计算机视觉 -- 图像分割
图像分割(image segmentation)技术是计算机视觉领域的个重要的研究方向,是图像语义理解的重要一环。图像分割是指将图像分成若干具有相似性质的区域的过程,从数学角度来看,图像分割是将图像划分成互不相交的区域的过程。近些年来随着深度学习技术的逐步深入,图像分割技术有了突飞猛进的发展,该技术相关的场景物体分割、人体前背景分割、人脸人体Parsing、三维重建等技术已经在无人驾驶、增强现实、
1. 图像分割
引入问题:
在自动驾驶系统中,如果用之前的检测网络(例如Faster-Rcnn),试想,倘若前方有一处急转弯,系统只在道路上给出一个矩形标识,这样一来车辆很有可能判断不出是该避让还是径直上前,车祸一触即发。因此,对新技术的诉求应运而生,该技术须能识别具体路况,以指引车辆顺利过弯。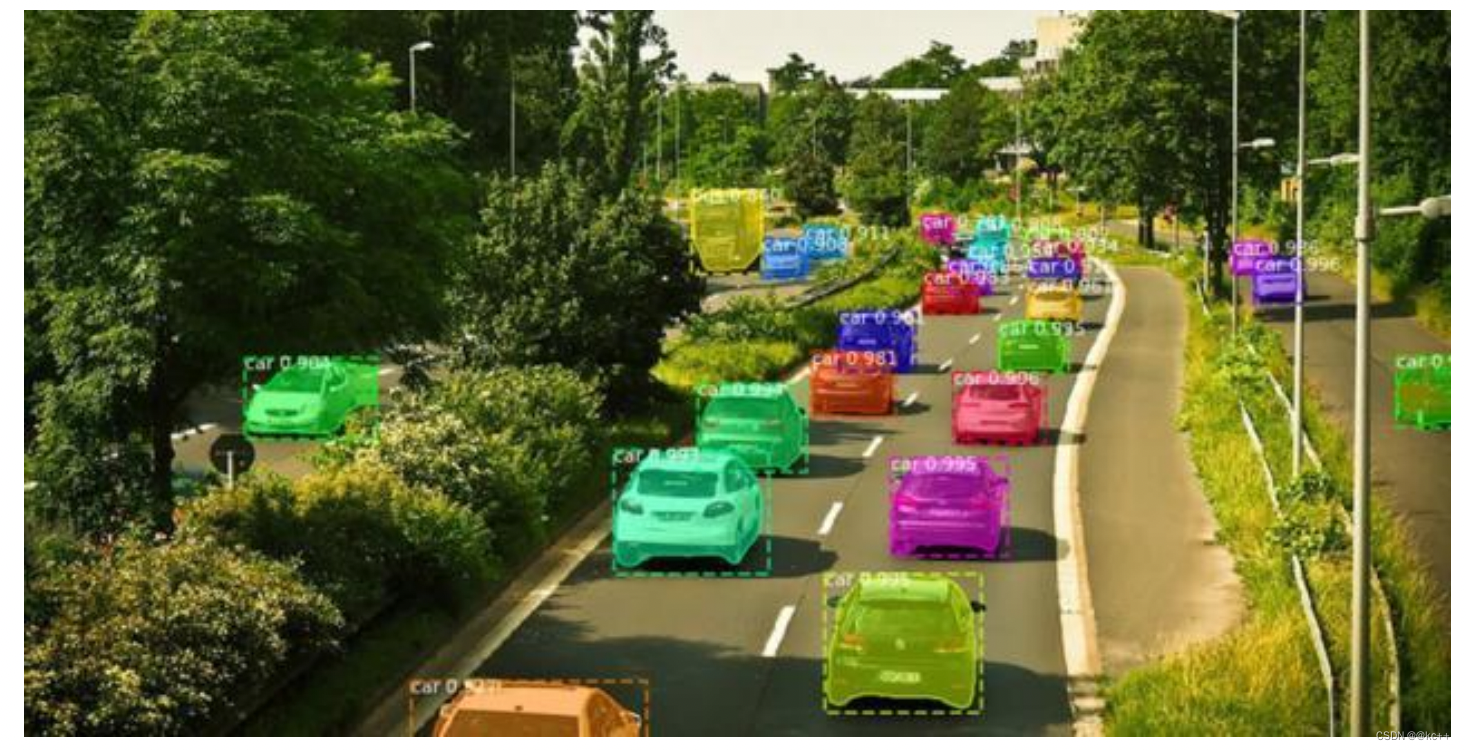
图像分割即为图片的每个对象创建一个像素级的掩膜,该技术可使大家对图像中的对象有更深入的了解。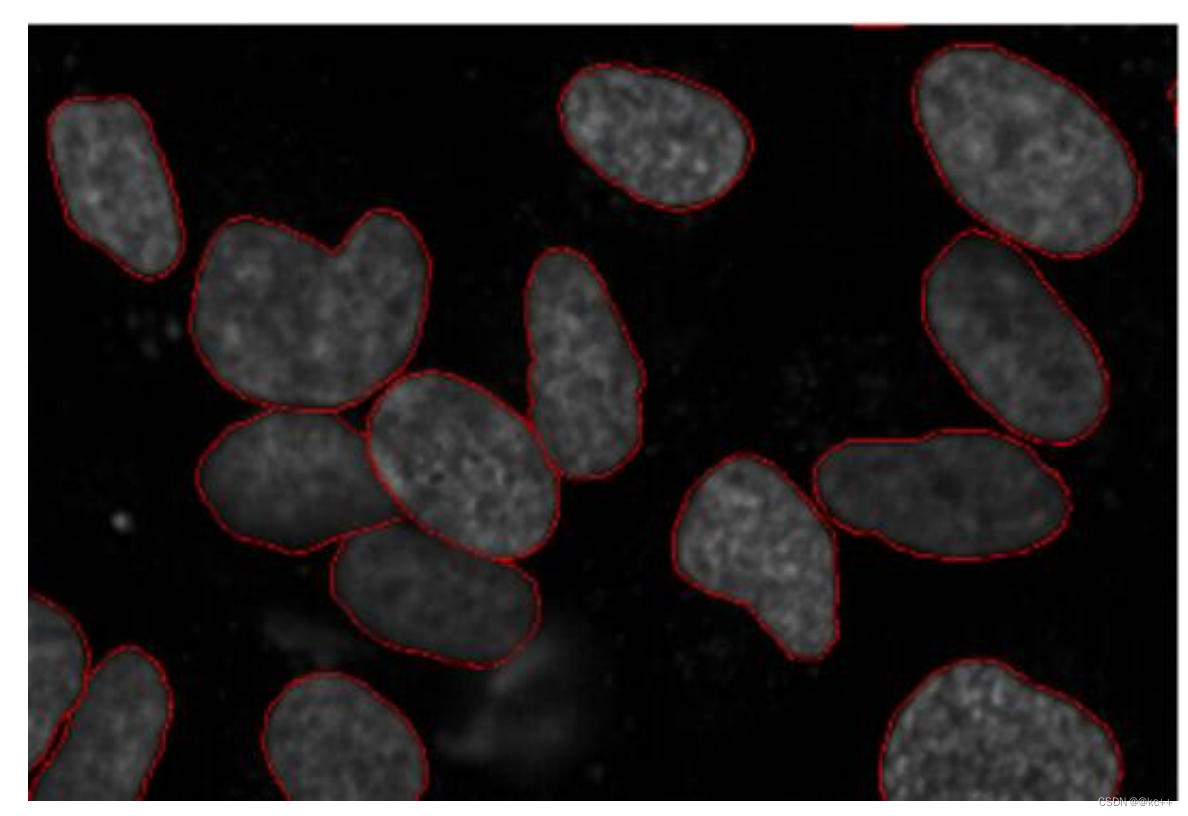
图像分割可分为两种:语义分割与实例分割。
- 左图五个对象均为人,因此语义分割会将这五个对象视为一个整体。
- 右图同样也有五个对象(亦均为人),但同一类别的不同对象在此被视为不同的实例,这就是实例分割。
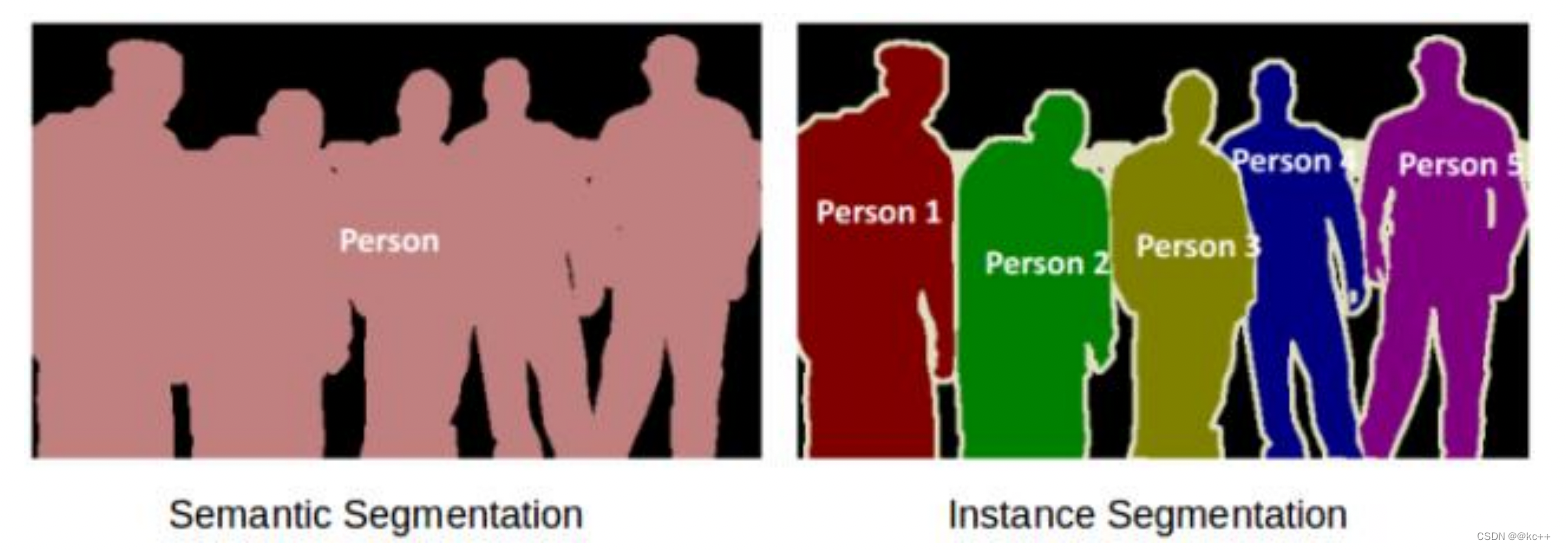
图像分类,语义分割,目标检测,实例分割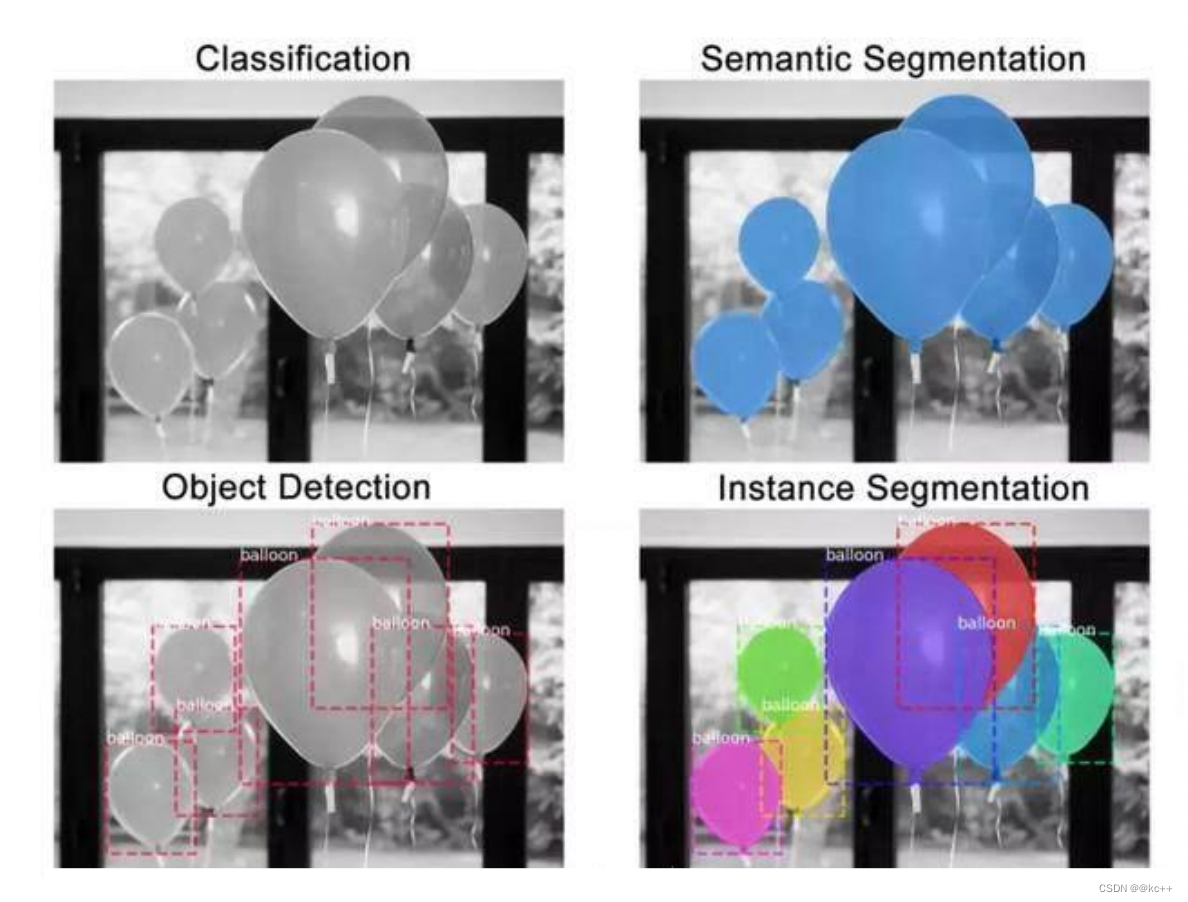
2. FCN
2.1 语义分割– FCN (Fully Convolutional Networks)
全卷积神经网络,顾名思义,该网络中没有全连接层,都是一些卷卷积的结构
FCN最主要的一个用法就是用于语义分割
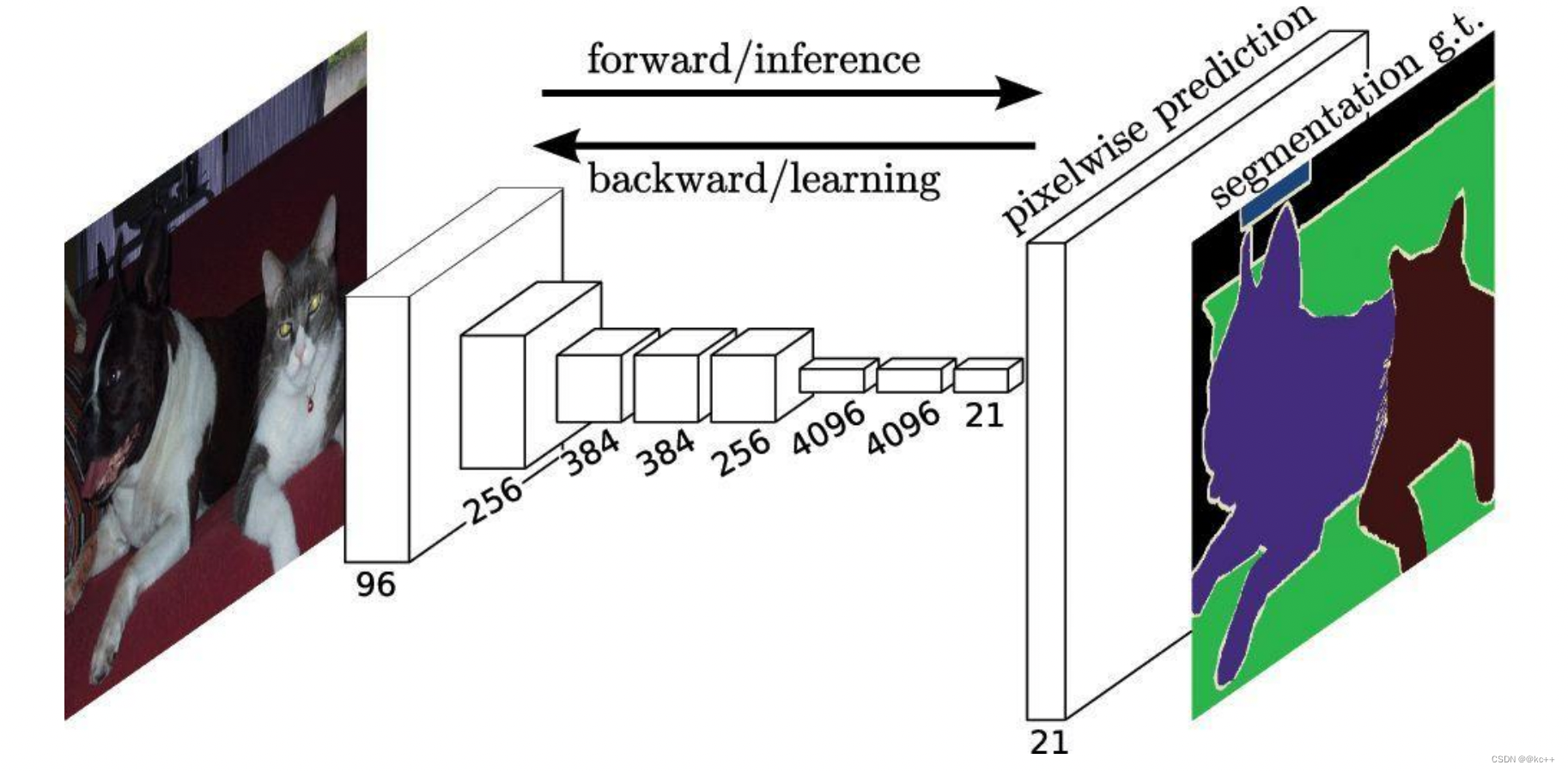
我们分类使用的网络通常会在最后连接几层全连接层,它会将原来二维的矩阵(图片)压扁成一维的,从而丢失了空间信息,最后训练输出一个标量,这就是我们的分类标签。
FCN网络和一般的网络的最大不同是,FCN产生的输出和输入的维度保持一致,即改变原本的CNN网络末端的全连接层,将其调整为卷积层,这样原本的分类网络最终输出一个热度图类型的图像。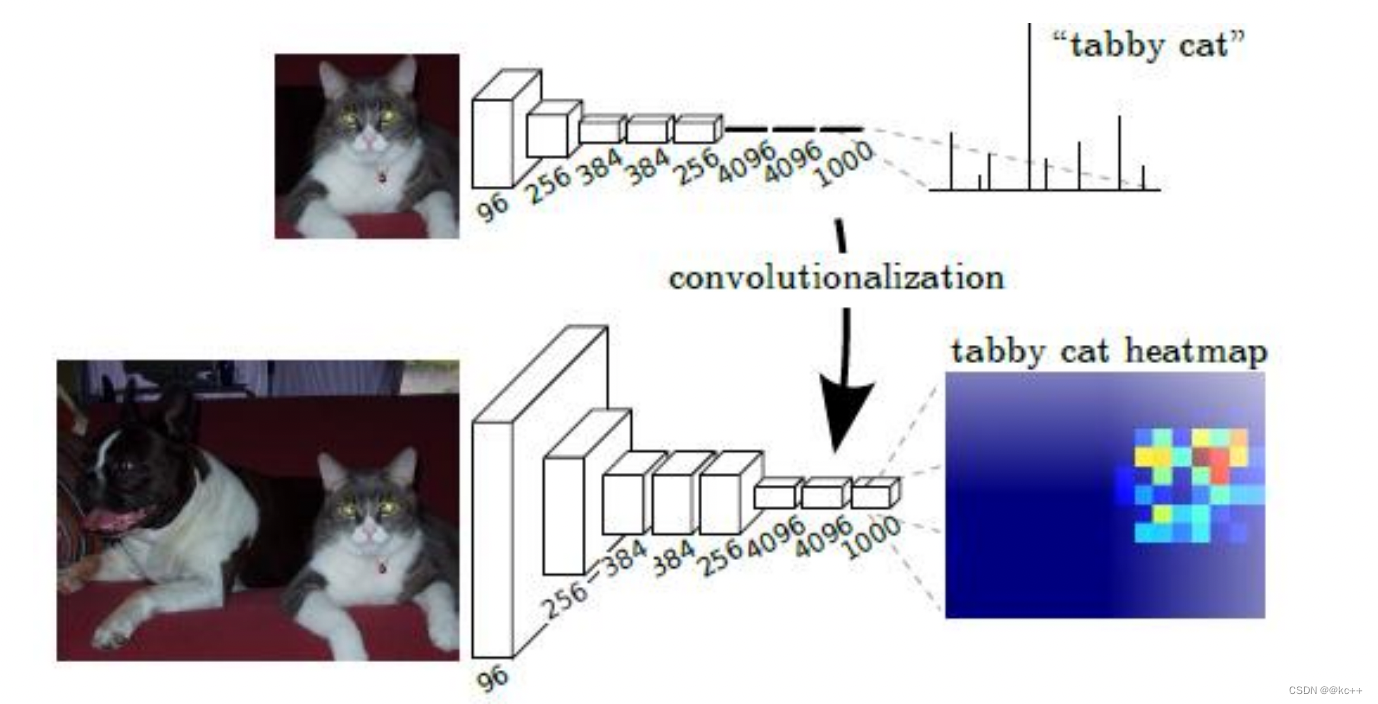
一句话概括原理:
FCN将传统卷积网络后面的全连接层换成了卷积层,这样网络输出不再是类别而是heatmap;同时为了解决因为卷积和池化对图像尺寸的影响,提出使用上采样的方式恢复尺寸。
核心思想:
- 不含全连接层(fc)的全卷积(fully conv)网络。可适应任意尺寸输入。
- 增大数据尺寸的反卷积(deconv)层。能够输出精细的结果。
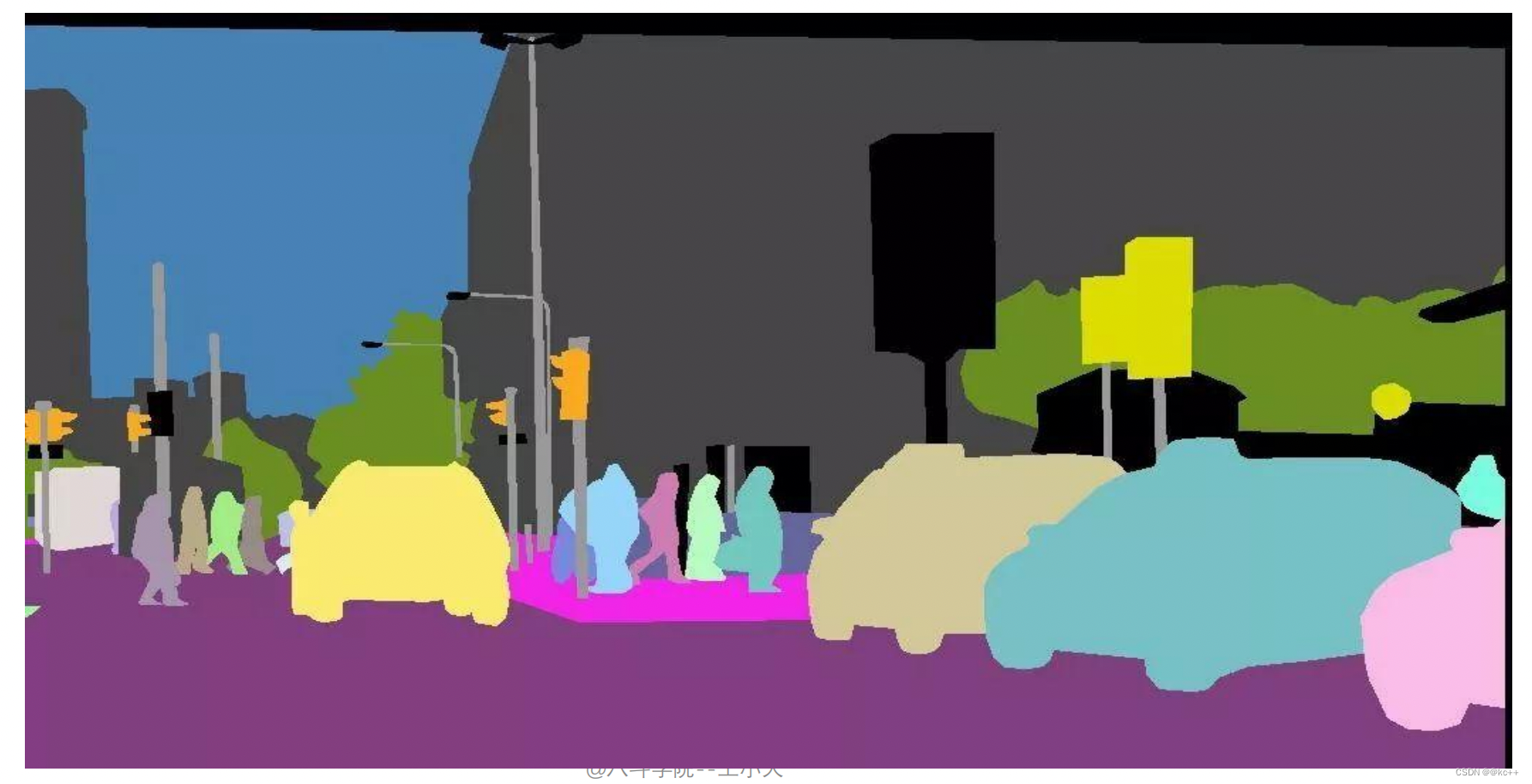
FCN对图像进行像素级的分类,从而解决了语义级别的图像分割(semantic segmentation)问题。
FCN可以接受任意尺寸的输入图像,采用反卷积层对最后一个卷积层的feature map进行上采样, 使它恢复到输入图像相同的尺寸,从而可以对每个像素都产生了一个预测, 同时保留了原始输入图像中的空间信息, 最后在上采样的特征图上进行逐像素分类。
最后逐个像素计算softmax分类的损失, 相当于每一个像素对应一个训练样本。
对全卷积网络的末端再进行upsampling(上采样),即可得到和原图大小一样的输出,这就是热度图了。这里上采样采用了deconvolutional(反卷积)的方法。
反卷积/转置卷积:它并不是正向卷积的完全逆过程。反卷积是一种特殊的正向卷积,先按照一定的比例通过补0来扩大输入图像的尺寸,接着旋转卷积核,再进行正向卷积。
大家可能对于反卷积的认识有一个误区,以为通过反卷积就可以获取到经过卷积之前的图片, 实际上通过反卷积操作并不能还原出卷积之前的图片, 只能还原出卷积之前图片的尺寸。
卷积和反卷积,并没有什么关系,操作的过程 也都是不可逆的。
2.2 FCN–deconv
反卷积用在什么地方?
- 反卷积/转置卷积在语义分割领域应用很广,如果说pooling层用于特征降维,那么在多个pooling层后,就需要用转置卷积来进行分辨率的恢复。
- 如果up-sampling采用双线性插值进行分辨率的提升,这种提升是非学习的。采用反卷积来完成上采样的工作,就可以通过学习的方式得到更高的精度
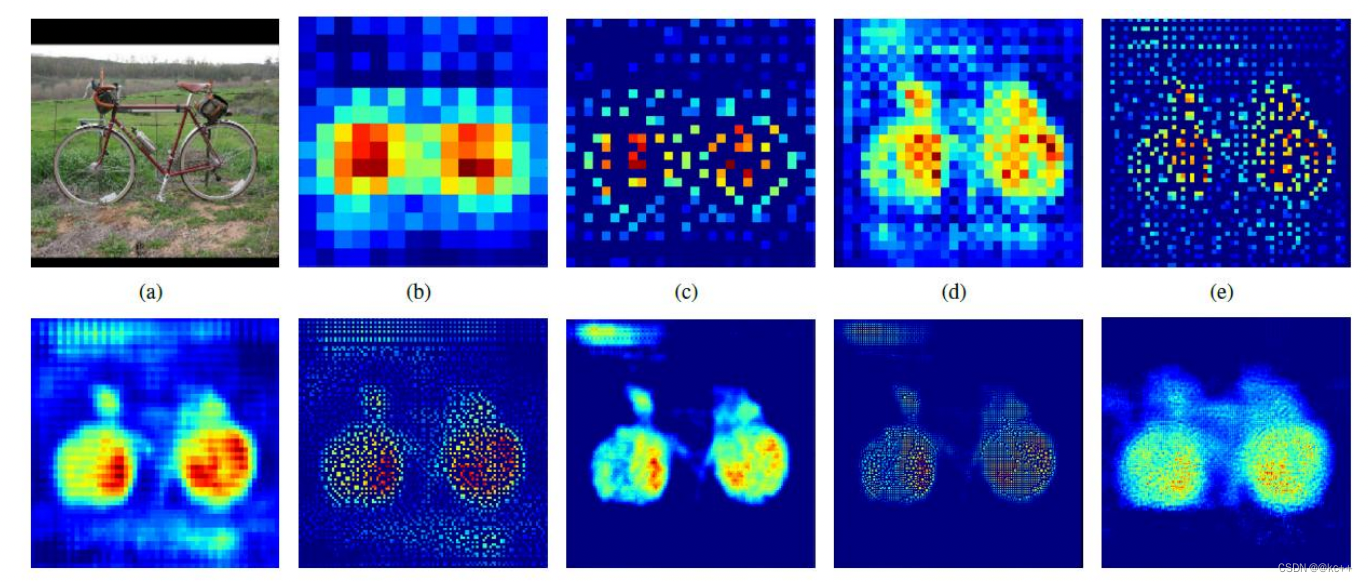
反卷积具体步骤:
- 将上一层的卷积核反转(上下左右方向进行反转)。
- 将上一层卷积的结果作为输入,做补0扩充操作,即往每一个元素后面补0。这一步是根据步长来的,对于每个元素沿着步长方向补(步长-1)个0。例如,步长为1就不用补0了。
- 在扩充后的输入基础上再对整体补0。以原始输入的shape作为输出shape,按照卷积padding规则,计算pading的补0的位置及个数,得到补0的位置及个数。
- 将补0后的卷积结果作为真正的输入,反转后的卷积核为filter,进行步长为1的卷积操作。
注意:计算padding按规则补0时,统一按照padding=‘SAME’、步长为1*1的方式来计算
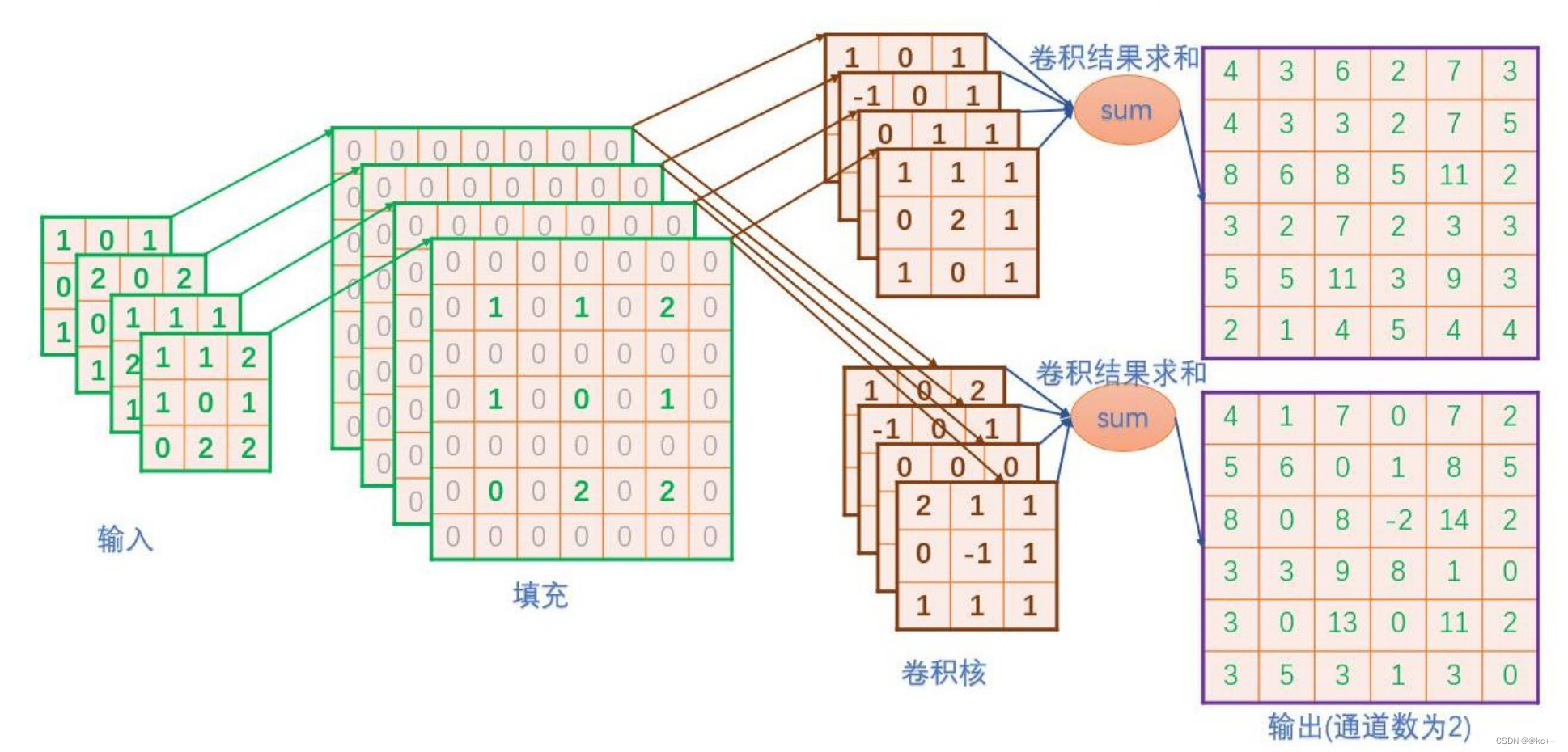
卷积: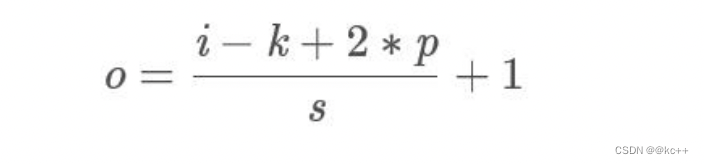
反卷积: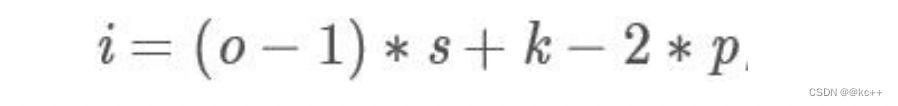
反卷积的缺点:
- 卷积矩阵是稀疏的(有大量的0),因此大量的信息是无用的;
- 求卷积矩阵的转置矩阵是非常耗费计算资源的。
2.3 Unpool
池化操作中最常见的最大池化和平均池化,因此最常见的反池化操作有反最大池化和反平均池化。反最大池化需要记录池化时最大值的位置,反平均池化不需要此过程。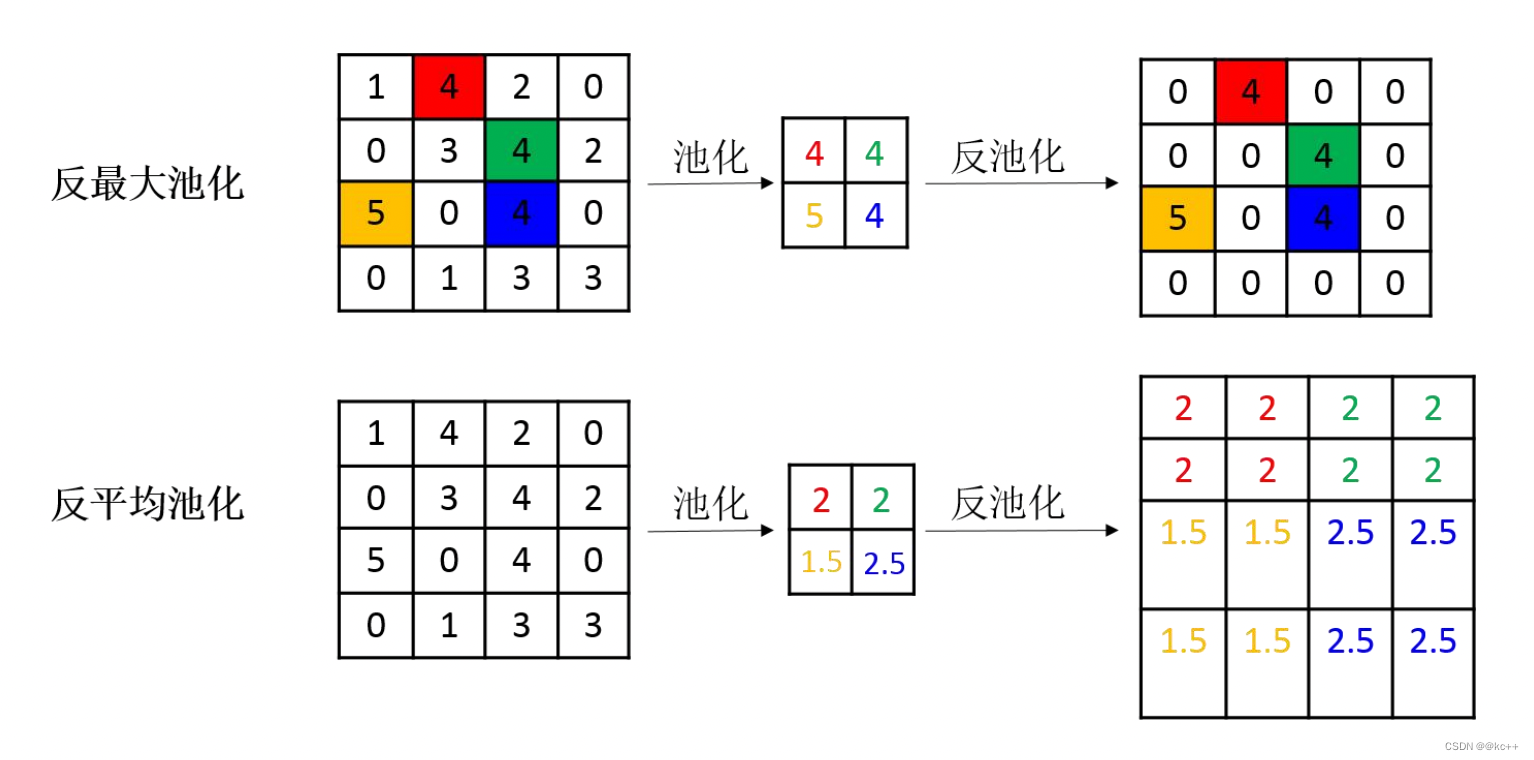
2.4 拓展–DeconvNet
这样的对称结构有种自编码器的感觉在里面,先编码再解码。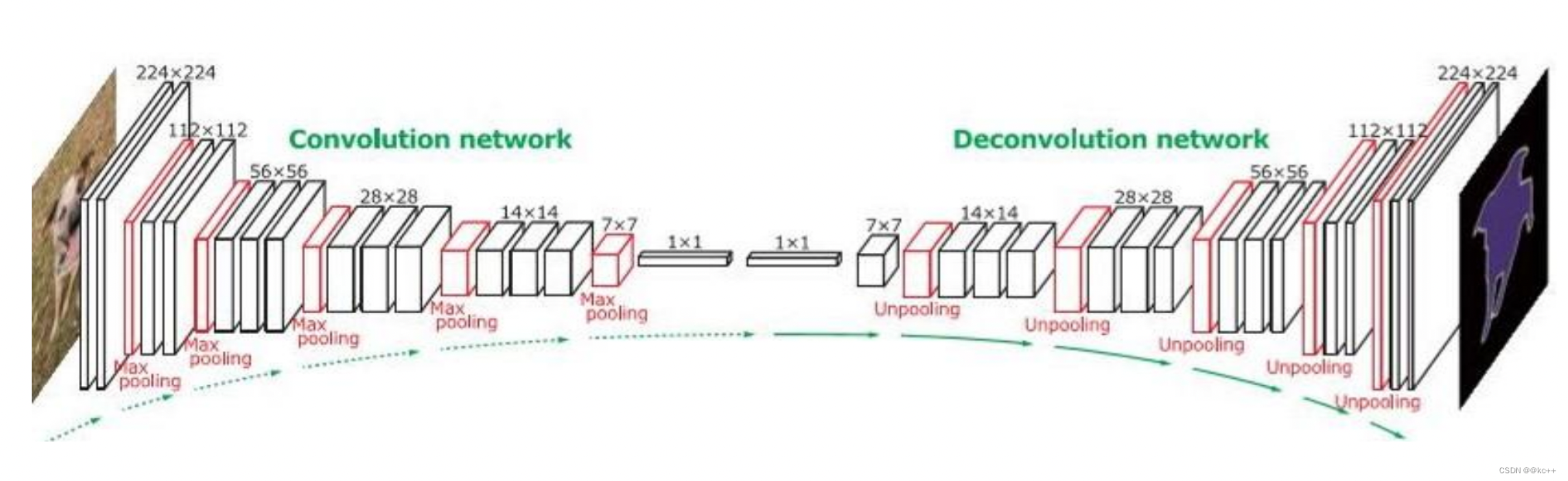
3. 实例分割

实例分割(instance segmentation)的难点在于:需要同时检测出目标的位置并且对目标进行分割,所以这就需要融合目标检测(框出目标的位置)以及语义分割(对像素进行分类,分割出目标)方法。
3.1 实例分割–Mask R-CNN
Mask R-CNN可算作是Faster R-CNN的升级版。
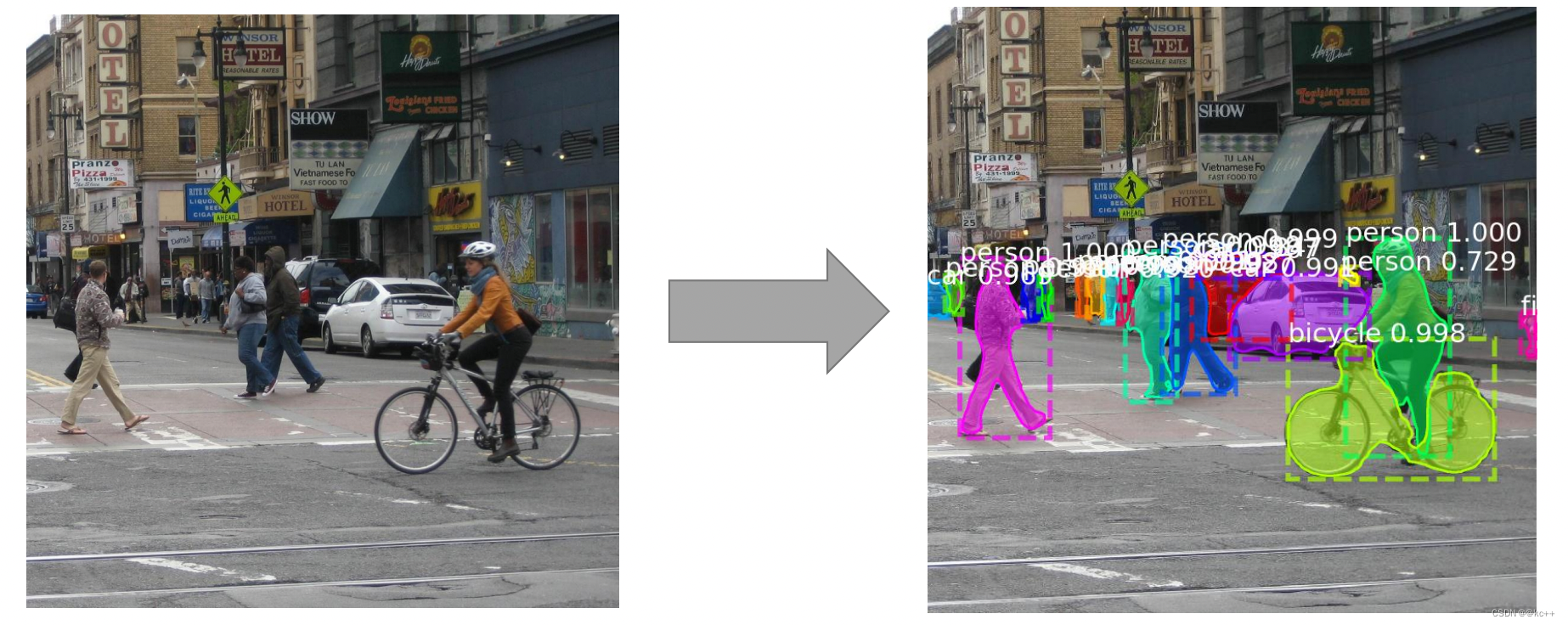
Faster R-CNN广泛用于目标检测。对于给定图像,它会给图中每个对象加上类别标签与边界框坐标。
Mask R-CNN框架是以Faster R-CNN为基础而架构的。因此,针对给定图像, Mask R-CNN不仅会给每个对象添加类标签与边界框坐标,还会返回其对象掩膜。
Mask R-CNN的抽象架构: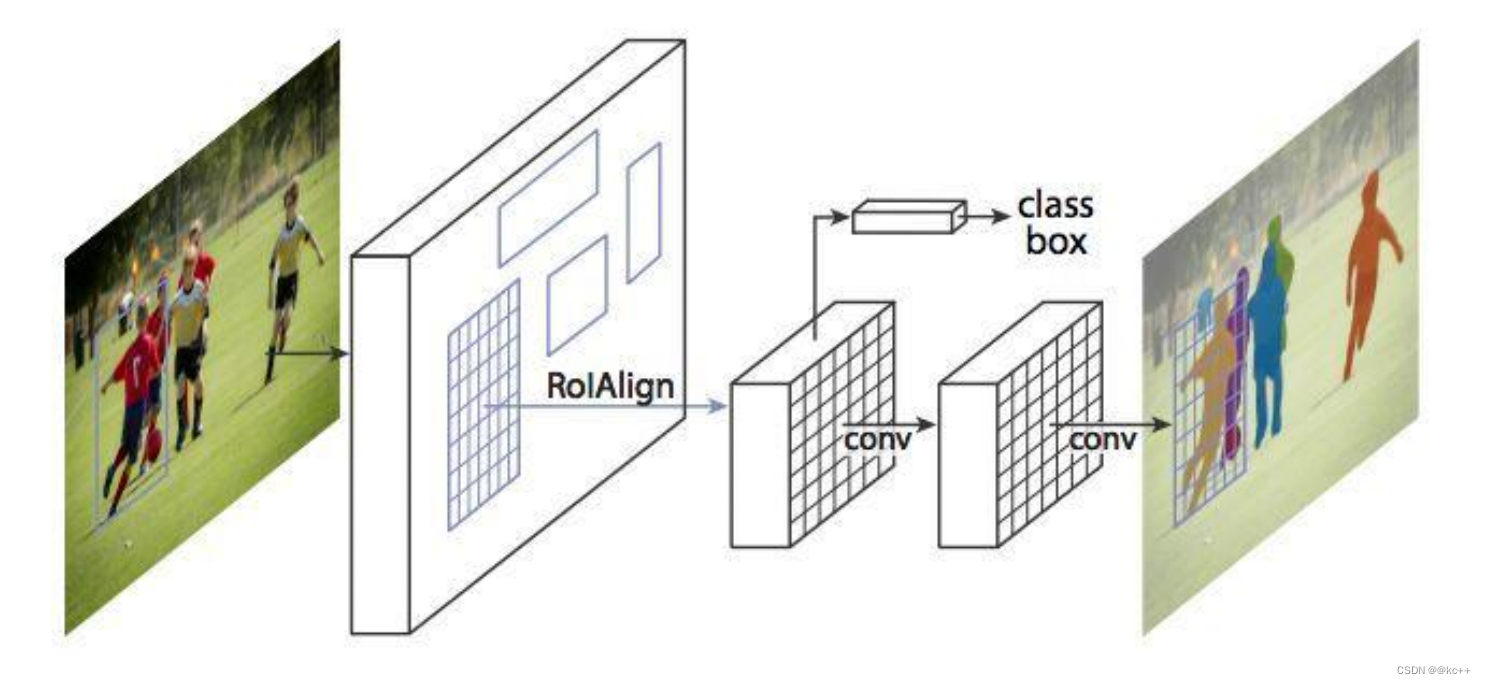
3.2 Mask R-CNN
Mask R-CNN在进行目标检测的同时进行实例分割,取得了出色的效果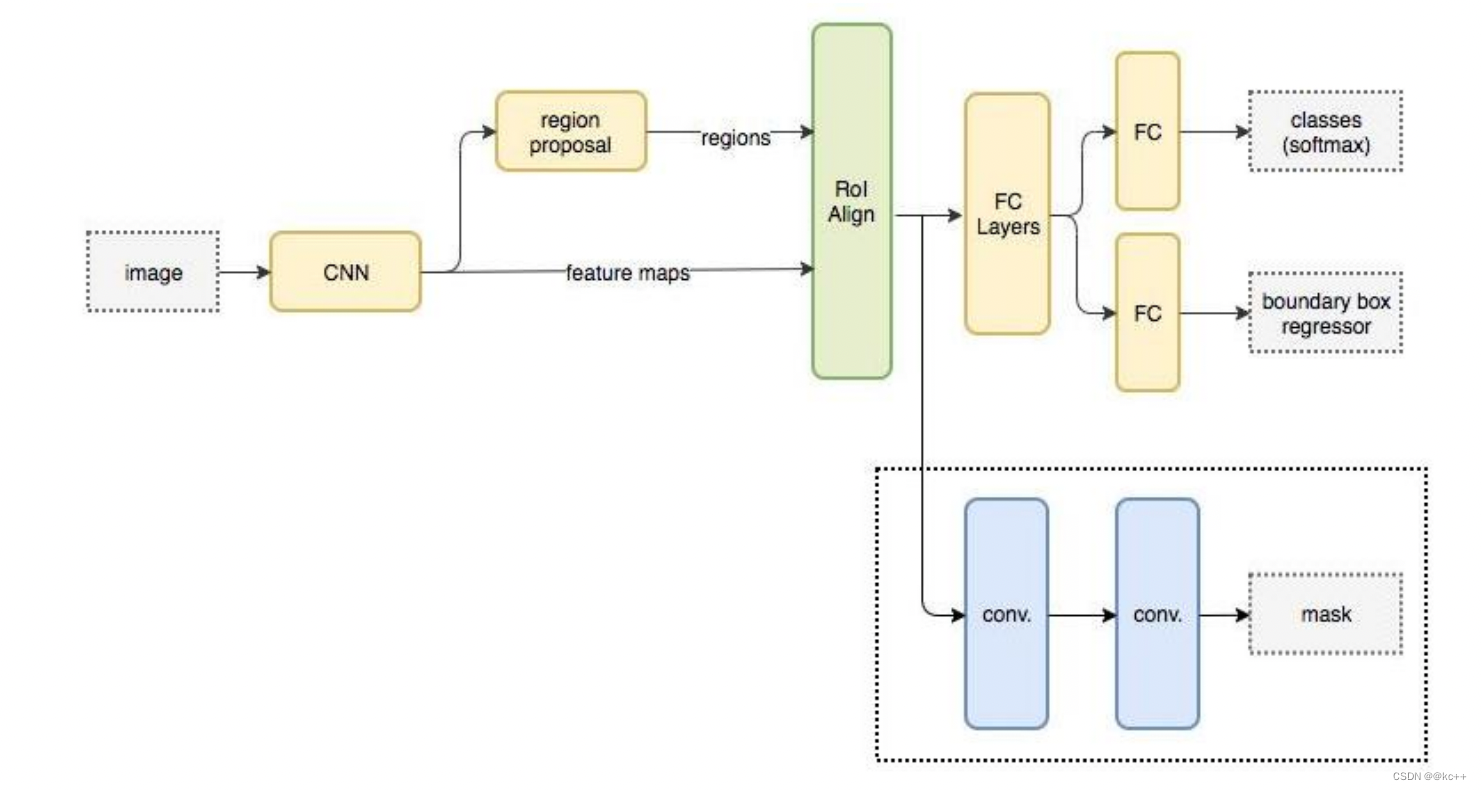
3.3 Faster R-CNN与 Mask R-CNN
Mask-RCNN 大体框架还是 Faster-RCNN 的框架,可以说在基础特征网络之后又加入了全连接的分割子网,由原来的两个任务(分类+回归)变为了三个任务(分类+回归+分割)。Mask R-CNN 是一个两阶段的框架,第一个阶段扫描图像并生成候选区域(proposals,即有可能包含一个目标的区域),第二阶段分类候选区域并生成边界框和掩码。
与Faster RCNN的区别:
- 使用ResNet网络作为backbone
- 将 Roi Pooling 层替换成了 RoiAlign;
- 添加并列的 Mask 层;
- 引入FPN 和 FCN
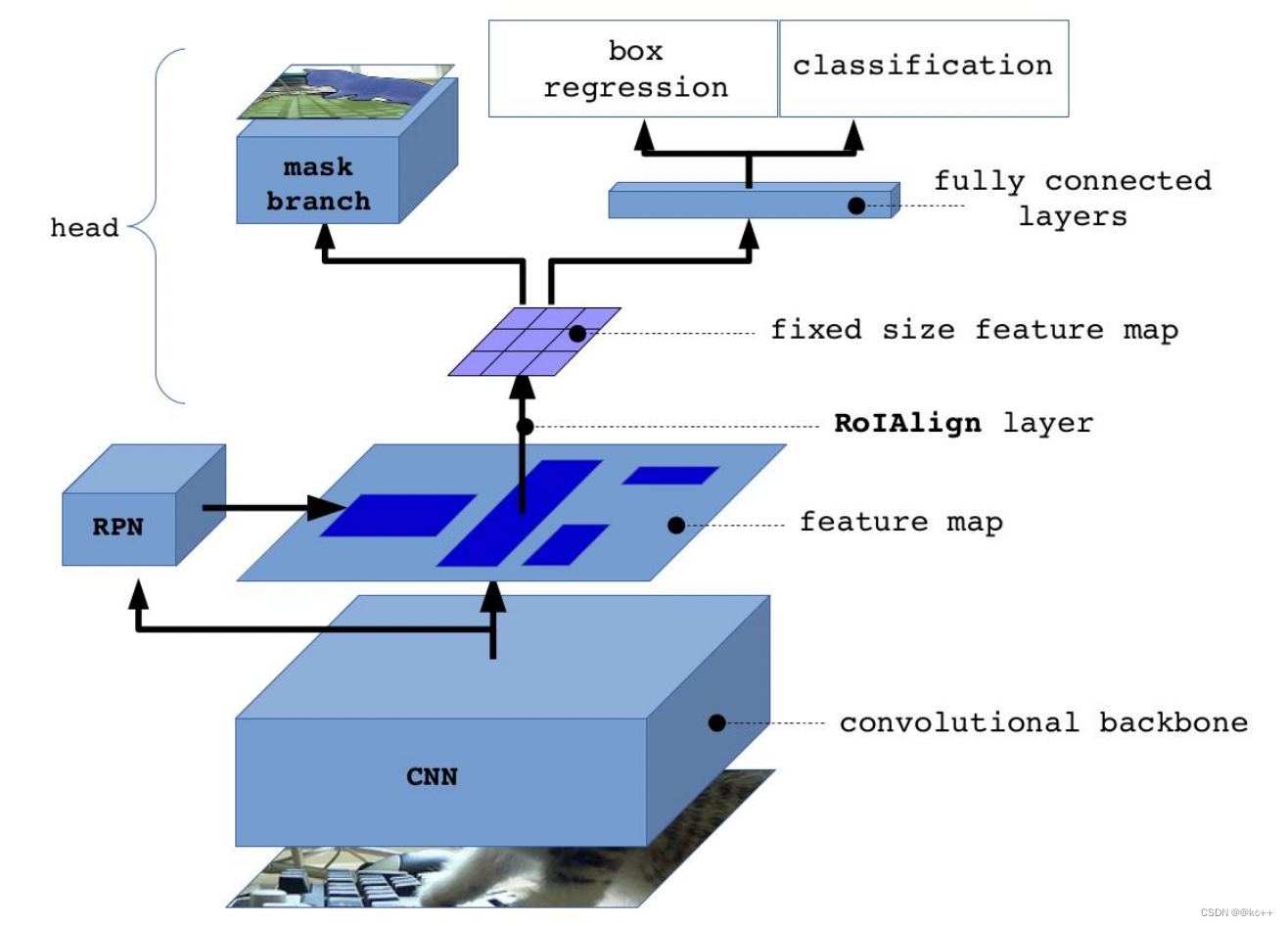
- 输入一幅你想处理的图片,然后进行对应的预处理操作,获得预处理后的图片;
- 将其输入到一个预训练好的神经网络中(ResNet等)获得对应的feature map;
- 对这个feature map中的每一点设定预定个的ROI,从而获得多个候选ROI;
- 将这些候选的ROI送入RPN网络进行二值分类(positive或negative)和BB回归,过滤掉一部分候选的ROI(截止到目前,Mask和Faster完全相同);
- 对这些剩下的ROI进行ROIAlign操作(ROIAlign为Mask R-CNN创新点1,比ROIPooling有长足进步);
- 最后,对这些ROI进行分类(N类别分类)、BB回归和MASK生成(在每一个ROI里面进行FCN操作)(引入FCN生成Mask是创新点2,使得此网络可以进行分割型任务)。
- backbone:Mask-RCNN使用 Resnet101作为主干特征提取网络, 对应着图像中的CNN部分。(当然也可以使用别的CNN网络)
- 在进行特征提取后,利用长宽压缩了两次、三次、四次、五次的特征层来进行特征金字塔结构的构造。
3.4 Mask R-CNN:Resnet101
Resnet 中 Conv Block和Identity Block的结构:
其中Conv Block输入和输出的维度是不一样的,所以不能连续串联,它的作用是改变网络的维度;Identity Block输入维度和输出维度相同,可以串联,用于加深网络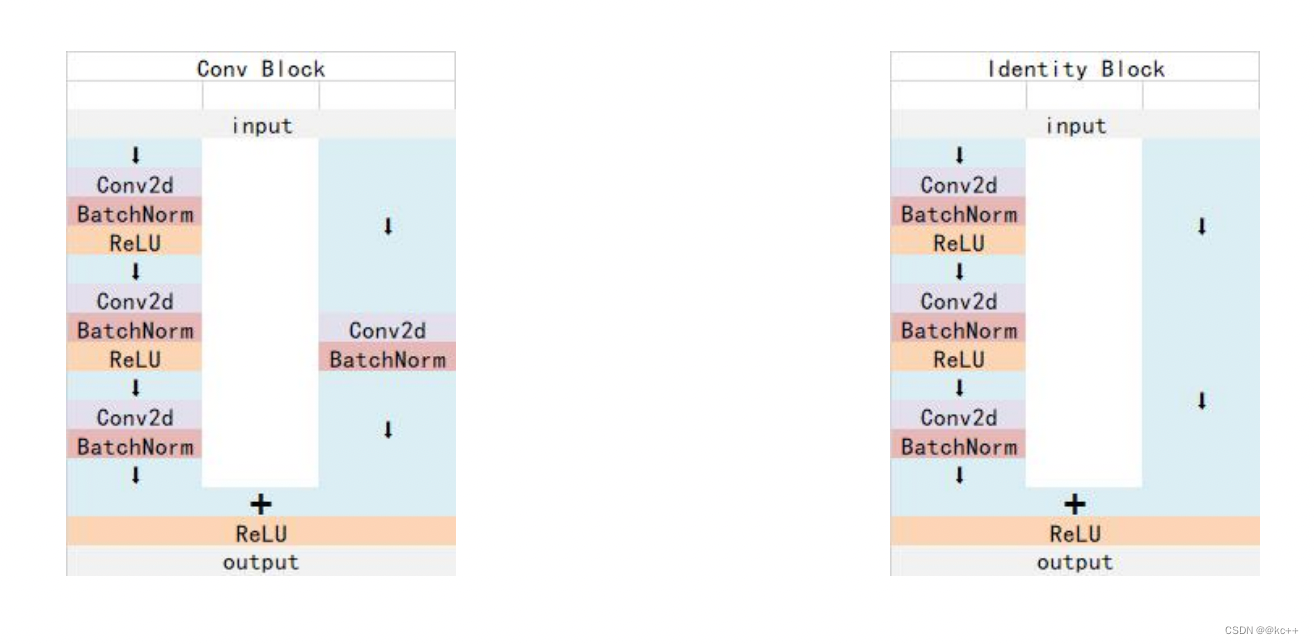
3.5 特征金字塔-Feature Pyramid Networks(FPN)
- 目标检测任务和语义分割任务里面常常需要检测小目标。但是当小目标比较小时,可能在原图里面只有几十个像素点。
- 对于深度卷积网络,从一个特征层卷积到另一个特征层,无论步长是1还是2还是更多,卷积核都要遍布整个图片进行卷积,大的目标所占的像素点比小目标多,所以大的目标被经过卷积核的次数远比小的目标多,所以在下一个特征层里,会更多的反应大目标的特点。
- 特别是在步长大于等于2的情况下,大目标的特点更容易得到保留,小目标的特征点容易被跳过。
- 因此,经过很多层的卷积之后,小目标的特点会越来越少。
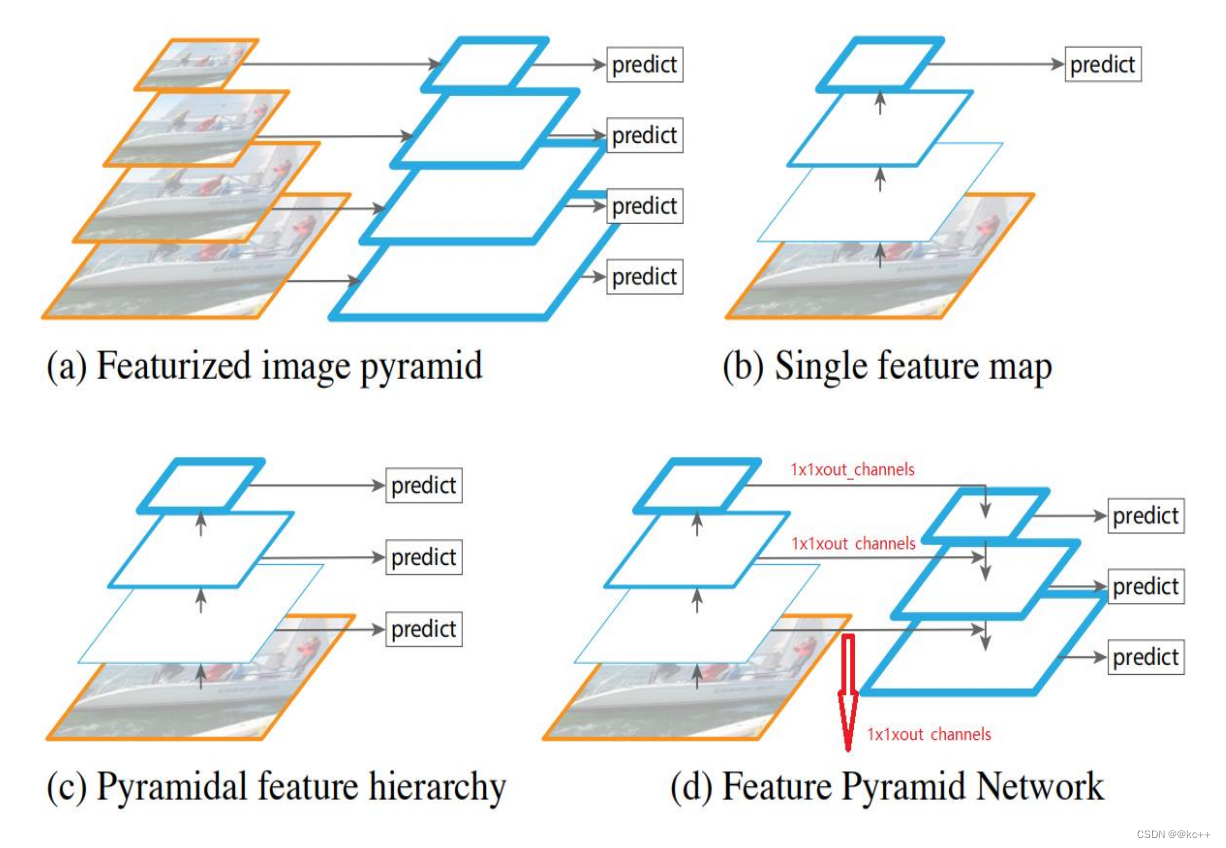
特征图(feature map)用蓝色轮廓表示, 较粗的轮廓表示语义上更强的特征图。
a. 使用图像金字塔构建特征金字塔。 特征是根据每个不同大小比例的图像独立计算的,每计算一次特征都需要resize一下图片大小,耗时,速度很慢。
b. 检测系统都在采用的为了更快地检测而使用的单尺度特征检测。
c. 由卷积计算的金字塔特征层次来进行目标位置预测,但底层feature map特征表达能力不足。
d. 特征金字塔网络(FPN)和b,c一样快, 但更准确。
FPN的提出是为了实现更好的feature maps融合,一般的网络都是直接使用最后一层的feature maps,虽然最后一层的 feature maps 语义强,但是位置和分辨率都比较低,容易 检测不到比较小的物体。FPN的功能就是融合了底层到高层 的feature maps ,从而充分的利用了提取到的各个阶段的特征(ResNet中的C2-C5)。
3.6 Mask R-CNN:FPN
特征金字塔FPN的构建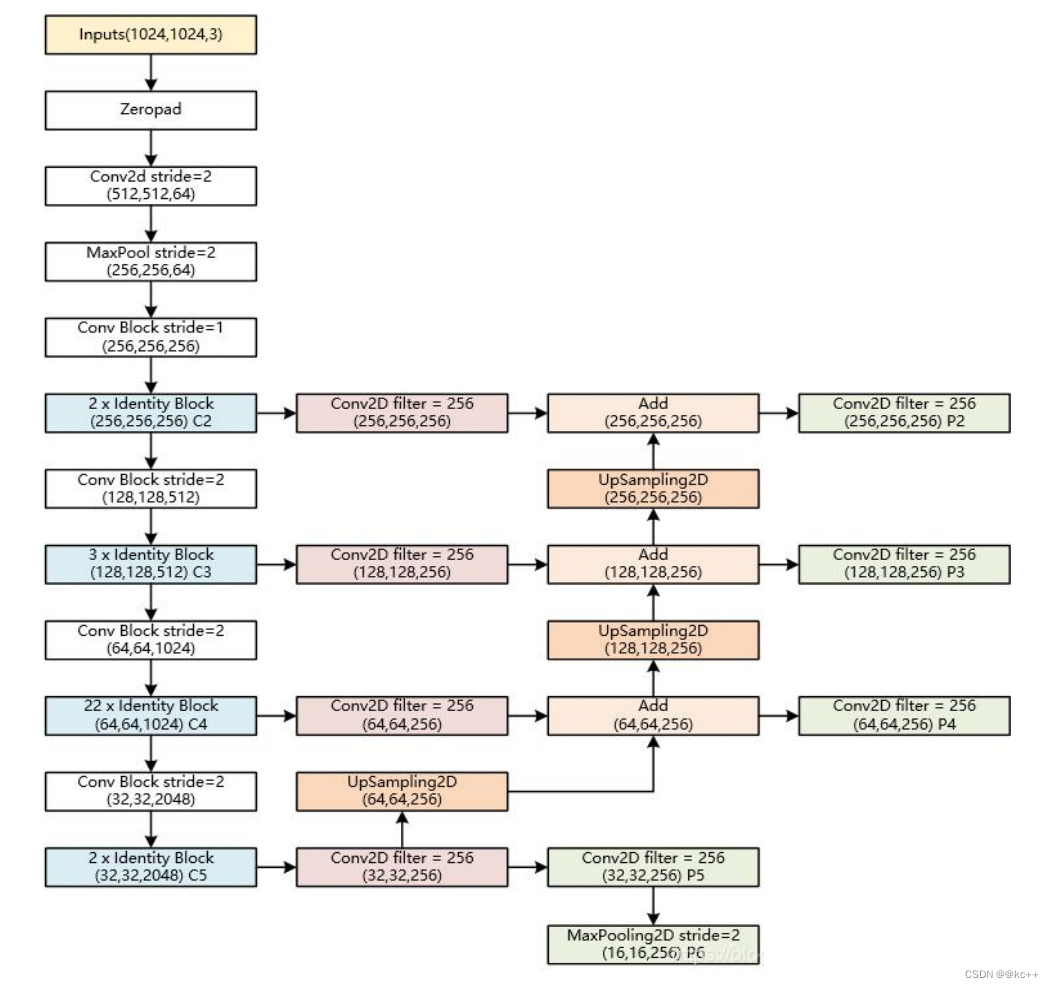
- 特征金字塔FPN的构建是为了实现特征多尺度的融合,在Mask R-CNN当中,我们取出在主干特征提取网络中长宽压缩了两次 C2、三次C3、四次C4、五次C5的结果来进行特征金字塔结构的构造。
- P2-P5是将来用于预测物体的bbox,box- regression,mask的。
- P2-P6是用于训练RPN的,即P6只用于RPN 网络中。
3.7 Faster-RCNN:Roi pooling
为何需要RoI Pooling?
对于传统的CNN(如AlexNet和VGG),当网络训练好后输入的图像尺寸必须是固定值,同时网络输出也是固定大小的vector or matrix。如果输入图像大小不定,这个问题就变得比较麻烦。
有2种解决办法:
- 从图像中crop一部分传入网络将图像(破坏了图像的完整结构)
- warp成需要的大小后传入网络(破坏了图像原始形状信息)

RoI Pooling原理
新参数pooled_w、pooled_h和spatial_scale(1/16)
RoI Pooling layer forward过程:
- 由于proposal是对应MN尺度的,所以首先使用spatial_scale参数将其映射回(M/16)(N/16)大小的feature map尺度;
- 再将每个proposal对应的feature map区域水平分为poold_w * pooled_h的网格;
- 对网格的每一份都进行max pooling处理。
这样处理后,即使大小不同的proposal输出结果都是poold_w * pooled_h固定大小,实现了固定长度输出。
再将每个proposal对应的feature map区 域水平分为poold_w * pooled_h的网格;
对网格的每一份都进行max pooling处理
这样处理后,即使大小不同的proposal输 出结果都是poold_w * pooled_h固定大小, 实现了固定长度输出。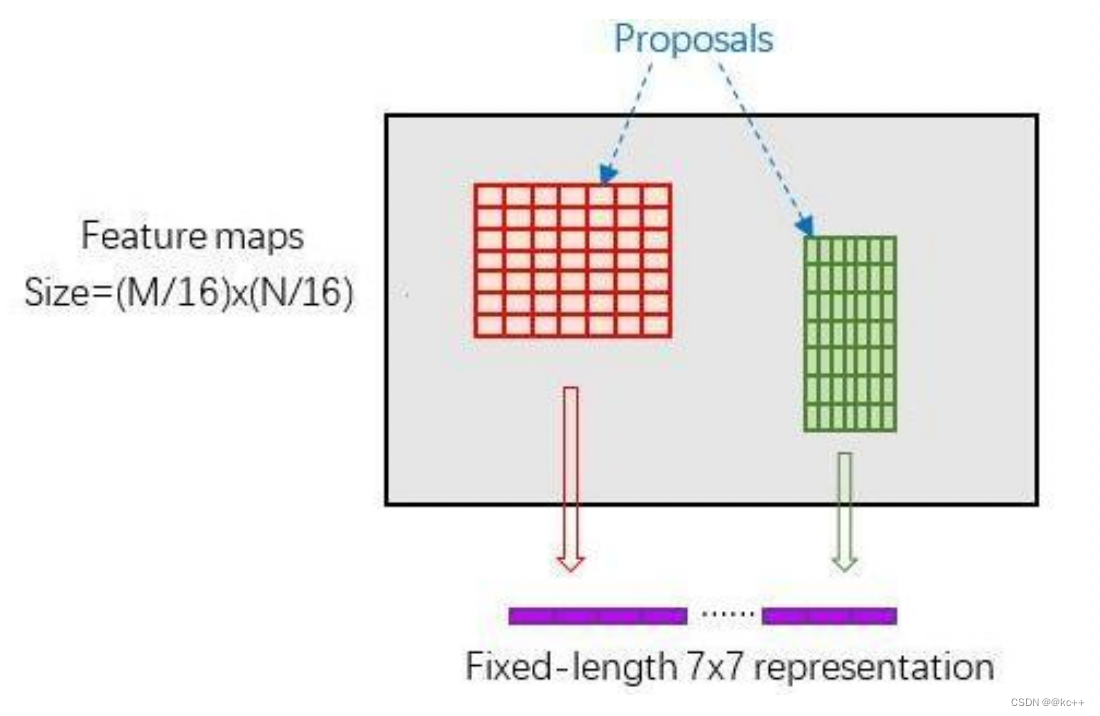
3.8 Mask R-CNN:Roi-Align
Roi-Align
Mask-RCNN中提出了一个新的思想就是RoIAlign,其实RoIAlign就是在RoI pooling上稍微改动过来的,但是为什么在模型中不继续使用RoI pooling呢?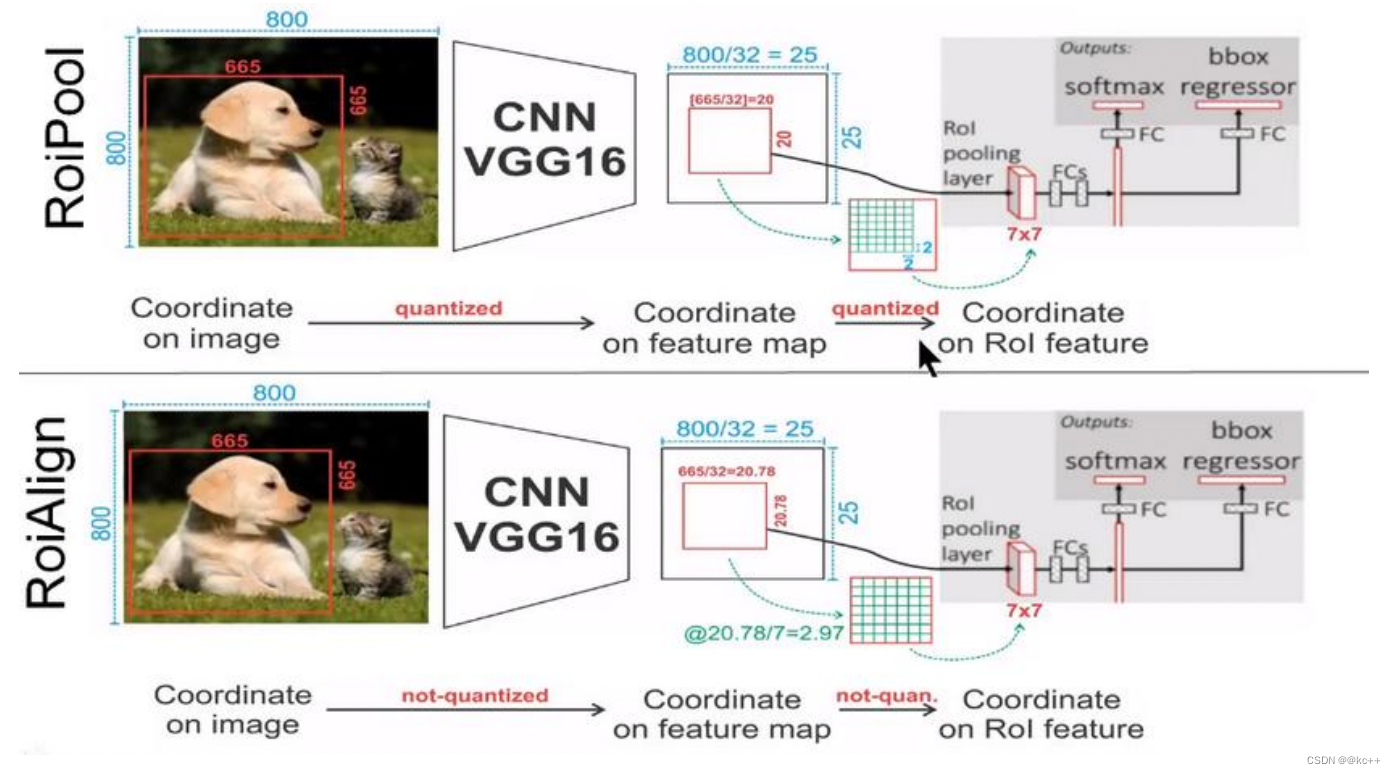
在RoI pooling中出现了两次的取整,虽然在feature maps上取整看起来只是小数级别的数,但是当把feature map还原到原图上时就会出现很大的偏差,比如第一次的取整是舍去了0.78 (665/32=20.78),还原到原图时是20*32=640,第一次取整就存在了25个像素点的偏差,在第二次的取整后的偏差更加的大。对于分类和物体检测来说可能这不是一个很大的误差,但是对于实例分割而言,这是一个非常大的偏差,因为mask出现没对齐的话在视觉上是很明显的。而RoIAlign的提出就是为了解决这个不对齐问题。
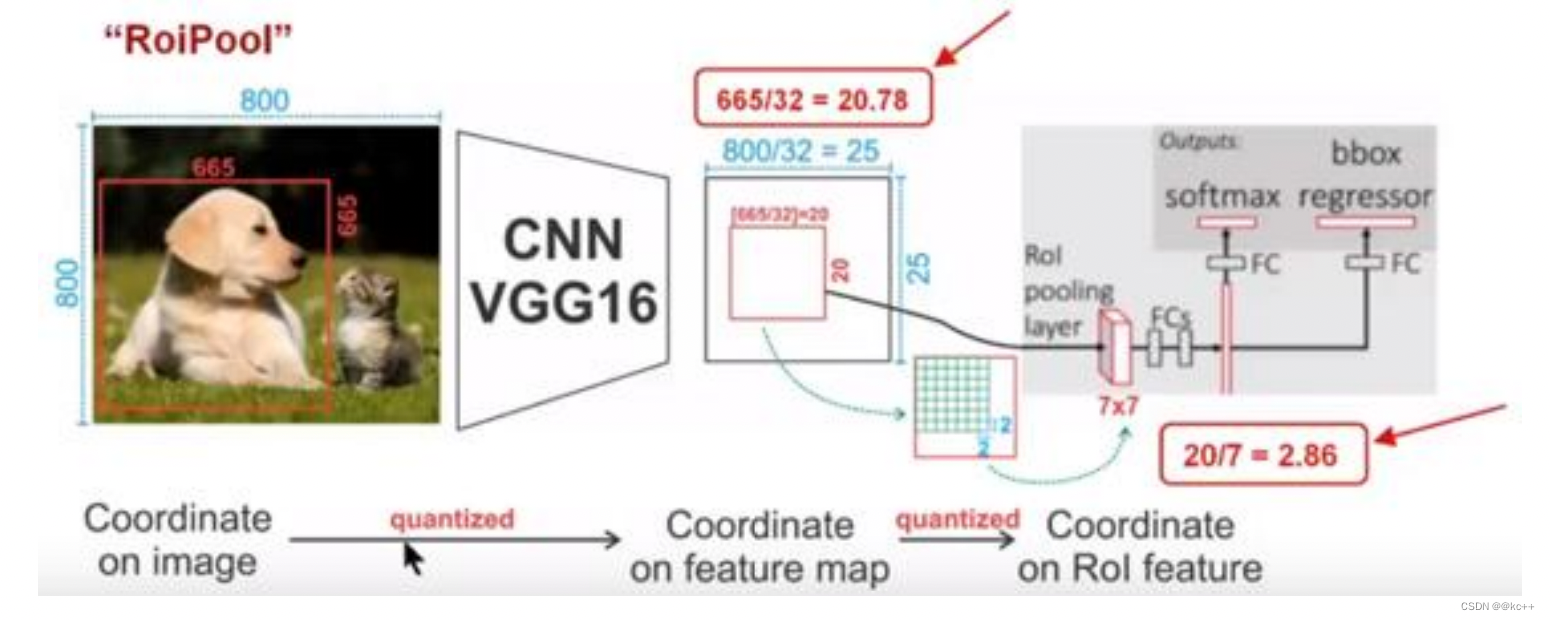
RoIAlign的思想其实很简单,就是取消了取整的这种粗暴做法,而是通过双线性插值来得到固定四个点坐标的像素值,从而使得不连续的操作变得连续起来,返回到原图的时候误差也就更加的小。
它充分的利用了原图中虚拟点(比如20.56这个浮点数。像素位置都是整数值,没有浮点值)四周的四个真实存在的像素值来共同决定目标图中的一个像素值,即可以将20.56这个虚拟的位置点对应的像素值估计出来。
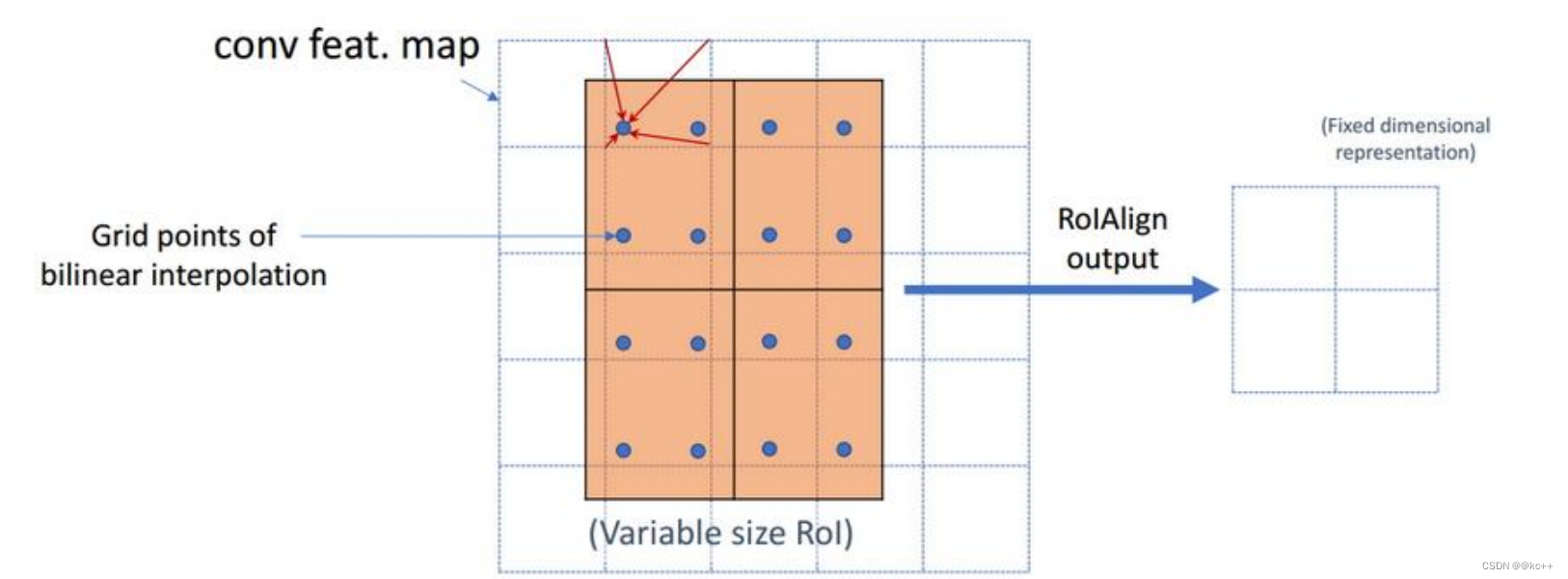
- 蓝色的虚线框表示卷积后获得的feature map,黑色实线框表示ROI feature。
- 最后需要输出的大小是2x2,那么我们就利用双线性插值来估计这些蓝点(虚拟坐标点,又称双线性插值的网格点)处所对应的像素值,最后得到相应的输出。
- 然后在每一个橘红色的区域里面进行max pooling或者average pooling操作,获得最终2x2的输出结果。我们的整个过程中没有用到量化操作,没有引入误差,即原图中的像素和feature map中的像素是完全对齐的,没有偏差,这不仅会提高检测的精度,同时也会有利于实例分割。
3.9 Mask R-CNN:分割掩膜
获得感兴趣区域(ROI)后,给已有框架加上一个掩膜分支,每个囊括特定对象的区域都会被赋予一个掩膜。每个区域都会被赋予一个m X m掩膜,并按比例放大以便推断。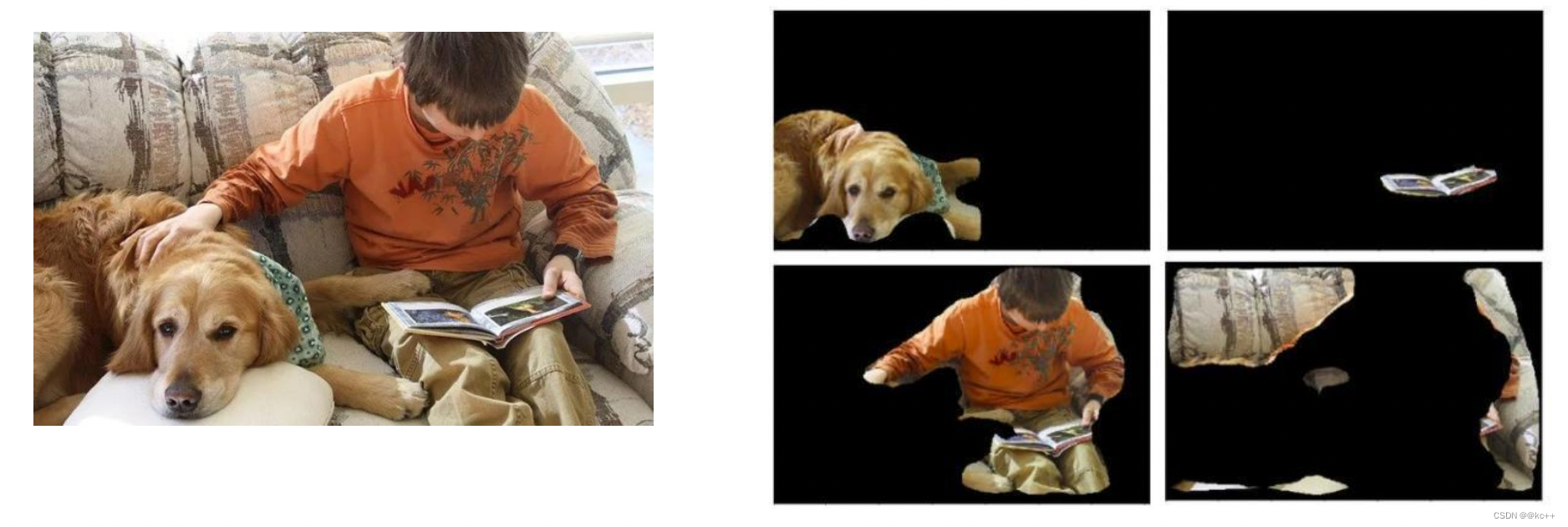
mask语义分割信息的获取
在之前的步骤中,我们获得了预测框,我们把这个预测框作为mask模型的区域截取部分,利用这个预测框对mask模型中用到的公用特征层进行截取。
截取后,利用mask模型再对像素点进行分类,获得语义分割结果。
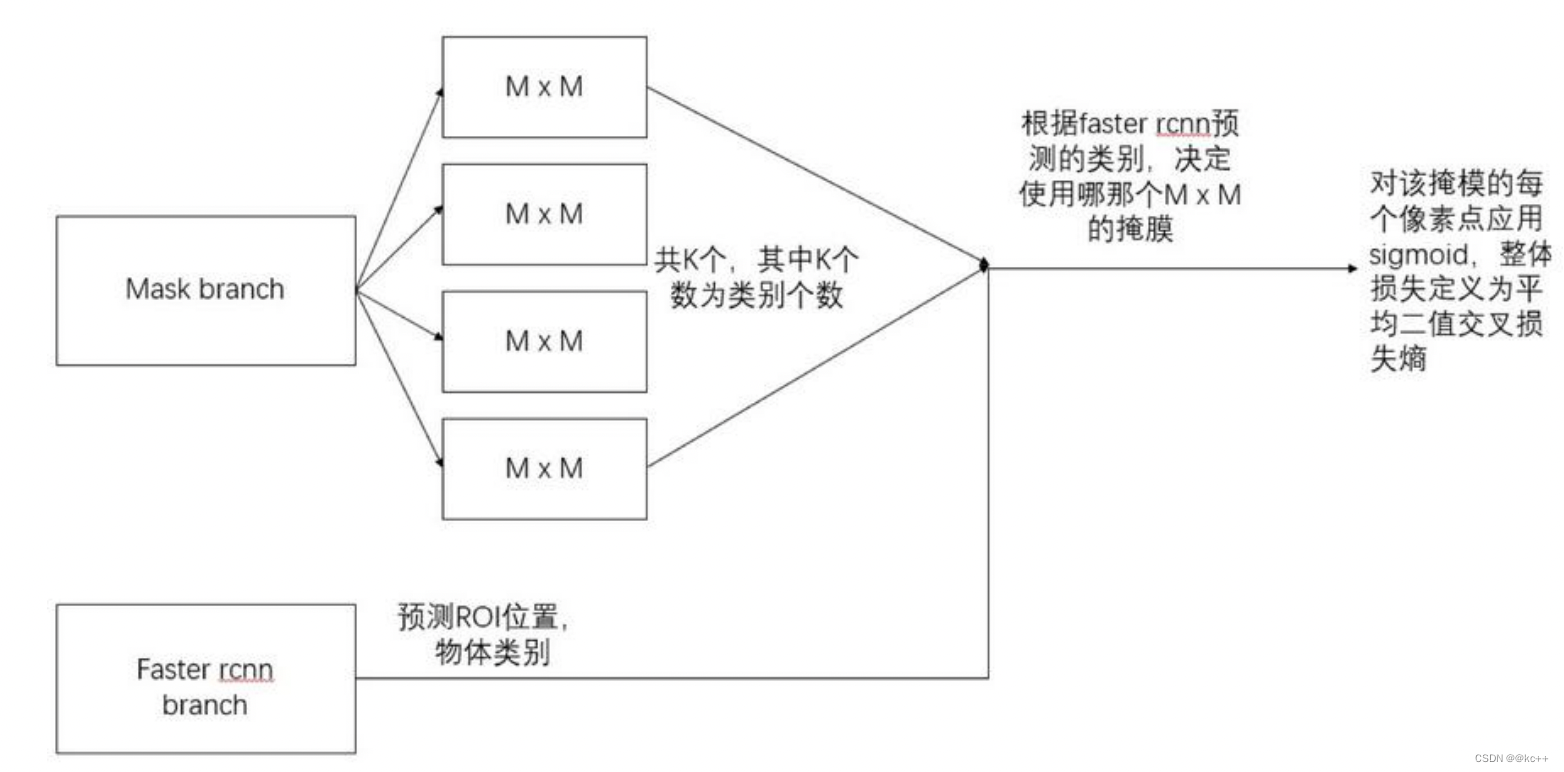
mask分支采用FCN对每个RoI产生一个Kmm的输出,即K个分辨率为m*m的二值的掩膜,K为分类物体的种类数目。
Kmm二值mask结构解释:最终的FCN输出一个K层的mask,每一层为一类。用0.5作为阈值进行二值化,产生背景和前景的分割Mask。
对于预测的二值掩膜输出,我们对每个像素点应用sigmoid函数(或softmax等),整体损失定义为交叉熵。引入预测K个输出的机制,允许每个类都生成独立的掩膜,避免类间竞争。这样做解耦了掩膜和种类预测。
Mask R-CNN的损失函数为: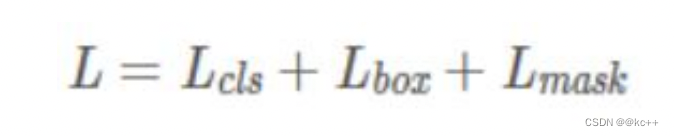
Lmask 使得网络能够输出每一类的 mask,且不会有不同类别 mask 间的竞争:
- 分类网络分支预测 object 类别标签,以选择输出 mask。对每一个ROI,如果检测得到的ROI属于哪一个分类,就只使用哪一个分支的交叉熵误差作为误差值进行计算。
- 举例说明:分类有3类(猫,狗,人),检测得到当前ROI属于“人”这一类,那么所使用的Lmask为 “人”这一分支的mask,即每个class类别对应一个mask可以有效避免类间竞争(其他class不贡献Loss)
- 对每一个像素应用sigmoid,然后取RoI上所有像素的交叉熵的平均值作为Lmask。
最后网络输出为1414或者2828大小的mask,如何与原图目标对应?
需要一个后处理,将模型预测的mask通过resize得到与proposal中目标相同大小的mask。
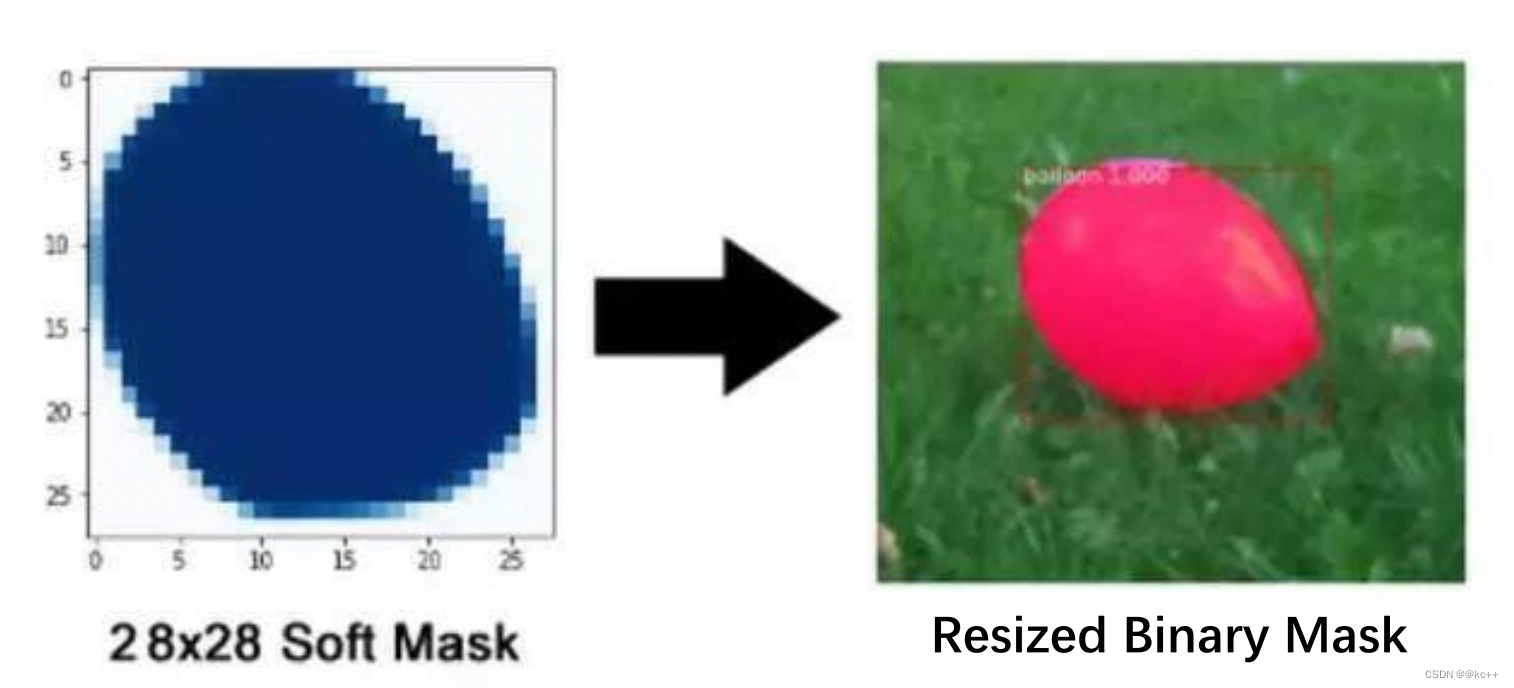
3.10 Mask R-CNN—总结
主要改进点:
- 基础网络的增强,ResNet-101+FPN的组合可以说是现在特征学习的王牌了;
- 分割 loss 的改进, 二值交叉熵会使得每一类的 mask 不相互竞争,而不是和其他类别的 mask 比较
- ROIAlign解决不对齐的问题,就是对 feature map 的插值。直接的ROIPooling的那种量化操作会使得得到的mask与实际物体位置有一个微小偏移,是工程上更好的实现方式。
3.11 Mask R-CNN:COCO数据集
MS COCO的全称是Microsoft Common Objects in Context,起源于微软于2014年出资标注的 Microsoft COCO数据集,与ImageNet竞赛一样,被视为是计算机视觉领域最受关注和最权威的比赛之一。
COCO数据集是一个大型的、丰富的物体检测,分割和字幕数据集。这个数据集以scene understanding为目标,主要从复杂的日常场景中截取图像中的目标,通过精确的segmentation 进行位置的标定。
包括:
- 对象分割;
- 在上下文中可识别;
- 超像素分割;
- 330K图像(> 200K标记);
- 150万个对象实例;
- 80个对象类别;
- 91个类别;
- 每张图片5个字幕;
- 有关键点的250,000人;
4. 视频结构化
视频结构化:
原始的视频图像实际上是一种非结构化的数据,它不能直接被计算机读取和识别,为了 让视频图像在安防等领域更好的应用,就必须使用智能视频分析技术对视频图像进行结构化处理,也就是视频结构化。
视频结构化,即视频数据的结构化处理,就是通过对原始视频进行智能分析,提取出关键信息
一段视频里面,需要提取的关键信息有哪些?
主要是有两类:
- 第一类是运动目标的识别,也就是画面中运动对象的识别,是人还是车;
- 第二类是运动目标特征的识别,也就是画面中运动的人、车、物有什么特征;
5. 代码示例
5.1 nets
layers.py
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.engine import Layer
import numpy as np
from utils import utils
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# Proposal Layer
# 该部分代码用于将先验框转化成建议框
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def apply_box_deltas_graph(boxes, deltas):
# 计算先验框的中心和宽高
height = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
width = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
center_y = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * height
center_x = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * width
# 计算出调整后的先验框的中心和宽高
center_y += deltas[:, 0] * height
center_x += deltas[:, 1] * width
height *= tf.exp(deltas[:, 2])
width *= tf.exp(deltas[:, 3])
# 计算左上角和右下角的点的坐标
y1 = center_y - 0.5 * height
x1 = center_x - 0.5 * width
y2 = y1 + height
x2 = x1 + width
result = tf.stack([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis=1, name="apply_box_deltas_out")
return result
def clip_boxes_graph(boxes, window):
"""
boxes: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
window: [4] in the form y1, x1, y2, x2
"""
# Split
wy1, wx1, wy2, wx2 = tf.split(window, 4)
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(boxes, 4, axis=1)
# Clip
y1 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(y1, wy2), wy1)
x1 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(x1, wx2), wx1)
y2 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(y2, wy2), wy1)
x2 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(x2, wx2), wx1)
clipped = tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis=1, name="clipped_boxes")
clipped.set_shape((clipped.shape[0], 4))
return clipped
class ProposalLayer(Layer):
def __init__(self, proposal_count, nms_threshold, config=None, **kwargs):
super(ProposalLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.config = config
self.proposal_count = proposal_count
self.nms_threshold = nms_threshold
# [rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors]
def call(self, inputs):
# 代表这个先验框内部是否有物体[batch, num_rois, 1]
scores = inputs[0][:, :, 1]
# 代表这个先验框的调整参数[batch, num_rois, 4]
deltas = inputs[1]
# [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2],改变数量级
deltas = deltas * np.reshape(self.config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV, [1, 1, 4])
# Anchors
anchors = inputs[2]
# 筛选出得分前6000个的框
pre_nms_limit = tf.minimum(self.config.PRE_NMS_LIMIT, tf.shape(anchors)[1])
# 获得这些框的索引
ix = tf.nn.top_k(scores, pre_nms_limit, sorted=True,
name="top_anchors").indices
# 获得这些框的得分
scores = utils.batch_slice([scores, ix], lambda x, y: tf.gather(x, y),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# 获得这些框的调整参数
deltas = utils.batch_slice([deltas, ix], lambda x, y: tf.gather(x, y),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# 获得这些框对应的先验框
pre_nms_anchors = utils.batch_slice([anchors, ix], lambda a, x: tf.gather(a, x),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU,
names=["pre_nms_anchors"])
# [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 对先验框进行解码
boxes = utils.batch_slice([pre_nms_anchors, deltas],
lambda x, y: apply_box_deltas_graph(x, y),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU,
names=["refined_anchors"])
# [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 防止超出图片范围
window = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1], dtype=np.float32)
boxes = utils.batch_slice(boxes,
lambda x: clip_boxes_graph(x, window),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU,
names=["refined_anchors_clipped"])
# 非极大抑制
def nms(boxes, scores):
indices = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
boxes, scores, self.proposal_count,
self.nms_threshold, name="rpn_non_max_suppression")
proposals = tf.gather(boxes, indices)
# 如果数量达不到设置的建议框数量的话
# 就padding
padding = tf.maximum(self.proposal_count - tf.shape(proposals)[0], 0)
proposals = tf.pad(proposals, [(0, padding), (0, 0)])
return proposals
proposals = utils.batch_slice([boxes, scores], nms,
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
return proposals
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (None, self.proposal_count, 4)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# ROIAlign Layer
# 利用建议框在特征层上截取内容
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def log2_graph(x):
return tf.log(x) / tf.log(2.0)
def parse_image_meta_graph(meta):
"""
将meta里面的参数进行分割
"""
image_id = meta[:, 0]
original_image_shape = meta[:, 1:4]
image_shape = meta[:, 4:7]
window = meta[:, 7:11] # (y1, x1, y2, x2) window of image in in pixels
scale = meta[:, 11]
active_class_ids = meta[:, 12:]
return {
"image_id": image_id,
"original_image_shape": original_image_shape,
"image_shape": image_shape,
"window": window,
"scale": scale,
"active_class_ids": active_class_ids,
}
class PyramidROIAlign(Layer):
def __init__(self, pool_shape, **kwargs):
super(PyramidROIAlign, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.pool_shape = tuple(pool_shape)
def call(self, inputs):
# 建议框的位置
boxes = inputs[0]
# image_meta包含了一些必要的图片信息
image_meta = inputs[1]
# 取出所有的特征层[batch, height, width, channels]
feature_maps = inputs[2:]
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(boxes, 4, axis=2)
h = y2 - y1
w = x2 - x1
# 获得输入进来的图像的大小
image_shape = parse_image_meta_graph(image_meta)['image_shape'][0]
# 通过建议框的大小找到这个建议框属于哪个特征层
image_area = tf.cast(image_shape[0] * image_shape[1], tf.float32)
roi_level = log2_graph(tf.sqrt(h * w) / (224.0 / tf.sqrt(image_area)))
roi_level = tf.minimum(5, tf.maximum(
2, 4 + tf.cast(tf.round(roi_level), tf.int32)))
# batch_size, box_num
roi_level = tf.squeeze(roi_level, 2)
# Loop through levels and apply ROI pooling to each. P2 to P5.
pooled = []
box_to_level = []
# 分别在P2-P5中进行截取
for i, level in enumerate(range(2, 6)):
# 找到每个特征层对应box
ix = tf.where(tf.equal(roi_level, level))
level_boxes = tf.gather_nd(boxes, ix)
box_to_level.append(ix)
# 获得这些box所属的图片
box_indices = tf.cast(ix[:, 0], tf.int32)
# 停止梯度下降
level_boxes = tf.stop_gradient(level_boxes)
box_indices = tf.stop_gradient(box_indices)
# Result: [batch * num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels]
pooled.append(tf.image.crop_and_resize(
feature_maps[i], level_boxes, box_indices, self.pool_shape,
method="bilinear"))
pooled = tf.concat(pooled, axis=0)
# 将顺序和所属的图片进行堆叠
box_to_level = tf.concat(box_to_level, axis=0)
box_range = tf.expand_dims(tf.range(tf.shape(box_to_level)[0]), 1)
box_to_level = tf.concat([tf.cast(box_to_level, tf.int32), box_range],
axis=1)
# box_to_level[:, 0]表示第几张图
# box_to_level[:, 1]表示第几张图里的第几个框
sorting_tensor = box_to_level[:, 0] * 100000 + box_to_level[:, 1]
# 进行排序,将同一张图里的某一些聚集在一起
ix = tf.nn.top_k(sorting_tensor, k=tf.shape(
box_to_level)[0]).indices[::-1]
# 按顺序获得图片的索引
ix = tf.gather(box_to_level[:, 2], ix)
pooled = tf.gather(pooled, ix)
# 重新reshape为原来的格式
# 也就是
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, POOL_SIZE, POOL_SIZE, channels]
shape = tf.concat([tf.shape(boxes)[:2], tf.shape(pooled)[1:]], axis=0)
pooled = tf.reshape(pooled, shape)
return pooled
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape[0][:2] + self.pool_shape + (input_shape[2][-1], )
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# Detection Layer
#
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def refine_detections_graph(rois, probs, deltas, window, config):
"""细化分类建议并过滤重叠部分并返回最终结果探测。
Inputs:
rois: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
probs: [N, num_classes]. Class probabilities.
deltas: [N, num_classes, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]. Class-specific
bounding box deltas.
window: (y1, x1, y2, x2) in normalized coordinates. The part of the image
that contains the image excluding the padding.
Returns detections shaped: [num_detections, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)] where
coordinates are normalized.
"""
# 找到得分最高的类
class_ids = tf.argmax(probs, axis=1, output_type=tf.int32)
# 序号+类
indices = tf.stack([tf.range(probs.shape[0]), class_ids], axis=1)
# 取出成绩
class_scores = tf.gather_nd(probs, indices)
# 还有框的调整参数
deltas_specific = tf.gather_nd(deltas, indices)
# 进行解码
# Shape: [boxes, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
refined_rois = apply_box_deltas_graph(
rois, deltas_specific * config.BBOX_STD_DEV)
# 防止超出0-1
refined_rois = clip_boxes_graph(refined_rois, window)
# 去除背景
keep = tf.where(class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
# 去除背景和得分小的区域
if config.DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE:
conf_keep = tf.where(class_scores >= config.DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE)[:, 0]
keep = tf.sets.set_intersection(tf.expand_dims(keep, 0),
tf.expand_dims(conf_keep, 0))
keep = tf.sparse_tensor_to_dense(keep)[0]
# 获得除去背景并且得分较高的框还有种类与得分
# 1. Prepare variables
pre_nms_class_ids = tf.gather(class_ids, keep)
pre_nms_scores = tf.gather(class_scores, keep)
pre_nms_rois = tf.gather(refined_rois, keep)
unique_pre_nms_class_ids = tf.unique(pre_nms_class_ids)[0]
def nms_keep_map(class_id):
ixs = tf.where(tf.equal(pre_nms_class_ids, class_id))[:, 0]
class_keep = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
tf.gather(pre_nms_rois, ixs),
tf.gather(pre_nms_scores, ixs),
max_output_size=config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES,
iou_threshold=config.DETECTION_NMS_THRESHOLD)
class_keep = tf.gather(keep, tf.gather(ixs, class_keep))
gap = config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES - tf.shape(class_keep)[0]
class_keep = tf.pad(class_keep, [(0, gap)],
mode='CONSTANT', constant_values=-1)
class_keep.set_shape([config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES])
return class_keep
# 2. 进行非极大抑制
nms_keep = tf.map_fn(nms_keep_map, unique_pre_nms_class_ids,
dtype=tf.int64)
# 3. 找到符合要求的需要被保留的建议框
nms_keep = tf.reshape(nms_keep, [-1])
nms_keep = tf.gather(nms_keep, tf.where(nms_keep > -1)[:, 0])
# 4. Compute intersection between keep and nms_keep
keep = tf.sets.set_intersection(tf.expand_dims(keep, 0),
tf.expand_dims(nms_keep, 0))
keep = tf.sparse_tensor_to_dense(keep)[0]
# 寻找得分最高的num_keep个框
roi_count = config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES
class_scores_keep = tf.gather(class_scores, keep)
num_keep = tf.minimum(tf.shape(class_scores_keep)[0], roi_count)
top_ids = tf.nn.top_k(class_scores_keep, k=num_keep, sorted=True)[1]
keep = tf.gather(keep, top_ids)
# Arrange output as [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)]
detections = tf.concat([
tf.gather(refined_rois, keep),
tf.to_float(tf.gather(class_ids, keep))[..., tf.newaxis],
tf.gather(class_scores, keep)[..., tf.newaxis]
], axis=1)
# 如果达不到数量的话就padding
gap = config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES - tf.shape(detections)[0]
detections = tf.pad(detections, [(0, gap), (0, 0)], "CONSTANT")
return detections
def norm_boxes_graph(boxes, shape):
h, w = tf.split(tf.cast(shape, tf.float32), 2)
scale = tf.concat([h, w, h, w], axis=-1) - tf.constant(1.0)
shift = tf.constant([0., 0., 1., 1.])
return tf.divide(boxes - shift, scale)
class DetectionLayer(Layer):
def __init__(self, config=None, **kwargs):
super(DetectionLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.config = config
def call(self, inputs):
rois = inputs[0]
mrcnn_class = inputs[1]
mrcnn_bbox = inputs[2]
image_meta = inputs[3]
# 找到window的小数形式
m = parse_image_meta_graph(image_meta)
image_shape = m['image_shape'][0]
window = norm_boxes_graph(m['window'], image_shape[:2])
# Run detection refinement graph on each item in the batch
detections_batch = utils.batch_slice(
[rois, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, window],
lambda x, y, w, z: refine_detections_graph(x, y, w, z, self.config),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# Reshape output
# [batch, num_detections, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, class_score)] in
# normalized coordinates
return tf.reshape(
detections_batch,
[self.config.BATCH_SIZE, self.config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES, 6])
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (None, self.config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES, 6)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# Detection Target Layer
# 该部分代码会输入建议框
# 判断建议框和真实框的重合情况
# 筛选出内部包含物体的建议框
# 利用建议框和真实框编码
# 调整mask的格式使得其和预测格式相同
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def overlaps_graph(boxes1, boxes2):
"""
用于计算boxes1和boxes2的重合程度
boxes1, boxes2: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)].
返回 [len(boxes1), len(boxes2)]
"""
b1 = tf.reshape(tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(boxes1, 1),
[1, 1, tf.shape(boxes2)[0]]), [-1, 4])
b2 = tf.tile(boxes2, [tf.shape(boxes1)[0], 1])
b1_y1, b1_x1, b1_y2, b1_x2 = tf.split(b1, 4, axis=1)
b2_y1, b2_x1, b2_y2, b2_x2 = tf.split(b2, 4, axis=1)
y1 = tf.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)
x1 = tf.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)
y2 = tf.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2)
x2 = tf.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2)
intersection = tf.maximum(x2 - x1, 0) * tf.maximum(y2 - y1, 0)
b1_area = (b1_y2 - b1_y1) * (b1_x2 - b1_x1)
b2_area = (b2_y2 - b2_y1) * (b2_x2 - b2_x1)
union = b1_area + b2_area - intersection
iou = intersection / union
overlaps = tf.reshape(iou, [tf.shape(boxes1)[0], tf.shape(boxes2)[0]])
return overlaps
def detection_targets_graph(proposals, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks, config):
asserts = [
tf.Assert(tf.greater(tf.shape(proposals)[0], 0), [proposals],
name="roi_assertion"),
]
with tf.control_dependencies(asserts):
proposals = tf.identity(proposals)
# 移除之前获得的padding的部分
proposals, _ = trim_zeros_graph(proposals, name="trim_proposals")
gt_boxes, non_zeros = trim_zeros_graph(gt_boxes, name="trim_gt_boxes")
gt_class_ids = tf.boolean_mask(gt_class_ids, non_zeros,
name="trim_gt_class_ids")
gt_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, tf.where(non_zeros)[:, 0], axis=2,
name="trim_gt_masks")
# Handle COCO crowds
# A crowd box in COCO is a bounding box around several instances. Exclude
# them from training. A crowd box is given a negative class ID.
crowd_ix = tf.where(gt_class_ids < 0)[:, 0]
non_crowd_ix = tf.where(gt_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
crowd_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, crowd_ix)
gt_class_ids = tf.gather(gt_class_ids, non_crowd_ix)
gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, non_crowd_ix)
gt_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, non_crowd_ix, axis=2)
# 计算建议框和所有真实框的重合程度 [proposals, gt_boxes]
overlaps = overlaps_graph(proposals, gt_boxes)
# 计算和 crowd boxes 的重合程度 [proposals, crowd_boxes]
crowd_overlaps = overlaps_graph(proposals, crowd_boxes)
crowd_iou_max = tf.reduce_max(crowd_overlaps, axis=1)
no_crowd_bool = (crowd_iou_max < 0.001)
# Determine positive and negative ROIs
roi_iou_max = tf.reduce_max(overlaps, axis=1)
# 1. 正样本建议框和真实框的重合程度大于0.5
positive_roi_bool = (roi_iou_max >= 0.5)
positive_indices = tf.where(positive_roi_bool)[:, 0]
# 2. 负样本建议框和真实框的重合程度小于0.5,Skip crowds.
negative_indices = tf.where(tf.logical_and(roi_iou_max < 0.5, no_crowd_bool))[:, 0]
# Subsample ROIs. Aim for 33% positive
# 进行正负样本的平衡
# 取出最大33%的正样本
positive_count = int(config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE *
config.ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO)
positive_indices = tf.random_shuffle(positive_indices)[:positive_count]
positive_count = tf.shape(positive_indices)[0]
# 保持正负样本比例
r = 1.0 / config.ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO
negative_count = tf.cast(r * tf.cast(positive_count, tf.float32), tf.int32) - positive_count
negative_indices = tf.random_shuffle(negative_indices)[:negative_count]
# 获得正样本和负样本
positive_rois = tf.gather(proposals, positive_indices)
negative_rois = tf.gather(proposals, negative_indices)
# 获取建议框和真实框重合程度
positive_overlaps = tf.gather(overlaps, positive_indices)
# 判断是否有真实框
roi_gt_box_assignment = tf.cond(
tf.greater(tf.shape(positive_overlaps)[1], 0),
true_fn = lambda: tf.argmax(positive_overlaps, axis=1),
false_fn = lambda: tf.cast(tf.constant([]),tf.int64)
)
# 找到每一个建议框对应的真实框和种类
roi_gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, roi_gt_box_assignment)
roi_gt_class_ids = tf.gather(gt_class_ids, roi_gt_box_assignment)
# 解码获得网络应该有得预测结果
deltas = utils.box_refinement_graph(positive_rois, roi_gt_boxes)
deltas /= config.BBOX_STD_DEV
# 切换mask的形式[N, height, width, 1]
transposed_masks = tf.expand_dims(tf.transpose(gt_masks, [2, 0, 1]), -1)
# 取出对应的层
roi_masks = tf.gather(transposed_masks, roi_gt_box_assignment)
# Compute mask targets
boxes = positive_rois
if config.USE_MINI_MASK:
# Transform ROI coordinates from normalized image space
# to normalized mini-mask space.
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(positive_rois, 4, axis=1)
gt_y1, gt_x1, gt_y2, gt_x2 = tf.split(roi_gt_boxes, 4, axis=1)
gt_h = gt_y2 - gt_y1
gt_w = gt_x2 - gt_x1
y1 = (y1 - gt_y1) / gt_h
x1 = (x1 - gt_x1) / gt_w
y2 = (y2 - gt_y1) / gt_h
x2 = (x2 - gt_x1) / gt_w
boxes = tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], 1)
box_ids = tf.range(0, tf.shape(roi_masks)[0])
masks = tf.image.crop_and_resize(tf.cast(roi_masks, tf.float32), boxes,
box_ids,
config.MASK_SHAPE)
# Remove the extra dimension from masks.
masks = tf.squeeze(masks, axis=3)
# 防止resize后的结果不是1或者0
masks = tf.round(masks)
# 一般传入config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE个建议框进行训练,
# 如果数量不够则padding
rois = tf.concat([positive_rois, negative_rois], axis=0)
N = tf.shape(negative_rois)[0]
P = tf.maximum(config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE - tf.shape(rois)[0], 0)
rois = tf.pad(rois, [(0, P), (0, 0)])
roi_gt_boxes = tf.pad(roi_gt_boxes, [(0, N + P), (0, 0)])
roi_gt_class_ids = tf.pad(roi_gt_class_ids, [(0, N + P)])
deltas = tf.pad(deltas, [(0, N + P), (0, 0)])
masks = tf.pad(masks, [[0, N + P], (0, 0), (0, 0)])
return rois, roi_gt_class_ids, deltas, masks
def trim_zeros_graph(boxes, name='trim_zeros'):
"""
如果前一步没有满POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING个建议框,会有padding
要去掉padding
"""
non_zeros = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(boxes), axis=1), tf.bool)
boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, non_zeros, name=name)
return boxes, non_zeros
class DetectionTargetLayer(Layer):
"""找到建议框的ground_truth
Inputs:
proposals: [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]建议框
gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]每个真实框对应的类
gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]真实框的位置
gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]真实框的语义分割情况
Returns:
rois: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]内部真实存在目标的建议框
target_class_ids: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE]每个建议框对应的类
target_deltas: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw)]每个建议框应该有的调整参数
target_mask: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, height, width]每个建议框语义分割情况
"""
def __init__(self, config, **kwargs):
super(DetectionTargetLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.config = config
def call(self, inputs):
proposals = inputs[0]
gt_class_ids = inputs[1]
gt_boxes = inputs[2]
gt_masks = inputs[3]
# 对真实框进行编码
names = ["rois", "target_class_ids", "target_bbox", "target_mask"]
outputs = utils.batch_slice(
[proposals, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks],
lambda w, x, y, z: detection_targets_graph(
w, x, y, z, self.config),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU, names=names)
return outputs
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return [
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, 4), # rois
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE), # class_ids
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, 4), # deltas
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, self.config.MASK_SHAPE[0],
self.config.MASK_SHAPE[1]) # masks
]
def compute_mask(self, inputs, mask=None):
return [None, None, None, None]
mrcnn_training.py
import tensorflow as tf
import keras.backend as K
import random
import numpy as np
import logging
from utils import utils
from utils.anchors import compute_backbone_shapes,generate_pyramid_anchors
############################################################
# Loss Functions
############################################################
def batch_pack_graph(x, counts, num_rows):
"""Picks different number of values from each row
in x depending on the values in counts.
"""
outputs = []
for i in range(num_rows):
outputs.append(x[i, :counts[i]])
return tf.concat(outputs, axis=0)
def smooth_l1_loss(y_true, y_pred):
"""Implements Smooth-L1 loss.
y_true and y_pred are typically: [N, 4], but could be any shape.
"""
diff = K.abs(y_true - y_pred)
less_than_one = K.cast(K.less(diff, 1.0), "float32")
loss = (less_than_one * 0.5 * diff**2) + (1 - less_than_one) * (diff - 0.5)
return loss
def rpn_class_loss_graph(rpn_match, rpn_class_logits):
"""RPN anchor classifier loss.
rpn_match: [batch, anchors, 1]. Anchor match type. 1=positive,
-1=negative, 0=neutral anchor.
rpn_class_logits: [batch, anchors, 2]. RPN classifier logits for BG/FG.
"""
# Squeeze last dim to simplify
rpn_match = tf.squeeze(rpn_match, -1)
# Get anchor classes. Convert the -1/+1 match to 0/1 values.
anchor_class = K.cast(K.equal(rpn_match, 1), tf.int32)
# Positive and Negative anchors contribute to the loss,
# but neutral anchors (match value = 0) don't.
indices = tf.where(K.not_equal(rpn_match, 0))
# Pick rows that contribute to the loss and filter out the rest.
rpn_class_logits = tf.gather_nd(rpn_class_logits, indices)
anchor_class = tf.gather_nd(anchor_class, indices)
# Cross entropy loss
loss = K.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(target=anchor_class,
output=rpn_class_logits,
from_logits=True)
loss = K.switch(tf.size(loss) > 0, K.mean(loss), tf.constant(0.0))
return loss
def rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, target_bbox, rpn_match, rpn_bbox):
"""Return the RPN bounding box loss graph.
config: the model config object.
target_bbox: [batch, max positive anchors, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))].
Uses 0 padding to fill in unsed bbox deltas.
rpn_match: [batch, anchors, 1]. Anchor match type. 1=positive,
-1=negative, 0=neutral anchor.
rpn_bbox: [batch, anchors, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
"""
# Positive anchors contribute to the loss, but negative and
# neutral anchors (match value of 0 or -1) don't.
rpn_match = K.squeeze(rpn_match, -1)
indices = tf.where(K.equal(rpn_match, 1))
# Pick bbox deltas that contribute to the loss
rpn_bbox = tf.gather_nd(rpn_bbox, indices)
# Trim target bounding box deltas to the same length as rpn_bbox.
batch_counts = K.sum(K.cast(K.equal(rpn_match, 1), tf.int32), axis=1)
target_bbox = batch_pack_graph(target_bbox, batch_counts,
config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
loss = smooth_l1_loss(target_bbox, rpn_bbox)
loss = K.switch(tf.size(loss) > 0, K.mean(loss), tf.constant(0.0))
return loss
def mrcnn_class_loss_graph(target_class_ids, pred_class_logits,
active_class_ids):
"""Loss for the classifier head of Mask RCNN.
target_class_ids: [batch, num_rois]. Integer class IDs. Uses zero
padding to fill in the array.
pred_class_logits: [batch, num_rois, num_classes]
active_class_ids: [batch, num_classes]. Has a value of 1 for
classes that are in the dataset of the image, and 0
for classes that are not in the dataset.
"""
# During model building, Keras calls this function with
# target_class_ids of type float32. Unclear why. Cast it
# to int to get around it.
target_class_ids = tf.cast(target_class_ids, 'int64')
# Find predictions of classes that are not in the dataset.
pred_class_ids = tf.argmax(pred_class_logits, axis=2)
# TODO: Update this line to work with batch > 1. Right now it assumes all
# images in a batch have the same active_class_ids
pred_active = tf.gather(active_class_ids[0], pred_class_ids)
# Loss
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=target_class_ids, logits=pred_class_logits)
# Erase losses of predictions of classes that are not in the active
# classes of the image.
loss = loss * pred_active
# Computer loss mean. Use only predictions that contribute
# to the loss to get a correct mean.
loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / tf.reduce_sum(pred_active)
return loss
def mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(target_bbox, target_class_ids, pred_bbox):
"""Loss for Mask R-CNN bounding box refinement.
target_bbox: [batch, num_rois, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
target_class_ids: [batch, num_rois]. Integer class IDs.
pred_bbox: [batch, num_rois, num_classes, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
"""
# Reshape to merge batch and roi dimensions for simplicity.
target_class_ids = K.reshape(target_class_ids, (-1,))
target_bbox = K.reshape(target_bbox, (-1, 4))
pred_bbox = K.reshape(pred_bbox, (-1, K.int_shape(pred_bbox)[2], 4))
# Only positive ROIs contribute to the loss. And only
# the right class_id of each ROI. Get their indices.
positive_roi_ix = tf.where(target_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
positive_roi_class_ids = tf.cast(
tf.gather(target_class_ids, positive_roi_ix), tf.int64)
indices = tf.stack([positive_roi_ix, positive_roi_class_ids], axis=1)
# Gather the deltas (predicted and true) that contribute to loss
target_bbox = tf.gather(target_bbox, positive_roi_ix)
pred_bbox = tf.gather_nd(pred_bbox, indices)
# Smooth-L1 Loss
loss = K.switch(tf.size(target_bbox) > 0,
smooth_l1_loss(y_true=target_bbox, y_pred=pred_bbox),
tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.mean(loss)
return loss
def mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(target_masks, target_class_ids, pred_masks):
"""Mask binary cross-entropy loss for the masks head.
target_masks: [batch, num_rois, height, width].
A float32 tensor of values 0 or 1. Uses zero padding to fill array.
target_class_ids: [batch, num_rois]. Integer class IDs. Zero padded.
pred_masks: [batch, proposals, height, width, num_classes] float32 tensor
with values from 0 to 1.
"""
# Reshape for simplicity. Merge first two dimensions into one.
target_class_ids = K.reshape(target_class_ids, (-1,))
mask_shape = tf.shape(target_masks)
target_masks = K.reshape(target_masks, (-1, mask_shape[2], mask_shape[3]))
pred_shape = tf.shape(pred_masks)
pred_masks = K.reshape(pred_masks,
(-1, pred_shape[2], pred_shape[3], pred_shape[4]))
# Permute predicted masks to [N, num_classes, height, width]
pred_masks = tf.transpose(pred_masks, [0, 3, 1, 2])
# Only positive ROIs contribute to the loss. And only
# the class specific mask of each ROI.
positive_ix = tf.where(target_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
positive_class_ids = tf.cast(
tf.gather(target_class_ids, positive_ix), tf.int64)
indices = tf.stack([positive_ix, positive_class_ids], axis=1)
# Gather the masks (predicted and true) that contribute to loss
y_true = tf.gather(target_masks, positive_ix)
y_pred = tf.gather_nd(pred_masks, indices)
# Compute binary cross entropy. If no positive ROIs, then return 0.
# shape: [batch, roi, num_classes]
loss = K.switch(tf.size(y_true) > 0,
K.binary_crossentropy(target=y_true, output=y_pred),
tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.mean(loss)
return loss
############################################################
# Data Generator
############################################################
def load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=False, augmentation=None,
use_mini_mask=False):
# 载入图片和语义分割效果
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
# print("\nbefore:",image_id,np.shape(mask),np.shape(class_ids))
# 原始shape
original_shape = image.shape
# 获得新图片,原图片在新图片中的位置,变化的尺度,填充的情况等
image, window, scale, padding, crop = utils.resize_image(
image,
min_dim=config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM,
min_scale=config.IMAGE_MIN_SCALE,
max_dim=config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM,
mode=config.IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE)
mask = utils.resize_mask(mask, scale, padding, crop)
# print("\nafter:",np.shape(mask),np.shape(class_ids))
# print(np.shape(image),np.shape(mask))
# 可以把图片进行翻转
if augment:
logging.warning("'augment' is deprecated. Use 'augmentation' instead.")
if random.randint(0, 1):
image = np.fliplr(image)
mask = np.fliplr(mask)
if augmentation:
import imgaug
# 可用于图像增强
MASK_AUGMENTERS = ["Sequential", "SomeOf", "OneOf", "Sometimes",
"Fliplr", "Flipud", "CropAndPad",
"Affine", "PiecewiseAffine"]
def hook(images, augmenter, parents, default):
"""Determines which augmenters to apply to masks."""
return augmenter.__class__.__name__ in MASK_AUGMENTERS
image_shape = image.shape
mask_shape = mask.shape
det = augmentation.to_deterministic()
image = det.augment_image(image)
mask = det.augment_image(mask.astype(np.uint8),
hooks=imgaug.HooksImages(activator=hook))
assert image.shape == image_shape, "Augmentation shouldn't change image size"
assert mask.shape == mask_shape, "Augmentation shouldn't change mask size"
mask = mask.astype(np.bool)
# 检漏,防止某些层内部实际上不存在语义分割情况
_idx = np.sum(mask, axis=(0, 1)) > 0
# print("\nafterer:",np.shape(mask),np.shape(_idx))
mask = mask[:, :, _idx]
class_ids = class_ids[_idx]
# 找到mask对应的box
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask)
active_class_ids = np.zeros([dataset.num_classes], dtype=np.int32)
source_class_ids = dataset.source_class_ids[dataset.image_info[image_id]["source"]]
active_class_ids[source_class_ids] = 1
if use_mini_mask:
mask = utils.minimize_mask(bbox, mask, config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE)
# 生成Image_meta
image_meta = utils.compose_image_meta(image_id, original_shape, image.shape,
window, scale, active_class_ids)
return image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask
def build_rpn_targets(image_shape, anchors, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, config):
# 1代表正样本
# -1代表负样本
# 0代表忽略
rpn_match = np.zeros([anchors.shape[0]], dtype=np.int32)
# 创建该部分内容利用先验框和真实框进行编码
rpn_bbox = np.zeros((config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE, 4))
'''
iscrowd=0的时候,表示这是一个单独的物体,轮廓用Polygon(多边形的点)表示,
iscrowd=1的时候表示两个没有分开的物体,轮廓用RLE编码表示,比如说一张图片里面有三个人,
一个人单独站一边,另外两个搂在一起(标注的时候距离太近分不开了),这个时候,
单独的那个人的注释里面的iscrowing=0,segmentation用Polygon表示,
而另外两个用放在同一个anatation的数组里面用一个segmention的RLE编码形式表示
'''
crowd_ix = np.where(gt_class_ids < 0)[0]
if crowd_ix.shape[0] > 0:
non_crowd_ix = np.where(gt_class_ids > 0)[0]
crowd_boxes = gt_boxes[crowd_ix]
gt_class_ids = gt_class_ids[non_crowd_ix]
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[non_crowd_ix]
crowd_overlaps = utils.compute_overlaps(anchors, crowd_boxes)
crowd_iou_max = np.amax(crowd_overlaps, axis=1)
no_crowd_bool = (crowd_iou_max < 0.001)
else:
no_crowd_bool = np.ones([anchors.shape[0]], dtype=bool)
# 计算先验框和真实框的重合程度 [num_anchors, num_gt_boxes]
overlaps = utils.compute_overlaps(anchors, gt_boxes)
# 1. 重合程度小于0.3则代表为负样本
anchor_iou_argmax = np.argmax(overlaps, axis=1)
anchor_iou_max = overlaps[np.arange(overlaps.shape[0]), anchor_iou_argmax]
rpn_match[(anchor_iou_max < 0.3) & (no_crowd_bool)] = -1
# 2. 每个真实框重合度最大的先验框是正样本
gt_iou_argmax = np.argwhere(overlaps == np.max(overlaps, axis=0))[:,0]
rpn_match[gt_iou_argmax] = 1
# 3. 重合度大于0.7则代表为正样本
rpn_match[anchor_iou_max >= 0.7] = 1
# 正负样本平衡
# 找到正样本的索引
ids = np.where(rpn_match == 1)[0]
# 如果大于(config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE // 2)则删掉一些
extra = len(ids) - (config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE // 2)
if extra > 0:
ids = np.random.choice(ids, extra, replace=False)
rpn_match[ids] = 0
# 找到负样本的索引
ids = np.where(rpn_match == -1)[0]
# 使得总数为config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE
extra = len(ids) - (config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE -
np.sum(rpn_match == 1))
if extra > 0:
# Rest the extra ones to neutral
ids = np.random.choice(ids, extra, replace=False)
rpn_match[ids] = 0
# 找到内部真实存在物体的先验框,进行编码
ids = np.where(rpn_match == 1)[0]
ix = 0
for i, a in zip(ids, anchors[ids]):
gt = gt_boxes[anchor_iou_argmax[i]]
# 计算真实框的中心,高宽
gt_h = gt[2] - gt[0]
gt_w = gt[3] - gt[1]
gt_center_y = gt[0] + 0.5 * gt_h
gt_center_x = gt[1] + 0.5 * gt_w
# 计算先验框中心,高宽
a_h = a[2] - a[0]
a_w = a[3] - a[1]
a_center_y = a[0] + 0.5 * a_h
a_center_x = a[1] + 0.5 * a_w
# 编码运算
rpn_bbox[ix] = [
(gt_center_y - a_center_y) / a_h,
(gt_center_x - a_center_x) / a_w,
np.log(gt_h / a_h),
np.log(gt_w / a_w),
]
# 改变数量级
rpn_bbox[ix] /= config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV
ix += 1
return rpn_match, rpn_bbox
def data_generator(dataset, config, shuffle=True, augment=False, augmentation=None,
batch_size=1, detection_targets=False,
no_augmentation_sources=None):
"""
inputs list:
- images: [batch, H, W, C]
- image_meta: [batch, (meta data)] Image details. See compose_image_meta()
- rpn_match: [batch, N] Integer (1=positive anchor, -1=negative, 0=neutral)
- rpn_bbox: [batch, N, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Anchor bbox deltas.
- gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] Integer class IDs
- gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
- gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]. The height and width
are those of the image unless use_mini_mask is True, in which
case they are defined in MINI_MASK_SHAPE.
outputs list: Usually empty in regular training. But if detection_targets
is True then the outputs list contains target class_ids, bbox deltas,
and masks.
"""
b = 0 # batch item index
image_index = -1
image_ids = np.copy(dataset.image_ids)
no_augmentation_sources = no_augmentation_sources or []
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 计算获得先验框
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(config, config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
anchors = generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
backbone_shapes,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
while True:
image_index = (image_index + 1) % len(image_ids)
if shuffle and image_index == 0:
np.random.shuffle(image_ids)
# 获得id
image_id = image_ids[image_index]
# 获得图片,真实框,语义分割结果等
if dataset.image_info[image_id]['source'] in no_augmentation_sources:
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=None,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)
else:
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=augmentation,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)
if not np.any(gt_class_ids > 0):
continue
# RPN Targets
rpn_match, rpn_bbox = build_rpn_targets(image.shape, anchors,
gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, config)
# 如果某张图片里面物体的数量大于最大值的话,则进行筛选,防止过大
if gt_boxes.shape[0] > config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES:
ids = np.random.choice(
np.arange(gt_boxes.shape[0]), config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES, replace=False)
gt_class_ids = gt_class_ids[ids]
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[ids]
gt_masks = gt_masks[:, :, ids]
# 初始化用于训练的内容
if b == 0:
batch_image_meta = np.zeros(
(batch_size,) + image_meta.shape, dtype=image_meta.dtype)
batch_rpn_match = np.zeros(
[batch_size, anchors.shape[0], 1], dtype=rpn_match.dtype)
batch_rpn_bbox = np.zeros(
[batch_size, config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE, 4], dtype=rpn_bbox.dtype)
batch_images = np.zeros(
(batch_size,) + image.shape, dtype=np.float32)
batch_gt_class_ids = np.zeros(
(batch_size, config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES), dtype=np.int32)
batch_gt_boxes = np.zeros(
(batch_size, config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES, 4), dtype=np.int32)
batch_gt_masks = np.zeros(
(batch_size, gt_masks.shape[0], gt_masks.shape[1],
config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES), dtype=gt_masks.dtype)
# Add to batch
batch_image_meta[b] = image_meta
batch_rpn_match[b] = rpn_match[:, np.newaxis]
batch_rpn_bbox[b] = rpn_bbox
batch_images[b] = utils.mold_image(image.astype(np.float32), config)
batch_gt_class_ids[b, :gt_class_ids.shape[0]] = gt_class_ids
batch_gt_boxes[b, :gt_boxes.shape[0]] = gt_boxes
batch_gt_masks[b, :, :, :gt_masks.shape[-1]] = gt_masks
b += 1
# Batch full?
if b >= batch_size:
inputs = [batch_images, batch_image_meta, batch_rpn_match, batch_rpn_bbox,
batch_gt_class_ids, batch_gt_boxes, batch_gt_masks]
outputs = []
yield inputs, outputs
# start a new batch
b = 0
mrcnn.py
from keras.layers import Input,ZeroPadding2D,Conv2D,MaxPooling2D,BatchNormalization,Activation,UpSampling2D,Add,Lambda,Concatenate
from keras.layers import Reshape,TimeDistributed,Dense,Conv2DTranspose
from keras.models import Model
import keras.backend as K
from nets.resnet import get_resnet
from nets.layers import ProposalLayer,PyramidROIAlign,DetectionLayer,DetectionTargetLayer
from nets.mrcnn_training import *
from utils.anchors import get_anchors
from utils.utils import norm_boxes_graph,parse_image_meta_graph
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
'''
TimeDistributed:
对FPN网络输出的多层卷积特征进行共享参数。
TimeDistributed的意义在于使不同层的特征图共享权重。
'''
#------------------------------------#
# 五个不同大小的特征层会传入到
# RPN当中,获得建议框
#------------------------------------#
def rpn_graph(feature_map, anchors_per_location):
shared = Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu',
name='rpn_conv_shared')(feature_map)
x = Conv2D(2 * anchors_per_location, (1, 1), padding='valid',
activation='linear', name='rpn_class_raw')(shared)
# batch_size,num_anchors,2
# 代表这个先验框对应的类
rpn_class_logits = Reshape([-1,2])(x)
rpn_probs = Activation(
"softmax", name="rpn_class_xxx")(rpn_class_logits)
x = Conv2D(anchors_per_location * 4, (1, 1), padding="valid",
activation='linear', name='rpn_bbox_pred')(shared)
# batch_size,num_anchors,4
# 这个先验框的调整参数
rpn_bbox = Reshape([-1,4])(x)
return [rpn_class_logits, rpn_probs, rpn_bbox]
#------------------------------------#
# 建立建议框网络模型
# RPN模型
#------------------------------------#
def build_rpn_model(anchors_per_location, depth):
input_feature_map = Input(shape=[None, None, depth],
name="input_rpn_feature_map")
outputs = rpn_graph(input_feature_map, anchors_per_location)
return Model([input_feature_map], outputs, name="rpn_model")
#------------------------------------#
# 建立classifier模型
# 这个模型的预测结果会调整建议框
# 获得最终的预测框
#------------------------------------#
def fpn_classifier_graph(rois, feature_maps, image_meta,
pool_size, num_classes, train_bn=True,
fc_layers_size=1024):
# ROI Pooling,利用建议框在特征层上进行截取
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, POOL_SIZE, POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = PyramidROIAlign([pool_size, pool_size],
name="roi_align_classifier")([rois, image_meta] + feature_maps)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, 1, 1, fc_layers_size],相当于两次全连接
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(fc_layers_size, (pool_size, pool_size), padding="valid"),
name="mrcnn_class_conv1")(x)
x = TimeDistributed(BatchNormalization(), name='mrcnn_class_bn1')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, 1, 1, fc_layers_size]
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(fc_layers_size, (1, 1)),
name="mrcnn_class_conv2")(x)
x = TimeDistributed(BatchNormalization(), name='mrcnn_class_bn2')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, fc_layers_size]
shared = Lambda(lambda x: K.squeeze(K.squeeze(x, 3), 2),
name="pool_squeeze")(x)
# Classifier head
# 这个的预测结果代表这个先验框内部的物体的种类
mrcnn_class_logits = TimeDistributed(Dense(num_classes),
name='mrcnn_class_logits')(shared)
mrcnn_probs = TimeDistributed(Activation("softmax"),
name="mrcnn_class")(mrcnn_class_logits)
# BBox head
# 这个的预测结果会对先验框进行调整
# [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES * (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
x = TimeDistributed(Dense(num_classes * 4, activation='linear'),
name='mrcnn_bbox_fc')(shared)
# Reshape to [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
mrcnn_bbox = Reshape((-1, num_classes, 4), name="mrcnn_bbox")(x)
return mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_probs, mrcnn_bbox
def build_fpn_mask_graph(rois, feature_maps, image_meta,
pool_size, num_classes, train_bn=True):
# ROI Align,利用建议框在特征层上进行截取
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = PyramidROIAlign([pool_size, pool_size],
name="roi_align_mask")([rois, image_meta] + feature_maps)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv1")(x)
x = TimeDistributed(BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn1')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv2")(x)
x = TimeDistributed(BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn2')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv3")(x)
x = TimeDistributed(BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn3')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv4")(x)
x = TimeDistributed(BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn4')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, 2xMASK_POOL_SIZE, 2xMASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2DTranspose(256, (2, 2), strides=2, activation="relu"),
name="mrcnn_mask_deconv")(x)
# 反卷积后再次进行一个1x1卷积调整通道,使其最终数量为numclasses,代表分的类
x = TimeDistributed(Conv2D(num_classes, (1, 1), strides=1, activation="sigmoid"),
name="mrcnn_mask")(x)
return x
def get_predict_model(config):
h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2]
if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6):
raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times "
"to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling."
"For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ")
# 输入进来的图片必须是2的6次方以上的倍数
input_image = Input(shape=[None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]], name="input_image")
# meta包含了一些必要信息
input_image_meta = Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_META_SIZE],name="input_image_meta")
# 输入进来的先验框
input_anchors = Input(shape=[None, 4], name="input_anchors")
# 获得Resnet里的压缩程度不同的一些层
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = get_resnet(input_image, stage5=True, train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# 组合成特征金字塔的结构
# P5长宽共压缩了5次
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5)
# P4长宽共压缩了4次
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = Add(name="fpn_p4add")([
UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5),
Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])
# P4长宽共压缩了3次
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = Add(name="fpn_p3add")([
UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4),
Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)])
# P4长宽共压缩了2次
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = Add(name="fpn_p2add")([
UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3),
Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)])
# 各自进行一次256通道的卷积,此时P2、P3、P4、P5通道数相同
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2)
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3)
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4)
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5)
# 在建议框网络里面还有一个P6用于获取建议框
# Height/64,Width/64,256
P6 = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5)
# P2, P3, P4, P5, P6可以用于获取建议框
rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6]
# P2, P3, P4, P5用于获取mask信息
mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5]
anchors = input_anchors
# 建立RPN模型
rpn = build_rpn_model(len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE)
rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox = [],[],[]
# 获得RPN网络的预测结果,进行格式调整,把五个特征层的结果进行堆叠
for p in rpn_feature_maps:
logits,classes,bbox = rpn([p])
rpn_class_logits.append(logits)
rpn_class.append(classes)
rpn_bbox.append(bbox)
rpn_class_logits = Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_class_logits")(rpn_class_logits)
rpn_class = Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_class")(rpn_class)
rpn_bbox = Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_bbox")(rpn_bbox)
# 此时获得的rpn_class_logits、rpn_class、rpn_bbox的维度是
# rpn_class_logits : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_class : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_bbox : Batch_size, num_anchors, 4
proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE
# Batch_size, proposal_count, 4
# 对先验框进行解码
rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(
proposal_count=proposal_count,
nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD,
name="ROI",
config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors])
# 获得classifier的结果
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\
fpn_classifier_graph(rpn_rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, input_image_meta,
config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN,
fc_layers_size=config.FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE)
detections = DetectionLayer(config, name="mrcnn_detection")(
[rpn_rois, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, input_image_meta])
detection_boxes = Lambda(lambda x: x[..., :4])(detections)
# 获得mask的结果
mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(detection_boxes, mrcnn_feature_maps,
input_image_meta,
config.MASK_POOL_SIZE,
config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# 作为输出
model = Model([input_image, input_image_meta, input_anchors],
[detections, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox,
mrcnn_mask, rpn_rois, rpn_class, rpn_bbox],
name='mask_rcnn')
return model
def get_train_model(config):
h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2]
if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6):
raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times "
"to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling."
"For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ")
# 输入进来的图片必须是2的6次方以上的倍数
input_image = Input(shape=[None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]], name="input_image")
# meta包含了一些必要信息
input_image_meta = Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_META_SIZE],name="input_image_meta")
# RPN建议框网络的真实框信息
input_rpn_match = Input(
shape=[None, 1], name="input_rpn_match", dtype=tf.int32)
input_rpn_bbox = Input(
shape=[None, 4], name="input_rpn_bbox", dtype=tf.float32)
# 种类信息
input_gt_class_ids = Input(shape=[None], name="input_gt_class_ids", dtype=tf.int32)
# 框的位置信息
input_gt_boxes = Input(shape=[None, 4], name="input_gt_boxes", dtype=tf.float32)
# 标准化到0-1之间
gt_boxes = Lambda(lambda x: norm_boxes_graph(x, K.shape(input_image)[1:3]))(input_gt_boxes)
# mask语义分析信息
# [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]
if config.USE_MINI_MASK:
input_gt_masks = Input(shape=[config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[0],config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[1], None],name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool)
else:
input_gt_masks = Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1], None],name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool)
# 获得Resnet里的压缩程度不同的一些层
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = get_resnet(input_image, stage5=True, train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# 组合成特征金字塔的结构
# P5长宽共压缩了5次
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5)
# P4长宽共压缩了4次
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = Add(name="fpn_p4add")([
UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5),
Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])
# P4长宽共压缩了3次
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = Add(name="fpn_p3add")([
UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4),
Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)])
# P4长宽共压缩了2次
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = Add(name="fpn_p2add")([
UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3),
Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)])
# 各自进行一次256通道的卷积,此时P2、P3、P4、P5通道数相同
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2)
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3)
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4)
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5)
# 在建议框网络里面还有一个P6用于获取建议框
# Height/64,Width/64,256
P6 = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5)
# P2, P3, P4, P5, P6可以用于获取建议框
rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6]
# P2, P3, P4, P5用于获取mask信息
mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5]
anchors = get_anchors(config,config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
# 拓展anchors的shape,第一个维度拓展为batch_size
anchors = np.broadcast_to(anchors, (config.BATCH_SIZE,) + anchors.shape)
# 将anchors转化成tensor的形式
anchors = Lambda(lambda x: tf.Variable(anchors), name="anchors")(input_image)
# 建立RPN模型
rpn = build_rpn_model(len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE)
rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox = [],[],[]
# 获得RPN网络的预测结果,进行格式调整,把五个特征层的结果进行堆叠
for p in rpn_feature_maps:
logits,classes,bbox = rpn([p])
rpn_class_logits.append(logits)
rpn_class.append(classes)
rpn_bbox.append(bbox)
rpn_class_logits = Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_class_logits")(rpn_class_logits)
rpn_class = Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_class")(rpn_class)
rpn_bbox = Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_bbox")(rpn_bbox)
# 此时获得的rpn_class_logits、rpn_class、rpn_bbox的维度是
# rpn_class_logits : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_class : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_bbox : Batch_size, num_anchors, 4
proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING
# Batch_size, proposal_count, 4
rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(
proposal_count=proposal_count,
nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD,
name="ROI",
config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors])
active_class_ids = Lambda(
lambda x: parse_image_meta_graph(x)["active_class_ids"]
)(input_image_meta)
if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS:
# 使用外部输入的建议框
input_rois = Input(shape=[config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING, 4],
name="input_roi", dtype=np.int32)
# Normalize coordinates
target_rois = Lambda(lambda x: norm_boxes_graph(
x, K.shape(input_image)[1:3]))(input_rois)
else:
# 利用预测到的建议框进行下一步的操作
target_rois = rpn_rois
"""找到建议框的ground_truth
Inputs:
proposals: [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]建议框
gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]每个真实框对应的类
gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]真实框的位置
gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]真实框的语义分割情况
Returns:
rois: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]内部真实存在目标的建议框
target_class_ids: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE]每个建议框对应的类
target_deltas: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw)]每个建议框应该有的调整参数
target_mask: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, height, width]每个建议框语义分割情况
"""
rois, target_class_ids, target_bbox, target_mask =\
DetectionTargetLayer(config, name="proposal_targets")([
target_rois, input_gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, input_gt_masks])
# 找到合适的建议框的classifier预测结果
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\
fpn_classifier_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, input_image_meta,
config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN,
fc_layers_size=config.FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE)
# 找到合适的建议框的mask预测结果
mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps,
input_image_meta,
config.MASK_POOL_SIZE,
config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
output_rois = Lambda(lambda x: x * 1, name="output_rois")(rois)
# Losses
rpn_class_loss = Lambda(lambda x: rpn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="rpn_class_loss")(
[input_rpn_match, rpn_class_logits])
rpn_bbox_loss = Lambda(lambda x: rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, *x), name="rpn_bbox_loss")(
[input_rpn_bbox, input_rpn_match, rpn_bbox])
class_loss = Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_class_loss")(
[target_class_ids, mrcnn_class_logits, active_class_ids])
bbox_loss = Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_bbox_loss")(
[target_bbox, target_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox])
mask_loss = Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_mask_loss")(
[target_mask, target_class_ids, mrcnn_mask])
# Model
inputs = [input_image, input_image_meta,
input_rpn_match, input_rpn_bbox, input_gt_class_ids, input_gt_boxes, input_gt_masks]
if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS:
inputs.append(input_rois)
outputs = [rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox,
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask,
rpn_rois, output_rois,
rpn_class_loss, rpn_bbox_loss, class_loss, bbox_loss, mask_loss]
model = Model(inputs, outputs, name='mask_rcnn')
return model
resnet.py
from keras.layers import ZeroPadding2D,Conv2D,MaxPooling2D,BatchNormalization,Activation,Add
def identity_block(input_tensor, kernel_size, filters, stage, block,
use_bias=True, train_bn=True):
nb_filter1, nb_filter2, nb_filter3 = filters
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
x = Conv2D(nb_filter1, (1, 1), name=conv_name_base + '2a',
use_bias=use_bias)(input_tensor)
x = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '2a')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Conv2D(nb_filter2, (kernel_size, kernel_size), padding='same',
name=conv_name_base + '2b', use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '2b')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Conv2D(nb_filter3, (1, 1), name=conv_name_base + '2c',
use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '2c')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Add()([x, input_tensor])
x = Activation('relu', name='res' + str(stage) + block + '_out')(x)
return x
def conv_block(input_tensor, kernel_size, filters, stage, block,
strides=(2, 2), use_bias=True, train_bn=True):
nb_filter1, nb_filter2, nb_filter3 = filters
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
x = Conv2D(nb_filter1, (1, 1), strides=strides,
name=conv_name_base + '2a', use_bias=use_bias)(input_tensor)
x = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '2a')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Conv2D(nb_filter2, (kernel_size, kernel_size), padding='same',
name=conv_name_base + '2b', use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '2b')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Conv2D(nb_filter3, (1, 1), name=conv_name_base +
'2c', use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '2c')(x, training=train_bn)
shortcut = Conv2D(nb_filter3, (1, 1), strides=strides,
name=conv_name_base + '1', use_bias=use_bias)(input_tensor)
shortcut = BatchNormalization(name=bn_name_base + '1')(shortcut, training=train_bn)
x = Add()([x, shortcut])
x = Activation('relu', name='res' + str(stage) + block + '_out')(x)
return x
def get_resnet(input_image,stage5=False, train_bn=True):
# Stage 1
x = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(input_image)
x = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides=(2, 2), name='conv1', use_bias=True)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name='bn_conv1')(x, training=train_bn)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
# Height/4,Width/4,64
C1 = x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same")(x)
# Stage 2
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1), train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b', train_bn=train_bn)
# Height/4,Width/4,256
C2 = x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c', train_bn=train_bn)
# Stage 3
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a', train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b', train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c', train_bn=train_bn)
# Height/8,Width/8,512
C3 = x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d', train_bn=train_bn)
# Stage 4
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a', train_bn=train_bn)
block_count = 22
for i in range(block_count):
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block=chr(98 + i), train_bn=train_bn)
# Height/16,Width/16,1024
C4 = x
# Stage 5
if stage5:
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a', train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b', train_bn=train_bn)
# Height/32,Width/32,2048
C5 = x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c', train_bn=train_bn)
else:
C5 = None
return [C1, C2, C3, C4, C5]
5.2 mask_rcnn.py
import os
import sys
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import skimage.io
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from nets.mrcnn import get_predict_model
from utils.config import Config
from utils.anchors import get_anchors
from utils.utils import mold_inputs,unmold_detections
from utils import visualize
import keras.backend as K
class MASK_RCNN(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'model_data/mask_rcnn_coco.h5',
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
"confidence": 0.7,
# 使用coco数据集检测的时候,IMAGE_MIN_DIM=1024,IMAGE_MAX_DIM=1024, RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512)
"RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES": (32, 64, 128, 256, 512),
"IMAGE_MIN_DIM": 1024,
"IMAGE_MAX_DIM": 1024,
# 在使用自己的数据集进行训练的时候,如果显存不足要调小图片大小
# 同时要调小anchors
#"IMAGE_MIN_DIM": 512,
#"IMAGE_MAX_DIM": 512,
#"RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES": (16, 32, 64, 128, 256)
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化Mask-Rcnn
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.config = self._get_config()
self.generate()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得所有的分类
#---------------------------------------------------#
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
class_names.insert(0,"BG")
return class_names
def _get_config(self):
class InferenceConfig(Config):
NUM_CLASSES = len(self.class_names)
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE = self.confidence
NAME = "shapes"
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = self.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = self.IMAGE_MIN_DIM
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = self.IMAGE_MAX_DIM
config = InferenceConfig()
config.display()
return config
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# 计算总的种类
self.num_classes = len(self.class_names)
# 载入模型,如果原来的模型里已经包括了模型结构则直接载入。
# 否则先构建模型再载入
self.model = get_predict_model(self.config)
self.model.load_weights(self.model_path,by_name=True)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
image = [np.array(image)]
molded_images, image_metas, windows = mold_inputs(self.config,image)
image_shape = molded_images[0].shape
anchors = get_anchors(self.config,image_shape)
anchors = np.broadcast_to(anchors, (1,) + anchors.shape)
detections, _, _, mrcnn_mask, _, _, _ =\
self.model.predict([molded_images, image_metas, anchors], verbose=0)
final_rois, final_class_ids, final_scores, final_masks =\
unmold_detections(detections[0], mrcnn_mask[0],
image[0].shape, molded_images[0].shape,
windows[0])
r = {
"rois": final_rois,
"class_ids": final_class_ids,
"scores": final_scores,
"masks": final_masks,
}
visualize.display_instances(image[0], r['rois'], r['masks'], r['class_ids'],
self.class_names, r['scores'])
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
5.3 train.py
import os
from PIL import Image
import keras
import numpy as np
import random
import tensorflow as tf
from utils import visualize
from utils.config import Config
from utils.anchors import get_anchors
from utils.utils import mold_inputs,unmold_detections
from nets.mrcnn import get_train_model,get_predict_model
from nets.mrcnn_training import data_generator,load_image_gt
from dataset import ShapesDataset
def log(text, array=None):
"""Prints a text message. And, optionally, if a Numpy array is provided it
prints it's shape, min, and max values.
"""
if array is not None:
text = text.ljust(25)
text += ("shape: {:20} ".format(str(array.shape)))
if array.size:
text += ("min: {:10.5f} max: {:10.5f}".format(array.min(),array.max()))
else:
text += ("min: {:10} max: {:10}".format("",""))
text += " {}".format(array.dtype)
print(text)
class ShapesConfig(Config):
NAME = "shapes"
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
BATCH_SIZE = 1
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (16, 32, 64, 128, 256)
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 512
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 512
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 250
VALIDATION_STEPS = 25
if __name__ == "__main__":
learning_rate = 1e-5
init_epoch = 0
epoch = 100
dataset_root_path="./train_dataset/"
img_floder = dataset_root_path + "imgs/"
mask_floder = dataset_root_path + "mask/"
yaml_floder = dataset_root_path + "yaml/"
imglist = os.listdir(img_floder)
count = len(imglist)
np.random.seed(10101)
np.random.shuffle(imglist)
train_imglist = imglist[:int(count*0.9)]
val_imglist = imglist[int(count*0.9):]
MODEL_DIR = "logs"
COCO_MODEL_PATH = "model_data/mask_rcnn_coco.h5"
config = ShapesConfig()
config.display()
# 训练数据集准备
dataset_train = ShapesDataset()
dataset_train.load_shapes(len(train_imglist), img_floder, mask_floder, train_imglist, yaml_floder)
dataset_train.prepare()
# 验证数据集准备
dataset_val = ShapesDataset()
dataset_val.load_shapes(len(val_imglist), img_floder, mask_floder, val_imglist, yaml_floder)
dataset_val.prepare()
# 获得训练模型
model = get_train_model(config)
model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH,by_name=True,skip_mismatch=True)
# 数据生成器
train_generator = data_generator(dataset_train, config, shuffle=True,
batch_size=config.BATCH_SIZE)
val_generator = data_generator(dataset_val, config, shuffle=True,
batch_size=config.BATCH_SIZE)
# 回执函数
# 每次训练一个世代都会保存
callbacks = [
keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=MODEL_DIR,
histogram_freq=0, write_graph=True, write_images=False),
keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, "epoch{epoch:03d}_loss{loss:.3f}_val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5"),
verbose=0, save_weights_only=True),
]
log("\nStarting at epoch {}. LR={}\n".format(init_epoch, learning_rate))
log("Checkpoint Path: {}".format(MODEL_DIR))
# 使用的优化器是
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=learning_rate)
# 设置一下loss信息
model._losses = []
model._per_input_losses = {}
loss_names = [
"rpn_class_loss", "rpn_bbox_loss",
"mrcnn_class_loss", "mrcnn_bbox_loss", "mrcnn_mask_loss"]
for name in loss_names:
layer = model.get_layer(name)
if layer.output in model.losses:
continue
loss = (
tf.reduce_mean(layer.output, keepdims=True)
* config.LOSS_WEIGHTS.get(name, 1.))
model.add_loss(loss)
# 增加L2正则化,放置过拟合
reg_losses = [
keras.regularizers.l2(config.WEIGHT_DECAY)(w) / tf.cast(tf.size(w), tf.float32)
for w in model.trainable_weights
if 'gamma' not in w.name and 'beta' not in w.name]
model.add_loss(tf.add_n(reg_losses))
# 进行编译
model.compile(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss=[None] * len(model.outputs)
)
# 用于显示训练情况
for name in loss_names:
if name in model.metrics_names:
print(name)
continue
layer = model.get_layer(name)
model.metrics_names.append(name)
loss = (
tf.reduce_mean(layer.output, keepdims=True)
* config.LOSS_WEIGHTS.get(name, 1.))
model.metrics_tensors.append(loss)
model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
initial_epoch=init_epoch,
epochs=epoch,
steps_per_epoch=config.STEPS_PER_EPOCH,
callbacks=callbacks,
validation_data=val_generator,
validation_steps=config.VALIDATION_STEPS,
max_queue_size=100
)
5.4 predict.py
from keras.layers import Input
from mask_rcnn import MASK_RCNN
from PIL import Image
mask_rcnn = MASK_RCNN()
while True:
img = input('img/street.jpg')
try:
image = Image.open('img/street.jpg')
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
mask_rcnn.detect_image(image)
mask_rcnn.close_session()
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)