LangGraph实战教程(6):Human-in-the-loop 实现,大模型入门到精通,收藏这篇就足够了!
Human-in-the-loop(HITL,人在回路/人机协同/人类监督)是一种AI系统设计范式,强调在关键决策点引入人类干预,形成“人工监督-AI执行-反馈优化”的闭环机制。
一、什么是Human-in-the-loop
Human-in-the-loop(HITL,人在回路/人机协同/人类监督)是一种AI系统设计范式,强调在关键决策点引入人类干预,形成“人工监督-AI执行-反馈优化”的闭环机制。在大模型智能体应用中,HITL能显著提升复杂任务的可靠性、可解释性与合规性,尤其在金融、医疗等高敏感领域。
核心目的
风险控制:防止AI的偏见、错误或不可预测行为,如自动执行高风险工具、AP的I调用,特别是一些产生数据更新的调用。
知识增强:人类提供专业经验,弥补AI在上下文理解上的不足,修正AI的输出结果,AI远远不是万能的,输出结果可能存在幻觉和错误的推理,通过人工的监督反馈,引导AI修正错误的输出结果。
工作流闭环:
是
否
AI自主执行
需人工干预?
暂停并请求人类输入
人工审核/编辑/反馈
更新状态并继续执行
完成输出
二、LangGraph实现Human-in-the-loop
LangGraph主要使用中断+恢复的机制来实现HITL,其中提供了两种中断图流程的方法:
- • 动态中断: 根据图的当前状态,使用中断从特定节点内部暂停图。
- • 静态中断: 使用interrupt_before和interrupt_after在定义的点暂停图形,在节点执行之前或之后。
动态中断
LangGraph主要使用中断interrupt 和Command来实现动态中断。
-
- 创建中断点interrupt:
interrupt之前需要使用checkpointer来保存节点执行的每一步状态,如果需要随时恢复,则建议使用能持久化的checkpointer,如数据库。
- 创建中断点interrupt:
from typing import TypedDictimport uuidfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaverfrom langgraph.constants import STARTfrom langgraph.graph import StateGraphfrom langgraph.types import interrupt, Commandclass State(TypedDict): messsage: str age: str# Human node进行中断def human_node(state: State): value = interrupt( { "messsage": state["messsage"] } ) return { "age": value }# Build the graphgraph_builder = StateGraph(State)graph_builder.add_node("human_node", human_node)graph_builder.add_edge(START, "human_node")checkpointer = InMemorySaver() graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)# Pass a thread ID to the graph to run it.config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": uuid.uuid4()}}# Run the graph until the interrupt is hit.result = graph.invoke({"messsage": "我的年龄是多少?"}, config=config) print(result['__interrupt__']) #输出[Interrupt(value={'messsage': '我的年龄是多少?'}, resumable=True, ns=['human_node:1a8de8ea-e477-7583-30aa-263f8e02571f'])]#使用Command原语来恢复print(graph.invoke(Command(resume="25"), config=config)) #输出:{'messsage': '我的年龄是多少?', 'age': '25'}
-
- 创建恢复命令command:
当使用interrupt()方法后,流程就会中断,此时可以通过Command原语来恢复流程执行。Command原语需要在图的invoke、ainvoke、stream或者astream方法中调用。
graph.invoke(Command(resume={"age": "25"}), thread_config)
静态中断
静态中断(也称为静态断点)在节点执行之前或之后触发。一般建议静态中断只在调试和测试中使用。
from typing_extensions import TypedDictfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, ENDclass State(TypedDict): input: strdef step_1(state): print("---Step 1---") passdef step_2(state): print("---Step 2---") passdef step_3(state): print("---Step 3---") passbuilder = StateGraph(State)builder.add_node("step_1", step_1)builder.add_node("step_2", step_2)builder.add_node("step_3", step_3)builder.add_edge(START, "step_1")builder.add_edge("step_1", "step_2")builder.add_edge("step_2", "step_3")builder.add_edge("step_3", END)# Set up a checkpointer checkpointer = InMemorySaver() # (1)!graph = builder.compile( checkpointer=checkpointer, # (2)! # interrupt_after=["step_1"] # 执行step1后,中断! interrupt_before=["step_3"], # 执行step3前,中断!)# Inputinitial_input = {"input": "hello world"}# Threadthread = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}# Run the graph until the first interruptionfor event in graph.stream(initial_input, thread, stream_mode="values"): print(event)# This will run until the breakpoint# You can get the state of the graph at this pointprint(graph.get_state(thread))# 可以输入 `None` 恢复流程 for event in graph.stream(None, thread, stream_mode="values"): print(event) # print(graph.get_state(thread))# for event in graph.stream(None, thread, stream_mode="values"):# print(event)
三、4种典型的Human-in-the-loop场景
1. 人工审批
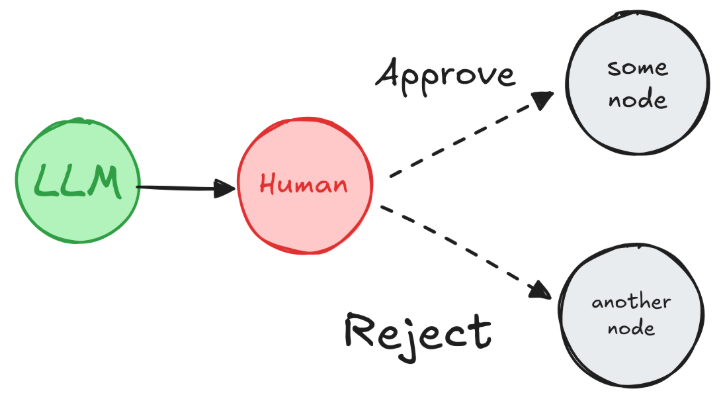
在一个关键步骤前中断流程,如一个工具调用,要求反馈用户同意或拒绝才继续执行流程。
from typing importLiteral, TypedDictimport uuidfrom langgraph.constants import START, ENDfrom langgraph.graph import StateGraphfrom langgraph.types import interrupt, Commandfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver# Define the shared graph stateclass State(TypedDict): llm_output: str decision: str# Simulate an LLM output nodedef generate_llm_output(state: State) -> State: return {"llm_output": "This is the generated output."}# 人工中断审核节点def human_approval(state: State) -> Command[Literal["approved_path", "rejected_path"]]: decision = interrupt({ "question": "Do you approve the following output?", "llm_output": state["llm_output"] })# 人工审核通过 if decision == "approve": return Command(goto="approved_path", update={"decision": "approved"})# 人工审核拒绝 else: return Command(goto="rejected_path", update={"decision": "rejected"})# Next steps after approvaldef approved_node(state: State) -> State: print("✅ Approved path taken.") return state# Alternative path after rejectiondef rejected_node(state: State) -> State: print("❌ Rejected path taken.") return state# Build the graphbuilder = StateGraph(State)builder.add_node("generate_llm_output", generate_llm_output)builder.add_node("human_approval", human_approval)builder.add_node("approved_path", approved_node)builder.add_node("rejected_path", rejected_node)builder.set_entry_point("generate_llm_output")builder.add_edge("generate_llm_output", "human_approval")builder.add_edge("approved_path", END)builder.add_edge("rejected_path", END)checkpointer = MemorySaver()graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)# Run until interruptconfig = {"configurable": {"thread_id": uuid.uuid4()}}result = graph.invoke({}, config=config)print(result["__interrupt__"])# Output:# Interrupt(value={'question': 'Do you approve the following output?', 'llm_output': 'This is the generated output.'}, ...)# 模拟人审核通过# 测试拒绝, 则替换 resume="approve" with resume="reject"final_result = graph.invoke(Command(resume="approve"), config=config)print(final_result)
2. 审查和修改状态
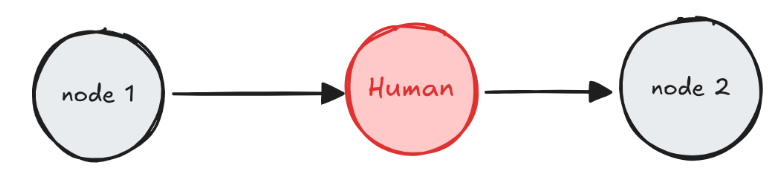
用户可以查看和编辑图的状态。这对于纠正错误或使用附加信息更新状态非常有用。
from typing import TypedDictimport uuidfrom langgraph.constants import START, ENDfrom langgraph.graph import StateGraphfrom langgraph.types import interrupt, Commandfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaverfrom typing import TypedDictimport uuidfrom langgraph.constants import START, ENDfrom langgraph.graph import StateGraphfrom langgraph.types import interrupt, Commandfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver# Define the graph stateclass State(TypedDict): summary: str# Simulate an LLM summary generationdef generate_summary(state: State) -> State: return { "summary": "The cat sat on the mat and looked at the stars." }# 用户审查和修改节点函数def human_review_edit(state: State) -> State: result = interrupt({ "task": "Please review and edit the generated summary if necessary.", "generated_summary": state["summary"] }) # 返回人工重新编辑修改summary return { "summary": result["edited_summary"] }# Simulate downstream use of the edited summarydef downstream_use(state: State) -> State: print(f"✅ Using edited summary: {state['summary']}") return state# Build the graphbuilder = StateGraph(State)builder.add_node("generate_summary", generate_summary)builder.add_node("human_review_edit", human_review_edit)builder.add_node("downstream_use", downstream_use)builder.set_entry_point("generate_summary")builder.add_edge("generate_summary", "human_review_edit")builder.add_edge("human_review_edit", "downstream_use")builder.add_edge("downstream_use", END)# Set up in-memory checkpointing for interrupt supportcheckpointer = MemorySaver()graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)# Invoke the graph until it hits the interruptconfig = {"configurable": {"thread_id": uuid.uuid4()}}result = graph.invoke({}, config=config)# Output interrupt payloadprint(result["__interrupt__"])# Example output:# Interrupt(# value={# 'task': 'Please review and edit the generated summary if necessary.',# 'generated_summary': 'The cat sat on the mat and looked at the stars.'# },# resumable=True,# ...# )# Resume the graph with human-edited inputedited_summary = "The cat lay on the rug, gazing peacefully at the night sky."resumed_result = graph.invoke( Command(resume={"edited_summary": edited_summary}), config=config)print(resumed_result)
3. 审核工具调用
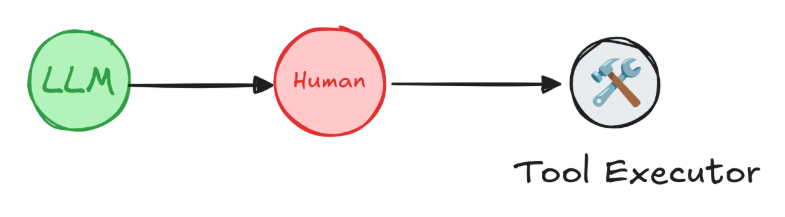
用户可以在调用工具之前进行检查和编辑LLM的输出,特别是在在LLM请求的工具调用可能很敏感或需要人工监督的应用程序中,如果轻易的任大模型调用有数据更新的工具或者API,可能会产生严重的后果。
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaverfrom langgraph.types import interruptfrom langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agentfrom dotenv import load_dotenv # 用于加载环境变量load_dotenv() # 加载 .env 文件中的环境变量# An example of a sensitive tool that requires human review / approvaldef book_hotel(hotel_name: str): """Book a hotel""" # 调用预订酒店API时中断点,等待用户确认 response = interrupt( f"Trying to call `book_hotel` with args {{'hotel_name': {hotel_name}}}. " "Please approve or suggest edits." ) if response["type"] == "accept": pass elif response["type"] == "edit": hotel_name = response["args"]["hotel_name"] else: raise ValueError(f"Unknown response type: {response['type']}") return f"Successfully booked a stay at {hotel_name}."checkpointer = InMemorySaver() agent = create_react_agent( model="deepseek:deepseek-chat", tools=[book_hotel], checkpointer=checkpointer, )config = { "configurable": { "thread_id": "1" }}for chunk in agent.stream( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "book a stay at McKittrick hotel"}]}, config): print(chunk) print("\n") from langgraph.types import Commandfor chunk in agent.stream( Command(resume={"type": "accept"}), # Command(resume={"type": "edit", "args": {"hotel_name": "McKittrick Hotel"}}), config): print(chunk) print("\n")
以上在工具实现函数调用前进行中断,实现起来比较侵入性比较强,官方提供一个工具包装函数, 在graph绑定工具时,用工具函数包装对应的工具对象即可:
from typing importCallablefrom langchain_core.tools import BaseTool, tool as create_toolfrom langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfigfrom langgraph.types import interrupt from langgraph.prebuilt.interrupt import HumanInterruptConfig, HumanInterruptfrom dotenv import load_dotenv # 用于加载环境变量load_dotenv() # 加载 .env 文件中的环境变量# 提供一个函数,用于包装工具,以便工具在调用前中断def add_human_in_the_loop( tool: Callable | BaseTool, *, interrupt_config: HumanInterruptConfig = None,) -> BaseTool: """Wrap a tool to support human-in-the-loop review.""" if not isinstance(tool, BaseTool): tool = create_tool(tool) if interrupt_config isNone: interrupt_config = { "allow_accept": True, "allow_edit": True, "allow_respond": True, } @create_tool( tool.name, description=tool.description, args_schema=tool.args_schema ) def call_tool_with_interrupt(config: RunnableConfig, **tool_input): request: HumanInterrupt = { "action_request": { "action": tool.name, "args": tool_input }, "config": interrupt_config, "description": "Please review the tool call" } response = interrupt([request])[0] # approve the tool call if response["type"] == "accept": tool_response = tool.invoke(tool_input, config) # update tool call args elif response["type"] == "edit": tool_input = response["args"]["args"] tool_response = tool.invoke(tool_input, config) # respond to the LLM with user feedback elif response["type"] == "response": user_feedback = response["args"] tool_response = user_feedback else: raise ValueError(f"Unsupported interrupt response type: {response['type']}") return tool_response return call_tool_with_interruptfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaverfrom langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agentcheckpointer = InMemorySaver()def book_hotel(hotel_name: str): """Book a hotel""" return f"Successfully booked a stay at {hotel_name}."agent = create_react_agent( model="deepseek:deepseek-chat", tools=[ add_human_in_the_loop(book_hotel), #包装需要人工确认的工具 ], checkpointer=checkpointer,)config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}# Run the agentfor chunk in agent.stream( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "book a stay at McKittrick hotel"}]}, config): print(chunk) print("\n") from langgraph.types import Command for chunk in agent.stream( Command(resume=[{"type": "accept"}]), # Command(resume=[{"type": "edit", "args": {"args": {"hotel_name": "McKittrick Hotel"}}}]), config): print(chunk) print("\n")
4. 用户输入校验
对话过程中,用户的关键信息输入有非常有必须进行校验的,验证人工的输入,可以通过在单个节点中使用多个中断调用来实现。
from langgraph.types import interruptdef human_node(state: State): """Human node with validation.""" question = "What is your age?" #循环多次中断校验,直到输入正确 while True: answer = interrupt(question) # 验证输入的正确格式 if not isinstance(answer, int) or answer < 0: question = f"'{answer} is not a valid age. What is your age?" answer = None continue else: # If the answer is valid, we can proceed. break print(f"The human in the loop is {answer} years old.") return { "age": answer }
四、总结
LangGraph 实现human-in-the-loop的流程总的来说就是一个断点续跑的过程:
-
- 创建一个中断点 Interrupt,提示用户进行反馈确认
-
- 用户回复后,使用Command 进行恢复续跑
-
- 实现这个的前提条件是需要有一个checkpointer,并指定threadId,checkpointer会记录当前中断点,并保存当前状态。
-
- human-in-the-loop过程经常会出现多次中断,可以使用循环或者递归进行实现。
想入门 AI 大模型却找不到清晰方向?备考大厂 AI 岗还在四处搜集零散资料?别再浪费时间啦!2025 年 AI 大模型全套学习资料已整理完毕,从学习路线到面试真题,从工具教程到行业报告,一站式覆盖你的所有需求,现在全部免费分享!
👇👇扫码免费领取全部内容👇👇

一、学习必备:100+本大模型电子书+26 份行业报告 + 600+ 套技术PPT,帮你看透 AI 趋势
想了解大模型的行业动态、商业落地案例?大模型电子书?这份资料帮你站在 “行业高度” 学 AI:
1. 100+本大模型方向电子书

2. 26 份行业研究报告:覆盖多领域实践与趋势
报告包含阿里、DeepSeek 等权威机构发布的核心内容,涵盖:
- 职业趋势:《AI + 职业趋势报告》《中国 AI 人才粮仓模型解析》;
- 商业落地:《生成式 AI 商业落地白皮书》《AI Agent 应用落地技术白皮书》;
- 领域细分:《AGI 在金融领域的应用报告》《AI GC 实践案例集》;
- 行业监测:《2024 年中国大模型季度监测报告》《2025 年中国技术市场发展趋势》。
3. 600+套技术大会 PPT:听行业大咖讲实战
PPT 整理自 2024-2025 年热门技术大会,包含百度、腾讯、字节等企业的一线实践:

- 安全方向:《端侧大模型的安全建设》《大模型驱动安全升级(腾讯代码安全实践)》;
- 产品与创新:《大模型产品如何创新与创收》《AI 时代的新范式:构建 AI 产品》;
- 多模态与 Agent:《Step-Video 开源模型(视频生成进展)》《Agentic RAG 的现在与未来》;
- 工程落地:《从原型到生产:AgentOps 加速字节 AI 应用落地》《智能代码助手 CodeFuse 的架构设计》。
二、求职必看:大厂 AI 岗面试 “弹药库”,300 + 真题 + 107 道面经直接抱走
想冲字节、腾讯、阿里、蔚来等大厂 AI 岗?这份面试资料帮你提前 “押题”,拒绝临场慌!
1. 107 道大厂面经:覆盖 Prompt、RAG、大模型应用工程师等热门岗位
面经整理自 2021-2025 年真实面试场景,包含 TPlink、字节、腾讯、蔚来、虾皮、中兴、科大讯飞、京东等企业的高频考题,每道题都附带思路解析:

2. 102 道 AI 大模型真题:直击大模型核心考点
针对大模型专属考题,从概念到实践全面覆盖,帮你理清底层逻辑:

3. 97 道 LLMs 真题:聚焦大型语言模型高频问题
专门拆解 LLMs 的核心痛点与解决方案,比如让很多人头疼的 “复读机问题”:

三、路线必明: AI 大模型学习路线图,1 张图理清核心内容
刚接触 AI 大模型,不知道该从哪学起?这份「AI大模型 学习路线图」直接帮你划重点,不用再盲目摸索!

路线图涵盖 5 大核心板块,从基础到进阶层层递进:一步步带你从入门到进阶,从理论到实战。
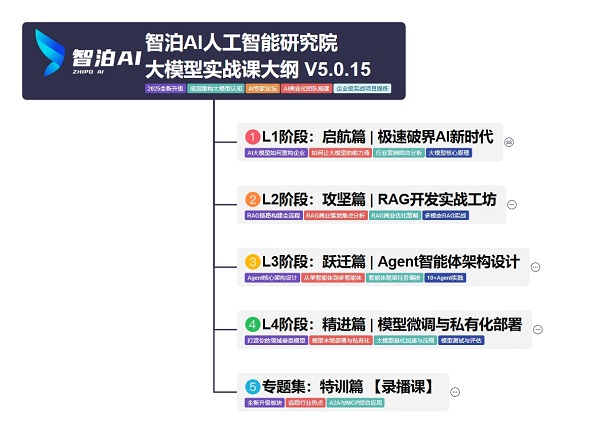
L1阶段:启航篇丨极速破界AI新时代
L1阶段:了解大模型的基础知识,以及大模型在各个行业的应用和分析,学习理解大模型的核心原理、关键技术以及大模型应用场景。
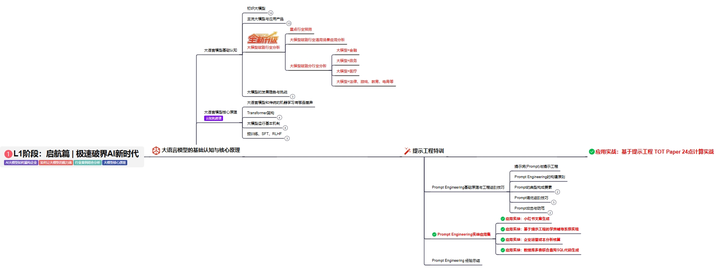
L2阶段:攻坚篇丨RAG开发实战工坊
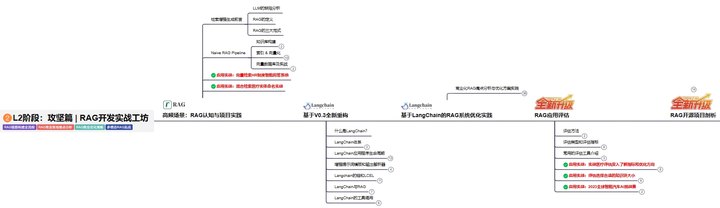
L2阶段:AI大模型RAG应用开发工程,主要学习RAG检索增强生成:包括Naive RAG、Advanced-RAG以及RAG性能评估,还有GraphRAG在内的多个RAG热门项目的分析。
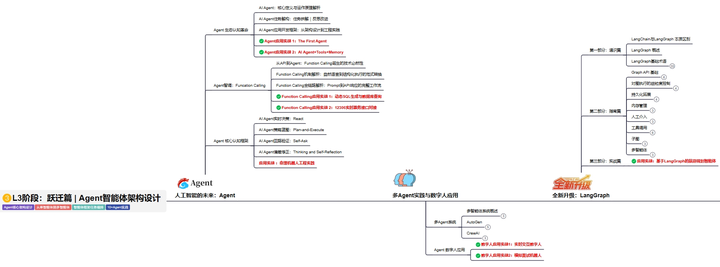
L3阶段:跃迁篇丨Agent智能体架构设计
L3阶段:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实现,主要学习LangChain、 LIamaIndex框架,也会学习到AutoGPT、 MetaGPT等多Agent系统,打造Agent智能体。
L4阶段:精进篇丨模型微调与私有化部署
L4阶段:大模型的微调和私有化部署,更加深入的探讨Transformer架构,学习大模型的微调技术,利用DeepSpeed、Lamam Factory等工具快速进行模型微调,并通过Ollama、vLLM等推理部署框架,实现模型的快速部署。

L5阶段:专题集丨特训篇 【录播课】
四、资料领取:全套内容免费抱走,学 AI 不用再找第二份
不管你是 0 基础想入门 AI 大模型,还是有基础想冲刺大厂、了解行业趋势,这份资料都能满足你!
现在只需按照提示操作,就能免费领取:
👇👇扫码免费领取全部内容👇👇

2025 年想抓住 AI 大模型的风口?别犹豫,这份免费资料就是你的 “起跑线”!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献114条内容
已为社区贡献114条内容






所有评论(0)