linux 堆利用基础知识
ptmalloc2 是目前 Linux 标准发行版中使用的堆分配器。malloc 函数返回对应大小字节的内存块的指针。此外,该函数还对一些异常情况进行了处理:用以扩展 chunk,相邻 chunk 闲置且空间充足则会进行合并,否则会重新分配 chunk。即通过 realloc 我们可以完成对一个 chunk 的 free,也就是说在特殊情况下 realloc 是可以当作 free 使用的,其中,在
ptmalloc2 是目前 Linux 标准发行版中使用的堆分配器。
内存分配基本思想
- 堆管理器负责向操作系统申请内存,然后将其返回给用户程序,但是频繁的系统调用会造成大量的开销。为了保持内存管理的高效性,内核一般都会预先分配很大的一块连续的内存,然后让堆管理器通过某种算法管理这块内存。只有当出现了堆空间不足的情况,堆管理器才会再次与操作系统进行交互。
- 一般来说,用户释放的内存并不是直接返还给操作系统的,而是由堆管理器进行管理。这些释放的内存可以来响应用户新申请的内存的请求。
堆的基本操作
malloc
malloc (memory allocation) 函数是 C 语言标准库中用于动态内存分配的一个基本函数。它分配一块至少为 size 字节的连续内存区域,并返回一个指向这块内存的指针
void *malloc(size_t size);
malloc 函数返回对应大小字节的内存块的指针。此外,该函数还对一些异常情况进行了处理:
- 当
n = 0时,返回当前系统允许的堆的最小内存块。 - 当
n为负数时,由于在大多数系统上,size_t是无符号数(这一点非常重要),所以程序就会申请很大的内存空间,但通常来说都会失败,因为系统没有那么多的内存可以分配。
realloc
realloc 函数用于重新分配之前通过 malloc ,calloc 或 realloc 函数分配的内存区域。它可以改变内存块的大小,或者释放内存块,或分配新的内存块。
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
ptr:指向需要重新分配的内存块的指针。size:新的内存块的大小,以字节为单位。
有如下情况:
ptr不为空,size = 0,相当于释放原来的堆块。ptr为空且size > 0,相当于malloc。ptr不为空,size大于原来的堆块大小则如果该堆块后面的堆块空闲则合并堆块,否则先释放原堆块,然后再申请一个更大的堆块,原堆块内容会被拷贝过去。ptr不为空,size不大于原来的堆块大小,如果切割后剩下的堆块大于等于MINSIZE则切割并释放,然后返回原堆块。
calloc
calloc (contiguous allocation) 函数是 C 语言标准库中用于动态内存分配的一个函数。与 malloc 相似,calloc 用于分配内存。该函数在分配时会清空 chunk 上的内容,这使得我们无法通过以往的重复存取后通过 chunk 上残留的脏数据的方式泄露信息(例如通过 bins 数组遗留的脏数据泄露 libc 基址等),同时该函数不从 tcache 中拿 chunk,但是 free() 函数默认还是会先往 tcache 里放的,这无疑增加了我们利用的难度。
void *calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size);
nmemb:需要分配的元素个数。size:每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
总的分配的字节大小是 nmemb * size 。
注意:如果 size 的 IS_MAPPED 位置 1 则不清空数据。
if (chunk_is_mmapped (p))
{
if (__builtin_expect (perturb_byte, 0))
return memset (mem, 0, sz);
return mem;
}
free
可以看出,free 函数会释放由 p 所指向的内存块。这个内存块有可能是通过 malloc 函数得到的,也有可能是通过相关的函数 realloc 得到的。
此外,该函数也同样对异常情况进行了处理:
- 当 p 为空指针时,函数不执行任何操作。
- 当 p 已经被释放之后,再次释放会出现乱七八糟的效果,这其实就是 double free。
- 除了被禁用 (mallopt) 的情况下,当释放很大的内存空间时,程序会将这些内存空间还给系统,以便于减小程序所使用的内存空间。
mallopt
mallopt 函数通过控制堆的特定参数用于改变堆的分配策略。
int mallopt(int param,int value)
param:指定要修改的动态内存分配参数。这个参数是一个整数,定义了哪一个特性将会被修改。例如,它可以是控制内存对齐、缓存大小或者相似行为的选项。M_MXFAST:设置malloc用于小块内存分配的最大 fast bin 的大小。M_TRIM_THRESHOLD:设置sbrk释放内存回操作系统的阈值。M_TOP_PAD:设置sbrk请求额外内存时,上面的额外内存量。M_MMAP_THRESHOLD:设置使用mmap进行内存分配的阈值。M_MMAP_MAX:设置可以使用mmap进行内存分配的最大数目。
value:新的值,针对 param 指定的特性。具体的值取决于 param,有些特性可能需要非零值来启用,零值来禁用,有些则需要具体的数值。- 返回值是一个整数,指示函数调用是否成功。
- 如果成功,返回非零值。
- 如果失败(例如,不支持的参数或值),返回零。
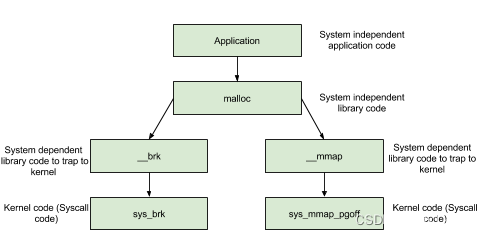
内存分配背后的系统调用
内存管理函数背后的系统调用主要是 (s)brk 函数以及 mmap, munmap 函数。
在 main arena 中通过 sbrk 扩展 heap,而在 thread arena 中通过 mmap 分配新的 heap。

(s)brk
对于堆的操作,操作系统提供了 brk 函数,glibc 库提供了 sbrk 函数,我们可以通过增加 brk 的大小来向操作系统申请内存。
初始时,堆的起始地址 start_brk 以及堆的当前末尾 brk 指向同一地址。根据是否开启 ASLR,两者的具体位置会有所不同
不开启 ASLR 保护时,start_brk 以及 brk 会指向 data/bss 段的结尾。
开启 ASLR 保护时,start_brk 以及 brk 也会指向同一位置,只是这个位置是在 data/bss 段结尾后的随机偏移处。

mmap
malloc 会使用 mmap 来创建独立的匿名映射段。匿名映射的目的主要是可以申请以 0 填充的内存,并且这块内存仅被调用进程所使用。
堆相关数据结构
malloc_par
在 ptmalloc 中使用 malloc_par 结构体来记录堆管理器的相关参数,该结构体定义于 malloc.c 中,如下:
struct malloc_par
{
/* Tunable parameters */
unsigned long trim_threshold;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T top_pad;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T mmap_threshold;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T arena_test;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T arena_max;
/* Memory map support */
int n_mmaps;
int n_mmaps_max;
int max_n_mmaps;
/* the mmap_threshold is dynamic, until the user sets
it manually, at which point we need to disable any
dynamic behavior. */
int no_dyn_threshold;
/* Statistics */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T mmapped_mem;
/*INTERNAL_SIZE_T sbrked_mem;*/
/*INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_sbrked_mem;*/
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_mmapped_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_total_mem; /* only kept for NO_THREADS */
/* First address handed out by MORECORE/sbrk. */
char *sbrk_base;
};
主要是定义了和 mmap 和 arena 相关的一些参数(如数量上限等),以及 sbrk 的基址,其中重要的参数解释如下:
top_pad:初始化或扩展堆的时候需要多申请的内存大小。mmap_threshold:决定sysmalloc是通过mmap还是sbrk分配内存的界限,即如果申请的内存大小不小于该值则采用mmap分配,否则采用sbrk扩展heap区域分配。并且这个值是动态调整的,如果释放的内存是通过mmap得到的则mmap_threshold与该内存大小取max。并且mmap_threshold最大不能超过DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MAX,即 0x2000000 。trim_threshold:用于main_arena中保留内存量的控制。当释放的chunk为mmap获得的,同时大小大于mmap_threshold,则除了更新mmap_threshold外还会将trim_threshold乘 2 。当释放的chunk大小不在 fast bin 范围合并完size大于FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD即 0x10000 ,且为main_arena,且 top chunk 的大小大于trim_threshold则将heap区域在 top chunk 不会小于pagesize的前提下减小top_pad。n_mmaps:mmap的内存数量,即 ptmalloc 每次成功mmap则n_mmaps加 1,ptmalloc 每次成功munmap则n_mmaps减 1 。n_mmaps_max:n_mmaps的上限,即最多能mmap的内存数量。max_n_mmaps:n_mmaps达到过的最大值。mmapped_mem:当前mmap的内存大小总和。max_mmapped_mem:mmap的内存大小总和达到过的最大值。sbrk_base:表示通过brk系统调用申请的heap区域的起始地址。no_dyn_threshold:表示是否禁用heap动态调整保留内存的大小,默认为 0 。
该结构体类型的实例 mp_ 用以记录 ptmalloc 相关参数,同样定义于 malloc.c 中,如下:
# define DEFAULT_TOP_PAD 131072 // 0x20000
#define DEFAULT_MMAP_MAX (65536) // 0x10000
#define DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MIN (128 * 1024)
#define DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MIN // 0x20000
#define DEFAULT_TRIM_THRESHOLD (128 * 1024) // 0x20000
static struct malloc_par mp_ =
{
.top_pad = DEFAULT_TOP_PAD,
.n_mmaps_max = DEFAULT_MMAP_MAX,
.mmap_threshold = DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD,
.trim_threshold = DEFAULT_TRIM_THRESHOLD,
#define NARENAS_FROM_NCORES(n) ((n) * (sizeof (long) == 4 ? 2 : 8))
.arena_test = NARENAS_FROM_NCORES (1)
};
heap_info
heap_info 位于一个 heap 块的开头,用以记录通过 mmap 系统调用从 Memory Mapping Segment 处申请到的内存块的信息。定义于 arena.c 中。
/* A heap is a single contiguous memory region holding (coalesceable)
malloc_chunks. It is allocated with mmap() and always starts at an
address aligned to HEAP_MAX_SIZE. */
typedef struct _heap_info
{
mstate ar_ptr; /* Arena for this heap. */
struct _heap_info *prev; /* Previous heap. */
size_t size; /* Current size in bytes. */
size_t mprotect_size; /* Size in bytes that has been mprotected
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE. */
/* Make sure the following data is properly aligned, particularly
that sizeof (heap_info) + 2 * SIZE_SZ is a multiple of
MALLOC_ALIGNMENT. */
char pad[-6 * SIZE_SZ & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK];
} heap_info;
heap_info 结构体的成员如下:
ar_ptr:指向管理该堆块的 arenaprev:该heap_info所链接的上一个 heap_infosize:记录该堆块的大小mprotect_size:记录该堆块中被保护(mprotected)的大小pad:即padding,用以在SIZE_SZ不正常的情况下进行填充以让内存对齐,正常情况下pad所占用空间应为 0 字节
arena
大部分情况下对于每个线程而言其都会单独有着一个 arena 实例用以管理属于该线程的堆内存区域。ptmalloc 内部的内存池结构是由 malloc_state 结构体进行定义的,即 arena 本身便为 malloc_state 的一个实例对象。
malloc_state 结构体定义于malloc/malloc.c 中,代码如下:
struct malloc_state
{
/* Serialize access. */
mutex_t mutex;
/* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
int flags;
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top;
/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
/* Bitmap of bins */
unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
/* Linked list */
struct malloc_state *next;
/* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized
by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
struct malloc_state *next_free;
/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on
the free list. Access to this field is serialized by
free_list_lock in arena.c. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;
/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
};
malloc_state 结构体的成员如下:
mutex:mutex变量即为多线程互斥锁,用以保证线程安全。flags:标志位,用以表示arena的一些状态,如:是否有fastbin、内存是否连续等。fastbinY:存放 fastbin chunk 的数组。top:指向 Top Chunk 的指针。last_remainder:chunk切割中的剩余部分。malloc在分配chunk时若是没找到size合适的chunk而是找到了一个size更大的chunk,则会从大chunk中切割掉一块返回给用户,剩下的那一块便是last_remainder,其随后会被放入 unsorted bin 中。bins:存放闲置chunk的数组。bins包括 large bin,small bin 和 unsorted bin 。binmap:记录bin是否为空的bitset。需要注意的是chunk被取出后若一个bin空了并不会立即被置 0 ,而会在下一次遍历到时重新置位。next:指向下一个arena的指针。一个进程内所有的arena串成了一条循环单向链表,malloc_state中的next指针便是用以指向下一个arena,方便后续的遍历arena的操作(因为不是所有的线程都有自己独立的arena)。next_free:指向下一个空闲的arena的指针。与next指针类似,只不过指向的是空闲的arena(即没有被任一线程所占用)。attached_threads:与该arena相关联的线程数。该变量用以表示有多少个线程与该arena相关联,这是因为aerna的数量是有限的,并非每一个线程都有机会分配到一个arena,在线程数量较大的情况下会存在着多个线程共用一个arena的情况。system_mem:记录当前arena在堆区中所分配到的内存的总大小。max_system_mem:当操作系统予进程以内存时,system_mem会随之增大,当内存被返还给操作系统时,sysyetm_mem会随之减小,max_system_mem变量便是用来记录在这个过程当中system_mem的峰值。
main_arena 为一个定义于 malloc.c 中的静态的 malloc_state 结构体。
static struct malloc_state main_arena =
{
.mutex = _LIBC_LOCK_INITIALIZER,
.next = &main_arena,
.attached_threads = 1
};
由于其为 libc 中的静态变量,该 arena 会被随着 libc 文件一同加载到 Memory Mapping Segment。因此在堆题中通常通过泄露 arena 的地址以获得 libc 在内存中的基地址。
chunk
在程序的执行过程中,我们称由 malloc 申请的内存为 chunk 。这块内存在 ptmalloc 内部用 malloc_chunk 结构体来表示。当程序申请的 chunk 被 free 后,会被加入到相应的空闲管理列表中。
malloc_chunk 定义如下:
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};
每个字段的具体的解释如下:
-
prev_size:如果物理相邻的前一地址chunk是空闲的话,那该字段记录的是前一个chunk的大小 (包括chunk头)。否则,该字段可以用来存储物理相邻的前一个chunk的数据。 -
size:该chunk的大小,大小必须是2 * SIZE_SZ的整数倍。该字段的低三个比特位对chunk的大小没有影响,它们从高到低分别表示为:NON_MAIN_ARENA,记录当前chunk是否不属于主线程,1 表示不属于,0 表示属于。IS_MAPPED,记录当前chunk是否是由mmap分配的。PREV_INUSE,记录前一个chunk块是否被分配。一般来说,堆中第一个被分配的内存块的size字段的P位都会被设置为 1,以便于防止访问前面的非法内存。当一个chunk的size的P位为 0 时,我们能通过prev_size字段来获取上一个chunk的大小以及地址。这也方便进行空闲chunk之间的合并。
-
fd,bk。chunk处于分配状态时,从fd字段开始是用户的数据。chunk空闲时,会被添加到对应的空闲管理链表中,其字段的含义如下fd指向下一个(非物理相邻)空闲的chunkbk指向上一个(非物理相邻)空闲的chunk
通过
fd和bk可以将空闲的chunk块加入到空闲的chunk块链表进行统一管理 -
fd_nextsize,bk_nextsize,也是只有chunk空闲的时候才使用,不过其用于较大的chunk(large chunk)。fd_nextsize指向前一个与当前chunk大小不同的第一个空闲块,不包含bin的头指针。bk_nextsize指向后一个与当前chunk大小不同的第一个空闲块,不包含 bin 的头指针。- 一般空闲的 large chunk 在
fd的遍历顺序中,按照由大到小的顺序排列。这样做可以避免在寻找合适chunk时挨个遍历。(好在 large bin 限制了值域范围,不然也会很慢)
chunk 的结构如下图所示:

bins
bins
我们曾经说过,用户释放掉的 chunk 不会马上归还给系统,ptmalloc 会统一管理 heap 和 mmap 映射区域中的空闲的 chunk。当用户再一次请求分配内存时,ptmalloc 分配器会试图在空闲的 chunk 中挑选一块合适的给用户。这样可以避免频繁的系统调用,降低内存分配的开销。
在具体的实现中,ptmalloc 采用分箱式方法对空闲的 chunk 进行管理。首先,它会根据空闲的 chunk 的大小以及使用状态将 chunk 初步分为 4 类:fast bins,small bins,large bins,unsorted bin 。对于 libc2.26 以上版本还有 tcache 。
概述
对于 small bins,large bins,unsorted bin 来说,ptmalloc 将它们维护在一个 bins 数组中。这些 bin 对应的数据结构在 malloc_state 中,如下:
#define NBINS 128
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[ NBINS * 2 - 2 ];
bins 数组实际上可以看做是以 chunk 为单位,只不过采用空间复用策略,因为实际用到的只有 fd 和 bk 。
/* addressing -- note that bin_at(0) does not exist */
#define bin_at(m, i) \
(mbinptr) (((char *) &((m)->bins[((i) - 1) * 2])) \
- offsetof (struct malloc_chunk, fd))

由于是双链表结构 bins 数组每连续两个 chunk 指针维护一个 bin(即 fd 和 bk ),其结构如下图所示(64位)。其中 small bins 中 chunk 大小已给出。large bins 的每个 bin 中的 chunk 大小在一个范围内。

large bin 的 chunk 范围如下:
| 编号 | 64位最小 | 64位最大 | 64位公差 | 32位最小 | 32位最大 | 32位公差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | 0x400 | 0x430 | 0x40 | 0x200 | 0x238 | 0x40 |
| 65 | 0x440 | 0x470 | 0x40 | 0x240 | 0x278 | 0x40 |
| 66 | 0x480 | 0x4b0 | 0x40 | 0x280 | 0x2b8 | 0x40 |
| 67 | 0x4c0 | 0x4f0 | 0x40 | 0x2c0 | 0x2f8 | 0x40 |
| 68 | 0x500 | 0x530 | 0x40 | 0x300 | 0x338 | 0x40 |
| 69 | 0x540 | 0x570 | 0x40 | 0x340 | 0x378 | 0x40 |
| 70 | 0x580 | 0x5b0 | 0x40 | 0x380 | 0x3b8 | 0x40 |
| 71 | 0x5c0 | 0x5f0 | 0x40 | 0x3c0 | 0x3f8 | 0x40 |
| 72 | 0x600 | 0x630 | 0x40 | 0x400 | 0x438 | 0x40 |
| 73 | 0x640 | 0x670 | 0x40 | 0x440 | 0x478 | 0x40 |
| 74 | 0x680 | 0x6b0 | 0x40 | 0x480 | 0x4b8 | 0x40 |
| 75 | 0x6c0 | 0x6f0 | 0x40 | 0x4c0 | 0x4f8 | 0x40 |
| 76 | 0x700 | 0x730 | 0x40 | 0x500 | 0x538 | 0x40 |
| 77 | 0x740 | 0x770 | 0x40 | 0x540 | 0x578 | 0x40 |
| 78 | 0x780 | 0x7b0 | 0x40 | 0x580 | 0x5b8 | 0x40 |
| 79 | 0x7c0 | 0x7f0 | 0x40 | 0x5c0 | 0x5f8 | 0x40 |
| 80 | 0x800 | 0x830 | 0x40 | 0x600 | 0x638 | 0x40 |
| 81 | 0x840 | 0x870 | 0x40 | 0x640 | 0x678 | 0x40 |
| 82 | 0x880 | 0x8b0 | 0x40 | 0x680 | 0x6b8 | 0x40 |
| 83 | 0x8c0 | 0x8f0 | 0x40 | 0x6c0 | 0x6f8 | 0x40 |
| 84 | 0x900 | 0x930 | 0x40 | 0x700 | 0x738 | 0x40 |
| 85 | 0x940 | 0x970 | 0x40 | 0x740 | 0x778 | 0x40 |
| 86 | 0x980 | 0x9b0 | 0x40 | 0x780 | 0x7b8 | 0x40 |
| 87 | 0x9c0 | 0x9f0 | 0x40 | 0x7c0 | 0x7f8 | 0x40 |
| 88 | 0xa00 | 0xa30 | 0x40 | 0x800 | 0x838 | 0x40 |
| 89 | 0xa40 | 0xa70 | 0x40 | 0x840 | 0x878 | 0x40 |
| 90 | 0xa80 | 0xab0 | 0x40 | 0x880 | 0x8b8 | 0x40 |
| 91 | 0xac0 | 0xaf0 | 0x40 | 0x8c0 | 0x8f8 | 0x40 |
| 92 | 0xb00 | 0xb30 | 0x40 | 0x900 | 0x938 | 0x40 |
| 93 | 0xb40 | 0xb70 | 0x40 | 0x940 | 0x978 | 0x40 |
| 94 | 0xb80 | 0xbb0 | 0x40 | 0x980 | 0x9b8 | 0x40 |
| 95 | 0xbc0 | 0xbf0 | 0x40 | 0x9c0 | 0x9f8 | 0x40 |
| 96 | 0xc00 | 0xc30 | 0x40 | 0xa00 | 0xbf8 | 0x200 |
| 97 | 0xc40 | 0xdf0 | 0x1c0 | 0xc00 | 0xdf8 | 0x200 |
| 98 | 0xe00 | 0xff0 | 0x200 | 0xe00 | 0xff8 | 0x200 |
| 99 | 0x1000 | 0x11f0 | 0x200 | 0x1000 | 0x11f8 | 0x200 |
| 100 | 0x1200 | 0x13f0 | 0x200 | 0x1200 | 0x13f8 | 0x200 |
| 101 | 0x1400 | 0x15f0 | 0x200 | 0x1400 | 0x15f8 | 0x200 |
| 102 | 0x1600 | 0x17f0 | 0x200 | 0x1600 | 0x17f8 | 0x200 |
| 103 | 0x1800 | 0x19f0 | 0x200 | 0x1800 | 0x19f8 | 0x200 |
| 104 | 0x1a00 | 0x1bf0 | 0x200 | 0x1a00 | 0x1bf8 | 0x200 |
| 105 | 0x1c00 | 0x1df0 | 0x200 | 0x1c00 | 0x1df8 | 0x200 |
| 106 | 0x1e00 | 0x1ff0 | 0x200 | 0x1e00 | 0x1ff8 | 0x200 |
| 107 | 0x2000 | 0x21f0 | 0x200 | 0x2000 | 0x21f8 | 0x200 |
| 108 | 0x2200 | 0x23f0 | 0x200 | 0x2200 | 0x23f8 | 0x200 |
| 109 | 0x2400 | 0x25f0 | 0x200 | 0x2400 | 0x25f8 | 0x200 |
| 110 | 0x2600 | 0x27f0 | 0x200 | 0x2600 | 0x27f8 | 0x200 |
| 111 | 0x2800 | 0x29f0 | 0x200 | 0x2800 | 0x29f8 | 0x200 |
| 112 | 0x2a00 | 0x2ff0 | 0x600 | 0x2a00 | 0x2ff8 | 0x600 |
| 113 | 0x3000 | 0x3ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x3000 | 0x3ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 114 | 0x4000 | 0x4ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x4000 | 0x4ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 115 | 0x5000 | 0x5ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x5000 | 0x5ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 116 | 0x6000 | 0x6ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x6000 | 0x6ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 117 | 0x7000 | 0x7ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x7000 | 0x7ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 118 | 0x8000 | 0x8ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x8000 | 0x8ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 119 | 0x9000 | 0x9ff0 | 0x1000 | 0x9000 | 0x9ff8 | 0x1000 |
| 120 | 0xa000 | 0xfff0 | 0x6000 | 0xa000 | 0xfff8 | 0x6000 |
| 121 | 0x10000 | 0x17ff0 | 0x8000 | 0x10000 | 0x17ff8 | 0x8000 |
| 122 | 0x18000 | 0x1fff0 | 0x8000 | 0x18000 | 0x1fff8 | 0x8000 |
| 123 | 0x20000 | 0x27ff0 | 0x8000 | 0x20000 | 0x27ff8 | 0x8000 |
| 124 | 0x28000 | 0x3fff0 | 0x18000 | 0x28000 | 0x3fff8 | 0x18000 |
| 125 | 0x40000 | 0x7fff0 | 0x40000 | 0x40000 | 0x7fff8 | 0x40000 |
| 126 | 0x80000 | inf | 0x80000 | inf |
对于 fast bin ,在 malloc_state 又单独定义了一个 fastbinsY 的结构维护。
typedef struct malloc_chunk *mfastbinptr;
/*
This is in malloc_state.
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[ NFASTBINS ];
*/
由于 fast bin 为单链表结构,因此数组中一个指针就可以维护一个 bin 。结构如图所示:

Fast Bin
为了避免大部分时间花在了合并、分割以及中间检查的过程中影响效率,因此 ptmalloc 中专门设计了 fast bin。
fast bin 采用单链表形式,结构如下图所示:

fast bin 有如下性质:
- 由于采用单链表结构,fast bin 采取 LIFO 策略。
- 每个 fast bin 中维护的 chunk 大小确定,并且 fast bin 维护的最大的
chunk为 128 字节(64位),因此不超过 0x80(chunk大小)的内存释放会进入 fast bin 。 - fast bin 范围的
chunk下一个相邻chunk的PREV_INUSE始终被置为 1。因此它们不会和其它被释放的chunk合并。除非调用malloc_consolidate函数。
安全检查:
-
size:在malloc()函数分配 fastbin size 范围的chunk时,若是对应的fastbin中有空闲chunk,在取出前会检查其size域与对应下标是否一致,不会检查标志位,若否便会触发abort。 -
double free:在
free()函数中会对 fast bin 链表的头结点进行检查,若将要被放入 fast bin 中的chunk与对应下标的链表的头结点为同一chunk,则会触发abort。 -
Safe linking 机制(only glibc2.32 and up):自 glibc 2.32 起引入了 safe-linking 机制,其核心思想是在链表上的
chunk中并不直接存放其所连接的下一个chunk的地址,而是存放下一个chunk的地址与【fd指针自身地址右移 12位】所异或得的值,使得攻击者在得知该chunk的地址之前无法直接利用其构造任意地址写。#define PROTECT_PTR(pos, ptr) \ ((__typeof (ptr)) ((((size_t) pos) >> 12) ^ ((size_t) ptr))) #define REVEAL_PTR(ptr) PROTECT_PTR (&ptr, ptr)需要注意的是 fast bin 的入口节点存放的仍是未经异或的
chunk地址。
另外第一个加入 fast bin 的chunk的fd字段可以泄露堆地址(右移 12 位)。unsigned int idx = fastbin_index(size); fb = &fastbin (av, idx); mchunkptr old = *fb, old2; ... p->fd = PROTECT_PTR (&p->fd, old); *fb = p;
Small Bin
small bin 采用双向链表,结构如下图所示。

small bin 有如下性质:
- small bins 中每个
bin对应的链表采用 FIFO 的规则。 - 每个 small bin 维护的
chunk大小确定,并且 small bin 维护的最大的chunk为 1008 字节(64位),即 0x3f0 的chunk大小。
Large Bin
large bins 中一共包括 63 个 bin,每个 bin 中的 chunk 的大小不一致,而是处于一定区间范围内。large bin 的结构如下:

关于 fd_nextsize 和 bk_nextsize 的机制,这里以 fd_nextsize 为例:
fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize与bins数组没有连接关系(这就解释了为什么bins上 没有体现fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize结构)。- large bin 里的
chunk在fd指针指向的方向上按照chunk大小降序排序。 - 当 large bin 里有一个
chunk时,fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize指向自己(如上面 large bin 的结构图所示)。 - 当 large bin 里同一大小的
chunk有多个时,只有相同大小chunk中的第一个的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize指针有效,其余的chunk的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize设为 NULL 。

- large bin 中有多个不同大小的
chunk时fd_nextsize连接比它小的第一个chunk,bk_nextsize就是把fd_nextsize反过来连到对应结构上。

- large bin 最小的一组
chunk中的第一个chunk的fd_nextsize连接的是最大的chunk,最大的chunk的bk_nextsize相反。
Unsorted Bin
unsorted bin 可以视为空闲 chunk 回归其所属 bin 之前的缓冲区。像 small bin 一样采用双向链表维护。chunk 大小乱序。
Top Chunk
程序第一次进行 malloc 的时候,heap 会被分为两块,一块给用户,剩下的那块就是 top chunk。其实,所谓的 top chunk 就是处于当前堆的物理地址最高的 chunk 。这个 chunk 不属于任何一个 bin ,它的作用在于当所有的 bin 都无法满足用户请求的大小时,如果其大小不小于指定的大小,就进行分配,并将剩下的部分作为新的 top chunk。否则,就对 heap 进行扩展后再进行分配。在 main_arena 中通过 sbrk 扩展 heap,而在 thread arena 中通过 mmap 分配新的 heap 。
需要注意的是,top chunk 的 prev_inuse 比特位始终为 1,否则其前面的 chunk 就会被合并到 top chunk 中。
last remainder
在用户使用 malloc 请求分配内存时,ptmalloc2 找到的 chunk 可能并不和申请的内存大小一致,这时候就将分割之后的剩余部分称之为 last remainder chunk ,unsort bin 也会存这一块。top chunk 分割剩下的部分不会作为 last_remainder 。
tcache
tcache 是 glibc 2.26 (ubuntu 17.10) 之后引入的一种技术,目的是提升堆管理的性能,与 fast bin 类似。tcache 引入了两个新的结构体,tcache_entry 和 tcache_perthread_struct 。
tcache_entry 定义如下:
typedef struct tcache_entry
{
struct tcache_entry *next;
} tcache_entry;
tcache_entry 用于链接空闲的 chunk 结构体,其中的 next 指针指向下一个大小相同的 chunk。需要注意的是这里的 next 指向 chunk 的 user data,而 fast bin 的 fd 指向 chunk 开头的地址。而且,tcache_entry 会复用空闲 chunk 的 user data 部分。
tcache_perthread_struct 定义如下:
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
# define TCACHE_MAX_BINS 64
static __thread tcache_perthread_struct *tcache = NULL;
对应结构如下:

每个 thread 都会维护一个 tcache_perthread_struct ,它是整个 tcache 的管理结构,一共有 TCACHE_MAX_BINS 个计数器和 TCACHE_MAX_BINS 项 tcache_entry。这个结构在 tcache_init 函数中被初始化在堆上,大小为 0x250(高版本为 0x290)。其中数据部分前 0x40 为 counts ,剩下的为 entries 结构。如果能控制这个堆块就可以控制整个 tcache 。
static void
tcache_init(void)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
void *victim = 0;
const size_t bytes = sizeof (tcache_perthread_struct);
if (tcache_shutting_down)
return;
arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL)
{
ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
}
if (ar_ptr != NULL)
__libc_lock_unlock (ar_ptr->mutex);
/* In a low memory situation, we may not be able to allocate memory
- in which case, we just keep trying later. However, we
typically do this very early, so either there is sufficient
memory, or there isn't enough memory to do non-trivial
allocations anyway. */
if (victim)
{
tcache = (tcache_perthread_struct *) victim;
memset (tcache, 0, sizeof (tcache_perthread_struct));
}
}
tcache_perthread_struct 中的 tcache_entry 用单向链表的方式链接了相同大小的处于空闲状态(free 后)的 chunk,这一点上和 fast bin 很像。
另外与 fast bin 相同的是释放进入 tcache 的 chunk 的下一个相邻 chunk 的 PREV_INUSE 位不清零。
counts 记录了 tcache_entry 链上空闲 chunk 的数目,每条链上最多可以有 7 个 chunk 。注意指针指向的位置是 fd 指针,这一点与 fast bin 不同。
结构如下:

stash 机制:
当申请的大小在 tcache 范围的 chunk 在 tcache 中没有,此时 ptmalloc 会在其他 bin 里面找,如果找到了会将该 chunk 放到 tcache 中,直到 tcache 填满,最后直接返回找到的 chunk 或是从 tcache 中取出并返回。
安全检查:
- tcache key(only libc2.29 and up):自 glibc2.29 版本起
tcache新增了一个 key 字段,该字段位于chunk的 bk 字段,值为tcache结构体的地址,若free()检测到chunk->bk == tcache则会遍历tcache查找对应链表中是否有该chunk
最新版本的一些老 glibc (如新版2.27等)也引入了该防护机制 - Safe linking 机制(only glibc2.32 and up):与 fast bin 类似。
绕过方法:- 在
tcache的一个entry中放入第一个chunk时,其同样会对该entry中的 “chunk” (NULL)进行异或运算后写入到将放入tcache中的chunk的fd字段,若是我们能够打印该 free chunk 的fd字段,便能够直接获得未经异或运算的堆上相关地址(右移 12 位) - 在
tcache->entry中存放的仍是未经加密过的地址,若是我们能够控制tcache管理器则仍可以在不知道堆相关地址时进行任意地址写。
- 在
关键过程
仅简要介绍大致过程,具体细节最好还是查看 libc 源码。
malloc
- 首先在 _libc_malloc 函数中先判断 __malloc_hook 函数指针是否为空,如果不为空则调用 __malloc_hook 函数。
- 如果存在 tcache 且有相应大小的 chunk 则将其从 tcache 中取出并返回结果。
- 调用 _int_malloc 函数。
- 首先把申请的内存的字节数转化为 chunk 的大小。
- 如果 arena 未初始化 ,则调用 sysmalloc 向系统申请内存,然后将获取的 chunk 返回。
- 如果申请的 chunk 大小不超过 fast bin 的最大值,则尝试从对应的 fast bin 的头部获取 chunk 。在获取到 chunk 后,如果对应的 fast bin 还有 chunk 并且大小在 tcache 范围就将它们依次从头结点取出放到 tcache 中,直到把 tcache 放满。最后将申请到的 chunk 返回。
- 如果申请的 chunk 在 small bin 大小范围则进行与 fast bin 一样的操作,只不过这次取 chunk 是依次从链表尾部取。
- 如果申请的 chunk 在 large bin 大小范围则调用 malloc_consolidate 函数将 fast bin 中的 chunk 合并后放入 unsorted bin 。
- 循环进行如下操作:
- 循环取 unsorted bin 最后一个 chunk 。
- 如果用户的请求为 small bin chunk,那么我们首先考虑 last remainder,如果当前 chunk 是 last remainder ,且 last remainder 是 unsorted bin 中的唯一一个 chunk , 并且 last remainder 的大小分割后还可以作为一个 chunk,则从 last reminder 中切下一块内存返回。
- 如果 chunk 的大小恰好等于申请的 chunk 大小,则如果该内存大小在 tcache 范围且 tcache 没有满,则先将其放入 tcache,之后会考虑从 tcache 中找 chunk 。否则直接将找到的 chunk 返回。
- 根据 chunk 的大小将其放入 small bin 或 large bin 中。对于 small bin 直接从链表头部加入;对于 large bin,首先特判加入链表尾部的情况,如果不在链表尾部则从头部遍历找位置,如果 large bin 中有与加入的 chunk 大小相同的 chunk ,则加到第一个相等 chunk 后面,否则加到合适位置后还需要更新 nextsize 指针。
- 尝试从 tcache 找 chunk 。
- 如果循环超过 10000 次则跳出循环。
- 尝试从 tcache 找 chunk 。
- 如果申请 chunk 大小不在 small bin 范围,则从后往前遍历对应 large bin ,找到第一个不小于申请 chunk 大小的 chunk 。为了 unlink 时避免修改 nextsize 的操作,如果存在多个合适的 chunk 则选择第二个 chunk 。如果选取的 chunk 比申请的 chunk 大不少于 MINSIZE ,则需要将多出来的部分切出来作为 remainder ,并将其加入 unsorted bin 头部。然后将获取的 chunk 返回。
- 找一个 chunk 范围比申请 chunk 大的非空 bin 里面找最后一个 chunk ,这个过程用 binmap 优化,同时也可以更新 binmap 的状态。这个 chunk 上切下所需的 chunk ,剩余部分放入 unsorted bin 头部。然后将获取的 chunk 返回。
- 如果 top chunk 切下所需 chunk 后剩余部分还是不小于 MINSIZE 则从top chunk 上切下所需 chunk 返回。
- 如果 fast bins 还有 chunk 则调用 malloc_consolidate 合并 fast bin 中的 chunk 并放入 unsorted bin 中,然后继续循环。
- 最后 sysmalloc 系统调用向操作系统申请内存分配 chunk 。
- 如果 arena 没有初始化或者申请的内存大于 mp_.mmap_threshold,并且 mmap 的次数小于最大值,则使用 mmap 申请内存。然后检查一下是否 16 字节对齐然后更新 mmap 次数和 mmap 申请过的最大内存大小后就将 chunk 返回。
- 如果 arena 没有初始化就返回 0
- 对之前的 top chunk 进行检查,如果是 dummy top 的话,因为是用 unsorted bin 表示的,因此 top chunk 的大小需要是 0 。否则堆的大小应该不小于 MINSIZE,并且前一个堆块应该处于使用中,并且堆的结束地址应该是页对齐的,由于页对齐的大小默认是 0x1000,所以低 12 个比特需要为 0。除此之外,top chunk 大小必须比申请 chunk 大小加上 MINSIZE 要小。
- 如果 arena 不是 main arena
- 尝试将 top chunk 所在的 heap 扩展大小,如果成功则更新 arena 记录的内存总大小 system_mem 和 top chunk 大小。
- 尝试申请一个新的 heap 。设置新的 heap 以及 arena 的参数并且将原来的 top chunk 先从尾部切下 2 个 0x10 大小的 chunk ,剩余部分如果不小于 MINSIZE 则将其释放掉。
- 否则,如果前面没有执行到 mmap 申请 chunk 的分支就尝试执行。
- 如果 arena 是 main arena
- 计算需要获取的内存大小。需要获取的内存大小等于申请的 chunk 大小加上 0x20000 和 MINSIZE 。如果堆空间连续,则可以再减去原来内存的大小。然后将需要获取的内存大小与页大小对齐。
- sbrk 扩展内存如果成功则会尝试调用一个 hook 函数,否则 mmap 申请内存,然后 brk 移到申请的内存处并设置堆不连续参数。
- 如果成功获取到内存,则更新 arena 记录的内存总大小 system_mem 和 sbrk_base。之后对一系列的情况进行处理,在这期间,之前的 top chunk 会被从尾部切下两个 0x10 大小的chunk,剩余部分如果不小于 MINSIZE 则将其释放掉。
- 最后从新获取的 top chunk 上切下所需的 chunk 并返回。
- 循环取 unsorted bin 最后一个 chunk 。
free
- 首先在 __libc_free 函数中先判断 __free_hook 函数指针是否为空,如果不为空则调用 __free_hook 函数。
- 如果 chunk 是 mmap 申请的,则调用 munmap_chunk 释放。
- 调用 _int_free 函数
- 如果释放的 chunk 大小在 tcache 范围且对应的 tcache 没有满,则直接放到 tcache 中然后返回。
- 如果在 fast bin 范围则加入到 fast bin 头部并返回。
- 如果不是 mmap 申请的内存
- 如果与释放 chunk 相邻的前一个 chunk 是空闲的,则将前一个 chunk 从 bin 中取出和释放 chunk 合并。
- 如果与释放 chunk 相邻的后一个 chunk 不是 top chunk
- 如果与释放 chunk 相邻的后一个 chunk 是空闲的,则将其从 bin 中取出和释放 chunk 合并,否则将其 PREV_INUSE 位置 0
- 将释放的 chunk 加入到 unsorted bin 头部。
- 否则将其合并到 top chunk
- 如果合并后的 chunk 的大小大于FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD 就向系统返还内存
- 否则调用 munmap_chunk 释放 chunk
源码注释(glibc-2.23)
__libc_malloc
void *
__libc_malloc (size_t bytes)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
//用于保存指向分配区的指针
void *victim;
//用于保存获得的mem指针:chunk_addr + 0x10
// 获取 __malloc_hook
void *(*hook) (size_t, const void *)
= atomic_forced_read (__malloc_hook);
// 如果 __malloc_hook 不为 NULL 则调用 __malloc_hook ,参数为申请的内存大小。
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
return (*hook)(bytes, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
// 获取本线程对应的 thread_arena ,即 malloc_state 结构体。
arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes);
// 调用 _int_malloc 申请内存
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
/* Retry with another arena only if we were able to find a usable arena
before. */
// 如果 ar_ptr 不为 NULL 且内存没有申请成功则重新申请一次内存
if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL)
{
LIBC_PROBE (memory_malloc_retry, 1, bytes);
//获取下一个分配区
ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes);
//再次调用_int_malloc
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
}
//如果此时分配区指针不为空,释放分配区,这里分配已经结束了
if (ar_ptr != NULL)
(void) mutex_unlock (&ar_ptr->mutex);
// 确保只有 3 种情况,即要么没有申请成功,要么是通过 mmap 获取的内存,要么内存是从当前线程对应的 thread_arena 管理的内存中获取的。
assert (!victim || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (victim)) ||
ar_ptr == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (victim)));
// 返回申请到的内存。
return victim;
}
__libc_calloc
void *
__libc_calloc (size_t n, size_t elem_size)
{
mstate av;
mchunkptr oldtop, p;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T bytes, sz, csz, oldtopsize;
void *mem;
unsigned long clearsize;
unsigned long nclears;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T *d;
/* size_t is unsigned so the behavior on overflow is defined. */
// 将需要申请的内存大小转换为以字节为单位
bytes = n * elem_size;
#define HALF_INTERNAL_SIZE_T \
(((INTERNAL_SIZE_T) 1) << (8 * sizeof (INTERNAL_SIZE_T) / 2))
/
// 如果 n 和 elem_size 中的任何一个不小于 HALF_INTERNAL_SIZE_T
// 以 64 位为例,HALF_INTERNAL_SIZE_T = 2^32
if (__builtin_expect ((n | elem_size) >= HALF_INTERNAL_SIZE_T, 0))
{
// 判断 bytes 是否溢出
if (elem_size != 0 && bytes / elem_size != n)
{
__set_errno (ENOMEM);
return 0;
}
}
// 获取 __malloc_hook
void *(*hook) (size_t, const void *) =
atomic_forced_read (__malloc_hook);
// 如果 __malloc_hook 不为 NULL 则调用 __malloc_hook,参数为申请内存的大小。
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
{
sz = bytes;
mem = (*hook)(sz, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
if (mem == 0)
return 0;
return memset (mem, 0, sz);
}
sz = bytes;
arena_get (av, sz);
if (av)
{
/* Check if we hand out the top chunk, in which case there may be no
need to clear. */
// 获取 top chunk 和 top chunk 的大小,这里的 top chunk 的大小是指 top chunk 头之后可以“控制”的的内存大小,具体看后面的解释。
// 获取这些的原因是无论是 main_arena 控制的 heap 区域通过 sbrk 扩展还是非 main_arena 区域通过对 heap_info 向后扩展受保护的内存区域,
// 新扩展的内存初始值为 0,即这些内存不需要清空,因此后面会将需要清零的内存大小减去和这部分内存重合的区域,提升程序效率。
#if MORECORE_CLEARS
oldtop = top (av);
oldtopsize = chunksize (top (av));
# if MORECORE_CLEARS < 2
/* Only newly allocated memory is guaranteed to be cleared. */
if (av == &main_arena &&
oldtopsize < mp_.sbrk_base + av->max_system_mem - (char *) oldtop)
// 对于 main_arena 管理的内存,top chunk 后需要清空的内存大小为 top chunk 到原先 heap 区域末尾位置
oldtopsize = (mp_.sbrk_base + av->max_system_mem - (char *) oldtop);
# endif
if (av != &main_arena)
{
// 对于非 main_arena 管理的内存,top chunk 后需要清空的内存大小为 top chunk 到原先 heap_info 受保护区域末尾位置
heap_info *heap = heap_for_ptr (oldtop);
if (oldtopsize < (char *) heap + heap->mprotect_size - (char *) oldtop)
oldtopsize = (char *) heap + heap->mprotect_size - (char *) oldtop;
}
#endif
}
else
{
/* No usable arenas. */
// av 为 NULL ,那么之后 _int_malloc 会直接 mmap 获取内存,而 mmap 获取的内存初始值为 0,因此不需要清零。
oldtop = 0;
oldtopsize = 0;
}
// 调用 _int_malloc 获取内存
mem = _int_malloc (av, sz);
// 同 __libc_malloc 的 3 种情况
assert (!mem || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (mem)) ||
av == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (mem)));
if (mem == 0 && av != NULL)
{
LIBC_PROBE (memory_calloc_retry, 1, sz);
av = arena_get_retry (av, sz);
mem = _int_malloc (av, sz);
}
if (av != NULL)
(void) mutex_unlock (&av->mutex);
/* Allocation failed even after a retry. */
if (mem == 0)
return 0;
p = mem2chunk (mem);
/* Two optional cases in which clearing not necessary */
// 如果是 mmap 获取的不需要清零,因此只要 chunk 的 size 字段中的 IS_MMAPPED 位置 1 就不会清零。
if (chunk_is_mmapped (p))
{
if (__builtin_expect (perturb_byte, 0))
return memset (mem, 0, sz);
return mem;
}
csz = chunksize (p);
#if MORECORE_CLEARS
// 如果是从 top chunk 上切下来的则只需要清零 top chunk 范围的内存。
if (perturb_byte == 0 && (p == oldtop && csz > oldtopsize))
{
/* clear only the bytes from non-freshly-sbrked memory */
csz = oldtopsize;
}
#endif
/* Unroll clear of <= 36 bytes (72 if 8byte sizes). We know that
contents have an odd number of INTERNAL_SIZE_T-sized words;
minimally 3. */
// 清空内存,包括下一个 chunk 的 prev_size 。
d = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T *) mem;
clearsize = csz - SIZE_SZ;
nclears = clearsize / sizeof (INTERNAL_SIZE_T);
assert (nclears >= 3);
if (nclears > 9)
return memset (d, 0, clearsize);
else
{
*(d + 0) = 0;
*(d + 1) = 0;
*(d + 2) = 0;
if (nclears > 4)
{
*(d + 3) = 0;
*(d + 4) = 0;
if (nclears > 6)
{
*(d + 5) = 0;
*(d + 6) = 0;
if (nclears > 8)
{
*(d + 7) = 0;
*(d + 8) = 0;
}
}
}
}
return mem;
}
__libc_realloc
void *
__libc_realloc (void *oldmem, size_t bytes)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb; /* padded request size */
void *newp; /* chunk to return */
// 调用 __realloc_hook
void *(*hook) (void *, size_t, const void *) =
atomic_forced_read (__realloc_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
return (*hook)(oldmem, bytes, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
//如果 bytes 为 0 则相当于 free(oldmem)
#if REALLOC_ZERO_BYTES_FREES
if (bytes == 0 && oldmem != NULL)
{
__libc_free (oldmem); return 0;
}
#endif
// 如果 oldmem 为 NULL 相当于 malloc(bytes)
/* realloc of null is supposed to be same as malloc */
if (oldmem == 0)
return __libc_malloc (bytes);
// 获取 oldmem 对应的 chunk 的指针和大小
/* chunk corresponding to oldmem */
const mchunkptr oldp = mem2chunk (oldmem);
/* its size */
const INTERNAL_SIZE_T oldsize = chunksize (oldp);
// 寻找 oldp 对应的 arena
if (chunk_is_mmapped (oldp))
ar_ptr = NULL;
else
ar_ptr = arena_for_chunk (oldp);
/* Little security check which won't hurt performance: the
allocator never wrapps around at the end of the address space.
Therefore we can exclude some size values which might appear
here by accident or by "design" from some intruder. */
// 检查 oldp + oldsize 是否超过地址上限
if (__builtin_expect ((uintptr_t) oldp > (uintptr_t) -oldsize, 0)
|| __builtin_expect (misaligned_chunk (oldp), 0))
{
malloc_printerr (check_action, "realloc(): invalid pointer", oldmem,
ar_ptr);
return NULL;
}
// 检查如果申请最小的 chunk 是否会超过地址上限
checked_request2size (bytes, nb);
// 如果是 mmap 得到的内存会单独处理
if (chunk_is_mmapped (oldp))
{
void *newmem;
#if HAVE_MREMAP
// 如果是 mmap 得到的内存则利用 mremap 系统调用实现 realloc。
// mremap 会重新分配一块内存并将之前的数据复制到新的内存上。
newp = mremap_chunk (oldp, nb);
if (newp)
return chunk2mem (newp);
#endif
/* Note the extra SIZE_SZ overhead. */
if (oldsize - SIZE_SZ >= nb)
return oldmem; /* do nothing */
/* Must alloc, copy, free. */
// 如果 mremap 获取不到所需的内存则通过 malloc 获取内存,并将原先内存的数据复制过来然后 munmap 将原先的内存释放掉
newmem = __libc_malloc (bytes);
if (newmem == 0)
return 0; /* propagate failure */
memcpy (newmem, oldmem, oldsize - 2 * SIZE_SZ);
munmap_chunk (oldp);
return newmem;
}
(void) mutex_lock (&ar_ptr->mutex);
// 调用 _int_realloc 调整内存
newp = _int_realloc (ar_ptr, oldp, oldsize, nb);
(void) mutex_unlock (&ar_ptr->mutex);
// 检查内存分配后的 3 种情况
assert (!newp || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (newp)) ||
ar_ptr == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (newp)));
// 如果 _int_realloc 没有成功则尝试调用 _int_malloc 重新分配内存
if (newp == NULL)
{
/* Try harder to allocate memory in other arenas. */
LIBC_PROBE (memory_realloc_retry, 2, bytes, oldmem);
newp = __libc_malloc (bytes);
// 如果 malloc 成功则将数据拷贝后释放原先的内存
if (newp != NULL)
{
memcpy (newp, oldmem, oldsize - SIZE_SZ);
_int_free (ar_ptr, oldp, 0);
}
}
return newp;
}
__libc_free
void
__libc_free (void *mem)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
mchunkptr p; /* chunk corresponding to mem */
// 调用 __free_hook ,参数是是否的内存的地址。
void (*hook) (void *, const void *)
= atomic_forced_read (__free_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
{
(*hook)(mem, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
return;
}
if (mem == 0) /* free(0) has no effect */
return;
p = mem2chunk (mem);
// 如果是 mmapp 得到的内存单独处理
if (chunk_is_mmapped (p)) /* release mmapped memory. */
{
/* see if the dynamic brk/mmap threshold needs adjusting */
// 释放的内存大小如果大于 mmap_threshold 并且小于 DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MAX(0x20000)
// 则更新 mmap_threshold 为释放内存的大小,trim_threshold 为两倍释放内存的大小。
// 其中 mmap_threshold 是 sysmalloc 中 brk 和 mmap 两种系统调用获取内存的选择的边界值
// trim_threshold 为是否 systrim 减少 ptmalloc 保留内存的参考值
if (!mp_.no_dyn_threshold
&& p->size > mp_.mmap_threshold
&& p->size <= DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MAX)
{
mp_.mmap_threshold = chunksize (p);
mp_.trim_threshold = 2 * mp_.mmap_threshold;
LIBC_PROBE (memory_mallopt_free_dyn_thresholds, 2,
mp_.mmap_threshold, mp_.trim_threshold);
}
// 调用 nummap 释放内存
munmap_chunk (p);
return;
}
// 调用 _int_free 释放内存
ar_ptr = arena_for_chunk (p);
_int_free (ar_ptr, p, 0);
}
_int_malloc
static void * _int_malloc (mstate av, size_t bytes) {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb; /* 请求的chunk_size */
unsigned int idx; /* 对应bin数组中的index */
mbinptr bin; /* 指向对应bin的指针 */
mchunkptr victim; /* 指向分配的chunk */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* 分配的chunk的size */
int victim_index; /* 分配的chunk的bin的index */
mchunkptr remainder; /* 指向分割后剩下的那块chunk */
unsigned long remainder_size; /* 分割后剩下的那块chunk的size */
unsigned int block; /* bit map traverser */
unsigned int bit; /* bit map traverser */
unsigned int map; /* 一个block值 */
mchunkptr fwd; /* 用于链表操作 */
mchunkptr bck; /* 用于链表操作 */
const char *errstr = NULL; /* 报错字符串指针 */
checked_request2size (bytes, nb); /* 计算chunk_size */
if (__glibc_unlikely (av == NULL)) {
//无可用的分配区,使用sysmalloc获取内存
void *p = sysmalloc (nb, av);
if (p != NULL)
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
//对数据用memset进行处理
return p;
}
if ((unsigned long) (nb) <= (unsigned long) (get_max_fast ())) {
//要分配的chunk大小小于global_max_fast则先从fastbin中寻找
idx = fastbin_index (nb);
//通过size获取在fastbin中对应的index
mfastbinptr *fb = &fastbin (av, idx);
//通过index获取分配区的fastbin中对应的bin
mchunkptr pp = *fb;
//获取bin的首个chunk
do {
victim = pp;
if (victim == NULL)
break;
} while ((pp = catomic_compare_and_exchange_val_acq (fb, victim->fd, victim)) != victim);
//将头指针的下一个chunk作为空闲chunk链表的头部,这里使用lock-free的技术实现.Lock-free算法的基础是CAS(Compareand-Swap)原子操作.避免了ABA问题
//此时victim是该fb原来的首个chunk,或者为0
if (victim != 0) {
//存在可使用的fastbin chunk
if (__builtin_expect (fastbin_index (chunksize (victim)) != idx, 0)) {
//检测该chunk的size是否符合该bin的index
errstr = "malloc(): memory corruption (fast)";
errout:
malloc_printerr (check_action, errstr, chunk2mem (victim), av);
return NULL;
}
check_remalloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
/*
#if !MALLOC_DEBUG
# define check_chunk(A, P)
# define check_free_chunk(A, P)
# define check_inuse_chunk(A, P)
# define check_remalloced_chunk(A, P, N)
# define check_malloced_chunk(A, P, N)
# define check_malloc_state(A)
非debug模式下这些宏定义为空
*/
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
//将chunk指针转化为mem指针,即指向data区域
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
/*
# define __glibc_unlikely(cond) (cond)
static int perturb_byte;
static void alloc_perturb (char *p, size_t n) {
if (__glibc_unlikely (perturb_byte))
memset (p, perturb_byte ^ 0xff, n);
}
该函数配合calloc使用
*/
return p;
//将分配出来的mem指针返回
}
}
//victim为0说明对应fastbin无空闲chunk,继续进行分配
if (in_smallbin_range (nb)) {
//所需的chunk大小属于smallbin
idx = smallbin_index (nb);
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
//根据index获得对应smallbin的表头
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin) {
//victim赋值为表尾,如果该表不为空
if (victim == 0)
//victim为0,表示smallbin还没有初始化为双向循环链表,调用malloc_consolidate函数,此时由于global_max_fast也未初始化,所以会调用malloc_init_state初始化
malloc_consolidate (av);
else {
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim)) {
//双向链表检测,last(bin)->bk->fd == last(bin)
errstr = "malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted";
goto errout;
}
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
//设置inuse标志
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
//将victim从smallbin的双向循环链表中取出
if (av != &main_arena)
//如果是非主分配区,将标志bit清零
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
//同上,正常的分配流程
}
}
//该表为空则继续分配
} else {
//所需的chunk大小属于largebin
idx = largebin_index (nb);
if (have_fastchunks (av))
//调用malloc_consolidate()函数合并fastbin chunk,并将这些空闲chunk加入unsorted_bin中
malloc_consolidate (av);
}
for (;;) {
int iters = 0;
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av)) {
//反向遍历unsorted_bin,遍历结束的条件是unsorted_bin为空
//victim是unsorted_bin中最后一个chunk
bck = victim->bk;
//bck是unsorted_bin中倒数第二个chunk
if (__builtin_expect (victim->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0) || __builtin_expect (victim->size > av->system_mem, 0))
//chunk的大小不能小于等于2 * SIZE_SZ,也不能超过该分配区总的内存分配量
malloc_printerr (check_action, "malloc(): memory corruption", chunk2mem (victim), av);
size = chunksize (victim);
//获取最后一个chunk的size
if (in_smallbin_range (nb) && bck == unsorted_chunks (av) && victim == av->last_remainder && (unsigned long) (size) > (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE)) {
//如果请求的chunk大小为smallbin范围,且unsorted_bin中只有一个last_remainder chunk,且其大小大于所需chunk的大小加上MINSIZE
remainder_size = size - nb;
//计算切分后剩余chunk的size
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
//计算切分后剩余chunk的地址
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = unsorted_chunks (av)->fd = remainder;
//将切分后剩余的chunk放入unsorted_bin
av->last_remainder = remainder;
//设置为last_remainder chunk
remainder->bk = remainder->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
//设置last_remainder chunk的bk和fd
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size)) {
//若剩下的chunk属于largebin chunk,将其fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize设置为NULL
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
//设置头部(addr + 0x8),包括大小和标志位,由于临近的前一个chunk一定位于使用中,所以PREV_INUSE为1
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
//同理,由于victim会被分配给用户,所以PREV_INUSE为1
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
//该chunk不在使用中,使用set_foot对该chunk的inuse标志位置零
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
//同上,正常的分配流程
}
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck;
bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
//不满足上述情况则将该chunk从unsorted_bin链表中取出
if (size == nb) {
//victim大小与所需的chunk大小一致
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
//对victim的inuse标志位置零
if (av != &main_arena)
//不属于主分配区则对对应的标志位置零
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
//同上,正常的分配流程
}
//到这说明该victim会放入对应的bin链表
if (in_smallbin_range (size)) {
//victim属于smallbin
victim_index = smallbin_index (size);
//获得所属smallbin的index
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);
//将该smallbin的链表表头赋值给bck
fwd = bck->fd;
//该smallbin第一个chunk赋值给fwd
//victim会插入到bck和fwd之间,作为该smallbin链表的第一个chunk.
} else {
//victim属于largebin
victim_index = largebin_index (size);
//获得所属largebin的index
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);
//将该largebin的链表表头赋值给bck
fwd = bck->fd;
//该largebin第一个chunk赋值给fwd
if (fwd != bck) {
//该largebin中有空闲chunk存在
size |= PREV_INUSE;
//将当前chunk的size的inuse标志bit置位,便于加快chunk大小的比较
assert ((bck->bk->size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0);
//断言该largebin最后一个chunk的size字段中的非主分配区的标志bit没有置位
if ((unsigned long) (size) < (unsigned long) (bck->bk->size)) {
//当前chunk比最后一个chunk小,就插入到该largebin的链表的最后
fwd = bck;
//fwd赋值为表头
bck = bck->bk;
//bck赋值为最后一个chunk
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
//将victim插入chunk size链表的尾部,该链表是从大到小排列的
} else {
assert ((fwd->size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0);
//断言该largebin第一个chunk的size字段中的非主分配区的标志bit没有置位
while ((unsigned long) size < fwd->size) {
//正向遍历chunk size链表,直到找到第一个小于等于当前chunk大小的chunk
fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize;
assert ((fwd->size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0);
}
if ((unsigned long) size == (unsigned long) fwd->size)
//同一大小的chunk已经存在,则不需要修改chunk size链表,当前chunk插入fwd之后
fwd = fwd->fd;
else {
//当前chunk大于fwd,则将当前chunk作为该chunk size的代表加入chunk size链表,位置为fwd的前面
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
}
} else
//如果largebin中没有chunk,直接将当前chunk加入chunk size链表,chunk size链表表头位于第一个chunk的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize,所以第一个chunk是最大的
victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim;
}
mark_bin (av, victim_index);
//将对应map里该index对应的标志位置1
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;
//将当前chunk插入到对应bin中
#define MAX_ITERS 10000
if (++iters >= MAX_ITERS)
//如果unsorted_bin中的chunk超过了10000个,最多遍历10000个就退出
break;
}
//此时unsorted_bin链表已经处理完成
if (!in_smallbin_range (nb)) {
//所需分配的chunk大小为largebin
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
//获取对应的bin
if ((victim = first (bin)) != bin && (unsigned long) (victim->size) >= (unsigned long) (nb)) {
//如果largebin链表不为空且链表中最大的chunk大于所需chunk的大小,则遍历该largebin链表,找到合适的chunk
victim = victim->bk_nextsize;
//从最后一个也就是最小一个开始遍历
while (((unsigned long) (size = chunksize (victim)) < (unsigned long) (nb)))
//反向遍历chunk size链表,直到找到第一个大于等于所需chunk大小的chunk退出循环
victim = victim->bk_nextsize;
if (victim != last (bin) && victim->size == victim->fd->size)
//如果victim不是链表中的最后一个chunk且与victim大小相同的chunk不止一个,意味着victim为chunk size链表中的节点,取victim->fd节点对应的chunk作为候选chunk
victim = victim->fd;
remainder_size = size - nb;
//由于size可能大于所需的chunk,所以要计算看是否要划分
unlink (av, victim, bck, fwd);
//调用unlink宏函数将victim从largebin链表中取出
if (remainder_size < MINSIZE) {
//如果将victim切分后剩余大小小于MINSIZE,则将整个victim返回,实际分配的chunk比所需的chunk要大一些
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
} else {
//从victim中切分出所需的chunk,剩余部分作为一个新的chunk加入到unsorted_bin,其他处理与前面类似
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
bck = unsorted_chunks (av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck)) {
//验证第一个chunk的bk
errstr = "malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks";
goto errout;
}
remainder->bk = bck;
remainder->fd = fwd;
bck->fd = remainder;
fwd->bk = remainder;
//将remainder插入为unsorted_bin的第一个chunk
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size)) {
//若剩下的chunk属于largebin chunk,将该chunk的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize设置为NULL
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
//划分后设置,同上
}
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
//返回chunk过程,同上
}
}
//从最合适的smallbin或largebin中都没有分配到需要的chunk,则查看比当前bin的index大的smallbin或largebin是否有空闲chunk可利用来分配所需的chunk
++idx;
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
//获取下一个相邻bin的空闲chunk链表
block = idx2block (idx);
map = av->binmap[block];
bit = idx2bit (idx);
//获取该bin对于binmap中的bit位的值,使用binmap可以加快查找bin是否包含空闲chunk,idx2bit宏将idx指定的位设置为1,其它位清零
for (;; ) {
if (bit > map || bit == 0) {
//map为0即该block所对应的所有bins中都没有空闲chunk.于是遍历binmap的下一个block,直到找到一个不为0的block或者遍历完所有的block
do {
if (++block >= BINMAPSIZE)
//遍历完所有的block都没有则使用top chunk分配
goto use_top;
} while ((map = av->binmap[block]) == 0);
bin = bin_at (av, (block << BINMAPSHIFT));
bit = 1;
}
while ((bit & map) == 0) {
//在一个block遍历对应的bin直到找到一个bit不为0退出遍历
bin = next_bin (bin);
bit <<= 1;
assert (bit != 0);
}
victim = last (bin);
//将bin链表中的最后一个chunk赋值给victim
if (victim == bin) {
//victim与bin链表头指针相同,表示该bin中没有空闲chunk,binmap中的相应位设置不准确,将binmap的相应bit位清零,获取当前bin下一个bin,将bit移到下一个bit位,即乘以2
av->binmap[block] = map &= ~bit;
bin = next_bin (bin);
bit <<= 1;
} else {
//当前bin中的最后一个chunk满足要求,获取该chunk的大小,计算切分出所需chunk后剩余部分的大小,然后将victim从bin的链表中取出
size = chunksize (victim);
assert ((unsigned long) (size) >= (unsigned long) (nb));
remainder_size = size - nb;
unlink (av, victim, bck, fwd);
if (remainder_size < MINSIZE) {
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
} else {
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
bck = unsorted_chunks (av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck)) {
errstr = "malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks 2";
goto errout;
}
remainder->bk = bck;
remainder->fd = fwd;
bck->fd = remainder;
fwd->bk = remainder;
if (in_smallbin_range (nb))
//剩余部分chunk属于smallbin,将分配区的last_remainder chunk设置为剩余部分构成的chunk
av->last_remainder = remainder;
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size)) {
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
}
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}
use_top:
//从top chunk中分配所需chunk
victim = av->top;
size = chunksize (victim);
//将当前分配区的top chunk赋值给victim,并获得victim的大小
if ((unsigned long) (size) >= (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE)) {
//top chunk切分出所需chunk后还需要MINSIZE的空间来作为fencepost
//切分后的剩余部分将作为新的top chunk,原top chunk的fencepost仍然作为新的top chunk的fencepost,所以切分之后剩余的chunk不用set_foot
remainder_size = size - nb;
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
av->top = remainder;
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
} else if (have_fastchunks (av)) {
//如果top chunk也不能满足要求,查看fastbin中是否有空闲chunk存在,因为free属于fastbin的chunk时不需要获得分配区的锁,调用malloc_consolidate函数并重新设置当前bin的index,再次循环
malloc_consolidate (av);
if (in_smallbin_range (nb))
idx = smallbin_index (nb);
else
idx = largebin_index (nb);
} else {
//如果fastbin中没有空闲chunk存在,向系统申请内存
void *p = sysmalloc (nb, av);
if (p != NULL)
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}
}
_int_realloc
// _int_realloc函数用于重新分配内存块。它尝试更改内存块的大小并可能移动它以满足新的大小要求。
// 参数:
// av - 指向内存状态的指针。
// oldp - 指向当前内存块的指针。
// oldsize - 当前内存块的大小。
// nb - 请求的新大小。
void* _int_realloc(mstate av, mchunkptr oldp, INTERNAL_SIZE_T oldsize, INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb) {
// 定义一系列局部变量来存储分配的状态和中间结果。
mchunkptr newp; // 新分配的内存块指针。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T newsize; // 新内存块的大小。
void* newmem; // 对应用户内存的指针。
mchunkptr next; // 指向oldp后面的连续内存块。
mchunkptr remainder; // 新分配内存后剩余的内存块。
unsigned long remainder_size; // 剩余内存块的大小。
mchunkptr bck; // 用于链接的临时变量。
mchunkptr fwd; // 用于链接的临时变量。
unsigned long copysize; // 需要复制的字节数。
unsigned int ncopies; // 需要复制的INTERNAL_SIZE_T字数。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T* s; // 复制源的指针。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T* d; // 复制目标的指针。
const char *errstr = NULL; // 用于错误处理的字符串。
// 检查oldp的大小是否合法。
if (__builtin_expect(oldp->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0) || __builtin_expect(oldsize >= av->system_mem, 0)) {
errstr = "realloc(): invalid old size";
goto errout;
}
check_inuse_chunk(av, oldp); // 检查oldp是否正在使用中。
assert(!chunk_is_mmapped(oldp)); // 确保oldp不是映射内存。
next = chunk_at_offset(oldp, oldsize); // 计算下一个内存块的位置。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize = chunksize(next); // 获取下一个内存块的大小。
// 检查下一个内存块的大小是否合法。
if (__builtin_expect(next->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0) || __builtin_expect(nextsize >= av->system_mem, 0)) {
errstr = "realloc(): invalid next size";
goto errout;
}
// 如果当前内存块已经足够大,则直接返回当前内存块。
if ((unsigned long)(oldsize) >= (unsigned long)(nb)) {
newp = oldp;
newsize = oldsize;
} else {
// 如果下一个内存块是顶部内存块,并且可以合并以满足请求的大小,则进行合并。
if (next == av->top && (unsigned long)(newsize = oldsize + nextsize) >= (unsigned long)(nb + MINSIZE)) {
set_head_size(oldp, nb | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
av->top = chunk_at_offset(oldp, nb);
set_head(av->top, (newsize - nb) | PREV_INUSE);
check_inuse_chunk(av, oldp);
return chunk2mem(oldp);
}
// 如果下一个内存块不在使用中,并且可以合并以满足请求的大小,则进行合并。
else if (next != av->top && !inuse(next) && (unsigned long)(newsize = oldsize + nextsize) >= (unsigned long)(nb)) {
newp = oldp;
unlink(av, next, bck, fwd);
}
// 否则,分配新内存,复制数据,然后释放旧内存。
else {
newmem = _int_malloc(av, nb - MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK);
if (newmem == 0)
return 0; // 如果分配失败,则返回0。
newp = mem2chunk(newmem);
newsize = chunksize(newp);
// 如果新分配的内存块紧跟在旧内存块后面,则合并这两个内存块。
if (newp == next) {
newsize += oldsize;
newp = oldp;
} else {
// 否则,复制旧内存块的内容到新内存块。
copysize = oldsize - SIZE_SZ;
s = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T*)(chunk2mem(oldp));
d = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T*)(newmem);
ncopies = copysize / sizeof(INTERNAL_SIZE_T);
assert(ncopies >= 3);
if (ncopies > 9)
memcpy(d, s, copysize);
else {
// 对于小内存块,使用手动复制以提高效率。
*(d + 0) = *(s + 0);
*(d + 1) = *(s + 1);
*(d + 2) = *(s + 2);
if (ncopies > 4) {
*(d + 3) = *(s + 3);
*(d + 4) = *(s + 4);
if (ncopies > 6) {
*(d + 5) = *(s + 5);
*(d + 6) = *(s + 6);
if (ncopies > 8) {
*(d + 7) = *(s + 7);
*(d + 8) = *(s + 8);
}
}
}
}
_int_free(av, oldp, 1); // 释放旧内存块。
check_inuse_chunk(av, newp); // 检查新内存块是否正在使用中。
return chunk2mem(newp); // 返回新内存块的用户可用部分。
}
}
}
// 尝试释放新内存块中的多余空间。
assert((unsigned long)(newsize) >= (unsigned long)(nb));
remainder_size = newsize - nb;
// 如果剩余空间太小,无法分割为独立的内存块,则保留它。
if (remainder_size < MINSIZE) {
set_head_size(newp, newsize | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_inuse_bit_at_offset(newp, newsize);
} else {
// 否则,分割剩余空间为独立的内存块。
remainder = chunk_at_offset(newp, nb);
set_head_size(newp, nb | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head(remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_inuse_bit_at_offset(remainder, remainder_size); // 标记剩余部分为正在使用中,以便_free()不会报错。
_int_free(av, remainder, 1); // 释放剩余部分。
}
check_inuse_chunk(av, newp); // 检查新内存块是否正在使用中。
return chunk2mem(newp); // 返回新内存块的用户可用部分。
}
_int_free
static void _int_free (mstate av, mchunkptr p, int have_lock) {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* 释放的chunk的size */
mfastbinptr *fb; /* 对应的fastbin */
mchunkptr nextchunk; /* 内存空间中下一个chunk */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize; /* 下一个chunk的大小 */
int nextinuse; /* 下一个chunk是否在使用 */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize; /* 内存空间中上一个chunk */
mchunkptr bck; /* 用于储存bin链表指针 */
mchunkptr fwd; /* 用于储存bin链表指针 */
const char *errstr = NULL;
int locked = 0;
size = chunksize (p);
if (__builtin_expect ((uintptr_t) p > (uintptr_t) -size, 0) || __builtin_expect (misaligned_chunk (p), 0)) {
//chunk的指针地址不能溢出
errstr = "free(): invalid pointer";
errout:
if (!have_lock && locked)
(void) mutex_unlock (&av->mutex);
malloc_printerr (check_action, errstr, chunk2mem (p), av);
return;
}
if (__glibc_unlikely (size < MINSIZE || !aligned_OK (size))) {
//chunk的大小必须大于等于MINSIZE且对齐
errstr = "free(): invalid size";
goto errout;
}
check_inuse_chunk(av, p);
if ((unsigned long)(size) <= (unsigned long)(get_max_fast ())
#if TRIM_FASTBINS
&& (chunk_at_offset(p, size) != av->top)
#endif
) {
//当前free的chunk属于fastbin
if (__builtin_expect (chunk_at_offset (p, size)->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0) || __builtin_expect (chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size)) >= av->system_mem, 0)) {
//查看下一个相邻的chunk的大小是否小于等于2 * SIZE_SZ,或是否大于分配区所分配的内存总量
if (have_lock || ({ assert (locked == 0); mutex_lock(&av->mutex); locked = 1; chunk_at_offset (p, size)->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ || chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size)) >= av->system_mem; })) {
errstr = "free(): invalid next size (fast)";
goto errout;
}
if (! have_lock) {
(void)mutex_unlock(&av->mutex);
locked = 0;
}
//读取分配区所分配的内存总量需要对分配区加锁,检查完以后,释放分配区的锁
}
free_perturb (chunk2mem(p), size - 2 * SIZE_SZ);
set_fastchunks(av);
unsigned int idx = fastbin_index(size);
fb = &fastbin (av, idx);
//设置当前分配区的fastbin的flag,表示当前分配区的fastbin中已有空闲chunk.然后根据当前free的chunk大小获取所属的fastbin
mchunkptr old = *fb, old2;
unsigned int old_idx = ~0u;
do {
if (__builtin_expect (old == p, 0)) {
//fastbin double free检测
errstr = "double free or corruption (fasttop)";
goto errout;
}
if (have_lock && old != NULL)
old_idx = fastbin_index(chunksize(old));
p->fd = old2 = old;
} while ((old = catomic_compare_and_exchange_val_rel (fb, p, old2)) != old2);
//使用lock-free技术实现fastbin的单向链表插入操作
if (have_lock && old != NULL && __builtin_expect (old_idx != idx, 0)) {
errstr = "invalid fastbin entry (free)";
goto errout;
}
} else if (!chunk_is_mmapped(p)) {
//当前free的chunk不是通过mmap分配的,并且当前还没有获得分配区的锁,获取分配区的锁
if (! have_lock) {
(void)mutex_lock(&av->mutex);
locked = 1;
}
nextchunk = chunk_at_offset(p, size);
if (__glibc_unlikely (p == av->top)) {
//free的是top chunk
errstr = "double free or corruption (top)";
goto errout;
}
if (__builtin_expect (contiguous (av) && (char *) nextchunk >= ((char *) av->top + chunksize(av->top)), 0)) {
//内存中下一个chunk的地址大于top chunk的末尾
errstr = "double free or corruption (out)";
goto errout;
}
if (__glibc_unlikely (!prev_inuse(nextchunk))) {
//该chunk已经是free状态
errstr = "double free or corruption (!prev)";
goto errout;
}
nextsize = chunksize(nextchunk);
if (__builtin_expect (nextchunk->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0) || __builtin_expect (nextsize >= av->system_mem, 0)) {
//查看下一个相邻的chunk的大小是否小于等于2 * SIZE_SZ,或是否大于分配区所分配的内存总量
errstr = "free(): invalid next size (normal)";
goto errout;
}
free_perturb (chunk2mem(p), size - 2 * SIZE_SZ);
if (!prev_inuse(p)) {
//如果当前free的chunk的前一个相邻chunk为空闲状态,与前一个空闲chunk合并
prevsize = p->prev_size;
size += prevsize;
p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize));
unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);
}
if (nextchunk != av->top) {
//与当前free的chunk相邻的下一个chunk不是分配区的top chunk
nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize);
if (!nextinuse) {
//如果当前free的chunk的下一个相邻chunk为空闲状态,与下一个空闲chunk合并
unlink(av, nextchunk, bck, fwd);
size += nextsize;
} else
//与当前free的chunk相邻的下一个chunk处于inuse状态,清除当前chunk的inuse状态
clear_inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, 0);
bck = unsorted_chunks(av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck)) {
//unsorted_bin第一个chunk的fd的bk不是第一个chunk
errstr = "free(): corrupted unsorted chunks";
goto errout;
}
p->fd = fwd;
p->bk = bck;
if (!in_smallbin_range(size)) {
p->fd_nextsize = NULL;
p->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
bck->fd = p;
fwd->bk = p;
//将合并后的chunk加入unsorted_bin的双向循环链表中
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot(p, size);
check_free_chunk(av, p);
} else {
//当前free的chunk下一个相邻的chunk为top chunk,则将当前chunk合并入top chunk
size += nextsize;
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
av->top = p;
check_chunk(av, p);
}
if ((unsigned long)(size) >= FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD) {
//如果合并后的chunk大小大于64KB
if (have_fastchunks(av))
malloc_consolidate(av);
if (av == &main_arena) {
#ifndef MORECORE_CANNOT_TRIM
if ((unsigned long)(chunksize(av->top)) >= (unsigned long)(mp_.trim_threshold))
//如果当前分配区为主分配区且top chunk的大小大于heap的收缩阈值,调用systrim函数收缩heap
systrim(mp_.top_pad, av);
#endif
} else {
//为非主分配区,调用heap_trim函数收缩非主分配区的sub_heap
heap_info *heap = heap_for_ptr(top(av));
assert(heap->ar_ptr == av);
heap_trim(heap, mp_.top_pad);
}
}
if (! have_lock) {
//有锁则对分配区解锁
assert (locked);
(void)mutex_unlock(&av->mutex);
}
} else {
//当前free的chunk是通过mmap分配则调用munma_chunk释放
munmap_chunk (p);
}
}
malloc_consolidate
static void malloc_consolidate(mstate av) {
mfastbinptr* fb;
mfastbinptr* maxfb;
mchunkptr p;
mchunkptr nextp;
mchunkptr unsorted_bin;
mchunkptr first_unsorted;
mchunkptr nextchunk;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize;
int nextinuse;
mchunkptr bck;
mchunkptr fwd;
if (get_max_fast () != 0) {
//global_max_fast不为0,表示ptmalloc已经初始化,清除分配区flag中fastbin的标志位
clear_fastchunks(av);
unsorted_bin = unsorted_chunks(av);
maxfb = &fastbin (av, NFASTBINS - 1);
fb = &fastbin (av, 0);
//将分配区最大的一个fastbin赋值给maxfb,第一个fastbin赋值给fb,然后遍历fastbin
do {
p = atomic_exchange_acq (fb, 0);
//获取当前遍历的fastbin中空闲chunk单向链表的头指针
if (p != 0) {
do {
check_inuse_chunk(av, p);
nextp = p->fd;
size = p->size & ~(PREV_INUSE|NON_MAIN_ARENA);
nextchunk = chunk_at_offset(p, size);
nextsize = chunksize(nextchunk);
//获得当前chunk的size并去除size中的PREV_INUSE和NON_MAIN_ARENA标志,获取相邻的下一个chunk和下一个chunk的大小
if (!prev_inuse(p)) {
//如果当前chunk的前一个chunk空闲则将当前chunk与前一个chunk合并成一个空闲chunk
prevsize = p->prev_size;
size += prevsize;
p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize));
unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);
}
if (nextchunk != av->top) {
//如果与当前chunk相邻的下一个chunk不是分配区的top chunk,查看与当前chunk相邻的下一个chunk是否处于inuse状态
nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize);
if (!nextinuse) {
//下一个chunk空闲则将当前chunk与下一个chunk合并成一个空闲chunk
size += nextsize;
unlink(av, nextchunk, bck, fwd);
} else
//与当前chunk相邻的下一个chunk处于inuse状态,清除当前chunk的inuse状态
clear_inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, 0);
first_unsorted = unsorted_bin->fd;
unsorted_bin->fd = p;
first_unsorted->bk = p;
//将合并后的chunk加入unsorted_bin的双向循环链表中
if (!in_smallbin_range (size)) {
p->fd_nextsize = NULL;
p->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
p->bk = unsorted_bin;
p->fd = first_unsorted;
set_foot(p, size);
} else {
//当前chunk的下一个chunk为top chunk则将当前chunk合并入top chunk
size += nextsize;
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
av->top = p;
}
} while ( (p = nextp) != 0);
//直到遍历完当前fastbin中的所有空闲chunk
}
} while (fb++ != maxfb);
//直到遍历完所有的fastbin
} else {
//如果ptmalloc没有初始化,初始化ptmalloc
malloc_init_state(av);
check_malloc_state(av);
}
}
void __libc_free (void *mem) {
mstate ar_ptr;
mchunkptr p;
void (*hook) (void *, const void *) = atomic_forced_read (__free_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0)) {
(*hook)(mem, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
return;
}
if (mem == 0)
return;
p = mem2chunk (mem);
if (chunk_is_mmapped (p)) {
//如果当前free的chunk是通过mmap分配的,调用munmap_chunk函数
if (!mp_.no_dyn_threshold && p->size > mp_.mmap_threshold && p->size <= DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MAX) {
//如果开启了mmap分配阈值动态调整机制且chunk的大小大于设置的mmap分配阈值,小于mmap分配阈值的最大值.则将当前chunk的大小赋值给mmap分配阈值,并修改mmap收缩阈值为mmap分配阈值的2倍
mp_.mmap_threshold = chunksize (p);
mp_.trim_threshold = 2 * mp_.mmap_threshold;
LIBC_PROBE (memory_mallopt_free_dyn_thresholds, 2, mp_.mmap_threshold, mp_.trim_threshold);
}
munmap_chunk (p);
return;
}
ar_ptr = arena_for_chunk (p);
_int_free (ar_ptr, p, 0);
//不需要对分配区加锁,调用_int_free函数执行实际的释放工作
}
sysmalloc
/*
sysmalloc函数处理需要从系统获取更多内存的malloc情况。
在进入函数时,假设av->top没有足够的空间来满足对nb字节的请求,
因此需要扩展或替换av->top。
*/
static void *
sysmalloc(INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb, mstate av)
{
mchunkptr old_top; // av->top的原始值。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T old_size; // 它的大小。
char *old_end; // 它的结束地址。
long size; // 参数给MORECORE或mmap调用。
char *brk; // MORECORE的返回值。
long correction; // 参数给第二个MORECORE调用。
char *snd_brk; // 第二个返回值。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T front_misalign; // 新空间前面的不可用字节。
INTERNAL_SIZE_T end_misalign; // 新空间末端的部分页。
char *aligned_brk; // 对齐的brk偏移。
mchunkptr p; // 分配/返回的内存块。
mchunkptr remainder; // 分配后的剩余部分。
unsigned long remainder_size; // 它的大小。
size_t pagesize = GLRO(dl_pagesize); // 系统页的大小。
bool tried_mmap = false; // 标记是否尝试过mmap。
/*
如果使用mmap,并且请求的大小达到mmap阈值,并且系统支持mmap,
并且当前分配的mmap区域数量较少,尝试直接映射这个请求,
而不是扩展top。
*/
if (av == NULL
|| ((unsigned long)(nb) >= (unsigned long)(mp_.mmap_threshold)
&& (mp_.n_mmaps < mp_.n_mmaps_max)))
{
char *mm; // mmap调用的返回值。
try_mmap:
/*
将大小上调到最近的页大小。对于mmapped区块,开销比普通区块多一个SIZE_SZ单位,
因为没有后续区块的prev_size字段可用。
对于glibc,没有必要进行进一步对齐,除非我们需要更高的对齐。
*/
if (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT == 2 * SIZE_SZ)
size = ALIGN_UP(nb + SIZE_SZ, pagesize);
else
size = ALIGN_UP(nb + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK, pagesize);
tried_mmap = true;
if ((unsigned long)(size) > (unsigned long)(nb))
{
mm = (char *)(MMAP(0, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, 0));
if (mm != MAP_FAILED)
{
/*
mmapped区域的开始偏移存储在区块的prev_size字段中。这允许我们在这里
和memalign()中调整返回的开始地址以满足对齐要求,并且仍然能够在
free()和realloc()中计算出正确的munmap参数地址。
*/
if (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT == 2 * SIZE_SZ)
{
/* 对于glibc,chunk2mem增加地址2*SIZE_SZ,并且MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK是2*SIZE_SZ-1。
每个mmap区域都是页面对齐的,因此一定是MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK对齐的。*/
assert(((INTERNAL_SIZE_T)chunk2mem(mm) & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) == 0);
front_misalign = 0;
}
else
{
front_misalign = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T)chunk2mem(mm) & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK;
if (front_misalign > 0)
{
correction = MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - front_misalign;
p = (mchunkptr)(mm + correction);
p->prev_size = correction;
set_head(p, (size - correction) | IS_MMAPPED);
}
else
{
p = (mchunkptr)mm;
set_head(p, size | IS_MMAPPED);
}
}
/* 更新统计数据 */
int new = atomic_exchange_and_add(&mp_.n_mmaps, 1) + 1;
atomic_max(&mp_.max_n_mmaps, new);
unsigned long sum;
sum = atomic_exchange_and_add(&mp_.mmapped_mem, size) + size;
atomic_max(&mp_.max_mmapped_mem, sum);
check_chunk(av, p);
return chunk2mem(p);
}
}
}
/* 如果没有可用的arena,并且mmap也失败了。 */
if (av == NULL)
return NULL;
/* 记录进入时top的配置 */
old_top = av->top;
old_size = chunksize(old_top);
old_end = (char *)(chunk_at_offset(old_top, old_size));
brk = snd_brk = (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE);
/*
如果不是第一次通过,我们需要old_size至少是MINSIZE,并且设置了prev_inuse位。
*/
assert((old_top == initial_top(av) && old_size == 0) ||
((unsigned long)(old_size) >= MINSIZE &&
prev_inuse(old_top) &&
((unsigned long)old_end & (pagesize - 1)) == 0));
/* 前提条件: 当前空间不足以满足nb请求 */
assert((unsigned long)(old_size) < (unsigned long)(nb + MINSIZE));
// 如果av不是主arena,则尝试扩展当前堆或创建新堆。
if (av != &main_arena)
{
heap_info *old_heap, *heap;
size_t old_heap_size;
/* 首先尝试扩展当前堆。 */
old_heap = heap_for_ptr(old_top);
old_heap_size = old_heap->size;
if ((long)(MINSIZE + nb - old_size) > 0
&& grow_heap(old_heap, MINSIZE + nb - old_size) == 0)
{
av->system_mem += old_heap->size - old_heap_size;
arena_mem += old_heap->size - old_heap_size;
set_head(old_top, (((char *)old_heap + old_heap->size) - (char *)old_top)
| PREV_INUSE);
}
else if ((heap = new_heap(nb + (MINSIZE + sizeof(*heap)), mp_.top_pad)))
{
/* 使用新分配的堆。 */
heap->ar_ptr = av;
heap->prev = old_heap;
av->system_mem += heap->size;
arena_mem += heap->size;
/* 设置新的 top chunk 。 */
top(av) = chunk_at_offset(heap, sizeof(*heap));
set_head(top(av), (heap->size - sizeof(*heap)) | PREV_INUSE);
/* 释放旧的 top chunk 。 */
old_size = (old_size - MINSIZE) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK;
set_head(chunk_at_offset(old_top, old_size + 2 * SIZE_SZ), 0 | PREV_INUSE);
if (old_size >= MINSIZE)
{
set_head(chunk_at_offset(old_top, old_size), (2 * SIZE_SZ) | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot(chunk_at_offset(old_top, old_size), (2 * SIZE_SZ));
set_head(old_top, old_size | PREV_INUSE | NON_MAIN_ARENA);
_int_free(av, old_top, 1);
}
else
{
set_head(old_top, (old_size + 2 * SIZE_SZ) | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot(old_top, (old_size + 2 * SIZE_SZ));
}
}
else if (!tried_mmap)
/* 至少可以尝试使用mmap内存。 */
goto try_mmap;
}
else /* av == main_arena */
{
/* 请求足够的空间来满足nb + pad + 开销 */
size = nb + mp_.top_pad + MINSIZE;
/*
如果是连续的,我们可以减去希望与新空间合并的现有空间。
我们稍后只在我们实际没有获得连续空间时再加回来。
*/
if (contiguous(av))
size -= old_size;
/*
将大小调整为页的倍数。
如果MORECORE不是连续的,这确保我们只用整页参数调用它。
并且如果MORECORE是连续的,并且这不是第一次通过,
这会保持先前调用的页对齐。
*/
size = ALIGN_UP(size, pagesize);
/*
如果参数太大,看起来是负的,不尝试调用MORECORE。
注意,由于mmap接受size_t参数,即使我们无法调用MORECORE,
下面如果使用mmap,也可能成功。
*/
if (size > 0)
{
brk = (char *)(MORECORE(size));
LIBC_PROBE(memory_sbrk_more, 2, brk, size);
}
if (brk != (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE))
{
/* 必要时调用 morecore hook 。 */
void (*hook)(void) = atomic_forced_read(__after_morecore_hook);
if (__builtin_expect(hook != NULL, 0))
(*hook)();
}
else
{
/*
如果有mmap,尝试使用它作为MORECORE失败或不能使用时的后备。
在地址空间有“洞”的系统上,这是值得做的,
所以sbrk不能扩展以提供连续的空间,但空间在其他地方是可用的。
注意我们忽略了mmap最大计数和阈值限制,
因为空间将不会被用作分离的mmap区域。
*/
/* 不能与旧的top合并,所以加回它的大小 */
if (contiguous(av))
size = ALIGN_UP(size + old_size, pagesize);
/* 如果我们依赖mmap作为后备,那么使用更大的单位 */
if ((unsigned long)(size) < (unsigned long)(MMAP_AS_MORECORE_SIZE))
size = MMAP_AS_MORECORE_SIZE;
if ((unsigned long)(size) > (unsigned long)(nb))
{
char *mbrk = (char *)(MMAP(0, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, 0));
if (mbrk != MAP_FAILED)
{
/* 我们不需要也不能使用另一个sbrk调用来找到结束 */
brk = mbrk;
snd_brk = brk + size;
/*
记录我们不再有一个连续的sbrk区域。
第一次使用mmap作为后备后,我们不再依赖连续的空间,
因为这可能会错误地连接区域。
*/
set_noncontiguous(av);
}
}
}
if (brk != (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE))
{
if (mp_.sbrk_base == 0)
mp_.sbrk_base = brk;
av->system_mem += size;
/*
如果MORECORE扩展了前一个空间,我们可以同样扩展top大小。
*/
if (brk == old_end && snd_brk == (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE))
set_head(old_top, (size + old_size) | PREV_INUSE);
else if (contiguous(av) && old_size && brk < old_end)
{
malloc_printerr(3, "break adjusted to free malloc space", brk, av);
}
/*
否则,做出调整:
* 如果是第一次通过或不连续,我们需要调用sbrk
只是为了找出内存的结束在哪里。
* 我们需要确保所有从malloc返回的内存块都满足
MALLOC_ALIGNMENT
* 如果有一个干预的外部sbrk,我们需要调整sbrk
请求大小以考虑到我们将无法与old_top中的现有空间合并。
* 几乎所有系统在内部都以整页为单位分配,
在这种情况下,我们最好使用请求的最后一页。
所以我们现在分配足够多的内存来达到页面边界,
这反过来会导致未来连续的调用进行页面对齐。
*/
else
{
front_misalign = 0;
end_misalign = 0;
correction = 0;
aligned_brk = brk;
/* 处理连续情况 */
if (contiguous(av))
{
/* 计算外部sbrk作为system_mem。 */
if (old_size)
av->system_mem += brk - old_end;
/* 确保第一个新区块符合对齐要求 */
front_misalign = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T)chunk2mem(brk) & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK;
if (front_misalign > 0)
{
/*
跳过一些字节以达到一个对齐的位置。
我们不需要特别标记这些浪费的前端字节。
它们永远不会被访问到,因为
av->top的prev_inuse(以及任何从它的开始创建的区块)
在初始化后总是为真。
*/
correction = MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - front_misalign;
aligned_brk += correction;
}
/*
如果这不是与现有空间相邻的,那么我们将无法
与old_top空间合并,所以必须在第二个请求中加上这部分。
*/
correction += old_size;
/* 扩展结束地址以达到页面边界 */
end_misalign = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T)(brk + size + correction);
correction += (ALIGN_UP(end_misalign, pagesize)) - end_misalign;
assert(correction >= 0);
snd_brk = (char *)(MORECORE(correction));
/*
如果不能分配修正空间,尝试至少找出当前的brk。
它可能足以继续进行而不会失败。
注意如果第二个sbrk没有失败,我们假设空间与第一个sbrk连续。
这是一个安全的假设,除非程序是多线程的但不使用锁,
并且在我们的第一个和第二个调用之间发生了一个外部的sbrk。
*/
if (snd_brk == (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE))
{
correction = 0;
snd_brk = (char *)(MORECORE(0));
}
else
{
/* 必要时调用 morecore hook 。 */
void (*hook)(void) = atomic_forced_read(__after_morecore_hook);
if (__builtin_expect(hook != NULL, 0))
(*hook)();
}
}
/* 处理非连续情况 */
else
{
if (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT == 2 * SIZE_SZ)
/* MORECORE/mmap必须正确对齐 */
assert(((unsigned long)chunk2mem(brk) & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) == 0);
else
{
front_misalign = (INTERNAL_SIZE_T)chunk2mem(brk) & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK;
if (front_misalign > 0)
{
/*
跳过一些字节以达到一个对齐的位置。
我们不需要特别标记这些浪费的前端字节。
它们永远不会被访问到,因为
av->top的prev_inuse(以及任何从它的开始创建的区块)
在初始化后总是为真。
*/
aligned_brk += MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - front_misalign;
}
}
/* 找出当前的内存结束位置 */
if (snd_brk == (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE))
{
snd_brk = (char *)(MORECORE(0));
}
}
/* 根据第二个sbrk的结果调整top */
if (snd_brk != (char *)(MORECORE_FAILURE))
{
av->top = (mchunkptr)aligned_brk;
set_head(av->top, (snd_brk - aligned_brk + correction) | PREV_INUSE);
av->system_mem += correction;
/*
如果不是第一次通过,我们要么有一个由于外部sbrk造成的间隙,
要么是一个非连续的区域。在old_top处插入一个双重栅栏防止合并
我们不拥有的空间。这些栅栏是标记为使用中的人工区块,
无论如何都太小而不能使用。我们需要两个栅栏以使大小和对齐工作。
*/
if (old_size != 0)
{
/*
缩小old_top以插入栅栏,保持大小为MALLOC_ALIGNMENT的倍数。
我们知道old_top中至少有足够的空间来做到这一点。
*/
old_size = (old_size - 4 * SIZE_SZ) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK;
set_head(old_top, old_size | PREV_INUSE);
/*
注意以下分配会完全覆盖old_top,
当old_size之前是MINSIZE时。这是故意的。
我们需要栅栏,即使old_top可能会因此丢失。
*/
chunk_at_offset(old_top, old_size)->size =
(2 * SIZE_SZ) | PREV_INUSE;
chunk_at_offset(old_top, old_size + 2 * SIZE_SZ)->size =
(2 * SIZE_SZ) | PREV_INUSE;
/* 如果可能,释放其余的部分。 */
if (old_size >= MINSIZE)
{
_int_free(av, old_top, 1);
}
}
}
}
}
} /* if (av != &main_arena) */
// 更新最大系统内存使用量。
if ((unsigned long)av->system_mem > (unsigned long)(av->max_system_mem))
av->max_system_mem = av->system_mem;
// 检查内存状态。
check_malloc_state(av);
/* 最后,执行分配 */
p = av->top;
size = chunksize(p);
/* 检查上述分配路径之一是否成功 */
if ((unsigned long)(size) >= (unsigned long)(nb + MINSIZE))
{
remainder_size = size - nb;
remainder = chunk_at_offset(p, nb);
av->top = remainder;
set_head(p, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head(remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
check_malloced_chunk(av, p, nb);
return chunk2mem(p);
}
/* 捕获所有失败的路径 */
__set_errno(ENOMEM);
return NULL;
}
systrim
static int systrim (size_t pad, mstate av) {
long top_size;
long extra;
long released;
char *current_brk;
char *new_brk;
size_t pagesize;
long top_area;
pagesize = GLRO (dl_pagesize);
top_size = chunksize (av->top);
top_area = top_size - MINSIZE - 1;
if (top_area <= pad)
return 0;
extra = ALIGN_DOWN(top_area - pad, pagesize);
//计算top chunk中最大可释放的整数页大小,top chunk中至少需要MINSIZE的内存保存fencepost
if (extra == 0)
return 0;
current_brk = (char *) (MORECORE (0));
if (current_brk == (char *) (av->top) + top_size) {
//如果当前top chunk的结束地址与当前的brk值相等,执行heap收缩
MORECORE (-extra);
//调用sbrk释放指定大小的内存
void (*hook) (void) = atomic_forced_read (__after_morecore_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
(*hook)();
new_brk = (char *) (MORECORE (0));
LIBC_PROBE (memory_sbrk_less, 2, new_brk, extra);
if (new_brk != (char *) MORECORE_FAILURE) {
//计算释放的内存大小,更新当前分配区所分配的内存总量,更新top chunk的大小
released = (long) (current_brk - new_brk);
if (released != 0) {
av->system_mem -= released;
set_head (av->top, (top_size - released) | PREV_INUSE);
check_malloc_state (av);
return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
版本变化
2.24
2.25
2.27
2.28
2.29
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)