使用 Ollama、Llama 3.1 和 Milvus 实现Function Calling 功能
将函数调用(Function Calling)与 LLM 相结合能够扩展您的 AI 应用的能力。通过将您的大语言模型(LLM)与用户定义的 Function 或 API 集成,您可以搭建高效的应用,解决实际问题。本文将介绍如何将 Llama 3.1 与 Milvus 和 API 等外部工具集成,构建具备上下文感知能力的应用。
前言
将函数调用(Function Calling)与 LLM 相结合能够扩展您的 AI 应用的能力。通过将您的大语言模型(LLM)与用户定义的 Function 或 API 集成,您可以搭建高效的应用,解决实际问题。
本文将介绍如何将 Llama 3.1 与 Milvus 和 API 等外部工具集成,构建具备上下文感知能力的应用。
Function Calling 简介
诸如 GPT-4、Mistral Nemo 和 Llama 3.1 之类的大语言模型(LLMs)现在可以检测何时需要调用函数,然后输出包含调用该函数参数的 JSON。这一突破能够有效提升您的 AI 应用的能力。
Functional calling 助力开发人员:
-
搭建 LLM 驱动数据提取和标记解决方案(例如:从维基百科文章中提取人物名字)
-
开发能够将自然语言转换为 API 命令或数据库查询语句的应用
-
打造对话式的知识库搜索引擎
使用的工具
-
Ollama: 支持在您的笔记本电脑上使用强大的 LLM,有效简化本地操作流程。
-
Milvus: 用于高效存储和检索数据的首选向量数据库
-
8B 模型的升级版本,支持多语言、更长的上下文长度(128K)和利用工具进行操作。

使用 Llama 3.1 和 Ollama
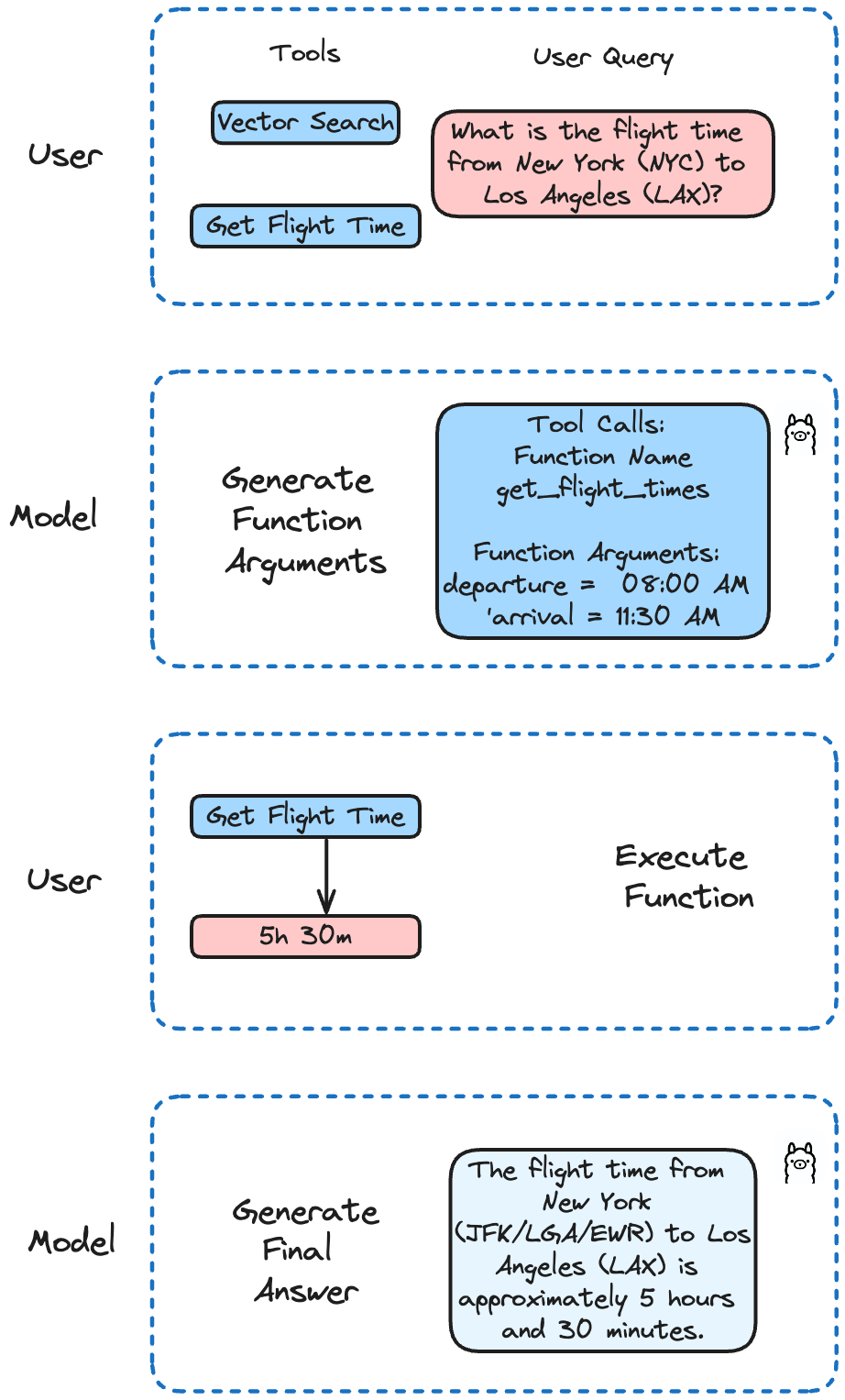
Llama 3.1 已经在 Function calling 方面进行了微调。它支持通过单一、嵌套和并行的方式调用函数,同时支持多轮调用函数。借助 Llama 3.1 您的 AI 应用可以处理涉及多个并行步骤的复杂任务。
在本文示例中,我们将通过不同的函数来模拟用于获取航班时间的 API,然后在 Milvus 中执行搜索。Llama 3.1 将根据用户的查询决定调用哪个函数。
03
安装依赖
首先,使用 Ollama 下载 Llama 3.1:
`ollama run llama3.1`
上述指令会将模型下载至您的笔记本电脑,您可以通过 Ollama 使用 Llama 3.1。接着,安装依赖:
! pip install ollama openai "pymilvus[model]"
本文安装 Milvus Lite 以及模型插件。Milvus 的模型插件支持用户使用 Milvus 中集成的模型将数据转换为 Embedding 向量。
将数据插入 Milvus
将数据插入至 Milvus 中。后续,Llama 3.1 将判断相关性并决定是否搜索此步骤中插入的数据。
创建 Collection 并插入数据
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, model
embedding_fn = model.DefaultEmbeddingFunction()
docs = [
"Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956.",
"Alan Turing was the first person to conduct substantial research in AI.",
"Born in Maida Vale, London, Turing was raised in southern England.",
]
vectors = embedding_fn.encode_documents(docs)
# The output vector has 768 dimensions, matching the collection that we just created.
print("Dim:", embedding_fn.dim, vectors[0].shape) # Dim: 768 (768,)
# Each entity has id, vector representation, raw text, and a subject label.
data = [
{"id": i, "vector": vectors[i], "text": docs[i], "subject": "history"}
for i in range(len(vectors))
]
print("Data has", len(data), "entities, each with fields: ", data[0].keys())
print("Vector dim:", len(data[0]["vector"]))
# Create a collection and insert the data
client = MilvusClient('./milvus_local.db')
client.create_collection(
collection_name="demo_collection",
dimension=768, # The vectors we will use in this demo has 768 dimensions
)
client.insert(collection_name="demo_collection", data=data)
新创建的 Collection 中含有 3 个元素。
06
定义需要使用的 Functions
本文将定义两个 Function。第一个与 API call 相似,用于获取航班时间。第二个用于在 Milvus 中执行搜索和查询。
from pymilvus import model
import json
import ollama
embedding_fn = model.DefaultEmbeddingFunction()
# Simulates an API call to get flight times
# In a real application, this would fetch data from a live database or API
def get_flight_times(departure: str, arrival: str) -> str:
flights = {
'NYC-LAX': {'departure': '08:00 AM', 'arrival': '11:30 AM', 'duration': '5h 30m'},
'LAX-NYC': {'departure': '02:00 PM', 'arrival': '10:30 PM', 'duration': '5h 30m'},
'LHR-JFK': {'departure': '10:00 AM', 'arrival': '01:00 PM', 'duration': '8h 00m'},
'JFK-LHR': {'departure': '09:00 PM', 'arrival': '09:00 AM', 'duration': '7h 00m'},
'CDG-DXB': {'departure': '11:00 AM', 'arrival': '08:00 PM', 'duration': '6h 00m'},
'DXB-CDG': {'departure': '03:00 AM', 'arrival': '07:30 AM', 'duration': '7h 30m'},
}
key = f'{departure}-{arrival}'.upper()
return json.dumps(flights.get(key, {'error': 'Flight not found'}))
# Search data related to Artificial Intelligence in a vector database
def search_data_in_vector_db(query: str) -> str:
query_vectors = embedding_fn.encode_queries([query])
res = client.search(
collection_name="demo_collection",
data=query_vectors,
limit=2,
output_fields=["text", "subject"], # specifies fields to be returned
)
print(res)
return json.dumps(res)
07
向 LLM 提供指令并使用定义的 Functions
向 LLM 提供指令。这样一来,LLM 可以使用我们上述定义的 Functions。
def run(model: str, question: str):
client = ollama.Client()
# Initialize conversation with a user query
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": question}]
# First API call: Send the query and function description to the model
response = client.chat(
model=model,
messages=messages,
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_flight_times",
"description": "Get the flight times between two cities",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"departure": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The departure city (airport code)",
},
"arrival": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The arrival city (airport code)",
},
},
"required": ["departure", "arrival"],
},
},
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_data_in_vector_db",
"description": "Search about Artificial Intelligence data in a vector database",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The search query",
},
},
"required": ["query"],
},
},
},
],
)
# Add the model's response to the conversation history
messages.append(response["message"])
# Check if the model decided to use the provided function
if not response["message"].get("tool_calls"):
print("The model didn't use the function. Its response was:")
print(response["message"]["content"])
return
# Process function calls made by the model
if response["message"].get("tool_calls"):
available_functions = {
"get_flight_times": get_flight_times,
"search_data_in_vector_db": search_data_in_vector_db,
}
for tool in response["message"]["tool_calls"]:
function_to_call = available_functions[tool["function"]["name"]]
function_args = tool["function"]["arguments"]
function_response = function_to_call(**function_args)
# Add function response to the conversation
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"content": function_response,
}
)
# Second API call: Get final response from the model
final_response = client.chat(model=model, messages=messages)
print(final_response["message"]["content"])
08
使用示例
让我们看看是否能顺利查询到特定航班的时间:
question = "What is the flight time from New York (NYC) to Los Angeles (LAX)?"
run('llama3.1', question)
结果如下:
The flight time from New York (JFK/LGA/EWR) to Los Angeles (LAX) is approximately 5 hours and 30 minutes. However, please note that this time may vary depending on the airline, flight schedule, and any potential layovers or delays. It's always best to check with your airline for the most up-to-date and accurate flight information.
现在,让我们看看 Llama 3.1 是否能使用 Milvus 进行向量搜索。
question = "What is Artificial Intelligence?"
run('llama3.1', question)
以下为 Milvus 搜索结果:
data: ["[{'id': 0, 'distance': 0.4702666699886322, 'entity': {'text': 'Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956.', 'subject': 'history'}}, {'id': 1, 'distance': 0.2702862620353699, 'entity': {'text': 'Alan Turing was the first person to conduct substantial research in AI.', 'subject': 'history'}}]"] , extra_info: {'cost': 0}
09
总结
Function Calling 与 LLM 的结合为我们创造了无限可能。通过将Llama 3.1与 外部工具(如 Milvus)和 API 集成,您可以构建具备上下文感知能力的应用,从而满足特定用例和解决实际问题。
最后的最后
感谢你们的阅读和喜欢,我收藏了很多技术干货,可以共享给喜欢我文章的朋友们,如果你肯花时间沉下心去学习,它们一定能帮到你。
因为这个行业不同于其他行业,知识体系实在是过于庞大,知识更新也非常快。作为一个普通人,无法全部学完,所以我们在提升技术的时候,首先需要明确一个目标,然后制定好完整的计划,同时找到好的学习方法,这样才能更快的提升自己。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

大模型知识脑图
为了成为更好的 AI大模型 开发者,这里为大家提供了总的路线图。它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。

经典书籍阅读
阅读AI大模型经典书籍可以帮助读者提高技术水平,开拓视野,掌握核心技术,提高解决问题的能力,同时也可以借鉴他人的经验。对于想要深入学习AI大模型开发的读者来说,阅读经典书籍是非常有必要的。

实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。

面试资料
我们学习AI大模型必然是想找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题都是总结当前最新、最热、最高频的面试题,并且每道题都有详细的答案,面试前刷完这套面试题资料,小小offer,不在话下

640套AI大模型报告合集
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。

这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容










所有评论(0)