C++中map查找元素是否存在的3种方式
1. map[key]通过键直接查找,如果存在就返回对应的值,如果不存在则返回02.map.find()3.map.count()
一键AI生成摘要,助你高效阅读
问答
·
1. map[key]
通过键直接查找,如果存在就返回对应的值,如果不存在则返回0
map<char, int>map1;
map1['a'] = 1;
map1['b'] = 2;
cout << map1['a'] << endl; // 返回1
cout << map1['c'] << endl; // 返回0
2. map.find(key)
返回key对应的迭代器,如果不存在则返回map.end(),时间复杂度为O(logN)
if (map1.find('d') == map1.end())
cout << "NOT FONUND" << endl;
cout << map1.find('a')->second << endl; // 输出1
3. map.count(key)
如果key存在就返回1,如果不存在则返回0。
cout << "map.count():" << endl;
cout << map1.count('b') << endl; // 返回1
cout << map1.count('d') << endl; // 返回0
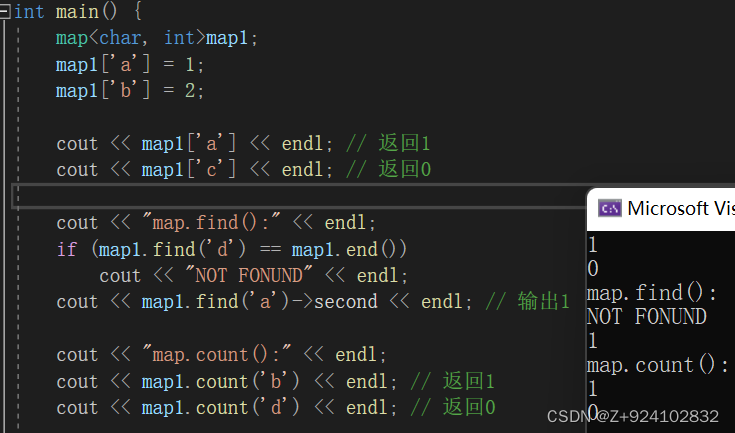
完整测试代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<char, int>map1;
map1['a'] = 1;
map1['b'] = 2;
cout << map1['a'] << endl; // 返回1
cout << map1['c'] << endl; // 返回0
cout << "map.find():" << endl;
if (map1.find('d') == map1.end())
cout << "NOT FONUND" << endl;
cout << map1.find('a')->second << endl; // 输出1
cout << "map.count():" << endl;
cout << map1.count('b') << endl; // 返回1
cout << map1.count('d') << endl; // 返回0
return 1;
}

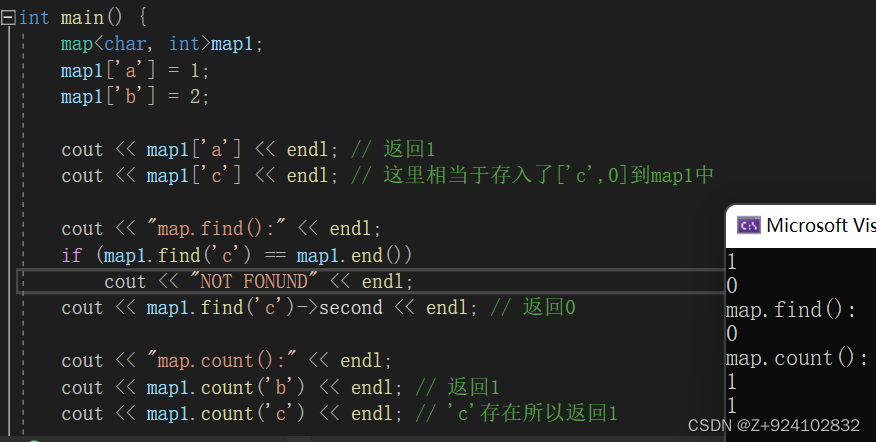
发现一个有趣的问题:
输出一个不存在的key的map映射值时,会把这个值存到map1里面,0为对应的value。
cout<<map[不存在的key];
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<char, int>map1;
map1['a'] = 1;
map1['b'] = 2;
cout << map1['a'] << endl; // 返回1
cout << map1['c'] << endl; // 这里相当于存入了['c',0]到map1中
cout << "map.find():" << endl;
if (map1.find('c') == map1.end())
cout << "NOT FONUND" << endl;
cout << map1.find('c')->second << endl; // 返回0
cout << "map.count():" << endl;
cout << map1.count('b') << endl; // 返回1
cout << map1.count('c') << endl; // 'c'存在所以返回1
return 1;
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)