破解AI出海难题:亚马逊云科技RAG+MCP,解决提示词膨胀
摘要:大语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂任务时面临上下文窗口限制的问题,尤其是调用大量外部工具时,会导致"提示词膨胀"(PromptBloat),降低模型性能和准确性。Amazon Bedrock知识库结合检索增强生成(RAG)和模型上下文协议(MCP),提出了一种解决方案:将工具描述存储在向量数据库中,通过语义检索动态选择相关工具,减少提示词长度,提升推理效率和精准度。文章详细介
大语言模型(LLM)有限的上下文窗口常常成为复杂任务的瓶颈,特别是在需要调用大量外部工具时,例如通过模型上下文协议(MCP)管理的工具,将所有工具描述嵌入提示词会导致“提示词膨胀”(Prompt Bloat)。这不仅挤占了宝贵的上下文空间,限制模型推理能力,还增加了工具选择的决策复杂性,降低准确性和性能。
Amazon Bedrock知识库通过结合检索增强生成(RAG)和MCP,提供了一种优雅的解决方案。

RAG-MCP架构将工具描述存储在向量数据库中,利用语义检索动态选择最相关的工具,从而大幅减少提示词长度,提升推理效率和工具调用的精准性。
本文将深入探讨RAG-MCP的架构设计、Ascendancy实现步骤、性能优势、实际案例和故障排除指南,为开发者和架构师提供全面的实践参考。
本实现基于《RAG-MCP:通过检索增强生成缓解LLM工具选择中的提示词膨胀》论文中描述的方法,该方法解决了LLM访问众多工具时面临的“提示词膨胀”挑战。
RAG与MCP的核心概念
检索增强生成(RAG)
RAG是一种通过检索外部知识库增强LLM生成能力的框架。它将用户查询与存储在向量数据库中的知识进行语义匹配,提取最相关的内容作为上下文,从而提升模型生成结果的准确性和相关性。
在Amazon Bedrock中,知识库提供了完全托管的RAG功能,支持高效的向量存储和检索。
模型上下文协议(MCP)
MCP(Model Context Protocol)是一种标准化协议,用于管理LLM与外部工具的交互。它通过定义工具的元数据(如名称、描述、参数)实现模型与工具的无缝集成。
MCP Server负责提供工具列表和执行工具调用,而MCP Client则负责与服务器交互,并将工具信息传递给模型。
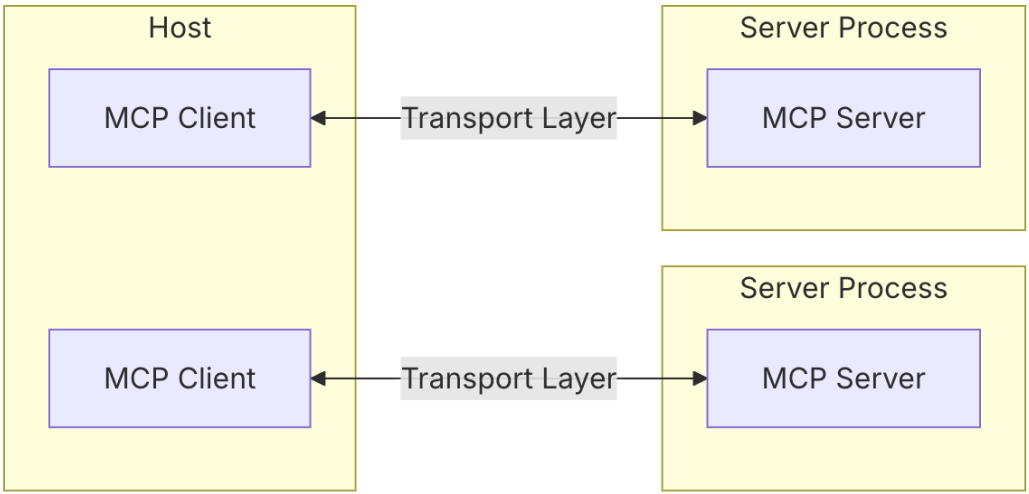
什么是MCP Tools
MCP Server中Tools是允许Servers暴露可执行函数,这些函数可以被Clients调用,并被LLM用于执行操作。
Tools的关键方面包括:
-
Discovery(发现):Clients可以通过tools/list端点列出可用的tools。
-
Invocation(调用):Tools使用tools/call端点调用,其中Servers执行请求的操作并返回结果。
-
Flexibility(灵活性):Tools的范围可以从简单的计算到复杂的API交互。
-
Tool定义结构:每个Tool都使用以下结构定义,从结构定义中可以看到,description和inputSchema都可能包含大量的文本提供给LLM,以方便LLM更精确地找到需要调用的Tool和传递的参数。
{name: string; // Tool 的唯一标识符description?: string; // 供人阅读的描述inputSchema: { // Tool 参数的 JSON Schematype: "object",properties: { ... } // Tool 特定的参数}}
左右滑动查看完整示意
下面选取一个MCP Server并获取到其Tools进行查看。
Filesystem MCP Server是一个用来管理本地文件夹的MCP Server,通过列出其中的Tools可以发现:一个MCP Server中的Tools如果不进行预筛选而直接发送给LLM,则需要耗费大量的Token,如果Tool Use过程出现多次,那么每次的Token花费会成倍增长。
=== All Available Tools (11 tools) ===1. 🔧 get_file_infoDescription: Retrieve detailed metadata about a file or directory. Returns comprehensive information including size, creation time, last modified time, permissions, and type. This tool is perfect for understanding file characteristics without reading the actual content. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: path2. 🔧 write_fileDescription: Create a new file or completely overwrite an existing file with new content. Use with caution as it will overwrite existing files without warning. Handles text content with proper encoding. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: path, content3. 🔧 move_fileDescription: Move or rename files and directories. Can move files between directories and rename them in a single operation. If the destination exists, the operation will fail. Works across different directories and can be used for simple renaming within the same directory. Both source and destination must be within allowed directories.Parameters: source, destination4. 🔧 edit_fileDescription: Make line-based edits to a text file. Each edit replaces exact line sequences with new content. Returns a git-style diff showing the changes made. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: path, edits, dryRun5. 🔧 read_multiple_filesDescription: Read the contents of multiple files simultaneously. This is more efficient than reading files one by one when you need to analyze or compare multiple files. Each file's content is returned with its path as a reference. Failed reads for individual files won't stop the entire operation. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: paths6. 🔧 create_directoryDescription: Create a new directory or ensure a directory exists. Can create multiple nested directories in one operation. If the directory already exists, this operation will succeed silently. Perfect for setting up directory structures for projects or ensuring required paths exist. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: path7. 🔧 read_fileDescription: Read the complete contents of a file from the file system. Handles various text encodings and provides detailed error messages if the file cannot be read. Use this tool when you need to examine the contents of a single file. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: path8. 🔧 directory_treeDescription: Get a recursive tree view of files and directories as a JSON structure. Each entry includes 'name', 'type' (file/directory), and'children'for directories. Files have no children array, while directories always have a children array (which may be empty). The output is formatted with 2-space indentation for readability. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: path9. 🔧 list_allowed_directoriesDescription: Returns the list of directories that this server is allowed to access. Use this to understand which directories are available before trying to access files.10. 🔧 search_filesDescription: Recursively search for files and directories matching a pattern. Searches through all subdirectories from the starting path. The search is case-insensitive and matches partial names. Returns full paths to all matching items. Great for finding files when you don't know their exact location. Only searches within allowed directories.Parameters: path, pattern, excludePatterns11. 🔧 list_directoryDescription: Get a detailed listing of all files and directories in a specified path. Results clearly distinguish between files and directories with [FILE] and [DIR] prefixes. This tool is essential for understanding directory structure and finding specific files within a directory. Only works within allowed directories.Parameters: pathTotal 11 tools
左右滑动查看完整示意
RAG-MCP的协同作用
通过结合RAG和MCP,可以实现:
-
动态工具检索:将MCP工具描述存储在向量数据库中,仅检索与用户查询语义最相关的工具,减少提示词中的冗余信息。
-
上下文增强:通过检索到的工具描述构建增强提示词(Augmented Prompt),为模型提供精准的上下文,提升推理能力。
-
可扩展性:支持大规模工具集,无需频繁修改提示词结构,适合动态更新的工具环境。
提示词膨胀的挑战
提示词膨胀是指在提示词中嵌入过多信息,导致上下文窗口被过度占用,主要挑战包括:
-
上下文窗口限制:LLM的上下文窗口通常在几千到几十万Token之间。嵌入所有工具描述会显著减少模型处理任务的可用空间。
-
决策开销:当工具数量较多时,模型需要从大量选项中选择合适的工具,增加计算复杂度和错误率。
-
性能下降:过长的提示词可能导致推理速度变慢,甚至因上下文溢出而无法处理复杂任务。
-
维护复杂性:工具集频繁更新时,需要手动调整提示词,增加了开发和维护成本。
RAG-MCP通过动态检索和上下文增强解决了这些问题,使得模型能够专注于推理而非工具选择。
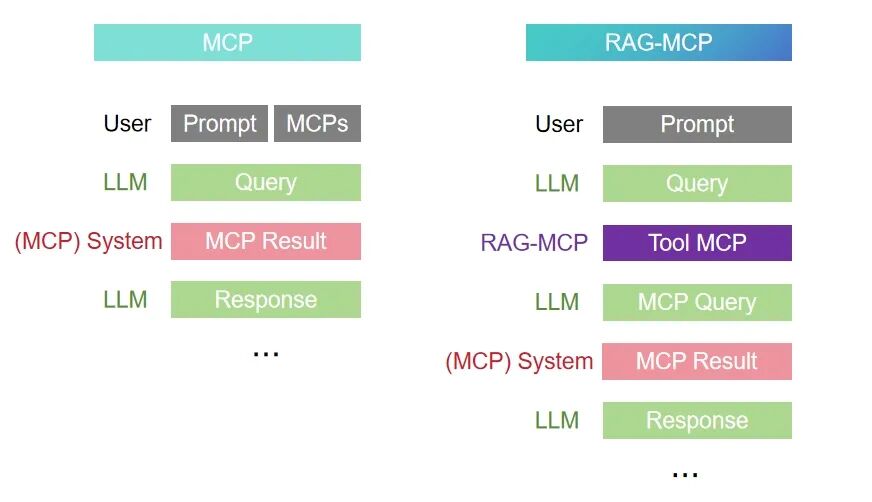
下图详细描述了RAG-MCP在使用过程中,和传统的MCP使用的区别。
结合Amazon Bedrock知识库,可以将上面的架构设计,具象化成下图所示的可执行流程。
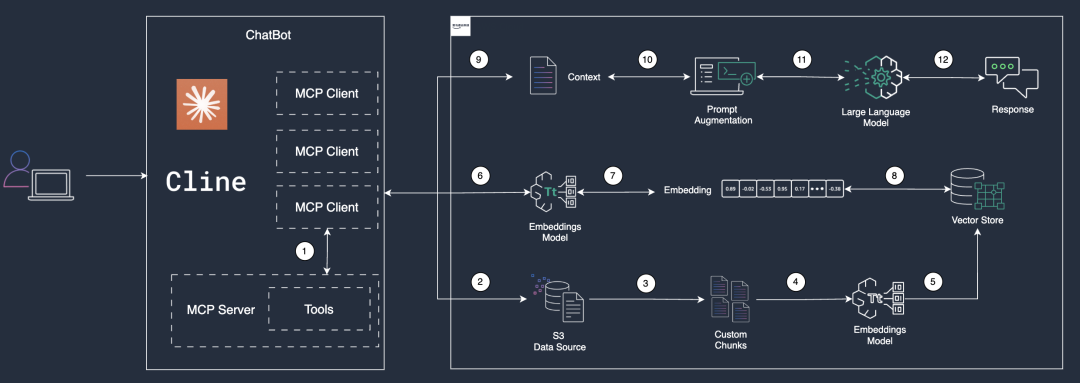
根据上面流程,总结出如下步骤:
1.MCP Client读取所有已启用的MCP Server的tools,并将tools保存成jsonl(JSON Lines)文件。
2.将生成的jsonl文件上传到Amazon Bedrock知识库的Data Source中。
3.使用自定义的Chunking方式,将jsonl文件切分成chunk文件。
4.提取的数据被分割成自定义块(Custom Chunks),以便于后续的嵌入(Embedding)处理。
5.数据块通过嵌入模型(Embeddings Model)转换为向量表示(Embeddings)。这一过程将文本或其他数据映射为高维向量,为后续的语义搜索或匹配奠定基础。
6.用户发起Tools检索,检索信息会输入给嵌入模型(Embeddings Model)。
7.嵌入模型(Embeddings Model)将检索内容转换成高维向量表示。
8.系统根据用户输入的语义特征,从向量数据库中检索出与输入最相似的嵌入向量。这一过程通过向量相似性计算完成,确保检索到的内容在语义上与用户需求高度相关。
9.根据检索到的嵌入向量,系统构建上下文,为后续的提示词生成提供背景信息。
10.系统基于上下文对提示词进行增强(Augmented Prompt),也就是将检索到的Tools当做提示词发送给LLM,以提高LLM的理解和生成能力。
11.增强后的提示词输入到LLM中,该模型根据输入选择是否有能够调用的Tool。
12.LLM生成的响应返回给客户端工具。
在上述步骤中,6-12会根据执行结果选择是否调用多次。
逐步指南
MCP Server Tools RAG检索
以下是在Amazon Bedrock中,实现RAG-MCP工具检索功能的完整流程,涵盖环境准备、数据处理、配置和检索优化。
前提条件
1.技术背景:
-
熟悉MCP协议及其架构,参考MCP文档。
-
了解Amazon Lambda、Amazon S3和Amazon Bedrock知识库的基本操作。
-
熟悉Amazon Web Services管理控制台和Amazon Web Services CLI。
2.环境准备:
-
配置Amazon Web Services账户,并授予Amazon Bedrock、Amazon S3、Amazon Lambda和Amazon OpenSearch Serverless的权限。
-
安装Python 3.8+及相关库(如boto3、mcp)。
-
配置MCP Server并确保可访问。
3.工具与依赖:
-
Amazon Web Services SDK for Python(boto3):用于与亚马逊云科技服务交互。
-
MCP Python SDK:用于与MCP Server通信。
-
Logging库:用于记录操作日志。
获取MCP工具列表
使用MCP Client从MCP Server获取工具列表,并将其转换为JSONL(JSON Lines)格式存储至本地临时文件。JSONL格式每行包含一个独立的JSON对象,适合大规模数据处理。确保工具描述包含关键元数据,如工具名称、功能、参数和调用方式。
-
注意事项:验证MCP Server的连接状态,确保返回的工具列表完整且符合JSON Schema规范。
-
建议:记录工具获取日志,便于调试和监控。
"""MCP (Model Context Protocol) client for tool integration."""import loggingfrom typing import Dict, List, Any, Optionalfrom mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParametersfrom mcp.client.stdio import stdio_clientfrom mcp.types import TextContentfrom .config import MCPConfigfrom .exceptions import MCPToolErrorlogger = logging.getLogger(__name__)class MCPClient:"""MCP client for handling tool interactions."""def __init__(self, config: MCPConfig):"""Initialize MCP client with configuration."""self.config = configself._session = Noneself._tools = Noneasync def __aenter__(self):"""Async context manager entry."""await self.connect()return selfasync def __aexit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):"""Async context manager exit."""await self.disconnect()async def connect(self):"""Connect to MCP server."""try:server_params = StdioServerParameters(command=self.config.command,args=self.config.args,env=self.config.env)self._stdio_context = stdio_client(server_params)self._read, self._write = await self._stdio_context.__aenter__()self._session_context = ClientSession(self._read, self._write)self._session = await self._session_context.__aenter__()# Initialize the connectionawait self._session.initialize()logger.info("Successfully connected to MCP server")except Exception as e:logger.error(f"Failed to connect to MCP server: {str(e)}")raise MCPToolError(f"Failed to connect to MCP server: {str(e)}")async def disconnect(self):"""Disconnect from MCP server."""try:# Close session firstif hasattr(self, '_session_context') and self._session_context:try:await self._session_context.__aexit__(None, None, None)except Exception as session_error:logger.warning(f"Error closing session: {str(session_error)}")finally:self._session_context = Noneself._session = None# Then close stdio connectionif hasattr(self, '_stdio_context') and self._stdio_context:try:# Use asyncio.wait_for to add timeout protectionimport asyncioawait asyncio.wait_for(self._stdio_context.__aexit__(None, None, None),timeout=5.0 # 5 second timeout)except asyncio.TimeoutError:logger.warning("MCP stdio disconnect timed out")except Exception as stdio_error:logger.warning(f"Error closing stdio: {str(stdio_error)}")finally:self._stdio_context = Nonelogger.info("Disconnected from MCP server")except Exception as e:logger.warning(f"Error during MCP disconnect: {str(e)}")async def list_tools(self):"""List available tools from MCP server."""ifnot self._session:raise MCPToolError("MCP session not initialized")try:tools_response = await self._session.list_tools()self._tools = tools_response.toolslogger.info(f"Retrieved {len(self._tools)} tools from MCP server")return tools_responseexcept Exception as e:logger.error(f"Failed to list MCP tools: {str(e)}")raise MCPToolError(f"Failed to list MCP tools: {str(e)}")async def call_tool(self, tool_name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]):"""Call a specific tool with given arguments.Args:tool_name: Name of the tool to callarguments: Arguments to pass to the toolReturns:Tool execution resultRaises:MCPToolError: If tool call fails"""ifnot self._session:raise MCPToolError("MCP session not initialized")try:logger.info(f"Calling tool {tool_name} with arguments: {arguments}")result = await self._session.call_tool(tool_name, arguments=arguments)logger.info(f"Tool {tool_name} result: {result}")if result.isError:error_msg = f"Tool {tool_name} execution failed"logger.error(error_msg)raise MCPToolError(error_msg)return resultexcept Exception as e:logger.error(f"Failed to call tool {tool_name}: {str(e)}")raise MCPToolError(f"Failed to call tool {tool_name}: {str(e)}")def convert_tools_to_bedrock_format(self, tools: List[Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:"""Convert MCP tools to Bedrock toolSpec format.Args:tools: List of MCP toolsReturns:Bedrock-compatible tool configurationRaises:MCPToolError: If conversion fails"""try:bedrock_tools = []for tool in tools:tool_spec = {"toolSpec": {"name":tool.name,"description": tool.description,"inputSchema": {"json": tool.inputSchema}}}bedrock_tools.append(tool_spec)return {"tools": bedrock_tools}except Exception as e:logger.error(f"Failed to convert tools to Bedrock format: {str(e)}")raise MCPToolError(f"Failed to convert tools to Bedrock format: {str(e)}")def extract_text_content(self, result) -> Optional[str]:"""Extract text content from MCP tool result.Args:result: MCP tool resultReturns:Extracted text content or None"""for content in result.content:if isinstance(content, TextContent):return content.textreturn None
左右滑动查看完整示意
上传工具数据至Amazon S3
将jsonl文件上传至Amazon S3,作为Amazon Bedrock知识库的数据源。配置Amazon S3存储桶以支持加密(使用Amazon KMS)和最小权限访问(通过Amazon IAM策略)。

上传完成后,启动Amazon Bedrock知识库的数据提取任务,将工具数据导入向量数据库。
-
注意事项:确保Amazon S3存储桶的URI格式正确(s3://<bucket-name>/<prefix>/<object>),并检查Amazon IAM权限以允许Amazon Bedrock访问。
-
建议:为数据源添加元数据文件(如工具类别、优先级),以增强后续检索效果。
def write_tools_to_knowledge_base(self, tools_data: Dict[str, Any]) -> IngestionJobResult:"""Clear Knowledge Base and write new tools data.Args:tools_data: Dictionary containing tool definitions in format {"tools": [...]}Returns:IngestionJobResult with job informationRaises:KnowledgeBaseError: If writing failsValueError: If tools_data format is invalid"""# Validate inputif not isinstance(tools_data, dict) or "tools" not in tools_data:raise ValueError("Invalid tools_data format: must contain 'tools' key")if not tools_data["tools"]:raise ValueError("Invalid tools_data format: 'tools'list cannot be empty")try:# Clear existing chunksif not self.clear_knowledge_base_chunks():raise KnowledgeBaseError("Failed to clear Knowledge Base chunks")# Create temporary JSONL filetemp_file_path = self._create_temp_jsonl_file(tools_data["tools"])try:# Upload to S3s3_key = self._upload_to_s3(temp_file_path)# Start ingestion jobresponse = self._start_ingestion_job()ingestion_job_id = response["ingestionJob"]["ingestionJobId"]logger.info(f"Started ingestion job: {ingestion_job_id}")# Wait for completionstatus = self.wait_for_ingestion_job(ingestion_job_id)return IngestionJobResult(job_id=ingestion_job_id,status=status,response=response)finally:# Clean up temporary fileself._cleanup_temp_file(temp_file_path)except Exception as e:logger.error(f"Error writing tools to Knowledge Base: {str(e)}")raise KnowledgeBaseError(f"Failed to write tools to Knowledge Base: {str(e)}")def _start_ingestion_job(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:"""Start an ingestion job."""try:response = self.bedrock_agent_client.start_ingestion_job(knowledgeBaseId=self.knowledge_base_id,dataSourceId=self.data_source_id)return responseexcept Exception as e:raise KnowledgeBaseError(f"Failed to start ingestion job: {str(e)}")
左右滑动查看完整示意
配置Amazon Bedrock知识库
在Amazon Bedrock管理控制台中创建并配置知识库,确保工具数据正确存储和向量化:
1.向量存储选择:推荐使用Amazon OpenSearch Serverless,支持高并发和低延迟,适合生产环境。也可选择Amazon Aurora with pgvector以降低成本,适用于小型项目。
2.数据源配置:指定Amazon S3存储桶的URI,并确保文件路径正确。可选:上传元数据文件以支持高级检索。
-
解析策略:默认解析器:适用于jsonl等纯文本数据,简单高效。
-
自定义解析器:通过Amazon Lambda实现特定格式的解析逻辑,适合定制化需求。
3.向量化配置:
-
选择嵌入模型(如Amazon Titan Text Embeddings V2)将工具描述转换为高维向量。
-
配置分块策略,使用自定义Chunk,平衡检索精度和性能。
-
可选:启用混合检索(语义+关键词)以提高复杂查询的准确性。
4.注意事项:验证嵌入模型是否适配工具描述的语言特性(如中文支持)。
5.建议:使用Amazon CloudWatch监控数据提取任务的状态和性能。
下面是创建截图:

在选择数据源中,使用Amazon S3作为数据源。
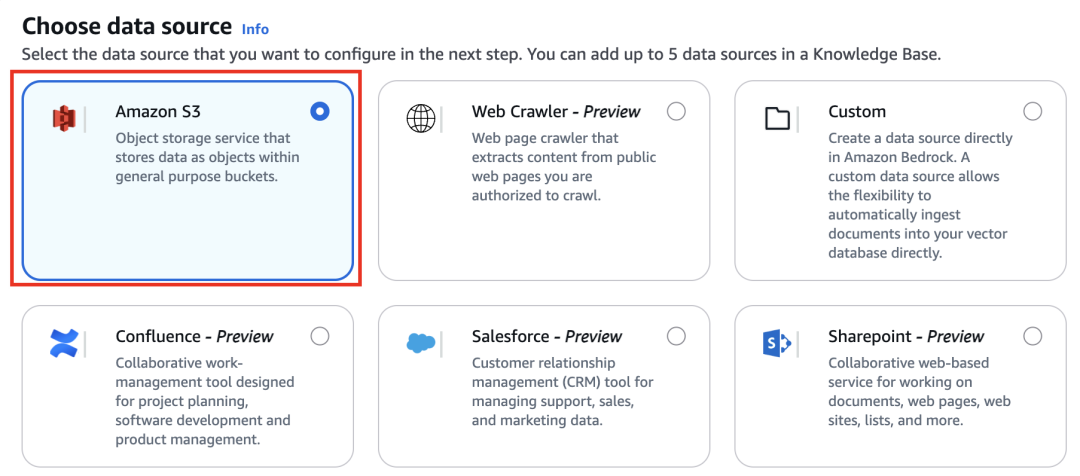
接下来选择配置数据源,选择配置好的Amazon S3存储桶。

选择转换策略,在此选择默认的转换策略,因为本例上传的都是文本,如果有对多模态的需求,可以详细查看Data Automation的功能。
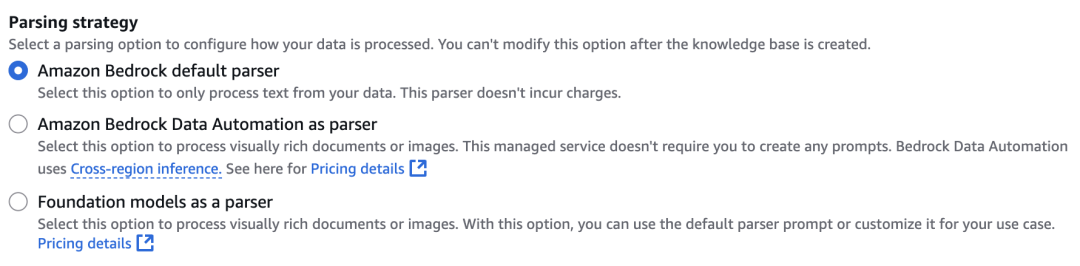
接下来,在Chunking strategy中,选择No chunking,旨在使用自定义的chunking策略。
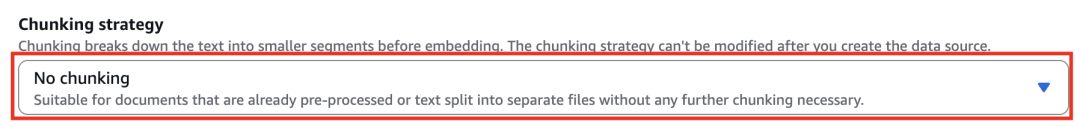
选择自定义Chunking的Amazon Lambda,这样可以自定义Chunking后的结果,旨在将每一个Tool作为一个Chunk进行存储,查询的时候能够查到一个完整的Tool。
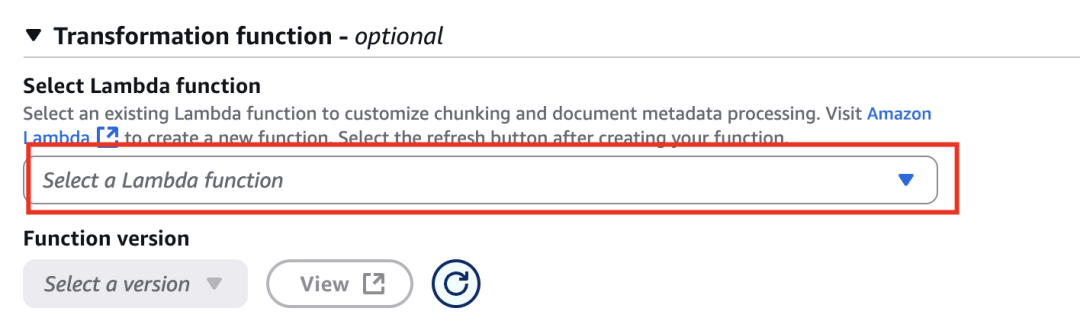
自定义Chunking,使用Amazon Lambda进行切分,并将切分块进行保存,在下面代码中,通过获取Tools列表,并将所有的Tools保存成一个jsonl文件,每个tool一行,这样会在Amazon Lambda中根据换行符进行切分,每个Tool作为一个Chunk。
import jsonfrom abc import abstractmethod, ABCfrom typing import Listimport boto3import logginglogger = logging.getLogger()logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)class Chunker(ABC):@abstractmethoddef chunk(self, text: str) -> List[str]:raise NotImplementedError()class SimpleChunker(Chunker):def chunk(self, text: str) -> List[str]:# Split text by newline and filter out empty linesreturn [line for line in text.split('\n') if line.strip()]def lambda_handler(event, context):logger.debug('input={}'.format(json.dumps(event, ensure_ascii=False)))s3 = boto3.client('s3')# Extract relevant information from the input eventinput_files = event.get('inputFiles')input_bucket = event.get('bucketName')ifnot all([input_files, input_bucket]):raise ValueError("Missing required input parameters")output_files = []chunker = SimpleChunker()for input_file in input_files:content_batches = input_file.get('contentBatches', [])file_metadata = input_file.get('fileMetadata', {})original_file_location = input_file.get('originalFileLocation', {})processed_batches = []for batch in content_batches:input_key = batch.get('key')ifnot input_key:raise ValueError("Missing uri in content batch")# Read file from S3file_content = read_s3_file(s3, input_bucket, input_key)# Process content (chunking)chunked_content = process_content(file_content, chunker)output_key = f"Output/{input_key}"# Write processed content back to S3write_to_s3(s3, input_bucket, output_key, chunked_content)# Add processed batch informationprocessed_batches.append({'key': output_key})# Prepare output file informationoutput_file = {'originalFileLocation': original_file_location,'fileMetadata': file_metadata,'contentBatches': processed_batches}output_files.append(output_file)result = {'outputFiles': output_files}logger.debug('output={}'.format(json.dumps(result, ensure_ascii=False)))return resultdef read_s3_file(s3_client, bucket, key):try:response = s3_client.get_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=key)content = response['Body'].read().decode('utf-8')# Try to parse as JSON first (for structured JSON input)try:return json.loads(content)except json.JSONDecodeError:# If not valid JSON, assume JSONL or plain text andreturn as-isreturn {'fileContents': [{'contentBody': content, 'contentType': 'text/plain', 'contentMetadata': {}}]}except Exception as e:logger.error(f"Error reading S3 file {bucket}/{key}: {str(e)}")raisedef write_to_s3(s3_client, bucket, key, content):try:s3_client.put_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=key, Body=json.dumps(content, ensure_ascii=False).encode('utf-8'))except Exception as e:logger.error(f"Error writing to S3 {bucket}/{key}: {str(e)}")raisedef process_content(file_content: dict, chunker: Chunker) -> dict:chunked_content = {'fileContents': []}for content in file_content.get('fileContents', []):content_body = content.get('contentBody', '')content_type = content.get('contentType', 'text/plain')content_metadata = content.get('contentMetadata', {})# Chunk the content body by newlineschunks = chunker.chunk(content_body)for chunk in chunks:chunked_content['fileContents'].append({'contentType': content_type,'contentMetadata': content_metadata,'contentBody': chunk})return chunked_content
左右滑动查看完整示意
创建完成后,便可以保存并调用。
语义检索与提示词增强
将用户查询通过嵌入模型转换为向量,在向量数据库中检索最相关的工具描述。检索结果用于构建增强提示词(Augmented Prompt),并发送至LLM进行推理。
推荐设置最大检索结果为5-10个,以优化提示词长度和推理效率。
-
注意事项:确保查询语言与嵌入模型兼容,避免语义偏差。
-
建议:启用混合检索以提高复杂查询的覆盖率,并记录检索日志以分析结果相关性。(在下面代码中使用的是语意检索,混合检索请参考文档)。
def query_semantic(self, query_text: str, max_results: int = 10) -> QueryResult:"""Perform semantic query on the Knowledge Base.Args:query_text: Semantic query text, e.g., "get weather in Suzhou"max_results: Maximum number of results to return(top-k)Returns:QueryResult containing matching tool definitions and metadataRaises:KnowledgeBaseError: If query fails"""try:logger.info(f"Performing semantic query: {query_text[:100]}...")response = self.bedrock_client.retrieve(knowledgeBaseId=self.knowledge_base_id,retrievalQuery={"text": query_text},retrievalConfiguration={"vectorSearchConfiguration": {"numberOfResults": max_results}})results = []for result in response["retrievalResults"]:try:content = json.loads(result["content"]["text"])results.append(content)logger.debug(f"Parsed query result: {content.get('toolSpec', {}).get('name', 'unknown')}")except json.JSONDecodeError as e:logger.warning(f"Failed to parse result content: {result['content']['text'][:100]}... "f"Error: {e}")continuelogger.info(f"Query returned {len(results)} valid results")return QueryResult(tools=results,total_results=len(results))except Exception as e:logger.error(f"Error querying Knowledge Base: {str(e)}")raise KnowledgeBaseError(f"Failed to query Knowledge Base: {str(e)}")
左右滑动查看完整示意
至此,可将Tools存储到RAG中,并通过SDK读取Tools的流程梳理清楚,详细代码请参阅GitHub代码库。
GitHub代码库:
https://github.com/memoverflow/rag-mcp
我们正处在Agentic AI爆发前夜。企业要从"成本优化"转向"创新驱动",通过完善的数据战略和AI云服务,把握全球化机遇。亚马逊将投入1000亿美元在AI算力、云基础设施等领域,通过领先的技术实力和帮助“中国企业出海“和”服务中国客户创新“的丰富经验,助力企业在AI时代突破。

为武汉地区的开发者提供学习、交流和合作的平台。社区聚集了众多技术爱好者和专业人士,涵盖了多个领域,包括人工智能、大数据、云计算、区块链等。社区定期举办技术分享、培训和活动,为开发者提供更多的学习和交流机会。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)