如何在 Python 中读取大文本文件
·
Python 文件对象提供了多种读取文本文件的方法。流行的方法是使用 readlines() 方法,该方法返回文件中所有行的列表。但是,不适合读取大文本文件,因为整个文件内容都会被加载到内存中。
在 Python 中读取大文本文件
我们可以将文件对象用作迭代器。迭代器会逐行返回,可以处理。这不会将整个文件读入内存,适合在 Python 中读取大文件。这是通过将 Python 视为迭代器来读取大文件的代码片段。
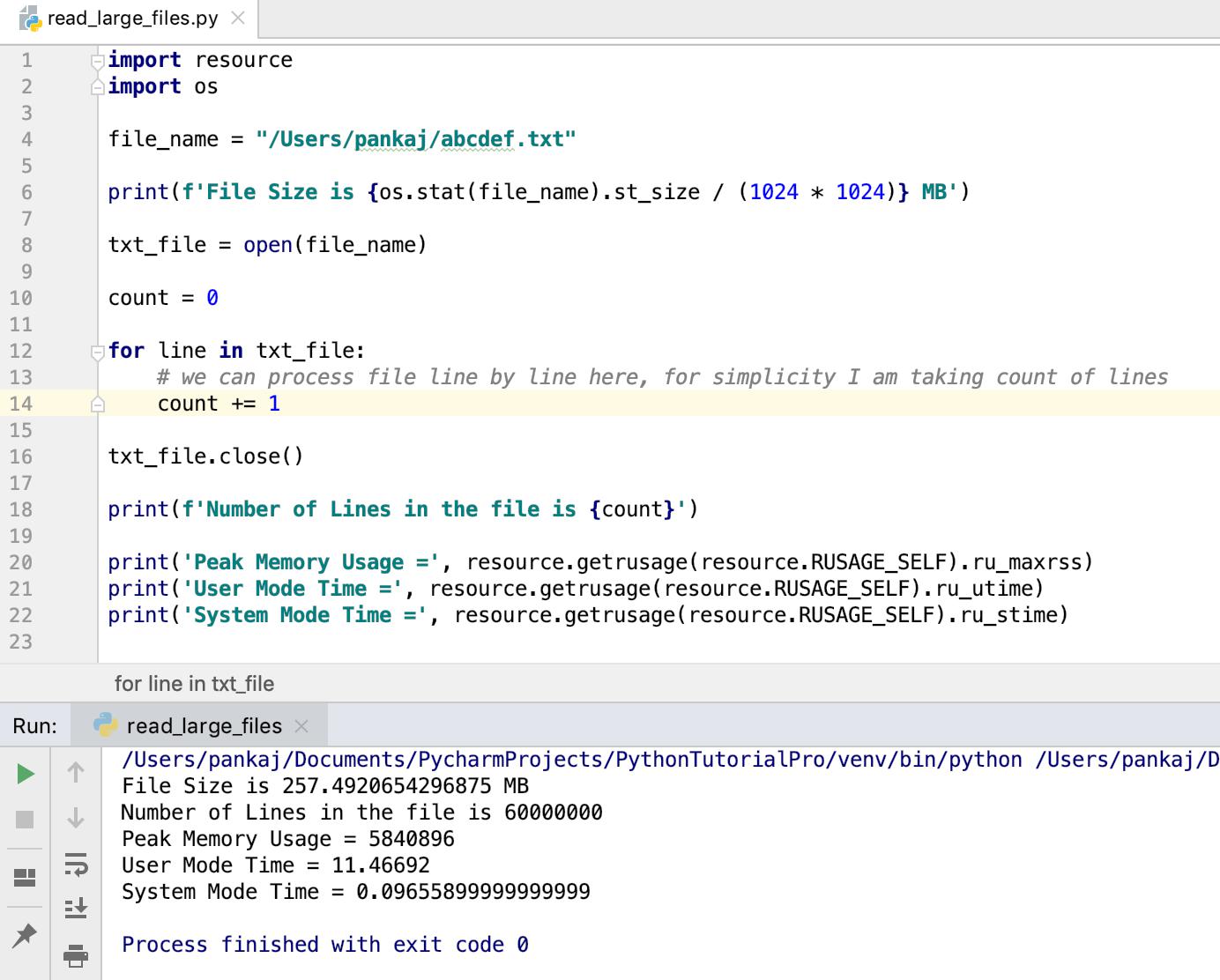
import resource
import os
file_name = "/Users/pankaj/abcdef.txt"
print(f'File Size is {os.stat(file_name).st_size / (1024 * 1024)} MB')
txt_file = open(file_name)
count = 0
for line in txt_file:
# we can process file line by line here, for simplicity I am taking count of lines
count += 1
txt_file.close()
print(f'Number of Lines in the file is {count}')
print('Peak Memory Usage =', resource.getrusage(resource.RUSAGE_SELF).ru_maxrss)
print('User Mode Time =', resource.getrusage(resource.RUSAGE_SELF).ru_utime)
print('System Mode Time =', resource.getrusage(resource.RUSAGE_SELF).ru_stime)
当我们运行这个程序时,产生的输出是:
File Size is 257.4920654296875 MB
Number of Lines in the file is 60000000
Peak Memory Usage = 5840896
User Mode Time = 11.46692
System Mode Time = 0.09655899999999999
Python 读取大文本文件
-
我正在使用os模块来打印文件的大小。
-
资源模块用于检查程序的内存和CPU时间使用情况。
我们也可以使用with语句来打开文件。在这种情况下,我们不必显式关闭文件对象。
with open(file_name) as txt_file:
for line in txt_file:
# process the line
pass
大文件没有行怎么办?
当大文件内容分成多行时,上面的代码会很好用。但是,如果一行中有大量数据,那么它将使用大量内存。在这种情况下,我们可以将文件内容读入缓冲区并进行处理。
with open(file_name) as f:
while True:
data = f.read(1024)
if not data:
break
print(data)
上面的代码会将文件数据读入一个 1024 字节的缓冲区。然后我们将它打印到控制台。当整个文件被读取时,数据将变为空,break 语句将终止while循环。此方法在读取图像、PDF、word 文档等二进制文件时也很有用。这里有一个简单的代码片段来制作文件的副本。
with open(destination_file_name, 'w') as out_file:
with open(source_file_name) as in_file:
for line in in_file:
out_file.write(line)
参考:StackOverflow 问题
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献126445条内容
已为社区贡献126445条内容







所有评论(0)