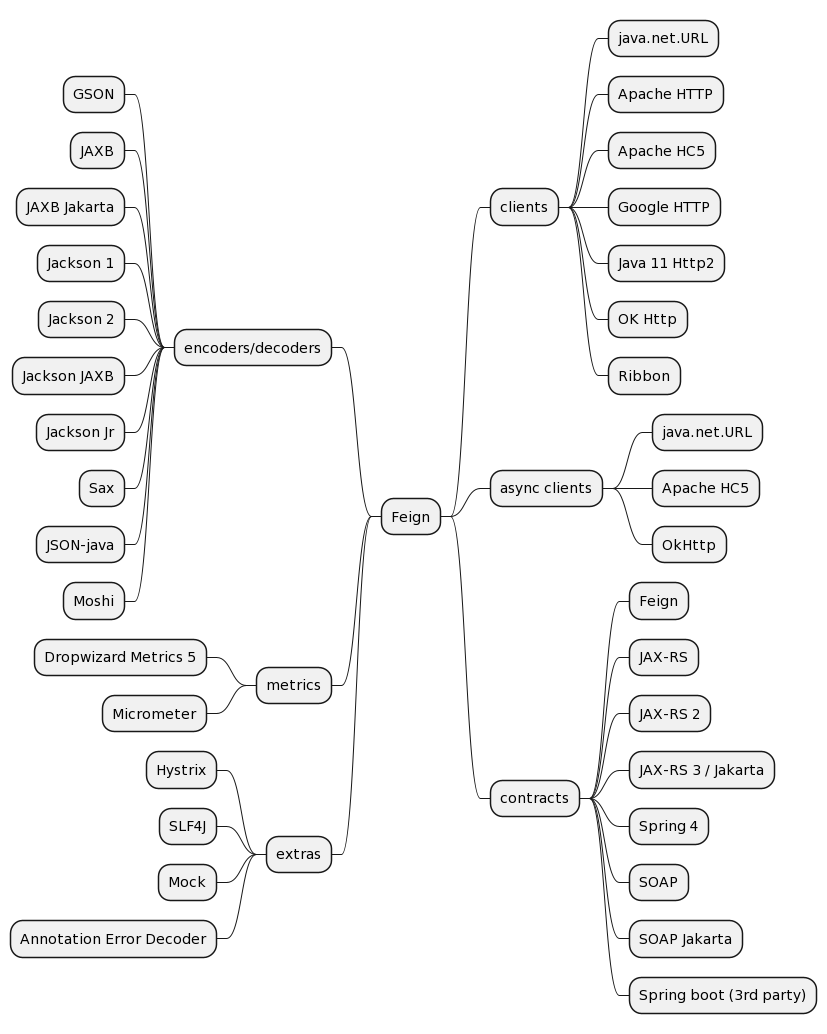
Spring Cloud OpenFeign官方文档学习
Feign是一个声明式的web服务客户端,让编写web服务客户端变得非常容易,只需创建一个接口并在接口上添加注解即可。Feign也支持可拔插式的编码器和解码器。Spring Cloud对Feign进行了封装,使其支持了Spring MVC标准注解和HttpMessageConverters。Feign可以与Eureka和Ribbon组合使用以支持负载均衡(也可以配合Spring Cloud Cir
文章目录
- 推荐
- 一、OpenFeign简介
- 二、Springboot集成OpenFeign
- 三、覆盖默认配置
- 四、手动创建feign客户端
- 五、Feign的SpringCloud断路器
- 六、Feign的继承重用
- 七、Feign请求响应的压缩
- 八、Feign Capability 的支持
- 九、Feign Metrics
- 十、开启Feign的缓存
- 十、@SpringQueryMap注解支持
- 十一、HATEOAS 的支持
- 十二、Spring @MatrixVariable 的支持
- 十三、FeignCollectionFormat的支持
- 十四、响应式的支持
- 十五、Spring Data 的支持
- 十六、Spring@RefreshScope的支持
- 十七、==支持向 Feign 客户端提供URL的方法==
- 十八、FeignClient的参数传递给服务提供方的方式
- 十九、feign实践
推荐
SpringCloud-OpenFeign官方文档使用大全详解
SpringCloud OpenFeign 全功能配置详解(一文吃透OpenFeign)
下面文档基本就是官方文档的翻译,源自:spring cloud openfeign官方文档介绍,做了一丢丢的补充
一、OpenFeign简介
github:https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign
官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-openfeign/docs/current/reference/html/#spring-cloud-feign
Feign 是一个声明式的 Web Service 客户端。它使编写 Web Service 客户端更容易。
要使用 Feign,需要创建一个接口并对其进行注解。
它有可插拔的注解支持,包括 Feign 注解和 JAX-RS 注解。Feign 还支持可插拔的编码器和解码器。
Spring Cloud 增加了对 Spring MVC 注解的支持,并支持使用 Spring Web 中默认使用的 HttpMessageConverters。
Spring Cloud 集成了 Eureka、Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker以及Spring Cloud LoadBalancer,以便在使用Feign时提供一个负载均衡的http客户端。
OpenFeign利用Ribbon维护了服务列表信息,并且通过轮询实现了客户端的负载均衡。而与Ribbon不同的是,通过feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法,优雅而简单的实现了服务调用。
二、Springboot集成OpenFeign
1、引入starter
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
在引入具体的版本之前,可以看下spring-cloud与springboot对应版本的兼容性
| Release Train | Spring Boot Generation |
|---|---|
| 2023.0.x aka Leyton | 3.2.x |
| 2022.0.x aka Kilburn | 3.0.x, 3.1.x (Starting with 2022.0.3) |
| 2021.0.x aka Jubilee | 2.6.x, 2.7.x (Starting with 2021.0.3) |
| 2020.0.x aka Ilford | 2.4.x, 2.5.x (Starting with 2020.0.3) |
| Hoxton | 2.2.x, 2.3.x (Starting with SR5) |
| Greenwich | 2.1.x |
| Finchley | 2.0.x |
| Edgware | 1.5.x |
| Dalston | 1.5.x |
2、在启动类或者配置类上加@EnableFeignClients注解:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
3、声明Feign接口
@FeignClient("stores")
public interface StoreClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/stores")
List<Store> getStores();
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/stores")
Page<Store> getStores(Pageable pageable);
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST,
value = "/stores/{storeId}",
consumes = "application/json")
Store update(@PathVariable("storeId") Long storeId, Store store);
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE, value = "/stores/{storeId:\\d+}")
void delete(@PathVariable Long storeId);
}
@FeignClient注解用于创建1个feign客户端,它在容器中的bean的名称就是接口的全限定名(可以通过@FeignClient注解的qualifiers属性来修改);
@FeignClient的value值为客户端的名称(此时可以做到负载均衡),当然也可以写完整的主机名或者是ip端口值;
可以通过@FeignClient的url属性来指定要访问的url(可以是全路径名,也可以是主机名);
上面例子中的feign客户端会去寻找stores服务对应的物理地址,如果你使用了Eureka作为注册中心,那么它就会从Eureka中服务列表中解析stores服务。如果你不想使用Eureka,你可以通过SimpleDiscoveryClient 配置stores服务列表。
4、@EnableFeignClients属性解析
@EnableFeignClients用于开启Feign自动配置。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
// basePackages的别名,允许更简洁的注释声明,
// 例如:@ComponentScan("org.my.pkg"), 而不是@ComponentScan(basePackages="org.my.pkg")
String[] value() default {};
// 用户扫描Feign客户端的包,也就是@FeignClient标注的类,与value同义,并且互斥
String[] basePackages() default {};
// basePackages()的类型安全替代方案,用于指定要扫描带注释的组件的包。每个指定类所在的包都将被扫描。
// 考虑在每个包中创建一个特殊的无操作标记类或接口,除了被该属性引用之外没有其他用途。
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
// 为所有扫描到的客户端定制@Configuration,默认配置都在FeignClientsConfiguration中,可以自己定制
Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {};
// 可以指定@FeignClient标注的类,如果不为空,就会禁用类路径扫描
Class<?>[] clients() default {};
}
5、@FeignClient属性解析
@FeignClient用于标注Feign客户端。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface FeignClient {
// name和value属性用于标注客户端名称,也可以用${propertyKey}获取配置属性
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
// 该类的Bean名称
String contextId() default "";
// name和value属性用于标注客户端名称,也可以用${propertyKey}获取配置属性
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
// 弃用 被qualifiers()替代。
@Deprecated
String qualifier() default "";
// 模拟客户端的@Qualifiers值。
// 如果qualifier()和qualifiers()都存在,我们将使用后者,
// 除非qualifier()返回的数组为空或只包含空值或空白值,
// 在这种情况下,我们将首先退回到qualifier(),
// 如果也不存在,则使用default = contextId + "FeignClient"。
String[] qualifiers() default {};
// 绝对URL或可解析主机名
String url() default "";
// 是否应该解码404而不是抛出FeignExceptions
boolean decode404() default false;
// 用于模拟客户端的自定义配置类。可以包含组成客户端部分的覆盖@Bean定义,
// 默认配置都在FeignClientsConfiguration类中,可以指定FeignClientsConfiguration类中所有的配置
Class<?>[] configuration() default {};
// 指定失败回调类
Class<?> fallback() default void.class;
// 为指定的假客户端接口定义一个fallback工厂。
// fallback工厂必须生成fallback类的实例,这些实例实现了由FeignClient注释的接口。
Class<?> fallbackFactory() default void.class;
// 所有方法级映射使用的路径前缀
String path() default "";
// 是否将虚拟代理标记为主bean。默认为true。
boolean primary() default true;
}
可以通过以下任何一种方式向Feign客户端提供URL:
三、覆盖默认配置
1、覆盖默认配置
在spring cloud feign中的1个核心概念就是命名客户端,每1个feign客户端都由各种组件,按照协议要求从远程服务器发起请求完成功能,每个这样的feign客户端都使用@FeignClient注解来标识。
spring cloud 会为每1个feign客户端使用FeignClientsConfiguration这个配置类创建1个spring容器,FeignClientsConfiguration类中定义的组件有:feign.Decoder、feign.Encoder、feign.Contract,并且可以使用@FeignClient注解的contextId属性来覆盖spring容器的名字。
在FeignClientsConfiguration类中,OpenFeign为我们做了很多默认配置,其中所有的配置我们都可以自定义并且覆盖。
@FeignClient(name = "stores", configuration = FooConfiguration.class)
public interface StoreClient {
//..
}
在指定了我们自定义的FooConfiguration配置类之后,FooConfiguration配置类中自定义的配置会与FeignClientsConfiguration中的配置合并,并且FooConfiguration中的配置的组件的优先级会更高(覆盖FeignClientsConfiguration配置类中给我们的默认配置)。
注意!FooConfiguration类并不需要@Configuration注解,如果加上了@Configuration,就会全局生效,那么它里面定义的feign.Decoder, feign.Encoder, feign.Contract, etc.等组件就会成为默认配置(如果不想要FooConfiguration类中定义的组件成为默认组件,但是FooConfiguration上又加了@Configuration注解,那么就需要排除它,不让它被扫描到)。如果只在==@FeignClient中指定,那么就会只在该@FeignClient标注的类中生效==。@EnableFeignClients注解也可以指定配置类,它会在由该注解扫描到的客户端中应用指定配置类中定义的组件。
注意!@FeignClient4.0.2以版本前,使用url属性时,不需要name属性。现在name属性是必需的。
// name属性和url属性支持占位符表达式
@FeignClient(name = "${feign.name}", url = "${feign.url}")
public interface StoreClient {
//..
}
2、配置列表
Spring Cloud OpenFeign默认为Feign提供了以下bean配置:
- Decoder feign解码器: 是一个ResponseEntityDecoder (被包装成了SpringDecoder)
- Encoder feign编码器: 是一个SpringEncoder
- Logger feign的Logger: 是一个Slf4jLogger
- MicrometerObservationCapability micrometerObservationCapability: 如果feign-micrometer在类路径中并且ObservationRegistry可用
- CachingCapability cachingCapability:如果使用了@EnableCaching注解会使用。可以通过spring.cloud.openfeign.cache.enabled配置禁用。
- Contract feignContract: 是一个==SpringMvcContract ==
- Feign.Builder feignBuilder: 是一个FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder
- Client feignClient: 如果Spring Cloud LoadBalancer在类路径上,则使用FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient。如果它们都不在类路径中,则使用默认的feign客户端。
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign支持spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer,但是因为后者是个可选依赖,如果想使用这个依赖的话,那么就需要自己引入它。
可以通过设置feign.okhttp.enabled、feign.httpclient.enabled、feign.httpclient.hc5.enabled为true,来分别开启对应的OkHttpClient、ApacheHttpClient 、ApacheHC5 客户端,并且要把它们的依赖放在类路径上。或者在容器中定义1个org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient、或者okhttp3.OkHttpClient、或者org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.CloseableHttpClient的客户端bean来切换不同的客户端实现。
Spring Cloud OpenFeign没有为Feign默认提供以下bean,但仍然从应用程序上下文中查找这些类型的bean来创建feign客户端:
- Logger.Level
- Retryer
- ErrorDecoder
- Request.Options
- Collection<RequestInterceptor>
- SetterFactory
- QueryMapEncoder
- Capability (MicrometerObservationCapability and CachingCapability are provided by default)
其中Retryer 默认是Retryer.NEVER_RETRY,这将禁止重试。请注意,这种重试行为不同于openfeign默认行为,它将自动重试IOExceptions,将它们视为暂时的网络相关异常,以及从ErrorDecoder抛出的任何RetryableException。
我们可以自定义以上任意一个Bean,来覆盖默认的配置:
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public Contract feignContract() {
return new feign.Contract.Default();
}
@Bean
public BasicAuthRequestInterceptor basicAuthRequestInterceptor() {
return new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("user", "password");
}
}
这个配置会使用feign.Contract.Default替换默认的SpringMvcContract,并且会将定义的BasicAuthRequestInterceptor这个bean添加到RequestInterceptor集合当中去。
3、使用配置文件进行配置
@FeignClient的配置也可以在配置文件中进行配置,其中feignName就是@FeignClient的value值、name值和contextId值,同时,在使用负载均衡时,这里的feignName也会被用来查询服务实例。
在如下配置中指定的类,必须在容器中有定义1个或者有1个默认的构造器。
feign:
client:
config:
feignName:
connectTimeout: 5000
readTimeout: 5000
loggerLevel: full
errorDecoder: com.example.SimpleErrorDecoder
retryer: com.example.SimpleRetryer
defaultQueryParameters:
query: queryValue
defaultRequestHeaders:
header: headerValue
requestInterceptors:
- com.example.FooRequestInterceptor
- com.example.BarRequestInterceptor
decode404: false
encoder: com.example.SimpleEncoder
decoder: com.example.SimpleDecoder
contract: com.example.SimpleContract
capabilities:
- com.example.FooCapability
- com.example.BarCapability
queryMapEncoder: com.example.SimpleQueryMapEncoder
metrics.enabled: false
也可以通过@EnableFeignClient注解的defaultConfiguration属性根据上面类似的方式来指定1个配置类,区别在于这种方式将会应用到所有的feign客户端。
也可以通过设置名为default的feignName来作全局的配置,并且配置文件优先(相比于配置类的方式,但是如果你想更改这个优先级,可以把feign.client.default-to-properties设置为false):
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
client:
config:
default:
connectTimeout: 5000
readTimeout: 5000
loggerLevel: basic
4、创建多个相同名称客户端
如果我们想要创建多个具有相同name或url的feign客户端,以便它们指向相同的服务器,但是每个客户端都具有不同的自定义配置,那么我们必须使用@FeignClient的contextId属性,以避免这些配置beans的名称冲突。
@FeignClient(contextId = "fooClient", name = "stores", configuration = FooConfiguration.class)
public interface FooClient {
//..
}
@FeignClient(contextId = "barClient", name = "stores", configuration = BarConfiguration.class)
public interface BarClient {
//..
}
5、配置FeignClient不从父上下文继承beans
可以通过配置1个FeignClientConfigurer的bean,并且重写这个bean的inheritParentConfiguration(),并且返回false,来配置feign客户端不从父容器中拿bean组件
@Configuration
public class CustomConfiguration {
@Bean
public FeignClientConfigurer feignClientConfigurer() {
return new FeignClientConfigurer() {
@Override
public boolean inheritParentConfiguration() {
return false;
}
};
}
}
提示:默认情况下,feign客户端不会对/编码,可以通过设置feign.client.decodeSlash为false来更改这个行为。
6、SpringEncoder 的配置
在我们提供的SpringEncoder中,我们为二进制内容类型设置空字符集,为所有其他内容类型设置UTF-8。
您可以通过将spring.cloud.openfeign.encoder.charset-from-content-type的值设置为true来修改此行为,以从Content-Type头字符集派生字符集。
7、Feign拦截器的配置及使用
拦截器是OpenFeign可用的一种强大的工具,它可以被用来在请求和响应前后进行一些额外的处理。要使用OpenFeign拦截器,可以通过以下步骤进行配置:
public class MyInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) {
// 在这里添加额外的处理逻辑,添加请求头
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (requestAttributes instanceof ServletRequestAttributes) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttributes;
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
String value = request.getHeader(headerName);
template.header(headerName, headerValue);
}
}
}
将拦截器注册到OpenFeign:
@Configuration
public class MyFeignConfiguration {
@Bean
public MyInterceptor myInterceptor() {
return new MyInterceptor();
}
// 非必须
@Bean
public Feign.Builder feignBuilder() {
return Feign.builder().requestInterceptor(myInterceptor());
}
}
8、OpenFeign超时时间设置
我们可以配置默认的超时时间,也可以为指定的feign客户端配置超时时间。
Open Feign提供了2个超时参数供设置:connectTimeout(防止由于服务器处理时间过长而阻塞调用者)、readTimeout(从连接建立开始到响应花费时间)
(1)使用配置文件配置
在应用程序的配置文件(application.yml或application.properties)中,可以使用以下属性设置超时时间:
# YAML
feign:
client:
config:
default:
connectTimeout: 5000 # 连接超时时间
readTimeout: 10000 # 读取超时时间
# Properties
feign.client.config.default.connectTimeout=5000 # 连接超时时间
feign.client.config.default.readTimeout=10000 # 读取超时时间
上述代码中,我们使用feign.client.config.default属性来配置全局默认的超时时间。connectTimeout属性设置连接超时时间,readTimeout属性设置读取超时时间。单位是毫秒。
(2)通过Java代码设置超时时间
如果你更喜欢使用Java代码来配置openfeign,可以通过以下方式设置超时时间:
import feign.Request;
// 创建一个Request.Options对象来设置超时时间
Request.Options options = new Request.Options(connectTimeoutMillis, readTimeoutMillis);
// 在创建Feign客户端时指定Options对象
MyApi myApi = Feign.builder().options(options).target(MyApi.class, "https://example.com");
在上述代码中,我们创建了一个Request.Options对象,该对象包含连接超时时间和读取超时时间。然后将Options对象传递给Feign客户端。
(3)使用@FeignClient设置超时时间
使用@FeignClient注解的configuration属性来指定配置类。
首先,创建一个配置类,继承自feign.Request.Options类,并重写connectTimeoutMillis和readTimeoutMillis方法,以设置超时时间。
import feign.Request;
public class MyApiConfiguration extends Request.Options {
public MyApiConfiguration(int connectTimeoutMillis, int readTimeoutMillis) {
super(connectTimeoutMillis, readTimeoutMillis);
}
@Override
public Integer connectTimeoutMillis() {
return 5000; // 设置连接超时时间为5秒
}
@Override
public Integer readTimeoutMillis() {
return 10000; // 设置读取超时时间为10秒
}
}
然后,在使用@FeignClient注解进行声明时,使用configuration属性指定该配置类。
@FeignClient(name = "my-service", configuration = MyApiConfiguration.class)
public interface MyApi {
// 接口定义
}
这样,只有针对MyApi接口的请求会使用这个配置类中的超时时间,级别更加细致。当然,你也可以在上述配置类中加入其它一些针对MyApi接口的配置,比如重试次数等等。
(4)使用拦截器设置超时时间
要为单独请求设置超时时间,可以通过实现RequestInterceptor接口,并在其中为请求添加超时时间信息。具体方法如下:
import feign.RequestInterceptor;
import feign.RequestTemplate;
public class TimeoutRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
private final int connectTimeoutMillis;
private final int readTimeoutMillis;
public TimeoutRequestInterceptor(int connectTimeoutMillis, int readTimeoutMillis) {
this.connectTimeoutMillis = connectTimeoutMillis;
this.readTimeoutMillis = readTimeoutMillis;
}
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
template.options(new Request.Options(connectTimeoutMillis, readTimeoutMillis));
}
}
在上述代码中,我们创建了一个TimeoutRequestInterceptor类,实现了RequestInterceptor接口,并重写了其中的apply方法。在该方法中,将请求的超时时间信息添加到请求模板中。
然后,在实际使用Feign客户端时,创建该拦截器对象并加入到Feign客户端的拦截器链中。
例如,我们想要对一个名为MyApi的Feign客户端接口的某个请求设置超时时间,可以这样:
MyApi myApi = Feign.builder()
.requestInterceptor(new TimeoutRequestInterceptor(3000, 5000)) // 为该客户端指定一个拦截器
.target(MyApi.class, "https://example.com");
在上述代码中,我们创建了一个TimeoutRequestInterceptor对象,并使用requestInterceptor方法将其加入到Feign客户端的拦截器链中。这样,在名为MyApi的Feign客户端中发出的所有请求都会使用该超时时间。
如果只想为某些请求设置超时时间,而不是所有请求,可以在该拦截器中添加一些判断逻辑,根据请求的条件来判断是否要添加超时时间信息。
(5)使用@Headers设置超时时间
通过在接口方法上加上@Headers注解,将超时时间信息直接加在请求头中,从而实现为单独请求设置超时时间。
例如,我们想要针对MyApi接口的someMethod方法单独设置超时时间,可以这样:
@Headers({"connect-timeout:5000", "read-timeout:10000"})
@GET("/someMethod")
String someMethod();
在上述代码中,我们在@Headers注解中添加了connect-timeout和read-timeout两个请求头信息,用于设置连接超时时间和读取超时时间。这样,在调用someMethod方法时,会使用这些请求头信息中指定的超时时间设置。
需要注意的是,这种方法需要在每个接口方法上都进行设置,因此比较麻烦。但它的优点是灵活性比较高,可以为不同的接口方法设置不同的超时时间。同时,也可以在其他注解中添加相应的超时信息,如@PostMapping、@PutMapping等。
(6)为单独接口设置超时时间
在feign接口里加入Request.Options这个参数就可以单独为接口单独设置超时时间了
@PostMapping("test/")
ResponseVO<?> test(Request.Options options, @RequestBody TestRequestEntity entity);
调用的时候new 一下Options对象
ResponseVO<?> resp = client.test(
new Request.Options(70, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 70, TimeUnit.SECONDS, true),
entity);
9、OpenFeign设置重试次数
(1)一般写法
定义一个继承自 Retryer 接口的类:
public class CustomRetryer implements Retryer {
private final int maxAttempts;
private final long backoff;
int attempt;
public CustomRetryer() {
this(5, 1000);
}
public CustomRetryer(int maxAttempts, long backoff) {
this.maxAttempts = maxAttempts;
this.backoff = backoff;
this.attempt = 1;
}
@Override
public void continueOrPropagate(RetryableException e) {
if (attempt++ >= maxAttempts) {
throw e;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(backoff);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw e;
}
}
@Override
public Retryer clone() {
return new CustomRetryer();
}
}
在 FeignClient 中使用上一步定义的重试器:
@FeignClient(name = "demo", url = "${demo.base-url}", configuration = CustomRetryer.class)
public interface DemoFeignClient {
//...
}
在这个例子中,使用的是自定义的重试器 CustomRetryer,它重试 5 次,在每次重试之间休眠 1000 毫秒。如果重试次数超限,则抛出 RetryableException 异常。
(2)简单写法
除了使用自定义的 Retryer 之外,OpenFeign 还提供了另外一种设置重试次数的方式,那就是通过 Feign 的配置项进行设置。具体操作如下:
在 FeignClient 中引入 Feign 的默认配置:
@FeignClient(name = "demo", url = "${demo.base-url}", configuration = FeignConfiguration.class)
public interface DemoFeignClient {
//...
}
自定义 FeignConfiguration 类:
@Configuration
public class FeignConfiguration {
@Bean
public Retryer retryer() {
return new Retryer.Default(500, 5000, 3);
}
}
在这里,我们使用 Retryer.Default 类生成一个默认的重试器,它会在当前请求失败后重试 3 次,并会在第一次重试前等待 500 毫秒,在第二次重试前等待 1000 毫秒,在第三次重试前等待 2000 毫秒,以此类推。
通过这两个步骤,我们就可以为每个 FeignClient 设置默认的重试次数了。
(3)为每个请求设置重试次数
如果我们需要为特定的请求设置不同的重试策略,则可以在对应的方法上加上 @Retryable 注解,并指定对应的 Retryer 类型,如下所示:
@FeignClient(name = "demo", url = "${demo.base-url}", configuration = FeignConfiguration.class)
public interface DemoFeignClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/get")
@Retryable(maxAttempts = 2, value = {SomeRetryer.class })
String getDemo();
}
在这个例子中,我们使用了自定义的重试器 SomeRetryer,并指定了最大重试次数为 2。注意,为了使用 @Retryable 注解,我们需要引入 Spring Retry 库的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
使用上述方式,我们可以为每个请求设置不同的重试策略,从而更加灵活地处理重试问题。
10、Feign请求日志级别设置
每1个feign客户端都会创建1个logger,默认情况下,logger的名字就是接口的全类名,feign日志只会对debug级别才打印出来。
Feign提供了日志打印功能,我们可以通过配置来调整日志级别,从而了解Feign中Http请求的细节。默认显示的是DEBUG级别日志。
// 设置指定客户端的日志
logging.level.com.zzhua.user.UserClient: DEBUG
就是对Feign接口的调用情况进行监控和输出。
总共有以下日志级别:
-
NONE:默认的,不显示任何日志。
-
BASIC:仅记录请求方法、URL、响应状态码、执行时间。
-
HEADERS:除了BASIC中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应头。
-
FULL:除了HEADERS中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的正文及元数据。
// 代码设置日志级别(修改默认的日志级别)
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
四、手动创建feign客户端
可以使用Feign Builder API创建客户端来进行定制。
// 手动创建两个Feign客户端并配置其拦截器和name属性,FeignClientsConfiguration.class仍然是它们的默认配置
// FeignClientsConfiguration是Spring Cloud OpenFeign提供的默认配置类
@Import(FeignClientsConfiguration.class)
class FooController {
private FooClient fooClient;
private FooClient adminClient;
@Autowired
public FooController(Client client,
Encoder encoder,
Decoder decoder,
Contract contract,
MicrometerObservationCapability micrometerObservationCapability) {
this.fooClient = Feign.builder().client(client)
.encoder(encoder)
.decoder(decoder)
// Contract 定义了在接口上能够使用的注解, 这里自动注入的Contract支持springmvc注解,
// 而不是feign的原始注解
.contract(contract)
.addCapability(micrometerObservationCapability)
.requestInterceptor(new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("user", "user"))
// PROD-SVC是请求的服务名
.target(FooClient.class, "https://PROD-SVC");
this.adminClient = Feign.builder().client(client)
.encoder(encoder)
.decoder(decoder)
.contract(contract)
.addCapability(micrometerObservationCapability)
.requestInterceptor(new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("admin", "admin"))
.target(FooClient.class, "https://PROD-SVC");
}
}
还可以使用Builder 来配置FeignClient不从父上下文继承beans。可以通过在生成器上重写调用“inheritParentContext(false)”来实现这一点。
五、Feign的SpringCloud断路器
如果Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker在classpath,并且spring.cloud.openfeign.circuitbreaker.enabled=true,Feign将使用断路器包装所有方法。
要在每个客户端的基础上禁用Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker支持,请创建一个普通的Feign.Builder。具有“prototype”范围的构建器,例如:
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public Feign.Builder feignBuilder() {
return Feign.builder();
}
}
断路器的名字遵循这样的格式:<feign客户端类名>#<被调用的方法名>(<参数类型>)。比如当调用1个FooClient接口的bar方法,并且这个方法没有参数时,断路器的名字就是:FooClient#bar()
注意:从2020.0.2开始,circuit breaker 名称模式已经从 <feignClientName>_<calledMethod> 改变。使用2020.0.4中引入的 CircuitBreakerNameResolver,circuit breaker 名称可以保留旧模式。
通过提供CircuitBreakerNameResolver的bean,可以更改断路器名称模式,如下所示。
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public CircuitBreakerNameResolver circuitBreakerNameResolver() {
return (String feignClientName, Target<?> target, Method method) ->
feignClientName + "_" + method.getName();
}
}
要启用Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker组,请将spring.cloud.openfeign.circuitbreaker.group.enabled属性设置为true(默认为false)。
1、使用配置属性配置断路器
假如说有一个Feign客户端:
@FeignClient(url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface DemoClient {
@GetMapping("demo")
String getDemo();
}
可以通过执行以下操作,使用配置属性对其进行配置:
spring:
cloud:
openfeign
circuitbreaker:
enabled: true
alphanumeric-ids:
enabled: true
resilience4j:
circuitbreaker:
instances:
DemoClientgetDemo:
minimumNumberOfCalls: 69
timelimiter:
instances:
DemoClientgetDemo:
timeoutDuration: 10s
如果你想切换回 Spring Cloud 2022.0.0 之前使用的 circuit breaker name,你可以将 spring.cloud.openfeign.circuitbreaker.alphanumeric-ids.enabled 设置为 false。
2、fallback
fallback降级处理
Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker支持fallback的概念:当电路断开或出现错误时,执行的默认代码路径。要为给定的@FeignClient启用降级,请将fallback属性设置为实现降级的类名。并且还需要将其定义为Spring bean。
@FeignClient(name = "test", url = "http://localhost:${server.port}/", fallback = Fallback.class)
protected interface TestClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
Hello getHello();
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hellonotfound")
String getException();
}
@Component
static class Fallback implements TestClient {
@Override
public Hello getHello() {
throw new NoFallbackAvailableException("Boom!", new RuntimeException());
}
@Override
public String getException() {
return "Fixed response";
}
}
fallbackFactory降级处理
如果有需要知道触发fallback的原因,可以使用@FeignClient中的fallbackFactory属性。
@FeignClient(name = "testClientWithFactory",
url = "http://localhost:${server.port}/",
// 使用fallbackFactory属性指定TestFallbackFactory(它要实现FallbackFactory)
fallbackFactory = TestFallbackFactory.class)
protected interface TestClientWithFactory {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
Hello getHello();
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hellonotfound")
String getException();
}
@Component // 实现FallbackFactory接口, 在create(Throwable)方法种返回1个实现了feign接口的对象
static class TestFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<FallbackWithFactory> {
@Override
public FallbackWithFactory create(Throwable cause) {
return new FallbackWithFactory();
}
}
static class FallbackWithFactory implements TestClientWithFactory {
@Override
public Hello getHello() {
throw new NoFallbackAvailableException("Boom!", new RuntimeException());
}
@Override
public String getException() {
return "Fixed response";
}
}
3、Feign客户端的primary属性
(要知道有这回事)
当使用Feign和Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 降级功能时,在ApplicationContext中有多个相同类型的beans。这将导致@Autowired不起作用,因为没有确切的一个bean,或者一个被标记为@Primary注解的bean。
为了解决这个问题,Spring Cloud OpenFeign将所有的Feign实例都标记为了@Primary,因此Spring Framework将知道要注入哪个bean。在某些情况下,这可能并不理想。要关闭此行为,请将@FeignClient的primary属性设置为false(默认为true)。
@FeignClient(name = "hello", primary = false)
public interface HelloClient {
// methods here
}
六、Feign的继承重用
Feign通过单一继承接口支持样板API。这允许将常见操作分组到方便的基本接口中。
// 共用接口实例
public interface UserService {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value ="/users/{id}")
User getUser(@PathVariable("id") long id);
}
// 提供(方)服务
@RestController
public class UserResource implements UserService {
}
// 调用(方)服务
@FeignClient("users")
public interface UserClient extends UserService {
}
注意:@FeignClient接口不应在服务端和客户端之间共享,并且不再支持在类级别上同时使用@RequestMapping和@FeignClient注解。
七、Feign请求响应的压缩
可以考虑为您的feign请求启用请求或响应GZIP压缩。您可以通过启用以下属性之一来实现这一点:
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.enabled=true
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.response.enabled=true
Feign请求压缩为您提供了类似于您可能为web服务器的设置:
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.enabled=true
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.mime-types=text/xml,application/xml,application/json
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.min-request-size=2048
以上这些属性压缩的媒体类型和最小请求阈值长度都是可选的。
注意!由于OkHttpClient使用“透明”压缩,如果存在content-encoding或accept-encoding头,则该压缩将被禁用,因此当feign.okhttp.OkHttpClient存在于classpath中并且spring.cloud.openfeign.okhttp.enabled设置为true时,我们不启用压缩。
八、Feign Capability 的支持
Feign Capability 暴露了Feign的核心组件,因此这些组件可以被修改。例如,这些功能可以接受客户端,对其进行装饰,并将装饰后的实例反馈给 Feign。对 Micrometer 的支持就是一个很好的现实生活中的例子。参见 [micrometer-support]。
创建一个或多个 Capability Bean并将其置于 @FeignClient 配置中,可以让你注册它们并修改相关客户端的行为
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
Capability customCapability() {
return new CustomCapability();
}
}
九、Feign Metrics
如果以下所有条件为 true,就会创建并注册一个 MicrometerCapability Bean,这样你的 Feign 客户端就可以被 Micrometer 观察到:
- feign-micrometer 在 classpath 上。
- MeterRegistry bean 可用。
- feign micrometer 属性设置为 true (默认)
- spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=true (针对所有客户)
- spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.feignName.micrometer.enabled=true (针对单个客户端)
如果你的应用程序已经使用了 Micrometer,启用这个功能就像把 feign-micrometer 放到你的classpath上一样简单。
你也可以通过以下两种方式禁用该功能:
- 从你的 classpath 中排除 feign-micrometer。
- 将 feign micrometer 一个属性设置为 false
- spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=false
- spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.feignName.micrometer.enabled=false
注意:spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=false 禁用所有 Feign 客户端的 Micrometer 支持,而不考虑客户端级标志的值:spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.feignName.micrometer.enabled。如果你想启用或禁用每个客户端的 Micrometer 支持,不要设置 spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled 并使用 spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.feignName.micrometer.enabled。
你也可以通过注册你自己的bean来自定义 MicrometerObservationCapability:
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public MicrometerObservationCapability micrometerObservationCapability(ObservationRegistry
registry) {
return new MicrometerObservationCapability(registry);
}
}
仍然可以在 Feign 中使用 MicrometerCapability(仅支持指标),你需要禁用 Micrometer 支持(spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=false)并创建一个 MicrometerCapability Bean:
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public MicrometerCapability micrometerCapability(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
return new MicrometerCapability(meterRegistry);
}
}
十、开启Feign的缓存
如果使用了@EnableCaching注释,将创建并注册一个CachingCapability bean,这样您的Feign客户端能够识别其接口上的@Cache*注解:
public interface DemoClient {
@GetMapping("/demo/{filterParam}")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "demo-cache", key = "#keyParam")
String demoEndpoint(String keyParam, @PathVariable String filterParam);
}
还可以通过属性spring.cloud.openfeign.cache.enabled=false禁用该功能。
十、@SpringQueryMap注解支持
Spring Cloud OpenFeign提供了一个等价的@SpringQueryMap注释,用于将POJO或Map参数注释为查询参数Map。
例如,Params类定义了参数param1和param2:
// Params.java
public class Params {
private String param1;
private String param2;
// [Getters and setters omitted for brevity]
}
下面的feign客户端通过使用@SpringQueryMap注解来使用Params类:
@FeignClient("demo")
public interface DemoTemplate {
@GetMapping(path = "/demo")
String demoEndpoint(@SpringQueryMap Params params);
}
如果您需要对生成的查询参数映射进行更多的控制,您可以实现一个自定义的QueryMapEncoder bean。
十一、HATEOAS 的支持
Spring提供了一些API来创建遵循 HATEOAS 原则的REST表示, Spring Hateoas 和 Spring Data REST。
如果你的项目使用 org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-hateoas starter 或 org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-rest starter,Feign HATEOAS 支持被默认启用。
当HATEOAS支持被启用时,Feign 客户端被允许序列化和反序列化 HATEOAS 表示模型: EntityModel、 CollectionModel 和 PagedModel.。
@FeignClient("demo")
public interface DemoTemplate {
@GetMapping(path = "/stores")
CollectionModel<Store> getStores();
}
十二、Spring @MatrixVariable 的支持
Spring Cloud OpenFeign提供对Spring @MatrixVariable 注解的支持。
如果一个 map 被作为方法参数传递,@MatrixVariable 的路径片段是通过用 = 连接 map 中的键值对来创建的。
如果传递了一个不同的对象,那么在 @MatrixVariable 注解中提供的 name(如果定义了的话)或者注解的变量名称将使用 = 与提供的方法参数结合起来。
尽管在服务器端,Spring 并不要求用户将路径段占位符的名称与 matrix variable 的名称相同,因为这在客户端太模糊了,Spring Cloud OpenFeign要求你添加一个路径段占位符,其名称要与 @MatrixVariable 注解(如果定义了)中提供的 name 或注解的变量名称相符。例如:
@GetMapping("/objects/links/{matrixVars}")
Map<String, List<String>> getObjects(@MatrixVariable Map<String, List<String>> matrixVars);
注意,变量名和 path 段占位符都被称为 matrixVars。
@FeignClient("demo")
public interface DemoTemplate {
@GetMapping(path = "/stores")
CollectionModel<Store> getStores();
}
十三、FeignCollectionFormat的支持
我们通过提供 @CollectionFormat 注解来支持 feign.CollectionFormat。你可以通过传递所需的 feign.CollectionFormat 作为注解值,用它来注解一个 Feign 客户端方法(或整个类来影响所有方法)。
在下面的例子中,使用 CSV 格式而不是默认的 EXPLODED 来处理这个方法。
@FeignClient(name = "demo")
protected interface DemoFeignClient {
@CollectionFormat(feign.CollectionFormat.CSV)
@GetMapping(path = "/test")
ResponseEntity performRequest(String test);
}
十四、响应式的支持
由于 OpenFeign项目 目前不支持响应式客户端,如 Spring WebClient,Spring Cloud OpenFeign也不支持。一旦核心项目中可用,我们将在这里添加对它的支持。
初始化错误
根据你使用 Feign 客户端的方式,你可能会在启动你的应用程序时看到初始化错误。为了解决这个问题,你可以在自动连接客户端时使用一个 ObjectProvider。
@Autowired
ObjectProvider<TestFeignClient> testFeignClient;
十五、Spring Data 的支持
如果 Jackson Databind 和 Spring Data Commons 在classpath上,org.springframework.data.domain.Page 和 org.springframework.data.domain.Sort 的 converter 将被自动添加。
要禁用这种行为,请设置:
spring.cloud.openfeign.autoconfiguration.jackson.enabled=false
详见 org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignAutoConfiguration.FeignJacksonConfiguration。
十六、Spring@RefreshScope的支持
如果启用了Feign客户端刷新,每个Feign客户端的创建都有:
- feign.Request.Options 作为一个 refresh scope 的bean。这意味着诸如 connectTimeout 和 readTimeout 等属性可以针对任何Feign客户端实例进行刷新。
- 在 org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.RefreshableUrl 下包装的url。这意味着如果用 spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.{feignName}.url 属性定义 Feign 客户端的URL,可以针对任何 Feign 客户端实例进行刷新。
你可以通过 POST /actuator/refresh 刷新这些属性。
默认情况下,Feign 客户端的刷新行为是禁用的。使用以下属性来启用刷新行为:
spring.cloud.openfeign.client.refresh-enabled=true
注意:不要在@FeignClient 接口上使用 @RefreshScope 注解
十七、支持向 Feign 客户端提供URL的方法
你可以通过以下任何一种方式向Feign客户端提供一个URL:
| 场景 | 例子 | 细节 |
|---|---|---|
| URL是在 @FeignClient 注解中提供的。 | @FeignClient(name=“testClient”, url=“http://localhost:8081”) | URL是从注解的 url 属性中解析出来的,没有负载均衡。 |
| URL是在 @FeignClient 注解和配置属性中提供的。 | @FeignClient(name=“testClient”, url=“http://localhost:8081”) 和定义在 application.yml 中的属性 spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.testClient.url=http://localhost:8081 | URL是从注解的 url 属性中解析出来的,没有负载均衡。在配置属性中提供的URL仍未使用。 |
| URL没有在 @FeignClient 注解中提供,而是在配置属性中提供。 | @FeignClient(name=“testClient”) 和定义在 application.yml 中的属性 spring.cloud.openfeign.client.config.testClient.url=http://localhost:8081 | URL 从配置属性中解析,没有负载均衡。如果 spring.cloud.openfeign.client.refresh-enabled=true,那么配置属性中定义的 URL 可以被刷新,如 Spring RefreshScope 的支持 中所述。 |
| 在 @FeignClient 注解中和配置属性中都没有提供这个URL。 | @FeignClient(name=“testClient”) | URL是从注解的 name 属性中解析出来的,具有负载均衡性。 |
十八、FeignClient的参数传递给服务提供方的方式
1、path路径上携带参数
/**
* 服务提供方:path路径上携带参数
*/
@GetMapping("/test1/{myId}")
public String test1(@PathVariable String myId) {
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test1");
System.out.println(myId);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:path路径上携带参数
*/
@GetMapping("/test1/{myId}")
String test1(@PathVariable("myId") String myId);
2、单个简单数据类型
/**
* 服务提供方:单个简单数据类型
*/
@GetMapping("/test2")
public String test2(String test2Str) {
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test2");
System.out.println(test2Str);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:单个简单数据类型
*/
@GetMapping("/test2")
String test2(@RequestParam("test2Str") String test2Str);
3、多个简单数据类型
/**
* 服务提供方:多个简单数据类型
*/
@GetMapping("/test3")
public String test3(String test3Str1, String test3Str2) {
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test3");
System.out.println(test3Str1 + "||" + test3Str2);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:多个简单数据类型
*/
@GetMapping("/test3")
String test3(@RequestParam("test3Str1") String test3Str1,
@RequestParam("test3Str2") String test3Str2);
4、Path + 多个简单数据类型
/**
* 服务提供方:Path + 多个简单数据类型
*/
@GetMapping("/test4/{myId}")
public String test4(@PathVariable String myId, String test4Str1, String test4Str2) {
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test4");
System.out.println(myId + "||" + test4Str1 + "||" + test4Str2);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:Path + 多个简单数据类型
*/
@GetMapping("/test4/{myId}")
String test4(@PathVariable("myId") String myId,
@RequestParam("test4Str1") String test4Str1,
@RequestParam("test4Str2") String test4Str2);
5、JavaBean对象
/**
* 服务提供方:JavaBean对象
*/
@GetMapping("/test5/{myId}")
public String test5(@PathVariable String myId, Student student) {
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test5");
System.out.println(myId + "||" + student);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:JavaBean对象、Map
*/
@GetMapping("/test5/{myId}")
String test5(@PathVariable("myId") String myId, Student student);
6、多path路径上携带参数
/**
* 服务提供方:多path路径上携带参数
*/
@GetMapping("/test6/{myId}/test66/{myId2}")
public String test6(@PathVariable("myId") String myId, @PathVariable("myId2") String myId2) {
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test6");
System.out.println(myId + "||" + myId2);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:多path路径上携带参数
*/
@GetMapping("/test6/{myId}/test66/{myId2}")
String test6(@PathVariable("myId") String myId, @PathVariable("myId2") String myId2);
7、post获取请求体
/**
* 服务提供方:post获取请求体
*/
@PostMapping("/test7/{myId}")
public String test7(@PathVariable("myId") String myId, @RequestBody Student student){
System.out.println("LiveRoomController.test7");
System.out.println(myId + "||" + student);
return "success";
}
/**
* FeignClient:post获取请求体
*/
@PostMapping("/test7/{myId}")
String test7(@PathVariable("myId") String myId, @RequestBody Student student);
测试一下吧
System.out.println(commonSurface.test1("this is test1"));
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println(commonSurface.test2("this is test2"));
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println(commonSurface.test3("this is test3", "this is test3-2"));
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println(commonSurface.test4("this is myId", "this is test4", "this is test4-2"));
System.out.println("-------------");
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(1);
s.setName("张三");
System.out.println(commonSurface.test5("this is myId", s));
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println(commonSurface.test6("this is myId", "this is myId2"));
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println(commonSurface.test7("this is myId", s));
System.out.println("-------------");
十九、feign实践
demo-learn-feign
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zzhua</groupId>
<artifactId>demo-learn-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR8</spring-cloud.version>
<alibaba.version>2.2.5.RELEASE</alibaba.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- springCloud -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
application.yml
server:
port: 8095
spring:
application:
name: feign-service
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848
hystrix:
command:
default:
circuitBreaker:
# 触发熔断的最小请求次数,默认20 每10s
requestVolumeThreshold: 2
# 熔断多少秒后再次去尝试请求
sleepWindowInMilliseconds: 10000
# 触发熔断的失败请求最小占比,默认50%
errorThresholdPercentage: 10
feign:
hystrix:
# 开启服务降级
enabled: true
client:
config:
# (配置文件的优先级高于代码中的配置)
# 所有feign客户端的默认配置
#default:
# 全局设置连接超时时间
#connectTimeout: 2000
# 全局设置读取响应超时时间
#readTimeout: 3000
# 仅针对name为configN的feign客户端(优先级高于default配置)
configN:
# 设置日志级别, 但前提是feign客户端日志级别必须是debug才会打印出来
loggerLevel: BASIC
# 设置读取响应超时时间, 超过5s将会抛出异常SocketTimeoutException: Read timed out
readTimeout: 5000
retryN:
# 自定义错误解码器
errorDecoder: com.zzhua.feign03.CustomErrorDecoder
# 设置重试器为Retryer.Default(默认的重试器), 或 Retryer.NEVER_RETRY(不重试)
retryer: feign.Retryer.Default
# 开启重试条件
retryable: true
# 最多重试4次
#maxAttempts: 4
#backoff:
# 开启退避算法
#enabled: true
# 初始重试间隔时间为1秒
#delay: 1000
# 最大重试间隔时间为5秒
#maxDelay: 5000
# 重试间隔时间按2的指数增长
#multiplier: 2.0
logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="false">
<!--定义日志文件的存储地址 勿在 LogBack 的配置中使用相对路径-->
<property name="LOG_BASE_PATH" value="logs/" />
<property name="maxFileSize" value="5MB"/>
<property name="maxHistory" value="30"/>
<property name="commonPattern" value="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}-${PID}-[%thread] %-5level %logger{30} - %msg%n"/>
<!--控制台日志, 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度,%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>${commonPattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--文件日志, 按照每天生成日志文件 -->
<appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${LOG_BASE_PATH}/feignApp.log</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名-->
<FileNamePattern>${LOG_BASE_PATH}/%d/xxx.log.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%i.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数-->
<MaxHistory>${maxHistory}</MaxHistory>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>${maxFileSize}</maxFileSize>
</timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>${commonPattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 在这里单独配置某个feign客户端, 让Feign能够打印日志, 至于打印多少日志, 就要设置Logger.Level了;
这里的name不能使用通配符哦, 但是可以设置为: com.zzhua.feign02, 它会将这个包下的所有类都设置为指定的日志级别
-->
<logger name="com.zzhua.feign02.ConfigFeignClient" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</logger>
<logger name="com.zzhua.feign03.RetryFeignClient" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</logger>
<!-- 日志输出级别 -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
<appender-ref ref="FILE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
FeignApp
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class FeignApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FeignApp.class, args);
}
}
feign01
IndexController
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@Autowired
private StaticRemoteFeignClient remoteFeignClient;
@GetMapping("findPerson")
public Person findPerson() {
Person person = remoteFeignClient.findPerson("zzhua",26);
return person;
}
@GetMapping("getPerson")
public Person getPerson() {
Person person = remoteFeignClient.getPerson(new Person("zzhua", 26, new Address("CN", "HN")));
return person;
}
@GetMapping("getPerson1")
public Person getPerson1() {
Person person = remoteFeignClient.getPerson1("zzhua", 26, new Address("CN", "HN"));
return person;
}
@GetMapping("getPerson2")
public Person getPerson2() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "zzhua");
map.put("age", 26);
map.put("address", new Address("CN", "HN"));
Person person = remoteFeignClient.getPerson2(map);
return person;
}
@GetMapping("addPerson")
public Person addPerson() {
Person person = remoteFeignClient.addPerson(new Person("zzhua", 26, new Address("CN", "HN")), 2);
return person;
}
@GetMapping("addPerson2")
public Person addPerson2() {
Person person = remoteFeignClient.addPerson2(new Person("zzhua", 26, new Address("CN", "HN")),
new Address("CN2", "HN2"));
return person;
}
@GetMapping("checkPerson")
public Person checkPerson() {
return remoteFeignClient.checkPerson(new Person("zzhua", 26, new Address("CN", "HN")),
new Integer[]{1,2,3});
}
@GetMapping("checkPerson2")
public Person checkPerson2() {
return remoteFeignClient.checkPerson2(new Person("zzhua", 26, new Address("CN", "HN")),
Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
}
}
StaticRemoteFeignClient
/* 重点是测试参数写法 */
@FeignClient(name = "remote",url = "http://localhost:8084",path = "/orderService/remote")
public interface StaticRemoteFeignClient {
// 接口提供方: http://localhost:8084/orderService/remote/findPerson?pName=zzhua&pAge=26 能通
@GetMapping("findPerson") // 多于1个参数,则必须写@RequestParam注解(并且必须写value)
Person findPerson(@RequestParam(name = "pName") String name,
@RequestParam(name = "pAge") Integer age);
@GetMapping("getPerson") // @RequestParam后面是自定义参数类型将不会封装到接口的方法参数中
Person getPerson(@RequestParam("person") Person person);
@GetMapping("getPerson1") // feign将会把url拼接成url?name=xx&age=yy&address=zz(address字符串形式)
// 这个address将会导致接口那边在获取address时,不能正常封装成Address对象而导致报错
Person getPerson1(@RequestParam(name = "name") String name,
@RequestParam(name = "age") Integer age
,@RequestParam(name = "address") Address address);
@PostMapping("getPerson2") // 可以使用Map封装(远程接口使用@RequestBody Map来接收(address属性能正常接收到))
Person getPerson2(Map<String,Object> map);
@PostMapping("addPerson") // 不能使用超过1个@RequestBody
Person addPerson(@RequestBody Person person, @RequestParam("pAge") Integer age);
@PostMapping("addPerson2") // @RequestParam后面是自定义参数Address将不会封装到接口的方法参数中
Person addPerson2(@RequestBody Person person,@RequestParam("addr") Address addr);
@PostMapping("checkPerson") // 多于1个参数,则必须写@RequestParam注解(并且必须写value)
// feign拼接url?ids=1%2C2%2C3 (%2C,即逗号)
Person checkPerson(@RequestBody Person person, @RequestParam("ids") Integer[] ids);
@PostMapping("checkPerson2") // 多于1个参数,则必须写@RequestParam注解(并且必须写value)
// feign拼接url?ids=1&ids=2&ids=3
Person checkPerson2(@RequestBody Person person, @RequestParam("ids") List<Integer> ids);
}
Person
@Data
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Address address;
}
Address
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Address {
private String country;
private String province;
}
feign02
ConfigController
@RestController
public class ConfigController {
@Autowired
private ConfigFeignClient configFeignClient;
// 测试日志配置
// (需要先配置对应的feign客户端的日志器的日志级别为DEBUG,
// 然后再通过java代码的方式配置1个Logger.Level的bean到@FeignClient注解指定的配置类中即可,
// 或者通过配置文件的方式配置:
// 在配置文件中配置feign.client.config.{feignName}.loggerLevel: BASIC
// 或者在配置文件中配置feign.client.config.default.loggerLevel: BASIC(全局))
@GetMapping("testLog")
public Object testLog() {
return configFeignClient.testLog();
}
// 测试响应超时配置
// (在配置文件中配置: 可以全局配置, 也可以给单个指定的feign客户端配置;
// 在代码中配置: 可以给全局配置, 也可以给单个指定的feign客户端配置;
// 在代码中给feign接口中的单个方法指定超时时间(如下面的testTimeout2方法所示);
// 当超过指定的时间还没有返回时, 就会抛出异常;
// 默认情况下(在配置文件和代码中都不配置超时时间), 默认的读取响应超时时间为60秒, 连接超时时间为10s,
// 也就是说, 如果发起响应后, 60秒之内还没有给出响应, 就会抛出异常了;)
@GetMapping("testTimeout")
public Object testTimeout(Long sec) {
return configFeignClient.testTimeout(sec);
}
@GetMapping("testTimeout2")
public Object testTimeout2(Long sec) {
Request.Options options = new Request.Options(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, true);
return configFeignClient.testTimeout2(options, sec);
}
}
ConfigFeignClient
/* 重点是验证各种配置 */
@FeignClient(name = "configN", url = "http://localhost:8084", path = "/orderService/config",
configuration = {ConfigFeignClientConfig.class})
public interface ConfigFeignClient {
// 访问: http://localhost:8084/orderService/config/testLog 能通
@GetMapping("/testLog")
String testLog();
// 访问: http://localhost:8084/orderService/config/testTimeout?sec=1 能通
@GetMapping("/testTimeout")
String testTimeout(@RequestParam("sec") Long sec);
@GetMapping("/testTimeout")
String testTimeout2(Request.Options options, @RequestParam("sec") Long sec);
}
ConfigFeignClientConfig
public class ConfigFeignClientConf {
/* 配置feign客户端打印日志的注意点:
1. feign客户端只有在配置feign客户端全类名对应的日志级别为debug的时候, 才有可能输出日志
2. 我们需要在配置类中如下定义1个Logger.Level的bean即可。
或者, 在配置文件中配置feign.client.config.{feignName}.loggerLevel: BASIC
或者, 在配置文件中配置feign.client.config.{feignName}.loggerLevel: BASIC(全局)
*/
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
// return Logger.Level.NONE;
// return Logger.Level.BASIC;
// return Logger.Level.HEADERS;
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
/* 也可以通过代码的方式配置超时时间 */
/*@Bean
public Request.Options requestOptions() {
return new Request.Options(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, true);
}*/
}
feign03
RetryController
@RestController
public class RetryController {
@Autowired
private RetryFeignClient retryFeignClient;
// 测试重试机制(默认不会重试)
// Feign的重试机制主要包括以下几个方面:
// 1. 配置重试次数和重试间隔时间
// 2. 配置重试条件和重试策略
// 3. 实现重试回退机制(这个不包括当前示例中)
// 什么情况下会重试?
// 默认情况下只有超时的情况下才会重试, 而如果被调用方抛出了其它异常, 则不会重试
// (其实是否重试, 不是由被调用方来决定的, 而是由调用方来确定的;
// 【默认情况下超时会引起重试】: 发起feign调用后, SynchronousMethodHandler#executeAndDecode 执行请求时,
// 会由于被调用方一直没有响应而抛出IO异常,捕获到IO异常后,转而抛出 RetryException,
// 抛出的RetryException在 SynchronousMethodHandler#invoke 的while(true)循环中又被捕捉到,从而交给retryer继续重试;
// 【被调用方抛出其它异常不会引起重试】: 发起feign调用后, SynchronousMethodHandler#executeAndDecode执行请求时,
// 会获得响应对象, 并将此响应对象交给 AsyncResponseHandler#handleResponse处理, 其中会根据响应状态码作不同处理,
// 如果状态码是200到300之间, 那么正常处理, 如果不是, 则会交给ErrorDecoder处理返回1个异常, 然后以异常结束, 然后返回到
// SynchronousMethodHandler#invoke 的while(true)循环中, 如果这个异常是 RetryException, 则交给retryer继续重试, 如果不是, 则跳出while循环;
// 【因此, 我们如果要重试就需要自己实现ErrorDecoder, 在需要重试的时候, 返回1个RetryException即可】)
// 如何配置重试?
// 可以通过配置文件的方式配置errorDecoder和retryer;
// 可以通过代码的方式配置1个errorDecoder的bean和1个Retryer的bean(这里的retryer可以配置重试次数)
// (使用配置文件配置的无效backoff无效、使用@Retryable注解配置的也无效, 后面再看)
@GetMapping("testRetry")
public Object testRetry(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
return retryFeignClient.testRetry(flag, sec);
}
@GetMapping("testRetry2")
public Object testRetry2(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
return retryFeignClient.testRetry2(flag, sec);
}
}
RetryFeignClient
@FeignClient(name = "retryN", url = "http://localhost:8084", path = "/orderService/config",
configuration = {RetryConfig.class})
public interface RetryFeignClient {
// 访问: http://localhost:8084/orderService/config/testRetry?flag=1 能通
@GetMapping("/testRetry")
String testRetry(@RequestParam("flag") Integer flag, @RequestParam("sec") Integer sec);
// 访问: http://localhost:8084/orderService/config/testRetry?flag=1 能通
@GetMapping("/testRetry")
// @Retryable(value = {IOException.class}, maxAttempts = 3, backoff = @Backoff(delay = 1000, maxDelay = 5000, multiplier = 2))
String testRetry2(@RequestParam("flag") Integer flag, @RequestParam("sec") Integer sec);
}
RetryConfig
public class RetryConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
// return Logger.Level.NONE;
return Logger.Level.BASIC;
// return Logger.Level.HEADERS;
// return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
/* 设置5s的超时时间, 以测定什么情况下会重试 */
@Bean
public Request.Options requestOptions() {
return new Request.Options(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, true);
}
/*
使用 Retryer.Default 类生成一个默认的重试器,
它会在当前请求失败后重试 3 次,并会在第一次重试前等待 500 毫秒,
在第二次重试前等待 1000 毫秒,第三次重试前等待 2000 毫秒,以此类推
*/
/*@Bean
public Retryer retryer() {
return new Retryer.Default(500, 5000, 3); // 最多请求3次
}*/
/*@Bean
public CustomErrorDecoder customErrorDecoder() {
return new CustomErrorDecoder();
}*/
}
CustomErrorDecoder
@Slf4j
public class CustomErrorDecoder implements ErrorDecoder {
@Override
public Exception decode(String methodKey, Response response) {
if (response.status() == 500) {
log.info("重试一波...");
// 认为有必要重试就返回RetryableException
return new RetryableException(
500,
"",
response.request().httpMethod(),
null,
response.request());
}
log.info("认为没必要重试...");
return new RuntimeException("Unknown error");
}
}
feign04
FallbackController
@RestController
public class FallbackController {
@Autowired
private FallbackFeignClient fallbackFeignClient;
// 测试降级、熔断
// 需要配置feign.hystrix.enabled: true, 来开启hystrix, 否则被调用方抛出异常后, 不会走指定的降级逻辑
// 访问1: http://localhost:8095/testFallback?flag=1&sec=0 正常返回 "ok"
// 访问2: http://localhost:8095/testFallback?flag=-1&sec=0 首先发1个请求给被调用方, 返回500状态码, 然后走降级逻辑 正常返回 "ojdk"
// 测试: 当在浏览器上多次快速点击访问2时, 刚开始, 请求会发起远程调用, 当多次后就会直接熔断, 然后直接走降级的方法, 多次都熔断之后, 我再访问1, 也是直接熔断走了降级方法。
// 但是熔断结束的时间很短, 稍微停一下, 就会发起远程调用。熔断的目的是为了保护下游服务, 在统计到下游服务多次响应失败后, 就会熔断一段时间, 等过会儿再去访问。
// 我们可以通过 hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.xxx来配置熔断相关的东西(如配置文件中所示)
// 降级:
// 可以使用@FeignClient的fallback来直接指定降级的类, 必须定义为bean且实现feign接口
// 也可以使用@FeignClient的fallbackFactory来直接指定降级的工厂类, 必须定义为bean且实现FallbackFactory, 并且在重写的方法中返回feign接口的实现类, 好处是可以拿到发生错误的异常
// fallback与fallbackFactory之间只能使用1个
@GetMapping("testFallback")
public Object testFallback(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
return fallbackFeignClient.testFallback(flag, sec);
}
}
FallbackFeignClient
@FeignClient(name = "fallbackN", url = "http://localhost:8084", path = "/orderService/config",
configuration = {FallbackConfig.class}
,fallback = FallbackFeignClientImpl.class
// ,fallbackFactory = FallbackFeignClientFactory.class
)
public interface FallbackFeignClient {
// 访问: http://localhost:8084/orderService/config/testFallback?flag=1 能通
@GetMapping("/testFallback")
String testFallback(@RequestParam("flag") Integer flag, @RequestParam("sec") Integer sec);
}
FallbackConfig
public class FallbackConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
// return Logger.Level.NONE;
// return Logger.Level.BASIC;
// return Logger.Level.HEADERS;
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
FallbackFeignClientImpl
// 容器中同时存在FallbackFeignClient接口实现的2个bean, 其中1个是feign的动态代理, 1个就是当前这个类
// 而feign的动态代理具有primary, 所以注入时, 会优先
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FallbackFeignClientImpl implements FallbackFeignClient {
@Override
public String testFallback(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
log.info("降级使用fallback...");
return "ojdk";
}
}
FallbackFeignClientFactory
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FallbackFeignClientFactory implements FallbackFactory<FallbackFeignClient> {
@Override
public FallbackFeignClient create(Throwable throwable) {
log.info("获取到异常: {}", throwable.toString());
return new FallbackFeignClient() {
@Override
public String testFallback(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
log.info("FallbackFeignClientFactory$1处理异常了...");
return "nook";
}
};
}
}
feign05
LbController
@RestController
public class LbController {
@Autowired
private LbFeignClient lbFeignClient;
// 测试负载均衡
// 访问: http://localhost:8095/testLb,
// 当没有服务时, 直接走的降级;
// 当启动1个order-service服务时, 立即访问, 仍然走的是降级, 过了一小段时间后, 成功调用到服务;
// 当再启动1个order-service服务时, 立即访问, 仍然调用的是第1个服务, 过了一小段时间后, 才会轮询访问;
// 当其中1个服务挂掉的时候, 还是会走降级逻辑(一直走降级方法), 过了一小段时间后, 一直成功调用到还存活的服务
// (这个是开启了feign.hystrix.enabled: true时的现象, 大概是因为只要有1个服务挂了, 就认为服务不可用, 然后直接熔断走的降级。
// 然后, 又试着关闭feign.hystrix.enabled: false, 再测试一遍, 负载均衡访问后, 关闭1个order-service, 在轮询到关闭的服务时, 稍微会等待一小会儿,
// 就把请求打到了还存活的服务上。);
@GetMapping("testLb")
public Object testLb() {
return lbFeignClient.testLb();
}
// 测试降级、熔断
// 需要配置feign.hystrix.enabled: true, 来开启hystrix, 否则被调用方抛出异常后, 不会走指定的降级逻辑
// 访问1: http://localhost:8095/testLb2?flag=1&sec=0 正常
// 访问2: http://localhost:8095/testLb2?flag=-1&sec=0 故意报错
// 行为同FallbackController中一致
@GetMapping("testLb2")
public Object testLb2(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
return lbFeignClient.testLb2(flag, sec);
}
}
LbFeignClient
@FeignClient(name = "order-service", path = "/orderService/config",
fallback = LbFeignClientImpl.class,
configuration = LbConfig.class)
public interface LbFeignClient {
@GetMapping("testLb")
String testLb();
@GetMapping("testLb2")
String testLb2(@RequestParam("flag") Integer flag, @RequestParam("sec") Integer sec);
}
LbConfig
public class LbConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
// return Logger.Level.NONE;
return Logger.Level.BASIC;
// return Logger.Level.HEADERS;
// return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
LbFeignClientImpl
@Slf4j
@Component
public class LbFeignClientImpl implements LbFeignClient{
@Override
public String testLb() {
log.info("lb2降级...");
return "lb~ok-降级";
}
@Override
public String testLb2(Integer flag, Integer sec) {
log.info("lb2降级...");
return "lb2~ok-降级";
}
}
order-service
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zzhua</groupId>
<artifactId>order-service</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR8</spring-cloud.version>
<alibaba.version>2.2.5.RELEASE</alibaba.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- springCloud -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
application.yml
server:
port: 8084
servlet:
context-path: /orderService
spring:
application:
name: order-service
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848
RemoteController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("remote")
public class RemoteController {
@GetMapping("findPerson")
Person findPerson(String pName, Integer pAge) {
return new Person(pName, pAge, new Address("CN", "HN"));
}
@GetMapping("getPerson")
Person getPerson(Person person) {
System.out.println(person);
return person;
}
@PostMapping("getPerson2")
Person getPerson2(@RequestBody Map<String,Object> cMap) {
System.out.println(cMap);
return new Person();
}
@PostMapping("addPerson")
Person addPerson(@RequestBody Person person,Integer pAge) {
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(pAge);
if (person.getAge() != null) {
person.setAge( person.getAge() + 1);
}
return person;
}
@PostMapping("addPerson2")
Person addPerson2(@RequestBody Person person,Address addr) {
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(addr);
if (person != null) {
person.setAddress(addr);
}
return person;
}
@PostMapping("checkPerson")
Person checkPerson(@RequestBody Person person, Integer[] ids) {
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(ids));
return person;
}
@PostMapping("checkPerson2") // List<Integer> ids必须要带@RequestParam注解才能接收到
Person checkPerson2(@RequestBody Person person, @RequestParam("ids") List<Integer> ids) {
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(ids);
return person;
}
}
ConfigController
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("config")
public class ConfigController {
@GetMapping("testLog")
String testLog() {
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/testTimeout")
String testTimeout(Long sec){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/testRetry")
String testRetry(Integer flag, @RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "0") Integer sec) throws Exception{
log.info("testRetry请求: {}", flag);
if (sec == 0) {
if (flag >= 0) {
return "ok";
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -1)) {
throw new RuntimeException("flag为-1");
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -2)) {
throw new NullPointerException("flag为-2");
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -3)) {
throw new IOException("flag为-3");
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("越界异常");
} else {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
return "ok2";
}
}
@GetMapping("/testFallback")
String testFallback(Integer flag, @RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "0") Integer sec) throws Exception{
log.info("testFallback请求: {}", flag);
if (sec == 0) {
if (flag >= 0) {
return "ok";
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -1)) {
throw new RuntimeException("flag为-1");
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -2)) {
throw new NullPointerException("flag为-2");
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -3)) {
throw new IOException("flag为-3");
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("越界异常");
} else {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
return "ok2";
}
}
@Value("${lb.name:unknown}")
private String lbName;
@GetMapping("testLb")
String testLb() {
return "loadBalance~" + lbName;
}
@GetMapping("/testLb2")
String testLb2(Integer flag, @RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "0") Integer sec) throws Exception{
log.info("testLb2请求: {}", flag);
if (sec == 0) {
if (flag >= 0) {
return "ok";
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -1)) {
throw new RuntimeException("flag为-1");
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -2)) {
throw new NullPointerException("flag为-2");
} else if (Objects.equals(flag, -3)) {
throw new IOException("flag为-3");
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("越界异常");
} else {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
return "ok2";
}
}
}
OrderApp
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderApp.class, args);
}
}
测试
启动nacos,再启动order-service,再启动demo-learn-feign即可
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)