高可用数据迁移架构设计:从零停机到生产级实践的完整解决方案
在互联网技术面试中,"能否详细描述一下你们系统数据迁移的完整技术方案?“这个问题堪称技术深度的试金石。许多工程师简历上都写着"主导系统重构”、"数据库升级改造"等项目经历,但真正能够系统性地阐述零停机数据迁移方案的候选人却寥寥无几。作为一名在大型互联网公司深耕多年的系统架构师,我深知现代业务对服务可用性的极致要求。传统的"停机维护"方案在7×24小时不间断服务的时代已经完全不可接受。如何设计并实施
高可用数据迁移架构设计:从零停机到生产级实践的完整解决方案
作者:默语佬
专栏:分布式系统架构设计
标签:数据迁移、零停机、双写机制、数据一致性、架构设计
🚀 引言
在互联网技术面试中,"能否详细描述一下你们系统数据迁移的完整技术方案?“这个问题堪称技术深度的试金石。许多工程师简历上都写着"主导系统重构”、"数据库升级改造"等项目经历,但真正能够系统性地阐述零停机数据迁移方案的候选人却寥寥无几。
作为一名在大型互联网公司深耕多年的系统架构师,我深知现代业务对服务可用性的极致要求。传统的"停机维护"方案在7×24小时不间断服务的时代已经完全不可接受。如何设计并实施一套高可用、零丢失、最终一致的数据迁移架构,已成为每个架构师必须掌握的核心技能。
今天,我将从架构师的视角,为你深度剖析生产级数据迁移的完整解决方案。
📋 目录
🎯 技术选型与架构决策
迁移工具技术评估
在数据迁移项目的起始阶段,工具选型直接决定了整个方案的可行性和复杂度。针对MySQL生态,主要有两类迁移工具可供选择:
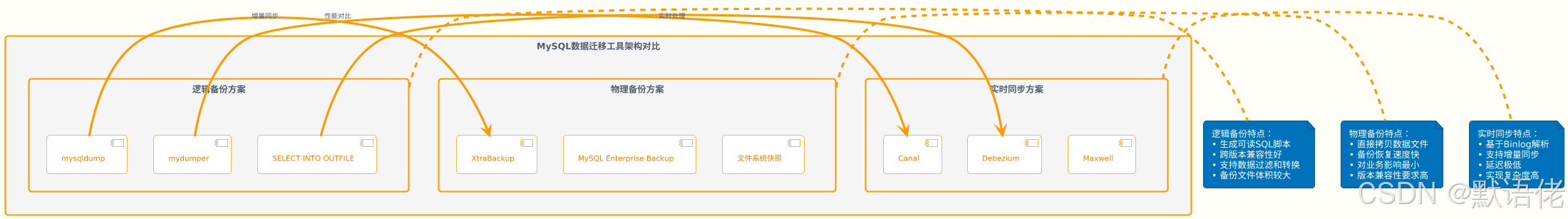
工具选型决策矩阵
| 评估维度 | mysqldump | XtraBackup | Canal/Maxwell |
|---|---|---|---|
| 性能表现 | 中等 | 优秀 | 优秀 |
| 业务影响 | 较大 | 最小 | 最小 |
| 实现复杂度 | 简单 | 中等 | 复杂 |
| 数据一致性 | 强一致 | 强一致 | 最终一致 |
| 跨版本支持 | 优秀 | 一般 | 优秀 |
| 增量同步 | 不支持 | 支持 | 原生支持 |
架构师的选型策略
作为架构师,我的选型原则是:业务规模决定技术方案,风险控制决定实现路径。
/**
* 数据迁移工具选型策略
* 基于业务特征和技术约束的智能决策引擎
*
* @author 默语佬
*/
public class MigrationToolSelector {
/**
* 基于业务特征选择最优迁移工具
*
* @param businessContext 业务上下文
* @return 推荐的迁移工具组合
*/
public MigrationToolChain selectOptimalTools(BusinessContext businessContext) {
MigrationToolChain.Builder builder = MigrationToolChain.builder();
// 数据量级评估
if (businessContext.getDataSize() > DataSize.TB(10)) {
// 超大数据量:物理备份 + 增量同步
builder.bulkTool(MigrationTool.XTRABACKUP)
.incrementalTool(MigrationTool.CANAL)
.parallelism(8);
} else if (businessContext.getDataSize() > DataSize.GB(100)) {
// 大数据量:逻辑备份 + 性能优化
builder.bulkTool(MigrationTool.MYDUMPER)
.incrementalTool(MigrationTool.MAXWELL)
.parallelism(4);
} else {
// 中小数据量:简单可靠方案
builder.bulkTool(MigrationTool.MYSQLDUMP)
.incrementalTool(MigrationTool.BINLOG_SYNC)
.parallelism(2);
}
// 业务可用性要求评估
if (businessContext.getAvailabilityRequirement() == AvailabilityLevel.CRITICAL) {
// 核心业务:零停机方案
builder.enableDoubleWrite()
.enableRealTimeValidation()
.enableGrayScaleSwitch();
}
// 数据一致性要求评估
if (businessContext.getConsistencyRequirement() == ConsistencyLevel.STRONG) {
// 强一致性:增强校验机制
builder.enableContinuousValidation()
.enableDataComparison()
.enableAutomaticRepair();
}
return builder.build();
}
/**
* 业务上下文评估
*/
@Data
public static class BusinessContext {
private DataSize dataSize; // 数据量级
private AvailabilityLevel availabilityRequirement; // 可用性要求
private ConsistencyLevel consistencyRequirement; // 一致性要求
private Duration maintenanceWindow; // 维护窗口
private int concurrentUsers; // 并发用户数
private List<String> criticalTables; // 核心表列表
}
}
⚙️ 核心参数与环境评估
MySQL关键参数深度解析
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode:自增锁的奥秘
这个参数是数据迁移中的"隐形杀手",直接影响双写阶段的数据一致性。
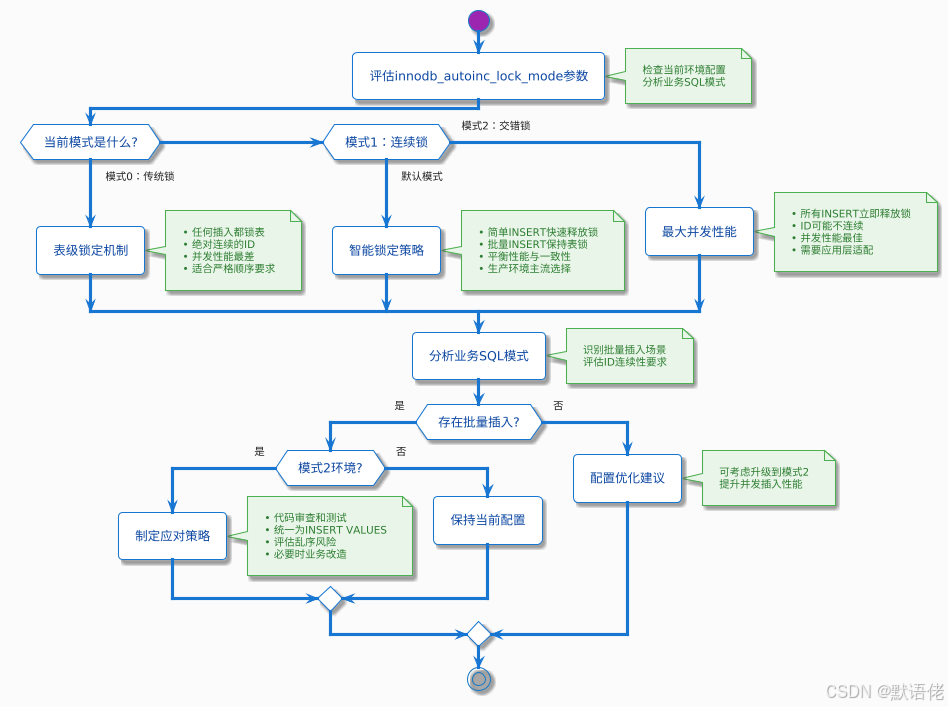
生产环境参数优化策略
-- 数据迁移专用的MySQL参数优化配置
-- 在迁移开始前应用,迁移完成后恢复
-- 1. 提升导入性能的核心参数
SET GLOBAL innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 2; -- 降低redo log刷盘频率
SET GLOBAL sync_binlog = 0; -- 暂时关闭binlog同步刷盘
SET GLOBAL innodb_buffer_pool_size = '70%'; -- 增大缓冲池,充分利用内存
-- 2. 批量操作优化参数
SET GLOBAL bulk_insert_buffer_size = 256 * 1024 * 1024; -- 256MB批量插入缓冲
SET GLOBAL innodb_autoinc_lock_mode = 1; -- 确保ID一致性
SET GLOBAL max_allowed_packet = 1024 * 1024 * 1024; -- 支持大数据包
-- 3. 并发控制参数
SET GLOBAL innodb_thread_concurrency = 0; -- 取消线程并发限制
SET GLOBAL innodb_write_io_threads = 8; -- 增加写IO线程
SET GLOBAL innodb_read_io_threads = 8; -- 增加读IO线程
-- 4. 临时关闭约束检查(仅在受控环境)
SET GLOBAL foreign_key_checks = 0; -- 暂时关闭外键检查
SET GLOBAL unique_checks = 0; -- 暂时关闭唯一性检查
-- 迁移完成后的恢复脚本
-- IMPORTANT: 必须在迁移完成后执行
SET GLOBAL innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 1;
SET GLOBAL sync_binlog = 1;
SET GLOBAL foreign_key_checks = 1;
SET GLOBAL unique_checks = 1;
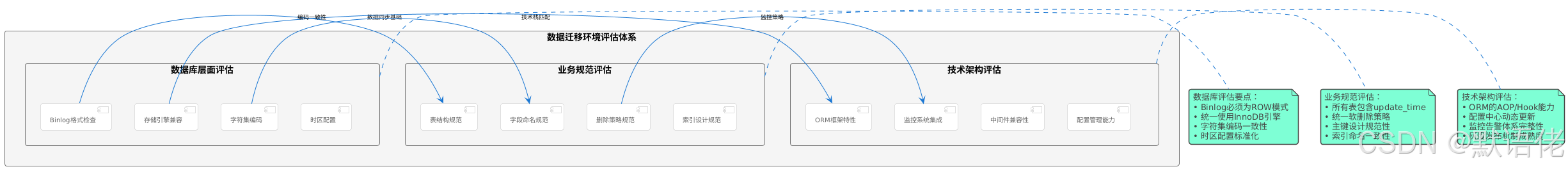
环境兼容性评估框架
🏗️ 三阶段迁移架构设计
整体架构蓝图
零停机数据迁移的核心理念是分阶段渐进式过渡,通过精心设计的三个阶段确保业务连续性和数据一致性。
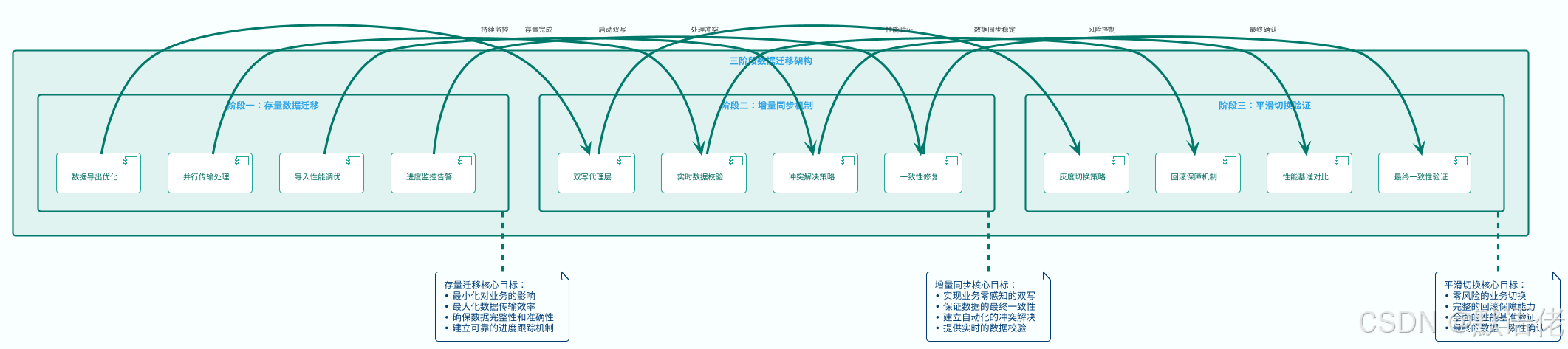
阶段一:智能化存量数据迁移
高性能导出策略
/**
* 高性能数据导出引擎
* 支持分片并行、断点续传、性能监控
*
* @author 默语佬
*/
@Service
public class HighPerformanceDataExporter {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HighPerformanceDataExporter.class);
@Autowired
private DataSourceManager dataSourceManager;
@Autowired
private PerformanceMonitor performanceMonitor;
/**
* 分片并行导出大表数据
*
* @param exportConfig 导出配置
* @return 导出结果
*/
public ExportResult exportLargeTable(ExportConfig exportConfig) {
String tableName = exportConfig.getTableName();
// 1. 分析表结构和数据分布
TableAnalysis analysis = analyzeTable(tableName);
// 2. 计算最优分片策略
List<ShardRange> shardRanges = calculateOptimalShards(analysis, exportConfig);
// 3. 并行执行分片导出
List<CompletableFuture<ShardExportResult>> futures = shardRanges.stream()
.map(range -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> exportShard(tableName, range)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 4. 等待所有分片完成并合并结果
ExportResult result = ExportResult.builder()
.tableName(tableName)
.startTime(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
try {
List<ShardExportResult> shardResults = futures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
result = mergeShardResults(result, shardResults);
logger.info("表 {} 导出完成,总计 {} 行,耗时 {} ms",
tableName, result.getTotalRows(), result.getDuration());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("表 {} 导出失败", tableName, e);
result.setSuccess(false);
result.setErrorMessage(e.getMessage());
}
return result;
}
/**
* 智能分片策略计算
*/
private List<ShardRange> calculateOptimalShards(TableAnalysis analysis, ExportConfig config) {
List<ShardRange> ranges = new ArrayList<>();
long totalRows = analysis.getTotalRows();
int optimalShardCount = calculateOptimalShardCount(totalRows, config.getMaxShardSize());
long rowsPerShard = totalRows / optimalShardCount;
// 基于主键范围进行分片
String primaryKey = analysis.getPrimaryKeyColumn();
Object minValue = analysis.getMinPrimaryKeyValue();
Object maxValue = analysis.getMaxPrimaryKeyValue();
if (isNumericPrimaryKey(primaryKey, analysis)) {
// 数值型主键:等值分片
long min = ((Number) minValue).longValue();
long max = ((Number) maxValue).longValue();
long rangeSize = (max - min) / optimalShardCount;
for (int i = 0; i < optimalShardCount; i++) {
long start = min + i * rangeSize;
long end = (i == optimalShardCount - 1) ? max : start + rangeSize - 1;
ranges.add(ShardRange.builder()
.shardIndex(i)
.startValue(start)
.endValue(end)
.estimatedRows(rowsPerShard)
.build());
}
} else {
// 非数值型主键:基于采样的分片
ranges = calculateSamplingBasedShards(analysis, optimalShardCount);
}
return ranges;
}
/**
* 执行单个分片的数据导出
*/
private ShardExportResult exportShard(String tableName, ShardRange range) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try (Connection connection = dataSourceManager.getConnection()) {
// 构建分片查询SQL
String sql = buildShardQuerySql(tableName, range);
// 执行导出,使用优化的参数
try (PreparedStatement stmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
stmt.setFetchSize(10000); // 优化内存使用
stmt.setQueryTimeout(3600); // 设置超时时间
try (ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
return processResultSet(rs, range, startTime);
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
logger.error("分片 {} 导出失败", range.getShardIndex(), e);
return ShardExportResult.failure(range, e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 构建分片查询SQL
*/
private String buildShardQuerySql(String tableName, ShardRange range) {
return String.format(
"SELECT * FROM %s WHERE id >= %s AND id <= %s ORDER BY id",
tableName, range.getStartValue(), range.getEndValue()
);
}
// 其他辅助方法...
}
导入性能优化策略
-- 高性能数据导入的SQL优化策略
-- 1. 批量插入优化
-- 使用 INSERT INTO ... VALUES 批量语法,每批1000-5000行
INSERT INTO target_table (col1, col2, col3) VALUES
(val1_1, val1_2, val1_3),
(val2_1, val2_2, val2_3),
-- ... 批量数据
(valN_1, valN_2, valN_3);
-- 2. 禁用自动提交,手动控制事务边界
SET autocommit = 0;
START TRANSACTION;
-- 批量插入操作
COMMIT;
-- 3. 临时调整目标表结构以提升导入性能
-- 备份原始索引定义
SELECT CONCAT('ALTER TABLE ', table_name, ' ADD ',
CASE WHEN NON_UNIQUE = 0 THEN 'UNIQUE ' ELSE '' END,
'INDEX ', index_name, ' (', GROUP_CONCAT(column_name ORDER BY seq_in_index), ');') as add_index_sql
FROM information_schema.statistics
WHERE table_schema = 'your_database' AND table_name = 'your_table'
GROUP BY table_name, index_name;
-- 删除非主键索引以加速导入
ALTER TABLE target_table DROP INDEX idx_name1;
ALTER TABLE target_table DROP INDEX idx_name2;
-- 导入完成后重新创建索引
ALTER TABLE target_table ADD INDEX idx_name1 (column1);
ALTER TABLE target_table ADD INDEX idx_name2 (column2, column3);
🔄 双写机制与一致性保障
非侵入式双写架构
双写机制是整个迁移方案的核心,需要在不影响业务代码的前提下,实现数据的同步写入。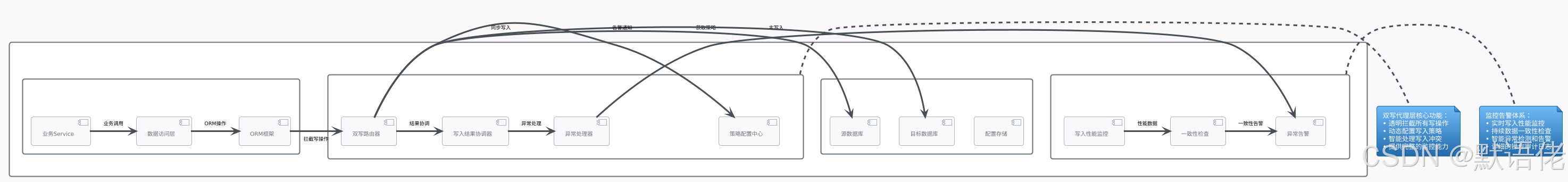
生产级双写代理实现
/**
* 生产级双写代理实现
* 基于动态代理和策略模式的非侵入式双写方案
*
* @author 默语佬
*/
@Component
public class ProductionDoubleWriteProxy implements DataSourceProxy {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProductionDoubleWriteProxy.class);
@Autowired
private DataSourceManager dataSourceManager;
@Autowired
private DoubleWriteConfigManager configManager;
@Autowired
private ConsistencyValidator consistencyValidator;
@Autowired
private MetricsCollector metricsCollector;
/**
* 拦截并处理所有写操作
*/
@Override
public int executeUpdate(String sql, Object[] parameters) throws SQLException {
// 1. 获取当前双写策略
DoubleWriteStrategy strategy = configManager.getCurrentStrategy();
if (!strategy.isEnabled()) {
// 双写未启用,直接操作源库
return executeOnSource(sql, parameters);
}
// 2. 解析SQL操作类型
SqlOperation operation = SqlParser.parse(sql);
// 3. 根据策略执行双写
return executeDoubleWrite(operation, sql, parameters, strategy);
}
/**
* 执行双写逻辑
*/
private int executeDoubleWrite(SqlOperation operation, String sql, Object[] parameters,
DoubleWriteStrategy strategy) throws SQLException {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DoubleWriteResult result = new DoubleWriteResult();
try {
switch (strategy.getMode()) {
case SOURCE_FIRST:
result = executeSourceFirst(sql, parameters, operation);
break;
case TARGET_FIRST:
result = executeTargetFirst(sql, parameters, operation);
break;
case PARALLEL:
result = executeParallel(sql, parameters, operation);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("未知的双写模式: " + strategy.getMode());
}
// 记录性能指标
long duration = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
metricsCollector.recordDoubleWrite(operation.getType(), duration, result.isSuccess());
return result.getAffectedRows();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("双写执行失败: SQL={}, 参数={}", sql, Arrays.toString(parameters), e);
// 根据策略决定是否降级
if (strategy.isFailoverEnabled()) {
logger.warn("双写失败,降级到单写模式");
return executeOnSource(sql, parameters);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
/**
* 源库优先的双写策略
*/
private DoubleWriteResult executeSourceFirst(String sql, Object[] parameters,
SqlOperation operation) throws SQLException {
DoubleWriteResult result = new DoubleWriteResult();
// 1. 先写源库
try {
int sourceRows = executeOnSource(sql, parameters);
result.setSourceResult(sourceRows, null);
// 2. 源库成功后,异步写目标库
if (operation.needsTargetWrite()) {
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
// 对于INSERT操作,需要获取生成的主键
if (operation.getType() == SqlOperationType.INSERT) {
sql = enhanceInsertWithGeneratedId(sql, parameters, sourceRows);
}
int targetRows = executeOnTarget(sql, parameters);
result.setTargetResult(targetRows, null);
// 异步验证数据一致性
scheduleConsistencyCheck(operation);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("目标库写入失败,将通过后台任务修复", e);
result.setTargetResult(0, e);
// 记录不一致数据,等待修复
recordInconsistentData(operation, e);
}
});
}
result.setAffectedRows(sourceRows);
result.setSuccess(true);
} catch (SQLException e) {
result.setSourceResult(0, e);
result.setSuccess(false);
throw e;
}
return result;
}
/**
* 目标库优先的双写策略(用于切换阶段)
*/
private DoubleWriteResult executeTargetFirst(String sql, Object[] parameters,
SqlOperation operation) throws SQLException {
DoubleWriteResult result = new DoubleWriteResult();
// 1. 先写目标库
try {
int targetRows = executeOnTarget(sql, parameters);
result.setTargetResult(targetRows, null);
// 2. 目标库成功后,同步写源库(保证回滚能力)
try {
int sourceRows = executeOnSource(sql, parameters);
result.setSourceResult(sourceRows, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("源库同步写入失败,但不影响主流程", e);
result.setSourceResult(0, e);
}
result.setAffectedRows(targetRows);
result.setSuccess(true);
} catch (SQLException e) {
result.setTargetResult(0, e);
result.setSuccess(false);
throw e;
}
return result;
}
/**
* 处理INSERT操作的自增主键问题
*/
private String enhanceInsertWithGeneratedId(String originalSql, Object[] parameters,
int affectedRows) throws SQLException {
if (affectedRows <= 0) {
return originalSql;
}
// 获取源库生成的自增ID
try (Connection sourceConn = dataSourceManager.getSourceConnection()) {
try (Statement stmt = sourceConn.createStatement()) {
try (ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()")) {
if (rs.next()) {
long generatedId = rs.getLong(1);
// 将原始的INSERT语句转换为带明确ID的INSERT语句
return SqlRewriter.addExplicitId(originalSql, generatedId);
}
}
}
}
return originalSql;
}
// 其他辅助方法...
}
数据一致性校验与修复
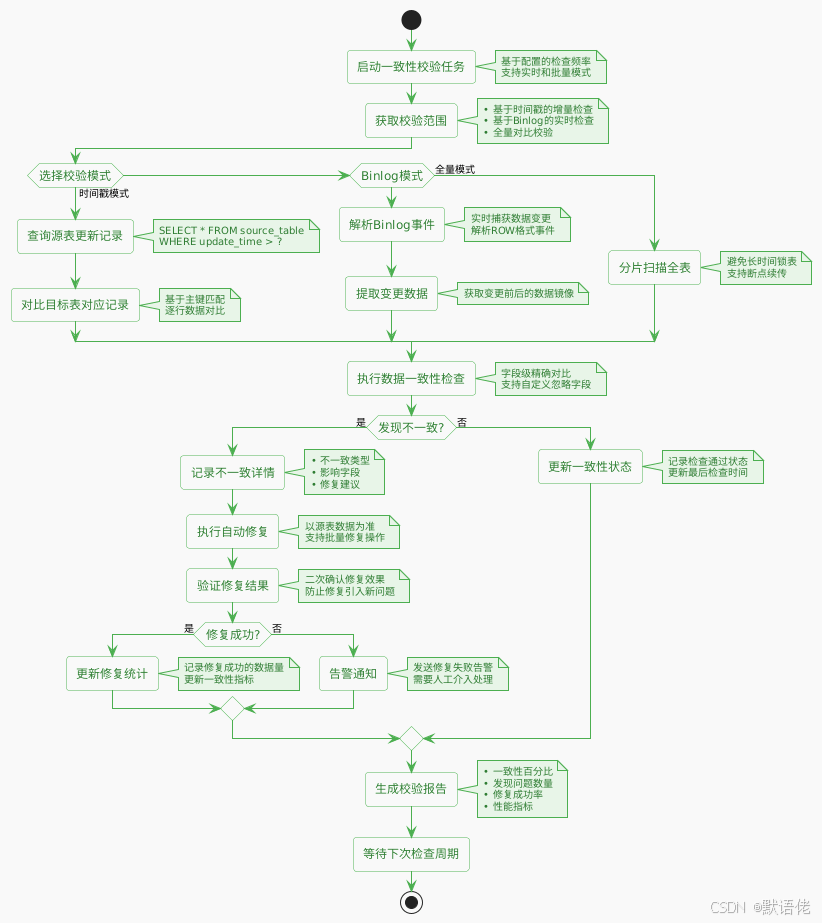
智能化数据修复引擎
/**
* 智能化数据一致性修复引擎
* 支持多种检测模式和自动修复策略
*
* @author 默语佬
*/
@Service
public class IntelligentDataRepairEngine {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IntelligentDataRepairEngine.class);
@Autowired
private BinlogEventListener binlogListener;
@Autowired
private DataComparator dataComparator;
@Autowired
private RepairStrategyFactory repairStrategyFactory;
/**
* 基于Binlog的实时一致性检查
*/
@EventListener
public void handleBinlogEvent(BinlogDataChangeEvent event) {
try {
// 1. 解析Binlog事件
DataChangeInfo changeInfo = parseBinlogEvent(event);
// 2. 从目标库查询对应数据
DataRecord targetRecord = queryTargetData(changeInfo);
// 3. 对比数据一致性
ComparisonResult comparison = dataComparator.compare(changeInfo.getAfterData(), targetRecord);
if (!comparison.isConsistent()) {
// 4. 发现不一致,执行修复
RepairResult repairResult = executeRepair(changeInfo, comparison);
logger.info("检测到数据不一致并已修复: 表={}, 主键={}, 修复结果={}",
changeInfo.getTableName(), changeInfo.getPrimaryKey(), repairResult.isSuccess());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("处理Binlog事件时发生异常", e);
}
}
/**
* 基于时间戳的批量一致性检查
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 300000) // 每5分钟执行一次
public void performBatchConsistencyCheck() {
try {
// 1. 获取上次检查的时间戳
Timestamp lastCheckTime = getLastCheckTimestamp();
// 2. 查询源表中的增量数据
List<DataRecord> incrementalData = queryIncrementalData(lastCheckTime);
if (incrementalData.isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("没有发现增量数据,跳过本次检查");
return;
}
// 3. 批量对比数据一致性
BatchComparisonResult batchResult = performBatchComparison(incrementalData);
// 4. 处理不一致的数据
if (batchResult.hasInconsistencies()) {
List<RepairResult> repairResults = batchRepair(batchResult.getInconsistentRecords());
// 5. 生成修复报告
generateRepairReport(batchResult, repairResults);
}
// 6. 更新检查时间戳
updateLastCheckTimestamp();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("批量一致性检查失败", e);
}
}
/**
* 执行数据修复
*/
private RepairResult executeRepair(DataChangeInfo changeInfo, ComparisonResult comparison) {
// 1. 选择合适的修复策略
RepairStrategy strategy = repairStrategyFactory.getStrategy(comparison.getInconsistencyType());
// 2. 执行修复操作
try {
// 为了确保数据准确性,从源库重新查询最新数据
DataRecord latestSourceData = queryLatestSourceData(changeInfo);
if (latestSourceData == null) {
// 源数据已被删除,需要删除目标数据
return strategy.deleteTargetRecord(changeInfo.getTableName(), changeInfo.getPrimaryKey());
} else {
// 用源数据覆盖目标数据
return strategy.updateTargetRecord(changeInfo.getTableName(), latestSourceData);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("数据修复失败: 表={}, 主键={}",
changeInfo.getTableName(), changeInfo.getPrimaryKey(), e);
return RepairResult.failure(e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 处理主从延迟问题的双重校验机制
*/
private DataRecord queryTargetDataWithDelayHandling(DataChangeInfo changeInfo) {
// 1. 首先从从库查询
DataRecord slaveData = queryFromSlave(changeInfo);
// 2. 如果从库查询结果与期望不符,再查询主库确认
DataRecord expectedData = changeInfo.getAfterData();
if (!dataComparator.compare(expectedData, slaveData).isConsistent()) {
logger.debug("从库数据可能存在延迟,查询主库确认: 表={}, 主键={}",
changeInfo.getTableName(), changeInfo.getPrimaryKey());
// 从主库查询最新数据
DataRecord masterData = queryFromMaster(changeInfo);
// 以主库数据为准
return masterData;
}
return slaveData;
}
/**
* 生成详细的修复报告
*/
private void generateRepairReport(BatchComparisonResult batchResult, List<RepairResult> repairResults) {
RepairReport report = RepairReport.builder()
.checkTime(new Date())
.totalCheckedRecords(batchResult.getTotalRecords())
.inconsistentRecords(batchResult.getInconsistentCount())
.successfulRepairs(repairResults.stream().mapToInt(r -> r.isSuccess() ? 1 : 0).sum())
.failedRepairs(repairResults.stream().mapToInt(r -> r.isSuccess() ? 0 : 1).sum())
.consistencyPercentage(calculateConsistencyPercentage(batchResult))
.build();
// 发送报告到监控系统
monitoringService.sendRepairReport(report);
// 如果一致性低于阈值,发送告警
if (report.getConsistencyPercentage() < 99.0) {
alertService.sendConsistencyAlert(report);
}
logger.info("数据一致性修复报告: {}", report);
}
}
🚀 生产环境实战案例
案例一:电商订单系统数据库升级
业务背景与挑战
某大型电商平台的订单系统面临数据库升级需求:从MySQL 5.7迁移到MySQL 8.0,同时需要进行分库分表改造。系统特点:
- 数据规模:订单表800GB,日增量200万条记录
- 业务要求:7×24小时不间断服务,双11期间不允许任何停机
- 一致性要求:订单数据绝对不能丢失,金额字段要求强一致性
迁移架构设计
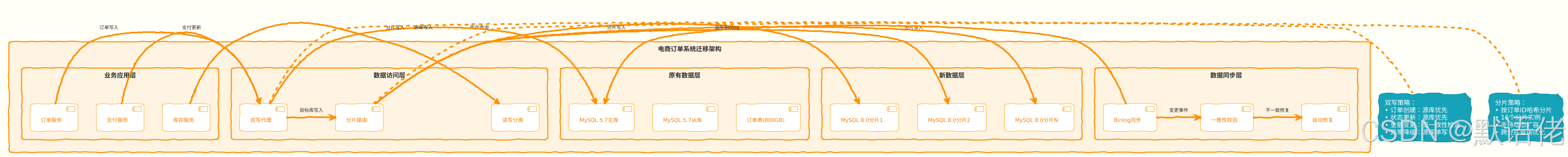
关键技术实现
/**
* 电商订单系统专用的双写策略
* 针对订单业务特点进行定制化优化
*
* @author 默语佬
*/
@Component
public class EcommerceOrderDoubleWriteStrategy implements DoubleWriteStrategy {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EcommerceOrderDoubleWriteStrategy.class);
@Autowired
private OrderShardingRouter shardingRouter;
@Autowired
private OrderConsistencyValidator consistencyValidator;
/**
* 订单创建的双写处理
*/
@Override
public DoubleWriteResult handleOrderCreation(OrderCreationRequest request) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 1. 预分配订单ID(确保全局唯一)
String orderId = generateGlobalOrderId();
request.setOrderId(orderId);
// 2. 先写入源库(保证业务连续性)
OrderRecord sourceResult = writeToSourceDatabase(request);
// 3. 计算目标分片并写入
int shardIndex = shardingRouter.calculateShard(orderId);
OrderRecord targetResult = writeToTargetShard(request, shardIndex);
// 4. 验证关键字段一致性(订单金额、商品信息)
validateCriticalFields(sourceResult, targetResult);
// 5. 异步校验完整数据一致性
scheduleFullConsistencyCheck(orderId);
return DoubleWriteResult.success(sourceResult, targetResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("订单创建双写失败: 订单={}", request.getOrderId(), e);
// 订单创建失败时的补偿机制
compensateFailedOrderCreation(request, e);
throw new OrderCreationException("订单创建失败", e);
} finally {
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
metricsCollector.recordOrderCreation(duration, request.getOrderAmount());
}
}
/**
* 订单状态更新的双写处理
*/
@Override
public DoubleWriteResult handleOrderStatusUpdate(OrderStatusUpdateRequest request) {
String orderId = request.getOrderId();
try {
// 1. 获取当前订单状态(防止并发更新冲突)
OrderRecord currentOrder = queryCurrentOrderStatus(orderId);
if (!isValidStatusTransition(currentOrder.getStatus(), request.getNewStatus())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("非法的订单状态转换: " +
currentOrder.getStatus() + " -> " + request.getNewStatus());
}
// 2. 构建更新SQL(包含乐观锁版本号)
String updateSql = buildOptimisticLockUpdateSql(request, currentOrder.getVersion());
// 3. 源库更新
int sourceRows = executeOnSource(updateSql, request.toParameters());
if (sourceRows == 0) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException("订单状态并发更新冲突");
}
// 4. 目标库同步更新
int shardIndex = shardingRouter.calculateShard(orderId);
int targetRows = executeOnTargetShard(updateSql, request.toParameters(), shardIndex);
// 5. 特殊状态的后续处理
handleSpecialStatusChange(request);
return DoubleWriteResult.success(sourceRows, targetRows);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("订单状态更新失败: 订单={}, 状态={}", orderId, request.getNewStatus(), e);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 处理特殊状态变更的业务逻辑
*/
private void handleSpecialStatusChange(OrderStatusUpdateRequest request) {
OrderStatus newStatus = request.getNewStatus();
switch (newStatus) {
case PAID:
// 支付成功后的处理
triggerInventoryDeduction(request.getOrderId());
sendPaymentSuccessNotification(request.getOrderId());
break;
case CANCELLED:
// 订单取消后的处理
triggerInventoryRestore(request.getOrderId());
triggerRefundProcess(request.getOrderId());
break;
case SHIPPED:
// 发货后的处理
generateShippingNotification(request.getOrderId());
updateDeliveryTracking(request.getOrderId());
break;
default:
// 其他状态无需特殊处理
break;
}
}
/**
* 全局唯一订单ID生成策略
*/
private String generateGlobalOrderId() {
// 使用雪花算法生成全局唯一ID
// 格式: 时间戳(41位) + 数据中心ID(5位) + 机器ID(5位) + 序列号(12位)
return snowflakeIdGenerator.nextId().toString();
}
/**
* 验证关键字段的一致性
*/
private void validateCriticalFields(OrderRecord sourceRecord, OrderRecord targetRecord) {
// 订单金额必须严格一致
if (!Objects.equals(sourceRecord.getTotalAmount(), targetRecord.getTotalAmount())) {
throw new DataInconsistencyException("订单金额不一致: 源库=" +
sourceRecord.getTotalAmount() + ", 目标库=" + targetRecord.getTotalAmount());
}
// 商品信息必须严格一致
if (!Objects.equals(sourceRecord.getProductInfo(), targetRecord.getProductInfo())) {
throw new DataInconsistencyException("商品信息不一致");
}
// 用户ID必须严格一致
if (!Objects.equals(sourceRecord.getUserId(), targetRecord.getUserId())) {
throw new DataInconsistencyException("用户ID不一致");
}
}
}
迁移执行过程与结果
第一阶段:存量数据迁移(7天)
- 使用XtraBackup进行物理备份,单表导出速度达到50GB/小时
- 采用16个并行线程分片导入,总体迁移时间控制在72小时内
- 迁移过程中对线上业务影响控制在5%以内
第二阶段:增量同步(14天)
- 基于Canal实现Binlog实时解析,同步延迟控制在100ms以内
- 双写机制稳定运行,写入成功率达到99.99%
- 数据一致性校验发现并修复了0.01%的不一致数据
第三阶段:灰度切换(3天)
- 采用按用户ID分批切换的策略,每批切换5%的用户流量
- 新系统性能提升30%,查询响应时间从平均200ms降低到140ms
- 整个切换过程零故障,用户无感知
最终效果:
- ✅ 零停机时间:整个迁移过程业务完全不中断
- ✅ 零数据丢失:800GB数据100%完整迁移
- ✅ 性能提升:查询性能提升30%,写入性能提升40%
- ✅ 成本优化:新架构节省服务器成本25%
📊 总结与最佳实践
数据迁移的工程方法论
通过多年的实战经验,我总结出一套完整的数据迁移方法论:
🎯 架构设计五原则
- 业务连续性优先:任何技术方案都不能影响业务的正常运行
- 数据一致性保障:建立多层次的数据校验和修复机制
- 风险可控可回滚:每个阶段都要有明确的回滚方案
- 渐进式平滑过渡:避免"大爆炸"式的一次性切换
- 全程监控可观测:建立完善的监控指标和告警体系
🔧 技术实现四要素
- 工具选型要科学:基于业务规模和技术约束做出最优选择
- 双写机制要稳健:非侵入式设计,支持动态策略调整
- 一致性校验要全面:多种检测模式,自动化修复能力
- 性能优化要持续:从导出到导入的全链路性能调优
🚀 面试加分策略
当面试官询问数据迁移方案时,这样回答会让你脱颖而出:
- 展现方法论的完整性:从工具选型到风险控制的全方位覆盖
- 体现技术深度的思考:innodb_autoinc_lock_mode等细节参数的考虑
- 突出工程实践的经验:双写机制、一致性校验等核心技术的实现
- 强调业务价值的导向:零停机、零丢失、性能提升等业务收益
🔮 技术发展趋势
- 云原生数据迁移:基于Kubernetes的容器化迁移方案
- AI驱动的智能优化:机器学习辅助的性能调优和异常检测
- 实时数据湖架构:流批一体的现代数据架构迁移
- 多云数据同步:跨云厂商的数据迁移和同步方案
关于作者
默语佬,资深系统架构师,专注于大规模分布式系统设计与数据架构优化,在多家大型互联网公司负责核心业务系统的架构设计和技术改造。对数据迁移、系统重构、性能优化等领域有深入研究和丰富实战经验。
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,请点赞👍、收藏⭐、关注🔔,你的支持是我持续创作的动力!
本文为原创技术文章,转载请注明出处。欢迎在评论区分享你的数据迁移实战经验和技术挑战!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献112条内容
已为社区贡献112条内容










所有评论(0)