LangChain之Tools
LangChain的Tools机制通过整合外部资源扩展了大语言模型的能力。摘要介绍了Tools的核心概念和两种自定义工具的方法:1)使用@tool装饰器快速创建简单工具;2)通过StructuredTool.from_function类方法实现更灵活的配置。两种方式都支持定义工具名称、描述、参数结构等要素,并可通过invoke方法调用。这些工具可以与Agent结合,使LLM能处理实时数据查询、计算
·
在 LangChain 中,Tools(工具) 是扩展大语言模型(LLM)能力的核心组件,允许模型调用外部资源(如 API、数据库、搜索引擎等)来完成仅凭自身知识无法解决的任务(如获取实时信息、执行计算、操作数据等)。
LangChain 拥有大量第三方工具。请访问工具集成查看可用工具列表。https://python.langchain.com/v0.2/docs/integrations/tools/
后续Tools与Agent结合示例在下一章中展示。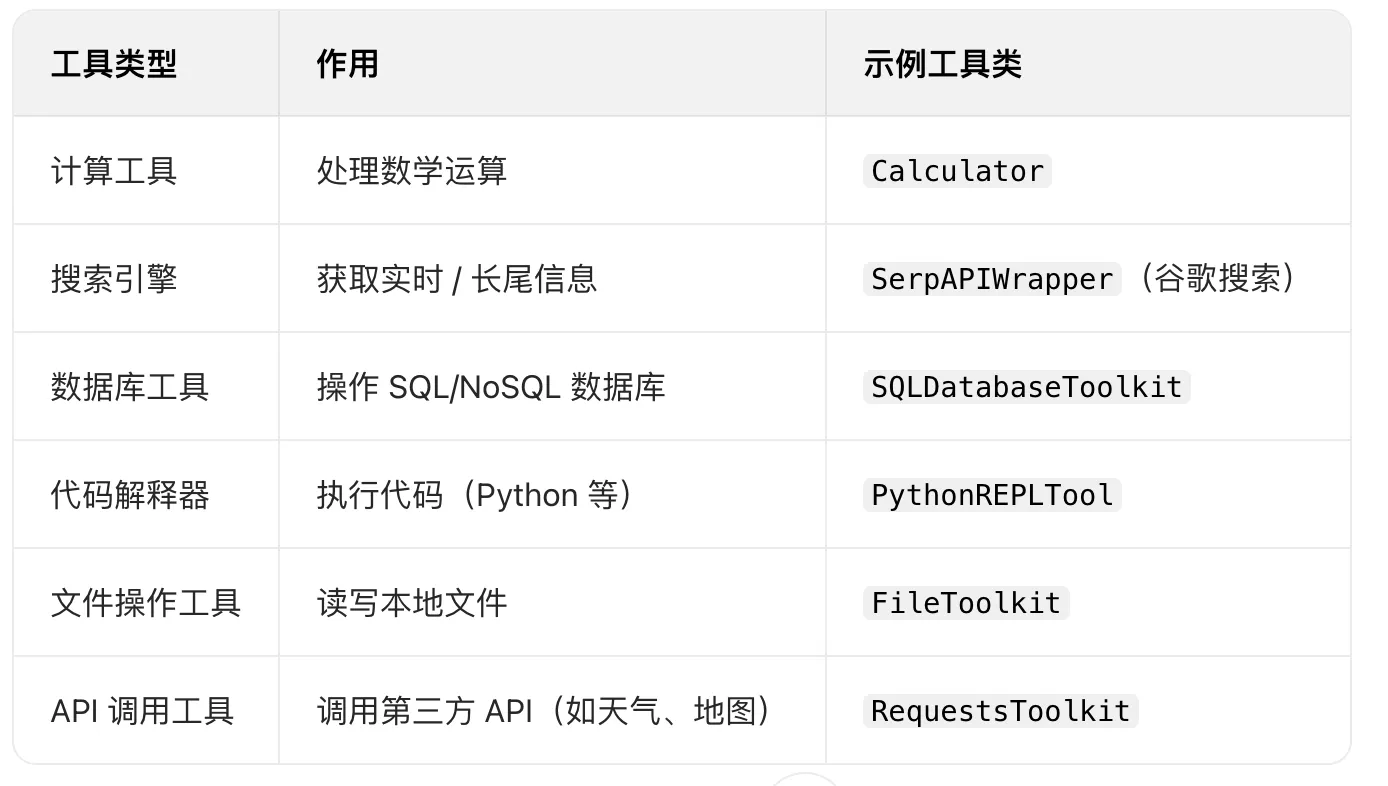
- Tool:单个工具的抽象,包含工具名称、描述、调用方法等。LLM 会根据工具描述决定是否调用。
- Toolkit:相关工具的集合(如数据库工具包包含查询、插入、删除等工具),简化复杂场景的工具管理。
Tool的要素: - name :工具的名称
- description :工具的功能描述
- 该工具输入的 JSON模式
- 要调用的函数
- return_direct :是否应将工具结果直接返回给用户(仅对Agent相关)
步骤: - 步骤1:将name、description 和 JSON模式作为上下文提供给LLM
- 步骤2:LLM会根据提示词推断出 需要调用哪些工具 ,并提供具体的调用参数信息
- 步骤3:用户需要根据返回的工具调用信息,自行触发相关工具的回调
自定义工具
一.使用 @tool 装饰器
from langchain.tools import tool
@tool(name_or_callable="add_two_number",description="two number add",return_direct=True)
def add_number(a:int,b:int)->int:
"""两个整数相加"""
return a + b
print(f"name = {add_number.name}")
print(f"args = {add_number.args}")
print(f"description = {add_number.description}")
print(f"return_direct = {add_number.return_direct}")
res = add_number.invoke({"a":10,"b":20})
print(res)
# name = add_two_number
# args = {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}
# description = two number add
# return_direct = True
# 30
二.使用StructuredTool.from_function类方法
StructuredTool.from_function 类方法提供了比 @tool 装饰器更多的可配置性,而无需太多额外的代码。
class FieldInfo(BaseModel):
input: str = Field(description="输入的关键词")
def hello_func(input:str)->str:
return "hello"
tool1 = StructuredTool.from_function(
func=hello_func,
name="Hello",
description="hello world",
args_schema=FieldInfo,
return_direct=True
)
print(f"name = {tool1.name}")
print(f"description = {tool1.description}")
print(f"return_direct = {tool1.return_direct}")
print(f"args = {tool1.args}")
print(tool1.invoke("hello"))
# name = Hello
# description = hello world
# return_direct = True
# args = {'input': {'description': '输入的关键词', 'title': 'Input', 'type': 'string'}}
# hello
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)