逆 天!从 STL 到 string,这 波 字 符 串 神 操 作 直 接 让 编 译 器 跪 了 - - - 程 序 员 必 学 的 开 挂 级 技 巧
这篇文章介绍了C++ STL中string类的使用技巧和STL基础知识。
逆 天!从 STL 到 string,这 波 字 符 串 神 操 作 直 接 让 编 译 器 跪 了 - - - 程 序 员 必 学 的 开 挂 级 技 巧
💻作 者 简 介:曾 与 你 一 样 迷 茫,现 以 经 验 助 你 入 门 C++。
💡个 人 主 页:@笑口常开xpr 的 个 人 主 页
📚系 列 专 栏:C++ 炼 魂 场:从 青 铜 到 王 者 的 进 阶 之 路
✨代 码 趣 语:迭 代 器 就 像 地 铁 检 票 员,从 起 点(begin)到 终 点(end),一 个 一 个 地 检 查(遍 历)乘 客(字 符)!
💪代 码 千 行,始 于 坚 持,每 日 敲 码,进 阶 编 程 之 路。
📦gitee 链 接:gitee

在 C++ 编 程 中,对 字 符 串 的 处 理 是 极 为 常 见 的 需 求。STL(标 准 模 板 库)中 的 string 类 作 为 专 门 用 于 字 符 串 管 理 的 工 具,封 装 了 丰 富 的 功 能,能 高 效 实 现 字 符 串 的 创 建、遍 历、增 删 查 改 等 操 作。本 文 将 从 STL 的 基 础 概 念 入 手,深 入 剖 析 string 类 的 使 用 细 节,助 力 开 发 者 熟 练 掌 握 这 一 实 用 工 具。
STL
定 义
STL(standard template libaray),即 标 准 模 版 库 的 一 部 分,I O 流 不 包 含 STL。STL 是 C++ 标 准 库 的 重 要 组 成 部 分,不 仅 是 一 个 可 复 用 的 组 件 库,而 且 是 一 个 包 含 数 据 结 构 与 算 法 的 软 件 框 架。
版 本
原 始 版 本
Alexander Stepanov、Meng Lee 在 惠 普 实 验 室 完 成 的 原 始 版 本,本着 开 源 精 神,他 们 声 明 允 许 任 何 人 任 意 运 用、拷 贝、修 改、传 播、商 业 使 用 这 些 代 码,无 需 付 费。唯 一 的 条 件 就 是 也 需 要 向 原 始 版 本 一 样 做 开 源 使 用。 HP 版 本 - - - 所 有 STL 实 现 版 本 的 始 祖。
P. J. 版 本
由 P. J. Plauger 开 发,继 承 自 HP 版 本,被 Windows Visual C++ 采 用,不 能 公 开 或 修 改。
缺 陷:可 读 性 比 较 低,符 号 命 名 比 较 怪 异。
RW 版 本
由 Rouge Wage 公 司 开 发,继 承 自 HP 版 本,被 C+ + Builder 采 用,不 能 公 开 或 修 改,可 读 性 一 般。
SGI 版 本
由 Silicon Graphics Computer Systems,Inc 公 司 开 发,继 承 自 HP 版 本。被 GCC(Linux) 采 用,可 移 植 性 好,可 公 开、修 改 甚 至 贩 卖,从 命 名 风 格 和 编 程 风 格 上 看,阅 读 性 非 常 高。
六 大 组 件
- 容 器
容 器 是 用 于 存 储 和 管 理 数 据 的 类 模 板,也 就 是 数 据 结 构,分 为 顺 序 容 器、关 联 容 器 和 容 器 适 配 器。
顺 序 容 器
vector:动 态 数 组,支 持 随 机 访 问,尾 部 插 入 / 删 除 效 率 高。
deque:双 端 队 列,支 持 头 尾 高 效 插 入 / 删 除。
list:双 向 链 表,支 持 任 意 位 置 高 效 插 入 / 删 除。
关 联 容 器
set/multiset:基 于 红 黑 树 实 现,元 素 自 动 排 序,set 不 允 许 重 复,multiset 允 许。
map/multimap:键 值 对 存 储,基 于 红 黑 树,map 键 唯 一,multimap 键 可 重 复。
-
算 法
STL 提 供 了 超 过 100 种 算 法,涵 盖 排 序、查 找、遍 历、修 改 等 操 作,通 过 迭 代 器 与 容 器 解 耦。 -
迭 代 器
迭 代 器 是 一 种 抽 象 的 指 针,用 于 遍 历 容 器 中 的 元 素,提 供 统 一 的 访 问 接 口。 -
仿 函 数
仿 函 数(也 称 函 数 对 象)是 重 载 了 operator() 的 类 或 结 构 体,可 作 为 算 法 的 参 数。 -
配 接 器
配 接 器 是 一 种 特 殊 的 函 数 对 象 或 容 器,用 于 修 改 其 他 组 件 的 接 口。 -
空 间 配 置 器
空 间 配 置 器 是 负 责 管 理 容 器 内 存 的 组 件,允 许 自 定 义 内 存 分 配 策 略。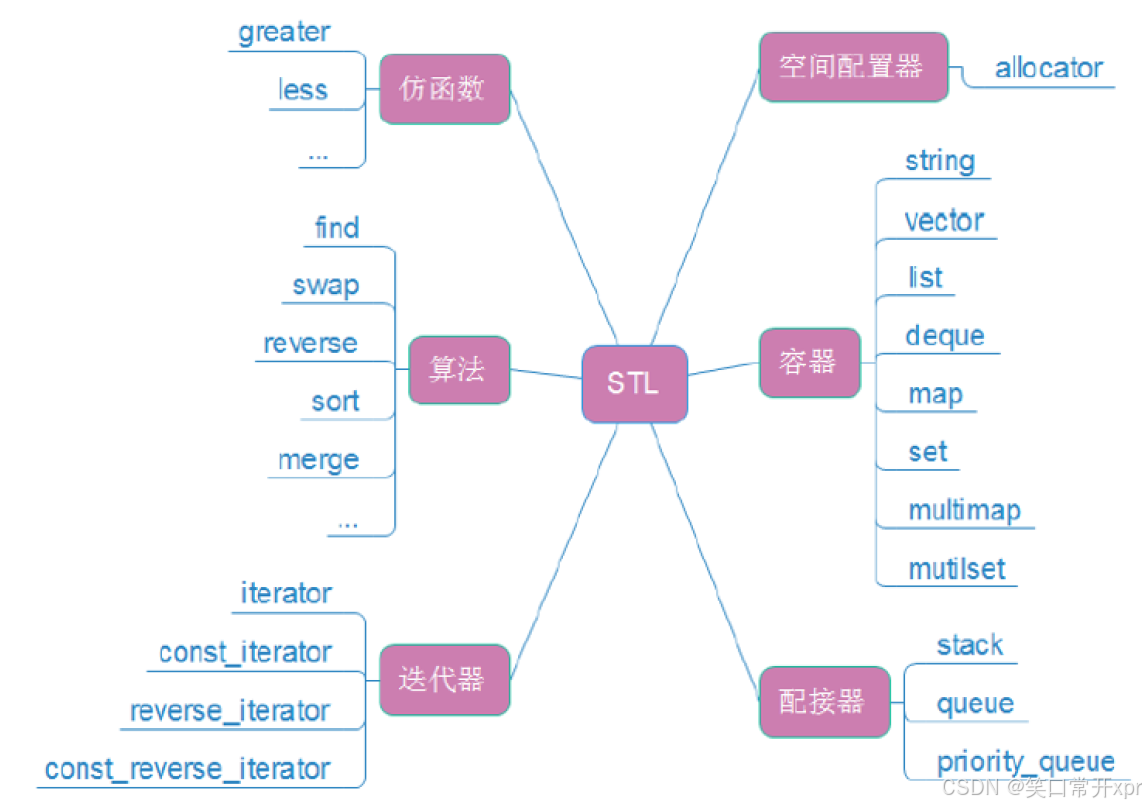
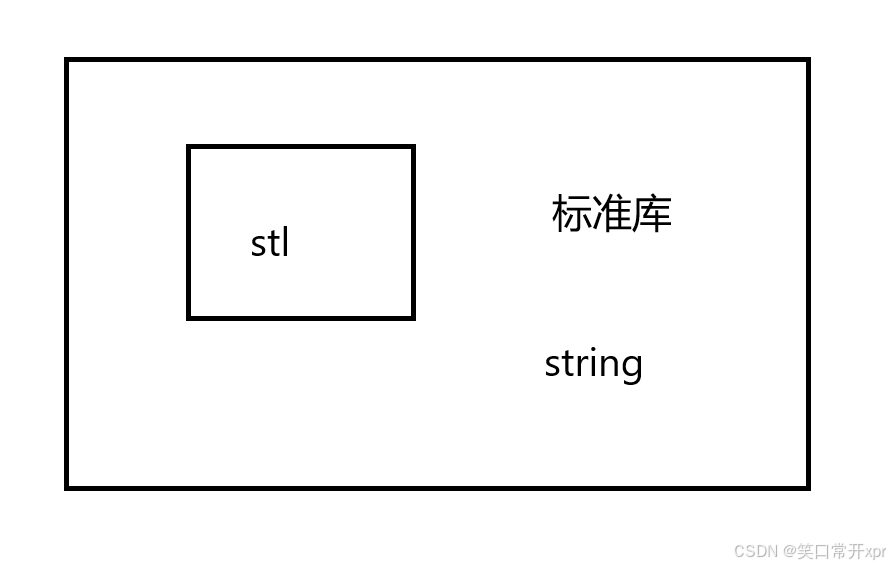
string 库
定 义
string 是 C++ 标 准 库(std)中 用 于 处 理 字 符 串 的 类,封 装 了 字 符 串 的 存 储、操 作 等 功 能,string 类 中 含 有 字 符 串 的 增 删 查 改 和 算 法,用 来 管 理 字 符 数 组。类 似 的,string 不 带 .h。
构 造 函 数
string 构 造 函 数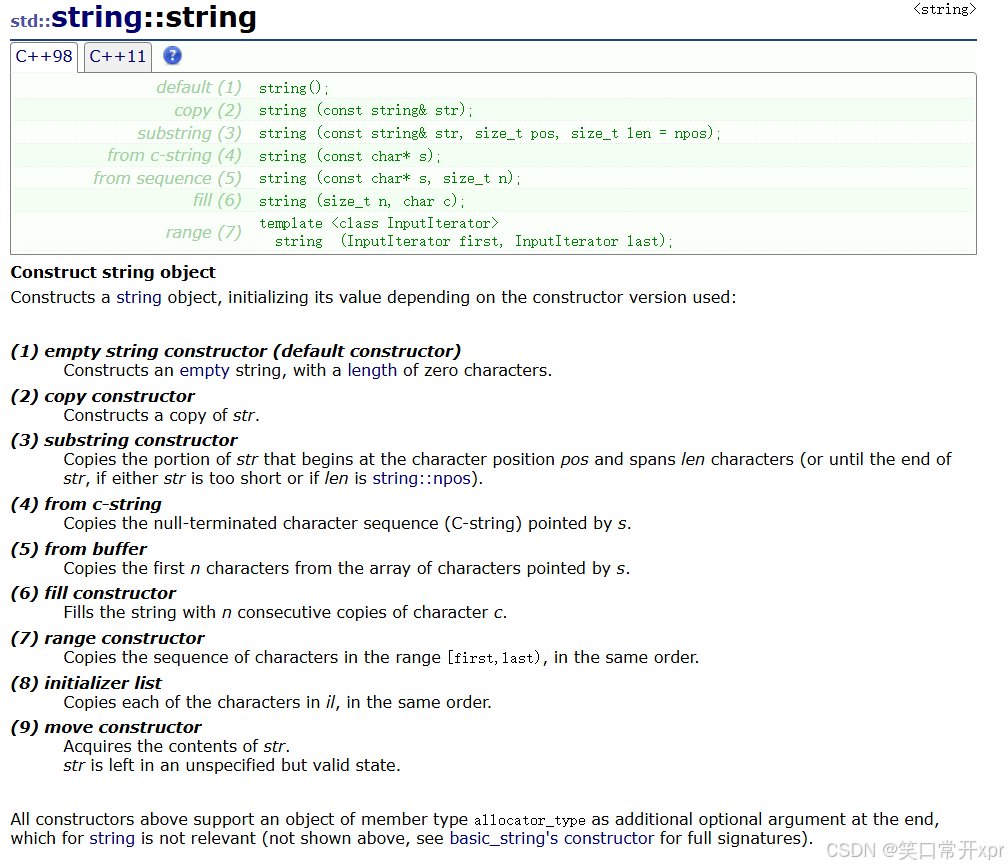
上 面 的 构 造 函 数 3、5、7 需 要 认 识,其 余 的 需 要 重 点 掌 握。
常 用 的 定 义 方 式
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;//string();
string s2("hello world");//string(const char* s);
string s3(10, '*');//n个字符初始化,string (size_t n, char c);
string s4(s2);//拷贝构造,string (const string& str);
return 0;
}
这 些 是 经 常 要 用 到 的 定 义 方 式,如 果 遇 到 不 会 的,建 议 读 者 多查 文 档。
拷 贝 字 符 串 的 一 部 分

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");//string(const char* s);
string s2(s2, 6, 5);//string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}

npos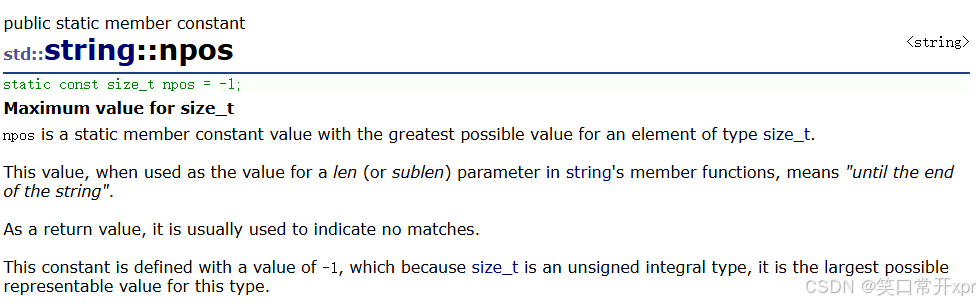
npos 是 缺 省 参 数,也 是 string 类 中 的 静 态 成 员 变 量,它 的 值 是 -1,即 默 认 的 是 整 形 的 最 大 值。如 果 npos 的 值 比 较 大 或 者 没 有 ,则 字 符 串 取 到 结 尾。
比 较 字 符 串
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("张三");
//比较
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
return 0;
}
0 表 示 false,即 条 件 不 成 立,1 表 示 true,即 条 件 成 立。
比 较 时 要 带 上 括 号,原 因 是 流 插 入 运 算 符 的 优 先 级 比 比 较 运 算 符 优 先 级 高。
字 符 串 分 割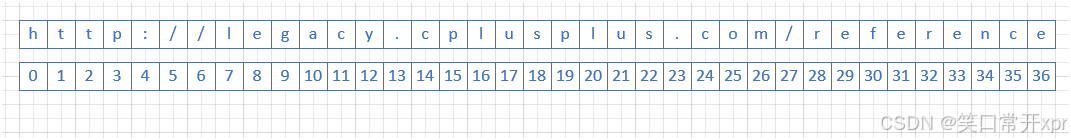
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string url("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference");
string sub1(url, 0, 5);
string sub2(url, 8, 20);
string sub3(url, 29, url.size() - 29);
cout << sub1 << endl;
cout << sub2 << endl;
cout << sub3 << endl;
return 0;
}

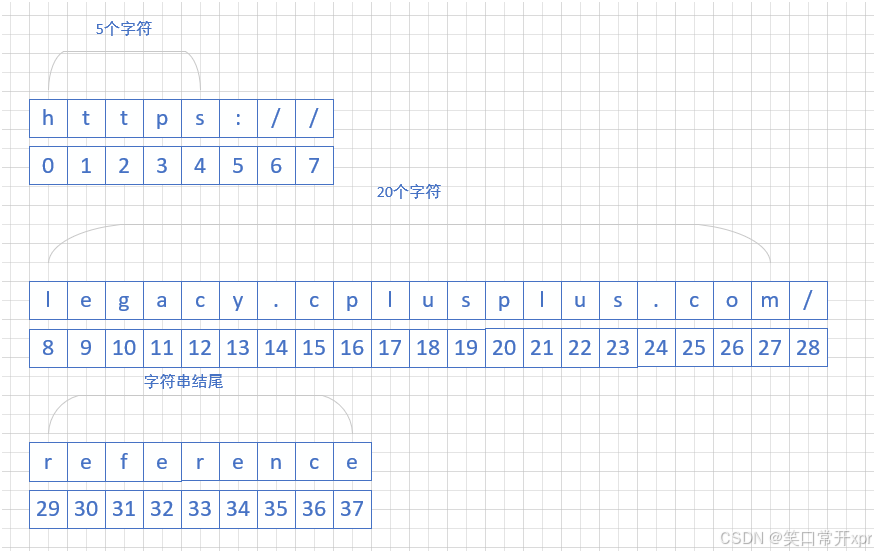
sub1 从 索 引 0 开 始 提 取 5 个 字 符。
sub2 从 索 引 8 开 始(跳 过 https://),提 取 20 个 字 符。
sub3 从 索 引 29 开 始,提 取 到 字 符 串 末 尾(url.size() 是 字 符 串 的 长 度, 减 去 前 面 的 所 有 字 符 个 数)。
赋 值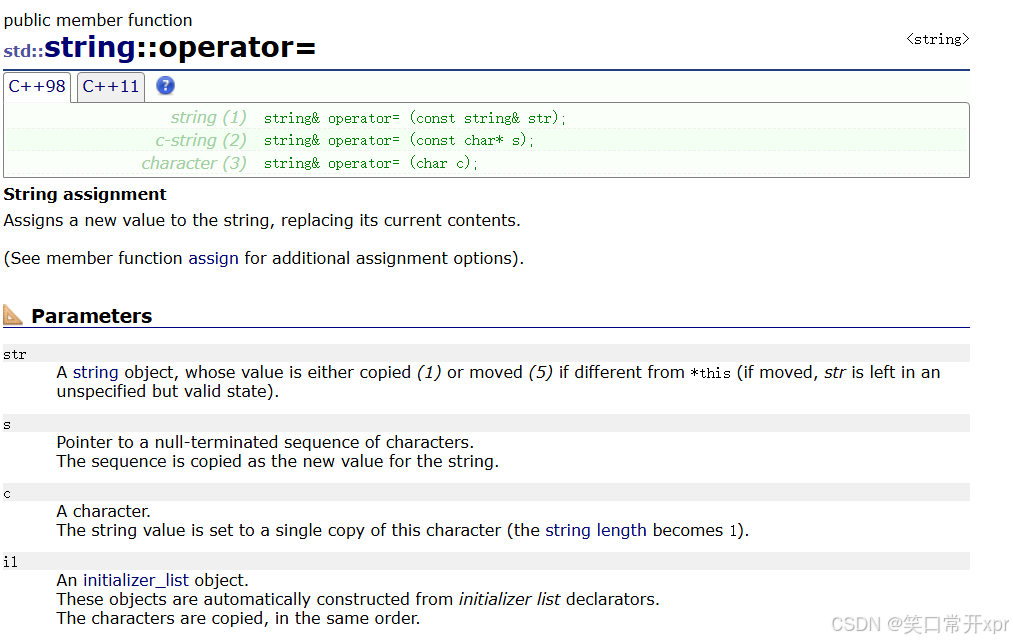
这 三 个 运 算 符 支 持 运 算 符 重 载 并 且 构 成 了 函 数 重 载。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("张三");
//operator=
s1 = s2;//string& operator=(const string & str);拷贝构造
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = "1111";//string& operator=(const char* s);常量字符串
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = '*';//string& operator=(char c);//字符
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}

析 构 函 数
析 构 函 数
对 象 出 了 作 用 域 会 自 动 调 用 析 构 函 数,我 们 不 用 写,编 译 器 会 自 动 生 成。
迭 代 器
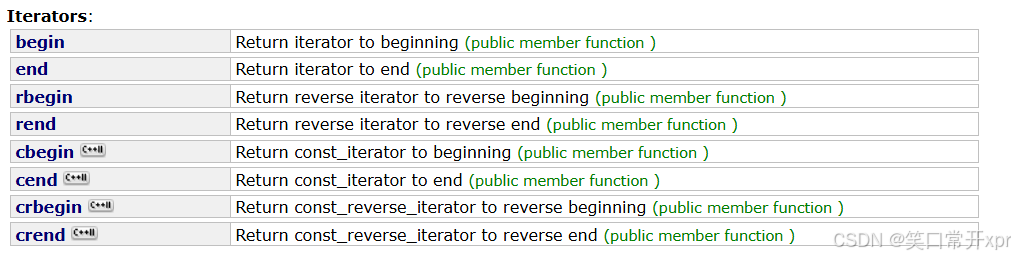
begin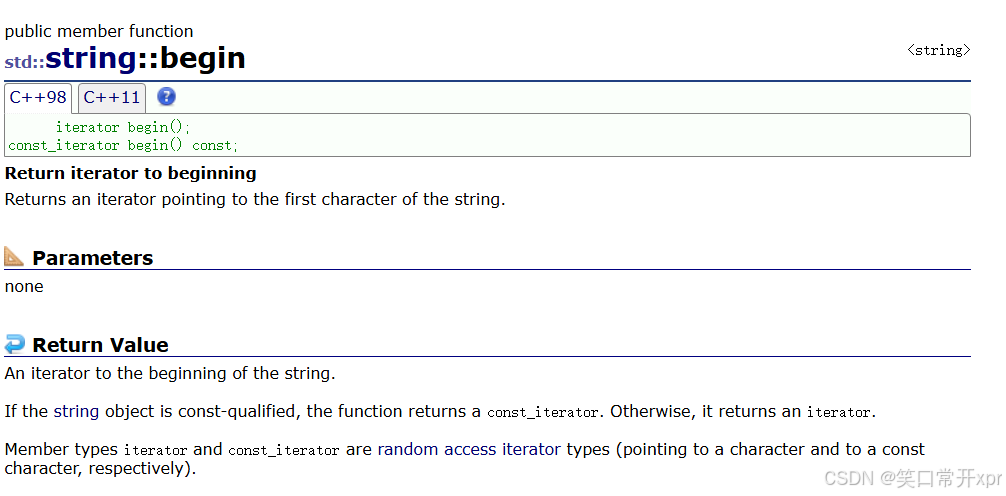
end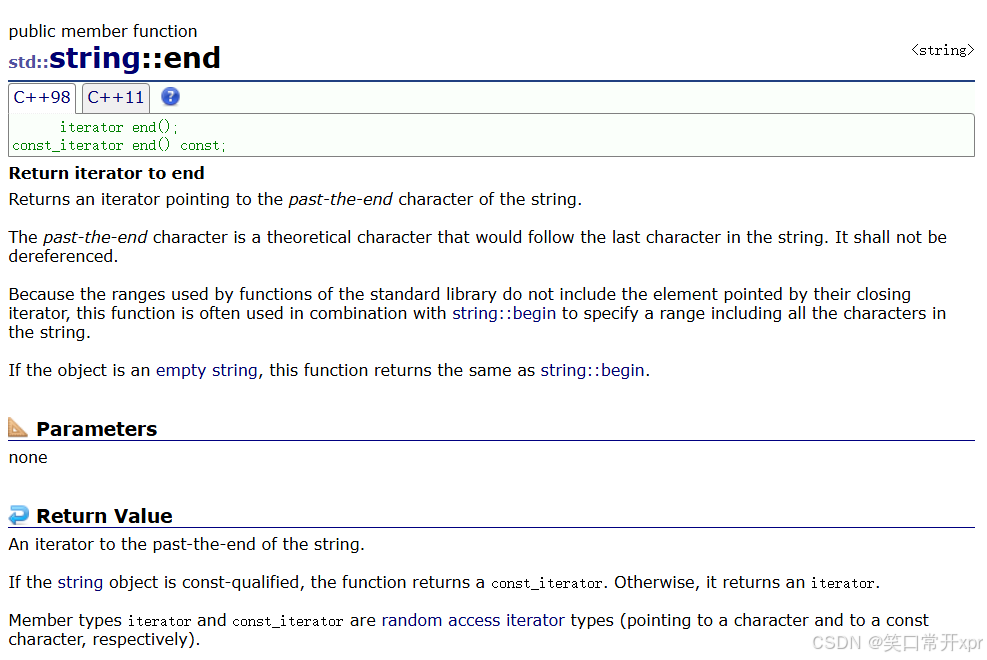
迭 代 器 是 像 指 针 一 样 的 类 型,迭 代 器 不 能 修 改。
任 何 容 器 都 支 持 迭 代 器,并 且 用 法 是 类 似 的。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
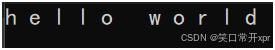
begin 和 end 是 左 闭 右 开 的 关 系,即 [begin, end)。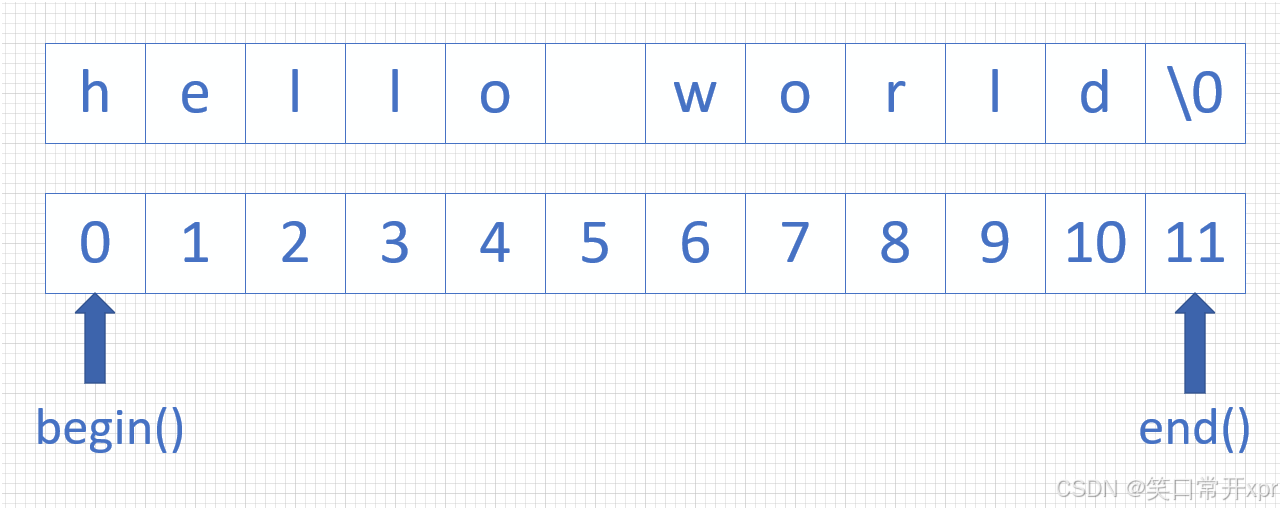
应 用 场 景
读 和 写
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//begin和end是左闭右开的关系
//[begin, end)
string s1("hello world");
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
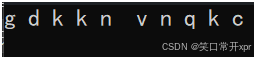
//写
while (it != s1.end())
{
(*it)--;
it++;
}
it = s1.begin();
//读
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
范 围 for
底 层 是 迭 代 器,范 围 for 只 能 正 着 遍 历,不 能 倒 着 遍 历。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
for (auto& ch : s1)
{
ch++;
}
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
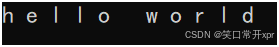
逆 置
reverse 是 一 个 函 数 模 板。迭 代 器 可 以 跟 容 器 配 合。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
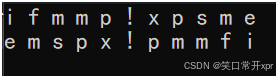
string s1("hello world");
for (auto& ch : s1)
{
ch++;
}
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());//逆置
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
反 向 迭 代 器
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
//string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
auto rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
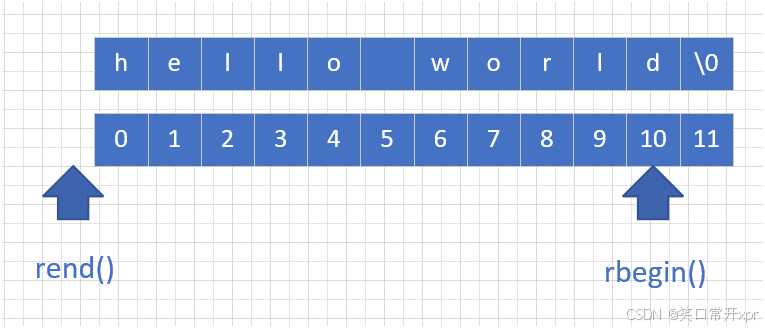
const 迭 代 器
当 函 数 传 参 时 使 用 const 应 该 使 用 const_iterator。
普 通 迭 代 器 可 以 读 和 写,const 迭 代 器 只 能 读。
类 似 的,反 向 迭 代 器 使 用 const 也 需 要 使 用 const 迭 代 器。
方 法 1
使 用 const
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void Func(const string& s)//不加引用需要深拷贝,代价较大
{
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
}
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
Func(s1);
return 0;
}
方 法 2
传 参 没 有 使 用 const,则 可 以 使 用 const 也 可 以 不 使 用 const 迭 代 器。这 里 是 权 限 的 缩 小。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void Func(string& s)//不加引用需要深拷贝,代价较大
{
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
}
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
Func(s1);
return 0;
}
总 结
iterator 提 供 一 种 统 一 的 方 式 访 问 和 修 改 容 器 中 的 数 据,算 法 就 可 以 通 过 迭 代 器,去 处 理 容 器 中 的 数 据。
容 量
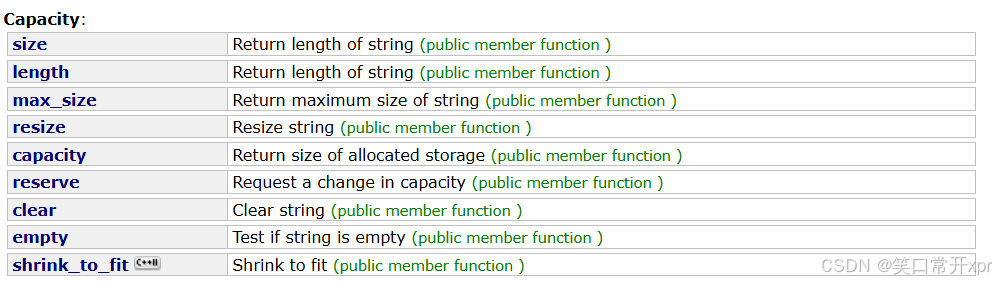
size
size 用 来 求 出 字 符 串 长 度,不 包 括 ‘\0’。
\0 是 表 示 字 符 串 的 特 殊 字 符 并 且 不 会 被 打 印 出 来。
length
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.size() << endl;//size是数据个数
cout << s1.length() << endl;//length是长度
return 0;
}
size 和 lenth 的 结 果 相 同,但 在 string 里 面 建 议 使 用 size。
max_size
字 符 串 可 以 达 到 的 最 大 长 度,不 同 编 译 器 的 结 果 是 不 一 样 的。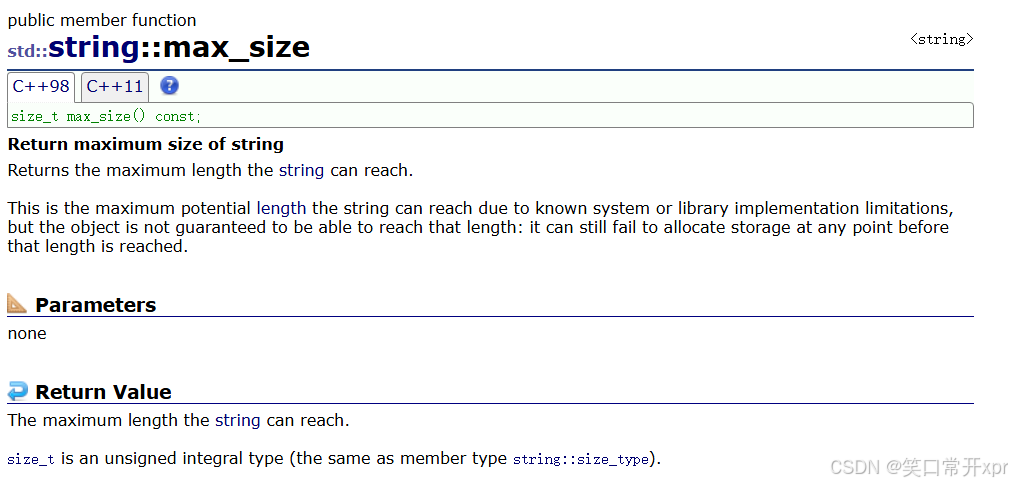
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
return 0;
}
capacity
返 回 当 前 为 字 符 串 分 配 的 存 储 空 间 的 大 小,以 字 节 表 示。在 不 同 版 本 下 扩 容 的 结 果 是 不 一 样 的。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
size_t old = s1.capacity();
for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
s1 += 'x';
if (old != s1.capacity())
{
cout << "扩容" << s1.capacity() << endl;
old = s1.capacity();
}
}
return 0;
}

clear
clear 可 以 清 除 字 符 串 的 内 容。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
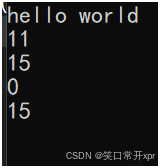
clear 可 以 清 除 size 的 数 据,无 法 清 除 capacity 的 数 据。
reserve
开 辟 已 知 的 空 间,可 能 会 开 辟 更 大 的 空 间,但 不 会 比 这 个 空 间 小,不 会 扩 容。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
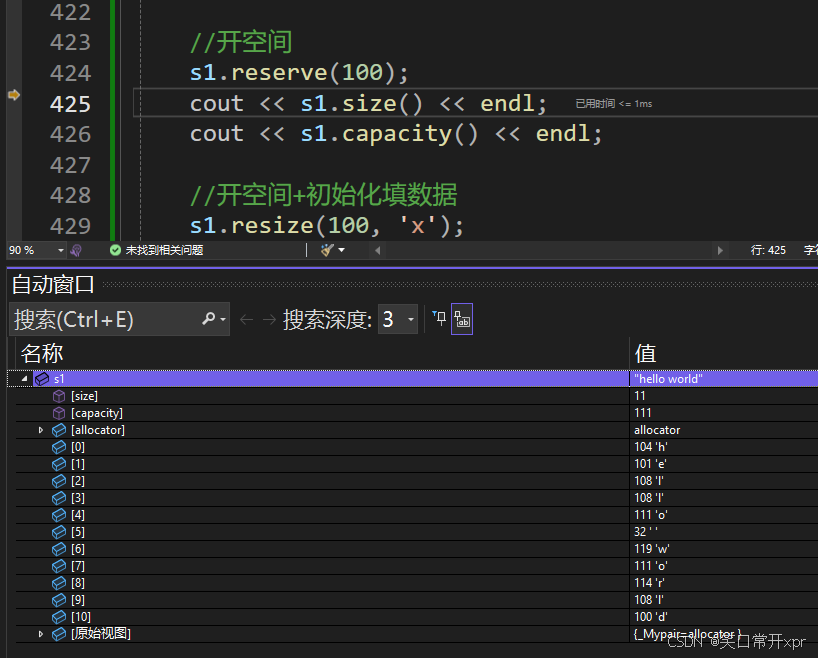
string s1("hello world");
s1.reserve(100);
size_t old = s1.capacity();
for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
s1 += 'x';
if (old != s1.capacity())
{
cout << "扩容" << s1.capacity() << endl;
old = s1.capacity();
}
}
return 0;
}

注 意
如 果 开 辟 的 空 间 没 有 存 储 数 据,可 以 缩 小 空 间,缩 小 空 间 是 将剩 余 的 数 据 拷 贝 到 另 一 份 空 间,然 后 释 放 掉 原 来 所 有 的 空 间,它 是 以 时 间 换 空 间 的 做 法。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.reserve(100);
size_t old = s1.capacity();
for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
s1 += 'x';
if (old != s1.capacity())
{
cout << "扩容" << s1.capacity() << endl;
old = s1.capacity();
}
}
//有数据
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.reserve(10);
old = s1.capacity();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//无数据
s1.clear();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.reserve(10);
old = s1.capacity();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
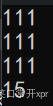
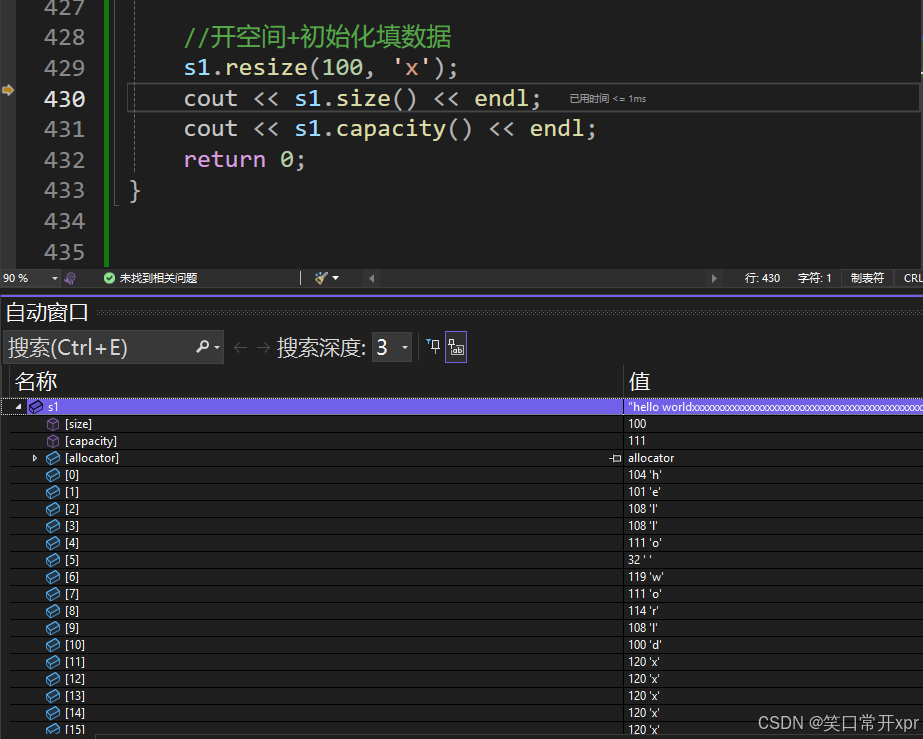
resize
resize 可 以 开 空 间 和 初 始 化 填 充 数 据。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
//开空间
s1.reserve(100);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//开空间+初始化填数据
s1.resize(100, 'x');
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
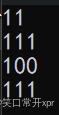
访 问 数 据

operator[ ]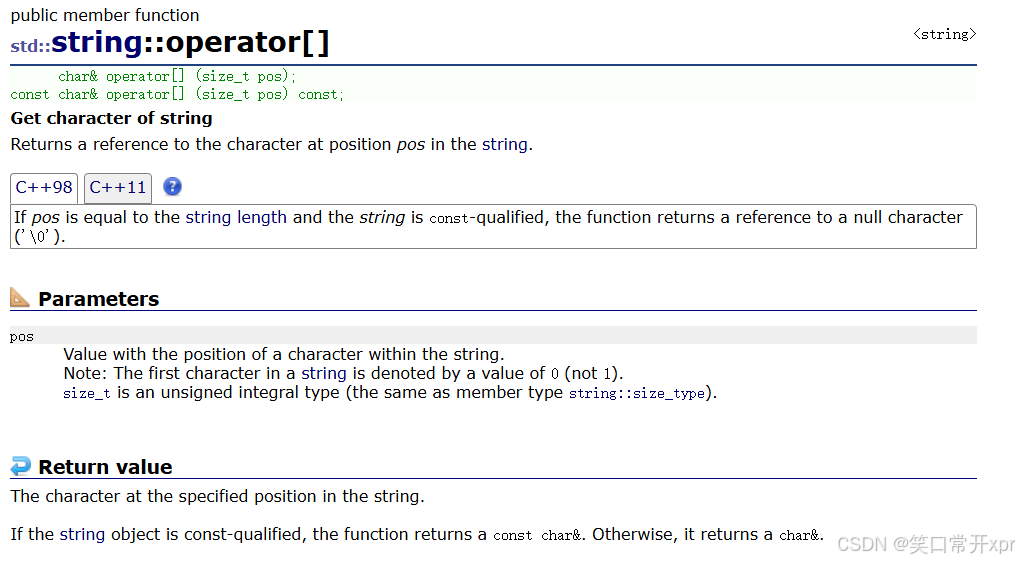
[ ] 本 质 上 是 解 引 用,是 数 组 用 来 访 问 元 素 的。
遍 历 字 符 串
方 法 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}

方 法 2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
//下标+[]
//cout << s2.size() << endl;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
s2[i]++;
}
for (i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
cout << s2[i];
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
区 分
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s2("hello world");
char s3[] = "hello world";
s2[1];//s1.operator[](1);
s3[1];//->*(s3 + 1)
return 0;
}
s2[1] 是 C++ string 类 的 重 载 运 算 符 调 用,实 际 执 行(s2.operator[ ] (1))。
s3[1] 是 数 组 访 问,等 价 于 指 针 运 算 *(s3 + 1),其 中 s3 退 化 为 指 向 首 元 素 的 指 针。
at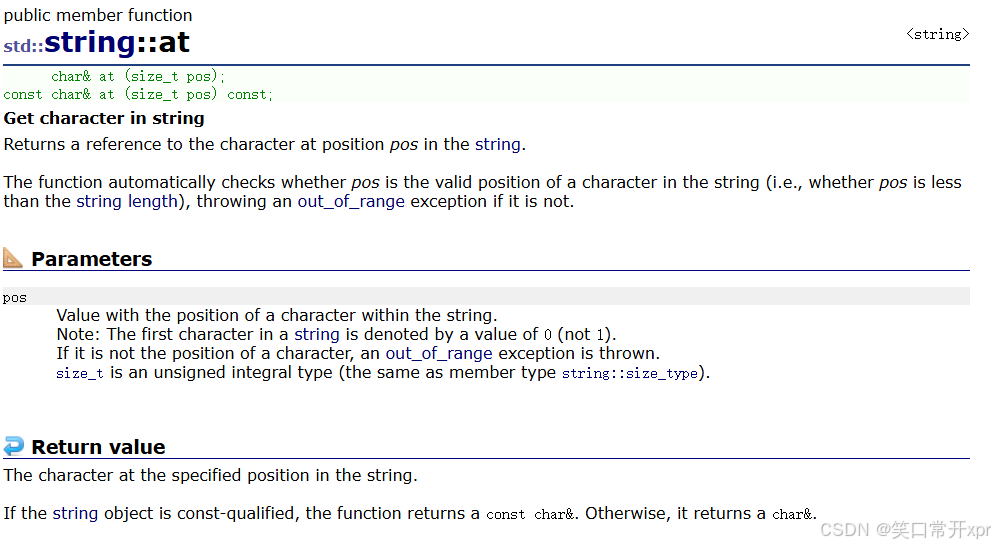
修 改 字 符 串 的 元 素,如 果 越 界 则 会 抛 出 异 常。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.at(0) = 'x';
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}

注 意
operator[ ] 越 界 会 断 言,at 越 界 是 抛 出 异 常。
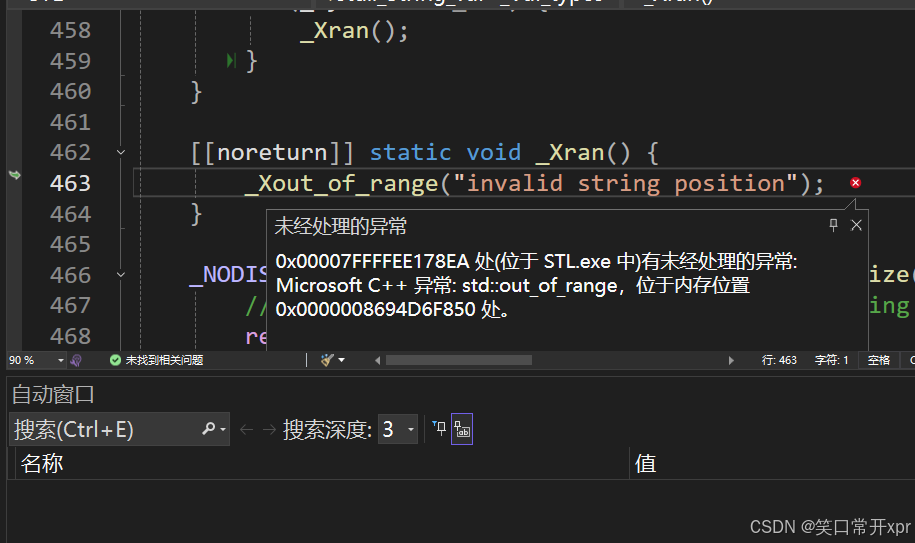
at 越 界
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.at(15) = 'x';
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
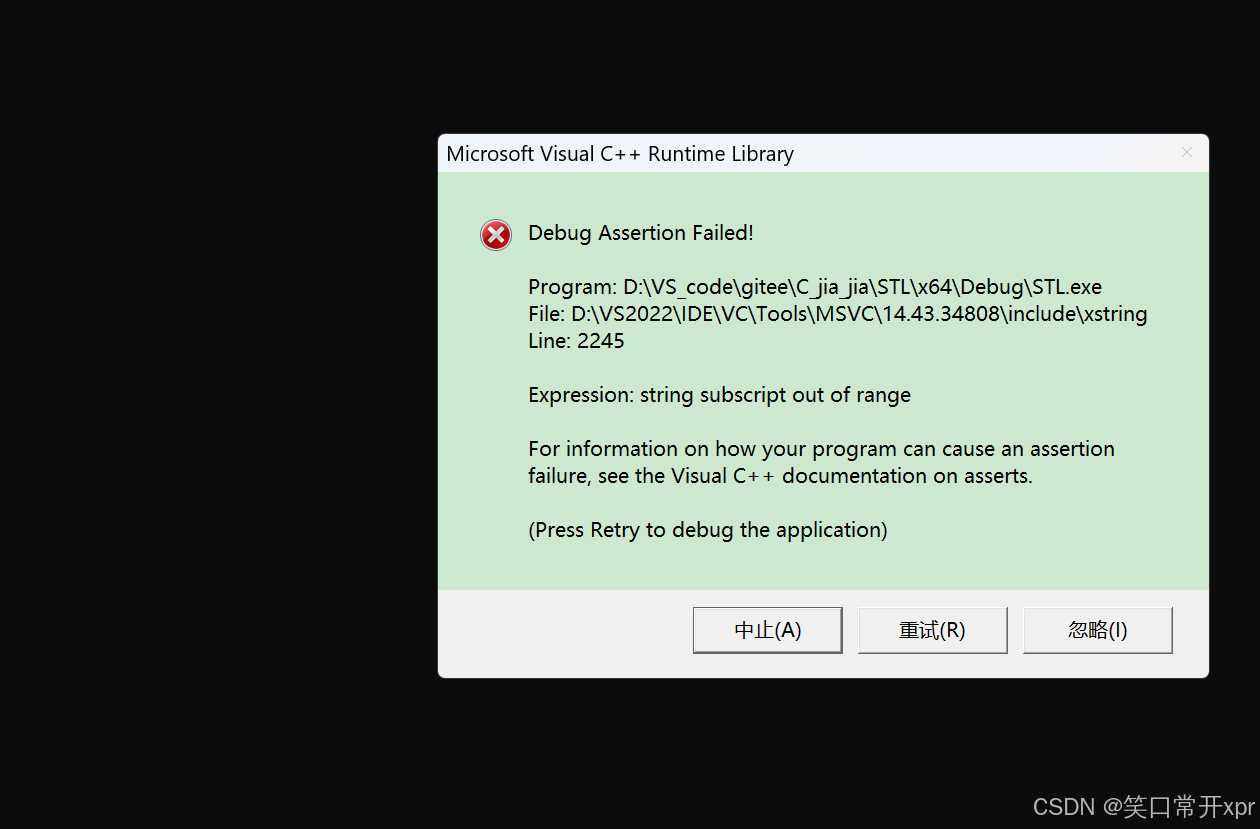
operator[ ] 越 界
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1[15] = 'x';//operator[ ]越界
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
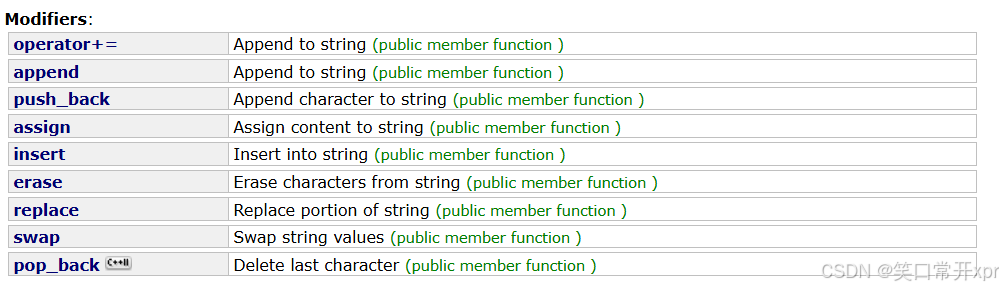
增 删 查 改
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//增
string s1("hello");
s1 += ' ';
s1 += "world";
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}

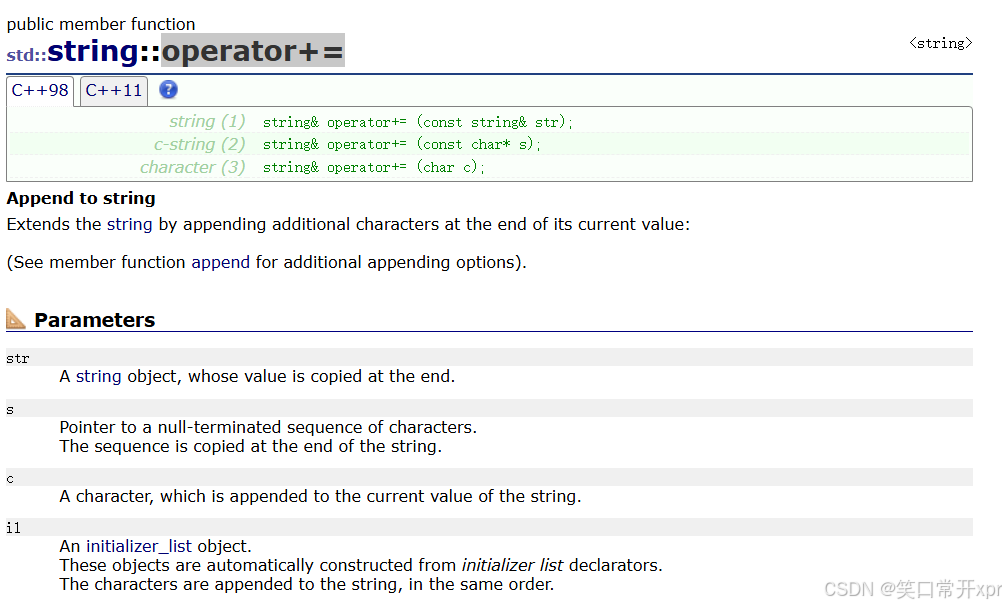
operator+= 字 符 调 用 push_back,operator+= 字 符 串 调 用 append。
将 x 转 成 string 对 象
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 0;
cin >> x;
string xstr;
while (x)
{
size_t val = x % 10;
xstr += ('0' + val);
x /= 10;
}
//逆置
return 0;
}
push_back(增)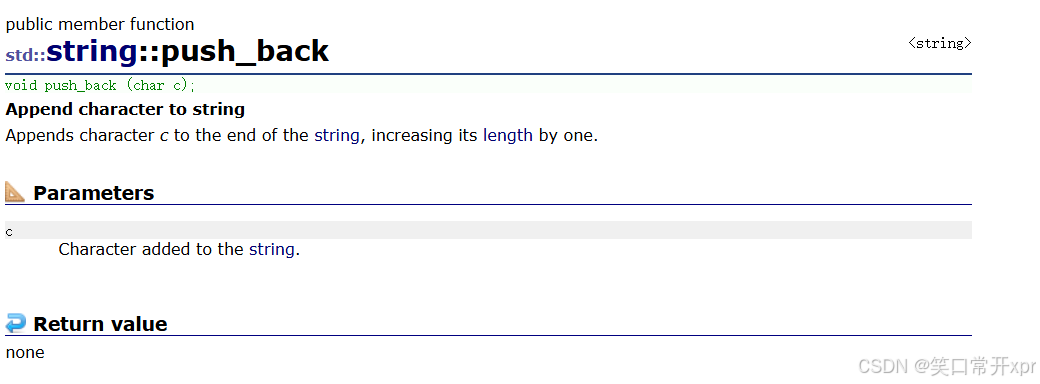
push_back 可 以 在 字 符 串 后 面 插 入 一 个 字 符。
append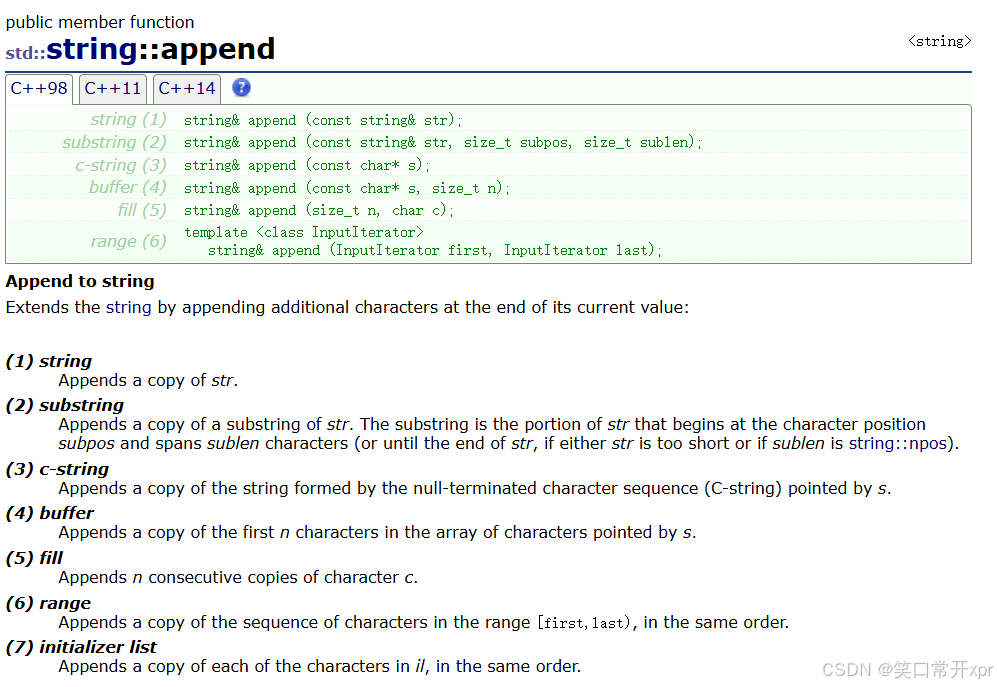
append 可 以 在 字 符 串 后 面 插 入 一 个 字 符 串。
如 果 空 间 不 够,会 自 动 扩 容。
代 码 示 例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//增
string s1("hello");
//尾插一个字符
s1.push_back(' ');
//尾插一个字符串
s1.append("world");
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
assign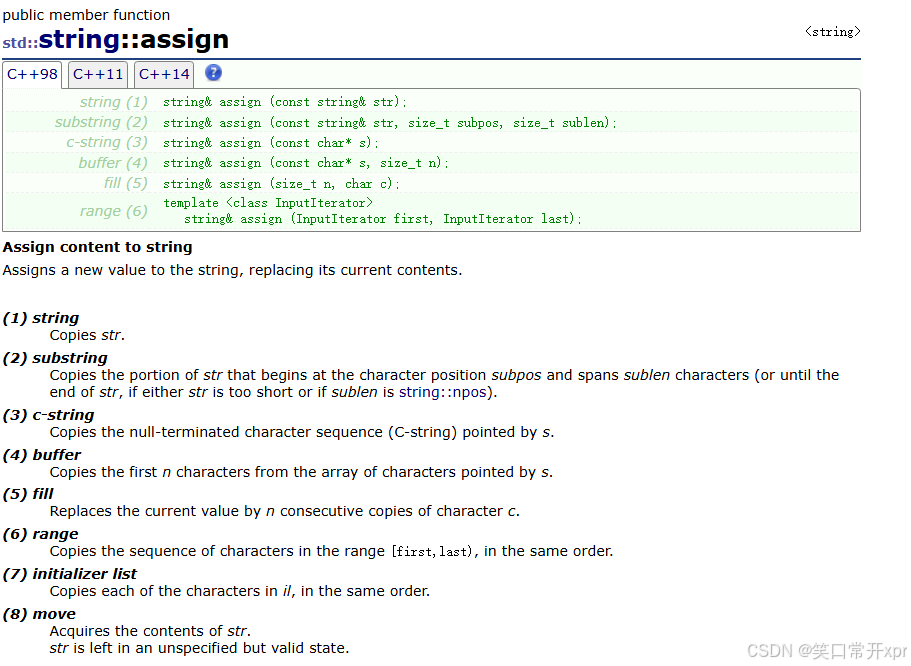
append 是 在 字 符 串 后 面 追 加,assign 是 覆 盖 掉 原 来 的 字 符 串。赋 值 也 可 以 覆 盖 掉 原 来 的 字 符 串。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello ");
//append追加
s1.append("world");
cout << s1 << endl;
//覆盖
s1.assign("111111111");
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}

insert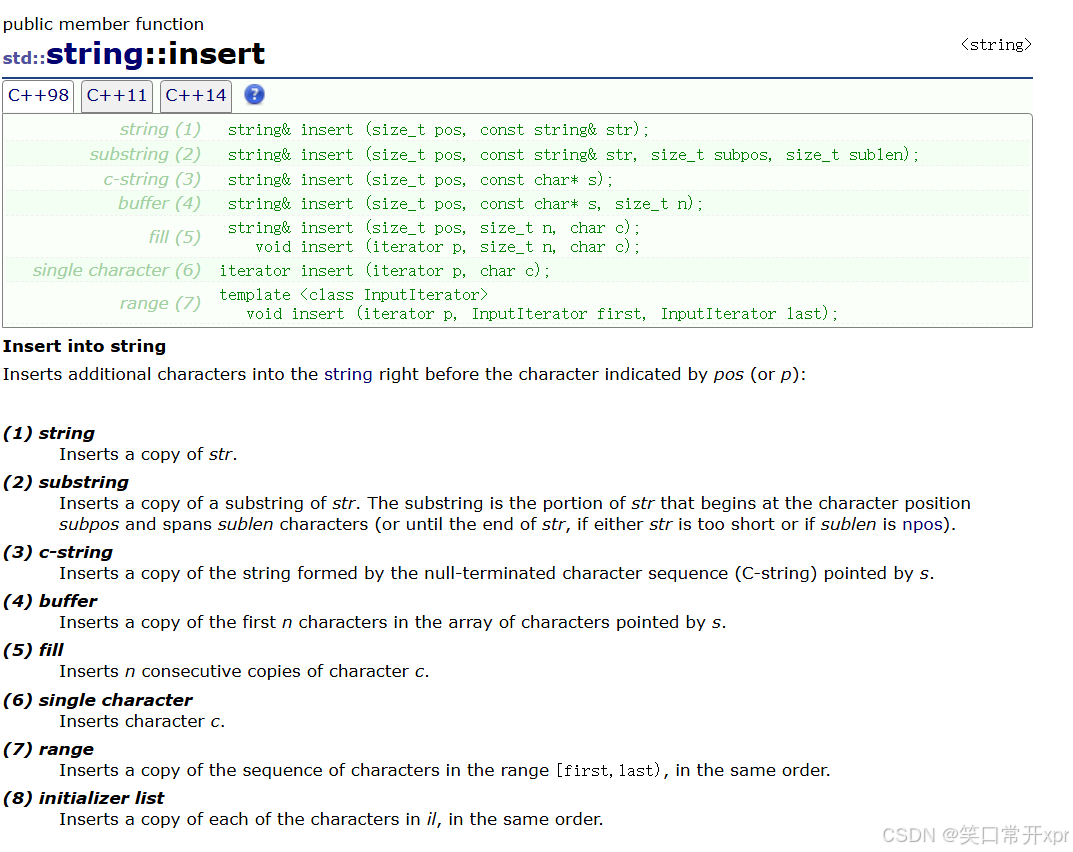
在 字 符 串 的 任 何 位 置 插 入 字 符。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("world");
s1.insert(0, "hello ");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(s1.begin() + 3, 10, 'z');
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
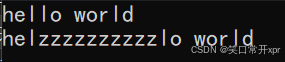
erase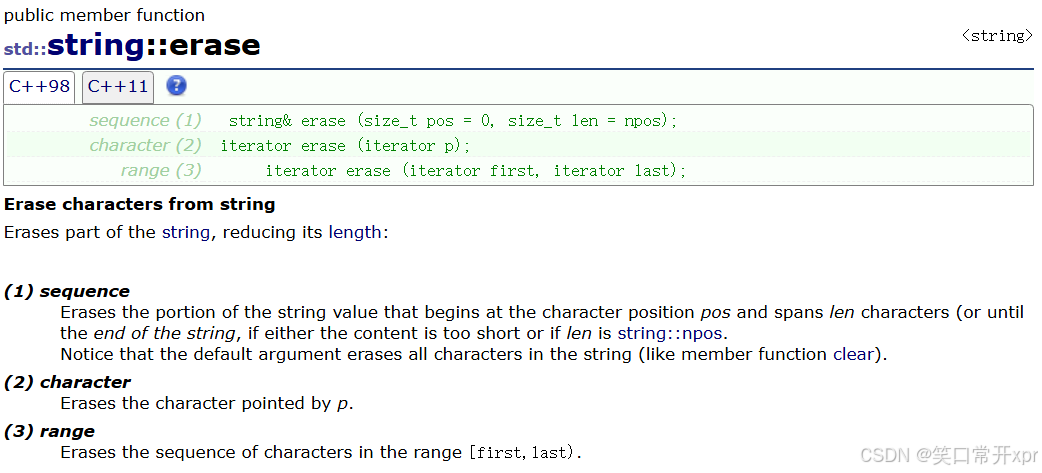
删 除 字 符 串 某 一 个 位 置 的 字 符。
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.erase(5, 1);
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.erase(5);
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
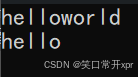
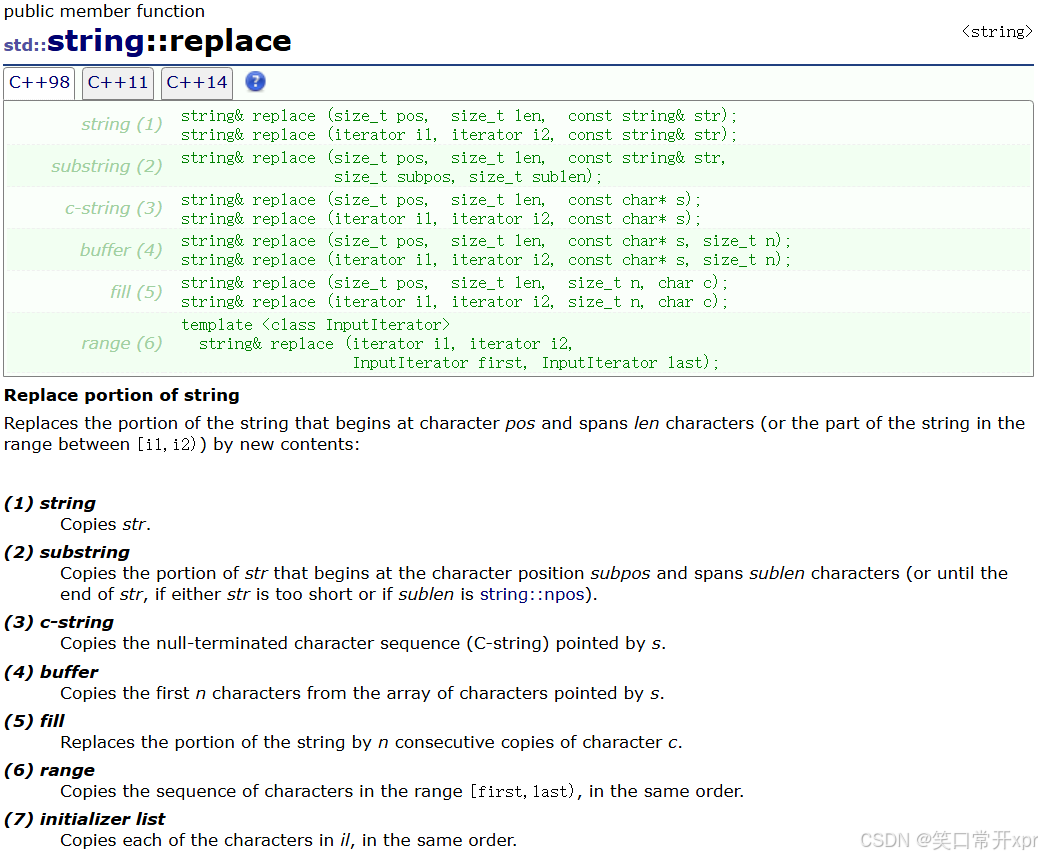
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.replace(6, 5, "xxxxxxxxxx");
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
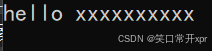
所 有 的 空 格 替 换 为 20%
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s2("hello world hello world");
string s3;
for (auto ch : s2)
{
if (ch == ' ')
{
s3 += "20%";
}
else
{
s3 += ch;
}
}
cout << s3 << endl;
return 0;
}

查 找
find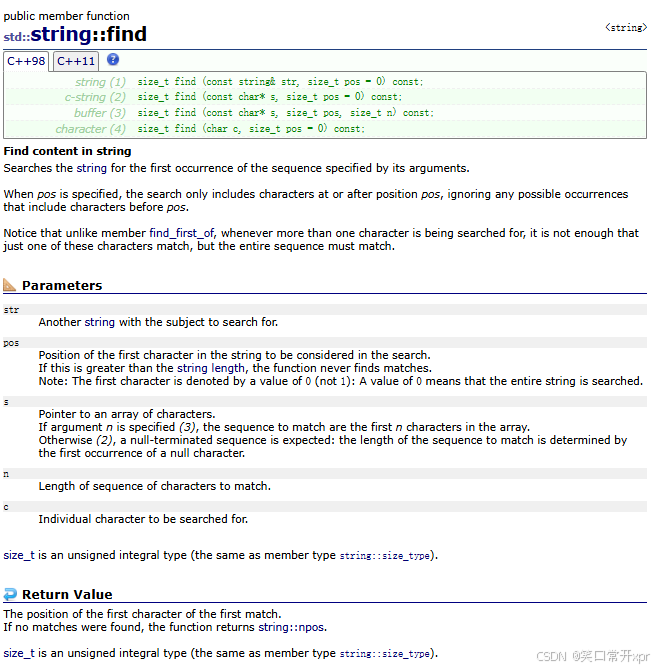
从 前 向 后 找,返 回 字 符 或 者 字 符 串 的 下 标。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string url = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string";
int ret1 = url.find("://");
if (ret1 != string::npos)
{
string s1(url, 0, ret1);
cout << s1 << endl;
}
int ret2 = url.find('/', ret1 + 3);
if (ret1 != string::npos)
{
string s2(url, ret1 + 3, ret2 - (ret1 + 3));
cout << s2 << endl;
}
string s3(url, ret2 + 1, url.length());
cout << s3 << endl;
return 0;
}


总 结
通 过 对 STL 及 string 类 的 系 统 梳 理,我 们 不 仅 掌 握 了 容 器、迭 代 器 等 核 心 概 念,更 熟 悉 了 string 类 从 构 造、遍 历 到 增 删 查 改 的 全 流 程 操 作。string 类 凭 借 封 装 性 和 便 捷 接 口,极 大 简 化 了 字 符 串 处 理 工 作。后 续 使 用 中,可 结 合 实 际 场 景 灵 活 调 用 相 关 接 口,同 时 注 意 内 存 管 理 与 效 率 优 化,让 STL 工 具 真 正 成 为 编 程 助 力。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容







所有评论(0)