RAG索引流程中的文档解析:工业级实践方案
搜索AI 搜索。
搜索
RAG索引流程中的文档解析:工业级实践方案


于 2025-07-03 02:45:00 发布


收藏 27

点赞数 26
CC 4.0 BY-SA版权
158 篇文章
已订阅
文章目录
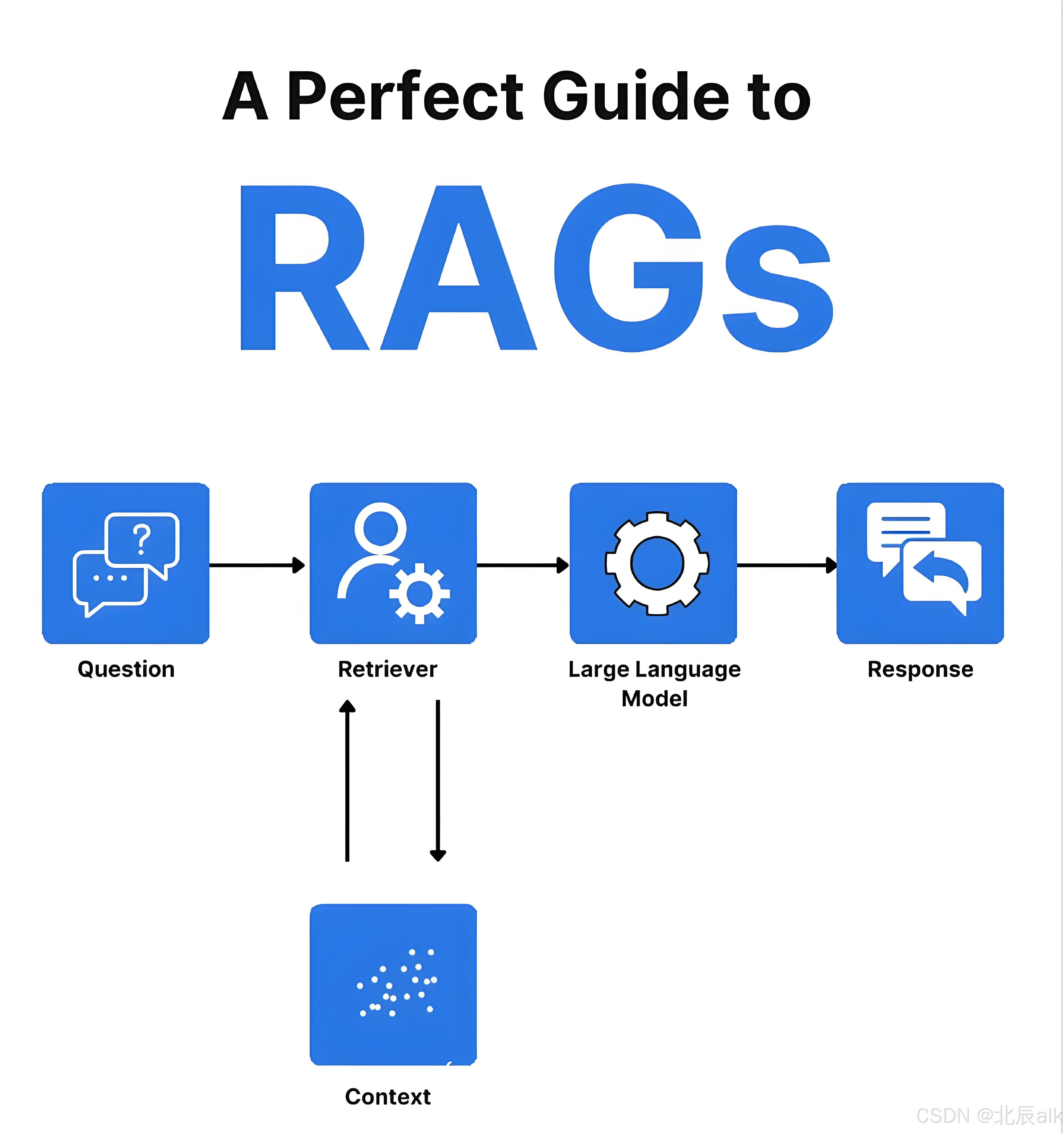
在RAG系统的索引流程中,文档解析是将原始文档转化为可检索知识的核心环节。以下是我们经过多个生产项目验证的完整解析方案,涵盖从基础解析到高级优化的全流程技术细节。
一、多格式文档解析框架
1. 模块化解析器设计
class DocumentParser:
def __init__(self):
self.parsers = {
'.pdf': PDFParser(),
'.docx': DocxParser(),
'.pptx': PptxParser(),
'.html': HTMLParser(),
'.txt': TextParser()
}
def parse(self, file_path):
ext = os.path.splitext(file_path)[1].lower()
parser = self.parsers.get(ext)
if not parser:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported file type: {ext}")
return parser.parse(file_path)
# 专用解析器实现示例
class PDFParser:
def __init__(self):
self.text_engine = pdfplumber.open
self.table_engine = camelot.read_pdf
def parse(self, file_path):
result = {'text': '', 'tables': []}
with self.text_engine(file_path) as pdf:
for page in pdf.pages:
result['text'] += page.extract_text() + '\n'
try:
tables = self.table_engine(file_path, flavor='stream')
result['tables'] = [table.df.to_dict() for table in tables]
except Exception as e:
logging.warning(f"Table extraction failed: {str(e)}")
return result
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
2. 复杂文档处理技术
-
扫描PDF处理:
def parse_scanned_pdf(file_path): # 使用OCR技术 images = pdf2image.convert_from_path(file_path) text = '' for img in images: text += pytesseract.image_to_string(img, lang='chi_sim+eng') return {'text': text, 'is_scanned': True}AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
-
嵌入式对象提取:
def extract_embedded_objects(doc_path): with zipfile.ZipFile(doc_path) as docx: embedded = {} for name in docx.namelist(): if name.startswith('word/embeddings/'): content = docx.read(name) file_ext = os.path.splitext(name)[1] embedded[name] = { 'content': content, 'type': file_ext } return embeddedAI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
二、文档结构分析与重建
1. 层次化结构解析
def analyze_document_structure(text):
structure = {
'title': '',
'sections': [],
'metadata': {}
}
# 标题检测
lines = text.split('\n')
structure['title'] = lines[0] if lines else ''
# 章节检测
current_section = None
for line in lines[1:]:
if is_section_header(line): # 基于正则或启发式规则
if current_section:
structure['sections'].append(current_section)
current_section = {
'heading': line.strip(),
'content': []
}
elif current_section:
current_section['content'].append(line)
return structure
def is_section_header(line):
patterns = [
r'^第[一二三四五六七八九十]+章', # 中文章节
r'^\d+\.\d+', # 数字编号
r'^[A-Z][A-Z\s]+$' # 全大写英文标题
]
return any(re.match(p, line.strip()) for p in patterns)
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
2. 表格与文本关联
class TableLinker:
def __init__(self):
self.table_ref_pattern = re.compile(r'表\d+')
def link_tables(self, text, tables):
refs = self.table_ref_pattern.findall(text)
linked = []
for i, ref in enumerate(refs):
if i < len(tables):
linked.append({
'reference': ref,
'table': tables[i],
'context': self._find_context(text, ref)
})
return linked
def _find_context(self, text, ref):
# 查找表格引用前后的文本
start = text.find(ref)
context_start = max(0, start - 100)
context_end = min(len(text), start + len(ref) + 100)
return text[context_start:context_end]
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
三、文本规范化流水线
1. 多阶段清洗流程
def text_normalization_pipeline(text):
# 阶段1:编码标准化
text = normalize_encoding(text)
# 阶段2:特殊字符处理
text = remove_control_chars(text)
# 阶段3:格式规范化
text = unify_whitespace(text)
# 阶段4:领域特定清洗
text = domain_specific_cleaning(text)
return text
def normalize_encoding(text):
return unicodedata.normalize('NFKC', text)
def remove_control_chars(text):
return re.sub(r'[\x00-\x1f\x7f-\x9f]', '', text)
def unify_whitespace(text):
return re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text).strip()
def domain_specific_cleaning(text):
# 示例:法律文档中的条款编号标准化
text = re.sub(r'第\s*([一二三四五六七八九十]+)\s*条', r'第\1条', text)
return text
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
2. 语义段落重组
def semantic_chunking(text, max_chunk_size=500):
sentences = sent_tokenize(text)
chunks = []
current_chunk = []
current_size = 0
for sent in sentences:
sent_size = len(sent)
if current_size + sent_size > max_chunk_size and current_chunk:
chunks.append(' '.join(current_chunk))
current_chunk = []
current_size = 0
current_chunk.append(sent)
current_size += sent_size
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(' '.join(current_chunk))
return chunks
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
四、元数据提取与增强
1. 结构化元数据抽取
class MetadataExtractor:
def __init__(self):
self.nlp = spacy.load('zh_core_web_lg')
self.date_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{4}年\d{1,2}月\d{1,2}日')
def extract(self, text):
doc = self.nlp(text)
dates = self._extract_dates(text)
entities = self._extract_entities(doc)
return {
'dates': dates,
'entities': entities,
'doc_type': self._classify_doc_type(text)
}
def _extract_dates(self, text):
return list(set(self.date_pattern.findall(text)))
def _extract_entities(self, doc):
return {
ent.label_: list(set([ent.text for ent in doc.ents if ent.label_ in ['ORG', 'PERSON']]))
for ent in doc.ents
}
def _classify_doc_type(self, text):
if '合同' in text or '协议' in text:
return 'contract'
elif any(w in text for w in ['报告', '分析']):
return 'report'
return 'other'
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
2. 动态元数据标记
def dynamic_metadata_tagging(text, embeddings):
# 基于嵌入聚类生成元标签
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=5)
tags = kmeans.fit_predict(embeddings)
# 提取每个簇的关键词
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=50)
tfidf = vectorizer.fit_transform([text])
feature_names = vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
cluster_keywords = {}
for i in range(5):
cluster_indices = np.where(tags == i)[0]
if len(cluster_indices) > 0:
top_indices = np.argsort(tfidf[cluster_indices].toarray().sum(axis=0))[-3:]
cluster_keywords[f'tag_{i}'] = [feature_names[idx] for idx in top_indices]
return cluster_keywords
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
五、质量验证与监控
1. 解析质量评估指标
def evaluate_parsing_quality(original, parsed):
# 内容保留率
original_words = set(jieba.cut(original))
parsed_words = set(jieba.cut(parsed['text']))
retention_rate = len(parsed_words & original_words) / len(original_words)
# 结构完整性得分
structure_score = 0
if parsed.get('sections'):
structure_score = min(1.0, len(parsed['sections']) / 5) # 假设至少应有5个章节
# 表格提取准确率
table_score = 1.0 if parsed.get('tables') else 0
return {
'retention_rate': retention_rate,
'structure_score': structure_score,
'table_score': table_score,
'overall': 0.6*retention_rate + 0.2*structure_score + 0.2*table_score
}
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
2. 实时监控告警
class ParsingMonitor:
def __init__(self, threshold=0.85):
self.threshold = threshold
self.baseline = None
def update_baseline(self, baseline_metrics):
self.baseline = baseline_metrics
def check_anomaly(self, current_metrics):
if not self.baseline:
return False
deviations = {
'retention': abs(current_metrics['retention_rate'] - self.baseline['retention_rate']),
'structure': abs(current_metrics['structure_score'] - self.baseline['structure_score'])
}
if any(v > 0.15 for v in deviations.values()):
alert_msg = f"质量下降警告:保留率偏差{deviations['retention']:.2f},结构偏差{deviations['structure']:.2f}"
send_alert(alert_msg)
return True
return False
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
六、生产环境优化实践
1. 分布式文档处理
from multiprocessing import Pool
def batch_parse_documents(file_list, workers=4):
with Pool(workers) as pool:
results = pool.map(parse_document, file_list)
# 结果整合与质量控制
valid_docs = []
for res in results:
if res['quality_score'] > 0.8:
valid_docs.append(res)
else:
logging.warning(f"低质量解析: {res['file_path']}")
return valid_docs
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2. 增量索引更新
class IncrementalIndexer:
def __init__(self, vector_db):
self.db = vector_db
self.version_control = {}
def update_index(self, new_docs, modified_docs=[]):
# 处理新增文档
new_ids = self.db.insert([doc['embedding'] for doc in new_docs])
# 处理修改文档
for doc in modified_docs:
self.db.update(doc['id'], doc['embedding'])
# 版本记录
self.version_control[datetime.now()] = {
'new': len(new_docs),
'updated': len(modified_docs)
}
return new_ids
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
3. 容错处理机制
def robust_parsing(file_path):
max_retries = 3
backoff_time = 1
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
return parse_document(file_path)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"解析失败 (尝试 {attempt+1}): {str(e)}")
if attempt < max_retries - 1:
time.sleep(backoff_time * (attempt + 1))
else:
return {
'text': backup_text_extraction(file_path),
'error': str(e),
'quality': 'low'
}
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
七、领域特定优化案例
1. 法律文档处理
def legal_document_parser(text):
# 条款提取
clauses = re.findall(r'第[一二三四五六七八九十]+条.*?(?=第[一二三四五六七八九十]+条|$)', text, re.DOTALL)
# 当事人识别
parties = []
for clause in clauses[:3]: # 通常在前三条出现
if '甲方' in clause or '乙方' in clause:
parties.extend(re.findall(r'(甲方|乙方).*?[::](.*?)[\n。]', clause))
return {
'clauses': clauses,
'parties': dict(parties),
'effective_date': extract_effective_date(text)
}
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2. 科研论文处理
def research_paper_parser(text):
sections = {
'abstract': extract_section(text, ['摘要', 'Abstract']),
'methodology': extract_section(text, ['方法', 'Methodology']),
'references': extract_references(text)
}
# 公式和图表引用
equations = re.findall(r'\$.*?\$|\\begin{equation}.*?\\end{equation}', text, re.DOTALL)
fig_refs = re.findall(r'图\s*\d+', text)
return {
**sections,
'equations': equations,
'figure_refs': fig_refs,
'citations': len(sections['references'])
}
AI写代码python运行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
通过以上系统化的文档解析方案,我们能够在RAG系统中实现:
- 高精度内容提取:保持原始信息的完整性
- 智能结构分析:保留文档逻辑关系
- 领域自适应:针对不同文档类型优化处理
- 生产级鲁棒性:处理各种边缘情况
实际应用中建议持续迭代优化解析规则,特别是在以下场景:
- 当新增文档类型时
- 发现检索结果出现信息缺失时
- 业务领域术语更新时
- 文档结构发生重大变化时
 商务合作/携手共进/技术交流
商务合作/携手共进/技术交流
 微信名片
微信名片
已关注
-
26
-

-
27
-
0
-

专栏目录
RAG私域问答场景升级版方案(第二期方案)[2]:工业级别构建私域问答(业务问题、性能问题、安全成本问题等详细解决方案)

850
RAG私域问答场景升级版方案(第二期方案)[2]:工业级别构建私域问答(业务问题、性能问题、安全成本问题等详细解决方案)

247

1万+

938

2868

1631
【文档智能 & RAG】RAG新基建-RAG性能增强关键技术点及通用文档解析工具-TextIn
余俊晖,NLP炼丹师,目前专注自然语言处理领域研究。曾获得国内外自然语言处理算法竞赛TOP奖项近二十项。

2512

502
企业级RAG落地避坑指南:从0到1拆解全流程优化方案,解锁高效生产级应用!

824
【四.RAG技术与应用】【9.向量数据库:RAG中的智能存储解决方案】
商务合作|问题讨论|交流学习 请联系作者微信,加微信请务必注明来意,博客主页有联系方式

220

1428

269

348

223

705

214

208
1.通道注意力模块复习 2.空间注意力模块 3.CBAM的定义

67

610
- 公安备案号11010502030143
- 京ICP备19004658号
- 京网文〔2020〕1039-165号
- 经营性网站备案信息
- 北京互联网违法和不良信息举报中心
- 家长监护
- 网络110报警服务
- 中国互联网举报中心
- Chrome商店下载
- 账号管理规范
- 版权与免责声明
- 版权申诉
- 出版物许可证
- 营业执照
- ©1999-2025北京创新乐知网络技术有限公司
博客等级

码龄11年
 全栈领域优质创作者
全栈领域优质创作者
 博客专家认证
博客专家认证
1万+
点赞
1万+
收藏
2万+
粉丝
TA的精选
- 新 深度学习微调中的优化器全景解析:从理论到实践
1207 阅读
- 新 PEFT(参数高效微调)技术全面解析:原理、方法与实战应用
796 阅读
- 热 C盘深度清理——小番茄评测
40594 阅读
- 热 DeepSeek:从入门到精通 —— 探索国产顶尖代码大模型的无限可能
15999 阅读
- 热 大模型巅峰对决:DeepSeek vs GPT-4/Claude/PaLM-2 全面对比与核心差异揭秘
15501 阅读
大家在看
- 【PHP开发900个实用技巧】498.事件溯源:可追溯状态变更的架构设计
- 银河麒麟桌面操作系统V10SP1 2403 的安装教程
- Access开发邮件接收功能
- 基于springboot的学生用品采购系统 编辑 474
- Bash Shell面试题高级汇总002 编辑 246
分类专栏
- 编辑Vue3+TypeScript+DeepSeek全栈开发实战付费62篇
- 编辑AI158篇
- 编辑java77篇
- 编辑golang4篇
- 编辑python22篇
- 编辑javascript44篇
- 编辑css16篇
- 编辑网络协议5篇
- 编辑前端221篇
- 编辑程序员10篇
- 编辑编辑器5篇
- 编辑vue103篇
- 编辑react33篇
- 编辑c++16篇
- 编辑uniapp7篇
- 编辑微信小程序5篇
- 编辑ide2篇
- 编辑鸿蒙38篇
- 编辑ecmascript7篇
- 编辑vscode2篇
- 编辑typescript4篇
- 编辑屏幕适配3篇
- 编辑echarts1篇
展开全部

上一篇:
下一篇:
目录
收起




AI提问

评论

笔记
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容



 400-660-0108
400-660-0108













所有评论(0)