的日志级别
"enableMcpTracing": True # 启用MCP消息追踪
}
# 合并配置
config.update(debug_config)
# 保存配置
return self.save_config(config)
def save_config(self, config: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool:
"""保存配置文件"""
config_path = self.get_config_path()
try:
# 确保目录存在
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(config_path), exist_ok=True)
# 保存配置
with open(config_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(config, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
print(f"✅ 配置保存成功: {config_path}")
print("🔄 请重启Claude Desktop以使配置生效")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 配置保存失败: {str(e)}")
return False
def restore_config(self) -> bool:
"""恢复备份的配置"""
if not self.backup_path or not os.path.exists(self.backup_path):
print("❌ 没有找到备份文件")
return False
config_path = self.get_config_path()
try:
import shutil
shutil.copy2(self.backup_path, config_path)
print("✅ 配置已恢复到备份状态")
print("🔄 请重启Claude Desktop以使配置生效")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 恢复配置失败: {str(e)}")
return False
def show_debug_config(self) -> None:
"""显示当前调试相关的配置"""
config = self.load_current_config()
debug_keys = [
"debugLogging", "logLevel", "enableConsoleLogging",
"mcpLogLevel", "enableMcpTracing"
]
print("\n=== 当前调试配置 ===")
for key in debug_keys:
value = config.get(key, "未设置")
status = "✅" if value not in [False, "未设置"] else "❌"
print(f"{status} {key}: {value}")
print("\n=== MCP服务器配置 ===")
mcp_servers = config.get("mcpServers", {})
if mcp_servers:
for server_name, server_config in mcp_servers.items():
print(f"📡 {server_name}: {server_config}")
else:
print("❌ 未配置MCP服务器")
# 使用示例
def demo_debug_config():
"""演示调试配置的使用"""
print("=== Claude Desktop调试配置演示 ===\n")
config_manager = ClaudeDesktopDebugConfig()
# 显示当前配置
print("1️⃣ 查看当前配置:")
config_manager.show_debug_config()
print("\n2️⃣ 启用调试模式:")
success = config_manager.enable_debug_logging("debug")
if success:
print("\n3️⃣ 调试模式已启用,新配置:")
config_manager.show_debug_config()
print("\n📝 接下来的操作步骤:")
print(" 1. 重启Claude Desktop应用")
print(" 2. 打开系统控制台查看日志")
print(" 3. 在Claude中执行一些MCP操作")
print(" 4. 观察详细的调试信息")
print(f"\n🔄 如需恢复原配置,请运行:")
print(f" config_manager.restore_config()")
return config_manager
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo_debug_config()
📊 三、日志输出级别详解
日志级别就像医院的检查项目一样,有基础体检、全面体检和专项检查。不同的级别能看到不同详细程度的"病情报告"。
日志级别对比表
| 级别 | 详细程度 | 信息类型 | 文件大小 | 适用场景 | 医院检查比喻 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERROR | 最低 | 只记录错误 | 最小 | 生产环境监控 | 急诊科,只看紧急情况 |
| WARN | 低 | 错误 + 警告 | 小 | 正常运行监控 | 普通门诊,关注异常 |
| INFO | 中 | 基础运行信息 | 中等 | 系统状态监控 | 体检中心,了解基本状况 |
| DEBUG | 高 | 详细执行过程 | 大 | 开发调试阶段 | 全面体检,事无巨细 |
日志分析工具实现
import re
from datetime import datetime
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
class LogLevel(Enum):
"""日志级别枚举"""
ERROR = "ERROR"
WARN = "WARN"
INFO = "INFO"
DEBUG = "DEBUG"
@dataclass
class LogEntry:
"""日志条目,就像病历记录"""
timestamp: datetime
level: LogLevel
component: str # 组件名称,如"MCP", "Claude", "Server"
message: str # 消息内容
thread_id: str = "" # 线程ID
request_id: str = "" # 请求ID
raw_line: str = "" # 原始日志行
class MCPLogAnalyzer:
"""MCP日志分析器,专业的日志医生"""
def __init__(self):
# 日志格式的正则表达式模式
self.log_patterns = {
# Claude Desktop日志格式
"claude_desktop": r"(\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}.\d{3})\s+\[(\w+)\]\s+(.+)",
# MCP服务器日志格式
"mcp_server": r"\[(\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}.\d{3}Z)\]\s+(\w+):\s+(.+)",
# JSON-RPC消息格式
"json_rpc": r'.*"jsonrpc":"2.0".*"method":"([^"]+)".*"id":([^,}]+)',
}
self.log_entries = []
self.mcp_messages = []
def parse_log_line(self, line: str, source_type: str = "claude_desktop") -> LogEntry:
"""解析单行日志,就像医生看化验单"""
pattern = self.log_patterns.get(source_type)
if not pattern:
# 默认解析
return LogEntry(
timestamp=datetime.now(),
level=LogLevel.INFO,
component="Unknown",
message=line.strip(),
raw_line=line
)
match = re.match(pattern, line)
if not match:
return LogEntry(
timestamp=datetime.now(),
level=LogLevel.INFO,
component="Unknown",
message=line.strip(),
raw_line=line
)
if source_type == "claude_desktop":
timestamp_str, level_str, message = match.groups()
timestamp = datetime.strptime(timestamp_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f")
# 尝试解析日志级别
try:
level = LogLevel(level_str.upper())
except ValueError:
level = LogLevel.INFO
# 从消息中提取组件信息
component = "Claude"
if "MCP" in message:
component = "MCP"
elif "Server" in message:
component = "Server"
return LogEntry(
timestamp=timestamp,
level=level,
component=component,
message=message,
raw_line=line
)
return LogEntry(
timestamp=datetime.now(),
level=LogLevel.INFO,
component="Unknown",
message=line.strip(),
raw_line=line
)
def analyze_log_file(self, file_path: str, source_type: str = "claude_desktop") -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""分析日志文件,生成诊断报告"""
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# 解析所有日志行
for line in lines:
if line.strip(): # 跳过空行
entry = self.parse_log_line(line, source_type)
self.log_entries.append(entry)
# 生成分析报告
return self.generate_analysis_report()
except Exception as e:
return {"error": f"日志分析失败: {str(e)}"}
def generate_analysis_report(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""生成日志分析报告"""
if not self.log_entries:
return {"error": "没有日志条目可分析"}
# 统计各级别日志数量
level_counts = {}
component_counts = {}
error_messages = []
for entry in self.log_entries:
# 级别统计
level_key = entry.level.value
level_counts[level_key] = level_counts.get(level_key, 0) + 1
# 组件统计
comp_key = entry.component
component_counts[comp_key] = component_counts.get(comp_key, 0) + 1
# 收集错误信息
if entry.level == LogLevel.ERROR:
error_messages.append({
"timestamp": entry.timestamp.isoformat(),
"component": entry.component,
"message": entry.message
})
# 时间范围
if self.log_entries:
start_time = min(entry.timestamp for entry in self.log_entries)
end_time = max(entry.timestamp for entry in self.log_entries)
duration = end_time - start_time
else:
start_time = end_time = datetime.now()
duration = 0
return {
"summary": {
"total_entries": len(self.log_entries),
"time_range": {
"start": start_time.isoformat(),
"end": end_time.isoformat(),
"duration_seconds": duration.total_seconds()
},
"level_distribution": level_counts,
"component_distribution": component_counts
},
"errors": error_messages[:10], # 最近10个错误
"warnings": [
entry for entry in self.log_entries
if entry.level == LogLevel.WARN
][:5], # 最近5个警告
"health_score": self.calculate_health_score(level_counts)
}
def calculate_health_score(self, level_counts: Dict[str, int]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""计算系统健康分数,就像体检报告的健康评分"""
total = sum(level_counts.values())
if total == 0:
return {"score": 100, "status": "优秀", "description": "没有日志数据"}
# 计算各级别权重分数
weights = {"ERROR": -10, "WARN": -2, "INFO": 1, "DEBUG": 0}
weighted_score = 0
for level, count in level_counts.items():
weight = weights.get(level, 0)
weighted_score += count * weight
# 基础分数100,根据加权分数调整
base_score = 100
adjusted_score = max(0, min(100, base_score + weighted_score * 100 / total))
# 确定健康状态
if adjusted_score >= 90:
status = "优秀"
description = "系统运行非常稳定"
elif adjusted_score >= 70:
status = "良好"
description = "系统运行正常,有少量警告"
elif adjusted_score >= 50:
status = "一般"
description = "系统有一些问题需要关注"
else:
status = "较差"
description = "系统存在较多错误,需要立即处理"
return {
"score": round(adjusted_score, 1),
"status": status,
"description": description,
"details": level_counts
}
# 模拟日志分析演示
def demo_log_analysis():
"""演示日志分析功能"""
# 创建模拟日志数据
sample_logs = [
"2024-12-15 10:30:15.123 [INFO] MCP server connection established",
"2024-12-15 10:30:16.456 [DEBUG] Sending JSON-RPC request: list_tools",
"2024-12-15 10:30:16.789 [INFO] Received tools response: 3 tools available",
"2024-12-15 10:30:20.012 [WARN] Tool execution timeout warning",
"2024-12-15 10:30:25.345 [ERROR] Connection to server lost",
"2024-12-15 10:30:26.678 [INFO] Attempting to reconnect...",
"2024-12-15 10:30:27.901 [INFO] Connection restored successfully"
]
print("=== MCP日志分析演示 ===\n")
analyzer = MCPLogAnalyzer()
# 解析模拟日志
for log_line in sample_logs:
entry = analyzer.parse_log_line(log_line)
analyzer.log_entries.append(entry)
# 生成分析报告
report = analyzer.generate_analysis_report()
print(" 日志分析报告:")
print(f" 总日志条目: {report['summary']['total_entries']}")
print(f" 时间跨度: {report['summary']['time_range']['duration_seconds']:.1f}秒")
print("\n 日志级别分布:")
for level, count in report['summary']['level_distribution'].items():
print(f" {level}: {count} 条")
print("\n 系统健康评分:")
health = report['health_score']
print(f" 分数: {health['score']}/100")
print(f" 状态: {health['status']}")
print(f" 说明: {health['description']}")
print("\n 错误信息:")
for error in report['errors']:
print(f" [{error['timestamp']}] {error['component']}: {error['message']}")
return analyzer
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo_log_analysis()
🔍 四、MCP消息追踪基础知识
MCP消息追踪就像给每个快递包裹装上GPS定位器,我们能实时看到它们在网络中的运行轨迹。掌握这个技能,你就能像快递客服一样,准确告诉用户包裹现在在哪里,什么时候能到。
MCP消息流程图
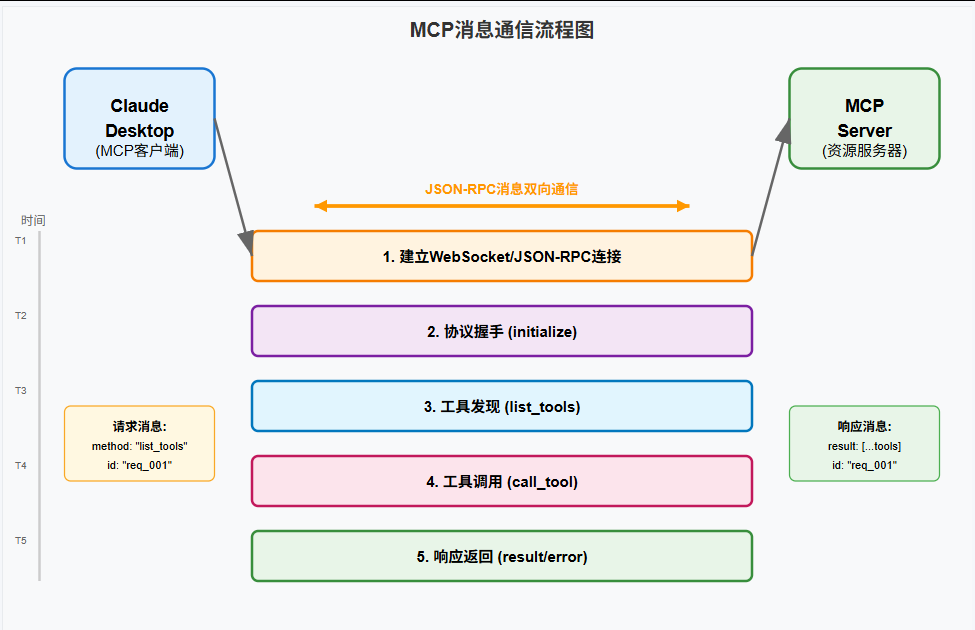
MCP消息关键信息表
| 信息类型 | 字段名称 | 数据类型 | 作用说明 | 调试价值 | 获取方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 消息标识 | id |
字符串/数字 | 唯一标识一次请求-响应 | 追踪消息配对 | JSON-RPC协议字段 |
| 时间戳 | timestamp |
ISO字符串 | 记录消息发送时间 | 计算延迟和超时 | 客户端/服务端添加 |
| 方法名称 | method |
字符串 | 指定要调用的功能 | 了解操作类型 | JSON-RPC请求字段 |
| 参数内容 | params |
对象/数组 | 传递给方法的参数 | 检查输入数据 | JSON-RPC请求字段 |
| 响应结果 | result/error |
任意类型 | 方法执行结果或错误 | 验证输出正确性 | JSON-RPC响应字段 |
| 执行耗时 | duration |
数字(毫秒) | 从请求到响应的时间 | 性能分析 | 客户端计算 |
看到这里,你是不是已经感受到了MCP调试的强大威力?就像给汽车装上了全套诊断设备,任何小毛病都逃不过我们的"火眼金睛"!在下一部分,我们将深入学习JSON-RPC消息的具体分析方法,以及如何处理各种异常情况。准备好成为MCP调试大师了吗?
欢迎大家关注同名公众号《凡人的工具箱》:关注就送学习大礼包

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容







所有评论(0)