每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 8 - MCP工具系统设计原理与实现机制(二)
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 8 - MCP工具系统设计原理与实现机制(二)!如果文章对你有帮助,还请给个三连好评,感谢感谢!
·
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP 第7天:MCP工具系统设计原理与实现机制(二)
欢迎回来!我们的MCP工具系统深度游继续进行。上半场我们搞懂了工具的基本架构,现在让我们来看看真正的"硬核"部分——错误处理和不同工具类型的实现差异。这就像学会了开车基本操作后,现在要学习如何应对各种路况!
第二部分:错误处理策略与工具类型差异
1. 工具错误处理策略:优雅地面对失败
程序出错就像生活中的意外,我们无法完全避免,但可以优雅地处理。MCP的错误处理就像一个经验丰富的客服,总能给出合适的回复!
错误分类体系:
| 错误类型 | 错误码范围 | 典型场景 | 处理策略 | 用户感知 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数错误 | 4000-4099 | 参数格式错误、缺失必填项 | 立即返回,提供修正建议 | 明确提示如何修正 |
| 权限错误 | 4100-4199 | 无访问权限、API密钥无效 | 返回权限提示 | 引导用户获取权限 |
| 资源错误 | 4200-4299 | 文件不存在、服务不可用 | 重试或降级处理 | 提供替代方案 |
| 业务错误 | 4300-4399 | 业务逻辑验证失败 | 返回业务提示 | 解释业务规则 |
| 系统错误 | 5000-5999 | 网络超时、服务器异常 | 自动重试、降级服务 | 用户友好的错误说明 |
// 错误处理中心 - 像一个智能的错误翻译官
class MCPErrorHandler {
private errorMessages: Map<string, string> = new Map([
['PARAMETER_MISSING', '看起来少了点什么参数哦!请检查必填项'],
['PARAMETER_TYPE_ERROR', '参数类型不对呢,我期望的是 {expected},但收到了 {actual}'],
['PERMISSION_DENIED', '权限不足,请联系管理员开通相关权限'],
['RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND', '找不到指定的资源,请检查路径是否正确'],
['BUSINESS_RULE_VIOLATION', '违反了业务规则:{rule}'],
['NETWORK_TIMEOUT', '网络请求超时,请稍后重试'],
['UNKNOWN_ERROR', '遇到了未知错误,技术小哥正在赶来的路上...']
]);
handleError(error: Error, context: any): MCPErrorResponse {
const errorCode = this.classifyError(error);
const userMessage = this.generateUserFriendlyMessage(error, context);
const suggestions = this.generateSuggestions(error, context);
// 记录错误日志(开发者看的)
console.error(`[MCP Error] ${errorCode}: ${error.message}`, {
stack: error.stack,
context: context,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
// 返回用户友好的错误信息
return {
success: false,
error: {
code: errorCode,
message: userMessage,
suggestions: suggestions,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
}
};
}
// 智能错误分类
private classifyError(error: Error): string {
if (error.name === 'ValidationError') return '4001';
if (error.name === 'PermissionError') return '4101';
if (error.name === 'NotFoundError') return '4201';
if (error.name === 'TimeoutError') return '5001';
if (error.message.includes('网络')) return '5002';
return '5000'; // 未知错误
}
// 生成修复建议
private generateSuggestions(error: Error, context: any): string[] {
const suggestions: string[] = [];
if (error.name === 'ValidationError') {
suggestions.push('检查参数格式是否正确');
suggestions.push('确认所有必填项都已提供');
} else if (error.name === 'TimeoutError') {
suggestions.push('检查网络连接');
suggestions.push('稍后重试');
suggestions.push('联系技术支持');
}
return suggestions;
}
}
降级处理机制:
class GracefulDegradationHandler {
async executeWithFallback(primaryTool: string, params: any, fallbackStrategies: string[]): Promise<any> {
try {
// 尝试执行主要工具
return await this.executePrimaryTool(primaryTool, params);
} catch (error) {
console.warn(`主工具执行失败: ${error.message},尝试降级处理...`);
// 按优先级尝试降级策略
for (const strategy of fallbackStrategies) {
try {
const result = await this.executeFallbackStrategy(strategy, params);
console.info(`降级策略 ${strategy} 执行成功`);
return {
...result,
warning: `主服务暂时不可用,已使用备用方案`,
fallbackUsed: strategy
};
} catch (fallbackError) {
console.warn(`降级策略 ${strategy} 也失败了: ${fallbackError.message}`);
}
}
// 所有策略都失败了,返回友好的错误信息
throw new Error('服务暂时不可用,请稍后重试');
}
}
}
2. 同步工具 vs 异步工具:不同的节奏,同样的精彩
想象同步工具像是现场表演,立即就有结果;异步工具像是外卖订餐,下单后需要等待。两者各有适用场景!
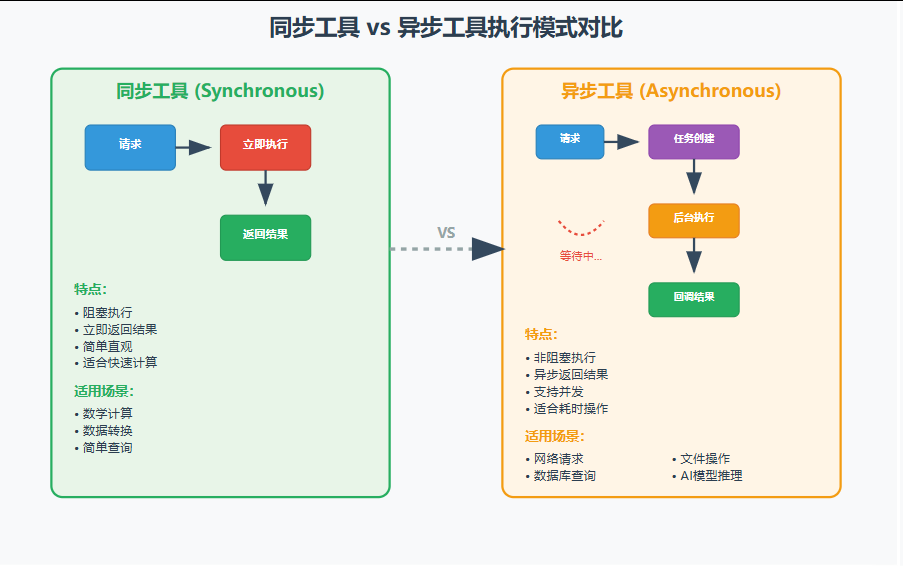
同步工具实现:
// 同步工具:简单直接,立竿见影
class SynchronousCalculatorTool implements MCPTool {
name = "sync_calculator";
description = "同步计算器,立即返回计算结果";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
expression: { type: "string", description: "数学表达式,如 '2 + 3 * 4'" }
},
required: ["expression"]
};
// 同步执行:一气呵成,没有等待
async execute(params: { expression: string }): Promise<any> {
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
// 安全的表达式计算(实际项目中建议使用math.js等库)
const result = this.safeEvaluate(params.expression);
return {
result: result,
expression: params.expression,
executionTime: Date.now() - startTime,
type: "synchronous"
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`计算表达式失败: ${error.message}`);
}
}
private safeEvaluate(expression: string): number {
// 简化的安全计算实现
const sanitized = expression.replace(/[^0-9+\-*/().\s]/g, '');
return Function(`"use strict"; return (${sanitized})`)();
}
}
异步工具实现:
// 异步工具:耐心等待,厚积薄发
class AsynchronousWeatherTool implements MCPTool {
name = "async_weather";
description = "异步天气查询,从远程服务获取天气信息";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
city: { type: "string", description: "城市名称" },
days: { type: "number", description: "预报天数", default: 1 }
},
required: ["city"]
};
// 异步执行:好事多磨,值得等待
async execute(params: { city: string; days?: number }): Promise<any> {
const taskId = this.generateTaskId();
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
console.log(`启动异步天气查询任务: ${taskId}`);
// 模拟异步网络请求
const weatherData = await this.fetchWeatherData(params.city, params.days || 1);
// 模拟一些数据处理时间
await this.processWeatherData(weatherData);
const result = {
taskId: taskId,
city: params.city,
weather: weatherData,
forecast: await this.generateForecast(weatherData),
executionTime: Date.now() - startTime,
type: "asynchronous",
completed: true
};
console.log(`异步任务完成: ${taskId},耗时: ${result.executionTime}ms`);
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.error(`异步任务失败: ${taskId}, 错误: ${error.message}`);
throw new Error(`天气查询失败: ${error.message}`);
}
}
private async fetchWeatherData(city: string, days: number): Promise<any> {
// 模拟网络延迟
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500));
// 模拟天气API响应
return {
current: {
temperature: Math.round(Math.random() * 30 + 5),
humidity: Math.round(Math.random() * 100),
description: ["晴朗", "多云", "小雨", "阴天"][Math.floor(Math.random() * 4)]
},
location: city
};
}
private generateTaskId(): string {
return `weather_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9)}`;
}
private async processWeatherData(data: any): Promise<void> {
// 模拟数据处理时间
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 500));
}
private async generateForecast(data: any): Promise<any[]> {
// 模拟预报生成
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 300));
return [
{ day: "今天", temp: data.current.temperature, desc: data.current.description },
{ day: "明天", temp: data.current.temperature + 2, desc: "多云" }
];
}
}
3. 简单工具 vs 复杂工具:从瑞士军刀到专业工具箱
简单工具像瑞士军刀,功能单一但精准;复杂工具像专业工具箱,功能丰富但需要更多配置。
工具复杂度对比表:
| 特征维度 | 简单工具 | 复杂工具 | 举例对比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 参数数量 | 1-3个 | 5个以上 | 计算器 vs 数据分析工具 |
| 依赖服务 | 无或单一 | 多个外部服务 | 字符串处理 vs 智能翻译 |
| 执行时间 | < 100ms | 可能数秒到数分钟 | 加法运算 vs 图像生成 |
| 错误场景 | 参数错误为主 | 网络、权限、业务等多种错误 | 类型检查 vs 支付处理 |
| 配置复杂度 | 即插即用 | 需要详细配置 | 随机数生成 vs 机器学习推理 |
// 简单工具示例:文本长度计算器
class SimpleTextLengthTool implements MCPTool {
name = "text_length";
description = "计算文本长度,支持字符数和字节数统计";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
text: { type: "string", description: "要计算长度的文本" },
mode: { type: "string", enum: ["chars", "bytes"], default: "chars" }
},
required: ["text"]
};
async execute(params: { text: string; mode?: string }): Promise<any> {
const mode = params.mode || "chars";
if (mode === "chars") {
return {
length: params.text.length,
mode: "characters",
text: params.text.substring(0, 50) + (params.text.length > 50 ? "..." : "")
};
} else {
const bytes = Buffer.from(params.text, 'utf8').length;
return {
length: bytes,
mode: "bytes",
text: params.text.substring(0, 50) + (params.text.length > 50 ? "..." : "")
};
}
}
}
// 复杂工具示例:智能数据分析器
class ComplexDataAnalysisTool implements MCPTool {
name = "data_analysis";
description = "复杂数据分析工具,支持多维度统计和可视化";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
dataSource: {
type: "object",
properties: {
type: { type: "string", enum: ["csv", "json", "database"] },
path: { type: "string" },
connectionConfig: { type: "object" }
}
},
analysisConfig: {
type: "object",
properties: {
metrics: { type: "array", items: { type: "string" } },
groupBy: { type: "array", items: { type: "string" } },
filters: { type: "object" },
timeRange: { type: "object" }
}
},
outputFormat: {
type: "string",
enum: ["summary", "detailed", "visualization"],
default: "summary"
}
},
required: ["dataSource", "analysisConfig"]
};
async execute(params: any): Promise<any> {
const taskId = `analysis_${Date.now()}`;
const steps = [
"数据源连接",
"数据加载",
"数据清洗",
"统计分析",
"结果生成"
];
try {
let progress = 0;
const results: any = { taskId, steps: [] };
for (const step of steps) {
console.log(`执行步骤: ${step} (${++progress}/${steps.length})`);
await this.executeAnalysisStep(step, params);
results.steps.push({
step,
completed: true,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
// 模拟每个步骤的处理时间
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 800));
}
// 生成最终分析报告
const analysisResult = await this.generateAnalysisReport(params);
return {
...results,
analysis: analysisResult,
completed: true,
totalExecutionTime: Date.now() - parseInt(taskId.split('_')[1])
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`数据分析失败: ${error.message}`);
}
}
private async executeAnalysisStep(step: string, params: any): Promise<void> {
// 根据不同步骤执行相应的处理逻辑
switch (step) {
case "数据源连接":
await this.connectDataSource(params.dataSource);
break;
case "数据加载":
await this.loadData(params.dataSource);
break;
case "数据清洗":
await this.cleanData(params.analysisConfig);
break;
case "统计分析":
await this.performAnalysis(params.analysisConfig);
break;
case "结果生成":
await this.generateResults(params.outputFormat);
break;
}
}
private async connectDataSource(config: any): Promise<void> {
// 数据源连接逻辑
console.log(`连接到 ${config.type} 数据源...`);
}
private async generateAnalysisReport(params: any): Promise<any> {
return {
summary: "数据分析完成",
recordsProcessed: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10000),
insights: [
"发现数据中存在明显的季节性趋势",
"某些指标之间存在强相关性",
"检测到3个异常数据点需要关注"
]
};
}
}
通过这些对比,我们可以看出,不同类型的工具有着截然不同的设计哲学和实现策略。选择合适的工具类型就像选择合适的交通工具一样——去楼下买菜用不着开飞机,跨国旅行也不能靠自行车!
理解了这些差异,你就能在设计MCP工具时做出明智的架构选择,创造出既高效又实用的工具系统。
欢迎大家关注同名公众号《凡人的工具箱》:关注就送学习大礼包

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容







所有评论(0)