14.Flink双流Join——DataStream
本文介绍了基于flink datastream的双流join
DataStream的双流Join
一、实现机制
流Join和批Join的不同点在于批数据是“有界”的,而流数据是“无界”的,在“无界”的数据上做Join,我们首先要做的就是确定一个范围,从“无界”数据上找到一个“界”,然后让这个范围内的数据做Join。
在流数据中的“界”有两种,一种是窗口,包含滚动窗口、滑动窗口、事件窗口;一种是间隔,即a流中的数据要和b流哪些范围的数据做join。
Flink Join底层实现都是基于状态,它会把我们所定义的“界”内的数据保存到状态中,当这个“界”内的数据执行后,再清空状态。
二、基于窗口
2.1内连接
内连接是Flink内置的操作,我们可以直接用
stream.join(otherStream)
.where(<KeySelector>)
.equalTo(<KeySelector>)
.window(<WindowAssigner>) //窗口定义,这里可以用滚动窗口、滑动窗口、事件窗口
.apply(<JoinFunction> / <FlatJoinFunction>);
一个具体事例:
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result = stream1
.join(stream2)
.where(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.equalTo(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(1)))
.apply( new JoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Integer> join(Tuple2<String, Integer> first, Tuple2<String, Integer> second)
throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<>(first.f0, first.f1 + second.f1);
}
}
);
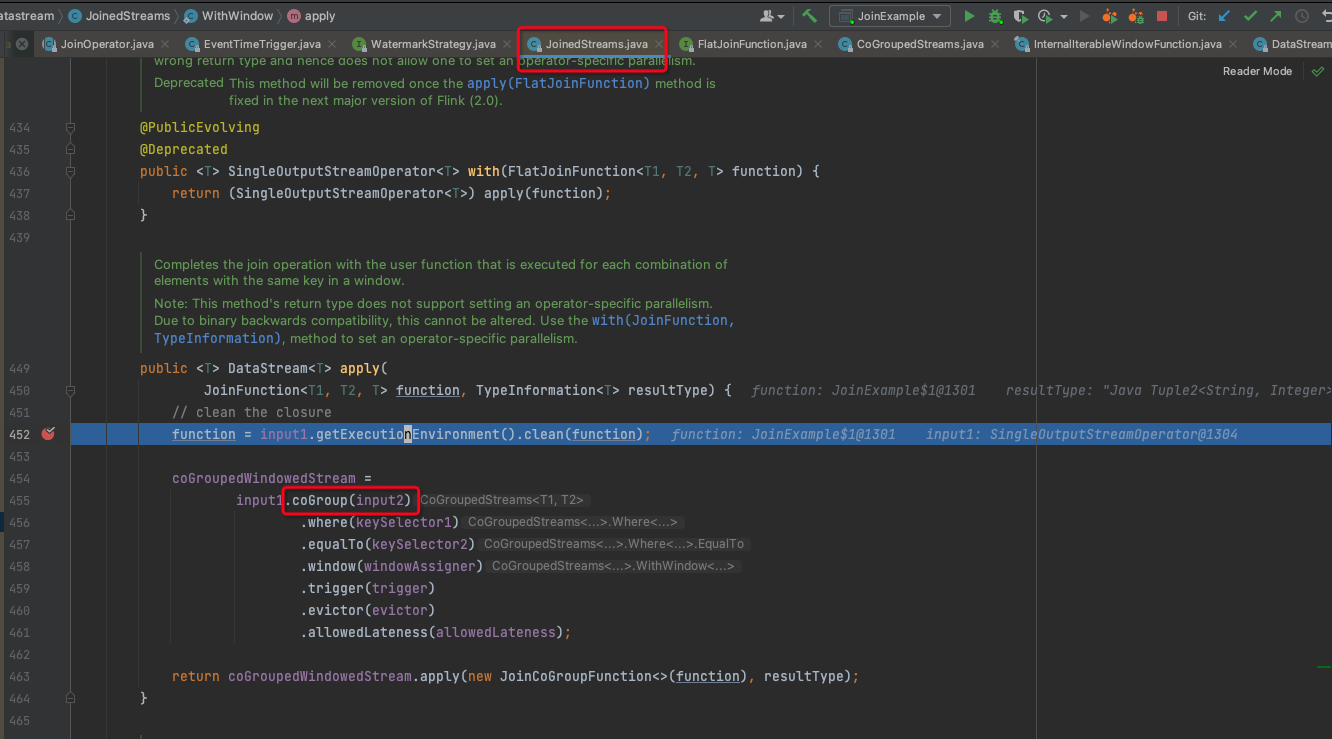
join的底层实现是用的coGroup实现的,在调用JoinedStreams的apply方法时,会将JoinedStream转成CoGroupedStream,源码如下图:

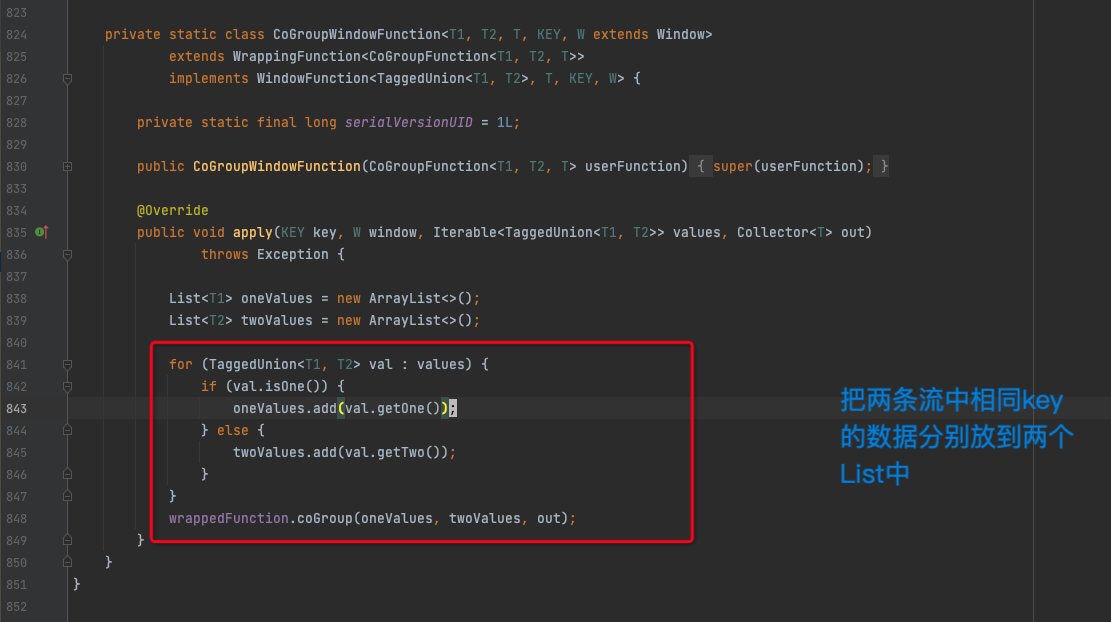
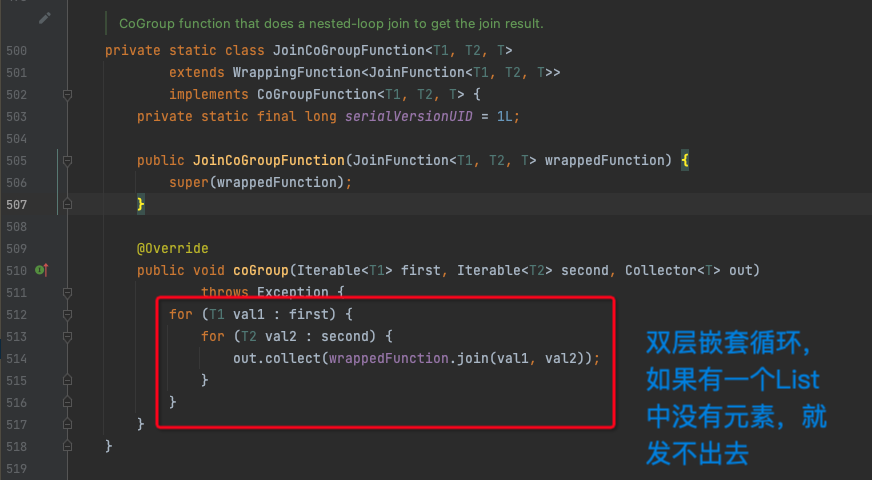
在CoGroupedStream的apply方法中,会把两条流中相同key的数据放到两个ArrayList oneValues和twoValues中,然后再用双层循环遍历这两个List,如果某一个List中没有元素,就会有一个循环进不去,导致数据发不出来,这样就实现了inner join
源码如下:
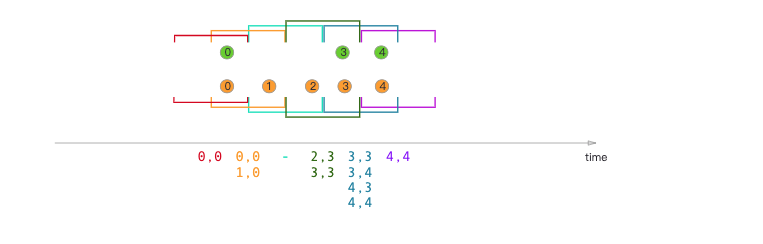
2.1.1 滚动窗口Join

2.1.2 滑动窗口Join
2.1.3 事件窗口Join
2.2外连接
Flink原生的sql语法只支持内连接,如果我们想实现外连接,用内连接的思路即可,即用cogroup实现,
DataStream<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>> result = stream1
.coGroup(stream2)
.where(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.equalTo(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(1)))
.apply(new CoGroupFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>>() {
@Override
public void coGroup(Iterable<Tuple2<String, Integer>> first, Iterable<Tuple2<String, Integer>> second, Collector<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>> out) throws Exception {
for(Tuple2<String, Integer> left: first) {
boolean flag = false;
for(Tuple2<String, Integer> right: second) {
flag = true;
out.collect(new Tuple3<>(left.f0, left.f1, right.f1));
}
if(!flag) {
out.collect(new Tuple3<>(left.f0, left.f1, null));
}
}
}
}
);
三、基于Interval

3.1 IntervalJoinOperator概述
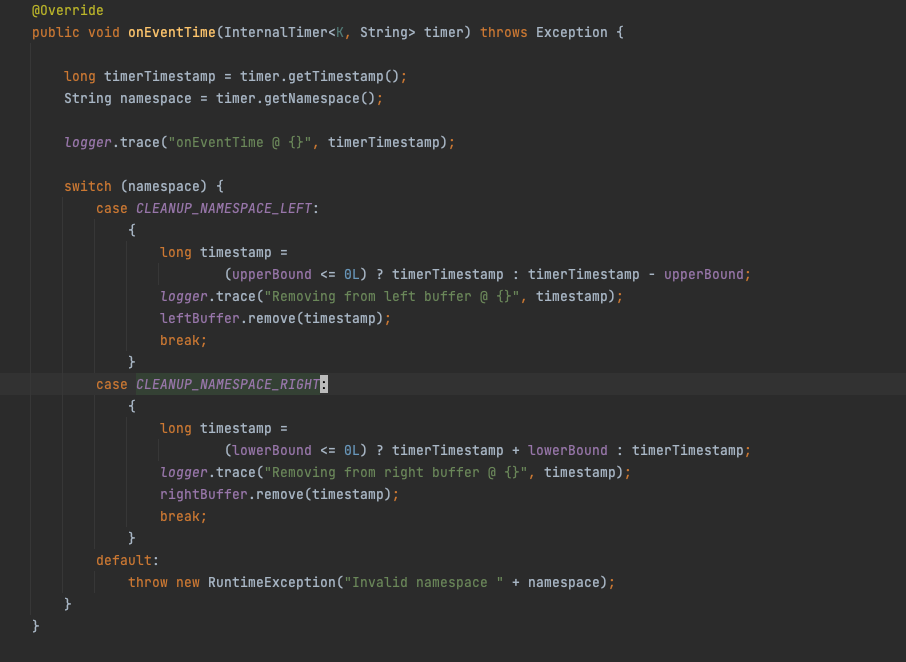
内连接的核心处理逻辑在IntervalJoinOperator中,这个Operator会把两条流的数据都缓存到状态中,用的是MapState<Long, V>,状态的key就是时间戳,V是用户数据,一个key可能对应多个v,存储方式就是HashMap;并且重写了OnEventTime函数,当这个函数被Trigger触发后,会对状态进行清除,源码如下
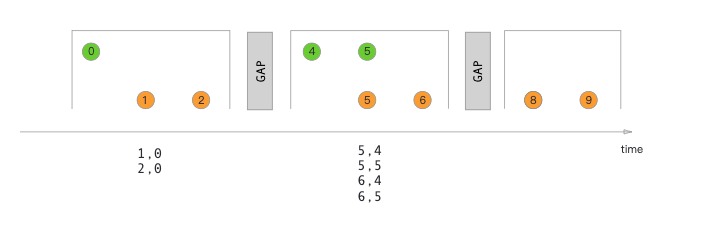
在做join时,就是来一条数据,就遍历另一条流的缓存,判断能否找到相同的key,如果能找到,就认为join成功,返回这两条数据

3.2 内连接
内连接是Flink内置的操作,直接使用interval函数即可
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String, Long, Integer>> newDataStream = dataStream1.keyBy(f -> f.f0)
.intervalJoin(dataStream2.keyBy(t -> t.f0))
.between(Time.seconds(-1), Time.seconds(1))
.process(
new ProcessJoinFunction<Tuple3<String, Long, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Long, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Long, Integer>>() {
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple3<String, Long, Integer> left, Tuple3<String, Long, Integer> right, Context ctx, Collector<Tuple3<String, Long, Integer>> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(new Tuple3<>(left.f0, left.f1, left.f2 + right.f2));
}
}
);
3.3 外连接
因为Flink DataStream内置的Join操作,只有Inner Join,而对于Outer Join支持的比较少,Window Outer Join我们可以用cogroup来实现,而Interval Outer Join相对复杂,所以自己参考Flink IntervalJoinOperator实现了一个IntervalLeftOuterJoinFunction,代码如下:
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.MapState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.MapStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.StateTtlConfig;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeutils.TypeSerializer;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeutils.base.ListSerializer;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeutils.base.LongSerializer;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.co.KeyedCoProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.operators.co.IntervalJoinOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.streamrecord.StreamRecord;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
import org.apache.flink.util.FlinkException;
import org.apache.flink.util.Preconditions;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author: ZhaoLei
* @Create date: 2023/8/1
* @Description: 自定义实现一个Interval的Left Join,主要参考 Flink IntervalJoinOperator,用户自定义的只能是Function,而不能是Operator,所以会和IntervalJoinOperator有些不同
*/
public abstract class IntervalLeftOuterJoinFunction<K, IN1, IN2, OUT> extends KeyedCoProcessFunction<K, IN1, IN2, OUT> {
private static final String LEFT_BUFFER = "LEFT_BUFFER";
private static final String RIGHT_BUFFER = "RIGHT_BUFFER";
private final long lowerBound;
private final long upperBound;
private transient MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<IN1>>> leftBuffer;
private transient MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<IN2>>> rightBuffer;
private final TypeSerializer<IN1> leftTypeSerializer;
private final TypeSerializer<IN2> rightTypeSerializer;
public IntervalLeftOuterJoinFunction(
Time lowerBound,
Time upperBound,
boolean lowerBoundInclusive,
boolean upperBoundInclusive,
TypeSerializer<IN1> leftTypeSerializer,
TypeSerializer<IN2> rightTypeSerializer
) {
long millLowerBound = lowerBound.toMilliseconds();
long millUpperBound = upperBound.toMilliseconds();
Preconditions.checkArgument(
millLowerBound <= millUpperBound, "lowerBound <= upperBound must be fulfilled");
// Move buffer by +1 / -1 depending on inclusiveness in order not needing
// to check for inclusiveness later on
this.lowerBound = (lowerBoundInclusive) ? millLowerBound : millLowerBound + 1L;
this.upperBound = (upperBoundInclusive) ? millUpperBound : millUpperBound - 1L;
this.leftTypeSerializer = leftTypeSerializer;
this.rightTypeSerializer = rightTypeSerializer;
}
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
super.open(parameters);
//定义状态的过期时间
StateTtlConfig ttlConfig = StateTtlConfig
.newBuilder(Time.milliseconds(this.upperBound))
.setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnCreateAndWrite)
.setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.NeverReturnExpired)
.build();
//左流状态
MapStateDescriptor<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<IN1>>> leftMapStateDescriptor =
new MapStateDescriptor<>(
LEFT_BUFFER,
LongSerializer.INSTANCE,
new ListSerializer<>(
new IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntrySerializer<>(leftTypeSerializer)
)
);
leftMapStateDescriptor.enableTimeToLive(ttlConfig);
//右流状态
MapStateDescriptor<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<IN2>>> rightMapStateDescriptor =
new MapStateDescriptor<>(
RIGHT_BUFFER,
LongSerializer.INSTANCE,
new ListSerializer<>(
new IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntrySerializer<>(rightTypeSerializer)
)
);
rightMapStateDescriptor.enableTimeToLive(ttlConfig);
this.leftBuffer = getRuntimeContext().getMapState(leftMapStateDescriptor);
this.rightBuffer = getRuntimeContext().getMapState(rightMapStateDescriptor);
}
//用户的Join逻辑
public abstract OUT userProcess(IN1 leftStream, IN2 rightStream);
//处理左流
@Override
public void processElement1(IN1 value, Context ctx, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception {
processElement(new StreamRecord<>(value, ctx.timestamp()), leftBuffer, rightBuffer, lowerBound, upperBound, true, out, ctx);
}
//处理右流
@Override
public void processElement2(IN2 value, Context ctx, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception {
processElement(new StreamRecord<>(value, ctx.timestamp()), rightBuffer, leftBuffer, -upperBound, -lowerBound, false, out, ctx);
}
private <THIS, OTHER> void processElement(
final StreamRecord<THIS> record,
final MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<THIS>>> ourBuffer,
final MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<OTHER>>> otherBuffer,
final long relativeLowerBound,
final long relativeUpperBound,
final boolean isLeft,
Collector<OUT> out,
Context ctx) throws Exception {
final THIS ourValue = record.getValue();
final long ourTimestamp = record.getTimestamp();
if (ourTimestamp == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
throw new FlinkException(
"Long.MIN_VALUE timestamp: Elements used in "
+ "interval stream joins need to have timestamps meaningful timestamps.");
}
if (isLate(ourTimestamp, ctx, record)) {
return;
}
//把数据放到状态中
addToBuffer(ourBuffer, ourValue, ourTimestamp);
boolean flag = false;
//去做join
for (Map.Entry<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<OTHER>>> bucket : otherBuffer.entries()) {
final long timestamp = bucket.getKey();
if (timestamp < ourTimestamp + relativeLowerBound
|| timestamp > ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound) {
continue;
}
for (IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<OTHER> entry : bucket.getValue()) {
flag = true;
if (isLeft) {
out.collect(
//调用用户定义的处理函数
userProcess((IN1)ourValue, (IN2) entry.getElement())
);
} else {
out.collect(
userProcess((IN1)entry.getElement(), (IN2) ourValue)
);
}
}
}
//如果没有join上,就把左流的数据发出去,右流置null
if(!flag && isLeft) {
out.collect(userProcess((IN1)ourValue, null));
}
long cleanupTime =
(relativeUpperBound > 0L) ? ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound : ourTimestamp;
ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(cleanupTime);
// System.out.println("value: " + ourValue + ", currentWatermark: " + ctx.timerService().currentWatermark()+ ", ctx_timestamp: " + ctx.timestamp());
}
private <This> boolean isLate(long timestamp, Context ctx, StreamRecord<This> value) {
long currentWatermark = ctx.timerService().currentWatermark();
// System.out.println("value: " + value.getValue() + ", timestamp: " + timestamp + ", currentWatermark: " + currentWatermark + ", ctx_timestamp: " + ctx.timestamp());
return currentWatermark != Long.MIN_VALUE && timestamp < currentWatermark;
}
//把数据添加到状态中
private static <T> void addToBuffer(
final MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<T>>> buffer,
final T value,
final long timestamp)
throws Exception {
List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<T>> elemsInBucket = buffer.get(timestamp);
if (elemsInBucket == null) {
elemsInBucket = new ArrayList<>();
}
elemsInBucket.add(new IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<>(value, false));
buffer.put(timestamp, elemsInBucket);
}
}
使用方法:
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeHint;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple3;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple4;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class IntervalOuterJoinExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
//watermark 自动添加水印调度时间
//env.getConfig().setAutoWatermarkInterval(200);
List<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>> tuple3List1 = Arrays.asList(
new Tuple3<>("A", 10, 1690700400000L),
new Tuple3<>("A", 11, 1690700402000L),
new Tuple3<>("B", 2, 1690700400021L),
new Tuple3<>("C", 3, 1690700400002L),
new Tuple3<>("D", 3, 1690700400003L)
);
List<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>> tuple3List2 = Arrays.asList(
new Tuple3<>("A", 13, 1690700400000L),
new Tuple3<>("A", 12, 1690700400000L),
new Tuple3<>("B", 21, 1690700400001L),
new Tuple3<>("C", 31, 1690700400002L),
new Tuple3<>("D", 41, 1690700400003L)
);
//Datastream 1
DataStream<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>> dataStream1 = env.fromCollection(tuple3List1)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((element, timestamp) -> element.f2));
//Datastream 2
DataStream<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>> dataStream2 = env.fromCollection(tuple3List2)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((element, timestamp) -> element.f2));
//对dataStream1和dataStream2两个数据流进行关联,没有关联也保留
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple4<String, Integer, Integer, Long>> newDataStream = dataStream1.connect(dataStream2)
.keyBy(f -> f.f0, t -> t.f0)
.process(
new IntervalLeftOuterJoinFunction<Object, Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>, Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>, Tuple4<String, Integer, Integer, Long>>(
Time.milliseconds(-10),
Time.milliseconds(10),
true,
true,
TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>>(){}).createSerializer(env.getConfig()),
TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint<Tuple3<String, Integer, Long>>(){}).createSerializer(env.getConfig())
) {
@Override
public Tuple4<String, Integer, Integer, Long> userProcess(Tuple3<String, Integer, Long> left, Tuple3<String, Integer, Long> right) {
if(right != null) {
return new Tuple4<>(left.f0, left.f1, right.f1, left.f2);
} else {
return new Tuple4<>(left.f0, left.f1, null, left.f2);
}
}
}
);
newDataStream.print();
env.execute("Flink Interval Join Example Job");
}
}
四、Regular Join
如果我们想要做普通的inner join、left join、right join,不考虑窗口和Interval,我们称之为Regular Join,实现方式就是把基于Interval Join的Function改一下, 改成不判断两边流的状态是否过期即可;如果我们担心状态过大,那么可以设置一个ttl。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)