【大模型】LongChain多任务应用开发
LongChain + Deepseek + Faiss 打造RAGLongChain的功能跟大模型中的 Function Call 类似。
LongChain + Deepseek + Faiss 打造RAG
LongChain的功能跟大模型中的 Function Call 类似
Longchain
Longchain: * 提供了一套工具、组件和接口
- 简化了创建LLM应用的过程
LangChain + DeepSeek + Faiss 打造RAG问答
Function Calling 的灵感就是从LangChain
Q:function call 跟传统编程里面的函数调用有啥区别
执行起来就是函数
大模型可以理解函数的description,以及参数的description => LLM就是生成 函数的调用,call a funcation (传入的参数)
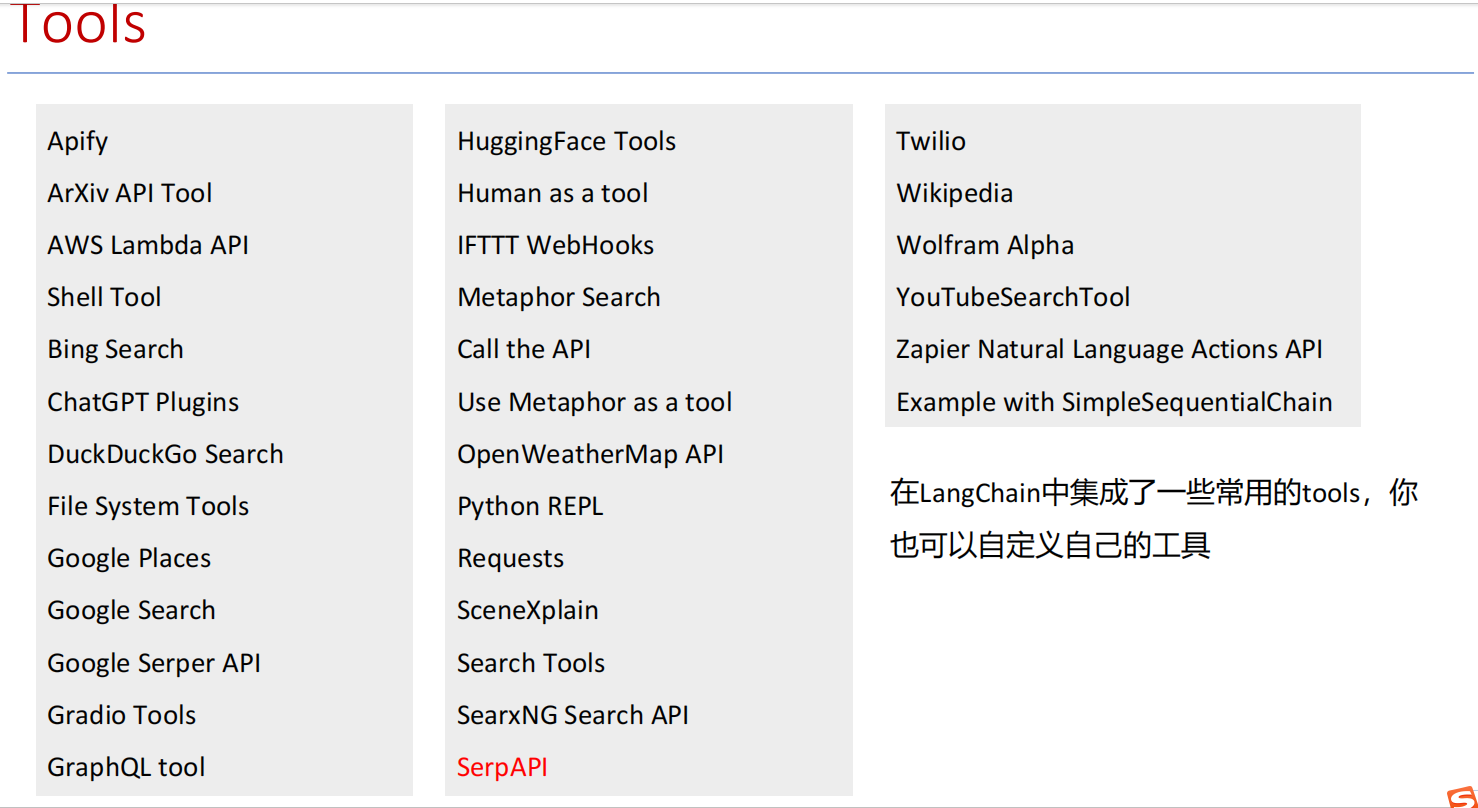
SERPAPI
SERPAPI:它是一个可以调用 Google、Bing、Baidu 等搜索引擎结果的 API,常用于智能体(agent)里做 联网搜索。
安装:
pip install google-search-results
https://serpapi.com/users/sign_in
通过邮箱和手机号码 confirm 之后,会跳转到信息页,有api-key
https://serpapi.com/manage-api-key
在环境变量中设置 serpAPI
from serpapi import GoogleSearch
params = {
"engine": "google",
"q": "雇主责任险",
"api_key": "你的_serpapi_api_key"
}
search = GoogleSearch(params)
results = search.get_dict()
# 打印标题和链接
for res in results.get("organic_results", []):
print(res["title"], res["link"])
SerpAPI 和 LangChain 的关系
- SerpAPI 是什么
定位:第三方搜索 API 服务,可以从 Google、Bing、百度、知乎、京东、微博等搜索引擎抓取结构化结果。
作用:让程序员不必自己写爬虫/解析 HTML,就能直接获取 JSON 格式的搜索结果。
本质:一个独立的外部数据源服务。
- LangChain 是什么
定位:大模型应用开发框架,用于把 LLM 和外部工具、知识库、API 连接起来。
作用:
提供 Agent 机制,让 LLM 可以调用外部工具。
提供 工具封装接口,可以把 REST API、数据库、搜索引擎等封装成工具。
内置对一些常用 API 的集成(包括 SerpAPI)。
- SerpAPI 与 LangChain 的关系
SerpAPI 是外部工具,LangChain 可以把它作为“搜索工具”集成进来。
LangChain 已经内置 SerpAPI 工具封装,你只需要提供 API Key 就能用。
总结:
SerpAPI 是搜索服务,LangChain 是连接大模型和外部工具的框架。LangChain 可以直接调用 SerpAPI,把它变成 LLM 的“联网搜索器”。
from langchain_community.utilities import SerpAPIWrapper
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, AgentType
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# 1. 配置 SerpAPI
search = SerpAPIWrapper(serpapi_api_key="你的_serpapi_key")
# 2. 配置大模型
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# 3. 创建 Agent,并把搜索工具加进去
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=[search],
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
verbose=True
)
# 4. 测试
agent.run("雇主责任险的保障范围有哪些?")
code
Langchain 1
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi # 导入通义千问Tongyi模型
import dashscope
import os
# 从环境变量获取 dashscope 的 API Key
api_key = os.environ.get('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY')
dashscope.api_key = api_key
# 加载 Tongyi 模型
llm = Tongyi(model_name="qwen-turbo", dashscope_api_key=api_key) # 使用通义千问qwen-turbo模型
# 创建Prompt Template
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["product"],
template="What is a good name for a company that makes {product}?",
)
# 新推荐用法:将 prompt 和 llm 组合成一个"可运行序列"
chain = prompt | llm
# 使用 invoke 方法传入输入
result1 = chain.invoke({"product": "colorful socks"})
print(result1)
result2 = chain.invoke({"product": "广告设计"})
print(result2)
import os
from langchain.agents import load_tools
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi # 导入通义千问Tongyi模型
from langchain.agents import AgentType
import dashscope
# 你需要在环境变量中添加 OPENAI_API_KEY 和 SERPAPI_API_KEY
#os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = '*******'
#os.environ["SERPAPI_API_KEY"] = '*******'
# 从环境变量获取 dashscope 的 API Key
api_key = os.environ.get('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY')
dashscope.api_key = api_key
# 加载模型
llm = Tongyi(model_name="qwen-turbo", dashscope_api_key=api_key) # 使用通义千问qwen-turbo模型
# 加载 serpapi 工具
tools = load_tools(["serpapi"])
"""
agent:代理类型
zero-shot-react-description: 根据工具的描述和请求内容的来决定使用哪个工具(最常用)
react-docstore: 使用 ReAct 框架和 docstore 交互, 使用Search 和Lookup 工具, 前者用来搜, 后者寻找term, 举例: Wipipedia 工具
self-ask-with-search 此代理只使用一个工具: Intermediate Answer, 它会为问题寻找事实答案(指的非 gpt 生成的答案, 而是在网络中,文本中已存在的), 如 Google search API 工具
conversational-react-description: 为会话设置而设计的代理, 它的prompt会被设计的具有会话性, 且还是会使用 ReAct 框架来决定使用来个工具, 并且将过往的会话交互存入内存
"""
# 工具加载后需要初始化,verbose=True 代表打印执行详情
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION, verbose=True)
# 运行 agent
agent.run("今天是几月几号?历史上的今天有哪些名人出生")
Memory
在这里插入图片描述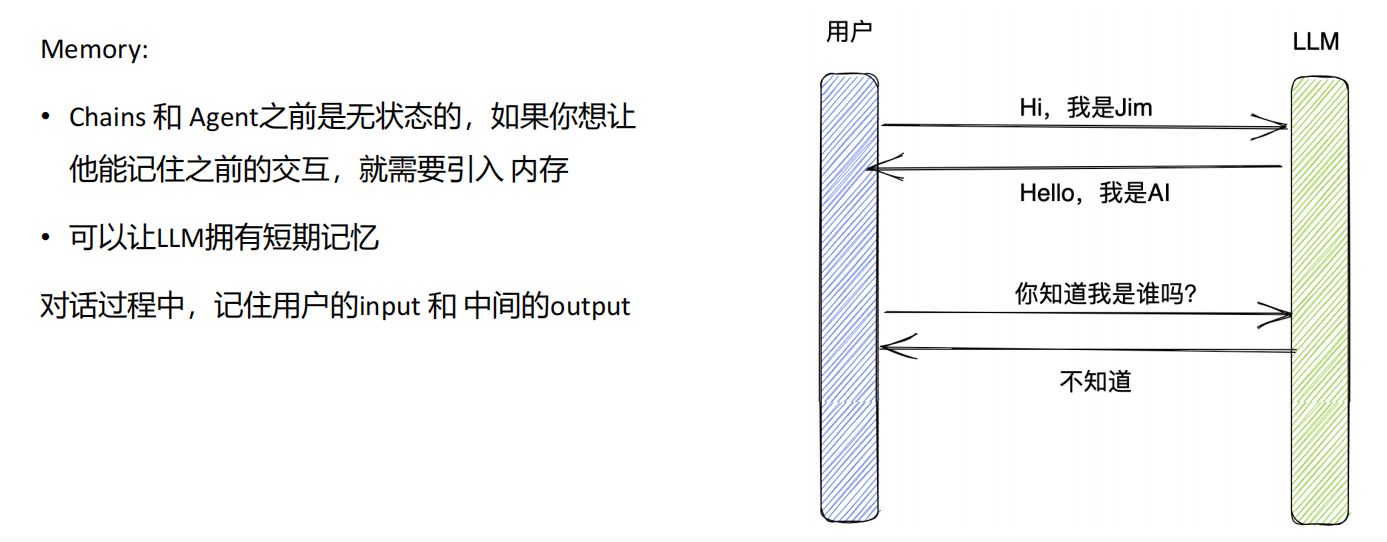
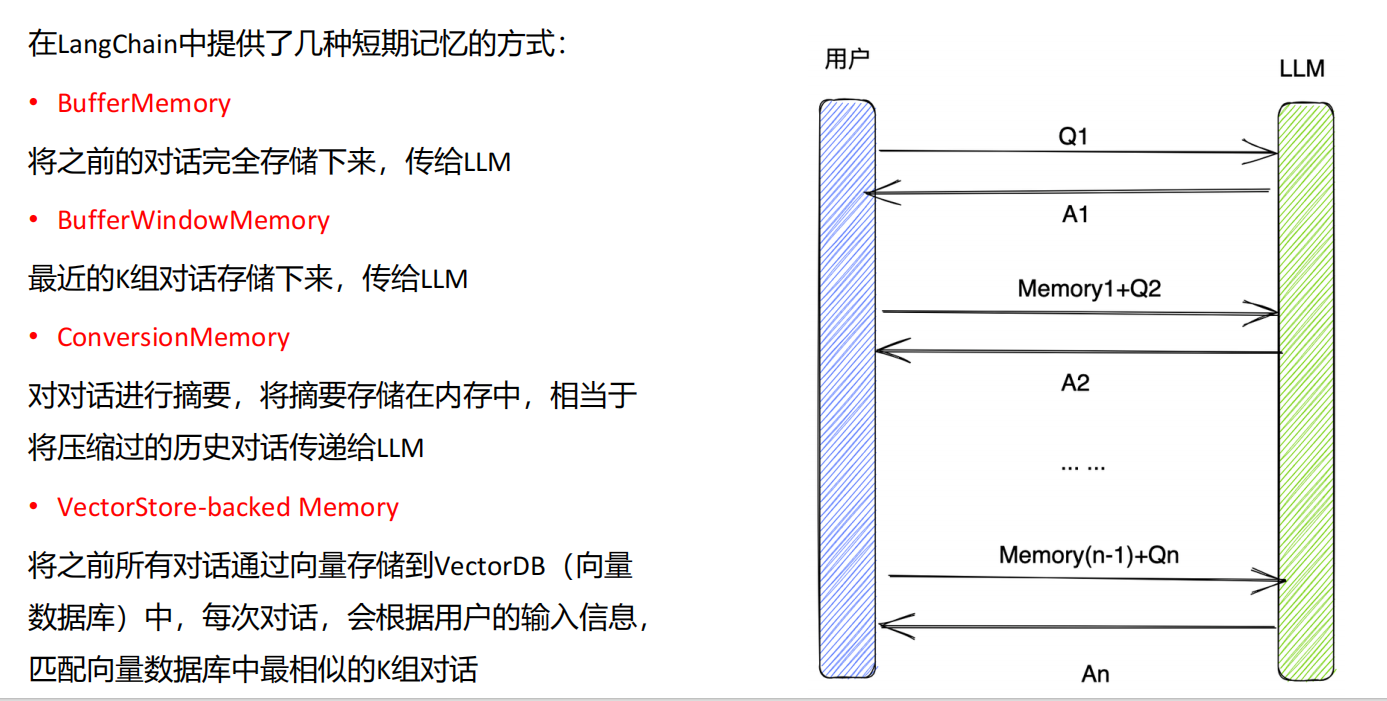
ConversationChain
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# In[1]:
import os
from langchain.agents import load_tools
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi # 导入通义千问Tongyi模型
from langchain.agents import AgentType
from langchain import ConversationChain
import dashscope
# 从环境变量获取 dashscope 的 API Key
api_key = os.environ.get('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY')
dashscope.api_key = api_key
# 加载 Tongyi 模型
llm = Tongyi(model_name="qwen-turbo", dashscope_api_key=api_key) # 使用通义千问qwen-turbo模型
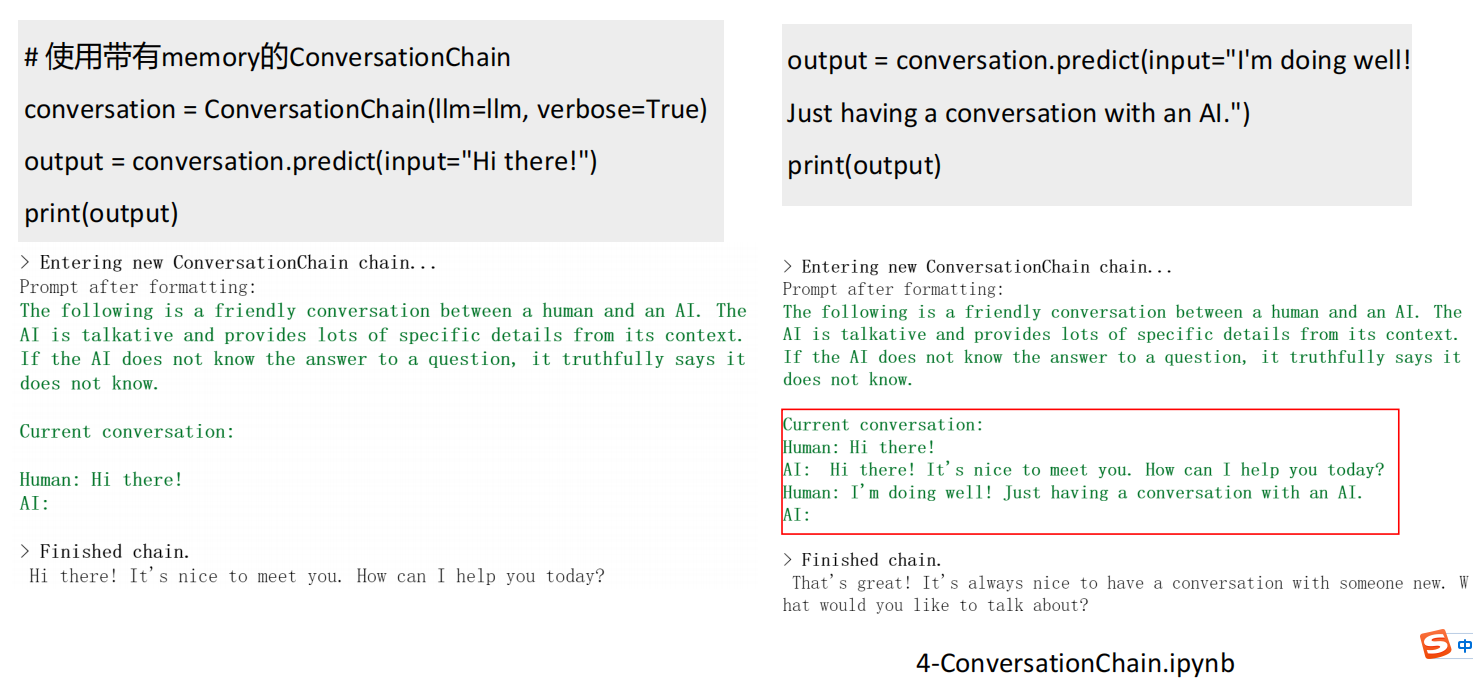
# 使用带有memory的ConversationChain
conversation = ConversationChain(llm=llm, verbose=True)
output = conversation.predict(input="Hi there!")
print(output)
# In[2]:
output = conversation.predict(input="I'm doing well! Just having a conversation with an AI.")
print(output)
langchain 和 qwen-agent 之间属于竞品关系,langchain 中也有很多智能体
Case - 工具链组合
from langchain.agents import Tool, AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import AgentAction, AgentFinish
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
import re
import json
from typing import List, Union, Dict, Any
import os
# 把工具制作好,传给 create_react_agent
# 设置通义千问API密钥
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY = 'sk-882e296067b744289acf27e6e20f3ec0'
# 自定义工具1:文本分析工具
class TextAnalysisTool:
"""文本分析工具,用于分析文本内容"""
def __init__(self):
self.name = "文本分析"
self.description = "分析文本内容,提取字数、字符数和情感倾向"
def run(self, text: str) -> str:
"""分析文本内容
参数:
text: 要分析的文本
返回:
分析结果
"""
# 简单的文本分析示例
word_count = len(text.split())
char_count = len(text)
# 简单的情感分析(示例)
positive_words = ["好", "优秀", "喜欢", "快乐", "成功", "美好"]
negative_words = ["差", "糟糕", "讨厌", "悲伤", "失败", "痛苦"]
positive_count = sum(1 for word in positive_words if word in text)
negative_count = sum(1 for word in negative_words if word in text)
sentiment = "积极" if positive_count > negative_count else "消极" if negative_count > positive_count else "中性"
return f"文本分析结果:\n- 字数: {word_count}\n- 字符数: {char_count}\n- 情感倾向: {sentiment}"
# 自定义工具2:数据转换工具
class DataConversionTool:
"""数据转换工具,用于在不同格式之间转换数据"""
def __init__(self):
self.name = "数据转换"
self.description = "在不同数据格式之间转换,如JSON、CSV等"
def run(self, input_data: str, input_format: str, output_format: str) -> str:
"""转换数据格式
参数:
input_data: 输入数据
input_format: 输入格式
output_format: 输出格式
返回:
转换后的数据
"""
try:
if input_format.lower() == "json" and output_format.lower() == "csv":
# JSON到CSV的转换示例
data = json.loads(input_data)
if isinstance(data, list):
if not data:
return "空数据"
# 获取所有可能的列
headers = set()
for item in data:
headers.update(item.keys())
headers = list(headers)
# 创建CSV
csv = ",".join(headers) + "\n"
for item in data:
row = [str(item.get(header, "")) for header in headers]
csv += ",".join(row) + "\n"
return csv
else:
return "输入数据必须是JSON数组"
elif input_format.lower() == "csv" and output_format.lower() == "json":
# CSV到JSON的转换示例
lines = input_data.strip().split("\n")
if len(lines) < 2:
return "CSV数据至少需要标题行和数据行"
headers = lines[0].split(",")
result = []
for line in lines[1:]:
values = line.split(",")
if len(values) != len(headers):
continue
item = {}
for i, header in enumerate(headers):
item[header] = values[i]
result.append(item)
return json.dumps(result, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
else:
return f"不支持的转换: {input_format} -> {output_format}"
except Exception as e:
return f"转换失败: {str(e)}"
# 自定义工具3:文本处理工具
class TextProcessingTool:
"""文本处理工具,用于处理文本内容"""
def __init__(self):
self.name = "文本处理"
self.description = "处理文本内容,如查找、替换、统计等"
def run(self, operation: str, content: str, **kwargs) -> str:
"""处理文本内容
参数:
operation: 操作类型
content: 文本内容
**kwargs: 其他参数
返回:
处理结果
"""
if operation == "count_lines":
return f"文本共有 {len(content.splitlines())} 行"
elif operation == "find_text":
search_text = kwargs.get("search_text", "")
if not search_text:
return "请提供要查找的文本"
lines = content.splitlines()
matches = []
for i, line in enumerate(lines):
if search_text in line:
matches.append(f"第 {i+1} 行: {line}")
if matches:
return f"找到 {len(matches)} 处匹配:\n" + "\n".join(matches)
else:
return f"未找到文本 '{search_text}'"
elif operation == "replace_text":
old_text = kwargs.get("old_text", "")
new_text = kwargs.get("new_text", "")
if not old_text:
return "请提供要替换的文本"
new_content = content.replace(old_text, new_text)
count = content.count(old_text)
return f"替换完成,共替换 {count} 处。\n新内容:\n{new_content}"
else:
return f"不支持的操作: {operation}"
# 创建工具链
def create_tool_chain():
"""创建工具链"""
# 创建工具
text_analysis = TextAnalysisTool()
data_conversion = DataConversionTool()
text_processing = TextProcessingTool()
# 组合工具
tools = [
Tool(
name=text_analysis.name,
func=text_analysis.run,
description="分析文本内容,提取字数、字符数和情感倾向"
),
Tool(
name=data_conversion.name,
func=data_conversion.run,
description="在不同数据格式之间转换,如JSON、CSV等"
),
Tool(
name=text_processing.name,
func=text_processing.run,
description="处理文本内容,如查找、替换、统计等"
)
]
# 初始化语言模型
llm = Tongyi(model_name="qwen-turbo", dashscope_api_key=DASHSCOPE_API_KEY)
# 创建提示模板
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""你是一个有用的AI助手,可以使用以下工具:
{tools}
可用工具名称: {tool_names}
使用以下格式:
问题: 你需要回答的问题
思考: 你应该始终思考要做什么
行动: 要使用的工具名称,必须是 [{tool_names}] 中的一个
行动输入: 工具的输入
观察: 工具的结果
... (这个思考/行动/行动输入/观察可以重复 N 次)
思考: 我现在已经有了最终答案
回答: 对原始问题的最终回答
开始!
问题: {input}
思考: {agent_scratchpad}"""
)
# 创建Agent
agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
# 创建Agent执行器
agent_executor = AgentExecutor.from_agent_and_tools(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
memory=ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history"),
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=False # 关闭自动重试, True会严格检查重试
)
return agent_executor
# 示例:使用工具链处理任务
def process_task(task_description):
"""
使用工具链处理任务
参数:
task_description: 任务描述
返回:
处理结果
"""
try:
agent_executor = create_tool_chain()
response = agent_executor.invoke({"input": task_description})
return response["output"] # 从返回的字典中提取输出
except Exception as e:
return f"处理任务时出错: {str(e)}"
# 示例用法
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 示例1: 文本分析与处理
task1 = "分析以下文本的情感倾向,并统计其中的行数:'这个产品非常好用,我很喜欢它的设计,使用体验非常棒!\n价格也很合理,推荐大家购买。\n客服态度也很好,解答问题很及时。'"
print("任务1:", task1)
print("结果:", process_task(task1))
# 示例2: 数据格式转换
task2 = "将以下CSV数据转换为JSON格式:'name,age,comment\n张三,25,这个产品很好\n李四,30,服务态度差\n王五,28,性价比高'"
print("\n任务2:", task2)
print("结果:", process_task(task2))
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi # 导入通义千问Tongyi模型
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# 设置通义千问API密钥
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY = 'sk-882e296067b744289acf27e6e20f3ec0'
# stream=True 让LLM支持流式输出
llm = Tongyi(model_name="qwen-turbo", dashscope_api_key=DASHSCOPE_API_KEY, stream=True)
# 定义三个子任务:翻译->处理->回译
translate_to_en = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Translate this to English: {input}") | llm | StrOutputParser()
process_text = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Analyze this text: {text}") | llm | StrOutputParser()
translate_to_cn = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Translate this to Chinese: {output}") | llm | StrOutputParser()
# 组合成多任务链
workflow = {"text": translate_to_en} | process_text | translate_to_cn
#workflow.invoke({"input": "北京有哪些好吃的地方,简略回答不超过200字"})
# 使用stream方法,边生成边打印
for chunk in workflow.stream({"input": "北京有哪些好吃的地方,简略回答不超过200字"}):
print(chunk, end="", flush=True)
print() # 换行
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)