MyBatis-Plus中的通用Mapper接口
mybatis-plus通用mapper接口
简介
1--> 通过CRUD封装BaseMapper接口, 为MyBatis-Plus启动时自动解析实体表关系映射转换为MyBatis内部对象注入容器
2--> 泛型T为任意实体对象
3-->参数Serializable为任意类型主键,MyBatis-Plus不推荐使用复合主键约定每一张表都有自己的唯一id主键
4-->对象Wrapper为条件构造器
操作准备
准备实体类Employee
@Data
public class Employee {
//设置id为自增
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String password;
private String email;
private int age;
private int admin;
//忽略这个字段
@TableField(exist = false)
private Long deptId;
}
BaseMapper方法集
我们编写一个EmployeeMapper接口去继承父接口BaseMapper<Employee> , ctrl点进这个父接口发现 , 一共有17个方法 , 1个insert方法 , 4个删除方法 , 10个查询方法, 2个更改方法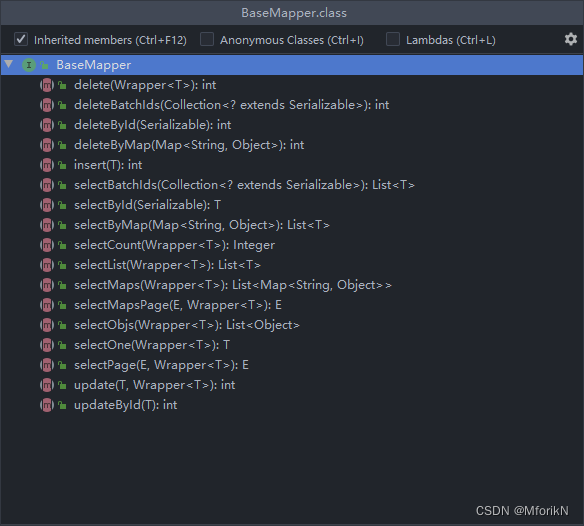
添加-insert
@Test
public void testSave() {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setAdmin(1);
employee.setAge(20);
employee.setDeptId(2L);
employee.setEmail("wangshanshan@qq.com");
employee.setName("王珊珊");
employee.setPassword("123");
employeeMapper.insert(employee);
}执行后的SQL : INSERT INTO employee ( name, password, email, age, admin ) VALUES ( ?, ?, ?, ?, ? )
更新-update
mybatis-plus中更新方法有2个: updateById , update
updateById
@Test
public void updateById(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(4L);
employee.setName("刘娜");
employeeMapper.updateById(employee);
}执行后的SQL : UPDATE employee SET name=?, age=?, admin=? WHERE id=?
改后 :
执行完了之后, 我们发现age和admin的数据发生了丢失 , 我们本来只想改name的属性值 , SQL语句应该是set name = ? ,但是SQL也拼接了age跟admin列的更新 , 这是怎么回事呢?
这里就涉及了MyBatis-Plus的SQL语句拼接的规则
MyBatis-Plus的SQL语句拼接的规则 :
1 . 实体对象作为方法参数 如果属性值为null , 该属性不参与SQL拼接 , 反之 , 则参与拼接
2 . 实体对象作为方法参数 如果属性作为基本类型 , 有默认值 ,该属性参与方法SQL拼接
上面的updateById方法操作中,name, password, email属性值都是null, 所以update sql语句set中并没有拼接name,password, email 列的更新。而 age, admin 2个属性属于基本类型,不显示设置属性值,那默认就是0,0。 MyBatis-Plus 认为该属性有值,便在update sql语句set 中拼接 age = ?, name = ?。这操作最终导致了表中数据丢失。
解决方案
方案1 :使用包装类型
private Integer age;
private Integer admin;方案2 : 使用先查询 , 在替换 , 后更新
@Test
public void testupdate{
//先查询
Employee = employee = employeeMapper.selectById(1L);
//在替换
employee.setName("刘娜");
//在更新
employeeMapper.updateById(employee);
}方案3 : 使用update(null,wrapper)方法
@Test
public void update() {
UpdateWrapper<Employee> wrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("id", 21L);
wrapper.set("name", "刘娜");
employeeMapper.update(null, wrapper);
}执行后的SQL : UPDATE employee SET name=? WHERE (id = ?) , 可以看见没有拼接age和admin
update跟updateById方法的选用
使用updateById场景
- where条件时id时候update场景
- 尽心全部的(全部的字段)更新的时候
使用update的场景
- where条件是不确定的 , 或者多条件的update场景
- 进行部分字段的更新的时候
删除-delete
mybatis-plus中删除方法有4个 : deleteById , deleteByMap ,delete , deleteBatchIds
deleteById
作用 : 根据id删除某条信息
//需求:删除id为1的员工信息
@Test
public void deleteById(){
int deleteById = employeeMapper.deleteById(1L);
System.out.println(deleteById);
}deleteBatchIds
用法: 批量删除指定多个id对象信息
//需求:删除id为1,2,3的员工信息
//DELETE FROM employee WHERE id IN ( ? , ? , ? )
@Test
public void DeleteBatchIds(){
employeeMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L,2L,3L));
}执行后的SQL : delete from employee where id in(?,?,?)
deleteByMap
作用 :按条件删除 , 具体条件要放在map中
//需求:删除name=dafei并且age=18的员工信息
//DELETE FROM employee WHERE name = ? AND age = ?
@Test
public void deleteMaps(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","dafei");
map.put("age",18);
employeeMapper.deleteByMap(map);
}执行后的SQL : delete form employee where name = ? and age = ?
delete
用法 : 按条件删除 , 具体条件通过跳进构造器拼接
//需求:删除name=dafei并且age=18的员工信息
//DELETE FROM employee WHERE (name = ? AND age = ?)
@Test
public void testDelete(){
QueryWrapper<Employee> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("name","刘娜");
wrapper.eq("age",20);
employeeMapper.delete(wrapper);
}执行后的SQL : delete from employee where (name = ? and age = ?)
查询 :select
mybatis-plus中有10个查询方法
1 . selecById
用法:查询指定的id对象信息
@Test
public void selectById(){
Employee employee = employeeMapper.seectById(4L);
System.out.println(employee);
}执行后的SQL: SELECT id,name,password,email,age,admin,dept_id FROM employee WHERE id=?
2 . selectBatchIds
用法 : 批量查询指定的id的对象信息
@Test
public void selectBatchIds(){
employeeMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L,2L,3L));
}执行后的SQL : select id ,name password , email ,age , admin , dept_id from employee where id in(?,?,?)
3 . selectByMap
用法: 查询满足条件的实体信息 , 条件封装到map中
@Test
public void selectByMaps(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age",18);
map.put("name","王珊珊");
List<Employee> list = employeeMapper.selectByMap(map);
}执行后的SQL : select id ,name, password , email ,age , admin , dept_id from employee where name= ? and age = ?
4 . selectCount
用法 : 查询满足条件实体信息纪录总条数
@Test
public void selectCount(){
QueryWrapper<Employee> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
Integer count= employeeMapper.selectCount(wrapper);
} 执行完SQL: select count(1) from employee
5 . selectList
用法 : 查询满足条件的实体信息 , 返回List<>对象
@Test
public void selectList(){
QueryWrapper<Employee> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
List<Employee> list = employeeMapper.selectList(wrapper);
for(Employee:employee:list)
System.out.println(employee);
}执行完后的SQL : select id ,name , password ,email,age ,admin , dept_id from employee
6 . selectMaps
用法:查询满足条件的实体信息纪录 ,返回List<Map<String,Object>>
@Test
public void selectMaps(){
QueryWrapper<Employee> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
List<Map<String,Object>> mapList = employeeMapper.selectMaps(wrapper);
for(Map<String,Object> map:mapList){
System.out.println(map);
}
}执行完后的SQL : SELECT id,name,password,email,age,admin,dept_id FROM employee
7 . selectPage
用法 : 分页查询满足条件的实体信息纪录
1 ,在SpringBoot项目中的配置类中添加分页插件 , 在启动类中添加分页插件
//分页
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor =
new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL);
paginationInnerInterceptor.setOverflow(true);
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor);
return interceptor;
2 . 编写分页代码
//分页查询满足条件实体信息记录
//查询第二页员工数据, 每页显示3条, (分页返回的数据是员工对象)
// SELECT COUNT(1) FROM employee
@Test
public void selectPageTest(){
QueryWrapper<Employee> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
Page<Employee> page = new Page<>(2,3);
Page<Employee> employeePage = employeeMapper.selectPage(page, wrapper);
System.out.println(employeePage == page);
System.out.println("当前页: "+ page.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每页显示的条数: "+page.getSize());
System.out.println("总页数: "+page.getPages());
System.out.println("当前页数据: "+page.getRecords());
}执行完SQL :
select count(1) from employee
select id,name,password,email,age,admin,dept_id from employee limit ?,?更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)