Have a plot with several diagonal lines with different slopes. I would like to annotate these lines with a text label that matches the slope of the lines.
Something like this:
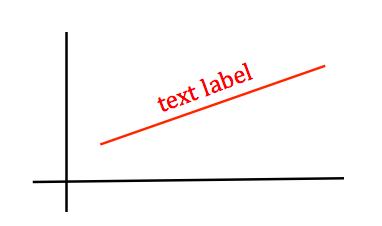
Is there a robust way to do this?
I've tried both text's and annotate's rotation parameters, but those are in screen coordinates, not data coordinates (i.e. it's always x degrees on the screen no matter the xy ranges). My x and y ranges differ by orders of magnitude, and obviously the apparent slope is affected by viewport size among other variables, so a fixed-degree rotation doesn't do the trick. Any other ideas?
Even though this question is old, I keep coming across it and get frustrated, that it does not quite work. I reworked it into a class LineAnnotation and helper line_annotate such that it
- uses the slope at a specific point
x,
- works with re-layouting and resizing, and
- accepts a relative offset perpendicular to the slope.
x = np.linspace(np.pi, 2*np.pi)
line, = plt.plot(x, np.sin(x))
for x in [3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0]:
line_annotate(str(x), line, x)
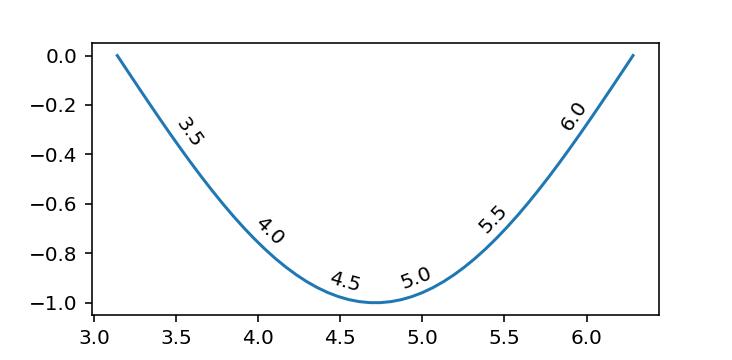
I originally put it into a public gist, but @Adam asked me to include it here.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.text import Annotation
from matplotlib.transforms import Affine2D
class LineAnnotation(Annotation):
"""A sloped annotation to *line* at position *x* with *text*
Optionally an arrow pointing from the text to the graph at *x* can be drawn.
Usage
-----
fig, ax = subplots()
x = linspace(0, 2*pi)
line, = ax.plot(x, sin(x))
ax.add_artist(LineAnnotation("text", line, 1.5))
"""
def __init__(
self, text, line, x, xytext=(0, 5), textcoords="offset points", **kwargs
):
"""Annotate the point at *x* of the graph *line* with text *text*.
By default, the text is displayed with the same rotation as the slope of the
graph at a relative position *xytext* above it (perpendicularly above).
An arrow pointing from the text to the annotated point *xy* can
be added by defining *arrowprops*.
Parameters
----------
text : str
The text of the annotation.
line : Line2D
Matplotlib line object to annotate
x : float
The point *x* to annotate. y is calculated from the points on the line.
xytext : (float, float), default: (0, 5)
The position *(x, y)* relative to the point *x* on the *line* to place the
text at. The coordinate system is determined by *textcoords*.
**kwargs
Additional keyword arguments are passed on to `Annotation`.
See also
--------
`Annotation`
`line_annotate`
"""
assert textcoords.startswith(
"offset "
), "*textcoords* must be 'offset points' or 'offset pixels'"
self.line = line
self.xytext = xytext
# Determine points of line immediately to the left and right of x
xs, ys = line.get_data()
def neighbours(x, xs, ys, try_invert=True):
inds, = np.where((xs <= x)[:-1] & (xs > x)[1:])
if len(inds) == 0:
assert try_invert, "line must cross x"
return neighbours(x, xs[::-1], ys[::-1], try_invert=False)
i = inds[0]
return np.asarray([(xs[i], ys[i]), (xs[i+1], ys[i+1])])
self.neighbours = n1, n2 = neighbours(x, xs, ys)
# Calculate y by interpolating neighbouring points
y = n1[1] + ((x - n1[0]) * (n2[1] - n1[1]) / (n2[0] - n1[0]))
kwargs = {
"horizontalalignment": "center",
"rotation_mode": "anchor",
**kwargs,
}
super().__init__(text, (x, y), xytext=xytext, textcoords=textcoords, **kwargs)
def get_rotation(self):
"""Determines angle of the slope of the neighbours in display coordinate system
"""
transData = self.line.get_transform()
dx, dy = np.diff(transData.transform(self.neighbours), axis=0).squeeze()
return np.rad2deg(np.arctan2(dy, dx))
def update_positions(self, renderer):
"""Updates relative position of annotation text
Note
----
Called during annotation `draw` call
"""
xytext = Affine2D().rotate_deg(self.get_rotation()).transform(self.xytext)
self.set_position(xytext)
super().update_positions(renderer)
def line_annotate(text, line, x, *args, **kwargs):
"""Add a sloped annotation to *line* at position *x* with *text*
Optionally an arrow pointing from the text to the graph at *x* can be drawn.
Usage
-----
x = linspace(0, 2*pi)
line, = ax.plot(x, sin(x))
line_annotate("sin(x)", line, 1.5)
See also
--------
`LineAnnotation`
`plt.annotate`
"""
ax = line.axes
a = LineAnnotation(text, line, x, *args, **kwargs)
if "clip_on" in kwargs:
a.set_clip_path(ax.patch)
ax.add_artist(a)
return a








 已为社区贡献126445条内容
已为社区贡献126445条内容

所有评论(0)