python调用C++程序
python调用C++程序Python / C APICFFI / ctypes
一、Python / C API
/src/python_c_api_function.hpp
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <Python.h>
long int _step(int x) {
if (x == 1 || x == 2) {
return x;
}
else {
return _step(x - 1) + _step(x - 2);
}
}
long int step(int x) {
return _step(x);
}
PyObject* step_function(PyObject* self, PyObject* args) {
long int py_x;
PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "l", &py_x);
long int x = step(py_x);
return Py_BuildValue("l", x);
}
/**
* 或者用下面代码
PyObject* step_function(PyObject* self, PyObject* args) {
PyObject* py_x;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "O!", &PyLong_Type, &py_x)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "入参不是 long int 类型!");
return nullptr;
}
long int x = step(PyLong_AsLong(py_x));
return Py_BuildValue("l", x);
}
*/
char* concat(char* a, char* b) {
std::string x(a), y(b);
char* c = const_cast<char*>((x + y).data());
return c;
}
PyObject* concat_function(PyObject* self, PyObject* args) {
char* py_a, * py_b;
PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "ss", &py_a, &py_b);
char* c = concat(py_a, py_b);
return Py_BuildValue("s", c);
}
/src/python_c_api_main.cpp
#include <Python.h>
#include "python_c_api_function.hpp"
static PyMethodDef xy_python_c_api_methods[] = {
{
"step", step_function, METH_VARARGS, ""
},
{
"concat", concat_function, METH_VARARGS, ""
},
{
nullptr, nullptr, 0, nullptr
}
};
static struct PyModuleDef xy_python_c_api_definition = {
PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT,
"xy_python_c_api",
"Python/C API 示例。",
-1,
xy_python_c_api_methods
};
PyMODINIT_FUNC PyInit_xy_python_c_api(void) {
Py_Initialize();
return PyModule_Create(&xy_python_c_api_definition);
}
/setup.py
# python setup.py build
# python setup.py install
import os
from distutils.core import setup, Extension
cpython_mod = Extension(
"xy_python_c_api",
sources=[r"src/python_c_api_main.cpp"]
)
setup(
name="xy_python_c_api_package",
version="1.0.0",
description="Python/C API 示例。",
ext_modules=[cpython_mod]
)
/test.py
import time
from xy_python_c_api import step, concat
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
n = step(45)
end = time.time()
print(f"耗时:{end - start},结果:{n}")
string = concat("asd", "123")
print("连接两个字符串的结果:{}".format(string))按目录创建好上面的代码后,切换到与 setup.py 同级目录,运行 python setup.py build 与 python setup.py install。
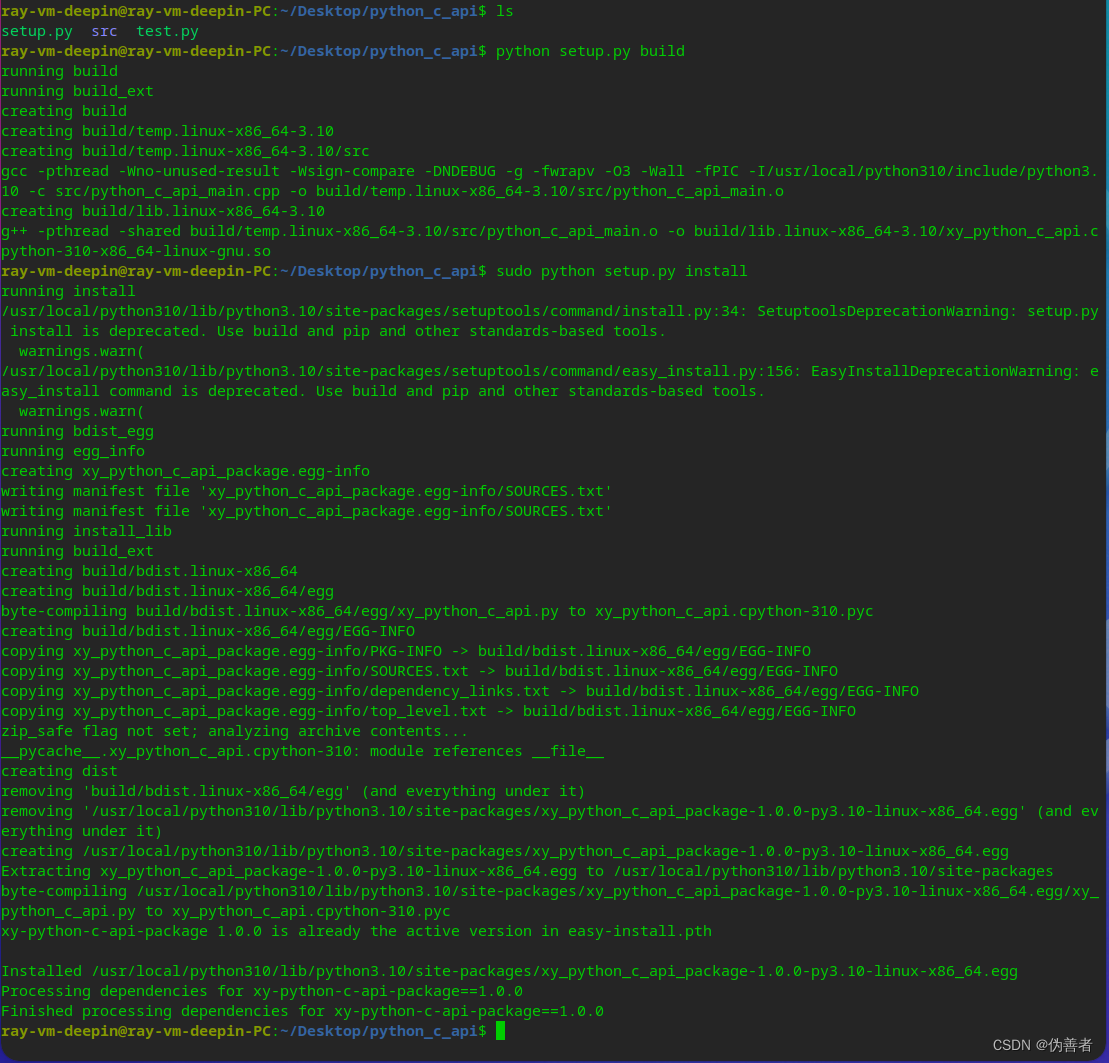
运行结果:

二、CFFI / ctypes
Linux:
同一运算的 C++ 和 python 实现:
C++:

python:

上述示例代码 python 的运算速度要比 C++ 慢 50 倍(C++编译未优化的情况下)。
一、生成 C++ so。
目录结构如下:
---------------
| -- pythonso.h
| -- pythonso.cpp
| -- pythonso.so(通过g++编译生成)
| -- test.pypythonso.h
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
long int step(int);
char* concat(char*, char*);
}
#endifpythonso.cpp
#include <string>
#include "pythonso.h"
long int _step(int x) {
if (x == 1 || x == 2) {
return x;
}
else {
return _step(x - 1) + _step(x - 2);
}
}
long int step(int x) {
return _step(x);
}
char* concat(char* a, char* b) {
std::string x(a), y(b);
char* c = const_cast<char*>((x + y).data());
return c;
}
运行命令行参数,在当前目录生成pythonso.so文件。
g++ -fPIC -shared ./pythonso.cpp -o ./pythonso.so二、用 python 调用刚生成的 pythonso.so。
test.py
import time
from ctypes import cdll, c_int, c_char_p
cso = cdll.LoadLibrary("./pythonso.so")
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
n = cso.step(c_int(45))
end = time.time()
print(f"耗时:{end - start},结果:{n}")
cso.concat.restype = c_char_p
string = cso.concat(c_char_p(b"asd"), c_char_p(b"123"))
print("连接两个字符串的结果:{}".format(string.decode("utf-8")))
运行结果:

Windows:
同一运算的 C++ 和 python 实现:
C++:

python:

上述示例代码 python 的运算速度要比 C++ 慢 100 倍。
一、生成 C++ dll。
目录结构如下:

pythondll.def
LIBRARY
EXPORTS
;step函数
step
;concat函数
concat
pythondll.h
extern "C" {
_declspec(dllexport) long int step(int);
_declspec(dllexport) char* concat(char*, char*);
}
pythondll.cpp
#include <string>
long int step(int x) {
if (x == 1 || x == 2) {
return x;
}
else {
return step(x - 1) + step(x - 2);
}
}
char* concat(char* a, char* b) {
std::string x(a), y(b);
char* c = const_cast<char*>((x + y).data());
return c;
}
然后设置配置类型为 dll

完成上述操作,即可生成 pythondll.dll。
二、用 python 调用刚生成的 pythondll.dll。
test.py
import time
from ctypes import CDLL, c_int, c_char_p
cdll = CDLL("./pythondll.dll")
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
n = cdll.step(c_int(45))
end = time.time()
print(f"耗时:{end - start},结果:{n}")
cdll.concat.restype = c_char_p
string = cdll.concat(c_char_p(b"asd"), c_char_p(b"123"))
print("连接两个字符串的结果:{}".format(string.decode("utf-8")))运行结果:

可见,对于一些耗时较多的运算,可以改用 C++ 来写,以此改善 python 运算效率。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)