基于 k8s和docker 构建一个高可用的 web 集群
100%[===================================================================================================================>] 7,621--.-K/s 用时 0s。#/dev/mapper/centos-swap swapswapdefaults0 0------->这行加注释。
目录
1.6.安装docker服务(这一步也可以放在最前面,先安装好docker,再做其他的操作)
1.7.安装kubeadm,kubelet和kubectl(初始化k8s需要的软件包)
1.10.实现master上的pod和node节点上的pod之间通信
6.1.打包使用python+flask完成的简单项目,制作成镜像
6.3.在k8s集群上安装ingress-nginx来暴露应用
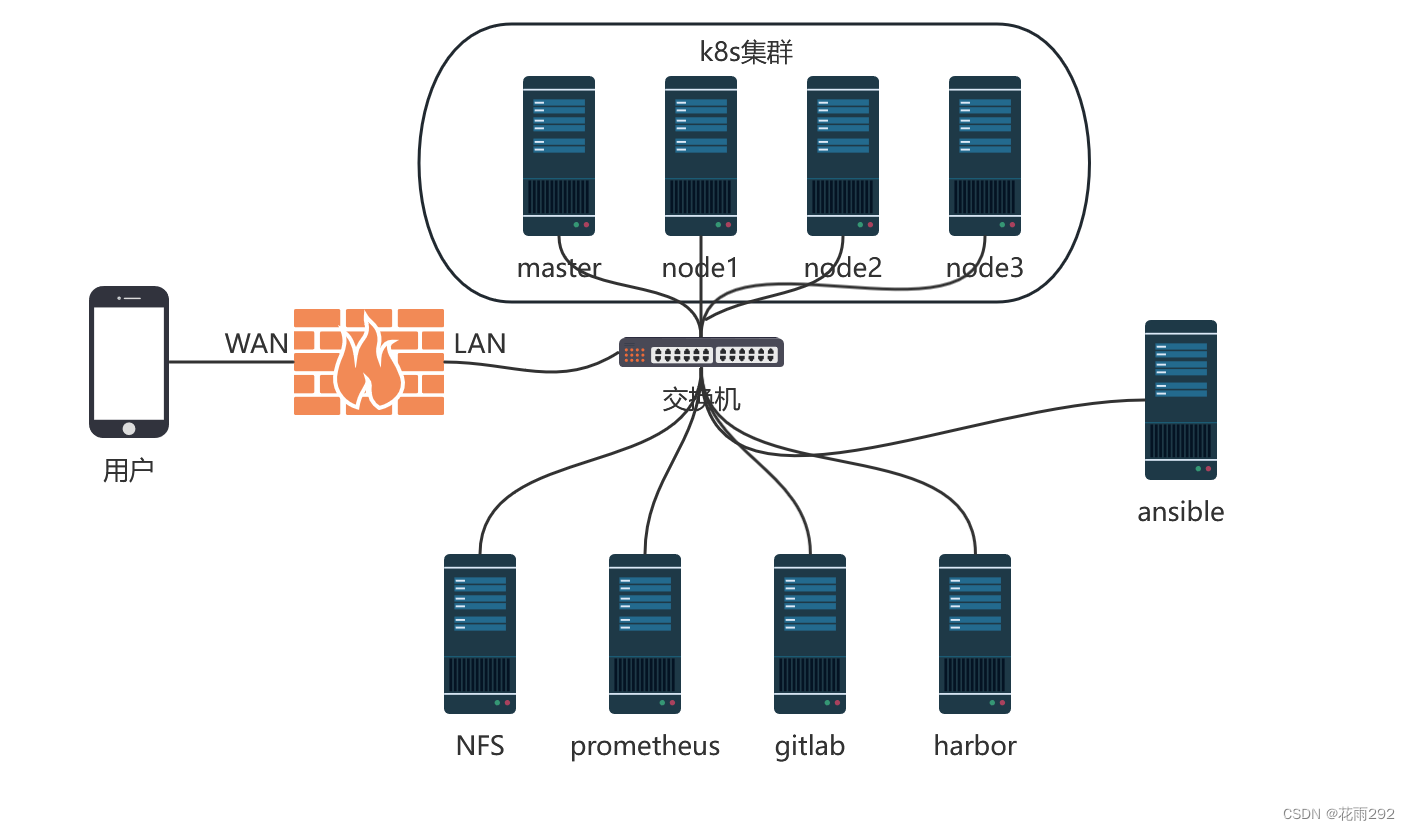
一、项目整体架构图

二、项目描述
三、项目准备
1.修改主机名
hostnamcectl set-hostname k8s-master
hostnamcectl set-hostname k8s-node1
- hostnamcectl set-hostname k8s-node2
- hostnamcectl set-hostname k8s-node3
2.规划项目集群机器的IP地址
| server | ip |
| k8s-master | 192.168.205.143 |
| k8s-node1 | 192.168.205.144 |
| k8s-node2 | 192.168.205.145 |
| k8s-node3 | 192.168.205.146 |
| ansible | 192.168.205.138 |
| nfs | 192.168.205.136 |
| harbor | 192.168.205.135 |
| prometheus | 192.168.205.134 |
| gitlab | 192.168.205.190 |
[root@k8s-master network-scripts]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@k8s-master network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens33[root@k8s-master network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-ens33
BOOTPROTO=none
NAME="ens33"
DEVICE="ens33"
ONBOOT="yes"
IPADDR=192.168.205.143
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
DNS1=114.114.114.114
3.关闭selinux和firewall
# 防火墙并且设置防火墙开启不启动
service firewalld stop && systemctl disable firewalld
# 临时关闭seLinux
setenforce 0
# 永久关闭seLinux
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@k8s-master network-scripts]# getenforce
Disabled
4.升级系统(也可以不升级)
yum update -y
5.添加域名解析
[root@k8s-master network-scripts]# vim /etc/hosts
[root@k8s-master network-scripts]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.205.143 k8s-master
192.168.205.144 k8s-node1
192.168.205.145 k8s-node2
192.168.205.146 k8s-node3
四、项目步骤
1.kubeadm安装k8s单master的集群环境
1.1.配置主机之间无密码登录
master节点:
[root@k8s-master ~]# ssh-keygen #一路回车,不输入密码
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:H5E2l2k7iN/XajAlHJjLCcQYUjfdlofaZSNCKH6NPl0 root@k8s-master
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| ..o=++.+ o |
| .o.+.=.Bo= |
| . . ==O=* . |
| . oo**E.. |
| oS.o.oo |
| oo.oo. . |
| .o .o. .|
| ... |
| .. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@k8s-master ~]#ssh-copy-id k8s-master
[root@k8s-master ~]#ssh-copy-id k8s-node1
[root@k8s-master ~]#ssh-copy-id k8s-node2
[root@k8s-master ~]#ssh-copy-id k8s-node3
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host 'k8s-node3 (192.168.205.13)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:lSTuuChFfqoAbSkAzqiWh3mx36qL9vU+640WXMtb70o.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:15:9a:e7:5d:39:01:85:d7:ce:26:0f:43:84:9f:ac:1d.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes ----这里填yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@k8s-node3's password: ----这里输入对应远程主机密码Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'k8s-node3'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
1.2.关闭交换分区
原因:Swap是交换分区,如果机器内存不够,会使用swap分区,但是swap分区的性能较低,k8s设计的时候为了能提升性能,默认是不允许使用交换分区的。Kubeadm初始化的时候会检测swap是否关闭,如果没关闭,那就初始化失败。如果不想要关闭交换分区,安装k8s的时候可以指定 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap 来解决。
# 临时关闭
[root@k8s-master ~]# swapoff -a
[root@k8s-node1~]# swapoff -a
[root@k8s-node2 ~]# swapoff -a
[root@k8s-node3~]# swapoff -a
# 永久关闭:注释swap挂载,给swap这行开头加一下注释
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim /etc/fstab
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Wed Mar 22 00:23:15 2023
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=e61480a4-6186-435e-839c-9d8ed1c4f824 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
#/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0 ------->这行加注释
[root@k8s-master ~]#
1.3.修改机器内核参数
[root@k8s-master ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@k8s-master ~]# echo "modprobe br_netfilter" >> /etc/profile
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf <<EOF
> net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
> net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
> net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
> EOF
[root@k8s-master ~]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1同步到node1/node2/node3节点
问题1:sysctl是做什么的?
在运行时配置内核参数
-p 从指定的文件加载系统参数,如不指定即从/etc/sysctl.conf中加载
问题2:为什么要执行modprobe br_netfilter?
修改/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf文件,增加如下三行参数:
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf出现报错:
sysctl: cannot stat /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-ip6tables: No such file or directory
sysctl: cannot stat /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables: No such file or directory
解决方法:
modprobe br_netfilter
问题3:为什么开启net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables内核参数?
在centos下安装docker,执行docker info出现如下警告:
WARNING: bridge-nf-call-iptables is disabled
WARNING: bridge-nf-call-ip6tables is disabled
解决办法:
vim /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
问题4:为什么要开启net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1参数?
kubeadm初始化k8s如果报错:
就表示没有开启ip_forward,需要开启。
net.ipv4.ip_forward是数据包转发:
出于安全考虑,Linux系统默认是禁止数据包转发的。所谓转发即当主机拥有多于一块的网卡时,其中一块收到数据包,根据数据包的目的ip地址将数据包发往本机另一块网卡,该网卡根据路由表继续发送数据包。这通常是路由器所要实现的功能。
要让Linux系统具有路由转发功能,需要配置一个Linux的内核参数net.ipv4.ip_forward。这个参数指定了Linux系统当前对路由转发功能的支持情况;其值为0时表示禁止进行IP转发;如果是1,则说明IP转发功能已经打开。
1.4.配置阿里云的repo源
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# cat kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
1.5.配置时间同步
master节点:
#把时间同步做成计划任务
[root@k8s-master ~]# crontab -e
* */1 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org
#重启crond服务
[root@k8s-master ~]# service crond restart
node1/2/3节点:
#把时间同步做成计划任务
[root@k8s-node1 ~]#crontab -e
* */1 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org
#重启crond服务
[root@k8s-node1 ~]#service crond restart
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart crond.service
1.6.安装docker服务(这一步也可以放在最前面,先安装好docker,再做其他的操作)
master和node节点上都操作:
--> 安装yum相关的工具,下载docker-ce.repo文件
[root@k8s-master ~]# yum install -y yum-utils -y
[root@k8s-master ~]#yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
--> 下载docker-ce.repo文件存放在/etc/yum.repos.d
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# pwd
/etc/yum.repos.d
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo docker-ce.repo
CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo CentOS-x86_64-kernel.repo nginx.repo
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]#
# 安装docker-ce软件
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin -y# container engine 容器引擎
# docker是一个容器管理的软件
# docker-ce 是服务器端软件 server
# docker-ce-cli 是客户端软件 client
# docker-compose-plugin 是compose插件,用来批量启动很多容器,在单台机器上
# containerd.io 底层用来启动容器的--> 启动docker,设置开机自启
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl start docker && systemctl enable docker.service
--> 查看docker的版本
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# docker --version
Docker version 24.0.5, build ced0996
1.7.安装kubeadm,kubelet和kubectl(初始化k8s需要的软件包)
master上操作:
[root@k8s-master ~]# yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl -->不指定版本默认下最新版
-->最好指定版本,因为1.24的版本默认的容器运行时环境不是docker了
[root@k8s-master ~]# yum install -y kubelet-1.23.6 kubeadm-1.23.6 kubectl-1.23.6
-->设置开机自启,因为kubelet是k8s在node节点上的代理,必须开机要运行的
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet# kubeadm: kubeadm是一个工具,用来初始化k8s集群的
# kubelet: 安装在集群所有节点上,用于启动Pod的
# kubectl: 通过kubectl可以部署和管理应用,查看各种资源,创建、删除和更新各种组件
1.8.部署Kubernetes的Master节点
[root@k8s-master ~]# docker pull coredns/coredns:1.8.4
[root@k8s-master ~]# docker pull coredns/coredns[root@k8s-master ~]# docker tag coredns/coredns:1.8.4 registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:v1.8.4
#初始化操作在master服务器上执行
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm init \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.205.143 \
--image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
--service-cidr=10.1.0.0/16 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16# 192.168.205.10 是master的ip
--> 执行命令出现提示操作,按照提示进行操作
[root@k8s-master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
[root@k8s-master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
[root@k8s-master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
1.9.node节点服务器加入k8s集群
node1/2/3节点:
[root@k8s-node1 ~]# kubeadm join 192.168.205.143:6443 --token 2fiwt1.47ss9cjmyaztw58b --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash
[root@k8s-node2 ~]# kubeadm join 192.168.205.143:6443 --token 2fiwt1.47ss9cjmyaztw58b --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash
[root@k8s-node3 ~]# kubeadm join 192.168.205.143:6443 --token 2fiwt1.47ss9cjmyaztw58b --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash
--> 查看节点状态
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 31d v1.23.6
k8s-node1 Ready <none> 31d v1.23.6
k8s-node2 Ready <none> 31d v1.23.6
k8s-node3 Ready <none> 31d v1.23.6
1.10.实现master上的pod和node节点上的pod之间通信
# 安装网络插件flannel(在master节点执行):
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim kube-flannel.yml
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat kube-flannel.yml
---
kind: Namespace
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: kube-flannel
labels:
pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce: privileged
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: flannel
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/status
verbs:
- patch
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: flannel
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: flannel
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: flannel
namespace: kube-flannel
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: flannel
namespace: kube-flannel
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
namespace: kube-flannel
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
data:
cni-conf.json: |
{
"name": "cbr0",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "flannel",
"delegate": {
"hairpinMode": true,
"isDefaultGateway": true
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {
"portMappings": true
}
}
]
}
net-conf.json: |
{
"Network": "10.244.0.0/16",
"Backend": {
"Type": "vxlan"
}
}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds
namespace: kube-flannel
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
hostNetwork: true
priorityClassName: system-node-critical
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni-plugin
#image: flannelcni/flannel-cni-plugin:v1.1.0 for ppc64le and mips64le (dockerhub limitations may apply)
image: docker.io/rancher/mirrored-flannelcni-flannel-cni-plugin:v1.1.0
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /flannel
- /opt/cni/bin/flannel
volumeMounts:
- name: cni-plugin
mountPath: /opt/cni/bin
- name: install-cni
#image: flannelcni/flannel:v0.19.2 for ppc64le and mips64le (dockerhub limitations may apply)
image: docker.io/rancher/mirrored-flannelcni-flannel:v0.19.2
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
#image: flannelcni/flannel:v0.19.2 for ppc64le and mips64le (dockerhub limitations may apply)
image: docker.io/rancher/mirrored-flannelcni-flannel:v0.19.2
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN", "NET_RAW"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: EVENT_QUEUE_DEPTH
value: "5000"
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
- name: xtables-lock
mountPath: /run/xtables.lock
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni-plugin
hostPath:
path: /opt/cni/bin
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
- name: xtables-lock
hostPath:
path: /run/xtables.lock
type: FileOrCreate
[root@k8s-master ~]#
# 部署flannel
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml[root@k8s-master ~]# ps aux|grep flannel
root 3810 0.0 1.3 1335164 25748 ? Ssl 16:06 0:17 /opt/bin/flanneld --ip-masq --kube-subnet-mgr
root 94146 0.0 0.0 112828 980 pts/1 S+ 21:26 0:00 grep --color=auto flannel# 查看各个节点的详细信息
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes -n kube-system -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 31d v1.23.6 192.168.205.143 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.95.1.el7.x86_64 docker://24.0.5
k8s-node1 Ready <none> 31d v1.23.6 192.168.205.144 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.95.1.el7.x86_64 docker://24.0.5
k8s-node2 Ready <none> 31d v1.23.6 192.168.205.145 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.95.1.el7.x86_64 docker://24.0.5
k8s-node3 Ready <none> 31d v1.23.6 192.168.205.146 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.95.1.el7.x86_64 docker://24.0.5
[root@k8s-master ~]#
2.部署ansible完成相关软件的自动化运维工作
2.1.建立免密通道 在ansible主机上生成密钥对
# 一路回车,不输入密码
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen -t ecdsa
Generating public/private ecdsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_ecdsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_ecdsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_ecdsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:d1s0FfCXztHrv/NmWouZqJv4s5ubvHeOdaDgiy+1a9k root@ansible
The key's randomart image is:
+---[ECDSA 256]---+
| ...o|
| ..o|
| o+o|
| .o.+|
| S.. ...+ |
| .o...oo |
| ..+... o.|
| .+==E+.=o=|
| o=^@oo=.**|
+----[SHA256]-----+[root@ansible ~]# cd /root/.ssh
[root@ansible .ssh]# ls
id_ecdsa id_ecdsa.pub
2.2.上传公钥到所有服务器的root用户家目录下
# 所有服务器上开启ssh服务 ,开放22号端口,允许root用户登录
--> k8s-master
[root@ansible .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_ecdsa.pub root@192.168.205.143
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "id_ecdsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.205.143 (192.168.205.143)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:lSTuuChFfqoAbSkAzqiWh3mx36qL9vU+640WXMtb70o.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:15:9a:e7:5d:39:01:85:d7:ce:26:0f:43:84:9f:ac:1d.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.205.143's password:Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.205.143'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.--> k8s-node1/node2/node3同样的方式(IP地址不同)
2.3.验证是否实现免密码密钥认证
[root@ansible .ssh]# ssh root@192.168.205.143
Last login: Wed Sep 13 20:40:08 2023 from 192.168.205.1
[root@k8s-master ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.205.143 closed.
[root@ansible .ssh]# ssh root@192.168.205.144
Last login: Wed Sep 13 19:07:12 2023 from 192.168.205.1
[root@k8s-node1 ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.205.144 closed.
[root@ansible .ssh]# ssh root@192.168.205.145
Last login: Wed Sep 13 19:07:02 2023 from 192.168.205.1
[root@k8s-node2 ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.205.145 closed.
[root@ansible .ssh]# ssh root@192.168.205.146
Last failed login: Wed Sep 13 22:55:00 CST 2023 from 192.168.205.138 on ssh:notty
There was 1 failed login attempt since the last successful login.
Last login: Wed Sep 13 19:09:31 2023 from 192.168.205.1
[root@k8s-node3 ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.205.146 closed.
2.4.在管理节点上安装ansible
[root@ansible .ssh]# yum install epel-release -y
[root@ansible .ssh]# yum install ansible -y
[root@ansible .ssh]# ansible --version
ansible 2.9.27
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u'/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Oct 14 2020, 14:45:30) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)]
2.5.编写主机配置
[root@ansible .ssh]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible ansible]# ls
ansible.cfg hosts roles
[root@ansible ansible]# vim hosts
[root@ansible ansible]# cat hosts
# This is the default ansible 'hosts' file.
#
# It should live in /etc/ansible/hosts
#
# - Comments begin with the '#' character
# - Blank lines are ignored
# - Groups of hosts are delimited by [header] elements
# - You can enter hostnames or ip addresses
# - A hostname/ip can be a member of multiple groups# Ex 1: Ungrouped hosts, specify before any group headers.
## green.example.com
## blue.example.com
## 192.168.100.1
## 192.168.100.10# Ex 2: A collection of hosts belonging to the 'webservers' group
## [webservers]
## alpha.example.org
## beta.example.org
## 192.168.1.100
## 192.168.1.110
[k8s-master]
192.168.205.143[k8s-node]
192.168.205.144
192.168.205.145
192.168.205.146[nfs]
192.168.205.136[prometheus]
192.168.205.134[harbor]
192.168.205.135[gitlab]
192.168.205.198# If you have multiple hosts following a pattern you can specify
# them like this:## www[001:006].example.com
# Ex 3: A collection of database servers in the 'dbservers' group
## [dbservers]
##
## db01.intranet.mydomain.net
## db02.intranet.mydomain.net
## 10.25.1.56
## 10.25.1.57# Here's another example of host ranges, this time there are no
# leading 0s:## db-[99:101]-node.example.com
[root@ansible ansible]#
3.部署nfs服务器,为整个web集群提供数据
3.1.搭建好nfs服务器
nfs的搭建参考以下:
模拟企业业务构建基于nginx的高可用web集群_花雨292的博客-CSDN博客
所有的web业务pod通过pv、pvc和卷挂载实现。
k8s-master/node1/node2/node3:
[root@k8s-master ~]# yum install nfs-utils -y
[root@k8s-master ~]# service nfs start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start nfs.service
[root@k8s-master ~]# service nfs restart
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart nfs.service
[root@k8s-master ~]# ps aux|grep nfs
root 28363 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 23:18 0:00 [nfsd4_callbacks]
root 28369 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28370 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28371 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28372 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28373 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28374 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28375 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28376 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 23:18 0:00 [nfsd]
root 28530 0.0 0.0 112824 976 pts/1 S+ 23:18 0:00 grep --color=auto nfs
3.2.设置共享目录
[root@nfs ~]# vim /etc/exports
[root@nfs ~]# cat /etc/exports
/data 192.168.205.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,no_all_squash,sync)
[root@nfs ~]# exportfs -r # 输出所有共享目录
[root@nfs ~]# exportfs -v # 显示输出的共享目录
/data 192.168.205.0/24(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,rw,secure,no_root_squash,no_all_squash)
3.3.挂载共享目录
[root@k8s-master ~]# mkdir /nfs-pv
[root@k8s-master ~]# mount 192.168.205.136:/data /nfs-pv/
[root@k8s-master ~]# df -Th|grep nfs
192.168.205.136:/data nfs4 17G 1.6G 16G 9% /nfs-pv# ps:取消挂载:umount /nfs-pv
3.4.创建pv及pvc使用nfs服务器上的共享目录
k8s官方文档:持久卷 | Kubernetes
1.在master节点上创建pv(持久卷PersistentVolume)
[root@k8s-master pv]# vim nfs-pv.yaml
[root@k8s-master pv]# cat nfs-pv.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv-data
labels:
type: pv-data
spec:
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
storageClassName: nfs
nfs:
path: /data
server: 192.168.205.136
[root@k8s-master pv]# pwd
/root/pv
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pv.yaml
persistentvolume/pv-data created
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pv-data 10Gi RWX Recycle Available nfs 12s
[root@k8s-master pv]#
2.创建pvc(持久卷申领PersistentVolumeClaim)使用pv[root@k8s-master pv]# vim nfs-pvc.yaml
[root@k8s-master pv]# cat nfs-pvc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
volumeMode: Filesystem
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: nfs
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f nfs-pvc.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc-data created
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc-data Bound pv-data 10Gi RWX nfs 14s
[root@k8s-master pv]#
使用:创建pod使用pvc
4.部署镜像仓库harbor
4.1.前提
前提条件:安装好docker和docker compose
[root@harbor ~]# yum install -y yum-utils -y
[root@harbor ~]# yum-config-manager \
> --add-repo \
> https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
[root@harbor yum.repos.d]# pwd
/etc/yum.repos.d
[root@harbor yum.repos.d]# yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin -y
[root@harbor yum.repos.d]# docker --version
Docker version 24.0.6, build ed223bc
[root@harbor yum.repos.d]# systemctl start docker
[root@harbor yum.repos.d]# ps aux|grep docker
root 8069 2.6 2.6 968988 48508 ? Ssl 18:39 0:00 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
root 8197 0.0 0.0 112824 976 pts/0 S+ 18:39 0:00 grep --color=auto docker
[root@harbor yum.repos.d]# systemctl enable docker
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
[root@harbor ~]# DOCKER_CONFIG=${DOCKER_CONFIG:-$HOME/.docker}
[root@harbor ~]# echo $DOCKER_CONFIG
/root/.docker
[root@harbor ~]# mkdir -p $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins
[root@harbor ~]# mv docker-compose /root/.docker/cli-plugins/
[root@harbor ~]# cd /root/.docker/cli-plugins/
[root@harbor cli-plugins]# ls
docker-compose
[root@harbor cli-plugins]# chmod +x docker-compose
[root@harbor cli-plugins]# docker compose version
Docker Compose version v2.7.0
[root@harbor cli-plugins]#
4.2.搭建harbor
1.下载harbor源码包
Release v2.7.3 · goharbor/harbor · GitHub
2.进入源码包网址,最下面点击下载源码包即可
3.解压源码包,安装配置harbor仓库
[root@harbor ~]# mkdir harbor
[root@harbor ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg kube-flannel.yml pv
harbor onekey_install.sh
[root@harbor ~]# cd harbor
[root@harbor harbor]# ls
[root@harbor harbor]# ls
harbor-offline-installer-v2.7.3.tgz
[root@harbor harbor]# tar xf harbor-offline-installer-v2.7.3.tgz
[root@harbor harbor]# ls
harbor harbor-offline-installer-v2.7.3.tgz
[root@harbor harbor]# cd harbor
[root@harbor harbor]# ls
common.sh harbor.yml.tmpl LICENSE
harbor.v2.7.3.tar.gz install.sh prepare
[root@harbor harbor]# cp harbor.yml.tmpl harbor.yml
[root@harbor harbor]# vim harbor.yml
[root@harbor harbor]# ./install.sh
安装成功的样子
在windows机器上访问网站,去配置harbor
http://192.168.205.135:8089/默认的登录的用户名和密码
admin
Harbor12345
5.搭建gitlab
5.1.官方部署文档
5.2.安装和配置必须的依赖项
[root@gitlab ~]#sudo yum install -y curl policycoreutils-python openssh-server perl [root@gitlab ~]#sudo systemctl enable sshd
[root@gitlab ~]#sudo systemctl start sshd
[root@gitlab ~]#sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http [root@gitlab ~]#sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
[root@gitlab ~]#sudo systemctl reload firewalld
5.3.下载/安装极狐GitLab
[root@gitlab ~]# curl -fsSL https://packages.gitlab.cn/repository/raw/scripts/setup.sh | /bin/bash
[root@gitlab ~]# sudo EXTERNAL_URL="http://192.168.205.190" yum install -y gitlab-jh
5.4.查看密码
[root@gitlab ~]# cat /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password
# WARNING: This value is valid only in the following conditions
# 1. If provided manually (either via `GITLAB_ROOT_PASSWORD` environment variable or via `gitlab_rails['initial_root_password']` setting in `gitlab.rb`, it was provided before database was seeded for the first time (usually, the first reconfigure run).
# 2. Password hasn't been changed manually, either via UI or via command line.
#
# If the password shown here doesn't work, you must reset the admin password following https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/security/reset_user_password.html#reset-your-root-password.Password: lfIo17qJgCLdR6H0daLxZs6pRMTITCiSOFRvfaJx/QI=
# NOTE: This file will be automatically deleted in the first reconfigure run after 24 hours.
[root@gitlab ~]#
5.5.部署成功后使用
使用文档:创建项目 | 极狐GitLab


6.部署简单的nginx业务
6.1.打包使用python+flask完成的简单项目,制作成镜像
TIPS:代码应上传至gitlab再打镜像,由于gitlab访问速度太慢,本次直接在linux打镜像
上传代码到虚拟机
[root@harbor ~]# cd flask/
[root@harbor flask]# ls
app.py config data.sqlite Dockerfile models requirements.txt router server.py static templates[root@harbor flask]# docker build -t flask:v1 .
[root@harborflask]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
flask v1 23b6a850131c 31 seconds ago 1.07GB
6.2.镜像上传至本地harbor仓库
[root@harbor docker]# docker tag flask:v1 192.168.205.135:8090/harbor/flask/flask:v1
要设置私有仓库地址为http才可以上传,否则需要为harbor配置https证书
[root@harbor docker]# vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
[root@harbor harbor]# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"insecure-registries": ["192.168.205.135:8090"]
}
[root@harbordocker]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@harbor docker]# systemctl restart docker
[root@harbor ~]# docker login 192.168.205.135:8090
Username: admin
Password:
WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /root/.docker/config.json.
Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-storeLogin Succeeded
[root@harbor docker]# docker push 192.168.205.135:8090/harbor/flask/flask:v1
6.3.在k8s集群上安装ingress-nginx来暴露应用
1.部署ingress-nginx
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.7.0/deploy/static/provider/baremetal/deploy.yaml
2.部署完后查看[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod,svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ingress-nginx-admission-create-f69pd 0/1 ErrImagePull 0 51s
pod/ingress-nginx-admission-patch-npf9v 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 51s
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-7557ffd88d-w76tv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 51sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/ingress-nginx-controller NodePort 10.1.245.103 <none> 80:31774/TCP,443:32409/TCP 51s
service/ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.1.51.224 <none> 443/TCP 51s
[root@k8s-master ~]#
6.4.使用dashboard对整个集群资源进行掌控
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.5.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
--2023-09-20 14:47:53-- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.5.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
正在解析主机 raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)... 185.199.111.133, 185.199.110.133, 185.199.109.133, ...
正在连接 raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)|185.199.111.133|:443... 已连接。
已发出 HTTP 请求,正在等待回应... 200 OK
长度:7621 (7.4K) [text/plain]
正在保存至: “recommended.yaml”100%[===================================================================================================================>] 7,621 --.-K/s 用时 0s
2023-09-20 14:47:54 (19.8 MB/s) - 已保存 “recommended.yaml” [7621/7621])
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# ls
recommended.yaml
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl apply -f recommended.yaml
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 40d
ingress-nginx Active 36m
kube-flannel Active 40d
kube-node-lease Active 40d
kube-public Active 40d
kube-system Active 40d
kubernetes-dashboard Active 15s
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl get pod -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper-799d786dbf-mbmwx 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubernetes-dashboard-546cbc58cd-9j6q6 1/1 Running 0 53m#查看dashboard对应的服务,因为发布服务的类型是ClusterIP ,外面的机器不能访问,不便于我们通过浏览器访问,因此需要改成NodePort
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.1.182.10 <none> 8000/TCP 54m
kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.1.252.34 <none> 443/TCP 54m
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl delete svc kubernetes-dashboard -n kubernetes-dashboard
service "kubernetes-dashboard" deleted
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# vim dashboard-svc.yml
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# cat dashboard-svc.yml
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 443
targetPort: 8443
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl apply -f dashboard-svc.yml
service/kubernetes-dashboard created
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.1.182.10 <none> 8000/TCP 57m
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.1.250.147 <none> 443:31312/TCP 17s
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# vim dashboard-svc-account.yaml
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# cat dashboard-svc-account.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: dashboard-admin
namespace: kube-system
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: dashboard-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: dashboard-admin
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
[root@k8s-master dashboard]#[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl apply -f dashboard-svc-account.yaml
serviceaccount/dashboard-admin created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/dashboard-admin created
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl get secret -n kube-system|grep admin|awk '{print $1}'
dashboard-admin-token-m58pp
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl describe secret dashboard-admin-token-m58pp -n kube-system
Name: dashboard-admin-token-m58pp
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: dashboard-admin
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: a35b61d0-3642-4664-a5cf-7509a8a029ccType: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1099 bytes
namespace: 11 bytes
token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Il83MjJseTFSM3pHMXZMZUpYbFdJbl9DbTNxWXZHVC1rQnlmMHZkNnExSGMifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlLXN5c3RlbSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUiOiJkYXNoYm9hcmQtYWRtaW4tdG9rZW4tbTU4cHAiLCJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLmlvL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50L3NlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudC5uYW1lIjoiZGFzaGJvYXJkLWFkbWluIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQudWlkIjoiYTM1YjYxZDAtMzY0Mi00NjY0LWE1Y2YtNzUwOWE4YTAyOWNjIiwic3ViIjoic3lzdGVtOnNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Omt1YmUtc3lzdGVtOmRhc2hib2FyZC1hZG1pbiJ9.TyoBrihRQEeVnjEgur5MM3sv5se5VpvB_F2OtiEIYLmjTJLi2YI1Pul13JcqgdXvD1Vud7j7cywJvU9B0A54p3KV0E7S16F0pZ-WNnJklBEmO4S7ZUooN7K0mbP-WrPnvCMh5mn8Aw5gsH9IfLSPTqNpXnPjtzww8DIcU3nzCLDTV19R4nPe0JfkXX6ulsV0vQwkxchC1yFcZJDVMZ6nBfkj0ci71J6ygxFerEF_HhJ7b6LMp-SdC1iwiLOlSxf5FzACV_oxs5QIcjdjWRcghhny10gbmDQMD1gRanAaw69HJTtgZkmim1jIqq-zld6AU7FCbxfMPJHPbcs184STJg
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl describe secret dashboard-admin-token-m58pp -n kube-system|awk '/^token/ {print $2}'
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Il83MjJseTFSM3pHMXZMZUpYbFdJbl9DbTNxWXZHVC1rQnlmMHZkNnExSGMifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlLXN5c3RlbSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUiOiJkYXNoYm9hcmQtYWRtaW4tdG9rZW4tbTU4cHAiLCJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLmlvL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50L3NlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudC5uYW1lIjoiZGFzaGJvYXJkLWFkbWluIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQudWlkIjoiYTM1YjYxZDAtMzY0Mi00NjY0LWE1Y2YtNzUwOWE4YTAyOWNjIiwic3ViIjoic3lzdGVtOnNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Omt1YmUtc3lzdGVtOmRhc2hib2FyZC1hZG1pbiJ9.TyoBrihRQEeVnjEgur5MM3sv5se5VpvB_F2OtiEIYLmjTJLi2YI1Pul13JcqgdXvD1Vud7j7cywJvU9B0A54p3KV0E7S16F0pZ-WNnJklBEmO4S7ZUooN7K0mbP-WrPnvCMh5mn8Aw5gsH9IfLSPTqNpXnPjtzww8DIcU3nzCLDTV19R4nPe0JfkXX6ulsV0vQwkxchC1yFcZJDVMZ6nBfkj0ci71J6ygxFerEF_HhJ7b6LMp-SdC1iwiLOlSxf5FzACV_oxs5QIcjdjWRcghhny10gbmDQMD1gRanAaw69HJTtgZkmim1jIqq-zld6AU7FCbxfMPJHPbcs184STJg
[root@k8s-master dashboard]# kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.1.182.10 <none> 8000/TCP 60m
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.1.250.147 <none> 443:31312/TCP 3m17s
浏览器访问:https://192.168.205.143:31312/#/login必须要加https前缀,选择无视风险继续访问即可,输入token
6.5.手工部署应用镜像到k8s使用
yaml文件内容如下:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: flask
name: falsk
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flask
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: flask
spec:
containers:
- image: 192.168.205.135:8090/harbor/flask/flask:v1
name: flask
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: flask
name: flask
spec:
ports:
- name: http-port
port: 5678
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: flask
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: flask
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: "test.flask.com"
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: flask
port:
number: 5678
6.6.部署过程有报错,报错及解决
#报错信息
[root@k8s-master flask]# kubectl apply -f flask.yml
deployment.apps/falsk unchanged
service/flask unchanged
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "flask.yml": Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io": failed to call webhook: Post "https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/networking/v1/ingresses?timeout=10s": dial tcp 10.1.51.224:443: connect: connection refused#解决方案
[root@k8s-master flask]# kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations
NAME WEBHOOKS AGE
ingress-nginx-admission 1 105m
[root@k8s-master flask]# kubectl delete -A ValidatingWebhookConfiguration ingress-nginx-admission
validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io "ingress-nginx-admission" deleted#重新部署
[root@k8s-master flask]# kubectl apply -f flask.yml
deployment.apps/falsk unchanged
service/flask unchanged
ingress.networking.k8s.io/flask created
PS:拓展
构建双master集群:通过keepalive+nginx实现k8s apiserver节点高可用
nginx:脚本安装:模拟企业业务构建基于nginx的高可用web集群_花雨292的博客-CSDN博客
keepalive:yum install keepalived -y
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容














所有评论(0)