Android 蓝牙通信(通过 BluetoothSocket 传输文件/文本)
Android 蓝牙通信,通过BluetoothSocket方式建立长连接并传输文本或文件。前段时间有个项目的功能需求是:AR眼镜通过蓝牙的方式连接北斗设备,当北斗设备收到文本/语音/图片消息时转发到AR眼镜上,AR眼镜也可以发送文本/语音/图片数据到北斗设备上并转发到指定的目标地址。刚开始在百度和github找了许多方法都不尽人意而且大多数据传输都仅仅停留在文字方面,不过好在最后临近项目dead
前言:Android 蓝牙通信,通过BluetoothSocket方式建立长连接并传输文本或文件。前段时间有个项目的功能需求是:AR眼镜通过蓝牙的方式连接北斗设备,当北斗设备收到文本/语音/图片消息时转发到AR眼镜上,AR眼镜也可以发送文本/语音/图片数据到北斗设备上并转发到指定的目标地址。刚开始在百度和github找了许多方法都不尽人意而且大多数据传输都仅仅停留在文字方面,不过好在最后临近项目deadline时想到了一种傻瓜也简单的方法实现了这个需求。如果你也恰好遇到了这种 "通过蓝牙或其他低效率的方式传输文件" 类似的情景可以参考这篇文章,希望这篇文章对你的思路有所启发,如果有错漏或可优化之处也欢迎提醒。
一、上代码
DEMO:https://github.com/LXTTTTTT/Android-Bluetooth-Chat-And-Transfer
源码资源:https://download.csdn.net/download/lxt1292352578/88677601
直接复制就能使用
package com.example.sockettransfer;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothServerSocket;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.util.Log;
import org.greenrobot.eventbus.EventBus;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
// 蓝牙 Socket 工具
public class BluetoothSocketUtil {
private static String TAG = "BluetoothSocketUtil";
private Context context;
private BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter;
private BluetoothSocket bluetoothSocket;
public BluetoothDevice nowDevice;
private InputStream inputStream;
private OutputStream outputStream;
private Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDeviceList;
private List<BluetoothDevice> devices = new ArrayList();
private ReceiveDataThread receiveDataThread;
private ListenThread listenThread;
private final UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString("550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000");
private int state = 0;
private final int STATE_DISCONNECT = 0;
private final int STATE_CONNECTING = 1;
private final int STATE_CONNECTED = 2;
public boolean isConnectedDevice = false;
public boolean isSendFile = false;
// 单例 ----------------------------------------------------------------
private static BluetoothSocketUtil bluetoothSocketUtil;
public static BluetoothSocketUtil getInstance() {
if (bluetoothSocketUtil == null) {
bluetoothSocketUtil = new BluetoothSocketUtil();
}
return bluetoothSocketUtil;
}
public BluetoothSocketUtil() {
bluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
}
public void init(Context context){
this.context = context;
registerBroadcast();
listen(); // 开启设备连接监听
}
public Set<BluetoothDevice> getPairedDeviceList(){
if(bluetoothAdapter!=null){
return bluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices();
}else {
return null;
}
}
public void searchDevice(){
if(bluetoothAdapter==null){return;}
if (bluetoothAdapter.isDiscovering()) {
bluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
}
devices.clear();
bluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();
}
public void stopSearch() {
if (bluetoothAdapter != null && bluetoothAdapter.isDiscovering()) {
bluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
}
}
public void registerBroadcast() {
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction("android.bluetooth.device.action.FOUND");
filter.addAction("android.bluetooth.adapter.action.DISCOVERY_FINISHED");
filter.addAction("android.bluetooth.device.action.ACL_CONNECTED");
filter.addAction("android.bluetooth.device.action.ACL_DISCONNECTED");
context.registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
Log.e(TAG, "广播注册成功");
}
// 蓝牙连接监听广播
private final BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
Log.e(TAG, "收到广播: "+action);
if ("android.bluetooth.device.action.FOUND".equals(action)) {
BluetoothDevice device = (BluetoothDevice) intent.getParcelableExtra("android.bluetooth.device.extra.DEVICE");
if (device.getName() == null) {return;}
if (device.getBondState() != BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED) {
if (!devices.contains(device)) {
devices.add(device);
if(onBluetoothSocketWork!=null){onBluetoothSocketWork.onDiscoverNewDevice(devices);}
}
}
}
}
};
public void listen(){
if(state!=STATE_DISCONNECT){return;}
if(listenThread!=null){
listenThread.cancel();
listenThread = null;
}
listenThread = new ListenThread();
listenThread.start();
}
private class ListenThread extends Thread{
private BluetoothServerSocket bluetoothServerSocket;
private boolean listen = false;
public ListenThread(){
try {
bluetoothServerSocket = bluetoothAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord("name", MY_UUID);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
listen = true;
Log.e(TAG, "开启设备连接监听"+listen+"/"+(state==STATE_DISCONNECT) );
while (listen && state==STATE_DISCONNECT){
try {
bluetoothSocket = bluetoothServerSocket.accept();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (bluetoothSocket != null) {
try {
Log.e(TAG, "监听到设备连接" );
state = STATE_CONNECTING;
if(onBluetoothSocketWork!=null){onBluetoothSocketWork.onConnecting();}
inputStream = bluetoothSocket.getInputStream();
outputStream = bluetoothSocket.getOutputStream();
state = STATE_CONNECTED;
isConnectedDevice = true;
nowDevice = bluetoothSocket.getRemoteDevice();
receiveDataThread = new ReceiveDataThread();
receiveDataThread.start(); // 开启读数据线程
if(onBluetoothSocketWork!=null){onBluetoothSocketWork.onConnected(nowDevice.getName());}
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.CONNECT_DEVICE;
msg.content = nowDevice.getName();
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void cancel(){
listen = false;
try {
if(bluetoothServerSocket!=null){
bluetoothServerSocket.close();
bluetoothServerSocket=null;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void connect(BluetoothDevice device) {
Log.e(TAG, "连接设备: " + device.getName()+"/"+state);
if (state == STATE_CONNECTING || state == STATE_CONNECTED) {return;}
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
bluetoothSocket = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
state = STATE_CONNECTING;
if(onBluetoothSocketWork!=null){onBluetoothSocketWork.onConnecting();}
bluetoothSocket.connect();
inputStream = bluetoothSocket.getInputStream();
outputStream = bluetoothSocket.getOutputStream();
state = STATE_CONNECTED;
isConnectedDevice = true;
nowDevice = device;
receiveDataThread = new ReceiveDataThread();
receiveDataThread.start(); // 开启读数据线程
if(onBluetoothSocketWork!=null){onBluetoothSocketWork.onConnected(device.getName());}
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.CONNECT_DEVICE;
msg.content = device.getName();
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
disconnect();
}
}
}).start();
}
private byte[] readBuffer = new byte[1024];
private class ReceiveDataThread extends Thread{
private boolean receive = false;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
@Override
public void run() {
if(inputStream==null){return;}
receive = true;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while (receive){
try{
int size = inputStream.read(buffer);
if(size>0){
baos.write(buffer, 0, size);
readBuffer = baos.toByteArray();
receiveData(readBuffer);
baos.reset();
}else if(size==-1){
Log.e(TAG, "BluetoothSocket: 断开了");
cancel();
disconnect();
break;
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
// 断开连接了,通常 inputStream.read 时触发这个
Log.e(TAG, "BluetoothSocket: 读取数据错误");
cancel();
disconnect();
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.DISCONNECT_DEVICE;
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
}
}
}
public void cancel(){
receive = false;
}
}
/**
* 自定义一个标识头来描述发送的数据
* 格式:$*x*$0000xxxx
* 前五位 "$*x*$" 中的x为可变数字,表示发送数据的类型,我这里用到的是 "1"-文本,"2"-图片,根据实际需求自定义
* 后八位 "0000xxxx" 为发送数据内容的长度,格式为固定8位的16进制数据,不足8位则高位补0,最多可以表示 0xFFFFFFFF 个字节,如果发送的文件超出了这个范围则需要自行修改
* 例子:
* 发送文本数据 "测试" 打包标识 "$*1*$" + 将"测试"以GB18030标准转化为byte[]后的长度(hex) —— "$*1*$00000004",后续发送转化后的byte[]
* 发送图片数据 打包标识 "$*2*$" + 读取指定路径的文件byte[]的长度(hex) —— "$*2*$0033CE27",后续发送读取到的文件byte[]
**/
public void send_text(String data_str){
if(outputStream==null){return;}
if(isSendFile){return;}
// 建议使用线程池
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
byte[] data_bytes = data_str.getBytes("GB18030");
String head = "$*1*$"+String.format("%08X", data_bytes.length);
Log.e(TAG, "发送文本,打包标识头: "+head );
outputStream.write(head.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.write(data_bytes);
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.SEND_TEXT;
msg.content = data_str;
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
public void send_file(String path){
if(outputStream==null){return;}
if(isSendFile){return;}
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.exists() || !file.isFile()) {
Log.e(TAG, "文件不存在");
return;
}else {
Log.e(TAG, "开始发送文件");
isSendFile = true;
}
byte[] file_byte = fileToBytes(path);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
String head;
head = "$*2*$"+String.format("%08X", file_byte.length);
Log.e(TAG, "发送文件,打包标识头: "+head );
outputStream.write(head.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.write(file_byte);
isSendFile = false;
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.SEND_FILE;
msg.content = path;
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "文件发送失败", e);
isSendFile = false;
}
}
}).start();
}
private boolean startReceiveFile = false; // 是否开始接收文件数据
private ByteArrayOutputStream file_bytes_baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
private long file_length = 0; // 文件数据长度
private int message_type = 0; // 消息类型:0-初始状态 1-文本 2-图片
private void receiveData(byte[] data_bytes) {
Log.e(TAG, "处理数据长度: "+data_bytes.length );
// 还没收到标识头,如果一直没有收到就舍弃直到收到标识头为止
if(!startReceiveFile){
try{
// 首先判断收到的数据是否包含了标识头
String data_str = new String(data_bytes,StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
int head_index = data_str.indexOf("$*");
// Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\$\\*\\d\\*\\$");
// Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(data_str);
// 有头
if(head_index>=0){
startReceiveFile = true;
String head = data_str.substring(head_index,head_index+13); // $*1*$00339433
String msg_type = head.substring(0,5); // $*1*$
if(msg_type.contains("1")){message_type = 1;} else {message_type = 2;}
String length_hex = head.substring(5); // 00339433
file_length = Long.parseLong(length_hex,16); // 解析文件数据长度
Log.e(TAG, "解析标识头 head: "+head+" 文件数据长度:"+file_length);
file_bytes_baos.write(data_bytes,13,data_bytes.length-13); // 存储标识以外的文件数据
// 如果文本数据的话则只有一波,这时要判断收到的数据总长度是否文件数据长度+标识头数据长度
if(data_bytes.length==file_length+13){
parseData();
}
}else {
Log.e(TAG, "receiveData: 没有头"+data_str );
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 后续的都是文件数据
else {
try {
file_bytes_baos.write(data_bytes); // 保存文件数据
Log.e(TAG, "总长度: "+file_length+" /已接收长度: "+file_bytes_baos.size());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "文件数据保存失败");
}
// 每次接收完数据判断一下存储的文件数据达到数据长度了吗
if(file_bytes_baos.size()>=file_length){
parseData();
}
}
}
public void parseData(){
if(message_type==0){return;}
if(message_type==1){
String content = "";
try {
content = new String(file_bytes_baos.toByteArray(),"GB18030"); // 文本消息直接转码
Log.e(TAG, "数据接收完毕,文本:"+content);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 初始化状态
startReceiveFile = false;
file_bytes_baos.reset();
file_length = 0;
message_type = 0;
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.RECEIVE_TEXT;
msg.content = content;
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
}else if(message_type==2){
Log.e(TAG, "数据接收完毕,图片" );
// 保存图片数据
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 默认保存在系统的 Download 目录下,自行处理
String imgFilePath= Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS).getAbsolutePath() + "/receiveImage.jpg";
File imageFile = new File(imgFilePath);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(imageFile)) {
fos.write(file_bytes_baos.toByteArray());
}
// 初始化状态
startReceiveFile = false;
file_bytes_baos.reset();
file_length = 0;
message_type = 0;
EventMsg msg = new EventMsg();
msg.msgType = EventMsg.RECEIVE_FILE;
msg.content = imgFilePath;
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
// 读取文件数据
public static byte[] fileToBytes(String filePath){
File file = new File(filePath);
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
return bos.toByteArray();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public void disconnect(){
try {
if(inputStream!=null){
inputStream.close();
inputStream=null;
}
if(outputStream!=null){
outputStream.close();
outputStream=null;
}
if(receiveDataThread!=null){
receiveDataThread.cancel();
receiveDataThread = null;
}
if(bluetoothSocket!=null){
bluetoothSocket.close();
bluetoothSocket = null;
}
if(onBluetoothSocketWork!=null){onBluetoothSocketWork.onDisconnect();}
state = STATE_DISCONNECT;
isConnectedDevice = false;
nowDevice = null;
listen(); // 断开后重新开启设备连接监听
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void destroy(){
disconnect();
if(listenThread!=null){listenThread.cancel();listenThread=null;}
if(context!=null){context.unregisterReceiver(receiver);}
}
// 接口 ---------------------------------------------
public interface OnBluetoothSocketWork{
void onConnecting();
void onConnected(String device_name);
void onDisconnect();
void onDiscoverNewDevice(List<BluetoothDevice> devices);
}
public OnBluetoothSocketWork onBluetoothSocketWork;
public void setOnBluetoothSocketWork(OnBluetoothSocketWork onBluetoothSocketWork){
this.onBluetoothSocketWork = onBluetoothSocketWork;
}
}
二、连接流程说明
1. 连接说明
在 BluetoothSocket 通信中主动发起连接的一方作为客户端,被动监听及接受连接的一方作为服务端。他们在连接时需要保证连接/监听过程中设置的 UUID 一致,并且需要先完成系统的配对操作,这里的配对操作有两种方式:
一种是先在系统的蓝牙页面手动配对,然后在APP里面获取已配对蓝牙并直接连接
第二种则是在APP里面扫描蓝牙设备并在首次连接时完成配对操作,但需要注意的一点是设备的蓝牙默认是无法被发现的因此作为接收方的服务端在连接之前需要开启蓝牙可被观测
new Intent(android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE);在完成配对并且 UUID 一致的情况下直接连接即可
2. 客户端连接
在进行连接之前先要获取到蓝牙设备,获取蓝牙设备的方式有两种,一种是直接获取系统的已配对设备
BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter().getBondedDevices();另一种则是通过开启蓝牙扫描并注册广播监听来获取扫描到的设备,这种方式则需要照应上文中提到的首次连接配对
BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter().startDiscovery();获取目标设备之后设置UUID创建 BluetoothSocket ,连接并取得对应的输入/输出流,同时开启子线程监听输入流的数据输出情况,在这里当这个读取数据线程的输入流断开时可视作Socket长连接的断开。创建BluetoothSocket的方法有两个 createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord 和 createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord 他们的主要区别在于连接的安全性,这里仅以安全连接作为例子
BluetoothSocket bluetoothSocket = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
bluetoothSocket.connect();
InputStream inputStream = bluetoothSocket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = bluetoothSocket.getOutputStream();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[1024];
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
if(inputStream==null){return;}
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
state = STATE_CONNECTED;
while (true){
try{
int size = inputStream.read(buffer);
if(size>0){
baos.write(buffer, 0, size);
readBuffer = baos.toByteArray();
receiveData(readBuffer); // 解析数据
baos.reset();
}else if(size==-1){
Log.e(TAG, "BluetoothSocket: 断开了");
break;
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
// 断开连接了,通常 inputStream.read 时触发这个
Log.e(TAG, "BluetoothSocket: 读取数据错误");
state = STATE_DISCONNECT;
}
}
}
}).start();
3. 服务端监听
服务端作为接受方不需要主动获取蓝牙设备,只需要开启监听线程等待连接即可
private BluetoothServerSocket bluetoothServerSocket;
private BluetoothSocket bluetoothSocket;
private InputStream inputStream;
private OutputStream outputStream;
private ListenThread listenThread;
public void listen(){
if(state!=STATE_DISCONNECT){return;}
if(listenThread!=null){
listenThread.cancel();
listenThread = null;
}
listenThread = new ListenThread();
listenThread.start();
}
private class ListenThread extends Thread{
private boolean listen = false;
public ListenThread(){
try {
bluetoothServerSocket = bluetoothAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord("name", MY_UUID);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
listen = true;
Log.e(TAG, "开启设备连接监听"+listen+"/"+(state==STATE_DISCONNECT) );
while (listen && state==STATE_DISCONNECT){
try {
if(bluetoothSocket==null){
bluetoothSocket = bluetoothServerSocket.accept();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (bluetoothSocket != null) {
try {
Log.e(TAG, "监听到设备连接" );
state = STATE_CONNECTING;
inputStream = bluetoothSocket.getInputStream();
outputStream = bluetoothSocket.getOutputStream();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[1024];
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
if(inputStream==null){return;}
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
state = STATE_CONNECTED;
while (true){
try{
int size = inputStream.read(buffer);
if(size>0){
baos.write(buffer, 0, size);
readBuffer = baos.toByteArray();
receiveData(readBuffer);
baos.reset();
}else if(size==-1){
Log.e(TAG, "BluetoothSocket: 断开了");
break;
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
// 断开连接了,通常 inputStream.read 时触发这个
Log.e(TAG, "BluetoothSocket: 读取数据错误");
state = STATE_DISCONNECT;
}
}
}
}).start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void cancel(){
listen = false;
try {
if (bluetoothServerSocket != null) {
bluetoothServerSocket.close();
bluetoothServerSocket = null;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}三、数据传输
1. 基本思路思路
其实整个连接流程非常简单,相对复杂的地方仅仅在于对流程的把控,这一点可以参考我的DEMO或者按照实际的需求自行调整。
本文的核心点在于数据传输功能,以往在项目中对数据传输的需求仅仅停留在文本数据的传输因此实现起来非常简单,只需要在发送时添加标识符并按照特定标准编码在接收时识别到标识符后转码并解析内容就好了。而本次的项目需求除了需要传输文本外还需要传输音频格式和图片格式的文件,按照以往的方法无法实现因此就到网上找了许多方法但是却发现大多都不尽人意,最后换了一种思路想到了一种比较简单的方法,经过验证也恰好可以满足本次需求。
总体思路很简单:传输的数据类型有三种,并且每次接收/处理数据之前要知道本次有效数据的长度和传输的数据类型是什么,再根据对应的类型对后续的特定长度的数据进行不同的处理。因此一个简单标识头就定义出来了,我只要在每次发送数据之前先封装一个标识头再发送后续的有效数据,而在接收时则根据这个标识头来判断数据类型和长度作不同处理即可
我定义的标识头格式很简单:"$*x*$"(x为数据类型:1-文本、2-图片、3-语音)+"固定8位长度的有效数据字节长度(16进制),不足8位则高位补0",以UTF-8标准转码
例如:
"$*1*$00000008********":具有8个字节长度的文本数据,将标识头后8位数据"********"以GB18030标准转化为字符串即可得到传输的文本内容
"$*2*$00078A00***...":具有494080个字节长度的图片数据,将标识头后494080位数据以jpg格式保存即可的得到传输内容
注意:这里定义的长度标识固定8位,最多能够表示0xFFFFFFFF个字节,按实际需求自行修改即可
2. 发送文本
发送文本数据之前先将文本内容以GB18030标准转为byte[],封装文本标识"$*1*$",将前面的文本byte[]长度转化为16进制并在高位补0封装长度标识,将封装好的标识头以UTF-8标准转码并发送然后再发送实际的文本数据即可
public void send_text(String data_str){
if(outputStream==null){return;}
if(isSendFile){return;}
// 建议使用线程池
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
byte[] data_bytes = data_str.getBytes("GB18030");
String head = "$*1*$"+String.format("%08X", data_bytes.length);
Log.e(TAG, "发送文本,打包标识头: "+head );
outputStream.write(head.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.write(data_bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}3. 发送文件(以图片为例)
发送文件数据之前先按照文件路径读取文件数据,封装文件标识"$*2*$",将前面的文件数据长度转化为16进制并在高位补0封装长度标识,将封装好的标识头以UTF-8标准转码并发送然后再发送实际的文件数据即可
public void send_file(String path){
if(outputStream==null){return;}
if(isSendFile){return;}
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.exists() || !file.isFile()) {
Log.e(TAG, "文件不存在");
return;
}else {
Log.e(TAG, "开始发送文件");
isSendFile = true;
}
byte[] file_byte = fileToBytes(path);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
String head;
head = "$*2*$"+String.format("%08X", file_byte.length);
Log.e(TAG, "发送文件,打包标识头: "+head );
outputStream.write(head.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.write(file_byte);
isSendFile = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "文件发送失败", e);
isSendFile = false;
}
}
}).start();
}读取文件数据方法
public static byte[] fileToBytes(String filePath){
File file = new File(filePath);
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
return bos.toByteArray();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}4. 解析数据
当数据长度超出最大单次传输数据长度限制时就会以分包的形式进行传输,而文本数据的长度大多都超出了这个限制,因此在接收文件数据时往往是按照多个分包数据的形式来处理。因而我们在每次处理新数据时的第一件事就是判断本轮数据是首条包含了标识头的数据还是后续的文件数据。首先初始化一个开始接收文件数据的标识变量,每次接收到新数据时将本轮数据以UTF-8标准转化为字符并判断是否包含了前面定义的标识头,如果有则表示开始接收新一轮的文件数据,将标识修改为true,当标识为true时则表示本轮收到的数据是文件数据,直接存储到字节数组缓存中,直到存储的长度达到了解析出来的有效数据长度才表示本轮文件数据接收完毕并修改标识为false等待下一个标识头的到来
private boolean startReceiveFile = false; // 是否开始接收文件数据
private ByteArrayOutputStream file_bytes_baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
private long file_length = 0; // 文件数据长度
private int message_type = 0; // 消息类型:0-初始状态 1-文本 2-图片
private void receiveData(byte[] data_bytes) {
Log.e(TAG, "处理数据长度: "+data_bytes.length );
// 还没收到标识头,如果一直没有收到就舍弃直到收到标识头为止
if(!startReceiveFile){
try{
// 首先判断收到的数据是否包含了标识头
String data_str = new String(data_bytes,StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
int head_index = data_str.indexOf("$*");
// Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\$\\*\\d\\*\\$");
// Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(data_str);
// 有头
if(head_index>=0){
startReceiveFile = true;
String head = data_str.substring(head_index,head_index+13); // $*1*$00339433
String msg_type = head.substring(0,5); // $*1*$
if(msg_type.contains("1")){message_type = 1;} else {message_type = 2;}
String length_hex = head.substring(5); // 00339433
file_length = Long.parseLong(length_hex,16); // 解析文件数据长度
Log.e(TAG, "解析标识头 head: "+head+" 文件数据长度:"+file_length);
file_bytes_baos.write(data_bytes,13,data_bytes.length-13); // 存储标识以外的文件数据
// 如果是文本数据的话则只有一波,这时要判断收到的数据总长度是否文件数据长度+标识头数据长度
if(data_bytes.length==file_length+13){
parseData(); // 处理数据
}
}else {
Log.e(TAG, "receiveData: 没有头"+data_str );
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 后续的都是文件数据
else {
try {
file_bytes_baos.write(data_bytes); // 保存文件数据
Log.e(TAG, "总长度: "+file_length+" /已接收长度: "+file_bytes_baos.size());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "文件数据保存失败");
}
// 每次接收完数据判断一下存储的文件数据达到数据长度了吗
if(file_bytes_baos.size()>=file_length){
parseData(); // 处理数据
}
}
}处理数据 :既然已经知道数据的类型并且拿到了他的原始数据那处理起来就很简单了,如果是文本的话直接将数据按照GB18030标准转码,如果是文件的话直接将数据按照特定的格式存储到指定路径就行了
public void parseData(){
if(message_type==0){return;}
if(message_type==1){
String content = "";
try {
content = new String(file_bytes_baos.toByteArray(),"GB18030"); // 文本消息直接转码
Log.e(TAG, "数据接收完毕,文本:"+content);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 初始化状态
startReceiveFile = false;
file_bytes_baos.reset();
file_length = 0;
message_type = 0;
}else if(message_type==2){
Log.e(TAG, "数据接收完毕,图片" );
// 保存图片数据
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 默认保存在系统的 Download 目录下,自行处理
String imgFilePath=Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS).getAbsolutePath() + "/receiveImage.jpg";
File imageFile = new File(imgFilePath);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(imageFile)) {
fos.write(file_bytes_baos.toByteArray());
}
// 初始化状态
startReceiveFile = false;
file_bytes_baos.reset();
file_length = 0;
message_type = 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}四、使用例子
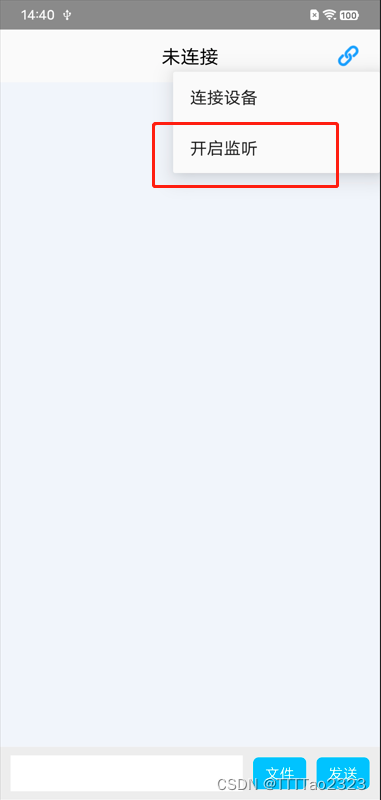
客户端开启蓝牙可被发现

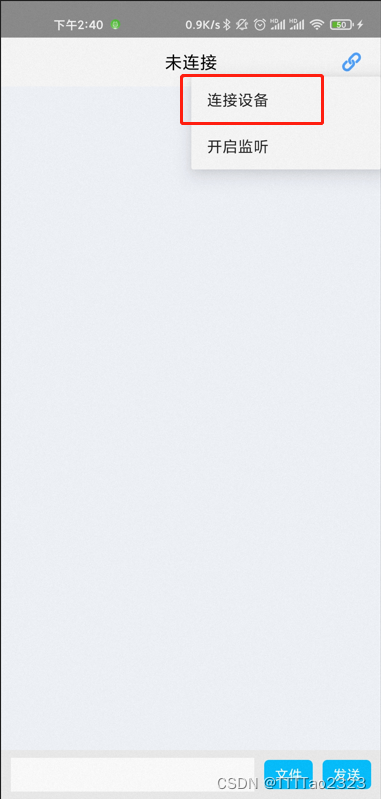
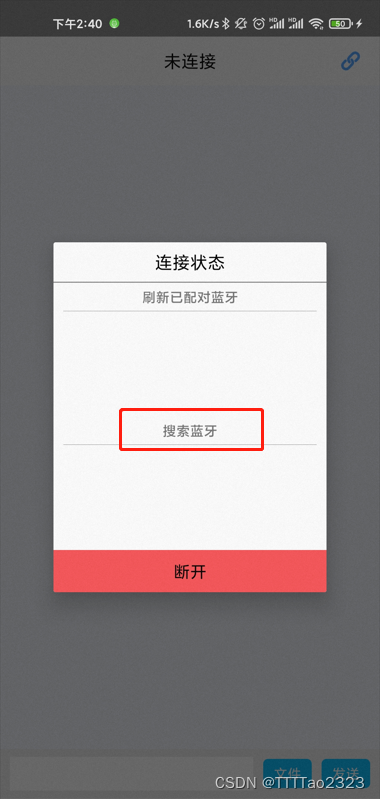
服务端扫描/连接目标设备

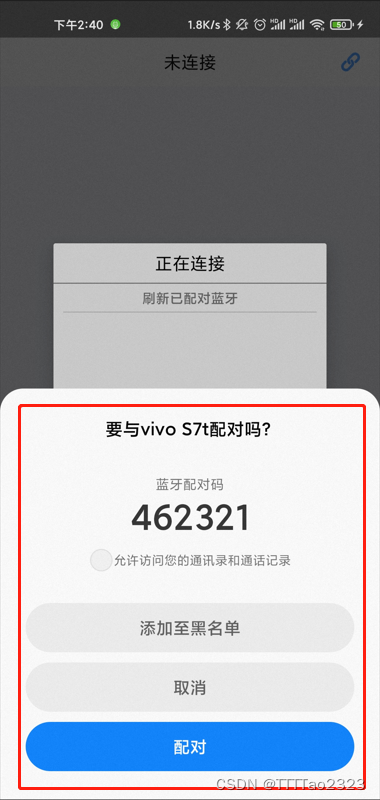
首次连接需要进行配对操作


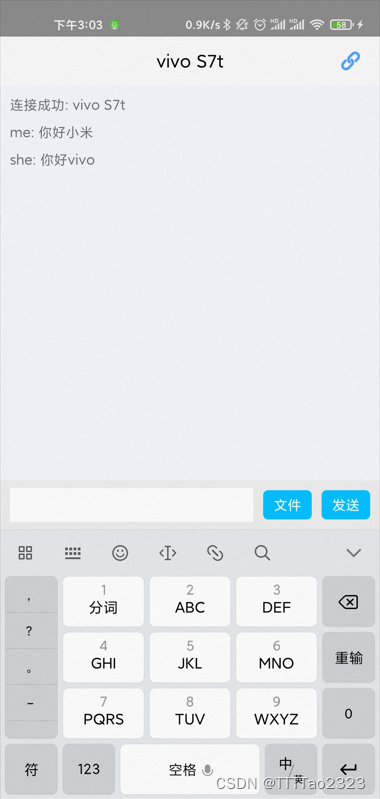
连接成功发送文本消息

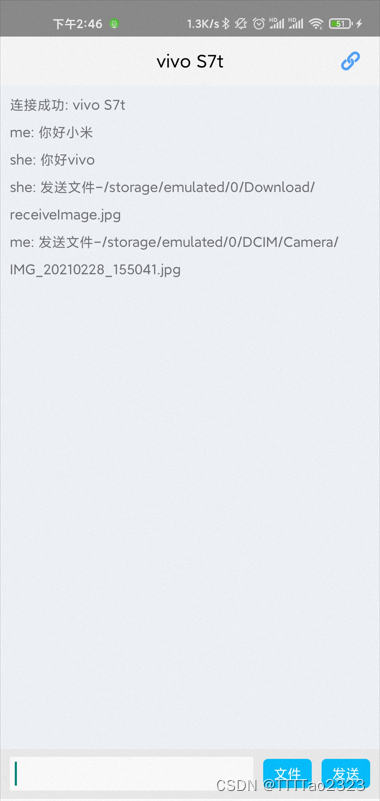
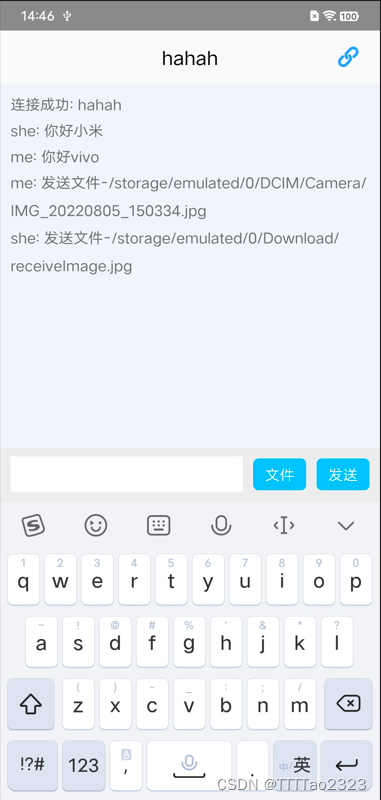
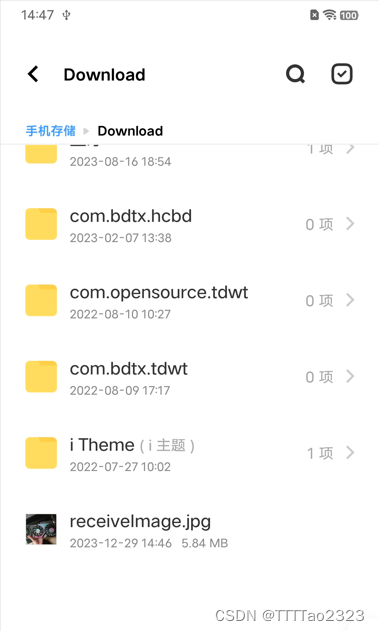
发送图片

五、小结
总体流程很简单,相对复杂的部分在于文件数据的传输,但只要找对了思路实现起来也并不难,在这里对连接和发送数据的流程做一个小结
1. 连接
服务端(被连接方)开启蓝牙可被侦测并不断监听指定UUID的客户端连接操作 → 客户端(连接方)扫描并连接目标设备 → 如果双方未配对则进行配对操作 → 连接成功各自获取输入/输出流 → 开启子线程监听输入流的数据输出/通过输出流写入数据
2. 通信
发送方:将需要发送的文本/文件转化为byte[] → 将消息类型和数据长度封装成特定格式的标识头 → 将标识头转化为byte[]并发送 → 发送文本/文件数据
接收方:收到数据后转化为文本判断是否包含标识头 → 解析标识头得到数据类型和有效数据长度 → 如果当前已接收的数据长度未达到有效数据长度则继续接收 → 如果长度达到则根据消息类型处理数据
3. DEMO
github:https://github.com/LXTTTTTT/Android-Bluetooth-Chat-And-Transfer
DEMO资源:https://download.csdn.net/download/lxt1292352578/88677601
完
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容










所有评论(0)