selenium爬虫chrome容器化部署实战
本文是作者在selenium自动运维中的实战总结,一扫网上诸多不清晰的介绍文章
需求和场景说明
最近要部署数据采集平台到生成环境上去。需要两个docker容器,一个运行采集脚本,一个是运行vnc+chrome的远程x11 server,也是跑在容器中。这个X11 server可以完成模拟登录,自动上传,自动发布的功能,包括自动idle以保持会话。之前在单机上正确运行无误,所以迁移到两个容器中也无碍。
基本需求:
- chrome要跑在docker容器中,以headless或headful方式运行。headful是因为有些自动化操作无法在headless下进行。
- 支持多个client同时访问chrome,也就是多个爬虫并行
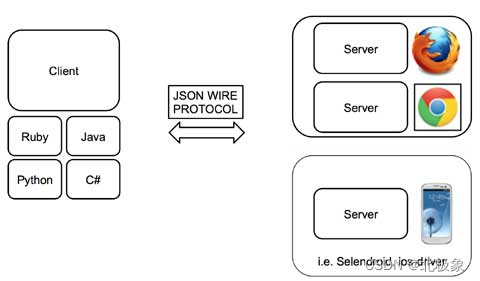
认识Selenium
selenium remote sever 其实就是通过webdriver Json与浏览器交互,这也就介绍了为什么selenium能够实现支持各种语言,
不管是java python 等,都是通过selenium API翻译成Json 与浏览器进行交互。掌握了webdriver protocol 可以通过自己直接写request来实现与浏览器交互。

以开发者视角认识Chrome
Chrome在网民手中不过是一个浏览器而已,但在开发者手中就是神兵利器。自动化测试、爬虫、抓包、调试诊断、逆向、以及自动化运维都少不了它。搭配一些可编程的代理工具,如mitmproxy,更是如有神助。
启动Chrome
以下是启动chrome,以供client远程连接的脚本:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
export DISPLAY=:1
export LC_ALL=zh_CN.UTF-8
export LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
export LANGUAGE=zh_CN.UTF-8
chrome --no-sandbox --disable-setuid-sandbox --no-default-browser-check --no-first-run --disable-dev-shm-usage --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir=/home/icool/data
连接远程容器中的Headless Chrome
这种场景最好采用别人制作好的镜像,否则各种安装依赖会让你深陷泥潭。服务器端,root用户是不能直接运行chrome的。不然无法启动chrome。可行的方法是切换用户,或者在启动chrome时添加‘–no-sandbox’参数。
目前普遍采用的镜像是:
docker pull selenium/standalone-chrome
运行方式:
docker run -d --cpus 6 -m 12GB --name my-chrome -p 4444:4444 -p 9898:80 -e SE_NODE_MAX_SESSIONS=8 --shm-size="2g" selenium/standalone-chrome
这个standalone-chrome镜像其实是把selenium grid的基本组件都集成在一起了。
注意:SE_NODE_MAX_SESSIONS如果不设置的话,只支持一个会话,就无法多个爬虫并发执行了。
连接selenium的代码示例如下:
def connect_remote_chrome(url_str):
print(f'Conencting to {url_str} ...')
time.sleep(5)
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
driver = webdriver.Remote(
command_executor="http://10.10.10.10:4444/wd/hub",
options=options
)
driver.get(url_str)
content = driver.title.split("_")[0]
print(content)
driver.close()
hub是selenium的一个组件,起到转发请求的作用。
制作一个自己的chrome容器
当然,如果你有更多的定制化需求,也完全可以打造一个自己的chrome容器。下面是一个简单的例子。
FROM node:10-slim
LABEL maintainer="Eric Bidelman <ebidel@>"
# Install utilities
RUN apt-get update --fix-missing && apt-get -y upgrade
# Install latest chrome dev package.
RUN wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | apt-key add - \
&& sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google.list' \
&& apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y google-chrome-unstable --no-install-recommends \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* \
&& rm -rf /src/*.deb
ADD https://github.com/Yelp/dumb-init/releases/download/v1.2.0/dumb-init_1.2.0_amd64 /usr/local/bin/dumb-init
RUN chmod +x /usr/local/bin/dumb-init
# Download latest Lighthouse from npm.
# cache bust so we always get the latest version of LH when building the image.
ARG CACHEBUST=1
RUN npm i lighthouse -g
# Install express.
COPY package.json .
RUN npm i --production
# Add the simple server.
COPY server.js /
RUN chmod +x /server.js
COPY entrypoint.sh /
RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh
# Add a chrome user and setup home dir.
RUN groupadd --system chrome && \
useradd --system --create-home --gid chrome --groups audio,video chrome && \
mkdir --parents /home/chrome/reports && \
chown --recursive chrome:chrome /home/chrome
USER chrome
#VOLUME /home/chrome/reports
#WORKDIR /home/chrome/reports
# Disable Lighthouse error reporting to prevent prompt.
ENV CI=true
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["dumb-init", "--", "/entrypoint.sh"]
#CMD ["lighthouse", "--help"]
远程启动的参数说明:
chrome.exe --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir=remote-profile
- chrome.exe: Chrome Browser Binary ( This is will different in all other operating systems like Unix, Mac, Linux)
- –remote-debugging-port: This is Chrome Preference to launch the browser in remote debug mode on a certain port, We can also use –remote-debugging-address.
- –user-date-dir: this is a directory where the browser stores the user profile, So we should always provide a new profile directory to save your default browser profile preferences.
连接远程容器中的headful Chrome
可以采用现有的镜像,如https://github.com/MeiK2333/headful-chrome-launch.git。
首先,在远程容器中启动chrome:
chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir=/root/chrome-data --no-sandbox
注意:笔者是以root身份启动的。
然后,在python中采用selenium连接远程chrome:
def get_remote_chrome():
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument(
"user-agent=Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/100.0.4896.127 Safari/537.36")
## 此处的100.100.100.100请换成真实的主机地址
options.add_experimental_option("debuggerAddress", f"100.100.100.100:9222")
options.add_argument('disable-infobars')
# options.add_argument("--headless")
options.add_argument("--disable-gpu")
# 针对反爬虫的设置
options.add_argument("--disable-blink-features")
options.add_argument("--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(chrome_options=options)
driver.maximize_window()
return driver
def test_remote():
driver = get_remote_chrome()
driver.get("https://www.csdn.net")
title = driver.title.split("_")[0]
print(title)
driver.close()
Chrome调试模式的安全限制
当我们运行上述python代码时,会报错。原因是以调试方式运行chrome时,由于chrome的安全限制,不允许我们通过chrome浏览器以外的机器去连接它的调试端口。通常遇到下面报错信息:
[0526/132024.480654:ERROR:socket_posix.cc(137)] bind() returned an error, errno=49: Can't assign requested address
[0526/132024.480766:ERROR:devtools_http_handler.cc(226)] Cannot start http server for devtools. Stop devtools.
即使你通过–remote-debugging-address 参数指定0.0.0.0也不行。不过这点好办,写个代理,跑在和chrome同一个台机器上,做转发不就完事了?没错,这几乎是对付这种场景的万能方案。
下面是一个Python写的端口转发程序:
import time
import socket
import threading
def log(strLog):
strs = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(strs +" -> "+strLog)
class pipethread(threading.Thread):
'''
classdocs
'''
def __init__(self,source,sink):
'''
Constructor
'''
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.source = source
self.sink = sink
log("New Pipe create:%s->%s" % (self.source.getpeername(),self.sink.getpeername()))
def run(self):
while True:
try:
data = self.source.recv(1024)
if not data: break
self.sink.send(data)
except Exception as ex:
log("redirect error:"+str(ex))
break
self.source.close()
self.sink.close()
class portmap(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, port, newhost, newport, local_ip = ''):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.newhost = newhost
self.newport = newport
self.port = port
self.local_ip = local_ip
self.protocol = 'tcp'
self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.sock.bind((self.local_ip, port))
self.sock.listen(5)
log("start listen protocol:%s,port:%d " % (self.protocol, port))
def run(self):
while True:
newsock, address = self.sock.accept()
log("new connection->protocol:%s,local port:%d,remote address:%s" % (self.protocol, self.port,address[0]))
fwd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
fwd.connect((self.newhost,self.newport))
except Exception as ex:
log("connet newhost error:"+str(ex))
break
p1 = pipethread(newsock, fwd)
p1.start()
p2 = pipethread(fwd, newsock)
p2.start()
class pipethreadUDP(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, connection, connectionTable, table_lock):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.connection = connection
self.connectionTable = connectionTable
self.table_lock = table_lock
log('new thread for new connction')
def run(self):
while True:
try:
data,addr = self.connection['socket'].recvfrom(4096)
#log('recv from addr"%s' % str(addr))
except Exception as ex:
log("recvfrom error:"+str(ex))
break
try:
self.connection['lock'].acquire()
self.connection['Serversocket'].sendto(data,self.connection['address'])
#log('sendto address:%s' % str(self.connection['address']))
except Exception as ex:
log("sendto error:"+str(ex))
break
finally:self.connection['lock'].release()
self.connection['time'] = time.time()
self.connection['socket'].close()
log("thread exit for: %s" % str(self.connection['address']))
self.table_lock.acquire()
self.connectionTable.pop(self.connection['address'])
self.table_lock.release()
log('Release udp connection for timeout:%s' % str(self.connection['address']))
class portmapUDP(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, port, newhost, newport, local_ip = ''):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.newhost = newhost
self.newport = newport
self.port = port
self.local_ip = local_ip
self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
self.sock.bind((self.local_ip,port))
self.connetcTable = {}
self.port_lock = threading.Lock()
self.table_lock = threading.Lock()
self.timeout = 300
#ScanUDP(self.connetcTable,self.table_lock).start()
log('udp port redirect run->local_ip:%s,local_port:%d,remote_ip:%s,remote_port:%d' % (local_ip,port,newhost,newport))
def run(self):
while True:
data,addr = self.sock.recvfrom(4096)
connection = None
newsock = None
self.table_lock.acquire()
connection = self.connetcTable.get(addr)
newconn = False
if connection is None:
connection = {}
connection['address'] = addr
newsock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
newsock.settimeout(self.timeout)
connection['socket'] = newsock
connection['lock'] = self.port_lock
connection['Serversocket'] = self.sock
connection['time'] = time.time()
newconn = True
log('new connection:%s' % str(addr))
self.table_lock.release()
try:
connection['socket'].sendto(data,(self.newhost,self.newport))
except Exception as ex:
log("sendto error:"+str(ex))
#break
if newconn:
self.connetcTable[addr] = connection
t1=pipethreadUDP(connection,self.connetcTable,self.table_lock)
t1.start()
log('main thread exit')
for key in self.connetcTable.keys():
self.connetcTable[key]['socket'].close()
if __name__=='__main__':
myp = portmap(9223, '127.0.0.1', 9222)
myp.start()
在chrome所在的docker容器运行它:
python ./portmap.py
即可将进入容器的9223端口上的请求转发到chrome上去。再次执行selenium访问代码即可正常操作浏览器了。
Headful chrome Dockerfile参考
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:focal
ENV TZ=Asia/Shanghai
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
RUN apt-get install -y locales
RUN sed -i -e 's/# zh_CN.UTF-8 UTF-8/zh_CN.UTF-8 UTF-8/' /etc/locale.gen && \
dpkg-reconfigure --frontend=noninteractive locales && \
update-locale LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
ENV LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
ENV LC_ALL=zh_CN.UTF-8
ENV LANGUAGE=zh_CN:zh:en
# Install front and others
RUN apt-get install -yq \
ca-certificates \
curl \
dumb-init \
ffmpeg \
fontconfig \
fonts-indic \
fonts-liberation \
fonts-noto-cjk \
fonts-noto-color-emoji \
fonts-thai-tlwg \
gconf-service \
libappindicator1 \
libappindicator3-1 \
libatk-bridge2.0-0 \
libatk1.0-0 \
libc6 \
libcairo2 \
libcups2 \
libdbus-1-3 \
libexpat1 \
libfontconfig1 \
libgbm1 \
libgcc1 \
libgconf-2-4 \
libgl1 \
libglib2.0-0 \
libgtk-3-0 \
libnspr4 \
libpango-1.0-0 \
libpangocairo-1.0-0 \
libstdc++6 \
libx11-6 \
libx11-xcb1 \
libxcb1 \
libxcomposite1 \
libxcursor1 \
libxdamage1 \
libxext6 \
libxfixes3 \
libxi6 \
libxrandr2 \
libxrender1 \
libxt6 \
libxtst6 \
locales \
lsb-release \
unzip \
wget \
x11-apps \
x11-xkb-utils \
x11vnc \
xdg-utils \
xfonts-100dpi \
xfonts-75dpi \
xfonts-cyrillic \
xfonts-scalable \
xvfb \
fvwm \
xterm
# Download Chrome
RUN cd /tmp && \
wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | apt-key add - && \
sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list' && \
apt-get update && \
apt-get install -yq google-chrome-stable
RUN apt-get -qq clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* /tmp/* /var/tmp/*
RUN mkdir /app
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
RUN npm install && \
npm install -g ts-node typescript
# RUN chown -R pwuser:pwuser /app
# Run everything after as non-privileged user.
# USER pwuser
CMD ["./start.sh"]
关于Selenium Grid

Grid的适用场景是多个node,每个node上运行一个浏览器,而且可以是不同类型的浏览器。这对提高并发,和做兼容性测试是非常有好处的。
MacOS下命令行运行chrome
直接在容器中运行headless chrome,会由于安全的限制,提示报错:
Failed to move to new namespace: PID namespaces supported, Network namespace supported, but failed: errno = Operation not permitted
采用open命令:
open -a Google\ Chrome –args -disable-web-security
或者直接运行(zsh下):
/Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir=/opt/tmp/chrome
Chrome命令行参数简介
chrome \
--headless \ # Runs Chrome in headless mode.
--disable-gpu \ # Temporarily needed if running on Windows.
--remote-debugging-port=9222 \
https://www.baidu.com # URL to open. Defaults to about:blank.
If you’re on the stable channel of Chrome and cannot get the Beta, I recommend using chrome-canary:
Download Chrome Canary here. https://www.google.com/chrome/canary/,每日构建版本
alias chrome="/Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome"
alias chrome-canary="/Applications/Google\ Chrome\ Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome\ Canary"
alias chromium="/Applications/Chromium.app/Contents/MacOS/Chromium"
Print the DOM:
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --dump-dom https://www.chromestatus.com/
The --print-to-pdf flag creates a PDF of the page:
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --print-to-pdf https://www.chromestatus.com/
To capture a screenshot of a page, use the --screenshot flag:
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot https://www.chromestatus.com/
# Size of a standard letterhead.
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot --window-size=1280,1696 https://www.chromestatus.com/
# Nexus 5x
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot --window-size=412,732 https://www.chromestatus.com/
The --repl flag runs Headless in a mode where you can evaluate JS expressions in the browser, right from the command line:
$ chrome --headless --disable-gpu --repl --crash-dumps-dir=./tmp https://www.chromestatus.com/
[0608/112805.245285:INFO:headless_shell.cc(278)] Type a Javascript expression to evaluate or "quit" to exit.
>>> location.href
{"result":{"type":"string","value":"https://www.chromestatus.com/features"}}
>>> quit
$
chrome实例池
只采用一个chrome实例往往不能满足需求,这时就需要用到实例池了。下面的脚本创建了一个chrome实例池。
let pool = genericPool.createPool({
create() {
return puppeteer.launch()
},
validate(browser) {
return Promise.race([
new Promise(res => setTimeout(() => res(false), 1500)),
browser.version().then(_ => true).catch(_ => false)
])
},
destroy(browser) {
return browser.close();
}
}, {
min: 2,
max: 10,
testOnBorrow: true,
acquireTimeoutMillis: 15000
})
结论
本文简要介绍了在容器中运行chrome,以及在容器外采用selenium库远程操纵chrome的两种模式:
- chrome以headless方式运行,这时用standalone selenium镜像既可解决
- chrome以headful方式运行,这是采用一个代理转发程序即可解决
相关链接
- https://googlechromelabs.github.io/chrome-for-testing/#stable
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)