【收藏必备】深入解析Dify工作流系统:AI大模型可视化开发的核心实现
Dify工作流系统是基于图的AI应用执行引擎,通过可视化界面设计和执行复杂工作流。系统由多种节点(LLM、条件分支、代码执行等)通过边连接形成有向图,图引擎控制执行顺序。变量池管理工作流数据传递,支持多种错误处理和并行执行机制,为AI应用开发提供了灵活且强大的可视化编程能力。
工作流系统(Workflow System)是 Dify 的核心组件,它支持通过可视化编程界面创建复杂的 AI 应用程序。它允许用户通过将不同的功能块连接在一起来设计工作流,以处理数据、与 AI 模型交互、管理条件并执行各种操作。
接下来将详细介绍 Dify 工作流的实现机制,通过分析代码实现、数据流动和执行过程,充分理解工作流的实现原理。
一、工作流系统概述
1.1 核心概念
Dify 工作流系统是一个基于图(Graph)的执行引擎,允许用户通过可视化界面设计和执行复杂的 AI 工作流。工作流由多种类型的节点(Node)组成,这些节点通过边(Edge)连接,形成有向图结构。
1.2 系统架构
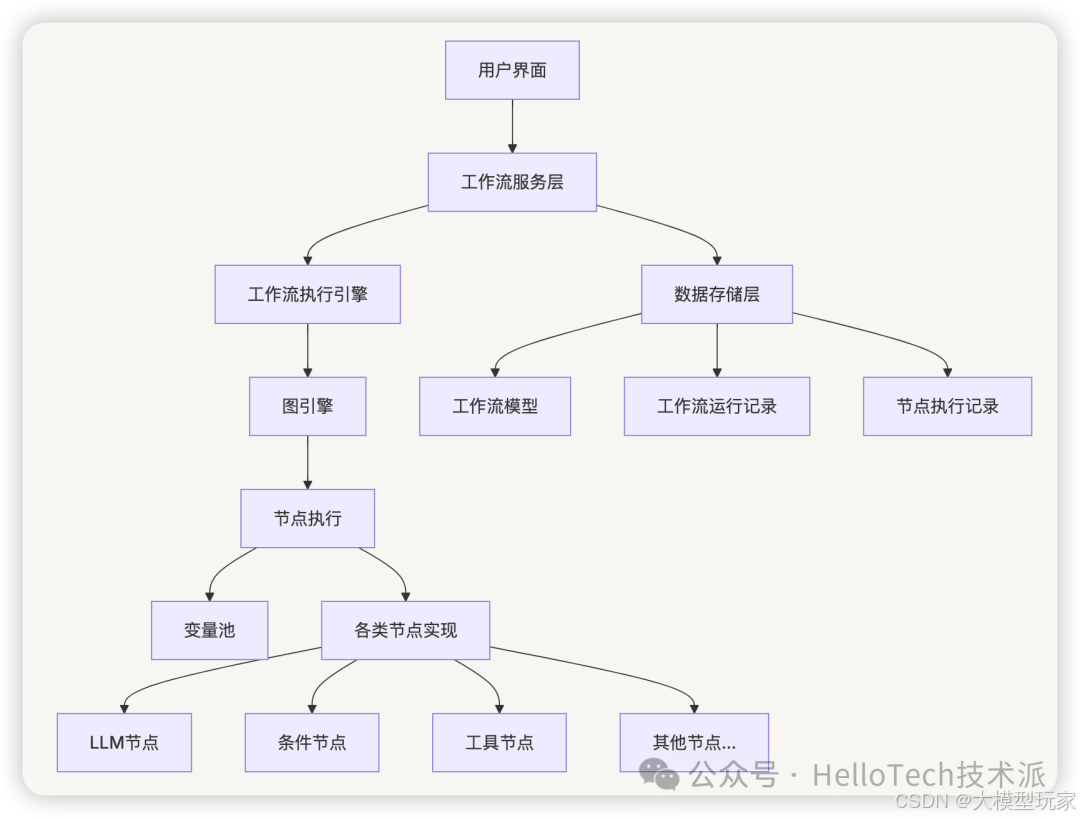
工作流系统主要由以下几个部分组成:
- 图引擎:负责解析工作流配置,构建执行图,并控制节点的执行顺序
- 节点实现:各种类型节点的具体实现,如 LLM、知识检索、条件分支等
- 变量管理:管理工作流执行过程中的变量传递和存储
- 执行记录:记录工作流和节点的执行状态、输入输出和性能指标
二、数据模型设计
2.1 工作流数据模型
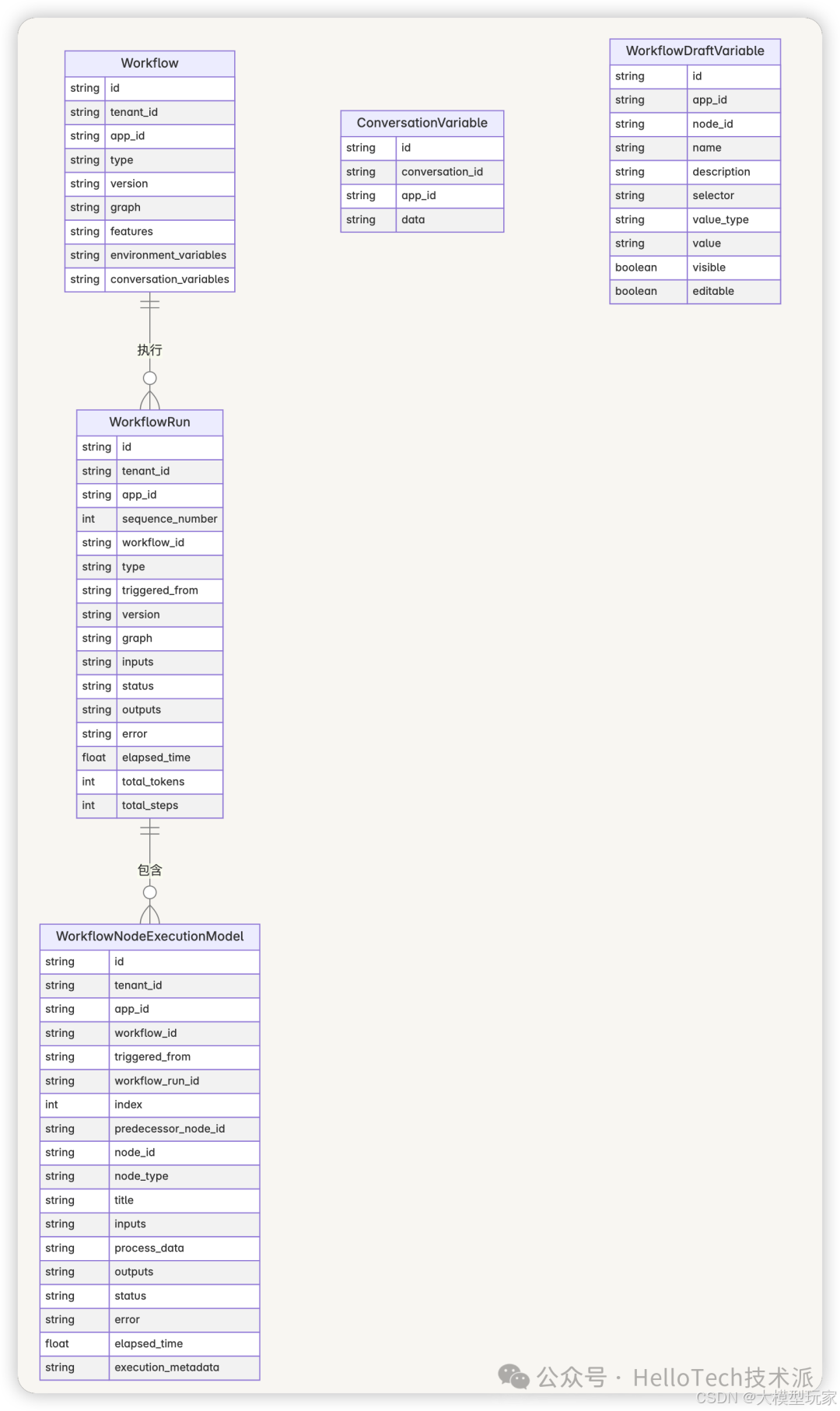
Dify 使用多个模型来表示工作流及其执行状态:
- WorkflowModel:工作流的基本信息,包括 ID、名称、描述、配置等
- WorkflowRunModel:工作流的执行记录,包括执行状态、开始时间、结束时间等
- WorkflowNodeExecutionModel:节点的执行记录,包括节点类型、输入、输出、状态等
- ConversationVariable:存储会话变量,包括名称、值类型、值等
- WorkflowDraftVariable:存储草稿工作流中的变量,包括会话变量、系统变量和节点变量
2.2 工作流节点类型
Dify 工作流支持多种类型的节点,每种节点有不同的功能和配置:
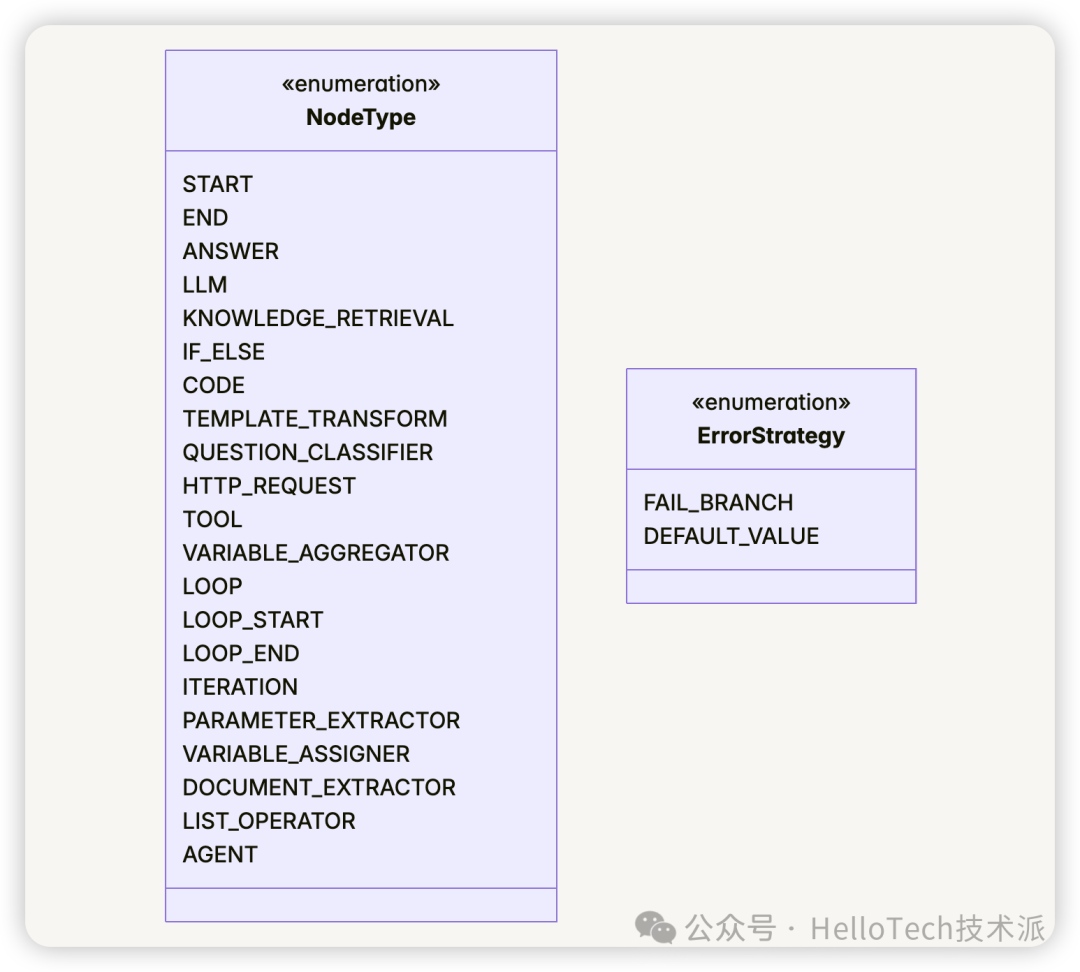
Dify 支持多种类型的节点,包括:
- START:工作流的起始节点
- END:工作流的结束节点
- LLM:大语言模型节点,用于生成文本
- KNOWLEDGE_RETRIEVAL:知识检索节点,用于从知识库中检索信息
- IF_ELSE:条件分支节点,根据条件选择执行路径
- CODE:代码执行节点,执行自定义代码
- HTTP_REQUEST:HTTP 请求节点,与外部 API 交互
- TOOL:工具节点,调用预定义的工具
- AGENT:代理节点,执行复杂的任务

三、工作流执行机制
3.1 工作流执行流程
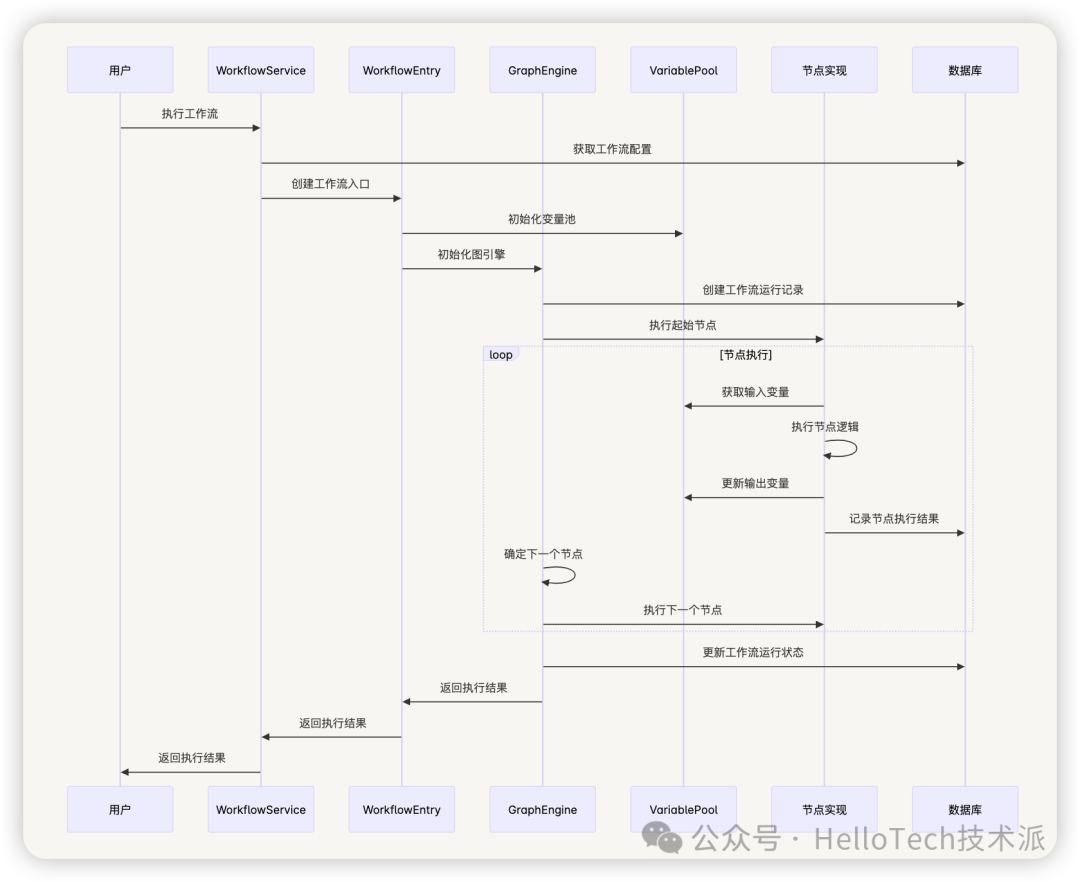
- 初始化工作流运行记录
- 解析工作流配置,构建执行图
- 从起始节点开始执行
- 根据图的边定义,确定下一个要执行的节点
- 执行节点,记录执行结果
- 重复步骤 4-5,直到达到结束节点或出现错误
- 完成工作流执行,更新运行记录
3.2 图引擎执行机制
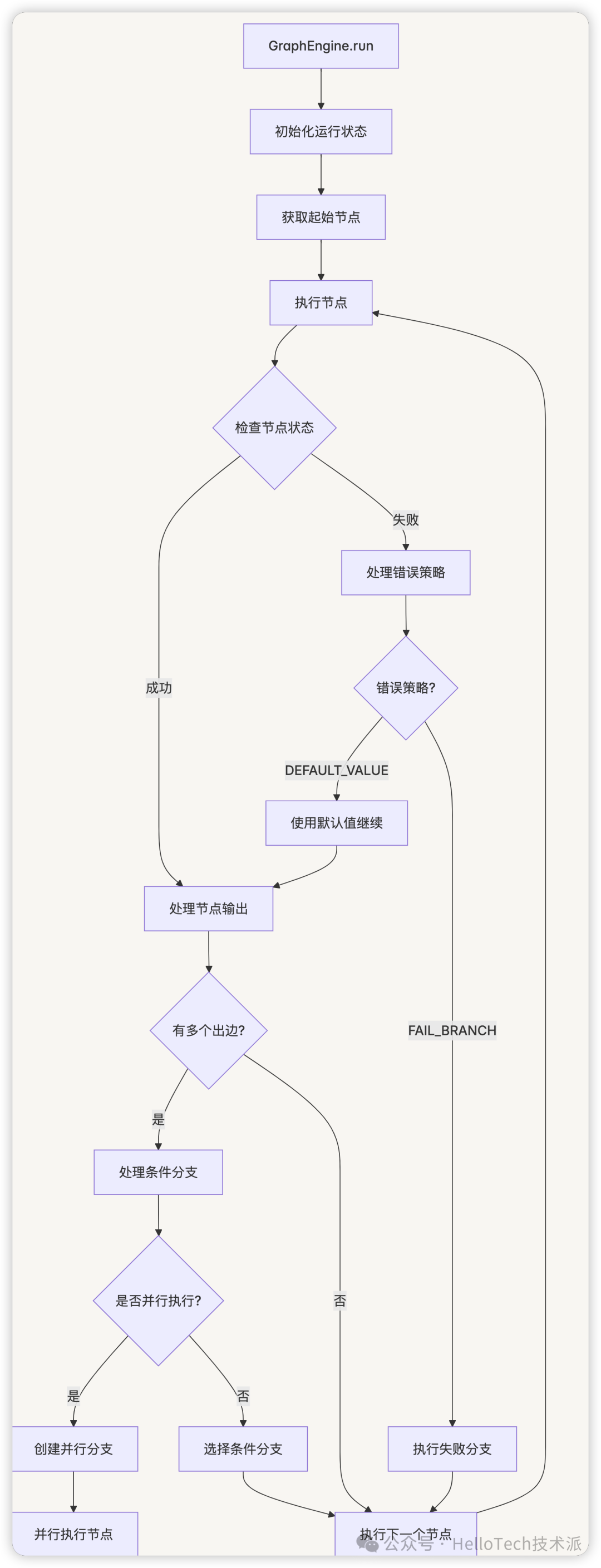
图引擎是工作流执行的核心,负责:
- 解析节点和边配置
- 构建边映射和反向边映射
- 识别根节点和叶子节点
- 检查节点连接性和循环
- 管理并行执行
- 控制执行流程
四、变量管理机制
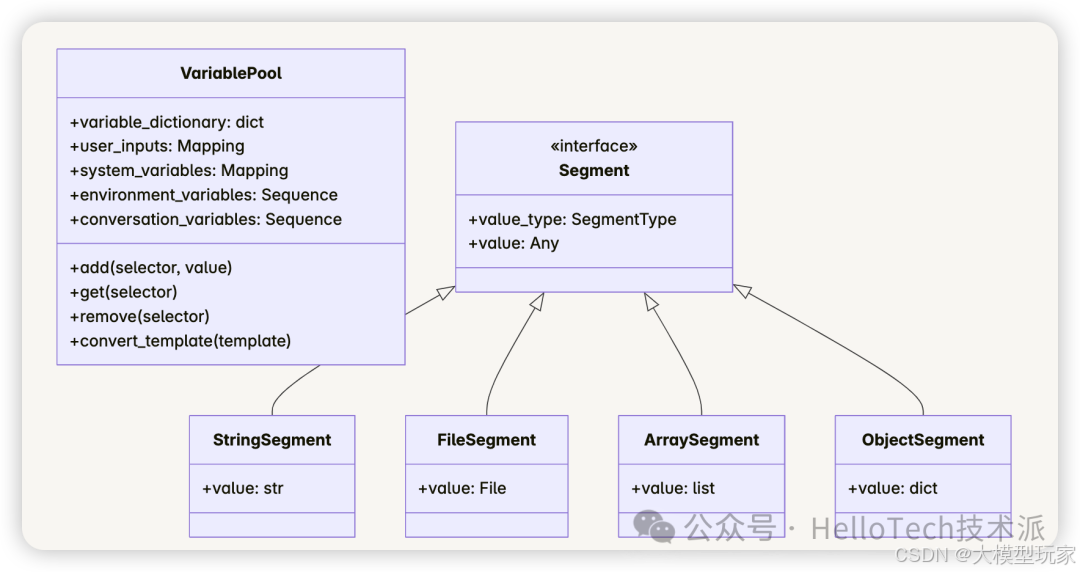
4.1 变量池设计
Dify 工作流使用变量池(VariablePool)管理工作流执行过程中的变量。变量池包含以下几类变量:
- 系统变量:以
sys.为前缀,如sys.query(用户输入)、sys.files(用户上传文件) - 环境变量:工作流级别的配置变量
- 会话变量:在会话中持久化的变量
- 节点变量:各节点的输入输出变量
4.2 变量传递机制
节点之间通过变量池传递数据。每个节点执行时:
- 节点执行后,将输出添加到变量池中
- 下一个节点从变量池中获取所需的输入变量
- 支持通过选择器和模板字符串引用变量
- 支持文件类型变量的传递
变量的引用使用 {{#node_id.variable_name#}} 的模板语法。
五、节点实现机制
5.1 基础节点结构
所有节点都继承自 BaseNode 抽象类,实现自己的 _run 方法:
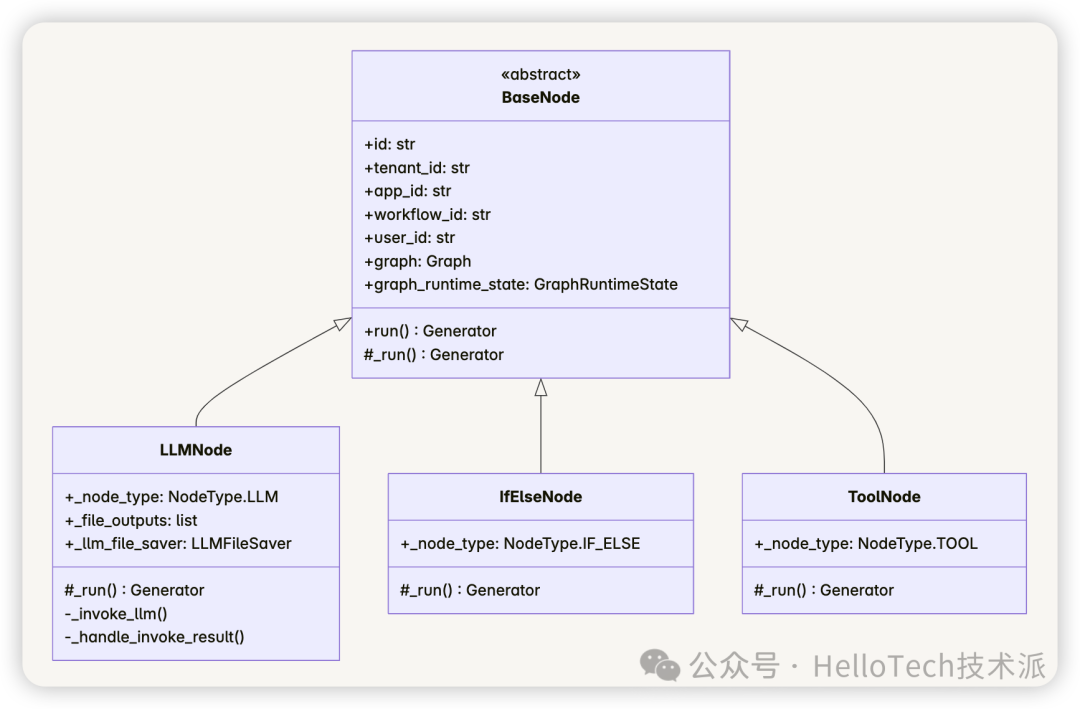
所有节点都继承自 BaseNode 类,实现以下方法:
- _run:节点的具体执行逻辑
- _get_inputs:获取节点的输入变量
- _get_outputs:处理节点的输出变量
以下是 BaseNode 类的核心实现:
class BaseNode(Generic[GenericNodeData]):
_node_data_cls: type[GenericNodeData]
_node_type: NodeType
def __init__(
self,
id: str,
config: Mapping[str, Any],
graph_init_params: "GraphInitParams",
graph: "Graph",
graph_runtime_state: "GraphRuntimeState",
previous_node_id: Optional[str] = None,
thread_pool_id: Optional[str] = None,
) -> None:
self.id = id
self.tenant_id = graph_init_params.tenant_id
self.app_id = graph_init_params.app_id
self.workflow_type = graph_init_params.workflow_type
self.workflow_id = graph_init_params.workflow_id
self.graph_config = graph_init_params.graph_config
self.user_id = graph_init_params.user_id
self.user_from = graph_init_params.user_from
self.invoke_from = graph_init_params.invoke_from
self.workflow_call_depth = graph_init_params.call_depth
self.graph = graph
self.graph_runtime_state = graph_runtime_state
self.previous_node_id = previous_node_id
self.thread_pool_id = thread_pool_id
node_id = config.get("id")
ifnot node_id:
raise ValueError("Node ID is required.")
self.node_id = node_id
node_data = self._node_data_cls.model_validate(config.get("data", {}))
self.node_data = node_data
@abstractmethod
def _run(self) -> NodeRunResult | Generator[Union[NodeEvent, "InNodeEvent"], None, None]:
"""
Run node
:return:
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def run(self) -> Generator[Union[NodeEvent, "InNodeEvent"], None, None]:
try:
result = self._run()
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(f"Node {self.node_id} failed to run")
result = NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
error=str(e),
error_type="WorkflowNodeError",
)
if isinstance(result, NodeRunResult):
yield RunCompletedEvent(run_result=result)
else:
yieldfrom result
BaseNode 类是所有节点的基类,它定义了节点的基本属性和方法:
- 初始化方法:接收节点 ID、配置、图引擎参数等,初始化节点的基本属性
- 抽象方法 _run:子类必须实现的方法,包含节点的具体执行逻辑
- run 方法:调用 _run 方法并处理异常,将结果包装为事件返回
5.2 节点类型实现
5.2.1 StartNode 实现
StartNode 是工作流的起始节点,负责将用户输入和系统变量作为节点的输出:
class StartNode(BaseNode[StartNodeData]):
_node_data_cls = StartNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.START
def _run(self) -> NodeRunResult:
node_inputs = dict(self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.user_inputs)
system_inputs = self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.system_variables
# TODO: System variables should be directly accessible, no need for special handling
# Set system variables as node outputs.
for var in system_inputs:
node_inputs[SYSTEM_VARIABLE_NODE_ID + "." + var] = system_inputs[var]
return NodeRunResult(status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.SUCCEEDED, inputs=node_inputs, outputs=node_inputs)
StartNode 的实现非常简单,它主要完成以下工作:
- 从变量池中获取用户输入和系统变量
- 将系统变量添加到节点输入中,以
SYSTEM_VARIABLE_NODE_ID.var的形式作为键 - 返回包含这些输入和输出的
NodeRunResult,状态为成功
5.2.2 IfElseNode 实现
IfElseNode 是条件分支节点,根据条件选择执行路径:
class IfElseNode(BaseNode[IfElseNodeData]):
_node_data_cls = IfElseNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.IF_ELSE
def _run(self) -> NodeRunResult:
"""
Run node
:return:
"""
node_inputs: dict[str, list] = {"conditions": []}
process_data: dict[str, list] = {"condition_results": []}
input_conditions = []
final_result = False
selected_case_id = None
condition_processor = ConditionProcessor()
try:
# Check if the new cases structure is used
if self.node_data.cases:
for case in self.node_data.cases:
input_conditions, group_result, final_result = condition_processor.process_conditions(
variable_pool=self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool,
conditions=case.conditions,
operator=case.logical_operator,
)
process_data["condition_results"].append(
{
"group": case.model_dump(),
"results": group_result,
"final_result": final_result,
}
)
# Break if a case passes (logical short-circuit)
if final_result:
selected_case_id = case.case_id # Capture the ID of the passing case
break
else:
# Fallback to old structure if cases are not defined
input_conditions, group_result, final_result = _should_not_use_old_function(
condition_processor=condition_processor,
variable_pool=self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool,
conditions=self.node_data.conditions or [],
operator=self.node_data.logical_operator or"and",
)
selected_case_id = "true"if final_result else"false"
process_data["condition_results"].append(
{"group": "default", "results": group_result, "final_result": final_result}
)
node_inputs["conditions"] = input_conditions
except Exception as e:
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED, inputs=node_inputs, process_data=process_data, error=str(e)
)
outputs = {"result": final_result, "selected_case_id": selected_case_id}
data = NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.SUCCEEDED,
inputs=node_inputs,
process_data=process_data,
edge_source_handle=selected_case_id or"false", # Use case ID or 'default'
outputs=outputs,
)
return data
IfElseNode 的实现主要完成以下工作:
- 使用
ConditionProcessor处理条件逻辑 - 遍历
cases结构中的条件组,并根据结果确定selected_case_id - 如果使用旧的结构,则调用
_should_not_use_old_function进行兼容处理 - 返回包含条件结果的
NodeRunResult,并设置edge_source_handle以指示下一个要执行的节点
5.2.3 LLM 节点实现
LLM 节点是工作流中最核心的节点之一,它负责调用大语言模型生成文本。LLM 节点的执行流程:
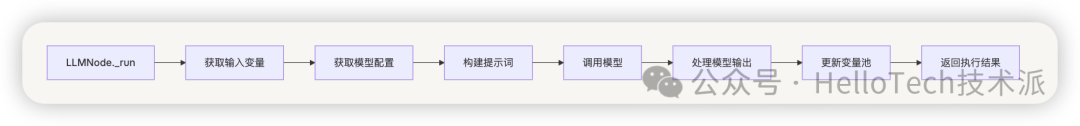
以下是 LLMNode 类的部分实现:
class LLMNode(BaseNode[LLMNodeData]):
_node_data_cls = LLMNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.LLM
# Instance attributes specific to LLMNode.
# Output variable for file
_file_outputs: list["File"]
_llm_file_saver: LLMFileSaver
def __init__(
self,
id: str,
config: Mapping[str, Any],
graph_init_params: "GraphInitParams",
graph: "Graph",
graph_runtime_state: "GraphRuntimeState",
previous_node_id: Optional[str] = None,
thread_pool_id: Optional[str] = None,
*,
llm_file_saver: LLMFileSaver | None = None,
) -> None:
super().__init__(
id=id,
config=config,
graph_init_params=graph_init_params,
graph=graph,
graph_runtime_state=graph_runtime_state,
previous_node_id=previous_node_id,
thread_pool_id=thread_pool_id,
)
# LLM file outputs, used for MultiModal outputs.
self._file_outputs: list[File] = []
if llm_file_saver isNone:
llm_file_saver = FileSaverImpl(
user_id=graph_init_params.user_id,
tenant_id=graph_init_params.tenant_id,
)
self._llm_file_saver = llm_file_saver
def _run(self) -> Generator[NodeEvent | InNodeEvent, None, None]:
def process_structured_output(text: str) -> Optional[dict[str, Any]]:
"""Process structured output if enabled"""
ifnot self.node_data.structured_output_enabled ornot self.node_data.structured_output:
returnNone
return self._parse_structured_output(text)
node_inputs: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None
process_data = None
result_text = ""
usage = LLMUsage.empty_usage()
finish_reason = None
try:
# init messages template
self.node_data.prompt_template = self._transform_chat_messages(self.node_data.prompt_template)
# fetch variables and fetch values from variable pool
inputs = self._fetch_inputs(node_data=self.node_data)
# fetch jinja2 inputs
jinja_inputs = self._fetch_jinja_inputs(node_data=self.node_data)
# merge inputs
inputs.update(jinja_inputs)
node_inputs = {}
# fetch files
files = (
self._fetch_files(selector=self.node_data.vision.configs.variable_selector)
if self.node_data.vision.enabled
else []
)
if files:
node_inputs["#files#"] = [file.to_dict() for file in files]
# fetch context value
generator = self._fetch_context(node_data=self.node_data)
context = None
for event in generator:
if isinstance(event, RunRetrieverResourceEvent):
context = event.context
yield event
if context:
node_inputs["#context#"] = context
# fetch model config
model_instance, model_config = self._fetch_model_config(self.node_data.model)
# ... 更多代码 ...
LLMNode 是一个典型的节点实现,负责调用大语言模型:
- 初始化节点参数和模型配置
- 处理输入变量和文件
- 构建提示消息
- 调用 LLM 模型
- 处理模型返回的结果
- 生成节点执行结果
5.2.4 ToolNode 实现
ToolNode 是工具节点,负责调用预定义的工具:
class ToolNode(BaseNode[ToolNodeData]):
"""
Tool Node
"""
_node_data_cls = ToolNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.TOOL
def _run(self) -> Generator:
"""
Run the tool node
"""
node_data = cast(ToolNodeData, self.node_data)
# fetch tool icon
tool_info = {
"provider_type": node_data.provider_type.value,
"provider_id": node_data.provider_id,
"plugin_unique_identifier": node_data.plugin_unique_identifier,
}
# get tool runtime
try:
from core.tools.tool_manager import ToolManager
tool_runtime = ToolManager.get_workflow_tool_runtime(
self.tenant_id, self.app_id, self.node_id, self.node_data, self.invoke_from
)
except ToolNodeError as e:
yield RunCompletedEvent(
run_result=NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs={},
metadata={WorkflowNodeExecutionMetadataKey.TOOL_INFO: tool_info},
error=f"Failed to get tool runtime: {str(e)}",
error_type=type(e).__name__,
)
)
return
# get parameters
tool_parameters = tool_runtime.get_merged_runtime_parameters() or []
parameters = self._generate_parameters(
tool_parameters=tool_parameters,
variable_pool=self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool,
node_data=self.node_data,
)
# get conversation id
conversation_id = self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.get_system_variable("conversation_id")
# invoke tool
try:
from core.tools.entities.tool_entities import ToolInvokeMessage
from core.tools.tool_engine import ToolEngine
# invoke tool
tool_invoke_message = ToolInvokeMessage(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
tool_parameters=parameters,
)
# invoke tool
tool_response = ToolEngine.generic_invoke(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
app_id=self.app_id,
tool_runtime=tool_runtime,
tool_invoke_message=tool_invoke_message,
user_id=self.user_id,
invoke_from=self.invoke_from,
)
# ... 处理工具响应 ...
except Exception as e:
# ... 处理异常 ...
ToolNode 的实现主要完成以下工作:
- 获取工具信息和工具运行时
- 生成工具参数
- 获取会话 ID
- 通过
ToolEngine.generic_invoke调用工具 - 处理工具返回的结果
- 生成节点执行结果
5.2.5 KnowledgeRetrievalNode 实现
KnowledgeRetrievalNode 是知识检索节点,负责从知识库中检索相关信息:
class KnowledgeRetrievalNode(LLMNode):
"""
Knowledge Retrieval Node
"""
_node_data_cls = KnowledgeRetrievalNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.KNOWLEDGE_RETRIEVAL
def _run(self) -> Generator[NodeEvent | InNodeEvent, None, None]:
"""
Run node
"""
node_data = cast(KnowledgeRetrievalNodeData, self.node_data)
# get query variable
query_variable = node_data.query_variable
ifnot query_variable:
yield RunCompletedEvent(
run_result=NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs={},
error="Query variable is not set",
)
)
return
# get query from variable pool
query = self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.get_variable(query_variable)
ifnot query:
yield RunCompletedEvent(
run_result=NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs={},
error=f"Query variable {query_variable} is empty",
)
)
return
# check rate limit
ifnot self._check_rate_limit():
yield RunCompletedEvent(
run_result=NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs={},
error="Rate limit exceeded",
)
)
return
# get retrieval model config
retrieval_model_config = {
"search_method": node_data.search_method,
"reranking_enable": node_data.reranking_enable,
"reranking_model": node_data.reranking_model,
"top_k": node_data.top_k,
"score_threshold": node_data.score_threshold,
}
# ... 执行知识检索逻辑 ...
KnowledgeRetrievalNode 的实现主要完成以下工作:
- 从变量池中提取查询变量
- 检查查询是否为空
- 进行速率限制检查
- 定义检索模型配置
- 执行知识检索
- 处理检索结果
- 生成节点执行结果
5.2.6 CodeNode 实现
CodeNode 是代码执行节点,负责执行用户定义的代码:
class CodeNode(BaseNode[CodeNodeData]):
"""
Code Node
"""
_node_data_cls = CodeNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.CODE
def _run(self) -> NodeRunResult:
"""
Run node
"""
node_data = cast(CodeNodeData, self.node_data)
# get code language and content
code_language = node_data.code_language
code_content = node_data.code_content
# get input variables
input_variables = {}
for input_variable in node_data.input_variables:
variable_name = input_variable.variable_name
variable_value = self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.get_variable(input_variable.variable_selector)
input_variables[variable_name] = variable_value
# execute code
try:
from core.workflow.nodes.code.code_executor import CodeExecutor
result = CodeExecutor.execute_workflow_code_template(
code_language=code_language,
code_content=code_content,
input_variables=input_variables,
)
# check output variables
outputs = {}
for output_variable in node_data.output_variables:
variable_name = output_variable.variable_name
if variable_name notin result:
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs=input_variables,
error=f"Output variable {variable_name} not found in code execution result",
)
variable_value = result[variable_name]
variable_type = output_variable.variable_type
# check variable type
if variable_type == "string":
ifnot self._check_string(variable_value, output_variable.max_length):
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs=input_variables,
error=f"Output variable {variable_name} is not a valid string or exceeds max length",
)
elif variable_type == "number":
ifnot self._check_number(variable_value):
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs=input_variables,
error=f"Output variable {variable_name} is not a valid number",
)
# ... 其他类型检查 ...
outputs[variable_name] = variable_value
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.SUCCEEDED,
inputs=input_variables,
outputs=outputs,
)
except (CodeExecutionError, CodeNodeError) as e:
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs=input_variables,
error=str(e),
)
CodeNode 的实现主要完成以下工作:
- 获取代码语言和代码内容
- 从变量池中获取输入变量
- 通过
CodeExecutor.execute_workflow_code_template执行代码 - 检查输出变量的类型和长度
- 处理执行结果和潜在的异常
- 生成节点执行结果
5.2.7 AgentNode 实现
AgentNode 是代理节点,负责调用 AI 代理执行复杂任务:
class AgentNode(ToolNode):
"""
Agent Node
"""
_node_data_cls = AgentNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.AGENT
def _run(self) -> Generator:
"""
Run the agent node
"""
node_data = cast(AgentNodeData, self.node_data)
# get agent strategy
try:
from core.agent.strategy.strategy_factory import StrategyFactory
strategy = StrategyFactory.create_strategy(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
app_id=self.app_id,
strategy_mode=node_data.strategy_mode,
strategy_config=node_data.strategy_config,
user_id=self.user_id,
invoke_from=self.invoke_from,
)
except Exception as e:
yield RunCompletedEvent(
run_result=NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs={},
error=f"Failed to create agent strategy: {str(e)}",
)
)
return
# generate agent parameters
agent_parameters = self._generate_parameters(
tool_parameters=node_data.parameters,
variable_pool=self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool,
node_data=node_data,
)
# get conversation id
conversation_id = self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.get_system_variable("conversation_id")
# invoke agent
try:
agent_response = strategy.invoke(
conversation_id=conversation_id,
inputs=agent_parameters,
files=[],
)
# ... 处理代理响应 ...
except Exception as e:
# ... 处理异常 ...
AgentNode 的实现主要完成以下工作:
- 获取代理策略
- 生成代理参数
- 获取会话 ID
- 通过
strategy.invoke调用代理 - 处理代理返回的结果
- 生成节点执行结果
5.2.8 HttpRequestNode 实现
HttpRequestNode 是 HTTP 请求节点,负责发送 HTTP 请求并处理响应:
class HttpRequestNode(BaseNode[HttpRequestNodeData]):
"""
Http Request Node
"""
_node_data_cls = HttpRequestNodeData
_node_type = NodeType.HTTP_REQUEST
def _run(self) -> NodeRunResult:
"""
Run node
"""
node_data = cast(HttpRequestNodeData, self.node_data)
# get default config
default_config = {
"method": node_data.method,
"url": node_data.url,
"headers": node_data.headers,
"params": node_data.params,
"body": node_data.body,
"timeout": node_data.timeout,
"retry_count": node_data.retry_count,
"retry_interval": node_data.retry_interval,
}
# init executor
executor = HttpRequestExecutor(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
app_id=self.app_id,
user_id=self.user_id,
variable_pool=self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool,
default_config=default_config,
)
# execute http request
try:
response = executor.execute()
# extract files
files = []
ifresponse.files:
for file inresponse.files:
files.append(file.to_dict())
# success
ifresponse.success:
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.SUCCEEDED,
inputs=response.request_info,
outputs={
"status_code": response.status_code,
"response_body": response.response_body,
"response_headers": response.response_headers,
"files": files,
},
)
# failed
else:
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs=response.request_info,
error=response.error,
)
except Exception as e:
return NodeRunResult(
status=WorkflowNodeExecutionStatus.FAILED,
inputs={},
error=str(e),
)
HttpRequestNode 的实现主要完成以下工作:
- 获取默认配置
- 初始化
HttpRequestExecutor - 执行 HTTP 请求
- 处理响应(包括成功和失败情况)
- 提取文件
- 生成节点执行结果
六、工作流数据流动
6.1 工作流创建和发布
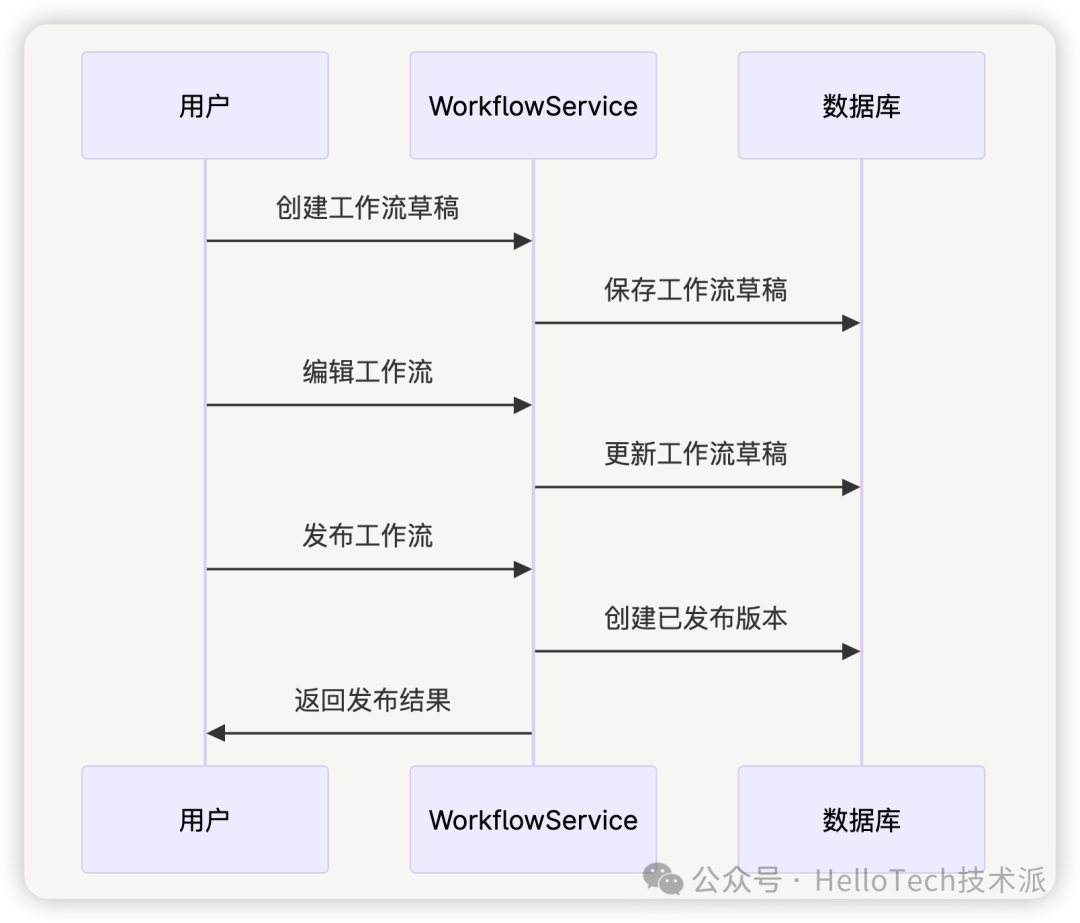
- 用户在界面上设计工作流,定义节点和连接
- 系统将设计转换为工作流配置
- 创建工作流模型和草稿变量
- 发布工作流,使其可被调用
6.2 工作流调试和执行
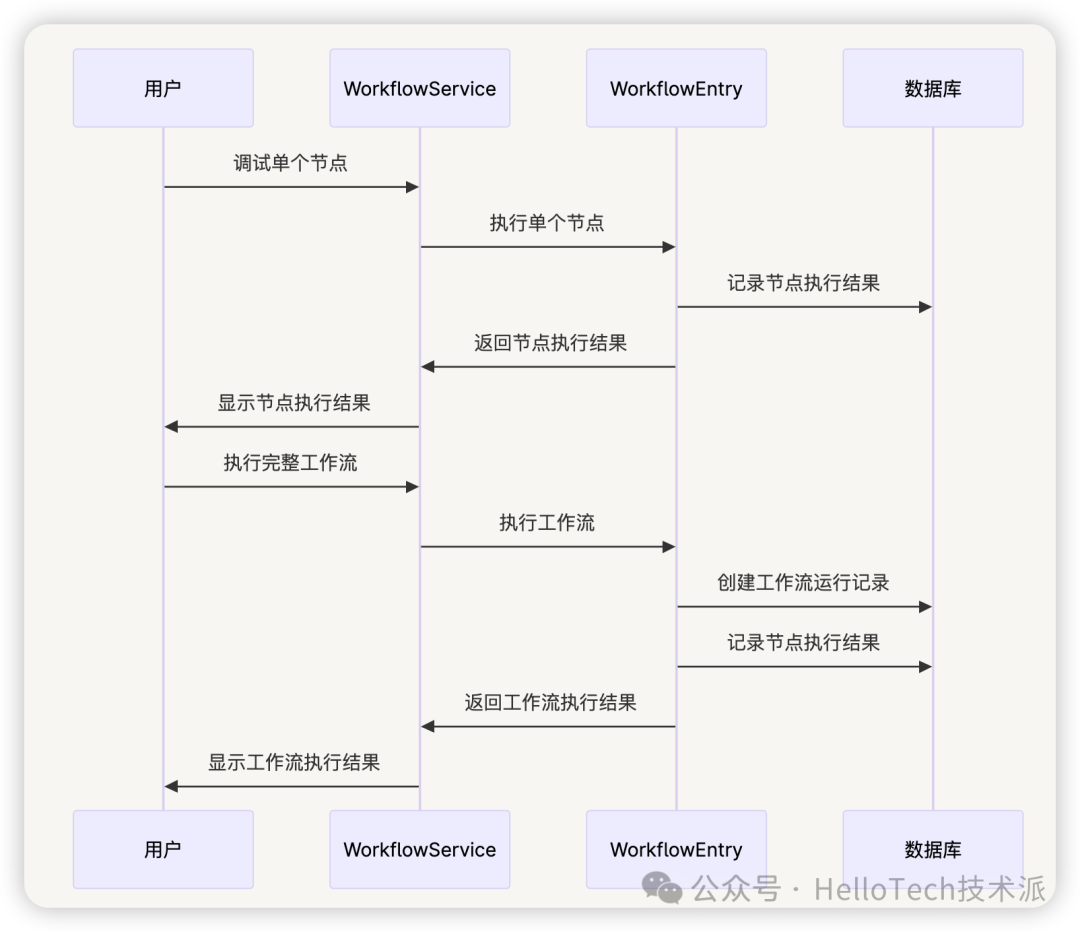
- 用户触发工作流执行
- 系统创建工作流运行记录
- 图引擎解析工作流配置,构建执行图
- 按照图的定义执行节点
- 记录每个节点的执行状态和结果
- 完成工作流执行,更新运行记录
七、图引擎机制
图引擎是工作流执行的核心,负责解析工作流图结构并执行节点。
7.1 图引擎实现
以下是 GraphEngine 类的部分实现:
class GraphEngine:
"""
Graph Engine
"""
def __init__(
self,
tenant_id: str,
app_id: str,
workflow_type: WorkflowType,
workflow_id: str,
user_id: str,
invoke_from: InvokeFrom,
) -> None:
"""
Initialize graph engine
"""
self.tenant_id = tenant_id
self.app_id = app_id
self.workflow_type = workflow_type
self.workflow_id = workflow_id
self.user_id = user_id
self.invoke_from = invoke_from
def execute(
self,
workflow_run_id: str,
workflow_config: dict[str, Any],
user_inputs: dict[str, Any],
system_variables: dict[str, Any],
environment_variables: dict[str, Any],
session_variables: dict[str, Any],
*,
event_handler: Optional[Callable[[WorkflowEvent], None]] = None,
) -> Generator[WorkflowEvent, None, None]:
"""
Execute workflow
"""
# Create graph init params
graph_init_params = GraphInitParams(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
app_id=self.app_id,
workflow_id=self.workflow_id,
workflow_run_id=workflow_run_id,
user_id=self.user_id,
invoke_from=self.invoke_from,
)
# Create variable pool
variable_pool = VariablePool(
user_inputs=user_inputs,
system_variables=system_variables,
environment_variables=environment_variables,
session_variables=session_variables,
)
# Create graph runtime state
graph_runtime_state = GraphRuntimeState(
variable_pool=variable_pool,
)
# Create graph
graph = Graph(
workflow_config=workflow_config,
graph_init_params=graph_init_params,
graph_runtime_state=graph_runtime_state,
)
# Create thread pool
thread_pool = GraphEngineThreadPool(max_workers=10)
# Execute graph
try:
# Yield workflow started event
yield WorkflowStartedEvent(
workflow_run_id=workflow_run_id,
)
# Execute graph
for event in graph.execute(thread_pool=thread_pool):
# Handle event
if event_handler:
event_handler(event)
# Yield event
yield event
# Check if workflow is completed
if isinstance(event, WorkflowCompletedEvent):
break
except Exception as e:
# Yield workflow failed event
yield WorkflowFailedEvent(
workflow_run_id=workflow_run_id,
error=str(e),
)
finally:
# Shutdown thread pool
thread_pool.shutdown(wait=True)
GraphEngineThreadPool 是一个继承自 ThreadPoolExecutor 的线程池,用于管理工作流的并行执行:
class GraphEngineThreadPool(ThreadPoolExecutor):
"""
Graph Engine Thread Pool
"""
def __init__(self, max_workers: Optional[int] = None) -> None:
"""
Initialize graph engine thread pool
"""
super().__init__(max_workers=max_workers)
self._futures: dict[str, Future] = {}
def submit_task(
self, thread_pool_id: str, fn: Callable, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> Future:
"""
Submit task to thread pool
"""
future = self.submit(fn, *args, **kwargs)
self._futures[thread_pool_id] = future
future.add_done_callback(lambda _: self._futures.pop(thread_pool_id, None))
returnfuture
def is_full(self) -> bool:
"""
Check if thread pool is full
"""
return len(self._futures) >= self._max_workers
def get_future(self, thread_pool_id: str) -> Optional[Future]:
"""
Get future by thread pool id
"""
return self._futures.get(thread_pool_id)
7.2 图结构解析
图引擎首先解析工作流的图结构,包括:
- 解析节点:解析工作流中的所有节点,包括节点类型、配置等
- 解析边:解析节点之间的连接关系,包括源节点、目标节点、源端口、目标端口等
- 构建节点映射:构建节点ID到节点对象的映射
- 构建边映射:构建边ID到边对象的映射
7.3 图结构实现
以下是 Graph 类的部分实现,它负责解析工作流配置并执行节点:
class Graph:
"""
Graph
"""
def __init__(
self,
workflow_config: dict[str, Any],
graph_init_params: GraphInitParams,
graph_runtime_state: GraphRuntimeState,
) -> None:
"""
Initialize graph
"""
self.workflow_config = workflow_config
self.graph_init_params = graph_init_params
self.graph_runtime_state = graph_runtime_state
# Parse workflow config
self.nodes = self._parse_nodes(workflow_config.get("nodes", {}))
self.edges = self._parse_edges(workflow_config.get("edges", {}))
# Build node and edge mappings
self.node_mapping = self._build_node_mapping(self.nodes)
self.edge_mapping = self._build_edge_mapping(self.edges)
# Build source and target node mappings
self.source_node_mapping = self._build_source_node_mapping(self.edges)
self.target_node_mapping = self._build_target_node_mapping(self.edges)
def execute(self, thread_pool: GraphEngineThreadPool) -> Generator[WorkflowEvent, None, None]:
"""
Execute graph
"""
# Find start node
start_node = self._find_start_node()
ifnot start_node:
yield WorkflowFailedEvent(
workflow_run_id=self.graph_init_params.workflow_run_id,
error="Start node not found",
)
return
# Execute start node
for event in self._execute_node(start_node, thread_pool=thread_pool):
yield event
# Yield workflow completed event
yield WorkflowCompletedEvent(
workflow_run_id=self.graph_init_params.workflow_run_id,
)
def _execute_node(
self, node: BaseNode, thread_pool: GraphEngineThreadPool, previous_node_id: Optional[str] = None
) -> Generator[WorkflowEvent, None, None]:
"""
Execute node
"""
# Yield node started event
yield NodeStartedEvent(
workflow_run_id=self.graph_init_params.workflow_run_id,
node_id=node.node_id,
node_type=node.node_type,
)
# Run node
try:
for event in node.run():
# Handle node event
if isinstance(event, RunCompletedEvent):
# Get node run result
node_run_result = event.run_result
# Update variable pool
if node_run_result.outputs:
for variable_name, variable_value in node_run_result.outputs.items():
self.graph_runtime_state.variable_pool.add(
node_id=node.node_id,
variable_name=variable_name,
variable_value=variable_value,
)
# Yield node completed event
yield NodeCompletedEvent(
workflow_run_id=self.graph_init_params.workflow_run_id,
node_id=node.node_id,
node_type=node.node_type,
status=node_run_result.status,
inputs=node_run_result.inputs,
outputs=node_run_result.outputs,
process_data=node_run_result.process_data,
error=node_run_result.error,
)
# Find next nodes
next_nodes = self._find_next_nodes(
node_id=node.node_id,
edge_source_handle=node_run_result.edge_source_handle,
)
# Execute next nodes
for next_node in next_nodes:
# Check if thread pool is full
if thread_pool.is_full():
# Execute next node in current thread
for event in self._execute_node(
node=next_node,
thread_pool=thread_pool,
previous_node_id=node.node_id,
):
yield event
else:
# Execute next node in new thread
thread_pool_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
thread_pool.submit_task(
thread_pool_id=thread_pool_id,
fn=self._execute_node_in_thread,
node=next_node,
thread_pool=thread_pool,
previous_node_id=node.node_id,
thread_pool_id=thread_pool_id,
)
else:
# Yield other events
yield event
except Exception as e:
# Yield node failed event
yield NodeFailedEvent(
workflow_run_id=self.graph_init_params.workflow_run_id,
node_id=node.node_id,
node_type=node.node_type,
error=str(e),
)
7.4 节点执行
图引擎根据图结构执行节点:
- 确定起始节点:通常是START节点
- 执行节点:调用节点的run方法
- 处理节点结果:根据节点执行结果确定下一个要执行的节点
- 处理并行执行:如果有多个分支,可以并行执行
7.4.1 节点执行的主要流程
节点执行的主要流程如下:
- 发出节点开始事件:触发
NodeRunStartedEvent,通知系统节点开始执行 - 调用节点的
run方法:执行节点的具体逻辑 - 处理节点事件:
- 处理
RunCompletedEvent:获取节点执行结果 - 处理
RunStreamChunkEvent:处理流式输出 - 处理
RunRetrieverResourceEvent:处理检索资源
- 处理
- 处理重试逻辑:如果节点执行失败且配置了重试,则进行重试
- 更新变量池:将节点输出变量添加到变量池中
- 发出节点完成事件:根据执行结果触发相应事件
- 成功:触发
NodeRunSucceededEvent - 失败:触发
NodeRunFailedEvent - 异常但继续:触发
NodeRunExceptionEvent
- 成功:触发
- 查找下一个要执行的节点:根据边映射和条件确定下一个节点
- 执行下一个节点:可能是串行执行或并行执行
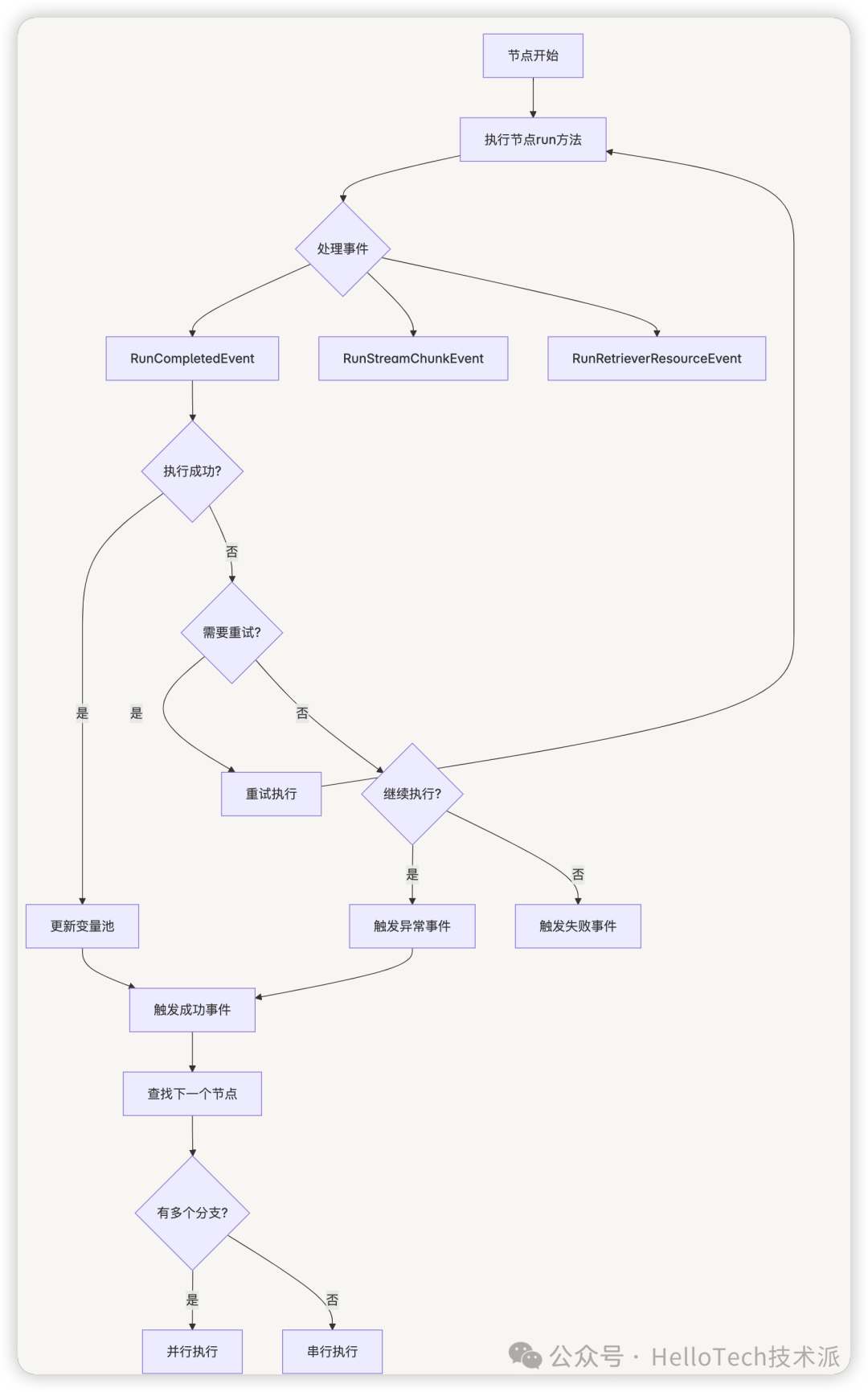
7.4.2 查找下一个节点的机制
在工作流执行过程中,确定下一个要执行的节点是关键步骤。GraphEngine 类的 _run 方法实现了这一机制:
-
获取边映射:通过
self.graph.edge_mapping.get(next_node_id)获取当前节点的所有出边 -
单边处理:如果只有一条出边,直接获取目标节点ID
if len(edge_mappings) == 1: edge = edge_mappings[0] # 检查是否有运行条件 if edge.run_condition: result = ConditionManager.get_condition_handler(...).check(...) if not result: break # 条件不满足,停止执行 next_node_id = edge.target_node_id -
多边处理:如果有多条出边,需要根据条件或并行策略确定下一个节点
-
条件分支:如果边有运行条件,根据条件结果确定要执行的分支
if any(edge.run_condition for edge in edge_mappings): # 按条件分组 condition_edge_mappings: dict[str, list[GraphEdge]] = {} # 检查每个条件组 for _, sub_edge_mappings in condition_edge_mappings.items(): # 检查条件是否满足 result = ConditionManager.get_condition_handler(...).check(...) if result: # 条件满足,确定下一个节点 if len(sub_edge_mappings) == 1: final_node_id = edge.target_node_id else: # 并行执行多个分支 parallel_generator = self._run_parallel_branches(...) -
并行分支:如果没有条件或条件满足,可能需要并行执行多个分支
else: parallel_generator = self._run_parallel_branches( edge_mappings=edge_mappings, in_parallel_id=in_parallel_id, parallel_start_node_id=parallel_start_node_id, handle_exceptions=handle_exceptions, )
-
-
并行分支执行:通过
_run_parallel_branches方法处理并行分支- 创建线程池和队列管理并行执行
- 为每个分支创建一个线程执行
- 收集并处理所有分支的执行结果
-
检查节点是否在当前并行分支内:确保节点执行不会跨越并行分支边界
if in_parallel_id and self.graph.node_parallel_mapping.get(next_node_id, "") != in_parallel_id: break
通过这种机制,工作流系统能够灵活地处理各种复杂的执行路径,包括条件分支和并行执行,确保工作流按照设计的逻辑正确执行。

八、图引擎与节点执行的通信机制
图引擎与节点执行之间的通信是通过事件驱动机制实现的,这种机制使得工作流执行过程中的各个组件能够松耦合地交互,提高了系统的可扩展性和可维护性。
8.1 事件驱动架构
工作流系统采用事件驱动架构,通过定义和传递各种事件来实现图引擎与节点之间的通信。这种架构具有以下特点:
- 松耦合:图引擎和节点之间通过事件进行通信,而不是直接调用,降低了组件间的依赖
- 可扩展:新的节点类型和事件类型可以轻松添加到系统中,而不需要修改现有代码
- 异步处理:事件可以异步处理,提高系统的响应性和吞吐量
- 状态追踪:通过事件可以追踪工作流的执行状态和历史
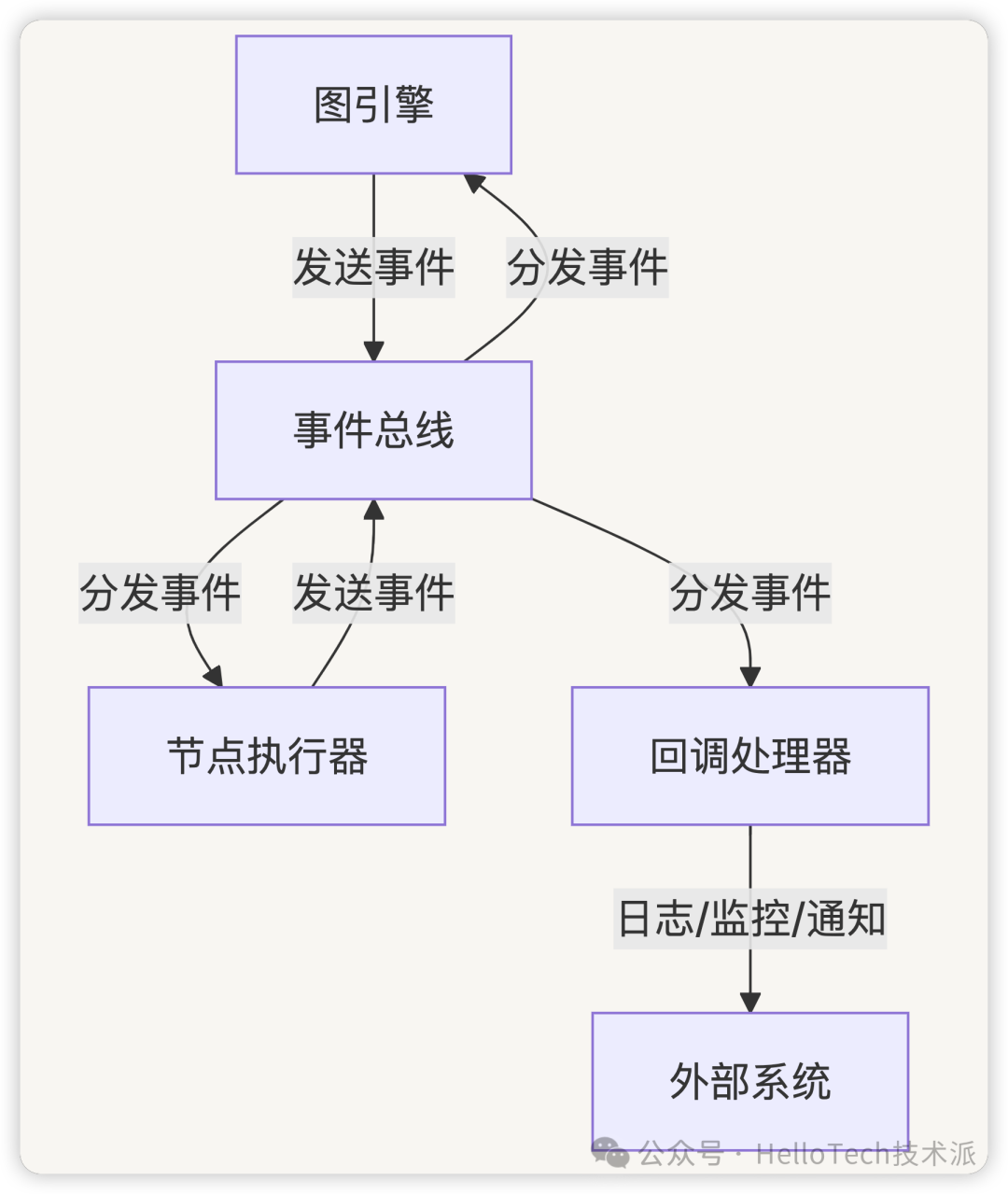
8.2 核心事件类型
工作流系统定义了多种事件类型,用于表示工作流执行过程中的不同状态和操作:
8.2.1 图级事件
- GraphRunStartedEvent:工作流开始执行
- GraphRunSucceededEvent:工作流成功完成
- GraphRunFailedEvent:工作流执行失败
- GraphRunPartialSucceededEvent:工作流部分成功(有些节点失败但不影响整体结果)
8.2.2 节点级事件
- NodeRunStartedEvent:节点开始执行
- NodeRunSucceededEvent:节点执行成功
- NodeRunFailedEvent:节点执行失败
- NodeRunExceptionEvent:节点执行异常但继续执行
- NodeRunRetryEvent:节点重试执行
- NodeRunStreamChunkEvent:节点产生流式输出
- NodeRunRetrieverResourceEvent:节点检索资源
8.2.3 并行分支事件
- ParallelBranchRunStartedEvent:并行分支开始执行
- ParallelBranchRunSucceededEvent:并行分支执行成功
- ParallelBranchRunFailedEvent:并行分支执行失败
8.2.4 迭代和循环事件
- IterationRunStartedEvent:迭代开始
- IterationRunNextEvent:迭代下一步
- IterationRunSucceededEvent:迭代成功完成
- IterationRunFailedEvent:迭代失败
- LoopRunStartedEvent:循环开始
- LoopRunNextEvent:循环下一步
- LoopRunSucceededEvent:循环成功完成
- LoopRunFailedEvent:循环失败
8.3 事件传递流程
事件在工作流系统中的传递流程如下:
-
事件生成:图引擎或节点执行器生成事件
yield NodeRunStartedEvent( id=node_instance.id, node_id=node_instance.node_id, node_type=node_instance.node_type, node_data=node_instance.node_data, route_node_state=route_node_state, predecessor_node_id=node_instance.previous_node_id, # 其他参数... ) -
事件传递:通过 Python 生成器(Generator)机制传递事件
def run(self) -> Generator[GraphEngineEvent, None, None]: # ... generator = graph_engine.run() for event in generator: # 处理事件 yield event -
事件处理:工作流入口点(WorkflowEntry)接收事件并分发给回调处理器
for event in generator: if callbacks: for callback in callbacks: callback.on_event(event=event) yield event -
回调处理:回调处理器根据事件类型执行相应的操作
def on_event(self, event: GraphEngineEvent) -> None: if isinstance(event, NodeRunStartedEvent): self.on_workflow_node_execute_started(event=event) elif isinstance(event, NodeRunSucceededEvent): self.on_workflow_node_execute_succeeded(event=event) # 处理其他事件类型...
8.4 事件处理回调
工作流系统定义了回调接口,允许外部系统注册回调函数来处理工作流事件:
class WorkflowCallback(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def on_event(self, event: GraphEngineEvent) -> None:
"""处理工作流事件"""
raise NotImplementedError
系统提供了多种内置回调实现,如:
- WorkflowLoggingCallback:记录工作流执行日志
- WorkflowAppRunnerCallback:处理应用级别的工作流事件
8.5 事件与状态管理
事件不仅用于通信,还用于管理工作流的状态:
-
节点状态追踪:通过事件记录节点的执行状态和结果
# 节点开始执行 yield NodeRunStartedEvent(...) # 节点执行成功 yield NodeRunSucceededEvent(...) -
变量传递:事件携带节点的输入和输出变量
# 节点执行成功事件包含输出变量 yield NodeRunSucceededEvent( # ... outputs=run_result.outputs, # ... ) -
错误处理:事件携带错误信息,用于错误处理和重试
# 节点执行失败事件包含错误信息 yield NodeRunFailedEvent( error=route_node_state.failed_reason or "Unknown error.", # ... )
8.6 事件转换与应用集成
工作流应用运行器(WorkflowAppRunner)将工作流事件转换为应用级别的队列事件,实现与应用系统的集成:
def _handle_event(self, workflow_entry: WorkflowEntry, event: GraphEngineEvent) -> None:
if isinstance(event, NodeRunSucceededEvent):
self._publish_event(
QueueNodeSucceededEvent(
node_execution_id=event.id,
node_id=event.node_id,
node_type=event.node_type,
node_data=event.node_data,
inputs=inputs,
process_data=process_data,
outputs=outputs,
execution_metadata=execution_metadata,
# 其他参数...
)
)
# 处理其他事件类型...
这种转换机制使得工作流系统能够与外部应用系统无缝集成,同时保持内部实现的独立性。
8.7 事件通信示例
以下是一个完整的事件通信流程示例,展示了从节点执行到事件处理的整个过程:
8.7.1 节点执行与事件生成
当图引擎执行一个节点时,会生成一系列事件:
# 1. 节点开始执行事件
yield NodeRunStartedEvent(
id=node_instance.id,
node_id=node_instance.node_id,
node_type=node_instance.node_type,
node_data=node_instance.node_data,
route_node_state=route_node_state,
# 其他参数...
)
# 2. 执行节点的run方法
generator = node_instance.run()
for item in generator:
# 传递节点产生的事件
yield item
# 3. 节点执行成功事件
yield NodeRunSucceededEvent(
id=node_instance.id,
node_id=node_instance.node_id,
node_type=node_instance.node_type,
node_data=node_instance.node_data,
route_node_state=route_node_state,
# 其他参数...
)
8.7.2 事件传递与处理
事件通过工作流入口点传递给回调处理器:
# WorkflowEntry.run方法
def run(self, *, callbacks: Sequence[WorkflowCallback]) -> Generator[GraphEngineEvent, None, None]:
generator = graph_engine.run()
for event in generator:
# 分发事件给回调处理器
for callback in callbacks:
callback.on_event(event=event)
# 继续传递事件
yield event
8.7.3 回调处理器处理事件
回调处理器根据事件类型执行相应的操作:
# WorkflowLoggingCallback.on_event方法
def on_event(self, event: GraphEngineEvent) -> None:
if isinstance(event, NodeRunStartedEvent):
self.print_text("\n[NodeRunStartedEvent]", color="yellow")
self.print_text(f"Node ID: {event.node_id}", color="yellow")
self.print_text(f"Node Title: {event.node_data.title}", color="yellow")
self.print_text(f"Type: {event.node_type.value}", color="yellow")
elif isinstance(event, NodeRunSucceededEvent):
self.print_text("\n[NodeRunSucceededEvent]", color="green")
# 打印节点执行结果
if event.route_node_state.node_run_result:
node_run_result = event.route_node_state.node_run_result
self.print_text(f"Outputs: {jsonable_encoder(node_run_result.outputs)}", color="green")
# 处理其他事件类型...
8.7.4 应用运行器处理事件
应用运行器将工作流事件转换为应用级别的队列事件:
# WorkflowAppRunner._handle_event方法
def _handle_event(self, workflow_entry: WorkflowEntry, event: GraphEngineEvent) -> None:
if isinstance(event, GraphRunStartedEvent):
self._publish_event(QueueWorkflowStartedEvent(...))
elif isinstance(event, NodeRunSucceededEvent):
self._publish_event(QueueNodeSucceededEvent(...))
elif isinstance(event, NodeRunFailedEvent):
self._publish_event(QueueNodeFailedEvent(...))
# 处理其他事件类型...
8.8 事件通信的优势
图引擎与节点执行之间基于事件的通信机制具有以下优势:
- 解耦组件:图引擎和节点执行器通过事件进行通信,而不是直接调用,降低了组件间的耦合度
- 简化调试:事件包含完整的上下文信息,便于调试和问题排查
- 支持异步执行:事件可以异步处理,支持并行执行和分布式部署
- 可扩展性:新的节点类型和事件类型可以轻松添加到系统中,而不需要修改现有代码
- 状态追踪:通过事件可以完整记录工作流的执行状态和历史,便于监控和审计
- 错误处理:事件携带错误信息,支持灵活的错误处理策略和重试机制
九、错误处理机制
工作流系统提供了完善的错误处理机制,包括错误策略、重试机制和异常处理,确保工作流在面对各种异常情况时能够灵活应对。
9.1 错误处理策略
工作流系统提供了两种主要的错误处理策略:
- FAIL_BRANCH:当节点执行失败时,沿着失败分支继续执行
- 将错误信息和类型添加到变量池
- 设置
edge_source_handle为FAILED,使工作流可以沿着专门处理失败情况的分支继续执行 - 适用于需要针对失败情况执行特定逻辑的场景
- DEFAULT_VALUE:当节点执行失败时,使用预定义的默认值继续执行
- 将错误信息和类型添加到变量池
- 使用节点配置中预定义的默认值作为节点输出
- 适用于即使失败也需要提供某种结果的场景
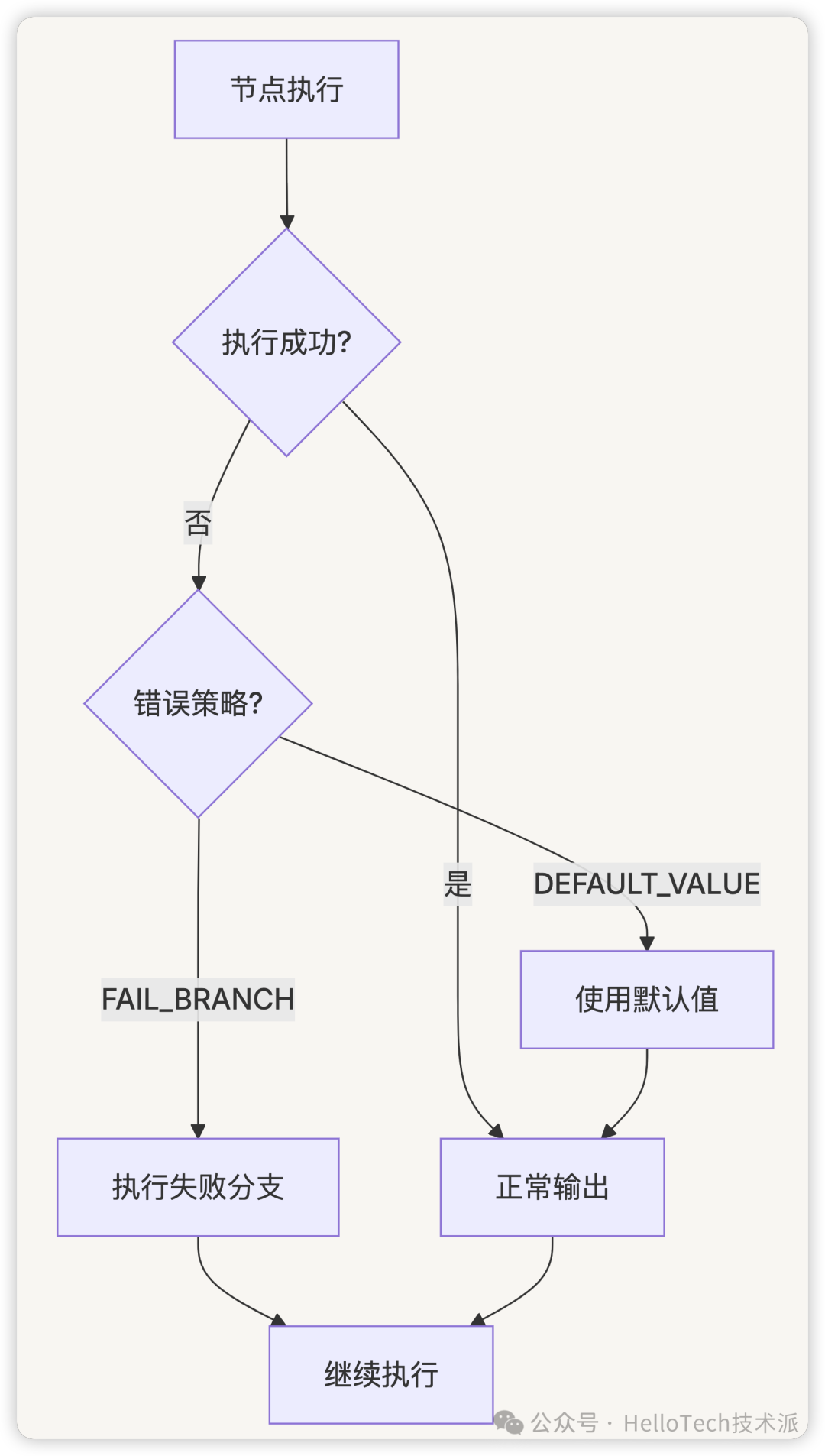
9.2 节点重试机制
对于某些类型的节点,系统支持在执行失败时进行重试:
- 重试配置:
max_retries:最大重试次数retry_interval_seconds:重试间隔时间(秒)
- 重试流程:
- 节点执行失败后,检查是否配置了重试
- 如果当前重试次数小于最大重试次数,触发
NodeRunRetryEvent事件 - 等待指定的重试间隔时间
- 重新执行节点
- 重试事件:
- 系统触发
NodeRunRetryEvent事件,包含重试索引、开始时间等信息 - 事件可用于监控和记录重试情况
- 系统触发
if node_instance.should_retry and retries < max_retries:
retries += 1
route_node_state.node_run_result = run_result
yield NodeRunRetryEvent(
id=str(uuid.uuid4()),
node_id=node_instance.node_id,
node_type=node_instance.node_type,
node_data=node_instance.node_data,
route_node_state=route_node_state,
error=run_result.error or "Unknown error",
retry_index=retries,
start_at=retry_start_at,
)
time.sleep(retry_interval)
8.3 可继续执行和可重试的节点类型
系统定义了特定类型的节点,它们在错误处理方面有特殊行为:
- 可继续执行的节点类型(
CONTINUE_ON_ERROR_NODE_TYPE):- 即使执行失败,工作流也可以继续执行
- 例如:HTTP请求节点、LLM节点等
- 这些节点可以配置错误策略(FAIL_BRANCH或DEFAULT_VALUE)
- 可重试的节点类型(
RETRY_ON_ERROR_NODE_TYPE):- 执行失败时可以自动重试
- 例如:HTTP请求节点、数据库操作节点等
- 这些节点可以配置最大重试次数和重试间隔
通过这些机制,工作流系统能够灵活处理各种错误情况,提高工作流的健壮性和可靠性。
9. 变量管理机制
变量管理是工作流执行的重要组成部分,负责管理工作流中的变量。
8.1 变量池
变量池是工作流中所有变量的集合,包括:
- 用户输入变量:用户提供的输入
- 系统变量:系统提供的变量,如时间戳、会话ID等
- 环境变量:环境相关的变量
- 会话变量:会话相关的变量
- 节点输出变量:节点执行后的输出变量
以下是 VariablePool 类的部分实现:
class VariablePool:
"""
Variable Pool
"""
def __init__(
self,
user_inputs: dict[str, Any],
system_variables: dict[str, Any],
environment_variables: dict[str, Any],
session_variables: dict[str, Any],
) -> None:
"""
Initialize variable pool
"""
self.user_inputs = user_inputs
self.system_variables = system_variables
self.environment_variables = environment_variables
self.session_variables = session_variables
# Initialize variable dictionary
self.variable_dictionary: dict[str, Any] = {}
def add(self, node_id: str, variable_name: str, variable_value: Any) -> None:
"""
Add variable to variable pool
"""
# Check if variable value is File
if isinstance(variable_value, File):
# Convert File to dict
variable_value = variable_value.to_dict()
# Add variable to variable dictionary
self.variable_dictionary[f"{node_id}.{variable_name}"] = variable_value
def get_variable(self, variable_selector: str) -> Any:
"""
Get variable from variable pool
"""
# Check if variable selector is empty
ifnot variable_selector:
returnNone
# Check if variable selector is system variable
if variable_selector.startswith(SYSTEM_VARIABLE_NODE_ID):
# Get system variable
variable_name = variable_selector.split(".", 1)[1]
return self.get_system_variable(variable_name)
# Check if variable selector is user input
if variable_selector.startswith(USER_INPUT_NODE_ID):
# Get user input
variable_name = variable_selector.split(".", 1)[1]
return self.get_user_input(variable_name)
# Check if variable selector is environment variable
if variable_selector.startswith(ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NODE_ID):
# Get environment variable
variable_name = variable_selector.split(".", 1)[1]
return self.get_environment_variable(variable_name)
# Check if variable selector is session variable
if variable_selector.startswith(SESSION_VARIABLE_NODE_ID):
# Get session variable
variable_name = variable_selector.split(".", 1)[1]
return self.get_session_variable(variable_name)
# Get variable from variable dictionary
return self.variable_dictionary.get(variable_selector)
8.2 变量传递
变量在节点之间的传递遵循以下规则:
- 变量选择器:通过变量选择器指定要使用的变量
- 变量作用域:变量的作用域为整个工作流
- 变量覆盖:后执行的节点可以覆盖先执行的节点的变量
变量选择器的格式为 node_id.variable_name,例如:
system.conversation_id:系统变量中的会话IDuser_input.query:用户输入中的查询node_1.result:节点1的输出变量 result
9. 并行执行机制
工作流支持并行执行多个分支,通过 GraphEngineThreadPool 实现:
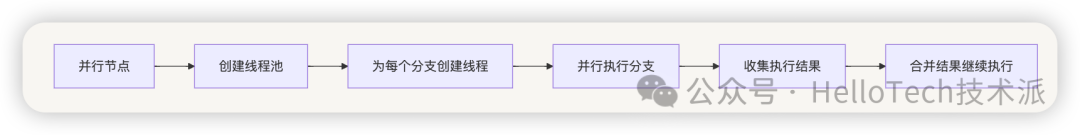
Dify 工作流支持并行执行多个分支:
- 通过
GraphParallel模型定义并行分支 - 使用
parallel_mapping和node_parallel_mapping管理并行关系 - 支持条件分支,根据条件选择执行路径
- 限制并行层级,避免过度复杂的执行图
十、总结
Dify 工作流系统是一个功能强大的可视化 AI 工作流引擎,通过图结构组织节点执行,使用变量池管理数据流动,支持多种节点类型、错误处理和并行执行。系统的核心组件包括:
- 工作流服务:管理工作流的生命周期
- 工作流入口:工作流执行的入口点
- 图引擎:负责节点的调度和执行
- 变量池:管理工作流中的变量
- 节点实现:各类节点的具体实现
通过这些组件的协同工作,Dify 工作流系统能够支持从简单到复杂的 AI 应用场景,为用户提供灵活且强大的工作流设计和执行能力。
普通人如何抓住AI大模型的风口?
领取方式在文末
为什么要学习大模型?
目前AI大模型的技术岗位与能力培养随着人工智能技术的迅速发展和应用 , 大模型作为其中的重要组成部分 , 正逐渐成为推动人工智能发展的重要引擎 。大模型以其强大的数据处理和模式识别能力, 广泛应用于自然语言处理 、计算机视觉 、 智能推荐等领域 ,为各行各业带来了革命性的改变和机遇 。
目前,开源人工智能大模型已应用于医疗、政务、法律、汽车、娱乐、金融、互联网、教育、制造业、企业服务等多个场景,其中,应用于金融、企业服务、制造业和法律领域的大模型在本次调研中占比超过 30%。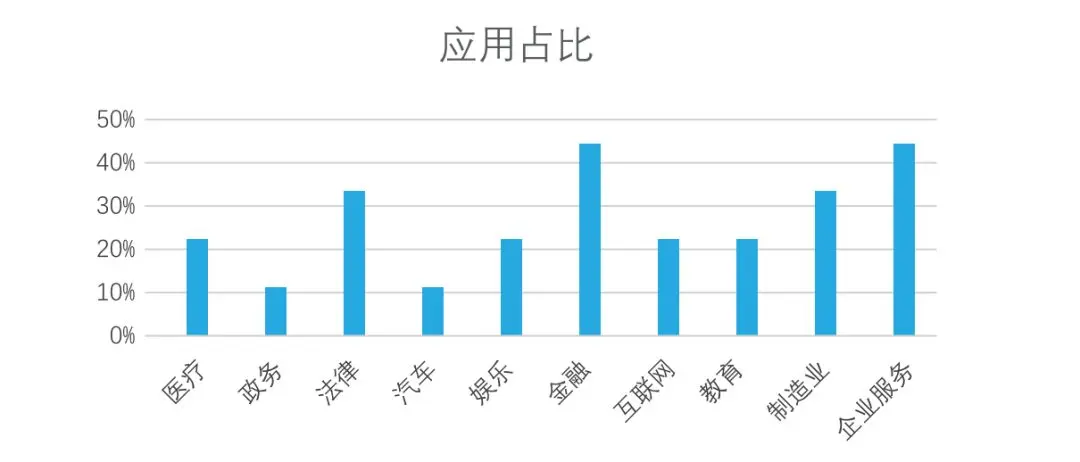
随着AI大模型技术的迅速发展,相关岗位的需求也日益增加。大模型产业链催生了一批高薪新职业:
人工智能大潮已来,不加入就可能被淘汰。如果你是技术人,尤其是互联网从业者,现在就开始学习AI大模型技术,真的是给你的人生一个重要建议!
最后
只要你真心想学习AI大模型技术,这份精心整理的学习资料我愿意无偿分享给你,但是想学技术去乱搞的人别来找我!
在当前这个人工智能高速发展的时代,AI大模型正在深刻改变各行各业。我国对高水平AI人才的需求也日益增长,真正懂技术、能落地的人才依旧紧缺。我也希望通过这份资料,能够帮助更多有志于AI领域的朋友入门并深入学习。
真诚无偿分享!!!
vx扫描下方二维码即可
加上后会一个个给大家发
大模型全套学习资料展示
自我们与MoPaaS魔泊云合作以来,我们不断打磨课程体系与技术内容,在细节上精益求精,同时在技术层面也新增了许多前沿且实用的内容,力求为大家带来更系统、更实战、更落地的大模型学习体验。
希望这份系统、实用的大模型学习路径,能够帮助你从零入门,进阶到实战,真正掌握AI时代的核心技能!
01 教学内容
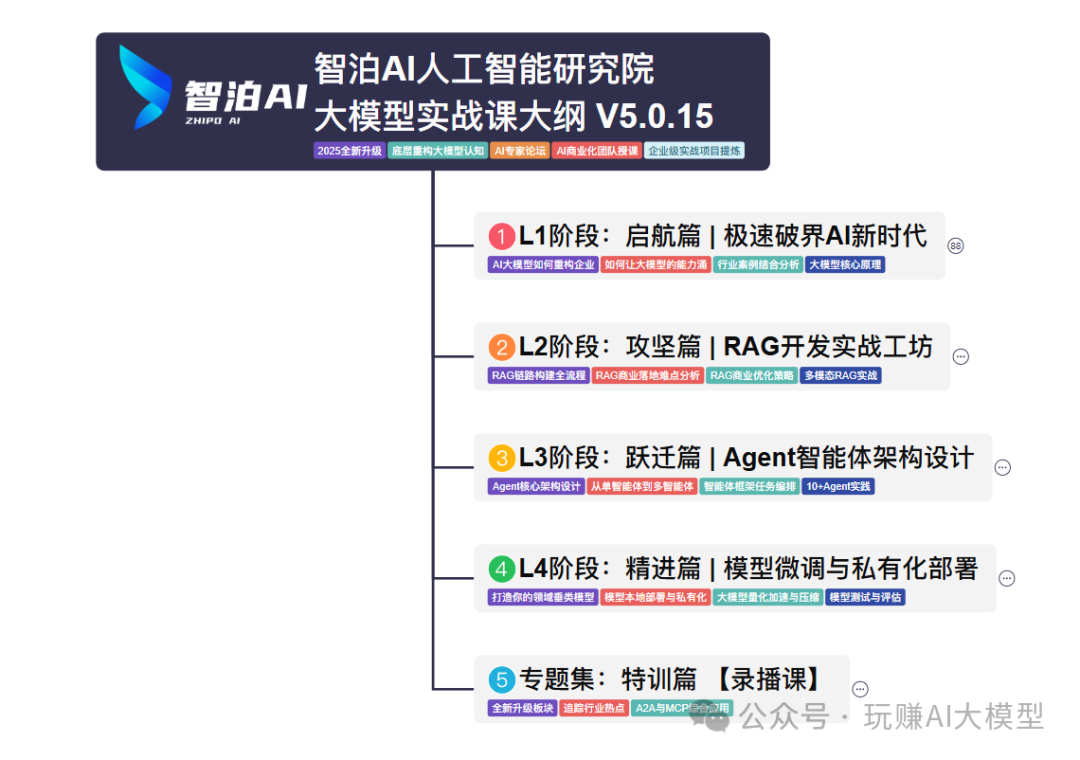
-
从零到精通完整闭环:【基础理论 →RAG开发 → Agent设计 → 模型微调与私有化部署调→热门技术】5大模块,内容比传统教材更贴近企业实战!
-
大量真实项目案例: 带你亲自上手搞数据清洗、模型调优这些硬核操作,把课本知识变成真本事!
02适学人群
应届毕业生: 无工作经验但想要系统学习AI大模型技术,期待通过实战项目掌握核心技术。
零基础转型: 非技术背景但关注AI应用场景,计划通过低代码工具实现“AI+行业”跨界。
业务赋能突破瓶颈: 传统开发者(Java/前端等)学习Transformer架构与LangChain框架,向AI全栈工程师转型。

vx扫描下方二维码即可
本教程比较珍贵,仅限大家自行学习,不要传播!更严禁商用!
03 入门到进阶学习路线图
大模型学习路线图,整体分为5个大的阶段: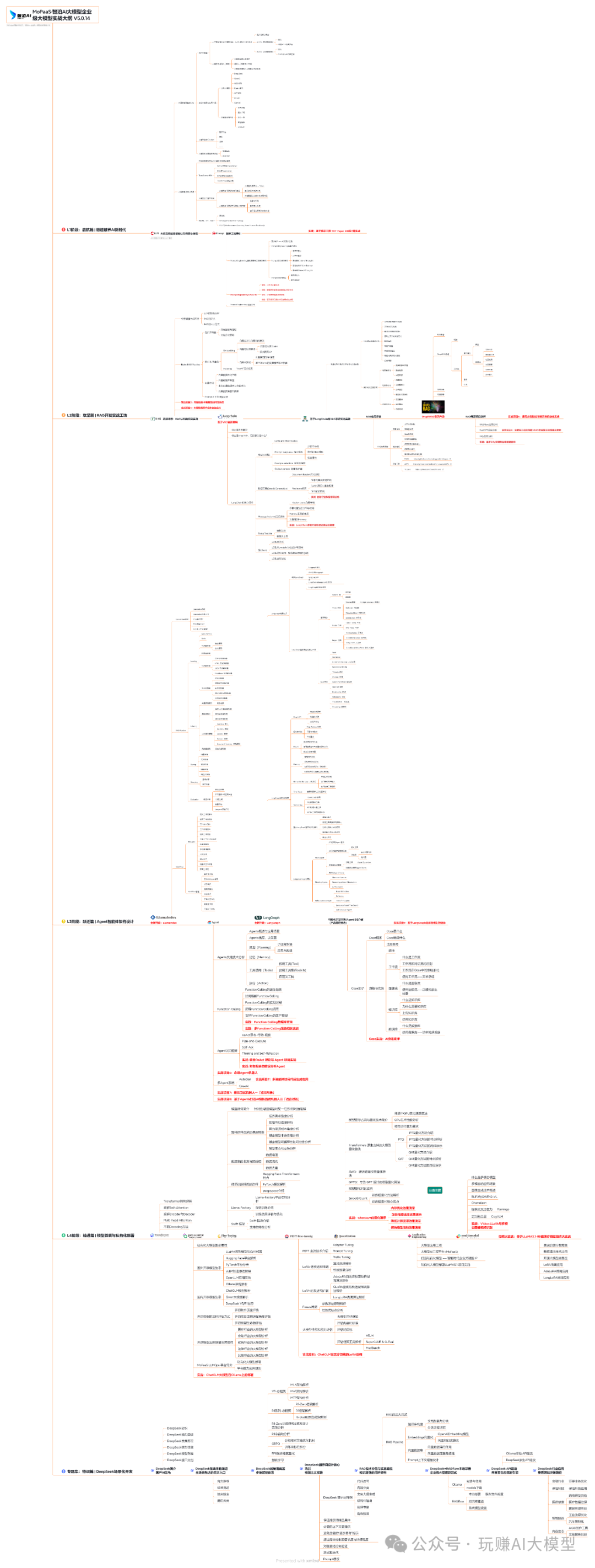
04 视频和书籍PDF合集

从0到掌握主流大模型技术视频教程(涵盖模型训练、微调、RAG、LangChain、Agent开发等实战方向)
新手必备的大模型学习PDF书单来了!全是硬核知识,帮你少走弯路(不吹牛,真有用)
05 行业报告+白皮书合集
收集70+报告与白皮书,了解行业最新动态!
06 90+份面试题/经验
AI大模型岗位面试经验总结(谁学技术不是为了赚$呢,找个好的岗位很重要)

07 deepseek部署包+技巧大全

由于篇幅有限
只展示部分资料
并且还在持续更新中…
真诚无偿分享!!!
vx扫描下方二维码即可
加上后会一个个给大家发
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献72条内容
已为社区贡献72条内容







所有评论(0)