Adam和AdamW的区别
Adam 与 Adamw的区别一句话版本Adamw 即 Adam + weight decate ,效果与 Adam + L2正则化相同,但是计算效率更高,因为L2正则化需要在loss中加入正则项,之后再算梯度,最后在反向传播,而Adamw直接将正则项的梯度加入反向传播的公式中,省去了手动在loss中加正则项这一步实验Adamw算法:图片参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/tfk
Adam 与 Adamw的区别
一句话版本
Adamw 即 Adam + weight decate ,效果与 Adam + L2正则化相同,但是计算效率更高,因为L2正则化需要在loss中加入正则项,之后再算梯度,最后在反向传播,而Adamw直接将正则项的梯度加入反向传播的公式中,省去了手动在loss中加正则项这一步
实验
Adamw算法:
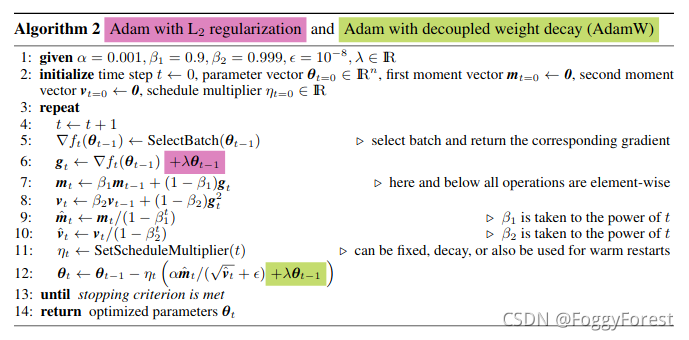
图片参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/tfknight/p/13425532.html
ps:以现在的源码为标准,图中的代码12行中:
λ
=
w
d
∗
l
r
\lambda = wd * lr
λ=wd∗lr
wd=weight decay, lr=learning rate
实验代码:
my_opt是手动实现的代码,主要验证梯度下降是否正确
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim.lr_scheduler
from torch.optim import AdamW, Adam
class M(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(3, 1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
class my_opt():
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
weight_decay=1e-2):
self.params = params
self.lr = lr
self.b1 = betas[0]
self.b2 = betas[1]
self.eps = eps
self.wd = weight_decay
self.m = 0
self.v = 0
self.b1t = 1.0
self.b2t = 1.0
# 模拟AdamW的step
def stepW(self):
for name, param in self.params.named_parameters():
if param.grad is None:
continue
g = param.grad
self.m = self.b1 * self.m + (1 - self.b1) * g
self.v = self.b2 * self.v + (1 - self.b2) * g * g
self.b1t *= self.b1
self.b2t *= self.b2
m = self.m / (1 - self.b1t)
v = self.v / (1 - self.b2t)
n = 1.0
param.data -= n * (self.lr * (m / (v.sqrt() + self.eps) + self.wd * param.data))
# 模拟Adam的step
def step(self):
for name, param in self.params.named_parameters():
if param.grad is None:
continue
g = param.grad
self.m = self.b1 * self.m + (1 - self.b1) * g
self.v = self.b2 * self.v + (1 - self.b2) * g * g
self.b1t *= self.b1
self.b2t *= self.b2
m = self.m / (1 - self.b1t)
v = self.v / (1 - self.b2t)
n = 1.0
param.data -= n * (self.lr * m / (v.sqrt() + self.eps))
adam_model = M()
adamw_model = M()
my_adam_model = M()
my_adamw_model = M()
# 使4个模型参数相同
adamw_model.load_state_dict(adam_model.state_dict())
my_adam_model.load_state_dict(adam_model.state_dict())
my_adamw_model.load_state_dict(adam_model.state_dict())
model_ls = {'adam_model': adam_model,
'adamw_model': adamw_model,
'my_adam_model': my_adam_model,
'my_adamw_model': my_adamw_model}
# 检查4个模型初始参数
for m in model_ls:
print(f"Model : {m}")
model = model_ls[m]
for name, parma in model.named_parameters():
print(name)
print(parma)
adam_opt = Adam(adam_model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
adamw_opt = AdamW(adamw_model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
my_adam_opt = my_opt(my_adam_model, lr=0.1)
my_adamw_opt = my_opt(my_adamw_model, lr=0.1)
opt_ls = {'adam_model': adam_opt,
'adamw_model': adamw_opt,
'my_adam_model': my_adam_opt,
'my_adamw_model': my_adamw_opt}
for i in range(5):
print(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> epoch", i)
ip = torch.rand(2, 3)
for m in model_ls:
print(f">>> Model : {m}")
model = model_ls[m]
opt = opt_ls[m]
loss = (model(ip).sum()) ** 2
loss.backward()
if m != 'my_adamw_model':
opt.step()
else:
opt.stepW()
for name, parma in model.named_parameters():
print(name)
print(parma)
model.zero_grad()
代码是照着图片公式写的,和源码还是有点区别的,但是可以验证每一步的梯度下降都对了
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)