Python中的ReLu函数
Relu 或 Rectified Linear Activation Function 是深度学习世界中最常见的激活函数选择。 Relu 提供最先进的结果,同时在计算上非常高效。
Relu激活函数的基本概念如下:
Return 0 if the input is negative otherwise return the input as it is.
我们可以用数学方法将其表示如下:
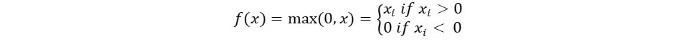
重启功能
Relu的伪代码如下:
if input > 0:
return input
else:
return 0
在本教程中,我们将学习如何实现我们自己的 ReLu 函数,了解它的一些缺点并了解更好的 ReLu 版本。
推荐阅读:机器学习的线性代数[Part 1/2]
让我们开始吧!
Python实现ReLu函数
让我们用 Python 编写我们自己的 Relu 实现。我们将使用内置的 max 函数来实现它。
ReLu 的代码如下:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
为了测试这个函数,让我们在几个输入上运行它。
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
完整代码
完整的代码如下:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
输出 :
Applying Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Relu on (-10.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Relu on (-20.0) gives 0.0
ReLu函数的梯度
让我们看看 ReLu 函数的梯度(导数)是多少。在微分时,我们将得到以下函数:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0, x<0
我们可以看到,对于 x 小于零的值,梯度为 0。这意味着某些神经元的权重和偏差没有更新。这可能是训练过程中的一个问题。
为了克服这个问题,我们有 **Leaky ReLu 函数。**让我们接下来了解它。
Leaky ReLu 函数
Leaky ReLu 函数是常规 ReLu 函数的即兴创作。为了解决负值的零梯度问题,Leaky ReLu 将 x 的一个极小的线性分量赋予负输入。
在数学上,我们可以将 Leaky ReLu 表示为:
f(x)= 0.01x, x<0
= x, x>=0
数学上:
-
f(x)u003d1 (x<0)
-
(αx)+1 (x>u003d0)(x)
这里 a 是一个小常数,就像我们上面采用的 0.01。
在图形上它可以显示为:
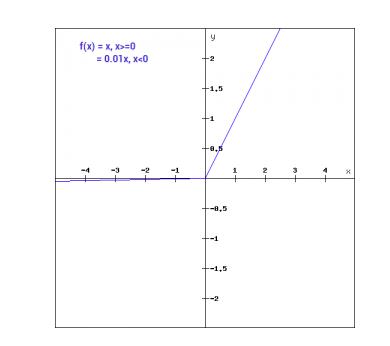
泄漏的 ReLu
Leaky ReLu 的梯度
让我们计算 Leaky ReLu 函数的梯度。梯度可以是:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0.01, x<0
在这种情况下,负输入的梯度是非零的。这意味着所有的神经元都将被更新。
在 Python 中实现 Leaky ReLu
Leaky ReLu 的实现如下:
def relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
让我们尝试一下现场输入。
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
完整代码
Leaky ReLu 的完整代码如下:
def leaky_relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
输出 :
Applying Leaky Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-10.0) gives -0.1
Applying Leaky Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-20.0) gives -0.2
结论
本教程是关于 Python 中的 ReLu 函数的。我们还看到了 ReLu 函数的改进版本。 Leaky ReLu 解决了 ReLu 函数中负值梯度为零的问题。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献126445条内容
已为社区贡献126445条内容







所有评论(0)