如何搭建一个基于vue2和element-ui的项目框架模板(两万四千字长文)
如何搭建一个基于vue2和element-ui的项目框架模板。包含Vuex 状态管理、Vue-router、Axios 封装及接口管理、ElementUI 组件按需加载、vue.config.js 基础配置、Sass 全局样式、svg-sprite-loader 图标引入、配置 打包分析、去掉 console.log、splitChunks 单独打包第三方模块等等
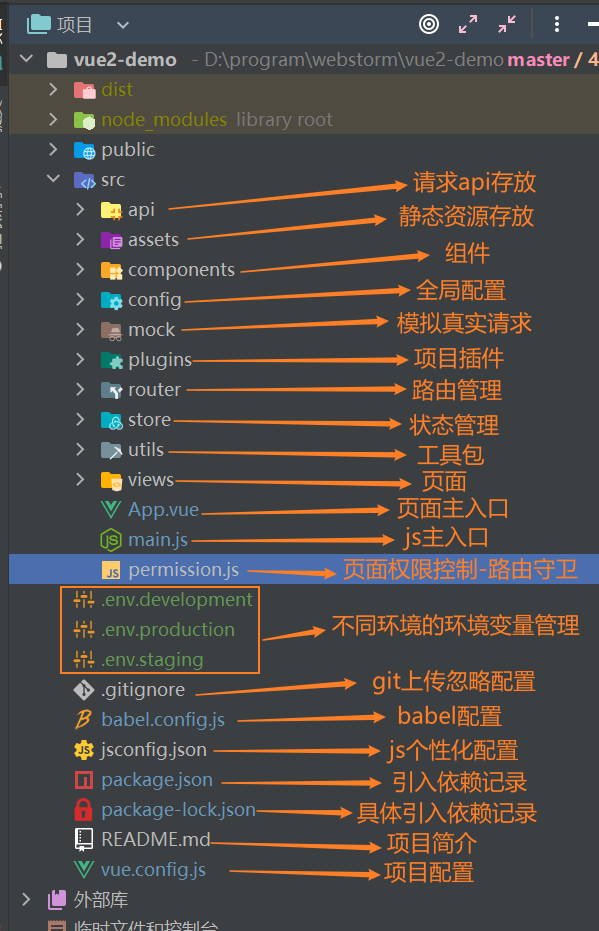
第一步 创建vue项目
使用vue
script标签引入
如果只是单纯的使用vue,可以使用<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>直接引入
npm安装vue
- 使用npm安装vue需要先安装node.js,如果你的电脑未安装node,可以参考我的个人碰到的前端问题总结及解决方案2第15个问题先安装nvm(node version manager),然后再安装npm。
- npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org (装完之后运行这个换下npm源,改成国内的,下载依赖速度会快些
- 安装好npm后,全局安装vue-cli(vue脚手架),命令如下,个人推荐安装vueCli3及以上版本(毕竟现在脚手架已经5.0了)。
//安装vueCli2
npm install vue-cli -g
//安装vueCli3及以上
npm install @vue/cli -g

vue项目的创建
创建vue项目有三种方式
- 编程工具直接创建。
比如webstorm创建项目如下:
第一步:点击文件 --> 点击新建 --> 点击项目

第二步:选择vue项目 --> 选择项目目录(我这里是默认的,可以自己修改)–> 选择要构建项目的vueCli位置,可以选择自己本地安装的vueCli目录,也可以使用webstorm默认的npx命令执行vueCli --> 创建项目

- vue ui创建。可视化的操作,创建、安装初始化依赖简单。但需要注意是若想使用vue的UI界面来创建项目,需先安装vue脚手架 3.0以上的版本。详细创建的步骤可以看下面参考的链接。
- vueCli创建。
第二步 vue-router、vuex、element ui、axios安装和配置
main.js
vue-router、vuex、element ui安装配置完后都需要在src目录下main.js(主js入口)里进行引用才会生效。
main.js
/**
* normalize.css重置浏览器css样式。
* 这里需要`npm install normalize.css`
* reset和normalize区别。
* reset的目的是将所有的浏览器的自带样式重置掉,这样更易于保持各浏览器渲染的一致性。
* normalize的理念则是尽量保留浏览器的默认样式,不进行太多的重置,而尽力让这些样式保持一致并尽可能与现代标准相符合。
*/
import "normalize.css/normalize.css";
import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import router from "./router"; //vue-router
import store from "./store"; //vuex
import "@/plugins/element-ui"; //按需引入的element组件
import './permission' //页面权限(vue-router的全局守卫配置)
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount("#app");
vue-route(vue路由管理)
安装
打开项目,在项目目录下运行下面命令进行安装。项目的package.json的dependencies里有vue-router就代表安装成功了。如果之前已经有了就不用执行安装命令。结果如图。
//vue2
npm install vue-router@3.6.5
//vue3
npm install vue-router

需要注意的是如果你使用的是vue2,那么不要直接npm install vue-router,这样会安装最新版本即4.x版本的vue-router,4.x版本的vue-router与vue2不兼容。
查看vue-router版本命令如图。

配置
项目src目录下新建router目录。内容如图。
- index.js里生成vue-router实例,并配置相关信息,然后暴露出去。
- router.config.js里存放页面路由信息。
分为静态路由和动态路由。
动态路由与用户角色权限相关,可配合后端存放取出。

index.js内容如下。
import Vue from "vue";
import Router from "vue-router";
import { constantRouterMap } from "@/router/route.config";
// 【优化】访问online功能测试 浏览器控制台抛出异常
try {
// 保存原来的push函数
const originalPush = Router.prototype.push;
// 重写push函数
Router.prototype.push = function push(location, onResolve, onReject) {
if (onResolve || onReject)
return originalPush.call(this, location, onResolve, onReject);
// 调用原来的push函数,并捕获异常
return originalPush.call(this, location).catch((err) => err);
};
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
Vue.use(Router);
const createRouter = () =>
new Router({
mode: "history", //hash、history两种模式
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes: constantRouterMap,
scrollBehavior: () => ({ y: 0 }),
});
const router = createRouter();
/**
* 重置注册的路由导航map
* 主要是为了通过addRoutes方法动态注入新路由时,避免重复注册相同name路由
*
* 修改用户角色、用户退出时调用
*/
export function resetRouter() {
const newRouter = createRouter();
router.matcher = newRouter.matcher; // reset router
}
export default router;
router.config.js内容如下:
import HomePage from "@/views/HomePage";
/**
* constantRouterMap
* 没有权限要求的基本页
* 所有角色都可以访问
* 不需要动态判断权限的路由
*/
export const constantRouterMap = [
{
path: "/",
name: "home",
component: HomePage,
meta: {
title: "首页",
},
},
{
path: "/403",
name: "403",
component: () => import("@/views/exception/403Page"),
},
{
path: "/500",
name: "500",
component: () => import("@/views/exception/500Page"),
},
];
/**
* 动态菜单,走权限控制
*
* 可从后端获取
* 可分多个角色
* 这里分为二个角色 管理员admin 普通角色 visitor
*/
export const asyncRouterMap = [
{
path: "/onlyAdminCanSee",
name: "adminPage",
component: () => import('@/views/AdminPage'),
meta: {
title: "管理员页面",
keepalive: false,
roles: ["admin"],
},
},
{
path: "/onlyLoginUserCanSee",
name: "visitPage",
component: () => import('@/views/VisitorPage'),
meta: {
title: "用户界面",
keepalive: false,
roles: ["admin", "visitor"],
},
},
{ path: '*', redirect: '/404',component: () => import('@/views/exception/404Page') }
];
全局守卫配置(router.beforeEach前置守卫、router.beforeEach后置守卫)
在src下新建permission.js,需要在main.js里引用。
需要安装一个轻量级的进度条组件NProgress
内容如下。
import Vue from "vue";
import router from "./router";
import store from "./store";
import NProgress from "nprogress"; // progress bar
import "nprogress/nprogress.css"; // progress bar style
import {ACCESS_TOKEN} from "@/store/mutation-types";
NProgress.configure({showSpinner: false}); // NProgress Configuration
const whiteList = ['/login','/home'] // 页面路由白名单
//前置守卫
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
NProgress.start(); // start progress bar
//判断是否是去登录页面,是,直接过
if (to.path === '/login') {
next()
NProgress.done()
} else {
//不是去登录页面,判断用户是否登录过
if (Vue.ls.get(ACCESS_TOKEN)) {
const hasRoles = store.getters.userRoles && store.getters.userRoles.length > 0
//登录了,判断是否有用户详细信息(如果有),比如角色权限,直接过
if (hasRoles) {
next()
} else {
//没有用户详细信息,代表用户刷新了,或者其他行为,重新获取一次用户信息,
// 并根据该用户的角色权限,来获取用户权限范围内能看到的界面
try {
//获取当前角色
const {roles} = await store.dispatch('app/getInfo')
//根据权限查询动态路由
const accessRoutes = await store.dispatch('permission/generateRoutes', roles)
//添加动态路由
for (let i = 0; i < accessRoutes.length; i++) {
const element = accessRoutes[i]
router.addRoute(element)
// router.addRoute('globalLayout', {
// path: element.path,
// name: element.path.slice(1, 2).toUpperCase() + element.path.slice(2),
// component: () => import('@/' + element.component),
// // meta: {
// // // title: '',
// // roles: [roles],
// // }
// })
}
// console.log(router.getRoutes())
//decodeURIComponent
const redirect = from.query.redirect || to.path
if (to.path === redirect) {
// 确保addRoutes已完成 ,set the replace: true so the navigation will not leave a history record
next({...to, replace: true})
} else {
// 跳转到目的路由
next({path: redirect})
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
await store.dispatch('app/Logout').then(() => {
next({path: '/login', query: {redirect: to.fullPath}})
})
NProgress.done()
}
}
}
else {
//如果没有登录
if (whiteList.indexOf(to.path) !== -1) {
// 在免登录白名单,直接进入
next()
} else {
//跳转到登录页面
next({path: '/login', query: {redirect: to.fullPath}})
NProgress.done()
}
}
}
});
vuex (vue状态管理)
安装
运行npm 安装命令。结果如图。
//vue2
npm install vuex@3.6.2
//vue3
npm install vuex

需要注意的是如果你使用的是vue2,那么不要直接npm install vuex,这样会安装最新版本即4.x版本的vuex,4.x版本的vuex与vue2不兼容。
查看vuex版本命令如图。

配置
项目src目录创建store目录,内容如图。
- index.js vuex的路口文件
- modules 项目各模块的状态管理,如果项目比较小的话,可以直接将内容写在入口文件里
permission.js里存放的是前端权限管理方法和操作。权限如果是前端控制才有会用到。即动态路由内容存放在前端。 - mutation-type.js 存放全局变量,比如请求头token名、登录状态名等

index.js
// you do not need `import app from './modules/app'`
// it will auto require all vuex module from modules file
const modules = modulesFiles.keys().reduce((modules, modulePath) => {
// set './app.js' => 'app'
const moduleName = modulePath.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1')
const value = modulesFiles(modulePath)
modules[moduleName] = value.default
return modules
}, {})
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules,
getters
})
export default store
app.js
const state = {
showText:'hello world',
}
const mutations = {
SET_SHOW_TEXT(state,showText){
state.showText=showText
}
}
const actions = {}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
permission.js
import { constantRouterMap, asyncRouterMap } from "@/router/route.config";
/**
* 通过meta.role判断是否与当前用户权限匹配
* @param roles
* @param route
*/
function hasPermission(roles, route) {
if (route.meta && route.meta.roles) {
// return roles.some(role => route.meta.roles.includes(role))
if (route.meta.roles.indexOf(roles) >= 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
return true;
}
}
/**
* 递归过滤异步路由表,返回符合用户角色权限的路由表
* @param routes asyncRoutes
* @param roles
*/
export function filterAsyncRoutes(routes, roles) {
const res = [];
routes.forEach((route) => {
const tmp = { ...route };
if (hasPermission(roles, tmp)) {
if (tmp.children) {
tmp.children = filterAsyncRoutes(tmp.children, roles);
}
res.push(tmp);
}
});
return res;
}
const state = {
routes: [],
addRoutes: [],
};
const mutations = {
SET_ROUTES: (state, routes) => {
state.addRoutes = routes;
state.routes = constantRouterMap.concat(routes);
},
};
const actions = {
//根据角色权限过滤生成动态路由
generateRoutes({ commit }, roles) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
let accessedRoutes;
accessedRoutes = filterAsyncRoutes(asyncRouterMap, roles);
commit("SET_ROUTES", accessedRoutes);
resolve(accessedRoutes);
});
},
};
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
};
mutation-types.js
//将常量放在单独的文件中,方便协作开发
export const ACCESS_TOKEN = "Access-Token"; //token存储名字
export const USER_INFO = "Login_Userinfo";
element ui(基于vue的组件库)
安装
npm 命令
npm i element-ui -S
配置(按需引入)
为什么要按需引入?
按需引入的目的是只引入用到的组件,以达到减小项目体积的目的。
要实现按需引入需要安装babel-plugin-component依赖
安装命令npm i babel-plugin-component -D,安装成功后需要在babel.config.js配置
module.exports = {
/**
compact: false解除babel处理文件的大小被限制在了500kb的限制,
用来解决npm run dev或者npm run build 出现...exceeds the max of 500KB
*/
compact: false,
presets: [
["@vue/cli-plugin-babel/preset"],
["@babel/preset-env", { modules: false }], //es2015
],
plugins: [
[
"component",
{
libraryName: "element-ui",
styleLibraryName: "theme-chalk",
},
],
],
};
官网的按需引入会报错,‘es2015’改成’@babel/preset-env’,就好了

然后就是按需引入element组件内容。
我是在src目录下新建了个plugins目录,如图。
element-ui.js里面存放的element按需引入的组件。
这里我引入了Button、Message、MessageBox组件,button组件首页HomePage有用到,Message、MessageBox消息组件下面的axios拦截器配置里有用到。

element-ui.js
// 按需全局引入 element ui组件
import Vue from "vue";
import { Button,MessageBox } from "element-ui";
import { Message } from "element-ui";
// import { message } from "@/config/message"; //全局配置message
Vue.use(Button);
Vue.prototype.$message = Message;
Vue.prototype.$msgbox = MessageBox;
Vue.prototype.$alert = MessageBox.alert;
Vue.prototype.$confirm = MessageBox.confirm;
Vue.prototype.$prompt = MessageBox.prompt;
按需引入区别?
vant-ui(移动端组件库)使用babel-plugin-import按需引入,element-ui使用babel-plugin-component,两者有啥区别?
babel-plugin-import 是 ant-design 团队出的,可以说其他绝大部分按需引入的插件都是在此基础上魔改的。
babel-plugin-component 是饿了么团队在前者的基础上做了一些改动。主要是因为 fork 的时间太早(2016 年 4 月),饿了么修复了一些早期 bug 却并没有 PR 到 ant-design 的仓库里去,但后来 ant-design 也有修复;再就是后来 ant-design 的有一些配置项的变动、而饿了么团队却没有跟进合并。所以二者还是有一些差异的。
axios (前后端交互)
安装
npm 安装命令
npm install axios
配置
在项目src目录下创建utils目录用来存放项目的工具类:
- request.js :创建axios实例,并配置axios的请求和响应拦截器。
- 请求拦截器一般会全局添加请求头token或调用element的loading组件。响应拦截器用来对于请求的报错信息进行提示。
创建api目录用来存放模块请求接口:
- index.js:引入utils目录下的request的axios实例,来封装一般的axios请求,比如get、post以及文件下载等请求。
- testApi (模块名): 项目模块引入index.js,请求后端。

utils/request.js
import Vue from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
import store from "@/store";
import { Message, MessageBox } from "element-ui";
import { ACCESS_TOKEN } from "@/store/mutation-types";
// 创建axios 实例
const service = axios.create({
baseURL: "/api", // api base_url
timeout: 90000, // 请求超时时间
});
const err = (error) => {
if (
error.code === "ECONNABORTED" ||
error.message === "Network Error" ||
error.message.includes("timeout")
) {
Message.error("请求超时,请稍候重试");
}
if (error.response) {
let data = error.response.data;
const token = Vue.ls.get(ACCESS_TOKEN);
console.log("------异常响应------", token);
console.log("------异常响应------", error.response.status);
var pathName = window.location.pathname;
switch (error.response.status) {
/**
* 401:未授权,请重新登录、403:拒绝访问、404:很抱歉,资源未找到!、408:请求超时
* 500:服务器内部错误、502:网关错误、504:网络超时、505:HTTP 版本不受支持
*/
case 401:
Message.error("未授权,请重新登录");
if (token) {
store.dispatch("Logout").then(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
window.location.reload();
}, 1500);
});
}
break;
case 403:
Message.error("拒绝访问");
break;
case 404:
Message.error("很抱歉,资源未找到!");
break;
case 408:
Message.error("请求超时");
break;
case 500:
Message.error("服务器内部错误");
break;
case 502:
Message.error("网关错误");
break;
case 504:
Message.error("网络超时");
break;
case 505:
Message.error("HTTP 版本不受支持");
break;
default:
Message.error(data.message || data);
break;
}
}
return Promise.reject(error);
// return Promise.reject(new Error(error))
};
// 请求拦截器,一般用来添加请求token和请求方法加loading
service.interceptors.request.use(
(config) => {
const token = Vue.ls.get(ACCESS_TOKEN);
if (token) {
config.headers["X-Access-Token"] = token; // 让每个请求携带自定义 token 请根据实际情况自行修改
}
return config;
},
(error) => {
return Promise.reject(error);
// return Promise.reject(new Error(error))
}
);
// 响应拦截器
service.interceptors.response.use((response) => {
return response.data;
}, err);
export { service as axios };
api/index.js
import { axios } from "@/utils/request";
/**
* get请求
* @param url 请求api
* @param parameter 请求参数
*/
export function getAction(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: "get",
params: parameter,
});
}
/**
* post请求
* @param url 请求api
* @param parameter 请求参数
*/
export function postAction(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: "post",
data: parameter,
});
}
export function postAction1(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: "post",
data: parameter,
contentType: "application/json", //请求头类型
});
}
export function postAction2(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: "post",
data: parameter,
timeout: 300000, // 请求超时时间
});
}
/**
* post method= {post | put}
*/
export function httpAction(url, parameter, method) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: method,
data: parameter,
});
}
/**
* put请求
*/
export function putAction(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: "put",
data: parameter,
});
}
/**
* delete请求
*/
export function deleteAction(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
method: "delete",
params: parameter,
});
}
/**
* 下载文件 用于excel导出
*/
export function downFile(url, parameter) {
return axios({
url: url,
params: parameter,
method: "get",
responseType: "blob",
});
}
api/testApi
import {postAction} from "@/api/index";
//登录
const login=(params)=>postAction("/sys/login",params);
export {
login
}
第三步:配置不同环境的后端请求地址(开发、测试、正式)
在src目录新建config目录。
index.js根据当前所属环境动态引入参数,比如开发环境下就会引入env.development.js下的变量内容。env.*.js配置全局的环境参数,比如后端请求地址,项目的静态文件引用的cdn地址,端口号等
在项目目录下创建.env.*文件。
.env.*是会根据npm命令调用,里面配置不同环境的参数。- 注意:千万不要建到src目录下,这样会导致如果你在.env.*里创建了VUE_APP_开头的环境变量后,在其他地方使用
process.env.VUE_APP_*就会报undefined,查不到。
自问自答环节:.env.*就可以根据不同环境定义不同环境的参数,为啥还定义index.js和env.*.js?
答:个人觉得这个更友好吧,含义更清晰。

在packge.json的scripts里添加"stage": "vue-cli-service build --mode staging",
npm run serve运行成功后就会使用开发环境的环境变量npm run bulid打包过程中里的js文件会使用正式环境的环境变量- 同理,
npm run stage打包过程中里的js文件会使用测试环境的环境变量

config/index.js
/**
* 以 VUE_APP_ 开头的变量,在代码中可以通过 process.env.VUE_APP_ 访问。
* 比如,VUE_APP_ENV = 'development' 通过process.env.VUE_APP_ENV 访问。
* 除了 VUE_APP_* 变量之外,在你的应用代码中始终可用的还有两个特殊的变量NODE_ENV 和BASE_URL
*/
// 根据环境引入不同配置 process.env.VUE_APP_ENV
const environment = process.env.VUE_APP_ENV || "production";
const config = require("./env." + environment);
module.exports = config;
config/env.*.js
env.development.js
// 本地环境配置
module.exports = {
title: "testDemo",
baseApi: "http://localhostxxx/api", // 本地api请求地址
port: 8080,
};
env.staging.js
// 测试环境配置
module.exports = {
title: "testDemo",
baseApi: "http://testxxx/api",
port: 8081,
};
env.productionxxx.js
// 正式环境配置
module.exports = {
title: "testDemo",
baseApi: "http://productionxxx/api",
port: 8082,
};
项目目录(我这里就是vue2-demo)/.env.*
.env.development
NODE_ENV='development'
# must start with VUE_APP_
VUE_APP_ENV = 'development'
.env.staging
NODE_ENV='staging'
# must start with VUE_APP_
VUE_APP_ENV = 'staging'
.env.production
NODE_ENV='production'
# must start with VUE_APP_
VUE_APP_ENV = 'production'
vue.config.js (基础配置+代理跨域、sass全局样式、图标引入、打包分析、生成环境去除console.log、splitChunks 单独打包第三方模块)
- sass全局样式需要安装node-sass和sass-loader。
我的node版本是14.15.4。运行下面命令。如图所示。npm install node-sass@4.14.1 sass-loader@12.0.0 -D

参考:
安装 node-sass 和 sass-loader 的过程及各 node 版本对应的 node-sass 版本号
Sass详解
sass官网
-
图标引入需要安装
svg-sprite-loader,将svg图片以雪碧图的方式在项目中加载。
雪碧图是一种将多个图片资源合并成一张大图片的做法,用到网页,能减少 HTTP 请求数量,以及提前加载一些还未使用的小图片。npm i svg-sprite-loader有两种方式——使用iconfont 集成到项目、使用svg图标。
-
打包分析需要安装webpack-bundle-analyzer(打包分析可视化工具)
npm install webpack-bundle-analyzer -D -
runtime.js处理策略。
npm add html-webpack-plugin script-ext-html-webpack-plugin -D -
vue.config.js代码如下。
"use strict"; const path = require("path"); const defaultSettings = require("./src/config/index.js"); const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require("webpack-bundle-analyzer").BundleAnalyzerPlugin; function resolve(dir) { return path.join(__dirname, dir); } const name = defaultSettings.title || "testDemo"; // 生产环境,测试和正式 const IS_PROD = ["production", "prod"].includes(process.env.NODE_ENV); const { defineConfig } = require("@vue/cli-service"); module.exports = defineConfig({ // publicPath: './', // 署应用包时的基本 URL。 vue-router hash 模式使用 //署应用包时的基本 URL。 vue-router history模式使用 publicPath: "/", // 生产环境构建文件的目录 outputDir: "dist", // outputDir的静态资源(js、css、img、fonts)目录 assetsDir: "static", //保存是否校验eslint lintOnSave: !IS_PROD, // js调试源码映射地图,如果你不需要生产环境的 source map,可以将其设置为 false,即打包时不会生成 .map 文件,以加速生产环境构建。 productionSourceMap: false, // 默认情况下 babel-loader 会忽略所有 node_modules 中的文件。你可以启用本选项,以避免构建后的代码中出现未转译的第三方依赖。 transpileDependencies: false, devServer: { port: defaultSettings.port, // 端口 open: false, // 启动后打开浏览器 client: { overlay: { //当出现编译器错误或警告时,在浏览器中显示全屏覆盖层 //设置错误在页面弹出、警告不在页面弹出 warnings: false, errors: true, }, }, //proxy代理 /** * 代理定义 * 正向代理:替客户端向服务器发送请求,可以解决跨域问题 * 反向代理:替服务器统一接收请求。 */ proxy: { //配置跨域 "/api": { target: defaultSettings.baseApi, // ws:true, changOrigin: true, pathRewrite: { "^/api": "", }, }, }, }, configureWebpack: (config) => { config.name = name; // 为生产环境修改配置... /** * 依赖模块采用第三方cdn资源 * externals: { * '包名' : '在项目中引入的名字' * 'vue': 'Vue', * 'vuex': 'Vuex', * 'vue-router': 'VueRouter', * 'element-ui': 'ELEMENT' * } */ // if (IS_PROD) { // // externals // config.externals = externals // } // 取消webpack警告的性能提示 config.performance = { hints: "warning", //入口起点的最大体积 maxEntrypointSize: 50000000, //生成文件的最大体积 maxAssetSize: 30000000, //只给出 js 文件的性能提示 assetFilter: function (assetFilename) { return assetFilename.endsWith(".js"); }, }; }, css: { extract: IS_PROD, // 是否将组件中的 CSS 提取至一个独立的 CSS 文件中 (而不是动态注入到 JavaScript 中的 inline 代码)。 sourceMap: false, loaderOptions: { //专门用来全局颜色、变量、mixin,千万不要引入全局样式,要不然每个页面都会重复引用 scss: { // 向全局sass样式传入共享的全局变量, $src可以配置图片cdn前缀 // 详情: https://cli.vuejs.org/guide/css.html#passing-options-to-pre-processor-loaders // $cdn: "${defaultSettings.$cdn}"; additionalData: ` @import "@/assets/styles/variables.scss"; //项目存放scss变量地址 ` } } }, chainWebpack: (config) => { // 目录别名 alias config.resolve.alias.set("@", resolve("src")); // .set("assets", resolve("src/assets")) // .set("api", resolve("src/api")) // .set("views", resolve("src/views")) // .set("components", resolve("src/components")); /** * cdn = { * css: [ * 'https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css' // element-ui css 样式表 * ], * js: [ * // vue must at first! * 'https://unpkg.com/vue@2.6.12/dist/vue.js', // vuejs * 'https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/index.js', // element-ui js * 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/xlsx@0.16.6/dist/xlsx.full.min.js', // xlsx * ] * } * 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Wy_so_serious/article/details/121044173 */ // config.plugin('html').tap(args => { // if (IS_PROD) { // args[0].cdn = cdn.build // } else { // args[0].cdn = cdn.dev // } // return args // }) // const oneOfsMap = config.module.rule("scss").oneOfs.store; // oneOfsMap.forEach(item => { // item // .use("style-resources-loader") // .loader("style-resources-loader") // .options({ // // 这里的路径不能使用 @ 符号,否则会报错 // // patterns: ["./src/assets/reset1.less", "./src/assets/reset2.less"] // patterns: "./src/assets/styles/variables.scss" // }) // .end() // }) /** * 设置保留空格 */ config.module .rule("vue") .use("vue-loader") .loader("vue-loader") .tap((options) => { options.compilerOptions.preserveWhitespace = true; return options; }) .end(); // config.module.rule('images') // .use('url-loader') // .tap(options => ({ // //[hash:10]取图片的hash的前10位 // //[ext]取文件原来扩展名 // name: './assets/images/[name].[ext]', // quality: 85, // limit: 8 * 1024, // // // encoding: true, // 默认为true, 是否使用默认编码base64,可以["utf8","utf16le","latin1","base64","hex","ascii","binary","ucs2"] // // generator: '', // 类型:{Function},默认值:() => type/subtype;encoding,base64_data,可以自定义数据编码。 // esModule: false, // 关掉es6模块化解析 // // fallback: 'file-loader', //指定当目标文件的大小超过限制时要使用的备用加载程序 // })); config.module.rule("images").set("parser", { dataUrlCondition: { maxSize: 8 * 1024, // 小于8K的图片将直接以base64的形式内联在代码中,可以减少一次http请求。 }, }); // svg-sprite-loader 将svg图片以雪碧图的方式在项目中加载 config.module.rule("svg").exclude.add(resolve("src/assets/icons")).end(); config.module .rule("icons") .test(/\.svg$/) //添加匹配规则 .include.add(resolve("src/assets/icons")) //添加我们要处理的文件路径 svg图片地址 .end() //上面的add方法改变了上下文,调用end()退回到include这一级 .use("svg-sprite-loader") //使用"svg-sprite-loader"这个依赖 .loader("svg-sprite-loader") //选中这个依赖 .options({ // 这个配置是这个包的配置不属于webpack,可以查看相关文档,symbolId指定我们使用svg图片的名字 symbolId: "icon-[name]", // 使用图标的方式 icon-文件名 }) //传入配置 .end(); /** * 打包分析 * https://blog.csdn.net/formylovetm/article/details/126424858 */ if (IS_PROD) { config.plugin("webpack-report").use(BundleAnalyzerPlugin, [ { analyzerMode: "static", }, ]); } /** * 是否开启源码映射调试 * https://www.cnblogs.com/suwanbin/p/16901247.html * 浏览器上调试代码的问题,但是代码在显示的时候会出现压缩编码等问题,代码和原来就不一样,这时候需要打开调试模式. * source-map: 在外部生成一个文件,在控制台会显示 错误代码准确信息 和 源代码的错误位置 * inline-source-map: 内嵌到bundle.js中, 只生成一个source-map,在控制台会显示 错误代码准确信息 和 源代码的错误位置 * hidden-source-map: 外部,错误代码错误原因,源代码的错误位置,不能追踪源代码错误,只能提示到构建后代码的错误位置 * eval-source-map: 内嵌,每一个文件都生成对应的source-map,在控制台会显示 错误代码准确信息,源代码的错误位置 * nosources-source-map: 外部,错误代码准确信息,没有任何源代码信息 * cheap-source-map: 外部,错误代码准确信息,源代码的错误位置,只能精准到行 * cheap-module-source-map: 外部,错误代码准确信息,源代码的错误位置,module会将loader的source-map加入 * * 内嵌与外部的区别: 1.外部生成单独的文件,内嵌没有 2.内嵌构建速度快 * 这么多source-map如何选择? * 开发环境:速度快,调试更友好 * 速度快( eval>inline>cheap>··· ) * 组合eval-cheap-source-map > eval-source-map,调试更友好 * source-map > cheap-module-source-map > cheap-source-map * 最终结果:cheap-module-source-map 和 eval-source-map (vuecli与react脚手架默认) *生产环境:源代码要不要隐藏?调试要不要更友好 *内嵌会让代码体积变大,所以在生产环境下不用内嵌 * nosources-source-map全部隐藏 * hidden-source-map 只隐藏源代码,会提示构建后代码错误信息 * 最终结果:source-map 和 cheap-module-source-map */ config // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#development .when(!IS_PROD, (config) => config.devtool("cheap-module-source-map")); config.when(IS_PROD, (config) => { /** * Vue预渲染prerender-spa-plugin+vue-meta-info * https://blog.csdn.net/milkgan/article/details/127509160 * 只有少量页面需要SEO优化 * 仅仅提高首屏的渲染速度,且首屏的几乎只有静态数据的情况 * preload 预加载,提前预加载提高切换路由的体验,加上这个,会打包报错 * Vue CLI 4.5 和更早版本会使用 Preload 技术 */ // config.plugin("preload").tap(() => [ // { // rel: "preload", // // to ignore runtime.js 注:这里要把 runtime 代码的 preload 去掉。 // fileBlacklist: [/\.map$/, /hot-update\.js$/, /runtime\..*\.js$/], // include: "initial" // } // ]); /** * https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36278221/article/details/128042470 * 多页面打包配置 * Object.keys(pages).forEach((element) => { * config.plugin('preload-' + element).tap(() => [ * { * rel: 'preload', * // to ignore runtime.js * fileBlacklist: [/\.map$/, /hot-update\.js$/, /runtime\..*\.js$/], * include: 'initial', * }, * ]) * config * .plugin("ScriptExtHtmlWebpackPlugin") * .after('html-' + element) * .use('script-ext-html-webpack-plugin', [ * { * // `runtime` must same as runtimeChunk name. default is `runtime` * inline: /runtime\..*\.js$/, * }, * ]) * .end() * config.plugins.delete('prefetch-' + element) * }) * runtime.js 处理策略 * 根据路由驱动页面的 runtime 代码默认情况是包含在 build 后的 app.hash.js 内的,如果我们改动其他路由,就会导致 runtime 代码改变。从而不光我们改动的路由对应的页面 js 会变,含 runtime 代码的 app.hash.js 也会变,对用户体验是非常不友好的。 * 为了解决这个问题要设定 runtime 代码单独抽取打包: * config.optimization.runtimeChunk('single') * 但是 runtime 代码由于只是驱动不同路由页面的关系,代码量比较少,请求 js 的时间都大于执行时间了, * 所以使用 script-ext-html-webpack-plugin 插件将其内链在 index.html 中比较友好。 */ config .plugin("ScriptExtHtmlWebpackPlugin") .after("html") .use("script-ext-html-webpack-plugin", [ { // 将 runtime 作为内联引入不单独存在 inline: /runtime\..*\.js$/, }, ]) .end(); //当有很多页面时,会导致太多无意义的请求 config.plugins.delete("prefetch"); /** * https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44786530/article/details/126936033 * 去掉代码中的console和debugger和注释 */ config.optimization.minimizer("terser").tap((options) => { options[0].terserOptions.compress.warnings = false; options[0].terserOptions.compress.drop_console = true; options[0].terserOptions.compress.drop_debugger = true; options[0].terserOptions.compress.pure_funcs = ["console.log"]; options[0].terserOptions.output = { //删除注释 comments: false, }; return options; }); /** * chunks 资源分块 * 如果使用了某些长期不会改变的库,像 element-ui ,打包完成有 600 多 KB , * 包含在默认 vendor 中显然不合适,每次用户都要加载这么大的文件体验不好,所以要单独打包 */ config.optimization.splitChunks({ chunks: "all", cacheGroups: { // cacheGroups 下可以可以配置多个组,每个组根据test设置条件,符合test条件的模块 commons: { name: "chunk-commons", test: resolve("src/components"), minChunks: 3, // 被至少用三次以上打包分离 priority: 5, // 优先级 reuseExistingChunk: true, // 表示是否使用已有的 chunk,如果为 true 则表示如果当前的 chunk 包含的模块已经被抽取出去了,那么将不会重新生成新的。 }, node_vendors: { name: "chunk-libs", chunks: "initial", // 只打包初始时依赖的第三方 test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/, priority: 10, }, vantUI: { name: "chunk-elementUI", // 单独将 vantUI 拆包 priority: 20, // 数字大权重到,满足多个 cacheGroups 的条件时候分到权重高的 test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]_?element-ui(.*)/, }, }, }); config.optimization.runtimeChunk("single"), { from: path.resolve(__dirname, "./public/robots.txt"), //防爬虫文件 to: "./", //到根目录下 }; }); }, pluginOptions: { "style-resources-loader": { preProcessor: "sass", patterns: [], }, }, });
参考:
Vue 配置全局样式(style-resources-loader)
设置全局css/less/sass样式and优化与style-resources-loader的理解
vue.config.js 全局配置
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)