MySQL 查询语句大全
超全MySQL查询语句,MySQL查询语句有这一篇就够了
目录
基础查询
直接查询
查询所有列
语法:select * from 表名;
-- 查询 student 表中所有内容
select * from student;
查询指定列
语法:select 字段 from 表名;
-- 查询 student 表中的name列 与 age列
select name, age from student;
AS起别名
使用 AS 给字段起别名
语法:select 字段 as 别名 from 表名;(as可省略)
-- 查询 student 表中的name列 与 age列
select name 名字, age 年龄 from student;
-- select name as 名字, age as 年龄 from student;

使用 AS 给表起别名
语法:select 字段 from 表名 as 别名;
-- 查询 student 表中的name列 与 age列,同时给student起个‘学生年龄表’别名
select name 名字, age 年龄 from student 学生年龄表;
去重(复)查询
DISTINCT 用于从表中获取不重复的数据
语法:select distinct 列名 from 表名;
-- 查询 student 表中所有的不同年龄
select distinct age from student;条件查询
语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 条件;
-- 从 student 表中查询 age = 18 的 name
select name from student where age = 18;
算术运算符查询
语法:>(大于), <(小于), =(等于), !=(不等于), <>(不等于), >=(大于等于), <=(小于等于)
-- 从 student 表中查询 age >=20 的所有记录
select * from student where age >= 20;
逻辑运算符查询
语法:and(且), or(或), not(非) sql 会首先执行 and 条件,再执行 or 语句。除非加括号
-- 从 student 表中查询 age >=20并且成绩高于50分的所有记录
select * from student where age >= 20 and score > 50;
-- 从 student 表中查询 age = 15 或 score = 70 的所有记录
select * from student where age = 15 or score = 70;
正则表达式查询⭐
正则表达式要用regexp
语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 regexp '正则表达式';
--从 student 表中查询 name 含有李的所有记录
select * from student where name regexp '李';
--从 student 表中查询 name 含有李或三的所有记录
select * from student where name regexp '李|三';
--从 student 表中查询 name 为李开头的所有记录
select * from student where name regexp '^李';
--从 student 表中查询 name 为五结尾的所有记录
select * from student where name regexp '五$';
-- 字符.用来替代字符串中的任意一个字符
--从 student 表中查询 name 含'赵'和'真'两个字符且中间只隔了一个字符的所有记录
select * from student where name regexp '赵.真';
-- 字符*和+都可以匹配多个该符号之前的字符。不同的是,+表示至少一个字符,而*可以表示 0 个字符。
-- 从 student 表中查询 name 含丰字的所有记录(三*表示丰字前面可以有0-无数个三,因此至少含有丰)
select * from student where name regexp '三*丰';
-- 从 student 表中查询 name 含丰且前面只少有一个三的所有记录(三+表示丰字前面至少个三,因此至少含有三丰)
select * from student where name regexp '三+丰';
-- 从 student 表中查询 name 包含李、三、 真 3 个字符中任意一个的记录
select * from student where name regexp '[李三真]';
-- 方括号[ ]还可以指定集合的区间。例如,“[a-z]”表示从 a~z 的所有字母;“[0-9]”表示从 0~9 的所有数字;“[a-z0-9]”表示包含所有的小写字母和数字;“[a-zA-Z]”表示匹配所有字符;“[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]”表示中文汉字
-- [^字符集合]用来匹配不在指定集合中的任何字符。
-- 查询 name 字段值包含字母 a~t 以外的字符的所有记录
select * from student where name regexp'[^a-t]';
-- 字符串{n,}表示字符串连续出现 n 次;字符串{n,m}表示字符串连续出现至少 n 次,最多 m 次。
-- a{2,} 表示字母 a 连续出现至少 2 次,也可以大于 2 次;a{2,4} 表示字母 a 连续出现最少 2 次,最多不能超过 4 次。
-- 查询 name 字段值出现字母‘e’ 至少 2 次的记录
select * from student where name regexp'e{2,}';
REGEXP 操作符中常用的匹配方式
| 选项 | 说明 | 例子 | 匹配值示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ^ | 匹配文本的开始字符 | ‘^b’ 匹配以字母 b 开头的字符串 | book、big、banana、bike |
| $ | 匹配文本的结束字符 | ‘st$’ 匹配以 st 结尾的字符串 | test、resist、persist |
| . | 匹配任何单个字符 | ‘b.t’ 匹配任何 b 和 t 之间有一个字符 | bit、bat、but、bite |
| * | 匹配零个或多个在它前面的字符 | ‘f*n’ 匹配字符 n 前面有任意个字符 f | fn、fan、faan、abcn |
| + | 匹配前面的字符 1 次或多次 | ‘ba+’ 匹配以 b 开头,后面至少紧跟一个 a | ba、bay、bare、battle |
| <字符串> | 匹配包含指定字符的文本 | ‘fa’ 匹配包含‘fa’的文本 | fan、afa、faad |
| [字符集合] | 匹配字符集合中的任何一个字符 | ‘[xz]’ 匹配 x 或者 z | dizzy、zebra、x-ray、extra |
| [^] | 匹配不在括号中的任何字符 | '[^abc]'匹配任何不包含 a、b 或 c 的字符串 | desk、fox、f8ke |
| 字符串{n,} | 匹配前面的字符串至少 n 次 | ‘b{2}’ 匹配 2 个或更多的 b | bbb、bbbb、bbbbbbb |
| 字符串{n,m} | 匹配前面的字符串至少 n 次, 至多 m 次 | ‘b{2,4}’ 匹配最少 2 个,最多 4 个 b | bbb、bbbb |
模糊查询
语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 like '%数据%';
-- 从 student 表中查询 name 中含有 '张' 的所有记录
select * from student where name like '%张%';
-- 从 student 表中查询 name 中姓 '张' 的所有记录
select * from student where name like '张%';
范围查询
in与not in between … and …:范围连续(包含端点)
语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 in(列表)//或 not in(列表);
-- 从 student 表中查询 age 为 (18, 19, 20) 之间的所有记录
select * from student where age in(18, 19, 20);
-- 从 student 表中查询 除了age 为 (18, 19, 20) 之间的所有记录
select * from student where age not in(18, 19, 20);
语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 between 值1 and 值2;
-- 从 student 表中查询 age 为 (18, 19, 20) 之间的所有记录
select * from student where age between 18 and 20;
是否非空判断查询
null(为空) not (非空) 判断是否为空要用is
语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 is null(not null);
--从 student 表中查询 age 未填写(为空)的所有记录
select * from student where age is null;优先级
优先级由高到低的顺序为:小括号 > NOT > 比较运算符 > 逻辑运算符
AND比OR先运算,如果同时出现并希望先算or,需要结合()使用
排序查询
语法:select 字段 from 表名 order by 字段 排序方式(升序 asc, 降序 desc);
-- 从 student 表中查询所有记录并按照 age 升序排序
select * from student order by age asc;
进阶 select 字段 from 表名 order by 字段 排序方式,字段 排序方式;
(当第一个字段相同时,按第二个字段排序顺序来)
-- 从 student 表中查询所有记录并按照 age 升序,当 age 相同时,按score降序排序
select * from student order by age asc,score desc;
限制查询(分页查询)
语法:limit可以限制制定查询结果的记录条数
注意 0 表示第一行记录,也是从 0 开始
select 字段 from 表名 limit n;查询前n行的记录
select 字段 from 表名 limit n, m;查询第n+1行到第m+n行的记录(也就是从第n+1行开始查询m行记录)
-- 从 student 表中查询第三行到第六行的记录,也就是第三行开始查询4条记录
select * from student limit 2, 4;
随机查询
-- 随机显示两个学生信息
select * from student order by rand() limit 2;分组查询
语法:select 字段 from 表名 group by 字段 ;
-- 从 student 表中查询age值和每个age都有多少人
select age ,count(*) from student group by age ;
GROUP BY子句必须出现在WHERE子句之后, ORDER BY子句之前
HAVING
HAVING 语句用于筛选(过滤)分组后的数据
语法:select 字段 from 表名 group by 字段 having 条件;
-- 从 student 表中查询age>19值和每个age>19都有多少人
select age ,count(*) from student group by age having age > 19;高级查询
子查询(嵌套查询)
一个 select 语句中,嵌入另外一个 select 语句, 被嵌入的 select 语句称为子查询语句,外部select语句则称为主查询。
主查询和子查询的关系
- 子查询是嵌入到主查询中
- 子查询是辅助主查询的,要么充当条件,要么充当数据源
- 子查询是可以独立存在的语句,是一条完整的 select 语句
语法:语法:嵌套查询也就是在查询语句中包含有子查询语句,所以叫嵌套查询,没有单独的语法,嵌套子查询通常位于查询语句的条件之后;
-- 先查询学生平均年龄,再查询大于平均年龄的学生
select * from student where age > (select avg(age) from student);排号
-- row_number() over (排序语句)
-- row_number()从1开始,为每一条分组记录返回一个数字
-- 查询名次 姓名 成绩
select row_number() over (order by score desc) 名次,name 姓名,score 成绩 from student;
排名
DENSE_RANK()是一个窗口函数,它为分区或结果集中的每一行分配排名,而排名值没有间隙。
- DENSE_RANK()。如果使用 DENSE_RANK() 进行排名会得到:1,1,2,3,4。
- RANK()。如果使用 RANK() 进行排名会得到:1,1,3,4,5。
- ROW_NUMBER()。如果使用 ROW_NUMBER() 进行排名会得到:1,2,3,4,5。(通常用来排号)
-- 排名
--排名并列后面名次挨着
select id 编号,name 姓名,score 分数,concat('第',dense_rank() over (order by score
desc),'名') 名次 from student;
--排名并列后面名次不挨着
select id 编号,name 姓名,score 分数,concat('第',rank() over (order by score
desc),'名') 名次 from student;
聚合函数
-- 聚合函数
-- 可以实现一些具体的功能,比如找最小值,找最大值,求和,计数等
-- min() 求最小值
语法:select min(字段) from 表名;
-- 从 student 中查询最小的 age
select min(age) from student;
-- max() 求最大值
语法:select max(字段) from 表名;
-- 从 student 中查询最大的 age
select max(age) from student;
-- sum() 求和
语法:select sum(字段) from 表名;
-- 从 student 中统计所有 age 的和
select sum(age) from student;
-- avg() 求平均值
语法:select avg(字段) from 表名;
-- 从 student 中对所有的 age 求平均值
select avg(age) from student;
-- count(字段) 统计个数
语法:select count(字段) from 表名;
-- 从 student 中查询 name 的记录个数
select count(name) from student;
连接查询
MySQL查询连接主要分为三类:内连接、外连接和交叉连接。
内连接
INNER JOIN
内连接意味着两张或多张表中的记录有对应关系,这种关系可以使用主键和外键来表示。内连接通过保留相同记录才会返回结果。也就是说,只有在两个表中都存在匹配的记录时,才会返回查询结果。
-- 内连接
语法:select 字段 from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
根据两个表中共有的字段进行匹配,然后将符合条件的合集进行拼接
on后面是连接条件,也就是共有字段
select * from student inner join engScore on student.name = engScore.name;
-- 将 student 表与 engScore 表通过相同的 name 拼接起来,简单的来说就是两个 excel 合并
例 假设我们有两张表student和course,它们的列和内容如下
student表:
| id | name | age |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jack | 18 |
| 2 | Tom | 19 |
| 3 | Jerry | 20 |
| 4 | Bob | 18 |
course表:
| course_id | course_name | student_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Math | 1 |
| 2 | English | 2 |
| 3 | Science | 2 |
| 4 | History | 3 |
现在我们想查询每个学生所选择的课程,可以使用如下的SQL语句:
SELECT student.name, course.course_name
FROM student
INNER JOIN course
ON student.id = course.student_id;该查询将返回以下结果:
| name | course_name |
|---|---|
| Jack | Math |
| Tom | English |
| Tom | Science |
| Jerry | History |
外连接
OUTER JOIN
对于外联结 outer关键字可以省略
外连接分为左连接和右连接,这种连接是指在连接两张或多张表时,包含了所有的记录。
左(外)连接
左连接意味着左侧表取所有记录,而右侧表仅取匹配的记录。如果左侧表与右侧表没有匹配的记录,则右侧表将返回NULL值。
-- 左连接
语法:select 字段 from 表1 left join 表2 on 连接条件;
select * from student left join engScore on student.name = engScore.name;
-- 与内连接形式相同,但左表为主表,指定字段都会显示,右表为从表,无内容会显示 null
例
还是以上面的student表和course表为例子,如果我们想查询每个学生所选择的课程,包括那些没有选课程的学生。可以使用以下的SQL语句:
SELECT student.name, course.course_name
FROM student
LEFT JOIN course
ON student.id = course.student_id;该查询将返回以下结果:
| name | course_name |
|---|---|
| Jack | Math |
| Tom | English |
| Tom | Science |
| Jerry | History |
| Bob | NULL |
右(外)连接
右连接与左连接相似,只是左侧表和右侧表的角色翻转了
-- 右连接
语法:select 字段 from 表1 right join 表2 on 连接条件;
select * from student right join engScore on student.name = engScore.name;
-- 与内连接形式相同,但右表为主表,指定字段都会显示,左表为从表,无内容会显示 null
继续使用上面的student表和course表为例子,如果我们想查询每门课程的学生,包括没有选该门课程的学生。可以使用以下的SQL语句:
SELECT student.name, course.course_name
FROM student
RIGHT JOIN course
ON student.id = course.student_id;该查询将返回以下结果:
| name | course_name |
|---|---|
| Jack | Math |
| Tom | English |
| Tom | Science |
| Jerry | History |
| NULL | Geography |
全外连接(组合)
在SQL中,外连接还有一种FULL OUTER JOIN(全外连接),但是MySQL不支持。因此,我们可以通过UNION语句来模拟全外连接。
union与union all
union会去重,如果在一个条件中返回了,下一个条件中就算是有也不会返回。union all不会去重, 如果在一个条件中返回了,下一个如果有重复的,也会返回。
select id, name, age from s1 where age >18union select id, name, agefrom s2 where age >18;
-- 查询s1和s2中所有年纪大于18的学生的id,name,age,并将结果放在一个表中,同时去掉重复 
交叉连接
CROSS JOIN
交叉连接是指在两张或多张表之间没有任何连接条件的连接。简单来说,交叉连接可以让你查询所有可能的组合。
tb1:
| d | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
我们可以使用以下的SQL语句来进行交叉连接:
SELECT t1.name, t2.name
FROM tb1 t1
CROSS JOIN tb1 t2;查询结果
| name | name |
|---|---|
| A | A |
| A | B |
| A | C |
| B | A |
| B | B |
| B | C |
| C | A |
| C | B |
| C | C |
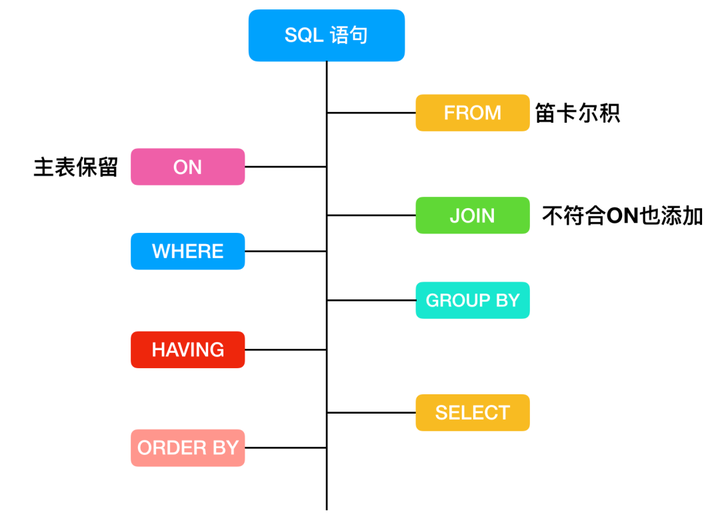
SELECT子句必须遵循的顺序

| 子句 | 说明 | 是否必须使用 |
| SELECT | 要返回的列或表达式 | 是 |
| FROM | 从中检索数据的表 | 仅在从表选择数据时使用 |
| WHERE | 行级过滤 | 否 |
| GROUP BY | 分组说明 | 仅在按组计算聚集时使用 |
| HAVING | 组级过滤 | 否 |
| ORDER BY | 输出排序顺序 | 否 |
| LIMIT | 要检索的行数 | 否 |
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容










所有评论(0)