自定义view,viewgroup的onMeasure 方法
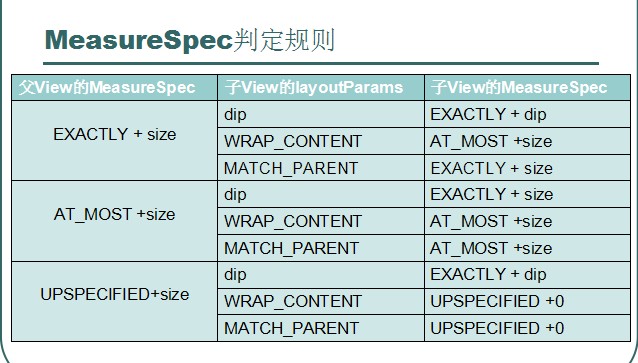
自定义view用了好久,用着用着吧感觉也就那么回事儿啊,如果想画个view,那就得知道view的大小。那么首当其中的就是onMeasure()方法啦。先上一张图,这是我当年自学android的时候看的黑马视频的图。珍藏了快两年啦这张图,第一次看基本看不懂onMeasure有三种 模式EXACTLY:精确父容器已经知道 这个view的大小AT_MOST:父容器 定了一个最大值,view不
自定义view用了好久,用着用着吧感觉也就那么回事儿啊,如果想画个view,那就得知道view的大小。
那么首当其中的就是onMeasure()方法啦。
先上一张图,这是我当年自学android的时候看的黑马视频的图。珍藏了快两年啦
这张图,第一次看基本看不懂
onMeasure有三种 模式
EXACTLY:精确 父容器已经知道 这个view的大小
AT_MOST:父容器 定了一个最大值,view不能大于这个值
UPSPECIFIED:父容器 不对view做限制,view想多大就多大 不用管这个模式,用不上
简单说上面的图怎么看呢:(不用看UPSPECIFIED)
先看子view的layoutParams(中间那列)
如果xml里面写的 是 dip 那么该view都是EXACTLY
如果xml里面写的 是 wrap_content 那么该view都是AT_MOST
如果xml里面写的 是 match_parent 那么子view就和父容器的一样
View的onMeasure()方法
先说一句啊,其实xml存在的意义呢 就是 让我们开发方便一些,可视化一些,mvc一些。所以呢xml里面的数值 属性都会 在代码里面提现,所以 xml 和代码同时 设置了 某个属性 那么 大多数都会以 代码为准(说话永远都不能太绝对)。
public class MyView extends View {
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
//这个就是测量啦
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
注意啦:widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec 并不是真正的宽高。是一个32位int值。高2位 代表SpecMode,低30为代表SpecSize 。一会儿会用到我们看看super 里面
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}其实呢 setMeasuredDimension(int,int)就是设置这个view的大小啦。 现在我们这样写
public class MyView extends View {
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(100,100);
//这样写呢 ,不管你xml里面的宽高些什么,都不管用了。view的宽高永远是100,100; 不信可以试一下
}
}
还有一个要注意的就是
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
这个getDefaultSize();是什么意思呢 进去看看
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;//给了一个默认值
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
//上面说的还记得吧,measureSpec是一个32为的int值 。MeasureSpec.getMode和MeasureSpec.getSize方法 分别获取 模式 和 真实的大小。
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED://如果是不限制大小 就给他一个默认值
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: //如果xml里面写的 是 wrap_content 那么该view都是AT_MOST
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://如果是精确的 那就是 精确的了
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
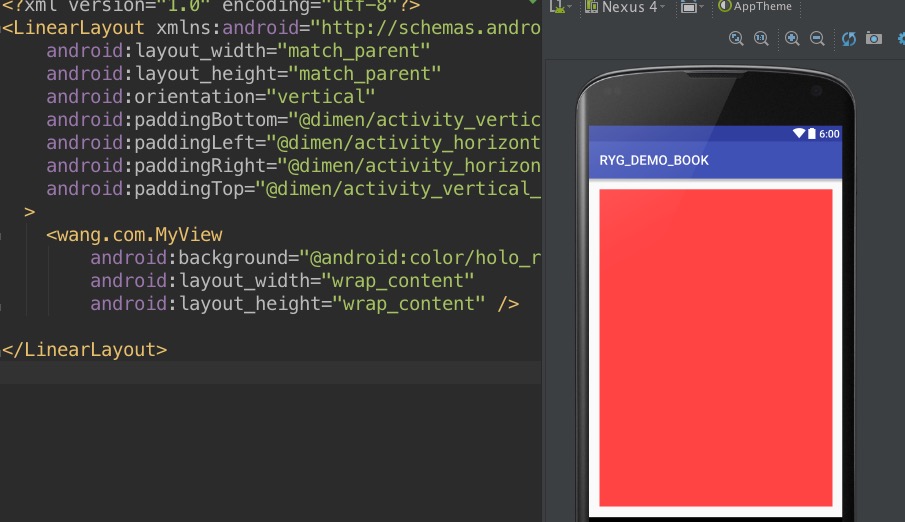
所以你会发现。如果你的view宽高是 wrap_content那么他的大小就是 父空间剩余的大小一样大了(要减去 padding marging)好啦。现在知道view 空间是如何 测量大小的了吧。 然后呢我们可以根据getDefaultSize()的 内容自己写一个。这里 改了一下 《android英雄传》里的代码 ,以后不要再因为onMeaure不会写 不敢自定义view啦。下面的代码直接复制 。上面解释 不看也行
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(200, widthMeasureSpec), measureHight(200, heightMeasureSpec));
}
private int measureWidth(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
System.out.println("EXACTLY:" + result);
} else {
result = size;//最小值是200px ,自己设定
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
private int measureHight(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = size;//最小值是200px ,自己设定
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
}如果你想弄个 jar包啊,复用的库啊 直接用上面方法,
如果你追求没那么高 直接用 setMeasuredDimension(int, int);就行啦。
ViewGroup的onMeasure
也很简单
public class MyViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
public MyViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(100, 200);
}
其实和view的完全一样。这个时候 viewgroup的宽高就是100,200了
如果这样呢:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
这个时候呢 ,不管xml里面不管是wrap_content,还是match_parent 这个自定义viewgroup的大小都是 match_parent
再进一步呢:测量子view的布局
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
// 挨个测量大小.好简单有没有
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}下面直接一步到位:
我们的自定义viewgroup考虑的问题
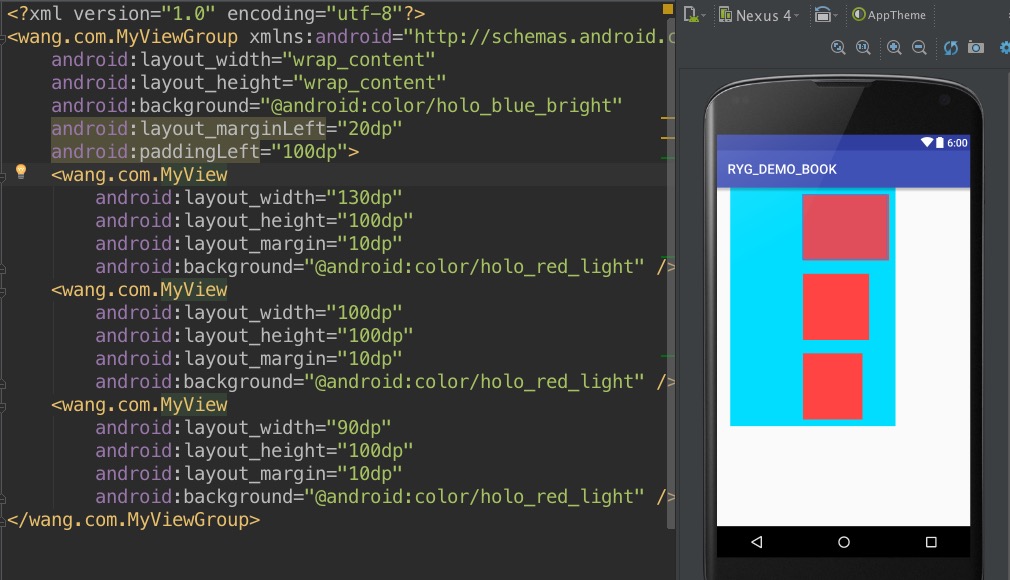
- padding margin
- 父窗体要在wrap_content的时候要根据子布局的大小而定,肯定是获取最大的那个子view的大小了
- 仿照一个linearlayout 的vertical 写一个简陋的 viewgroup
这样的。
package wang.com;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* 创建日期: 16/3/16 上午11:16
* 作者:wanghao
* 描述:
*/
public class MyViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
public MyViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 这里确定吧子view的布局放在那里. 很好理解吧.一般简单的就是 横着放 竖着放 .
// 不断地更改每个子布局的位置 .
int height = 0;
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MyLayoutParams ml = (MyLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(//
getPaddingLeft() + ml.leftMargin,//
getPaddingTop() + ml.topMargin + height,//
getPaddingLeft() + ml.leftMargin + child.getMeasuredWidth(),//
getPaddingTop() + ml.topMargin + child.getMeasuredHeight() + height//
);
height += child.getMeasuredHeight() + ml.bottomMargin + ml.topMargin;
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int parentWidth = 0;//父窗体根据子布局的大小变化 其实就是档wrap_content的时候
int parentHeight = 0;
int cacheWidth = 0;//缓存父宽度
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
// 直接获取第一个view的宽度 ,之后就和其他的view进行对比了
View firstchild = getChildAt(0);
MyLayoutParams firstml = (MyLayoutParams) firstchild.getLayoutParams();
cacheWidth = firstchild.getMeasuredWidth() + firstml.leftMargin + firstml.rightMargin;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 必须要自定义 然后继承MarginLayoutParams 才能获取margin ,不然空指针
MyLayoutParams ml = (MyLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//我们想获取竖着的 宽度最大值的那个view的宽度作为 父窗体的宽度 (这么绕嘴呢)
parentWidth = Math.max(cacheWidth, child.getMeasuredWidth() + ml.leftMargin + ml.rightMargin);
cacheWidth = parentWidth;//把最大值赋值给缓存 在进行和下一个的比较
parentHeight += child.getMeasuredHeight() + ml.topMargin + ml.bottomMargin;
}
//获取padding边距
parentWidth += getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
parentHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
}
// 设置最终测量值O
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSize(parentWidth, widthMeasureSpec), resolveSize(parentHeight, heightMeasureSpec));
// resolveSize(int,int);这个方法不要怕,就是 在 两个int值里面选择一个 作为最后只 赋值给viewgroup
// 总之就是:在AT_MOST模式下 从xml里面获取的值 和viewgroup获取子view占的面积的值 选择最小的
}
/*———————————————如果想获取margin 所有自定义viewgroup都要自定义这个,可以参考LinearLayout,FrameLayout等 ———————————————————*/
public static class MyLayoutParams extends MarginLayoutParams {
public MyLayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public MyLayoutParams(android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public MyLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
}
public MyLayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
}
@Override
protected MyLayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MyLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
}
@Override
protected android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new MyLayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MyLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof MyLayoutParams;
}
}这里面用到了几个 方法 简单说下:
- getChildCount() :获取几个子view的值
getChildAt(i):获取 某个子view
resolveSize(int ,int )
/**
* Version of {@link #resolveSizeAndState(int, int, int)}
* returning only the {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK} bits of the result.
*/
public static int resolveSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
return resolveSizeAndState(size, measureSpec, 0) & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
}
在进去看看呢
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: 当viewgroup时wrap_content,match_parent的时候
if (specSize < size) {//选择了最小的那个值。
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://精确的是 就显示 精确的值
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED://不用管
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
最后感觉自定义viewgroup还是比较复杂的。考虑的因素比较复杂的如何获取控件的大小
git上的demo,欢迎start fork
参考《android开发艺术探索》,《android群英传》。
自重原创:http://blog.csdn.net/wanghao200906/article/details/50906799
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)