《Linux驱动:Nor flash驱动看这一篇就够了》
这一篇主要总结Nor Flash驱动的工作方式和逻辑,熟悉nor flash驱动的框架,并分析了不同规范的Nor Flash芯片的识别过程,比如CFI规范和JEDEC规范的nor flash。Nor flash驱动构建一般分为以下几个步骤根据硬件电路和芯片书册设置struct map_info结构体。调用do_map_probe接口识别对应规范的Nor Flash芯片,并获取到一个对应芯片的str
文章目录
一,前言
这一篇主要总结Nor Flash驱动的工作方式和逻辑,熟悉nor flash驱动的框架,并分析了不同规范的Nor Flash芯片的识别过程,比如CFI规范和JEDEC规范的nor flash 。
二,硬件电路
2.1 脚位功能
LDATA0~LDATA15:数据传输
LADDR1~LADDR19:地址传输
nRESET:复位
LnOE:读状态信号
LnWE:写状态信号
nGCS0:片选信号
2.2 地址移位
S3c2440的LADDR1接到Nor flash的A0,所以2440向Nor flash发送其需要的地址时,实际应该发出“需要的地址”<< 1,才能让Nor flash真正收到其所需要的地址。比如Nor flash需要的地址是0x555,那么2440应该发出0x555<<1即0xaaa。

三,Nand Flash和Nor Flash的区别
| Nand | Nor | |
|---|---|---|
| 接口 | 引脚少,数据和地址复用 | 引脚多,数据和地址引脚分开 |
| 容量 | 大,128M/256M/xG | 小,1M/2M/32M |
| 读数据 | 复杂 | 简单,像内存一样读 |
| 价格 | 便宜 | 贵 |
| 硬件特性 | 位反转,坏块 | 无位反转 |
| 片上执行程序 | 不可 | 可在片上直接执行程序 |
四,Nor flash CFI规范和JEDEC规范
4.1 JEDEC规范
老式的Nor Flash一般是jedec规范,其一般只包含识别 ID、擦除芯片、烧写数据的命令。要想知道其容量大小等信息,就需要先读出其芯片id,然后到内核中的jedec_table数组中比较得到对应的芯片信息,比较麻烦。另外如果内核jedec_table数组中事先没有对应芯片id的信息,还需要先在该数组中添加。
jedec_table数组

4.2 CFI规范
目前的Nor Flash一般都支持CFI规范,其除了提供识别 ID、擦除芯片、烧写数据的命令之后,还提供了进入CFI模式的命令,进入CFI模式后就可以通过读取相应地址的数据获取芯片属性信息,如容量、电压等信息。
进入CFI模式(往地址0x55处写入0x98)

读取芯片容量(从地址0x27处读取容量大小 )

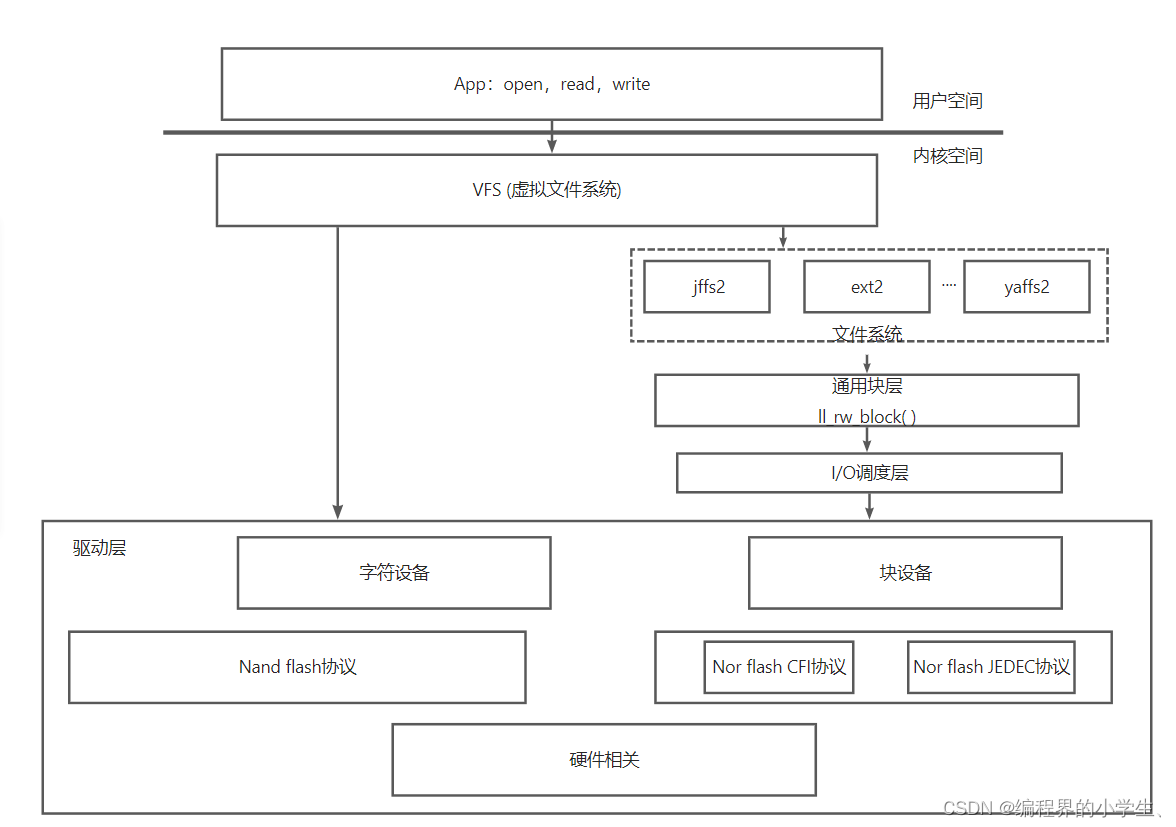
五,Nor flash驱动框架

六,Nor Flash驱动分析
6.1 配置Nor Flash驱动编译
make menuconfig
-> Device Drivers │
-> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support (MTD [=y]) │
-> Mapping drivers for chip access
<M> CFI Flash device in physical memory map // 将驱动编译位内核模块,方便调试,设位y为编译进内核 │ │
(0x0) Physical start address of flash mapping // 配置基地址 │ │
(0x1000000) Physical length of flash mapping // 配置物理大小 │ │
(2) Bank width in octets // 配置位宽 2*8=16
保存,退出make menuconfig后可以在linux-2.6.22.6/.config中看下如下信息
CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP=m
CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_START=0x0
CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN=0x1000000
CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_BANKWIDTH=2
6.2 Nor Flash驱动入口函数
// linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/mtd/maps/physmap.c
static int __init physmap_init(void)
{
int err;
err = platform_driver_register(&physmap_flash_driver);
#ifdef PHYSMAP_COMPAT
if (err == 0)
platform_device_register(&physmap_flash);
#endif
return err;
}
// make menuconfig时配置生成的.config中,定义了CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN宏
// 所以这里将会定义#define PHYSMAP_COMPAT,
// 进而会在驱动入口函数中执行platform_device_register接口调用。
#ifdef CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN
#if CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN != 0
#warning using PHYSMAP compat code
#define PHYSMAP_COMPAT
#endif
#endif
static struct platform_driver physmap_flash_driver = {
.probe = physmap_flash_probe,
.remove = physmap_flash_remove,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
.suspend = physmap_flash_suspend,
.resume = physmap_flash_resume,
.shutdown = physmap_flash_shutdown,
#endif
.driver = {
.name = "physmap-flash",
},
};
6.3 驱动probe函数分析
注册平台驱动,注册平台设备以及它们的匹配,最终调用驱动的probe函数的流程在之前的文章中分析过多次,这里不再赘述。直接进入probe函数分析。
struct physmap_flash_info {
struct mtd_info *mtd;
struct map_info map; //需要定义一个map_info结构体
struct resource *res;
#ifdef CONFIG_MTD_PARTITIONS
int nr_parts;
struct mtd_partition *parts;
#endif
};
// 设备信息
static struct physmap_flash_data physmap_flash_data = {
.width = CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_BANKWIDTH,
};
static struct resource physmap_flash_resource = {
.start = CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_START,
.end = CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_START + CONFIG_MTD_PHYSMAP_LEN - 1,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
};
static int physmap_flash_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
struct physmap_flash_data *physmap_data;
struct physmap_flash_info *info;
const char **probe_type;
int err;
physmap_data = dev->dev.platform_data;
if (physmap_data == NULL)
return -ENODEV;
printk(KERN_NOTICE "physmap platform flash device: %.8llx at %.8llx\n",
(unsigned long long)(dev->resource->end - dev->resource->start + 1),
(unsigned long long)dev->resource->start);
info = kzalloc(sizeof(struct physmap_flash_info), GFP_KERNEL);
if (info == NULL) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_out;
}
platform_set_drvdata(dev, info);
info->res = request_mem_region(dev->resource->start,
dev->resource->end - dev->resource->start + 1,
dev->dev.bus_id);
if (info->res == NULL) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "Could not reserve memory region\n");
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_out;
}
// 设置map_info结构体
info->map.name = dev->dev.bus_id;
info->map.phys = dev->resource->start; // 起始地址
info->map.size = dev->resource->end - dev->resource->start + 1; //大小
info->map.bankwidth = physmap_data->width; // 位宽
info->map.set_vpp = physmap_data->set_vpp;
info->map.virt = ioremap(info->map.phys, info->map.size); // 物理地址到虚拟地址的映射
if (info->map.virt == NULL) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "Failed to ioremap flash region\n");
err = EIO;
goto err_out;
}
simple_map_init(&info->map);
// { "cfi_probe", "jedec_probe", "map_rom", NULL }; cfi规范、jedec规范、内存模拟的nor flash
probe_type = rom_probe_types;
for (; info->mtd == NULL && *probe_type != NULL; probe_type++)
// 识别指定规范的nor flash,获取mtd结构体
info->mtd = do_map_probe(*probe_type, &info->map);
if (info->mtd == NULL) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "map_probe failed\n");
err = -ENXIO;
goto err_out;
}
info->mtd->owner = THIS_MODULE;
#ifdef CONFIG_MTD_PARTITIONS
// { "cmdlinepart", "RedBoot", NULL },添加cmdlinepart分区和RedBoot分区
// 获取这个两个分区的信息,然后添加这俩个分区,并为其创建对应的字符设备节点和块设备节点
err = parse_mtd_partitions(info->mtd, part_probe_types, &info->parts, 0);
if (err > 0) {
add_mtd_partitions(info->mtd, info->parts, err);
return 0;
}
// 在设备信息中配置了分区的话,就添加对应的分区。这里没有配置,即physmap_data->nr_parts=0,没有要添加额外的分区。
if (physmap_data->nr_parts) {
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Using physmap partition information\n");
add_mtd_partitions(info->mtd, physmap_data->parts,
physmap_data->nr_parts);
return 0;
}
#endif
// 添加主分区创建对应的字符设备节点和块设备节点。
add_mtd_device(info->mtd);
return 0;
err_out:
physmap_flash_remove(dev);
return err;
}
6.4 CFI规范Flash识别分析
6.4.1 CFI协议层
// cfi协议层
// linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/mtd/chips/chipreg.c
void register_mtd_chip_driver(struct mtd_chip_driver *drv)
{
spin_lock(&chip_drvs_lock);
// 将协议层接口放到chip_drvs_list链表中
list_add(&drv->list, &chip_drvs_list);
spin_unlock(&chip_drvs_lock);
}
//linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/mtd/chips/cfi_probe.c
// 内核初始化时被调用
static int __init cfi_probe_init(void)
{
register_mtd_chip_driver(&cfi_chipdrv);
return 0;
}
static struct mtd_chip_driver cfi_chipdrv = {
.probe = cfi_probe,
.name = "cfi_probe",
.module = THIS_MODULE
};
struct mtd_info *cfi_probe(struct map_info *map)
{
/*
* Just use the generic probe stuff to call our CFI-specific
* chip_probe routine in all the possible permutations, etc.
*/
return mtd_do_chip_probe(map, &cfi_chip_probe);
}
static struct chip_probe cfi_chip_probe = {
.name = "CFI",
.probe_chip = cfi_probe_chip
};
6.4.2 CFI 规范Flash识别过程
// linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/mtd/chips/chipreg.c
// *probe_type--"cfi_probe"
info->mtd = do_map_probe(*probe_type, &info->map) ->
drv = get_mtd_chip_driver(name) ->
......
// 从chip_drvs_list链表中取出对应协议层接口
// chip_drvs_list链表在register_mtd_chip_driver接口中设置
// register_mtd_chip_driver接口在协议层调用
// cfi_probe_init/jedec_probe_init/map_ram_init
list_for_each(pos, &chip_drvs_list)
this = list_entry(pos, typeof(*this), list);
if (!strcmp(this->name, name)) {
ret = this;
break;
}
......
return ret;
// 执行协议层的probe函数 即上面分析的cfi_probe接口
drv->probe(map)-> //即cfi_probe(map)
// cfi_chip_probe 结构体中有一个.probe_chip接口(cfi_probe_chip)
mtd_do_chip_probe(map, &cfi_chip_probe)->
genprobe_ident_chips(map, cp) ->
genprobe_new_chip(map, cp, &cfi) ->
// 在该函数中,进入通过命令CFI模式,读取芯片信息
cp->probe_chip(map, 0, NULL, cfi) -> //即cfi_probe_chip
// 进入CFI模式
cfi_send_gen_cmd(0xF0, 0, base, map, cfi, cfi->device_type, NULL);
cfi_send_gen_cmd(0xFF, 0, base, map, cfi, cfi->device_type, NULL);
cfi_send_gen_cmd(0x98, 0x55, base, map, cfi, cfi->device_type, NULL);
// 读取芯片信息,比如cfi->cfiq->P_ID = 0x0000 0002
// 由芯片手册知
// P_ID: Primary vendor command set and control interface ID code
cfi_chip_setup(map, cfi) ->
......
for (i=0; i<(sizeof(struct cfi_ident) + num_erase_regions * 4); i++)
((unsigned char *)cfi->cfiq)[i] = cfi_read_query(map,base + (0x10 + i)*ofs_factor);
.....
// 根据上面读取到的P_ID调用相应的接口申请并设置struct mtd_info结构体
mtd = check_cmd_set(map, 1) ->
......
case 0x0002:
return cfi_cmdset_0002(map, primary) ->
.......
mtd = kzalloc(sizeof(*mtd), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!mtd) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to allocate memory for MTD device\n");
return NULL;
}
mtd->priv = map;
mtd->type = MTD_NORFLASH;
/* Fill in the default mtd operations */
mtd->erase = cfi_amdstd_erase_varsize;
mtd->write = cfi_amdstd_write_words;
mtd->read = cfi_amdstd_read;
mtd->sync = cfi_amdstd_sync;
mtd->suspend = cfi_amdstd_suspend;
mtd->resume = cfi_amdstd_resume;
mtd->flags = MTD_CAP_NORFLASH;
.......
......
return mtd;
6.5 JEDEC规范Flash识别分析
6.5.1 JEDEC协议层
// jedec协议层
// linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/mtd/chips/chipreg.c
void register_mtd_chip_driver(struct mtd_chip_driver *drv)
{
spin_lock(&chip_drvs_lock);
// 将协议层接口放到chip_drvs_list链表中
list_add(&drv->list, &chip_drvs_list);
spin_unlock(&chip_drvs_lock);
}
// linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/mtd/chips/jedec_probe.c
static int __init jedec_probe_init(void)
{
register_mtd_chip_driver(&jedec_chipdrv);
return 0;
}
static struct mtd_chip_driver jedec_chipdrv = {
.probe = jedec_probe,
.name = "jedec_probe",
.module = THIS_MODULE
};
static struct mtd_info *jedec_probe(struct map_info *map)
{
/*
* Just use the generic probe stuff to call our CFI-specific
* chip_probe routine in all the possible permutations, etc.
*/
return mtd_do_chip_probe(map, &jedec_chip_probe);
}
static struct chip_probe jedec_chip_probe = {
.name = "JEDEC",
.probe_chip = jedec_probe_chip
};
6.5.2 JEDEC规范Flash识别过程
info->mtd = do_map_probe(*probe_type, &info->map) ->
drv = get_mtd_chip_driver(name) ->
......
// 从chip_drvs_list链表中取出对应协议层驱动
// chip_drvs_list链表在register_mtd_chip_driver接口中设置
// register_mtd_chip_driver接口在协议层调用
// cfi_probe_init/jedec_probe_init/map_ram_init
list_for_each(pos, &chip_drvs_list)
this = list_entry(pos, typeof(*this), list);
if (!strcmp(this->name, name)) {
ret = this;
break;
}
......
return ret;
// 执行协议层的probe函数 即上面分析的cfi_probe接口
ret = drv->probe(map)-> //jedec_probe(map)
// jedec_chip_probe 结构体中有一个.probe_chip接口(jedec_probe_chip)
mtd_do_chip_probe(map, &jedec_chip_probe) ->
genprobe_ident_chips(map, cp) ->
genprobe_new_chip(map, cp, &cfi) ->
// 读取芯片的id,和jedec_table数组比较得到芯片信息
cp->probe_chip(map, 0, NULL, cfi) -> //即jedec_probe_chip
jedec_match( base, map, cfi, &jedec_table[i] )
cfi_jedec_setup(cfi, i) ->
p_cfi->cfiq->P_ID = jedec_table[index].CmdSet;
// 根据读取到的p_cfi->cfiq->P_ID来调用对应接口申请并设置struct mtd_info
mtd = check_cmd_set(map, 1)
return mtd;
return ret;
6.6 添加分区接口add_mtd_partitions分析
// 在physmap_flash_probe函数中调用,err为分区个数
add_mtd_partitions(info->mtd, info->parts, err) ->
......
for (i = 0; i < nbparts; i++)
// 将该分区添加到mtd_partitions链表中,以便后面删除分区
list_add(&slave->list, &mtd_partitions)
// 设置分区的struct mtd_info结构体
......
slave->mtd.type = master->type;
slave->mtd.flags = master->flags & ~parts[i].mask_flags;
slave->mtd.size = parts[i].size;
slave->mtd.writesize = master->writesize;
slave->mtd.oobsize = master->oobsize;
slave->mtd.oobavail = master->oobavail;
slave->mtd.subpage_sft = master->subpage_sft;
......
// 为分区创建对应的字符设备节点和块设备节点
add_mtd_device(&slave->mtd);
......
6.7 physmap_flash_probe函数添加主分区
// 添加主分区创建对应的字符设备节点和块设备节点。
add_mtd_device(info->mtd); // 和前一篇nand flash驱动一致,这里不再赘述
七,自行构建Nor Flash驱动
/*
* 参考 drivers\mtd\maps\physmap.c
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/mtd/mtd.h>
#include <linux/mtd/map.h>
#include <linux/mtd/partitions.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
static struct map_info *s3c_nor_map;
static struct mtd_info *s3c_nor_mtd;
static struct mtd_partition s3c_nor_parts[] = {
[0] = {
.name = "bootloader_nor",
.size = 0x00040000,
.offset = 0,
},
[1] = {
.name = "root_nor",
.offset = MTDPART_OFS_APPEND,
.size = MTDPART_SIZ_FULL,
}
};
static int s3c_nor_init(void)
{
/* 1. 分配map_info结构体 */
s3c_nor_map = kzalloc(sizeof(struct map_info), GFP_KERNEL);;
/* 2. 设置: 物理基地址(phys), 大小(size), 位宽(bankwidth), 虚拟基地址(virt) */
s3c_nor_map->name = "s3c_nor";
s3c_nor_map->phys = 0;
s3c_nor_map->size = 0x1000000; /* >= NOR的真正大小 */
s3c_nor_map->bankwidth = 2;
s3c_nor_map->virt = ioremap(s3c_nor_map->phys, s3c_nor_map->size);
simple_map_init(s3c_nor_map);
/* 3. 使用: 调用NOR FLASH协议层提供的函数来识别 */
printk("use cfi_probe\n");
s3c_nor_mtd = do_map_probe("cfi_probe", s3c_nor_map);
if (!s3c_nor_mtd)
{
printk("use jedec_probe\n");
s3c_nor_mtd = do_map_probe("jedec_probe", s3c_nor_map);
}
if (!s3c_nor_mtd)
{
iounmap(s3c_nor_map->virt);
kfree(s3c_nor_map);
return -EIO;
}
/* 4. add_mtd_partitions */
add_mtd_partitions(s3c_nor_mtd, s3c_nor_parts, 2);
return 0;
}
static void s3c_nor_exit(void)
{
del_mtd_partitions(s3c_nor_mtd);
iounmap(s3c_nor_map->virt);
kfree(s3c_nor_map);
}
module_init(s3c_nor_init);
module_exit(s3c_nor_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
八,总结
Nor flash驱动构建一般分为以下几个步骤
- 根据硬件电路和芯片书册设置struct map_info结构体。
- 调用do_map_probe接口识别对应规范的Nor Flash芯片,并获取到一个对应芯片的struct mtd_info结构体。
- 需要添加除主分区以外的子分区,则调用add_mtd_partitions接口添加。
- 调用add_mtd_device接口创建主分区的字符设备节点以及块设备节点。块设备节点一般用于数据的读写,字符设备节点在ioctl接口中提供了各种对设备的操作,比如擦除分区。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)