每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 8 - MCP工具系统设计原理与实现机制(一)
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 8 - MCP工具系统设计原理与实现机制(一)!如果文章对你有帮助,还请给个三连好评,感谢感谢!
·
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP 第8天:MCP工具系统设计原理与实现机制(一)
哈喽!欢迎来到第7天的学习!今天我们要深入MCP工具系统的内核,就像拆解一台精密的瑞士手表一样,看看每个齿轮是怎么完美配合的。别担心,我会用最通俗的话让你明白这些看似复杂的概念!
第一部分:MCP工具系统核心设计理念
1. 工具抽象:把复杂变简单的魔法
想象一下,你有一个万能遥控器,无论是电视、空调还是音响,都能用同样的方式操控。MCP工具系统的抽象就是这个道理!
核心理念:统一接口,多样实现
// MCP工具的抽象定义 - 就像定义遥控器的标准按钮
interface MCPTool {
name: string; // 工具名称(比如"计算器")
description: string; // 工具描述(告诉AI这工具干啥的)
inputSchema: object; // 输入参数格式(按哪些按钮)
execute: (params: any) => Promise<any>; // 执行函数(按下去会发生什么)
}
// 具体的工具实现 - 就像不同品牌的遥控器
class CalculatorTool implements MCPTool {
name = "calculator";
description = "执行基础数学运算,支持加减乘除";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
operation: { type: "string", enum: ["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"] },
a: { type: "number" },
b: { type: "number" }
},
required: ["operation", "a", "b"]
};
async execute(params: { operation: string; a: number; b: number }) {
const { operation, a, b } = params;
switch (operation) {
case "add": return { result: a + b };
case "subtract": return { result: a - b };
case "multiply": return { result: a * b };
case "divide":
if (b === 0) throw new Error("除数不能为零!数学老师会生气的!");
return { result: a / b };
default:
throw new Error(`不支持的运算:${operation}`);
}
}
}
2. 接口标准化:让所有工具说同一种语言
就像全世界的USB接口都是标准化的一样,MCP工具也有统一的"接口规范"。
工具注册表结构:
| 字段名 | 类型 | 必需 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | ✅ | 工具唯一标识符 | “weather_query” |
| description | string | ✅ | 工具功能描述 | “查询指定城市的天气信息” |
| inputSchema | object | ✅ | JSON Schema格式的参数定义 | 见下方示例 |
| outputSchema | object | ❌ | 返回值格式定义 | 可选,用于文档和验证 |
| metadata | object | ❌ | 额外元数据 | 版本、作者、标签等 |
// 天气查询工具的完整定义
const weatherTool = {
name: "weather_query",
description: "查询指定城市的实时天气信息,支持中英文城市名",
// 输入参数的JSON Schema定义
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
city: {
type: "string",
description: "城市名称",
examples: ["北京", "Shanghai", "New York"]
},
unit: {
type: "string",
description: "温度单位",
enum: ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
default: "celsius"
}
},
required: ["city"]
},
// 输出格式定义(可选)
outputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
temperature: { type: "number" },
humidity: { type: "number" },
description: { type: "string" },
city: { type: "string" }
}
},
// 元数据信息
metadata: {
version: "1.0.0",
author: "Weather API Team",
tags: ["weather", "api", "real-time"]
}
};
3. 执行流程控制:工具运行的生命周期
想象工具执行就像做菜一样,有固定的步骤:准备食材(参数验证)→ 下锅炒制(业务逻辑)→ 装盘上桌(结果返回)。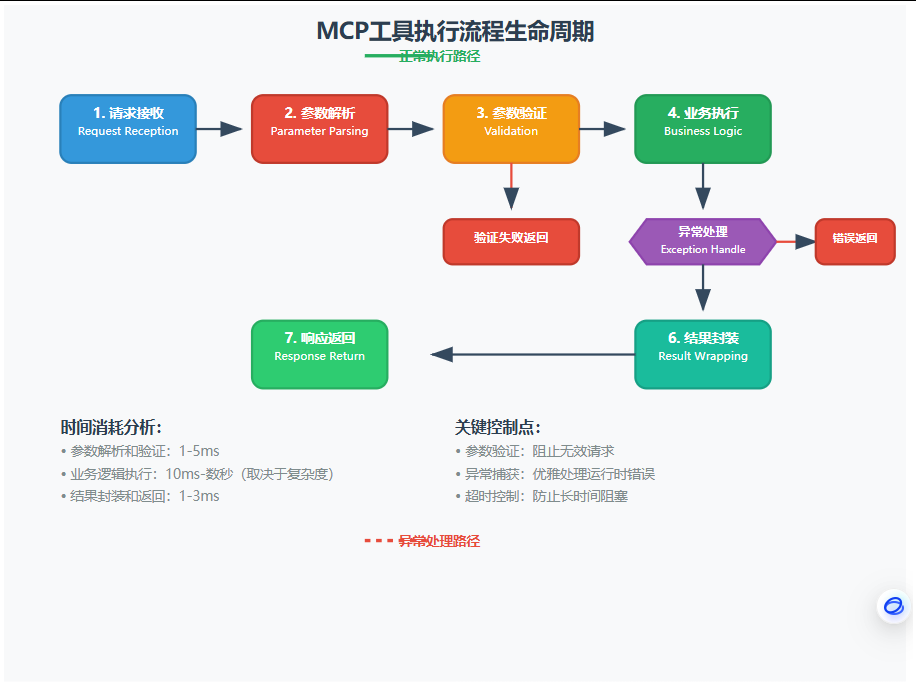
流程控制核心代码:
class MCPToolExecutor {
async executeToolCall(toolName: string, params: any): Promise<any> {
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
// 1. 请求接收 - 记录执行开始
console.log(`🚀 开始执行工具: ${toolName}`);
// 2. 参数解析 - 确保参数格式正确
const parsedParams = this.parseParameters(params);
// 3. 参数验证 - 这是第一道防线!
const validationResult = await this.validateParameters(toolName, parsedParams);
if (!validationResult.isValid) {
throw new ValidationError(`参数验证失败: ${validationResult.errors.join(', ')}`);
}
// 4. 业务逻辑执行 - 这里是真正干活的地方
const tool = this.getTool(toolName);
const result = await this.executeWithTimeout(tool, parsedParams, 30000); // 30秒超时
// 5. 结果封装 - 统一返回格式
const wrappedResult = {
success: true,
data: result,
executionTime: Date.now() - startTime,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
};
console.log(`✅ 工具执行成功,耗时: ${wrappedResult.executionTime}ms`);
return wrappedResult;
} catch (error) {
// 6. 异常处理 - 优雅地处理各种错误
const errorResult = {
success: false,
error: {
type: error.constructor.name,
message: error.message,
code: this.getErrorCode(error)
},
executionTime: Date.now() - startTime,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
};
console.error(`❌ 工具执行失败: ${error.message}`);
return errorResult;
}
}
// 带超时的执行器 - 防止工具执行时间过长
private async executeWithTimeout(tool: MCPTool, params: any, timeoutMs: number) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
reject(new TimeoutError(`工具执行超时 (${timeoutMs}ms)`));
}, timeoutMs);
tool.execute(params)
.then(result => {
clearTimeout(timer);
resolve(result);
})
.catch(error => {
clearTimeout(timer);
reject(error);
});
});
}
}
4. 参数验证体系:多层防护的安全门
就像机场安检有多道关卡一样,MCP工具的参数验证也是多层次的。每一层都在守护系统的安全和稳定!
验证层级结构:
| 验证层级 | 验证内容 | 失败后果 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 类型检查 | 数据类型是否正确 | 立即拒绝 | string传入了number |
| 格式验证 | 格式是否符合规范 | 立即拒绝 | 邮箱格式不正确 |
| 取值范围 | 值是否在允许范围内 | 立即拒绝 | 年龄传入-5 |
| 业务规则 | 是否符合业务逻辑 | 警告或拒绝 | 结束时间早于开始时间 |
class ParameterValidator {
// 多层验证器
async validateParameters(toolSchema: any, params: any): Promise<ValidationResult> {
const errors: string[] = [];
// 第一层:基础类型检查
const typeErrors = this.validateTypes(toolSchema, params);
errors.push(...typeErrors);
// 第二层:格式验证
const formatErrors = this.validateFormats(toolSchema, params);
errors.push(...formatErrors);
// 第三层:取值范围检查
const rangeErrors = this.validateRanges(toolSchema, params);
errors.push(...rangeErrors);
// 第四层:复杂业务规则验证
const businessErrors = await this.validateBusinessRules(toolSchema, params);
errors.push(...businessErrors);
return {
isValid: errors.length === 0,
errors: errors,
warnings: this.generateWarnings(toolSchema, params)
};
}
// 类型检查实现
private validateTypes(schema: any, params: any): string[] {
const errors: string[] = [];
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(params)) {
const fieldSchema = schema.properties[key];
if (!fieldSchema) continue;
const expectedType = fieldSchema.type;
const actualType = typeof value;
// 类型映射检查
const typeMap: { [key: string]: string } = {
'string': 'string',
'number': 'number',
'boolean': 'boolean',
'array': 'object',
'object': 'object'
};
if (expectedType === 'array' && !Array.isArray(value)) {
errors.push(`字段 '${key}' 应该是数组,但收到了 ${actualType}`);
} else if (expectedType !== 'array' && typeMap[expectedType] !== actualType) {
errors.push(`字段 '${key}' 应该是 ${expectedType},但收到了 ${actualType}`);
}
}
return errors;
}
}
看到这里,你可能会想:"哇,这么多验证,不会很慢吗?"别担心!这就像高速公路的ETC,看起来复杂,但实际上只需要几毫秒就能完成所有检查。而且这些验证能帮我们避免99%的运行时错误,绝对是物超所值的投资!
欢迎大家关注同名公众号《凡人的工具箱》:关注就送学习大礼包

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容







所有评论(0)