【万字长文】 Vue全家桶从入门到实战,超详细笔记整理 ( 一 ) (建议收藏)
笔记根据B站编程不良人视频整理,视频链接:【编程不良人】VUE全家桶入门到实战,学VUE看这个就够了,已完结!基于企业最流行Vue实战技术,需要md格式笔记的可以私信我。目录1、Vue 引言2、Vue入门2.1、下载Vuejs2.2、Vue第一个入门应用3、v-text和v-html3.1、v-text3.2、v-html3.3、v-text和v-html对比4、vue中事件绑定(v-on)4、v
笔记根据B站编程不良人视频整理,视频链接:【编程不良人】VUE全家桶入门到实战,学VUE看这个就够了,已完结!基于企业最流行Vue实战技术, 需要md格式笔记的可以私信我。
目录
1、Vue 引言
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-w5ZKiCvv-1627348740556)(Vue实战笔记(一).assets/image-20210129104929487.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/57127a2bab669e8b851996c4aaa15225.png)
渐进式JavaScript 框架 --摘自官网
# 渐进式
1. 易用 html css javascript
2. 高效 开发前端页面 非常高效
3. 灵活 开发灵活 多样性
# 总结
Vue 是一个javascript 框架 js 简化页面js操作
bootstrap 是一个css框架 封装css
# 后端服务端开发人员:
页面标签 dom jquery js document.getElementById("xxx")
Vue 渐进式javascript框架: 让我们通过操作很少的DOM,甚至不需要操作页面中任何DOM元素,就很容易的完成数据和视图绑定 ====> 双向绑定 MVVM
注意:日后在使用vue过程中页面不要再引入Jquery框架
html css--->javascript(document.getElementById()...) ---->jquery($("#xx")) ---> angularjs --->vue(前后端分离架构核心)
vue 前端系统 <-----JSON-----> 后台系统springcloud
# Vue 作者
尤雨溪 国内的
2、Vue入门
2.1、下载Vuejs
//开发版本:
<!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
//生产版本:
<!-- 生产环境版本,优化了尺寸和速度 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
2.2、Vue第一个入门应用
1、vue第一个入门应用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{msg}}
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<span>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<span>
<span>{{msg}}</span>
</span>
</span>
<h3>用户名:{{username}}</h3>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app= new Vue({
el:"#app", //element:元素 作用:用来指定vue实例作用范围 日后在el指定的作用范围内可以直接使用{{属性名}}获取data中的属性
data:{ //data:数据 作用:用来给vue实例对象绑定一系列数据
msg: "Vue欢迎您!",
username: "小陈!!",
}
});
</script>
2、vue实例中定义对象,数组等相关数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<h2>{{age}}</h2>
<h2>姓名:{{user.name}} 描述:{{user.des}}</h2>
<h2>{{schools[0]}}-{{schools[1]}}-{{schools[2]}}-{{schools[3]}}</h2>
<h2>姓名:{{users[0].name}} 年龄:{{users[0].age}} 生日:{{users[0].bir}}</h2>
<h2>姓名:{{users[1].name}} 年龄:{{users[1].age}} 生日:{{users[1].bir}}</h2>
<h2>姓名:{{users[2].name}} 年龄:{{users[2].age}} 生日:{{users[2].bir}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"百知欢迎您!!!",
age:"23",
user:{name:"小陈",des:"他在百知,百知等你!!"}, //定义对象
schools:["河南校区","北京校区","天津校区","山西校区"], //定义一个数组
users:[
{name:"小王",age:23,bir:"2012-12-01"},
{name:"小李",age:24,bir:"2013-12-01"},
{name:"小赵",age:25,bir:"2014-12-01"},
]
}
});
</script>
3、使用{{属性名}}获取data数据时,使用表达式 运算符等相关操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--{{属性名}}:使用这种方式获取数据时,可以进行相关的运算(算数,逻辑),调用获取值类型相关js方法-->
<h2>{{msg + '您好'}}</h2>
<h2>{{msg == 'hello vue'}}</h2>
<h2>{{msg.toUpperCase()}}</h2>
<h2>{{age + 1}}</h2>
<h2>{{age == 23}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
age:23,
}
});
</script>
4、使用vue时el属性指定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" class="aa">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue作用范围
// 书写格式:使用css选择器 id选择器 html选择器 类选择器 推荐使用id选择器 id选择器具有唯一性
// 注意事项:不要将el指向body或html标签 Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
}
});
</script>
5、总结
# 总结:
1.vue实例(对象)中el属性: 代表Vue的作用范围 日后在Vue的作用范围内都可以使用Vue的语法
2.vue实例(对象)中data属性: 用来给Vue实例绑定一些相关数据, 绑定的数据可以通过{{变量名}}在Vue作用范围内取出
3.在使用{{}}进行获取data中数据时,可以在{{}}中书写表达式,运算符,调用相关方法,以及逻辑运算等
4.el属性中可以书写任意的CSS选择器[jquery选择器],但是在使用Vue开发是推荐使用 id选择器 注意: el属性值不能指定body或html标签
3、v-text和v-html
3.1、v-text
v-text:用来获取data中数据将数据以文本的形式渲染到指定标签内部 类似于javascript 中 innerText
<div id="app" class="aa">
<span >{{ message }}</span>
<span v-text="message"></span>
</div>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message:"百知欢迎您"
}
})
</script>
# 总结
1.{{}}(插值表达式)和v-text获取数据的区别在于
a.使用v-text取值会将标签中原有的数据覆盖 使用插值表达式的形式不会覆盖标签原有的数据
b.使用v-text可以避免在网络环境较差的情况下出现插值闪烁
3.2、v-html
v-html:用来获取data中数据将数据中含有的html标签先解析在渲染到指定标签的内部 类似于javascript中 innerHTML
<div id="app" class="aa">
<span>{{message}}</span>
<br>
<span v-text="message"></span>
<br>
<span v-html="message">xxxxxx</span>
</div>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message:"<a href=''>百知欢迎您</a>"
}
})
</script> } }) </script>
3.3、v-text和v-html对比
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" class="aa">
<h2>{{msg}} 您好</h2>
<!--vue提供两个指令: v-text v-html 都可以直接根据属性名获取data数据渲染到指定标签内-->
<!--v-text-->
<h2><span v-text="msg"></span> 您好</h2>
<!--
v-text: {{}} 取值区别:
1.使用{{}}取值不会将标签原始数据覆盖 使用v-text获取数据会将标签中原始内容覆盖
2.v-text获取数据时不会出现插值闪烁 {{属性名}} ===> 插值表达式:容易出现插值闪烁 插值闪烁:当网络不好条件情况下使用{{}}方式获取数据
-->
<h2 v-html="msg"></h2>
<!--
共同点:都可以直接根据data中数据名,将数据渲染到标签内部
v-text: v-text将获取数据直接以文本形式渲染到标签内部 innerText
v-html: v-html将获取数据中含有html标签解析之后渲染到对应标签内部 innerHtml
-->
<h1 >{{content}}</h1>
<h1 v-text="content"></h1>
<h1 v-html="content"></h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
content : "欢迎来到<a href='http://www.baidu.com'>百度</a>",
}
});
</script>
运行结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LdfpoTfT-1627348740558)(Vue实战笔记(一).assets/image-20210709215316787.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/1a3f42da0d7f309812de76a72a790459.png)
4、vue中事件绑定(v-on)
4.1、绑定事件基本语法
1、vue事件绑定(一)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<h2 v-text="msg"></h2>
<h2 v-html="msg"></h2>
<!--
js 事件三要素
1.事件源:发生事件源头称之为事件源,一般指的是html标签
2.事件:发生特定动作 onclick单击 dbclick 双击 onkeyup ......
3.监听器:事件处理器程序 事件处理函数 function(){}
vue 事件:v-on
1.在vue中给对应标签绑定事件可以通过vue提供v-on指令进行事件绑定 ==> v-on:事件名
2.在vue中事件处理函数统一声明在vue实例中methods属性
-->
<!--给button按钮绑定多个事件-->
<input type="button" value="点我" v-on:click="aaa" v-on:mouseover="bbb" v-on:mouseout="ccc">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
},
methods:{ //用来给当前vue实例对象,声明一系列函数
aaa: function () {
alert("aaa");
},
bbb: function () {
console.log("mouse over");
},
ccc: function () {
console.log("mouse out");
}
}
});
</script>
2、vue事件绑定(二)
给一个按钮绑定点击+1事件。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<h1>{{age}}</h1>
<!--
vue事件:
1. 使用v-on:事件名
2. 函数名统一定义在vue实例中 methods 属性中
-->
<input type="button" value="点我给年龄+1" v-on:click="incrmentAge">
<input type="button" value="点我给年龄-1" v-on:click="decrmentAge">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
age:23,
},
methods:{ //用来给当前vue实例对象,声明一系列函数
incrmentAge:function () {
//this对象代表当前vue实例对象
console.log(this);
console.log(this.age)
if(this.age >= 120) return;
this.age ++; //vue实例中data数据age发生变化
},
decrmentAge:function () { //定义函数
if(this.age < 2) return ;
this.age --;
}
}
});
</script>
3、总结
事件源: 发生事件dom元素 事件: 发生特定的动作 click.... 监听器 发生特定动作之后的事件处理程序 通常是js中函数
-
在
vue中绑定事件是通过v-on指令来完成的v-on:事件名 如v-on:click -
在
v-on:事件名的赋值语句中是当前事件触发调用的函数名 -
在
vue中事件的函数统一定义在Vue实例的methods属性中 -
在
vue定义的事件中this指的就是当前的Vue实例,日后可以在事件中通过使用this获取Vue实例中相关数据 调用methods中相关方法
4.2、Vue中事件的简化语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<h1>{{age}}</h1>
<!--
vue事件绑定 v-on:事件名 简化写法===> @事件名
-->
<input type="button" value="点我改变年龄" @click="changeAge">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
age:23,
},
methods:{
changeAge:function () {
this.age ++ ;
}
}
});
</script>
# 总结:
1.日后在vue中绑定事件时可以通过@符号形式 简化 v-on 的事件绑定
4.3、Vue事件函数两种写法
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
age:23,
},
methods:{
/*changeAge:function () { //定义事件 简化写法
this.age ++ ;
}*/
changeAge(){ //es6语法 ecmascript 6版本
this.age ++ ;
}
}
});
</script>
# 总结:
1.在Vue中事件定义存在两种写法
一种是 函数名:function(){}
一种是 函数名(){} 推荐
4.4、Vue事件参数传递
我们还可以给vue事件中传递参数。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<h1>{{age}}</h1>
<!--
vue事件绑定 v-on:事件名 简化 @事件名="事件函数名(参数......)"
-->
<!--多个参数使用','隔开-->
<input type="button" value="点我改变年龄的值" @click="changeAge(10,'xiaohei')">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
age:23,
},
methods:{
changeAge(number,name){ //定义事件
console.log(number);
console.log(name);
this.age += number ;
}
}
});
</script>
# 总结:
1.在使用事件时,可以直接在事件调用处给事件进行参数传递,在事件定义处通过定义对应变量接收传递的参数
5、v-show v-if v-bind
5.1、v-show、v-if使用
v-show: 用来控制页面中某个标签元素是否展示
v-if: 用来控制页面元素是否展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--
v-if、v-show : 作用:都是用来控制页面中标签是否展示和隐藏 使用:标签:v-if="true|false" v-show="true|false"
区别:
v-show: 底层在控制页面标签是否展示时底层使用的是css 中 display 属性来标签展示和隐藏 推荐使用:v-show 数据量比较大 控制显示状态切换频繁
v-if : 底层在控制页面标签是否展示时底层是直接操作dom元素,通过对dom元素删除和添加来控制标签的展示和隐藏
-->
<!--v-show-->
<h1 v-show="isShow">{{content}}</h1>
<!--v-if-->
<h1 v-if="isShow">{{content}}</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
content: "vue学习",
isShow:true
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
}
});
</script>
总结:
- 在使用v-show时可以直接书写boolean值控制元素展示,也可以通过变量控制标签展示和隐藏。
- 在v-show中可以通过boolean表达式控制标签的展示和隐藏。
- v-if、v-show : 作用:都是用来控制页面中标签是否展示和隐藏 使用:标签:
v-if="true|false",v-show="true|false" - 区别:
- v-show: 底层在控制页面标签是否展示时底层使用的是css 中 display 属性来标签展示和隐藏 。推荐使用:v-show 在数据量比较大和控制显示状态切换频繁时。
- v-if : 底层在控制页面标签是否展示时底层是直接操作dom元素,通过对dom元素删除和添加来控制标签的展示和隐藏。
5.2、v-show、v-if小案例
1、v-show、v-if显示隐藏案例(一)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<!-- v-show v-if -->
<h2 v-show="isShow">{{msg}}</h2>
<!--绑定事件 单击事件 @click-->
<input type="button" value="显示" @click="show">
<input type="button" value="隐藏" @click="hidden">
<input type="button" value="切换显示状态" @click="changeState">
<input type="button" value="切换显示状态,另一种写法" @click="isShow=!isShow">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
isShow:true
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
show(){ //用来显示
this.isShow = true;
},
hidden(){//用来隐藏
this.isShow = false;
},
changeState(){ //切换显示状态
this.isShow = !this.isShow;
},
}
});
</script>
2、v-show、v-if显示隐藏案例(二)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<!-- v-show v-if -->
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--图片添加鼠标移入事件-->
<img width="200" v-show="isShow" @mouseover="hide" style="border: 5px red solid" src="https://img0.baidu.com/it/u=384452397,1089369801&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg" alt="这是图片">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
isShow:true
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
hide(){
this.isShow = false;
}
}
});
</script>
5.3、v-bind
v-bind: 用来绑定标签的属性从而通过vue动态修改标签的属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--
v-bind: 绑定 作用:用来将html标签中相关属性绑定到vue实例中,日后通过对vue实例中数据修改,影响到对应标签中属性变化
语法:v-bind:属性名
-->
<img v-bind:width="width" v-bind:src="imgSrc" v-bind:alt="tip">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
imgSrc:"https://img0.baidu.com/it/u=384452397,1089369801&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg",
width:200,
tip:"这是图片"
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
}
});
</script>
5.4、v-bind 简化写法
vue为了方便我们日后绑定标签的属性提供了对属性绑定的简化写法如
v-bind:属性名简化之后:属性名
<!--
v-bind: 绑定 作用:用来将html标签中相关属性绑定到vue实例中,日后通过对vue实例中数据修改,影响到对应标签中属性变化
语法:v-bind:属性名 =====> 简化写法:属性名
-->
<img :width="width" :src="imgSrc" :alt="tip">
扩展v-bind使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
<style>
.aa{
border: 5px red solid;
}
.bb{
border: 5px darkorange solid;
}
</style>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--
v-bind: 绑定 作用:用来将html标签中相关属性绑定到vue实例中,日后通过对vue实例中数据修改,影响到对应标签中属性变化
语法:v-bind:属性名 =====> 简化写法:属性名
-->
<img :width="width" :src="imgSrc" :alt="tip" :class="isClass?'aa':'bb'">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
imgSrc:"https://img0.baidu.com/it/u=384452397,1089369801&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg",
width:200,
tip:"这是图片",
isClass:true, //ture 显示red false 显示orange
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
}
});
</script>
5.5、v-bind案例
实现鼠标移入和移出对图片和边框的切换。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
<style>
.aa{
border: 5px red solid;
}
.bb{
border: 5px darkorange solid;
}
</style>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--属性绑定-->
<img width="200" @mou="change" :src="src" :class="cls" @mouseover="change" @mouseout="recover">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
src:"https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=1077360284,2857506492&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg",
cls:"aa"
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
change(){
this.src = "https://img1.baidu.com/it/u=3229045480,3780302107&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg";
this.cls = "bb";
},
recover(){
this.src = "https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=1077360284,2857506492&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg";
this.cls = "aa";
}
}
});
</script>
6、v-for的使用
v-for: 作用就是用来对对象进行遍历的(数组也是对象的一种)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--
v-for : 作用:用来给vue实例中数据进行遍历
-->
<h1>遍历对象</h1>
<h2 v-for="(value,key,index) in user">
index: {{index}} key:{{key}} value:{{value}}
</h2>
<h1>遍历数组</h1>
<h2 v-for="(school,index) in schools">
index:{{index}} schools:{{school}}
</h2>
<h1>遍历数组中含有对象</h1>
<h2 v-for="(user,index) in users" :key = "user.id">
index: {{index}} name:{{user.name}} age:{{user.age}} bir:{{user.bir}}
</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
user:{name:"小王",age:23,bir:"2012-02-06"},
schools:["北京","重庆","天津"],
users:[
{id:"1",name:"小王",age:23,bir:"2012-02-06"},
{id:"2",name:"小李",age:34,bir:"2016-02-06"},
{id:"3",name:"小赵",age:12,bir:"2014-02-06"},
]
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
}
});
</script>
# 总结
1.在使用v-for的时候一定要注意加入:key 用来给vue内部提供重用和排序的唯一key
7、v-model 双向绑定
7.1、v-model
v-model: 作用用来绑定标签元素的值与vue实例对象中data数据保持一致,从而实现双向的数据绑定机制
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body >
<div id="app" >
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!--
v-model : 作用:用来绑定from表单标签中的value属性交给vue实例进行管理 input select checxbox button ...
-->
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
<input type="button" value="改变data数据" @click="change">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue.js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //指定vue实例作用范围
data:{ //用来给vue实例绑定一系列数据
msg:"hello vue",
},
methods:{ //用来给vue实例定义事件处理函数
change(){
this.msg = "vue学习"
}
}
});
</script>
总结:
# 总结
1.使用v-model指令可以实现数据的双向绑定
2.所谓双向绑定 表单中数据变化导致vue实例data数据变化 vue实例中data数据的变化导致表单中数据变化 称之为双向绑定
# MVVM架构 双向绑定机制
Model: 数据 Vue实例中绑定数据
VM: ViewModel 监听器
View: 页面 页面展示的数据
学完v-model以后,我们一起来做两个小案例。
7.2、两个案例
备忘录案例实现
需求:

代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<!-- v-if(dom)、v-show(css display) : 作用:都是用来控制页面中标签是否展示和隐藏-->
输入备忘录内容:<input type="text" v-model="content"> <input type="button" value="添加到备忘录" @click="saveItem"> <br>
<ul v-show="items.length > 0">
<li v-for="(item,index) in items">{{index+1}}. {{item}} <a href="javascript:;" @click="delItem(index)">删除</a></li>
</ul>
<h5 v-show="items.length == 0">当前备忘录中还没有任何内容~~,请添加!</h5>
<h3>当前备忘录中共:{{items.length}}条</h3>
<input type="button" value="清空备忘录" @click="delAllItems">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue的js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //代表vue实例作用范围
data:{ //在vue实例中定义一系列数据
msg:"备忘录功能实现",
items:["今天去买菜","今天要好好学习","今天要取快递"],
content:""
},
methods:{ //在vue实例中定义相关函数
saveItem(){ //添加备忘录方法
console.log(this.content);
if(!this.content) {
alert("请输入备忘录内容!!!")
return;
}
this.items.push(this.content); //将新增的内容添加到数组中
this.content="";
},
delItem(index){ //根据下标删除指定元素
console.log(index);
this.items.splice(index,1); //根据下标删除元素 //参数1:删除起始下标 参数2:删除元素个数
},
delAllItems(){ //清空备忘录
this.items = [];
}
}
});
</script>
效果:

购物车案例实现
需求:

代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>小计</th>
</tr>
<!--v-for-->
<tr v-for="(item,index) in items" :key="item.id">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td><input type="button" value="-" @click="decrCount(index)">{{item.count}}<input type="button" value="+" @click="incrCount(index)"></td>
<td>{{(item.price * item.count).toFixed(2)}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<h3>总价格:{{getTotalPrice()}}</h3>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue的js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //代表vue实例作用范围
data:{ //在vue实例中定义一系列数据
msg:"购物车功能实现",
items:[
{id:1,name:"苹果iphone12",count:1,price:28.28},
{id:2,name:"华为mate40 pro",count:1,price:30.28},
]
},
methods:{ //在vue实例中定义相关函数
incrCount(index){ //数量增加的方法
console.log(this.items[index].count);
this.items[index].count++;
},
decrCount(index){ //数量减少的方法
console.log(this.items[index].count);
if( this.items[index].count >= 1){
this.items[index].count--;
}else{
alert("不能在少了!");
return ;
}
},
getTotalPrice(){
var totalPrice = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++){
totalPrice += this.items[i].count * this.items[i].price;
}
return totalPrice.toFixed(2);
}
}
});
</script>
效果:

8、计算属性
计算属性:computed: vue官方提供一个计算属性
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<!--
computed: vue官方提供一个计算属性
作用:在完成某种业务时,往往页面结果需要经过多次计算才能获取,computed属性就是用来完成页面结果多次计算
好处:在完成计算同时也会将本次计算结果进行缓存,如果数据没有发生变化,在页面中多次使用,计算方法仅执行一次
使用:{{ 属性名}} 属性名即方法名称
-->
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>小计</th>
</tr>
<!--v-for-->
<tr v-for="(item,index) in items" :key="item.id">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td><input type="button" value="-" @click="decrCount(index)">{{item.count}}<input type="button" value="+" @click="incrCount(index)"></td>
<td>{{(item.price * item.count).toFixed(2)}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!--使用methods方法完成计算业务:
缺点:
1.只要调用了一次计算方法,整个计算方法就会执行一次,如果在一个页面中多次使用到计算结果,可能会导致造成重复计算,导致页面加载性能变低
-->
<h3>总价格:{{totalPrice}}</h3>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue的js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //代表vue实例作用范围
data:{ //在vue实例中定义一系列数据
msg:"购物车功能实现之methods方法实现总价格",
items:[
{id:1,name:"苹果iphone12",count:1,price:28.28},
{id:2,name:"华为mate40 pro",count:1,price:30.28},
]
},
methods:{ //在vue实例中定义相关函数
incrCount(index){ //数量增加的方法
console.log(this.items[index].count);
this.items[index].count++;
},
decrCount(index){ //数量减少的方法
console.log(this.items[index].count);
if( this.items[index].count >= 1){
this.items[index].count--;
}else{
alert("不能在少了!");
return ;
}
},
},
computed:{ //用来书写计算相关方法 计算属性
totalPrice(){ //计算方法 好处:只进行一次计算,多次使用时直接使用第一次计算之后缓存结果
var totalPrice = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++){
totalPrice += this.items[i].count * this.items[i].price;
}
return totalPrice.toFixed(2);
}
}
});
</script>
总结:
- 作用:在完成某种业务时,往往页面结果需要经过多次计算才能获取,computed属性就是用来完成页面结果多次计算
- 好处:在完成计算同时也会将本次计算结果进行缓存,如果数据没有发生变化,在页面中多次使用,计算方法仅执行一次
- 使用:{{ 属性名}} 属性名即方法名称
9、事件修饰符
修饰符: 用来和事件连用,用来决定事件触发条件或者是阻止事件的触发机制
# 1.常用的事件修饰符
.stop 停止
.prevent 阻止
.self 独自
.once 一次
9.1 stop事件修饰符
用来阻止事件冒泡
<h2>stop事件修饰符</h2>
<!--.stop 事件修饰符 作用:用来阻止事件的冒泡-->
<div style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background: red" @click="parent">
<!--对孩子中单击事件进行修饰:不进行事件冒泡处理 .stop-->
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background: green" @click.stop="child"></div>
</div>
9.2 prevent 事件修饰符
用来阻止标签的默认行为
<h2>prevent事件修饰符</h2>
<!--默认行为:根据href连接自动跳转 .prevent 阻止事件默认行为-->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="search">百度一下</a>
<a href="javascript:void(0);" @click.prevent="search">百度一下</a>
<a href="javascript:;" @click.prevent="search">百度一下</a>
9.3 self 事件修饰符
用来针对于当前标签的事件触发 ===========> 只触发自己标签的上特定动作的事件 只关心自己标签上触发的事件 不监听事件冒泡
<h2>slef事件修饰符</h2>
<!--self: 只监听自身标签触发的对应事件-->
<div style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background: aqua" @click.self="parent">
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background: green" @click="child"></div>
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background: brown" @click="child"></div>
</div>
9.4 once 事件修饰符
once 一次作用: 就是让指定事件只触发一次
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<!--
事件修饰符 作用:用来和事件连用,用来决定事件触发条件和决定事件触发机制
.stop 停止事件冒泡
.prevent 阻止默认行为
.slef 只触发自身行为
.once 一次事件
注意:事件修饰符可以多个连用
-->
<h2>stop事件修饰符</h2>
<!--.stop 事件修饰符 作用:用来阻止事件的冒泡-->
<div style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background: red" @click="parent">
<!--对孩子中单击事件进行修饰:不进行事件冒泡处理 .stop-->
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background: green" @click.stop.once="child"></div>
</div>
<h2>prevent事件修饰符</h2>
<!--默认行为:根据href连接自动跳转 .prevent 阻止事件默认行为-->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="search">百度一下</a>
<a href="javascript:void(0);" @click.prevent="search">百度一下</a>
<a href="javascript:;" @click.prevent="search">百度一下</a>
<h2>slef事件修饰符</h2>
<!--self: 只监听自身标签触发的对应事件-->
<div style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background: aqua" @click.self="parent">
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background: green" @click="child"></div>
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background: brown" @click="child"></div>
</div>
<h2>once事件修饰符</h2>
<!--once事件修饰符:作用:只能让标签上的对应事件执行一次-->
<input type="button" value="点我" @click.once="clickMe">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue的js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //代表vue实例作用范围
data:{ //在vue实例中定义一系列数据
msg:"事件修饰符",
},
methods:{ //在vue实例中定义相关函数
parent(){
alert("parent div event");
},
child(){
alert("child div event");
},
search(){
alert("a click event");
},
clickMe(){
alert("click me!!!")
}
},
computed:{ //用来书写计算相关方法 计算属性
}
});
</script>
10、按键修饰符
作用: 用来与键盘中按键事件绑定在一起,用来修饰特定的按键事件的修饰符
# 按键修饰符
.enter
.tab
.delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键)
.esc
.space
.up
.down
.left
.right
10.1 enter 回车键
用来在触发回车按键之后触发的事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<!--
按键修饰符:作用:用来和键盘上事件(keyup,keydown......)进行连用,用来修饰键盘上特定的按键来触发对应的事件
.enter
.tab
.delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键)
.esc
.space
.up
.down
.left
.right
-->
<!--.enter 回车按键修饰符-->
<input type="text" v-model="msg" @keyup.enter="test">
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入vue的js文件-->
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app", //代表vue实例作用范围
data:{ //在vue实例中定义一系列数据
msg:"按键修饰符",
},
methods:{ //在vue实例中定义相关函数
test(){
console.log("test");
}
},
computed:{ //用来书写计算相关方法 计算属性
}
});
</script>
10.2 tab 键
用来捕获到tab键执行到当前标签是才会触发
<input type="text" @keyup.tab="test">
11、Axios 基本使用
11.1、引言
Axios是一个异步请求技术,核心作用就是用来在页面中发送异步请求,并获取对应数据在页面中渲染 页面局部更新技术 Ajax
11.2、Axios 第一个程序
中文网站:https://www.kancloud.cn/yunye/axios/234845
安装: https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js
11.2.1、GET方式的请求
后端代码:
package com.xiao.controller;
import com.xiao.entity.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import java.util.Date;
@RestController //代表接口中返回的都是json格式数据
@CrossOrigin //运行所有的请求 所有域访问 解决:跨域问题
public class AdminController {
//user接口
//rest接口 url/11/
@GetMapping("user/{id}")
public User FindUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
System.out.println("id: "+id);
System.out.println("user...");
return new User(id,"小李",23,new Date());
}
//queryString接口 url?id=11
@GetMapping("user")
public User user(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){
System.out.println("id: "+id);
System.out.println("user...");
return new User(id,"小陈",23,new Date());
}
//测试接口
@GetMapping("demo")
public String demo(){
System.out.println("demo...");
return "demo ok";
}
}
前端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "app">
<h1>axios的GET方式请求</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入axios异步请求核心js文件-->
<script src="js/axios.min.js"></script>
<!--测试异步请求-->
<script>
//发送axios 的GET方式请求
/*axios.get("http://localhost:8989/user?id=11").then(function (res){
console.log(res.data);
console.log(res.data.id);
console.log(res.data.name);
console.log(res.data.age);
console.log(res.data.bir);
});*/
//es6中简化写法function(){}简化写法java中lambada表达式 ()=>
axios.get("http://localhost:8989/user/11").then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data);
console.log(res.data.id);
console.log(res.data.name);
console.log(res.data.age);
console.log(res.data.bir);
});
/*axios.get("http://localhost:8989/demo").then(function (resonse){ //then 正确请求返回处理结果
console.log(resonse.data);
}).catch(function (error){ //请求地址值出错的处理结果
console.log(error)
}); //发送异步请求方式*/
</script>
11.2.2 POST方式请求
后端代码:
//定义post接口
@PostMapping("user")
public Map<String,Object> save(@RequestBody User user){ //@RequestBody 将json格式数据转换成java对象
System.out.println("user:" + user);
HashMap<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("success",true);
result.put("msg","添加成功~~");
return result;
}
前端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "app">
<h1>axios的POST方式请求</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!--引入axios异步请求核心js文件-->
<script src="js/axios.min.js"></script>
<!--测试异步请求-->
<script>
//发送post方式请求
//参数1: url地址 参数2: 请求数据
axios.post("http://localhost:8989/user",{
name:"小李",
age:23,
bir:"2012-02-05"
}).then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data);
});
</script>
11.2.3 axios并发请求
并发请求: 将多个请求在同一时刻发送到后端服务接口,最后在集中处理每个请求的响应结果

//axios并发请求
//定义demo请求
function demo(){
return axios.get("http://localhost:8989/demo");
}
//定义user请求
function user(){
return axios.get("http://localhost:8989/user?id=11");
}
axios.all([demo(), user()]).then(axios.spread((demoRes,useRes)=>{ //并发请求
console.log(demoRes);
console.log(useRes);
}));
11.2.4 拦截器

12、Vue 生命周期
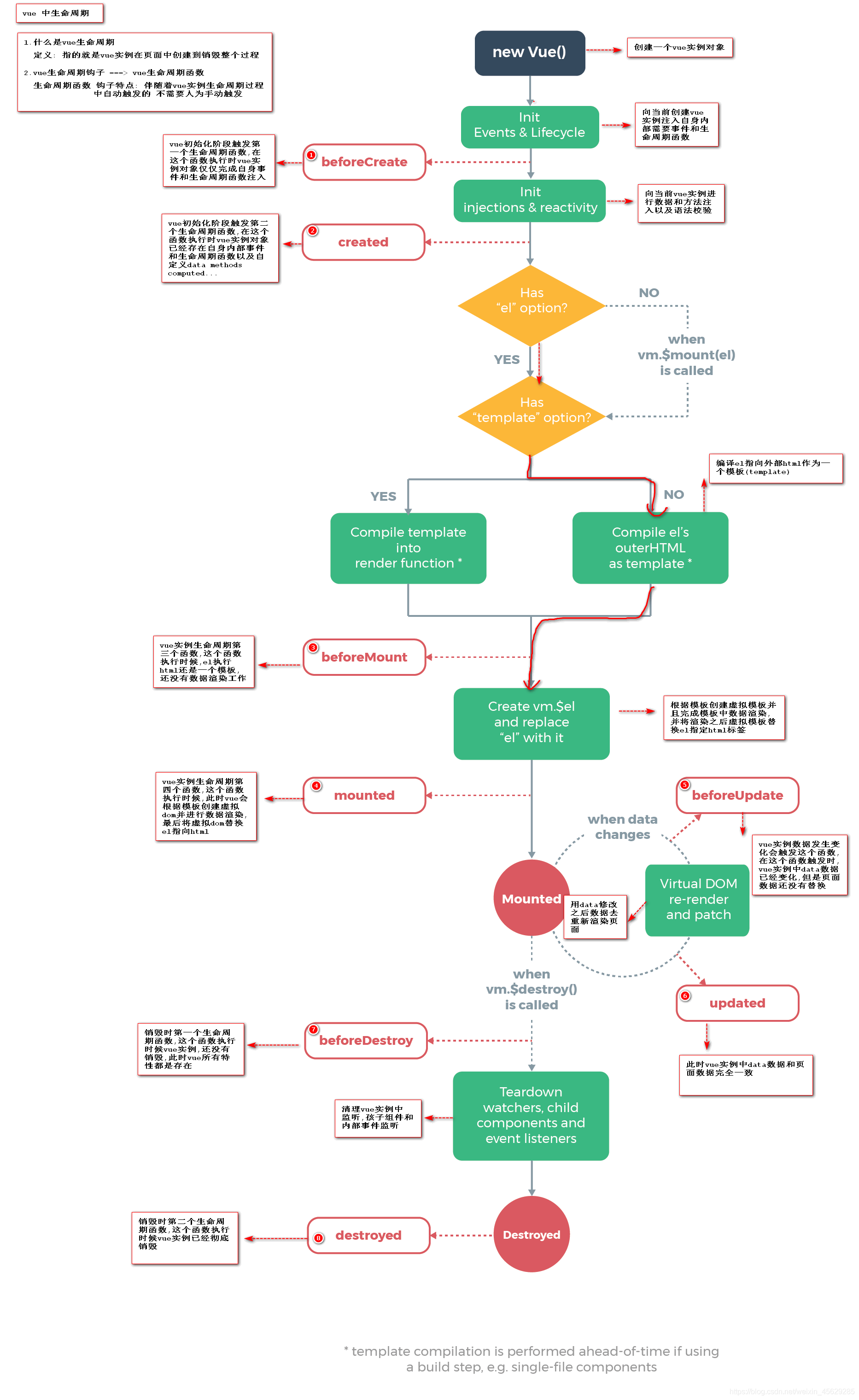
Vue 实例生命周期 ===> java 对象生命周期(初始化阶段 运行阶段 销毁阶段)
生命周期钩子====>生命周期函数Vue实例从创建到销毁过程中自动触发一系列函数 ====> Vue生命周期函数(钩子)
Vue生命周期总结
#
- 1.初始化阶段
beforeCreate(){ //1.生命周期中第一个函数,该函数在执行时Vue实例仅仅完成了自身事件的绑定和生命周期函数的初始化工作,Vue实例中还没有 Data el methods相关属性
console.log("beforeCreate: "+this.msg);
},
created(){ //2.生命周期中第二个函数,该函数在执行时Vue实例已经初始化了data属性和methods中相关方法
console.log("created: "+this.msg);
},
beforeMount(){//3.生命周期中第三个函数,该函数在执行时Vue将El中指定作用范围作为模板编译
console.log("beforeMount: "+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
mounted(){//4.生命周期中第四个函数,该函数在执行过程中,已经将数据渲染到界面中并且已经更新页面
console.log("Mounted: "+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
}
- 2.运行阶段
beforeUpdate(){//5.生命周期中第五个函数,该函数是data中数据发生变化时执行 这个事件执行时仅仅是Vue实例中data数据变化页面显示的依然是原始数据
console.log("beforeUpdate:"+this.msg);
console.log("beforeUpdate:"+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
updated(){ //6.生命周期中第六个函数,该函数执行时data中数据发生变化,页面中数据也发生了变化 页面中数据已经和data中数据一致
console.log("updated:"+this.msg);
console.log("updated:"+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
- 3.销毁阶段
beforeDestory(){//7.生命周期第七个函数,该函数执行时,Vue中所有数据 methods componet 都没销毁
},
destoryed(){ //8.生命周期的第八个函数,该函数执行时,Vue实例彻底销毁
}
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue系列课程</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "app">
<h1 id="sp">{{msg}}</h1>
<input type="button" value="修改数据" @click="changeData">
<!--
vue生命周期分为三个阶段:
1.初始化阶段
beforeCreate(){ //1.生命周期中第一个函数,该函数在执行时Vue实例仅仅完成了自身事件的绑定和生命周期函数的初始化工作,Vue实例中还没有 Data el methods相关属性
console.log("beforeCreate: "+this.msg);
},
created(){ //2.生命周期中第二个函数,该函数在执行时Vue实例已经初始化了data属性和methods中相关方法
console.log("created: "+this.msg);
},
beforeMount(){//3.生命周期中第三个函数,该函数在执行时Vue将El中指定作用范围作为模板编译
console.log("beforeMount: "+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
mounted(){ //4.生命周期中第四个函数,该函数在执行过程中,已经将数据渲染到界面中并且已经更新页面
console.log("Mounted: "+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
}
2.运行阶段
beforeUpdate(){//5.生命周期中第五个函数,该函数是data中数据发生变化时执行 这个事件执行时仅仅是Vue实例中data数据变化页面显示的依然是原始数据
console.log("beforeUpdate:"+this.msg);
console.log("beforeUpdate:"+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
updated(){ //6.生命周期中第六个函数,该函数执行时data中数据发生变化,页面中数据也发生了变化 页面中数据已经和data中数据一致
console.log("updated:"+this.msg);
console.log("updated:"+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
3.销毁阶段
beforeDestory(){//7.生命周期第七个函数,该函数执行时,Vue中所有数据 methods componet 都没销毁
},
destoryed(){ //8.生命周期的第八个函数,该函数执行时,Vue实例彻底销毁
}
-->
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data:{
msg:"vue 生命周期",
},
methods:{
changeData(){
this.msg="vue 生命周期讲解";
}
},
computed:{},
beforeCreate(){ //1.生命周期中第一个函数,该函数在执行时Vue实例仅仅完成了自身事件的绑定和生命周期函数的初始化工作,Vue实例中还没有 Data el methods相关属性
console.log("beforeCreate: "+this.msg);
},
created(){ //2.生命周期中第二个函数,该函数在执行时Vue实例已经初始化了data属性和methods中相关方法
console.log("created: "+this.msg);
},
beforeMount(){//3.生命周期中第三个函数,该函数在执行时Vue将El中指定作用范围作为模板编译
console.log("beforeMount: "+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
mounted(){ //4.生命周期中第四个函数,该函数在执行过程中,已经将数据渲染到界面中并且已经更新页面
console.log("Mounted: "+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
beforeUpdate(){//5.生命周期中第五个函数,该函数是data中数据发生变化时执行 这个事件执行时仅仅是Vue实例中data数据变化页面显示的依然是原始数据
console.log("beforeUpdate:"+this.msg);
console.log("beforeUpdate:"+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
updated(){ //6.生命周期中第六个函数,该函数执行时data中数据发生变化,页面中数据也发生了变化 页面中数据已经和data中数据一致
console.log("updated:"+this.msg);
console.log("updated:"+document.getElementById("sp").innerText);
},
beforeDestory(){//7.生命周期第七个函数,该函数执行时,Vue中所有数据 methods componet 都没销毁
},
destoryed(){ //8.生命周期的第八个函数,该函数执行时,Vue实例彻底销毁
}
});
</script>

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容








所有评论(0)