【GitHub项目推荐--PySpur:AI智能体工作流可视化开发平台】
PySpur 是一个革命性的AI智能体开发平台,提供可视化界面来构建、测试和部署AI智能体工作流。它旨在帮助AI工程师和开发者以10倍的速度迭代AI智能体,无需重复造轮子。🔗 GitHub地址🚀 核心价值:AI智能体开发 · 可视化工作流 · 快速迭代 · 生产部署 · 开源免费项目背景:AI开发痛点:解决AI智能体开发中的重复工作和调试困难可视化需求:提供直观的可视化开
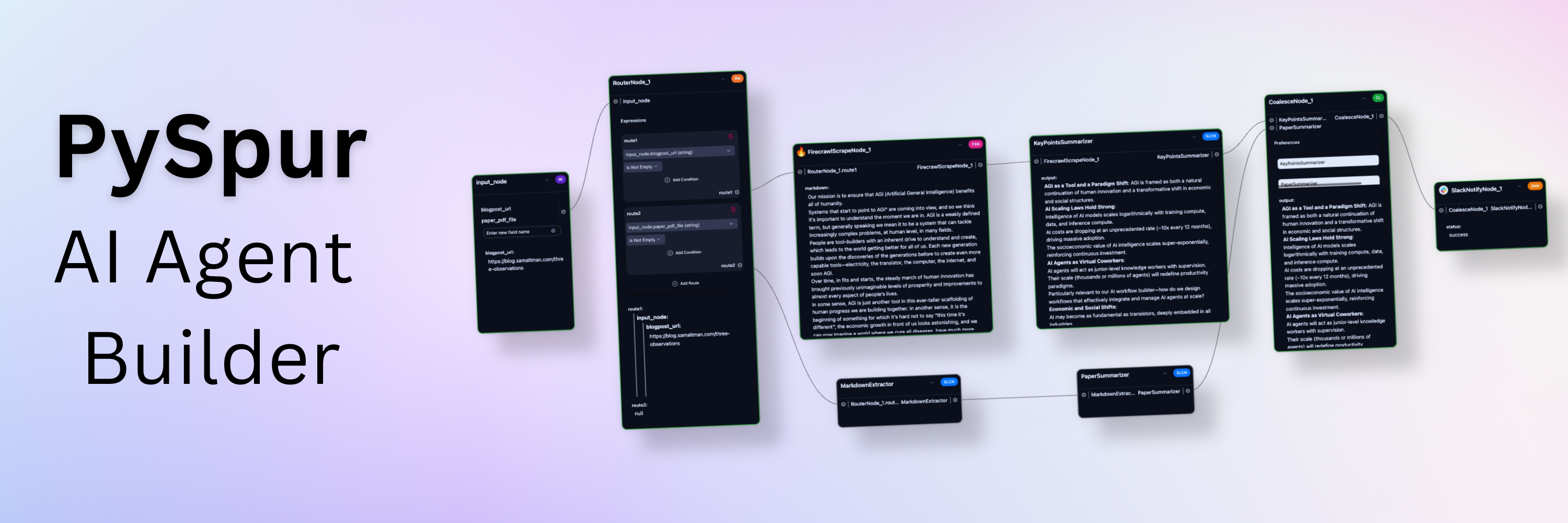
简介
PySpur 是一个革命性的AI智能体开发平台,提供可视化界面来构建、测试和部署AI智能体工作流。它旨在帮助AI工程师和开发者以10倍的速度迭代AI智能体,无需重复造轮子。
🔗 GitHub地址:
https://github.com/PySpur-Dev/pyspur
🚀 核心价值:
AI智能体开发 · 可视化工作流 · 快速迭代 · 生产部署 · 开源免费
项目背景:
-
AI开发痛点:解决AI智能体开发中的重复工作和调试困难
-
可视化需求:提供直观的可视化开发界面
-
迭代效率:大幅提升开发迭代速度
-
生产就绪:生产环境部署就绪的解决方案
-
开源社区:开源社区驱动的AI开发工具
项目特色:
-
🎨 可视化开发:拖拽式工作流构建
-
🤖 多模态支持:支持多种数据类型
-
🔄 快速迭代:10倍迭代速度提升
-
🚀 一键部署:生产环境一键部署
-
🆓 完全开源:代码完全开源免费
技术亮点:
-
工作流引擎:强大的工作流引擎
-
多模型集成:多种AI模型集成
-
可视化调试:可视化调试和跟踪
-
评估系统:自动化评估系统
-
扩展架构:模块化扩展架构
主要功能
1. 核心功能体系
PySpur提供了一套完整的AI智能体开发解决方案,涵盖工作流设计、模型集成、测试评估、部署监控等多个方面。
可视化开发功能:
工作流设计:
- 拖拽界面: 直观的拖拽式界面
- 节点库: 丰富的预建节点
- 连接管理: 可视化连接管理
- 参数配置: 图形化参数配置
- 模板系统: 可复用工作流模板
节点类型:
- 输入节点: 数据输入和处理
- 处理节点: 数据处理和转换
- AI节点: AI模型调用和处理
- 输出节点: 结果输出和导出
- 控制节点: 流程控制逻辑
界面功能:
- 实时预览: 实时结果预览
- 版本控制: 工作流版本管理
- 协作编辑: 多用户协作编辑
- 导入导出: 工作流导入导出
- 历史记录: 操作历史记录AI模型集成:
模型支持:
- LLM提供商: 100+ LLM提供商支持
- 多模态模型: 文本、图像、音频、视频
- 嵌入模型: 多种嵌入模型支持
- 向量数据库: 多种向量数据库集成
- 自定义模型: 自定义模型集成
模型管理:
- API密钥管理: 集中API密钥管理
- 模型配置: 模型参数配置
- 性能监控: 模型性能监控
- 成本控制: 使用成本控制
- 故障转移: 自动故障转移
工具集成:
- 外部工具: Slack、Google Sheets等集成
- 数据工具: 数据处理工具集成
- 分析工具: 数据分析工具集成
- 部署工具: 部署工具集成
- 监控工具: 监控工具集成测试评估功能:
测试框架:
- 测试用例: 测试用例管理
- 自动化测试: 自动化测试执行
- 性能测试: 性能测试工具
- 回归测试: 回归测试支持
- 负载测试: 负载测试能力
评估指标:
- 准确性: 结果准确性评估
- 性能: 响应性能评估
- 成本: 使用成本评估
- 可靠性: 系统可靠性评估
- 用户体验: 用户体验评估
数据管理:
- 测试数据: 测试数据集管理
- 结果分析: 测试结果分析
- 比较工具: 多版本结果比较
- 报告生成: 测试报告生成
- 数据可视化: 数据可视化展示部署监控功能:
部署选项:
- API部署: RESTful API部署
- 云部署: 云平台部署支持
- 本地部署: 本地服务器部署
- 边缘部署: 边缘设备部署
- 混合部署: 混合部署模式
监控能力:
- 实时监控: 实时性能监控
- 日志管理: 详细日志记录
- 告警系统: 智能告警系统
- 性能分析: 性能分析工具
- 使用统计: 使用统计报告
运维支持:
- 扩缩容: 自动扩缩容支持
- 备份恢复: 数据备份恢复
- 安全审计: 安全审计功能
- 版本管理: 版本管理支持
- 更新维护: 系统更新维护2. 高级功能
多模态处理:
数据类型:
- 文本处理: 自然语言文本处理
- 图像处理: 图像识别和处理
- 音频处理: 音频分析和处理
- 视频处理: 视频内容分析
- 文档处理: PDF、Word等文档处理
处理能力:
- 内容提取: 多模态内容提取
- 特征识别: 特征识别和分析
- 转换处理: 格式转换和处理
- 融合分析: 多模态融合分析
- 生成能力: 多模态内容生成
集成支持:
- 文件上传: 文件上传支持
- URL处理: 网络资源处理
- 实时流: 实时流数据处理
- 批量处理: 批量数据处理
- 存储集成: 云存储集成RAG功能:
RAG流程:
- 文档解析: 文档内容解析
- 文本分块: 智能文本分块
- 向量嵌入: 向量嵌入处理
- 向量存储: 向量数据库存储
- 检索查询: 智能检索查询
增强能力:
- 知识增强: 知识库增强检索
- 上下文理解: 深度上下文理解
- 相关性排序: 相关性排序优化
- 多源检索: 多数据源检索
- 实时更新: 知识实时更新
应用场景:
- 问答系统: 智能问答系统
- 文档分析: 文档内容分析
- 研究辅助: 研究辅助工具
- 内容生成: 知识增强生成
- 决策支持: 决策支持系统人类参与循环:
交互模式:
- 审批节点: 人工审批节点
- 反馈收集: 用户反馈收集
- 质量控制: 人工质量控制
- 决策支持: 人工决策支持
- 异常处理: 人工异常处理
工作流集成:
- 暂停恢复: 工作流暂停恢复
- 通知提醒: 通知和提醒系统
- 任务分配: 任务分配和管理
- 进度跟踪: 进度跟踪管理
- 审计日志: 操作审计日志
用户体验:
- 界面友好: 用户友好界面
- 移动支持: 移动设备支持
- 响应式设计: 响应式设计
- 无障碍访问: 无障碍访问支持
- 多语言: 多语言支持安装与配置
1. 环境准备
系统要求:
硬件要求:
- 内存: 8GB+ RAM (推荐16GB)
- 存储: 20GB+ 可用空间
- CPU: 多核处理器
- 网络: 稳定网络连接
软件要求:
- Python: 3.11+ 版本
- Node.js: 18.x+ 版本
- Docker: 容器化支持
- 数据库: SQLite/PostgreSQL
服务要求:
- AI服务: OpenAI/Anthropic等API访问
- 向量数据库: Pinecone/Weaviate等(可选)
- 云存储: AWS S3/Google Cloud Storage(可选)2. 安装步骤
快速安装:
# 使用pip安装
pip install pyspur
# 初始化新项目
pyspur init my-ai-project
cd my-ai-project
# 启动开发服务器
pyspur serve --sqlite
# 访问应用
# http://localhost:6080Docker安装:
# 使用Docker Compose
git clone https://github.com/PySpur-Dev/pyspur.git
cd pyspur
# 启动开发环境
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up --build -d
# 或生产环境
docker-compose up -d开发环境设置:
# 开发容器设置(推荐)
# 1. 使用VS Code或Cursor
# 2. 打开项目文件夹
# 3. 选择"Reopen in Container"
# 4. 自动配置开发环境
# 手动开发设置
pip install -e ".[dev]"
npm install
pre-commit install3. 配置说明
环境配置:
# .env 配置文件示例
DATABASE_URL=sqlite:///./app.db
# 或使用PostgreSQL
# DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:pass@localhost:5432/pyspur
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your-anthropic-api-key
# 可选配置
PINECONE_API_KEY=your-pinecone-key
WEAVIATE_URL=your-weaviate-url
AWS_ACCESS_KEY=your-aws-key
AWS_SECRET_KEY=your-aws-secret
LOG_LEVEL=INFO
DEBUG=false
PORT=6080API密钥配置:
# 通过UI配置或编辑config/api_keys.yaml
api_keys:
openai:
api_key: sk-...
organization: org-...
anthropic:
api_key: sk-ant-...
cohere:
api_key: ...
huggingface:
api_key: hf_...
# 工具API密钥
slack:
bot_token: xoxb-...
google:
client_id: ...
client_secret: ...
github:
token: ghp_...工作流配置:
# 工作流配置文件示例
workflow:
name: "文档处理流水线"
version: "1.0.0"
description: "多模态文档处理和分析流水线"
nodes:
- type: "input"
id: "file_upload"
config:
accept: [".pdf", ".docx", ".txt"]
max_size: "10MB"
- type: "processor"
id: "document_parser"
config:
parser: "pdfplumber"
extract_images: true
extract_tables: true
- type: "ai"
id: "content_analyzer"
config:
model: "gpt-4-turbo"
temperature: 0.1
max_tokens: 4000
- type: "output"
id: "result_exporter"
config:
format: "json"
include_source: true
connections:
- from: "file_upload"
to: "document_parser"
- from: "document_parser"
to: "content_analyzer"
- from: "content_analyzer"
to: "result_exporter"使用指南
1. 基本工作流
使用PySpur的基本流程包括:环境准备 → 项目初始化 → 工作流设计 → 测试评估 → 部署监控。整个过程设计为简单直观。
2. 基本使用
项目初始化:
# 创建新项目
pyspur init my-ai-agent
cd my-ai-agent
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 配置环境变量
cp .env.example .env
# 编辑.env文件配置API密钥
# 启动开发服务器
pyspur serve
# 或使用生产模式
pyspur serve --production工作流创建:
# 通过Python代码创建工作流
from pyspur import Workflow, Node
# 创建新工作流
workflow = Workflow("智能文档分析")
# 添加输入节点
input_node = Node(
type="input",
name="文档上传",
config={
"accept": [".pdf", ".docx", ".txt"],
"max_size": "10MB"
}
)
# 添加处理节点
parser_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="文档解析",
config={
"parser": "pdfplumber",
"extract_images": True
}
)
# 添加AI节点
ai_node = Node(
type="ai",
name="内容分析",
config={
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"temperature": 0.1
}
)
# 添加输出节点
output_node = Node(
type="output",
name="结果导出",
config={
"format": "json"
}
)
# 连接节点
workflow.connect(input_node, parser_node)
workflow.connect(parser_node, ai_node)
workflow.connect(ai_node, output_node)
# 保存工作流
workflow.save()可视化开发:
# 通过UI界面开发工作流
# 1. 启动服务器: pyspur serve
# 2. 访问 http://localhost:6080
# 3. 使用拖拽界面创建工作流
# 4. 配置节点参数
# 5. 连接节点建立流程
# 6. 保存工作流
# 工作流测试
workflow.test_with_file("document.pdf")
# 批量测试
workflow.batch_test("test_cases/")
# 性能评估
results = workflow.evaluate_performance()
# 部署工作流
deployment = workflow.deploy(
name="production-api",
environment="production"
)API使用:
# 使用PySpur API
from pyspur import PySpurClient
# 初始化客户端
client = PySpurClient(
base_url="http://localhost:6080",
api_key="your-api-key"
)
# 列出工作流
workflows = client.list_workflows()
# 执行工作流
result = client.execute_workflow(
workflow_id="doc-analysis-001",
input_data={
"file": "document.pdf",
"options": {
"extract_tables": True,
"analyze_images": True
}
}
)
# 监控执行
execution = client.get_execution("exec-123")
status = execution.status
logs = execution.get_logs()
# 获取评估结果
evaluation = client.get_evaluation("eval-456")
metrics = evaluation.metrics3. 高级用法
自定义节点开发:
# 自定义处理节点
from pyspur.core import BaseNode
class CustomProcessorNode(BaseNode):
def __init__(self, config=None):
super().__init__(config)
self.node_type = "processor"
self.version = "1.0.0"
async def execute(self, input_data, context):
"""执行节点处理"""
try:
# 处理输入数据
processed_data = await self.process_data(input_data)
# 更新执行上下文
context.update({
"processed_at": datetime.now(),
"processing_time": time.time() - context.start_time
})
return {
"success": True,
"data": processed_data,
"metadata": context
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"success": False,
"error": str(e),
"metadata": context
}
async def process_data(self, data):
"""自定义数据处理逻辑"""
# 实现具体处理逻辑
if isinstance(data, str):
return self.process_text(data)
elif isinstance(data, dict):
return self.process_json(data)
else:
return data
def process_text(self, text):
"""文本处理逻辑"""
# 文本清洗、分析等
return {
"cleaned_text": text.strip(),
"word_count": len(text.split()),
"processed": True
}
def process_json(self, json_data):
"""JSON处理逻辑"""
# JSON数据处理
return {
**json_data,
"processed": True,
"processed_at": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
# 注册自定义节点
from pyspur.registry import NodeRegistry
NodeRegistry.register("custom_processor", CustomProcessorNode)工作流组合:
# 复杂工作流组合
class DocumentAnalysisWorkflow:
def __init__(self):
self.workflows = {}
self.setup_workflows()
def setup_workflows(self):
# 文档提取工作流
self.workflows['extraction'] = Workflow("文档提取")
self.workflows['extraction'].add_nodes([
Node("input", "file_upload"),
Node("processor", "pdf_extractor"),
Node("processor", "text_cleaner"),
Node("output", "extracted_data")
])
# 内容分析工作流
self.workflows['analysis'] = Workflow("内容分析")
self.workflows['analysis'].add_nodes([
Node("input", "text_input"),
Node("ai", "summarizer"),
Node("ai", "sentiment_analyzer"),
Node("output", "analysis_results")
])
# 报告生成工作流
self.workflows['reporting'] = Workflow("报告生成")
self.workflows['reporting'].add_nodes([
Node("input", "analysis_data"),
Node("processor", "report_generator"),
Node("output", "final_report")
])
async def execute_pipeline(self, input_file):
"""执行完整管道"""
# 执行文档提取
extraction_result = await self.workflows['extraction'].execute({
"file": input_file
})
if not extraction_result['success']:
raise Exception("文档提取失败")
# 执行内容分析
analysis_result = await self.workflows['analysis'].execute({
"text": extraction_result['data']['content']
})
if not analysis_result['success']:
raise Exception("内容分析失败")
# 执行报告生成
report_result = await self.workflows['reporting'].execute({
"data": analysis_result['data']
})
return {
"extraction": extraction_result,
"analysis": analysis_result,
"report": report_result
}评估和监控:
# 工作流评估和监控
class WorkflowEvaluator:
def __init__(self, workflow):
self.workflow = workflow
self.metrics = {
'accuracy': 0,
'performance': 0,
'cost': 0,
'reliability': 0
}
self.test_cases = []
async def run_evaluation(self, test_dataset):
"""运行完整评估"""
results = []
for test_case in test_dataset:
result = await self.run_test_case(test_case)
results.append(result)
# 更新指标
self.update_metrics(result)
return {
'results': results,
'metrics': self.metrics,
'summary': self.generate_summary()
}
async def run_test_case(self, test_case):
"""执行单个测试用例"""
start_time = time.time()
try:
result = await self.workflow.execute(test_case['input'])
return {
'success': True,
'execution_time': time.time() - start_time,
'result': result,
'expected': test_case['expected'],
'match_score': self.calculate_match_score(result, test_case['expected'])
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'success': False,
'error': str(e),
'execution_time': time.time() - start_time
}
def calculate_match_score(self, actual, expected):
"""计算结果匹配度"""
# 实现匹配度计算逻辑
if isinstance(actual, dict) and isinstance(expected, dict):
return self.dict_match_score(actual, expected)
elif isinstance(actual, str) and isinstance(expected, str):
return self.text_match_score(actual, expected)
else:
return 0.0
def generate_summary(self):
"""生成评估摘要"""
return {
'total_tests': len(self.test_cases),
'success_rate': self.calculate_success_rate(),
'average_time': self.calculate_average_time(),
'total_cost': self.calculate_total_cost()
}应用场景实例
案例1:智能客服系统
场景:企业级智能客服系统
解决方案:使用PySpur构建智能客服工作流。
实施方法:
class CustomerServiceWorkflow:
def __init__(self):
self.workflow = self.create_customer_service_workflow()
def create_customer_service_workflow(self):
"""创建客服工作流"""
workflow = Workflow("智能客服系统")
# 输入节点 - 客户查询
input_node = Node(
type="input",
name="客户查询输入",
config={
"sources": ["web", "mobile", "email", "chat"],
"format": "text"
}
)
# 处理节点 - 查询解析
parser_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="查询解析",
config={
"language": "auto",
"extract_entities": True,
"detect_intent": True
}
)
# AI节点 - 意图识别
intent_node = Node(
type="ai",
name="意图识别",
config={
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"temperature": 0.1,
"max_tokens": 1000
}
)
# 知识库节点 - RAG检索
rag_node = Node(
type="rag",
name="知识检索",
config={
"collection": "customer_service_kb",
"max_results": 3,
"similarity_threshold": 0.7
}
)
# AI节点 - 响应生成
response_node = Node(
type="ai",
name="响应生成",
config={
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 2000
}
)
# 人工审核节点
review_node = Node(
type="human",
name="人工审核",
config={
"required": False,
"approval_threshold": 0.8,
"reviewers": ["supervisor@company.com"]
}
)
# 输出节点 - 响应输出
output_node = Node(
type="output",
name="响应输出",
config={
"formats": ["text", "html", "json"],
"channels": ["web", "email", "chat"]
}
)
# 添加节点
workflow.add_nodes([
input_node, parser_node, intent_node,
rag_node, response_node, review_node, output_node
])
# 连接节点
workflow.connect(input_node, parser_node)
workflow.connect(parser_node, intent_node)
workflow.connect(intent_node, rag_node)
workflow.connect(rag_node, response_node)
workflow.connect(response_node, review_node)
workflow.connect(review_node, output_node)
# 设置条件分支
workflow.add_condition(intent_node, "urgent", review_node)
return workflow
async def handle_customer_query(self, query, context=None):
"""处理客户查询"""
result = await self.workflow.execute({
"query": query,
"context": context or {},
"customer_info": self.get_customer_info()
})
if result['success']:
return {
"response": result['data']['response'],
"confidence": result['data']['confidence'],
"sources": result['data']['sources']
}
else:
# 降级处理
return await self.fallback_response(query)
async def fallback_response(self, query):
"""降级响应处理"""
return {
"response": "抱歉,我暂时无法处理您的查询。已转接人工客服,请稍等。",
"confidence": 0.0,
"escalated": True
}
def get_customer_info(self):
"""获取客户信息"""
# 从CRM系统获取客户信息
return {
"tier": "premium",
"history": [],
"preferences": {}
}
# 使用示例
async def customer_service_example():
service = CustomerServiceWorkflow()
# 处理客户查询
response = await service.handle_customer_query(
"我的订单状态如何?订单号123456"
)
print("客服响应:", response['response'])
print("置信度:", response['confidence'])
# 启动服务
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
asyncio.run(customer_service_example())客服系统价值:
-
智能响应:AI驱动的智能响应
-
知识增强:知识库增强响应
-
人工审核:人工审核和干预
-
多渠道:多渠道响应支持
-
性能监控:实时性能监控
案例2:内容审核系统
场景:多平台内容审核
解决方案:使用PySpur构建内容审核工作流。
实施方法:
class ContentModerationWorkflow:
def __init__(self):
self.workflow = self.create_moderation_workflow()
self.policies = self.load_moderation_policies()
def create_moderation_workflow(self):
"""创建内容审核工作流"""
workflow = Workflow("内容审核系统")
# 多模态输入节点
input_node = Node(
type="input",
name="内容输入",
config={
"types": ["text", "image", "video"],
"sources": ["social_media", "forum", "upload"]
}
)
# 内容解析节点
parser_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="内容解析",
config={
"text_extraction": True,
"image_analysis": True,
"video_analysis": True
}
)
# 多模态分析节点
analysis_node = Node(
type="ai",
name="多模态分析",
config={
"models": {
"text": "gpt-4-turbo",
"image": "clip-vit-large",
"video": "video-analysis-v1"
},
"confidence_threshold": 0.8
}
)
# 策略检查节点
policy_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="策略检查",
config={
"rule_engine": "rego",
"policies": "moderation_policies.rego"
}
)
# 人工审核节点
human_review_node = Node(
type="human",
name="人工审核",
config={
"required": True,
"reviewers": ["moderator@company.com"],
"sla_minutes":[]
}
)
# 决策节点
decision_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="审核决策",
config={
"actions": ["approve", "reject", "escalate"],
"default_action": "escalate"
}
)
# 输出节点
output_node = Node(
type="output",
name="审核结果",
config={
"formats": ["json", "webhook", "database"],
"notifications": True
}
)
# 添加节点
workflow.add_nodes([
input_node, parser_node, analysis_node,
policy_node, human_review_node, decision_node, output_node
])
# 连接节点
workflow.connect(input_node, parser_node)
workflow.connect(parser_node, analysis_node)
workflow.connect(analysis_node, policy_node)
workflow.connect(policy_node, human_review_node)
workflow.connect(human_review_node, decision_node)
workflow.connect(decision_node, output_node)
# 设置条件分支
workflow.add_condition(analysis_node, "high_confidence", decision_node)
workflow.add_condition(policy_node, "clear_violation", decision_node)
return workflow
def load_moderation_policies(self):
"""加载审核策略"""
return {
"hate_speech": {
"threshold": 0.9,
"action": "reject",
"escalate": True
},
"violence": {
"threshold": 0.85,
"action": "reject",
"escalate": True
},
"spam": {
"threshold": 0.8,
"action": "reject",
"escalate": False
},
"nsfw": {
"threshold": 0.7,
"action": "review",
"escalate": True
}
}
async def moderate_content(self, content, content_type="text"):
"""审核内容"""
result = await self.workflow.execute({
"content": content,
"content_type": content_type,
"policies": self.policies,
"context": {
"user_reputation": self.get_user_reputation(),
"platform_rules": self.get_platform_rules()
}
})
if result['success']:
return {
"decision": result['data']['decision'],
"confidence": result['data']['confidence'],
"reasons": result['data']['reasons'],
"moderator": result['data']['moderator']
}
else:
return {
"decision": "escalate",
"confidence": 0.0,
"reasons": ["system_error"],
"error": result['error']
}
def get_user_reputation(self):
"""获取用户信誉评分"""
# 从用户系统获取信誉数据
return {
"score": 85,
"violations": 2,
"age_days": 365
}
def get_platform_rules(self):
"""获取平台规则"""
return {
"strict_mode": False,
"regional_laws": ["gdpr", "ccpa"],
"content_guidelines": "community_standards_v2"
}
# 使用示例
async def moderation_example():
moderator = ContentModerationWorkflow()
# 审核文本内容
text_result = await moderator.moderate_content(
"这是一段需要审核的文本内容",
"text"
)
print("文本审核结果:", text_result['decision'])
print("置信度:", text_result['confidence'])
# 审核图片内容
image_result = await moderator.moderate_content(
"https://example.com/image.jpg",
"image"
)
print("图片审核结果:", image_result['decision'])
# 启动审核服务
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
asyncio.run(moderation_example())内容审核价值:
-
多模态审核:文本、图像、视频多模态审核
-
策略驱动:灵活的审核策略配置
-
人工审核:人工审核和决策支持
-
实时处理:实时内容审核处理
-
合规支持:法规合规支持
案例3:智能数据分析
场景:企业数据分析和报告生成
解决方案:使用PySpur构建数据分析工作流。
实施方法:
class DataAnalysisWorkflow:
def __init__(self):
self.workflow = self.create_analysis_workflow()
self.data_sources = self.configure_data_sources()
def create_analysis_workflow(self):
"""创建数据分析工作流"""
workflow = Workflow("智能数据分析")
# 数据输入节点
input_node = Node(
type="input",
name="数据输入",
config={
"sources": ["database", "api", "file", "stream"],
"formats": ["json", "csv", "xml", "parquet"]
}
)
# 数据清洗节点
cleaning_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="数据清洗",
config={
"operations": ["deduplication", "normalization", "validation"],
"quality_checks": True
}
)
# 数据分析节点
analysis_node = Node(
type="ai",
name="智能分析",
config={
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"analysis_types": ["trends", "patterns", "anomalies", "predictions"],
"max_tokens": 4000
}
)
# 可视化节点
visualization_node = Node(
type="processor",
name="可视化生成",
config={
"chart_types": ["line", "bar", "pie", "scatter"],
"interactive": True,
"export_formats": ["png", "svg", "html"]
}
)
# 报告生成节点
report_node = Node(
type="ai",
name="报告生成",
config={
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"templates": ["executive", "technical", "summary"],
"language": "auto"
}
)
# 输出节点
output_node = Node(
type="output",
name="分析结果",
config={
"destinations": ["email", "slack", "database", "cloud_storage"],
"formats": ["pdf", "html", "json", "presentation"]
}
)
# 添加节点
workflow.add_nodes([
input_node, cleaning_node, analysis_node,
visualization_node, report_node, output_node
])
# 连接节点
workflow.connect(input_node, cleaning_node)
workflow.connect(cleaning_node, analysis_node)
workflow.connect(analysis_node, visualization_node)
workflow.connect(visualization_node, report_node)
workflow.connect(report_node, output_node)
return workflow
def configure_data_sources(self):
"""配置数据源"""
return {
"sales_db": {
"type": "postgresql",
"connection": "postgresql://user:pass@localhost:5432/sales",
"tables": ["orders", "customers", "products"]
},
"marketing_api": {
"type": "rest",
"endpoint": "https://api.marketing.com/v1/data",
"auth": "bearer_token"
},
"customer_feedback": {
"type": "csv",
"path": "/data/feedback/",
"format": "csv"
}
}
async def analyze_data(self, dataset, analysis_type="trends"):
"""分析数据"""
result = await self.workflow.execute({
"dataset": dataset,
"analysis_type": analysis_type,
"data_sources": self.data_sources,
"timeframe": {
"start": "2024-01-01",
"end": "2024-09-30"
},
"metrics": ["revenue", "conversion", "retention"]
})
if result['success']:
return {
"insights": result['data']['insights'],
"visualizations": result['data']['visualizations'],
"report": result['data']['report'],
"recommendations": result['data']['recommendations']
}
else:
raise Exception(f"分析失败: {result['error']}")
async def generate_report(self, analysis_results, report_type="executive"):
"""生成报告"""
report_data = {
"analysis": analysis_results,
"type": report_type,
"audience": "executive",
"key_metrics": self.extract_key_metrics(analysis_results)
}
return await self.workflow.execute({
"action": "generate_report",
"data": report_data
})
def extract_key_metrics(self, analysis_results):
"""提取关键指标"""
return {
"revenue_growth": analysis_results.get('revenue_growth', 0),
"conversion_rate": analysis_results.get('conversion_rate', 0),
"customer_satisfaction": analysis_results.get('satisfaction_score', 0),
"anomalies_detected": len(analysis_results.get('anomalies', []))
}
# 使用示例
async def data_analysis_example():
analyzer = DataAnalysisWorkflow()
# 分析销售数据
sales_data = {
"source": "sales_db",
"table": "orders",
"filters": {
"status": "completed",
"date_range": ["2024-01-01", "2024-09-30"]
}
}
try:
# 执行分析
results = await analyzer.analyze_data(sales_data, "trends")
print("分析完成!")
print("关键洞察:", results['insights'][:3])
print("可视化数量:", len(results['visualizations']))
# 生成报告
report = await analyzer.generate_report(results, "executive")
print("报告生成成功:", report['success'])
except Exception as e:
print("分析错误:", str(e))
# 启动分析服务
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
asyncio.run(data_analysis_example())数据分析价值:
-
智能分析:AI驱动的数据分析
-
可视化:自动可视化生成
-
报告生成:自动报告生成
-
多数据源:多数据源支持
-
决策支持:数据驱动的决策支持
总结
PySpur作为一个革命性的AI智能体开发平台,通过其可视化界面、强大的工作流引擎、多模态支持和生产部署能力,为AI开发提供了完整的解决方案。
核心优势:
-
🎨 可视化开发:拖拽式工作流设计
-
🤖 AI集成:多种AI模型集成
-
📊 多模态支持:文本、图像、视频多模态处理
-
🚀 快速迭代:10倍开发速度提升
-
🆓 完全开源:代码完全开源免费
适用场景:
-
AI智能体开发和测试
-
多模态内容处理和分析
-
自动化工作流构建
-
数据分析和报告生成
-
内容审核和监控
立即开始使用:
# 安装PySpur
pip install pyspur
# 初始化项目
pyspur init my-ai-project
# 启动开发服务器
pyspur serve
# 访问应用
# http://localhost:6080资源链接:
-
📚 项目地址:GitHub仓库
-
📖 官方文档:详细技术文档
-
💬 社区支持:GitHub讨论区
-
🎥 演示示例:在线演示示例
-
🔧 配置参考:配置选项参考
通过PySpur,您可以:
-
快速开发:快速开发AI智能体
-
可视化调试:可视化调试和测试
-
生产部署:生产环境一键部署
-
性能优化:性能监控和优化
-
社区贡献:参与开源社区贡献
无论您是AI工程师、数据科学家、开发者还是技术爱好者,PySpur都能为您提供强大、灵活且免费的AI开发解决方案!
特别提示:
-
🔍 API配置:正确配置API密钥
-
📖 文档阅读:详细阅读技术文档
-
🤝 社区参与:积极参与社区贡献
-
🔧 性能优化:根据需求优化配置
-
⚠️ 生产准备:生产环境准备注意事项
通过PySpur,共同推动AI智能体开发的发展!
未来发展:
-
🚀 更多功能:持续添加新功能
-
🤖 模型扩展:支持更多AI模型
-
🌍 多语言:更多语言支持扩展
-
📊 性能优化:进一步性能优化
-
🔧 生态建设:开发者生态建设
加入社区:
参与方式:
- GitHub Issues: 问题反馈和功能建议
- 文档贡献: 技术文档改进贡献
- 代码贡献: 代码改进和功能添加
- 示例贡献: 示例项目贡献
- 插件开发: 插件和扩展开发
社区价值:
- 技术交流和学习
- 问题解答和支持
- 功能建议和讨论
- 项目贡献和认可
- 职业发展机会通过PySpur,共同构建更好的AI开发未来!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献63条内容
已为社区贡献63条内容






所有评论(0)