使用Python进行机器学习-方法
使用Python进行机器学习-方法 (Machine Learning with Python - Methods)Advertisements广告Previous Page上一页Next Page下一页There are various ML algorithms, techniques and methods that can be used...
使用Python进行机器学习-方法 (Machine Learning with Python - Methods)
There are various ML algorithms, techniques and methods that can be used to build models for solving real-life problems by using data. In this chapter, we are going to discuss such different kinds of methods.
可以使用多种ML算法,技术和方法来构建用于通过使用数据解决实际问题的模型。 在本章中,我们将讨论这种不同类型的方法。
不同类型的方法 (Different Types of Methods)
The following are various ML methods based on some broad categories −
以下是基于一些广泛类别的各种ML方法-
基于人的监督 (Based on human supervision)
In the learning process, some of the methods that are based on human supervision are as follows −
在学习过程中,一些基于人工监督的方法如下:
Supervised Learning
监督学习
Supervised learning algorithms or methods are the most commonly used ML algorithms. This method or learning algorithm take the data sample i.e. the training data and its associated output i.e. labels or responses with each data samples during the training process.
监督学习算法或方法是最常用的机器学习算法。 该方法或学习算法在训练过程中获取数据样本(即训练数据)及其相关输出(即每个数据样本的标签或响应)。
The main objective of supervised learning algorithms is to learn an association between input data samples and corresponding outputs after performing multiple training data instances.
监督学习算法的主要目标是在执行多个训练数据实例之后,学习输入数据样本与相应输出之间的关联。
For example, we have
例如,我们有
x: Input variables and
x :输入变量和
Y: Output variable
Y :输出变量
Now, apply an algorithm to learn the mapping function from the input to output as follows −
现在,应用一种算法来学习从输入到输出的映射函数,如下所示:
Y=f(x)
Y = f(x)
Now, the main objective would be to approximate the mapping function so well that even when we have new input data (x), we can easily predict the output variable (Y) for that new input data.
现在,主要目标将是很好地近似映射函数,从而即使我们有新的输入数据(x),我们也可以轻松地预测该新输入数据的输出变量(Y)。
It is called supervised because the whole process of learning can be thought as it is being supervised by a teacher or supervisor. Examples of supervised machine learning algorithms includes Decision tree, Random Forest, KNN, Logistic Regression etc.
之所以称其为有监督的,是因为可以在老师或主管的指导下思考整个学习过程。 监督机器学习算法的示例包括决策树,随机森林,KNN,逻辑回归等。
Based on the ML tasks, supervised learning algorithms can be divided into following two broad classes −
基于ML任务,监督学习算法可以分为以下两大类-
- Classification 分类
- Regression 回归
Classification
分类
The key objective of classification-based tasks is to predict categorial output labels or responses for the given input data. The output will be based on what the model has learned in training phase. As we know that the categorial output responses means unordered and discrete values, hence each output response will belong to a specific class or category. We will discuss Classification and associated algorithms in detail in the upcoming chapters also.
基于分类的任务的主要目标是预测给定输入数据的分类输出标签或响应。 输出将基于模型在训练阶段学到的知识。 众所周知,分类输出响应表示无序且离散的值,因此每个输出响应将属于特定的类或类别。 我们还将在接下来的章节中详细讨论分类和相关算法。
Regression
回归
The key objective of regression-based tasks is to predict output labels or responses which are continues numeric values, for the given input data. The output will be based on what the model has learned in its training phase. Basically, regression models use the input data features (independent variables) and their corresponding continuous numeric output values (dependent or outcome variables) to learn specific association between inputs and corresponding outputs. We will discuss regression and associated algorithms in detail in further chapters also.
基于回归的任务的主要目标是针对给定的输入数据,预测输出标签或响应(连续的数值)。 输出将基于模型在其训练阶段中学到的内容。 基本上,回归模型使用输入数据特征(独立变量)及其对应的连续数值输出值(因变量或结果变量)来学习输入与对应输出之间的特定关联。 我们还将在后面的章节中详细讨论回归和相关算法。
无监督学习 (Unsupervised Learning)
As the name suggests, it is opposite to supervised ML methods or algorithms which means in unsupervised machine learning algorithms we do not have any supervisor to provide any sort of guidance. Unsupervised learning algorithms are handy in the scenario in which we do not have the liberty, like in supervised learning algorithms, of having pre-labeled training data and we want to extract useful pattern from input data.
顾名思义,它与监督式机器学习方法或算法相反,这意味着在无监督的机器学习算法中,我们没有任何监督者可以提供任何类型的指导。 在没有监督学习算法那样的自由的情况下,无监督学习算法非常方便,因为在这种情况下我们没有预先标记训练数据,而我们想从输入数据中提取有用的模式。
For example, it can be understood as follows −
例如,可以理解如下:
Suppose we have −
假设我们有-
x: Input variables, then there would be no corresponding output variable and the algorithms need to discover the interesting pattern in data for learning.
x:输入变量 ,则将没有相应的输出变量,并且算法需要发现数据中有趣的模式以进行学习。
Examples of unsupervised machine learning algorithms includes K-means clustering, K-nearest neighbors etc.
无监督机器学习算法的示例包括K均值聚类, K最近邻等。
Based on the ML tasks, unsupervised learning algorithms can be divided into following broad classes −
基于ML任务,无监督学习算法可以分为以下几大类-
- Clustering 聚类
- Association 协会
- Dimensionality Reduction 降维
Clustering
聚类
Clustering methods are one of the most useful unsupervised ML methods. These algorithms used to find similarity as well as relationship patterns among data samples and then cluster those samples into groups having similarity based on features. The real-world example of clustering is to group the customers by their purchasing behavior.
聚类方法是最有用的无监督ML方法之一。 这些算法用于查找数据样本之间的相似性以及关系模式,然后将这些样本基于特征聚类为具有相似性的组。 集群的真实示例是根据客户的购买行为对其进行分组。
Association
协会
Another useful unsupervised ML method is Association which is used to analyze large dataset to find patterns which further represents the interesting relationships between various items. It is also termed as Association Rule Mining or Market basket analysis which is mainly used to analyze customer shopping patterns.
另一个有用的无监督ML方法是关联 ,它用于分析大型数据集以查找模式,该模式进一步表示各种项目之间的有趣关系。 它也被称为关联规则挖掘或市场购物篮分析 ,主要用于分析客户购物模式。
Dimensionality Reduction
降维
This unsupervised ML method is used to reduce the number of feature variables for each data sample by selecting set of principal or representative features. A question arises here is that why we need to reduce the dimensionality? The reason behind is the problem of feature space complexity which arises when we start analyzing and extracting millions of features from data samples. This problem generally refers to “curse of dimensionality”. PCA (Principal Component Analysis), K-nearest neighbors and discriminant analysis are some of the popular algorithms for this purpose.
此无监督的ML方法用于通过选择一组主要特征或代表性特征来减少每个数据样本的特征变量的数量。 这里出现的一个问题是,为什么我们需要减小尺寸? 背后的原因是特征空间复杂性的问题,当我们开始分析并从数据样本中提取数百万个特征时就会出现。 这个问题通常指的是“维数的诅咒”。 PCA(主成分分析),K最近邻和判别分析是用于此目的的一些流行算法。
Anomaly Detection
异常检测
This unsupervised ML method is used to find out the occurrences of rare events or observations that generally do not occur. By using the learned knowledge, anomaly detection methods would be able to differentiate between anomalous or a normal data point. Some of the unsupervised algorithms like clustering, KNN can detect anomalies based on the data and its features.
这种无监督的ML方法用于找出罕见事件或通常不会发生的观测值的发生。 通过使用所学的知识,异常检测方法将能够区分异常或正常数据点。 诸如聚类,KNN之类的一些无监督算法可以根据数据及其特征检测异常。
半监督学习 (Semi-supervised Learning)
Such kind of algorithms or methods are neither fully supervised nor fully unsupervised. They basically fall between the two i.e. supervised and unsupervised learning methods. These kinds of algorithms generally use small supervised learning component i.e. small amount of pre-labeled annotated data and large unsupervised learning component i.e. lots of unlabeled data for training. We can follow any of the following approaches for implementing semi-supervised learning methods −
这类算法或方法既没有完全监督也没有完全监督。 它们基本上介于两种方法之间,即有监督的学习方法和无监督的学习方法。 这些类型的算法通常使用小的监督学习组件(即,少量的预先标记的带注释的数据)和较大的非监督学习组件(即,大量的未标记的数据)进行训练。 我们可以采用以下任何一种方法来实施半监督学习方法-
The first and simple approach is to build the supervised model based on small amount of labeled and annotated data and then build the unsupervised model by applying the same to the large amounts of unlabeled data to get more labeled samples. Now, train the model on them and repeat the process.
第一种简单方法是基于少量标记和注释数据构建监督模型,然后通过将其应用于大量未标记数据来构建无监督模型以获得更多标记样本。 现在,在其上训练模型并重复该过程。
The second approach needs some extra efforts. In this approach, we can first use the unsupervised methods to cluster similar data samples, annotate these groups and then use a combination of this information to train the model.
第二种方法需要付出额外的努力。 在这种方法中,我们可以首先使用无监督方法对相似的数据样本进行聚类,为这些组添加注释,然后使用这些信息的组合来训练模型。
强化学习 (Reinforcement Learning)
These methods are different from previously studied methods and very rarely used also. In this kind of learning algorithms, there would be an agent that we want to train over a period of time so that it can interact with a specific environment. The agent will follow a set of strategies for interacting with the environment and then after observing the environment it will take actions regards the current state of the environment. The following are the main steps of reinforcement learning methods −
这些方法不同于以前研究的方法,也很少使用。 在这种学习算法中,我们需要在一段时间内训练一个代理,以便它可以与特定环境交互。 代理将遵循一系列与环境进行交互的策略,然后在观察环境之后,它将针对环境的当前状态采取措施。 以下是强化学习方法的主要步骤-
Step 1 − First, we need to prepare an agent with some initial set of strategies.
步骤1-首先,我们需要准备具有一些初始策略的代理。
Step 2 − Then observe the environment and its current state.
步骤2-然后观察环境及其当前状态。
Step 3 − Next, select the optimal policy regards the current state of the environment and perform important action.
步骤3-接下来,根据环境的当前状态选择最佳策略并执行重要操作。
Step 4 − Now, the agent can get corresponding reward or penalty as per accordance with the action taken by it in previous step.
步骤4-现在,代理可以根据其在上一步中采取的行动获得相应的奖励或惩罚。
Step 5 − Now, we can update the strategies if it is required so.
步骤5-现在,如果需要,我们可以更新策略。
Step 6 − At last, repeat steps 2-5 until the agent got to learn and adopt the optimal policies.
步骤6-最后,重复步骤2-5,直到代理学习并采用最佳策略为止。
适合机器学习的任务 (Tasks Suited for Machine Learning)
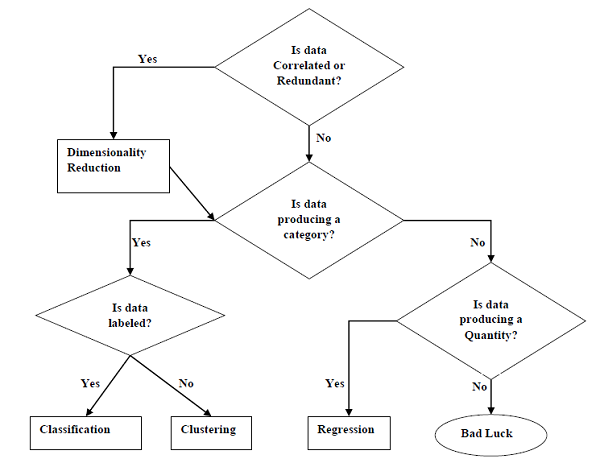
The following diagram shows what type of task is appropriate for various ML problems −
下图显示了哪种类型的任务适合于各种ML问题-
基于学习能力 (Based on learning ability)
In the learning process, the following are some methods that are based on learning ability −
在学习过程中,以下是一些基于学习能力的方法-
Batch Learning
批量学习
In many cases, we have end-to-end Machine Learning systems in which we need to train the model in one go by using whole available training data. Such kind of learning method or algorithm is called Batch or Offline learning. It is called Batch or Offline learning because it is a one-time procedure and the model will be trained with data in one single batch. The following are the main steps of Batch learning methods −
在许多情况下,我们拥有端到端机器学习系统,其中我们需要使用全部可用的训练数据来一次性训练模型。 这种学习方法或算法称为批量学习或离线学习 。 之所以称为批处理或脱机学习,是因为它是一次性过程,并且模型将在一个批处理中使用数据进行训练。 以下是批处理学习方法的主要步骤-
Step 1 − First, we need to collect all the training data for start training the model.
步骤1-首先,我们需要收集所有训练数据以开始训练模型。
Step 2 − Now, start the training of model by providing whole training data in one go.
步骤2-现在,通过一次性提供整个训练数据来开始模型训练。
Step 3 − Next, stop learning/training process once you got satisfactory results/performance.
步骤3-接下来,一旦获得令人满意的结果/性能,就停止学习/培训过程。
Step 4 − Finally, deploy this trained model into production. Here, it will predict the output for new data sample.
步骤4-最后,将此经过训练的模型部署到生产中。 在这里,它将预测新数据样本的输出。
在线学习 (Online Learning)
It is completely opposite to the batch or offline learning methods. In these learning methods, the training data is supplied in multiple incremental batches, called mini-batches, to the algorithm. Followings are the main steps of Online learning methods −
它与批处理或脱机学习方法完全相反。 在这些学习方法中,训练数据以称为小批量的多个增量批次提供给算法。 以下是在线学习方法的主要步骤-
Step 1 − First, we need to collect all the training data for starting training of the model.
步骤1-首先,我们需要收集所有训练数据以开始模型的训练。
Step 2 − Now, start the training of model by providing a mini-batch of training data to the algorithm.
步骤2-现在,通过向算法提供训练数据的小批量开始模型的训练。
Step 3 − Next, we need to provide the mini-batches of training data in multiple increments to the algorithm.
步骤3-接下来,我们需要为算法提供多个增量的小批量训练数据。
Step 4 − As it will not stop like batch learning hence after providing whole training data in mini-batches, provide new data samples also to it.
步骤4-由于它不会像批量学习那样停止,因此在以小批量提供完整的训练数据之后,也要为其提供新的数据样本。
Step 5 − Finally, it will keep learning over a period of time based on the new data samples.
步骤5-最后,它将在一段时间内根据新数据样本继续学习。
基于归纳法 (Based on Generalization Approach)
In the learning process, followings are some methods that are based on generalization approaches −
在学习过程中,以下是基于泛化方法的一些方法-
基于实例的学习 (Instance based Learning)
Instance based learning method is one of the useful methods that build the ML models by doing generalization based on the input data. It is opposite to the previously studied learning methods in the way that this kind of learning involves ML systems as well as methods that uses the raw data points themselves to draw the outcomes for newer data samples without building an explicit model on training data.
基于实例的学习方法是通过基于输入数据进行泛化来构建ML模型的有用方法之一。 与以前研究的学习方法相反,这种学习涉及ML系统以及使用原始数据点本身来绘制更新数据样本的结果而无需建立训练数据显式模型的方法。
In simple words, instance-based learning basically starts working by looking at the input data points and then using a similarity metric, it will generalize and predict the new data points.
简而言之,基于实例的学习基本上是通过查看输入数据点然后使用相似性度量开始的,它将概括并预测新数据点。
基于模型的学习 (Model based Learning)
In Model based learning methods, an iterative process takes place on the ML models that are built based on various model parameters, called hyperparameters and in which input data is used to extract the features. In this learning, hyperparameters are optimized based on various model validation techniques. That is why we can say that Model based learning methods uses more traditional ML approach towards generalization.
在基于模型的学习方法中,对基于各种模型参数(称为超参数)构建的ML模型进行迭代处理,并使用输入数据提取特征。 在此学习中,基于各种模型验证技术对超参数进行了优化。 这就是为什么我们可以说基于模型的学习方法使用更传统的ML方法进行泛化的原因。
翻译自: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/machine_learning_with_python/machine_learning_with_python_methods.htm
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)