Vue3 + vite + Ts + pinia + 实战 +electron(学习ing,笔记未完待续......)
vue3学习
说明:本笔记为本人基于小满ZS的vue3系列教程的学习笔记(目前已经更新),需要的请到Vue3 + vite + Ts + pinia + 实战 + 源码 +electron,建议跟着视频学习~
文章目录
-
- 一、构建项目
- 二、vue3基础使用学习
-
- 1、模板语法&vue指令
- 2、Vue核心虚拟Dom和 diff 算法(了解)
- 3、ref和reactive
- 4、toRef、toRefs、toRaw
- 5、computed计算属性
- 6、watch监听
- 7、watchEffect高级监听
- 8、生命周期
- 9、父子组件传参
- 10、全局组件注册
- 11、动态组件
- 12、插槽
- 13、异步组件(涉及性能优化)
- 14、Teleport传送组件
- 15、keep-alive缓存组件
- 16、依赖注入Provide / Inject
- 17、兄弟组件传参
- 18、tsx组件
- 19、v-model
- 20、自定义指令
- 21、自定义hook
- 22、定义全局函数和全局变量
- 23、
一、构建项目
1、创建项目
npm init vite@latest
或使用npm init vue@latest,这种方式配置多一点,包括router,pinia等,专门为构建vue用的,齐全一点,vite(vite? 、vite和webpack区别?🔎)可以构建其他项目,比如react或其他,下面是用第一种方式npm init vite@latest:
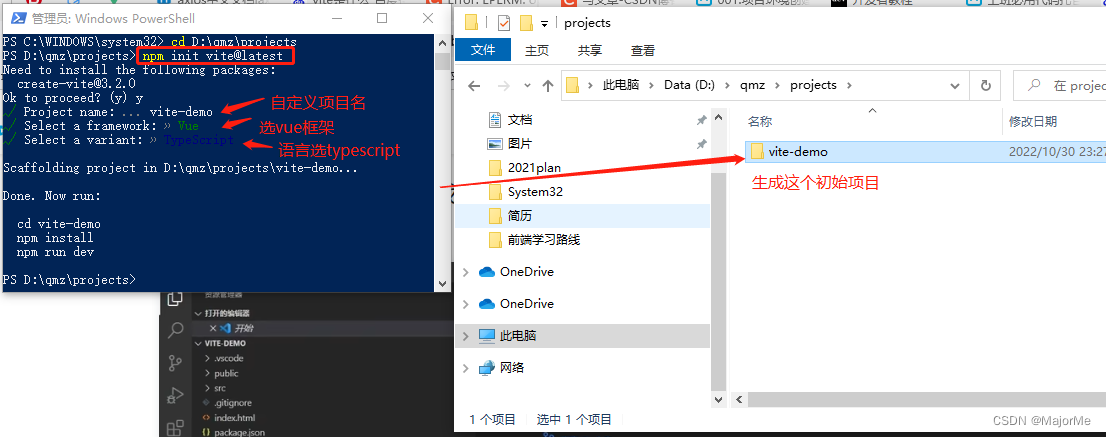
在vsCode打开项目,vite构建的vue项目目录如下:
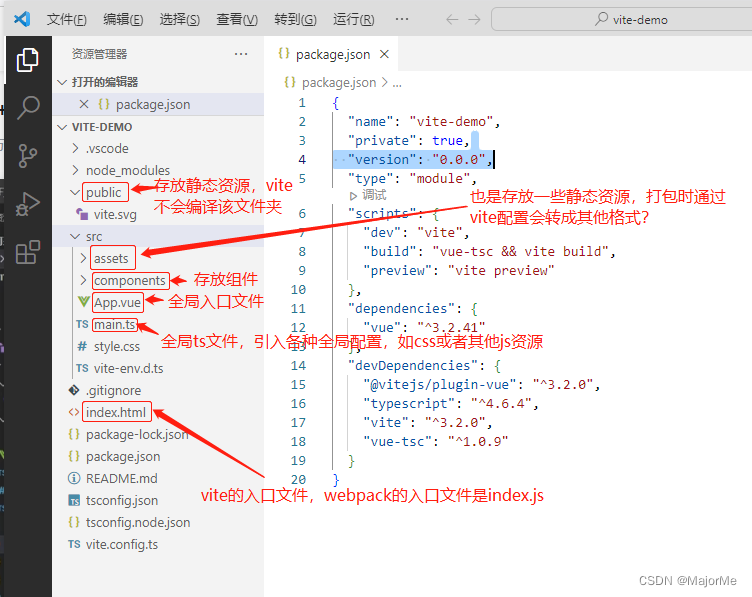
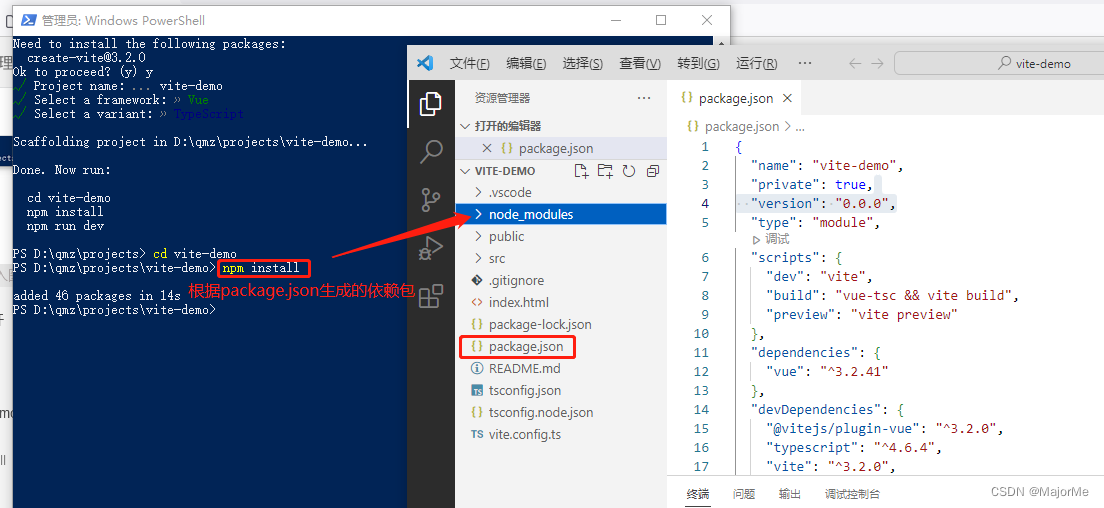
2、安装依赖
进入vite-demo目录,安装依赖(根据项目中的package.json文件安装依赖)
npm install
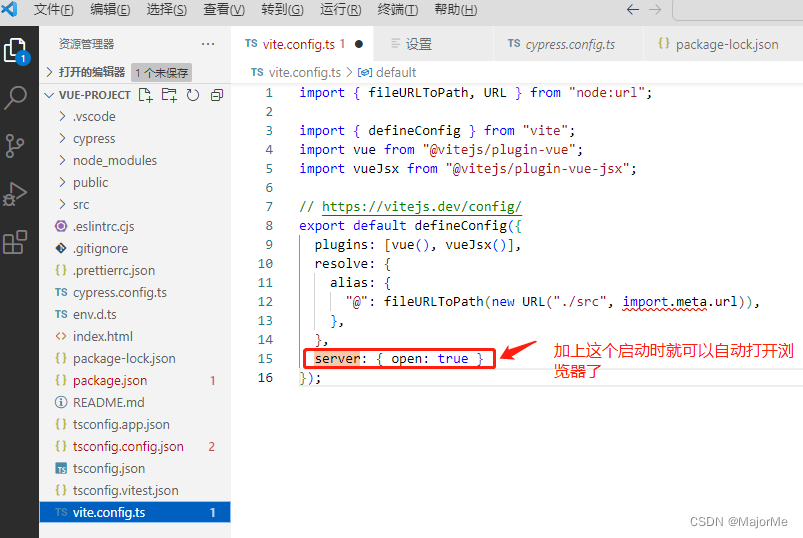
3、运行
- 设置默认启动项目自动开启浏览器:
server: { open: true }
- 运行项目
npm run dev
页面显示如下,项目运行成功 !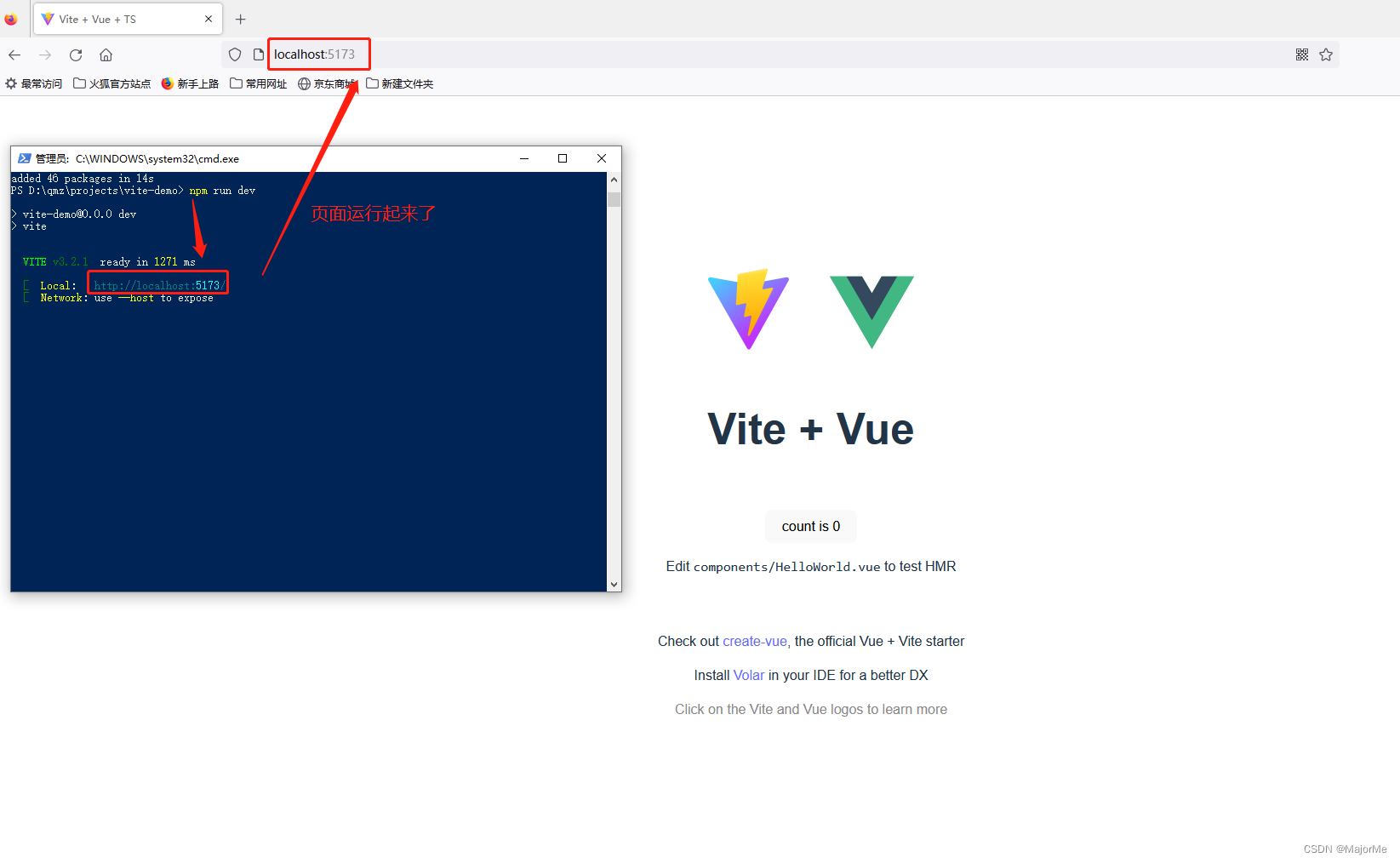
4、安装插件
1、 Vue Language Features (Volar), TypeScript Vue Plugin (Volar)插件
安装后就可以写vue3代码了~
注意:若之前开发vue2有安装vetur插件(对.vue文件中的语法进行高亮显示),开发vue3需要禁用这个插件
2、AutoImport插件
安装插件:npm i -D unplugin-auto-import
配置vite.config.ts: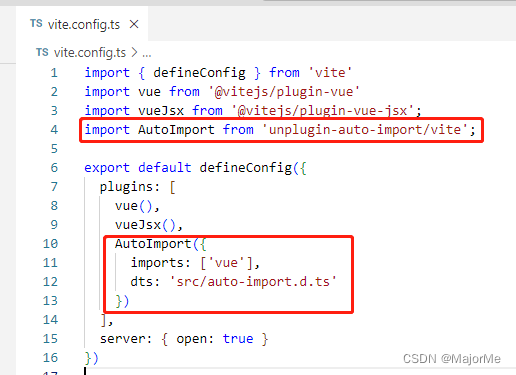
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
import vueJsx from '@vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx';
import AutoImport from 'unplugin-auto-import/vite';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
vue(),
vueJsx(),
AutoImport({
imports: ['vue'],
dts: 'src/auto-import.d.ts'
})
],
server: { open: true }
})
<template>
<div class="parent">
// 省略了.value
<button @click="flag=!flag">切换</button>
{{flag}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
let flag = ref<boolean>(true)
</script>
5、配置用户代码块
- 配置
设置—配置用户代码片段—选择vue(vue)或者vue.json(vue)
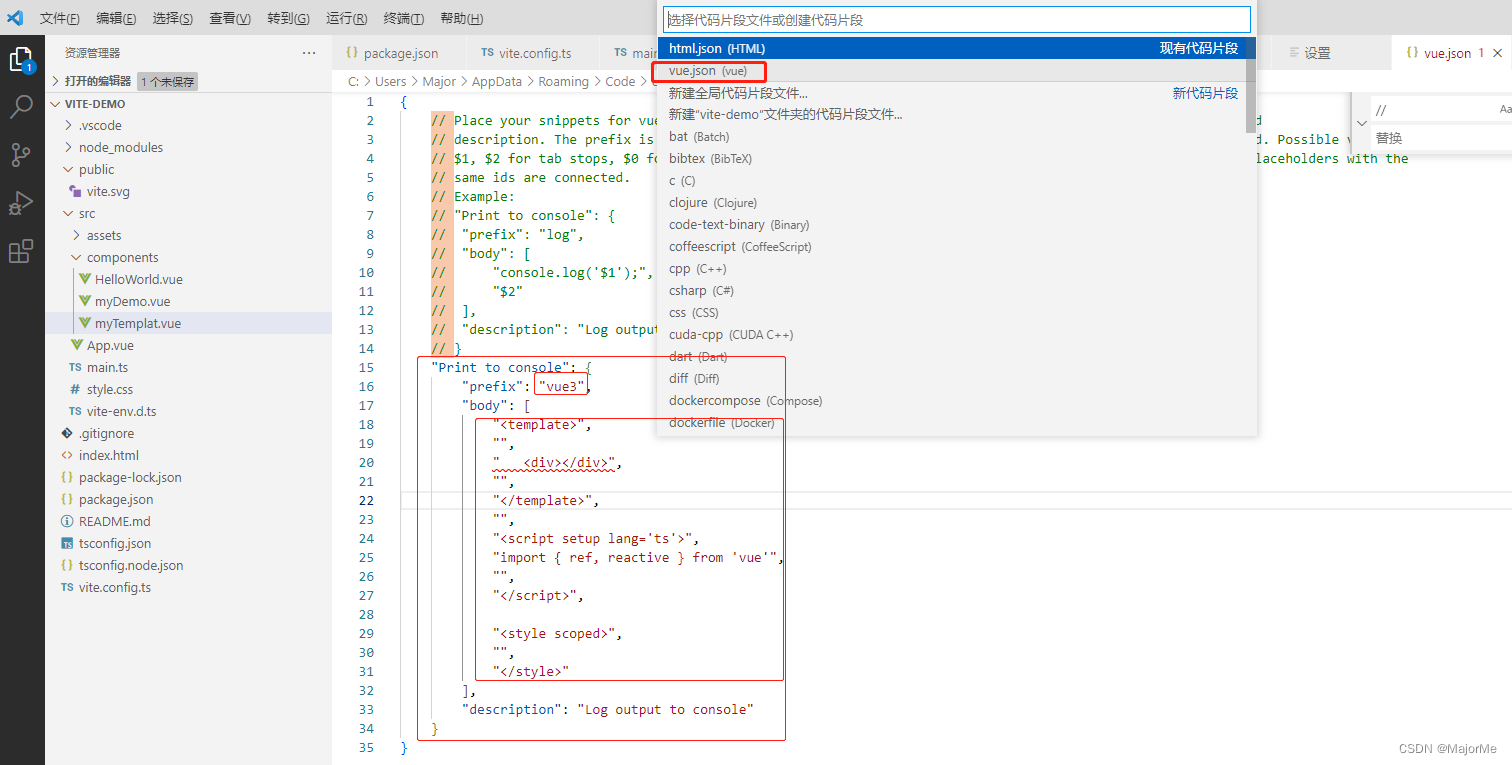
把下面代码复制到vue.json里面
{
"Print to console": {
"prefix": "vue3",
"body": [
"<template>",
"",
" <div></div>",
"",
"</template>",
"",
"<script setup lang='ts'>",
"import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'",
"",
"</script>",
// 注意 lang='less'前提是安装了less,安装方法在第7点
"<style lang='less' scoped>",
"",
"</style>"
],
"description": "Log output to console"
}
}
- 使用示例
新建一个.vue文件,输入vue3,回车,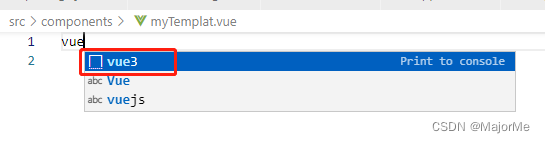
即可一键生成模板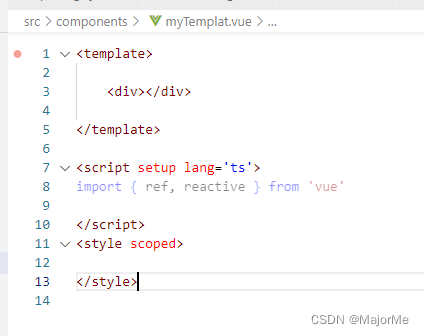
6、安装UI组件库ElementPlus
1)官方说明文档:
2)安装element-plus
- 在项目路径下执行命令安装:
npm install element-plus --save
- 安装成功后,全局配置(main.ts):
// main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import './style.css'
import App from './App.vue'
import ElementPlus from 'element-plus' // 引入ElementPlus 组件
import 'element-plus/dist/index.css' // 引入ElementPlus 组件样式
// createApp(App).mount('#app')
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(ElementPlus) // 使用ElementPlus组件
app.mount('#app')
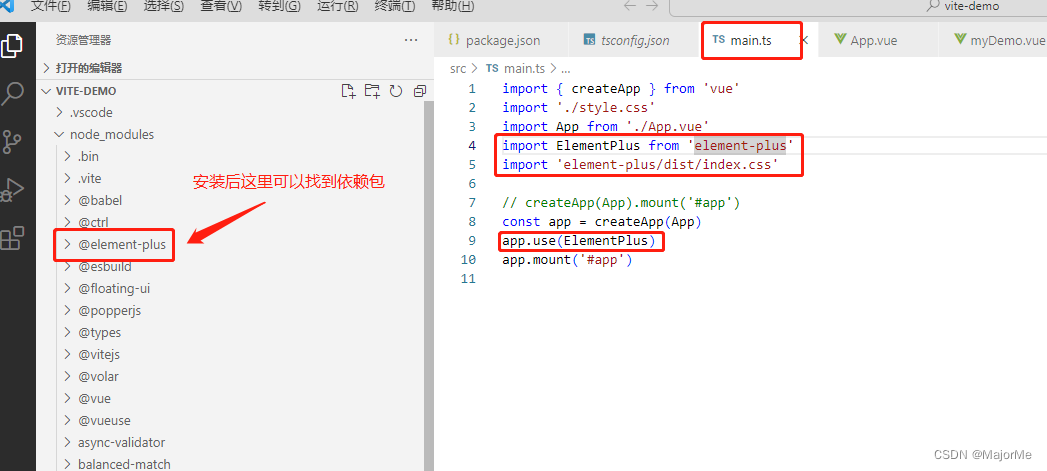
此外还有其他导入方式(自动导入/按需导入、手动导入),请参考官方使用教程
- 使用示例(按钮组件)
<template>
<div>
<ElButton>按钮</ElButton >
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ElButton } from 'element-plus' // 引入按钮组件
</script>
3)安装icon图标
- 安装
npm install @element-plus/icons-vue
- 注册所有图标(main.ts)
// main.ts
// 如果您正在使用CDN引入,请删除下面一行。
import * as ElementPlusIconsVue from '@element-plus/icons-vue'
const app = createApp(App)
for (const [key, component] of Object.entries(ElementPlusIconsVue)) {
app.component(key, component)
}
7、搭建页面layout,认识less、scoped、一些css新特性
1)less的安装和使用
- 安装less
在项目根目录下执行以下命令:
npm install less less-loader -D
- 使用声明
<style lang="less" scoped>
</style>
2)了解和配置css reset
由于浏览器支持和理解的CSS 规范不同,导致渲染页面效果不一致,会出现很多兼容性问题,比如旧 IE 浏览器不支持 HTML5+标签,不同浏览器对 CSS 行为也不统一,这就导致两个问题:
处理浏览器的兼容性。 跨浏览器样式表现统一。为解决上面问题,出现了CSS Reaet ,根据对默认样式的改写的轻重程度,可分为三类:
完全重置——硬重置。 规范化重置——软重置。 个性化重置。
- 配置css reset
在src\assets\ 下新建css\reset.less,把css reset样式代码复制到reset.less文件中,如下:
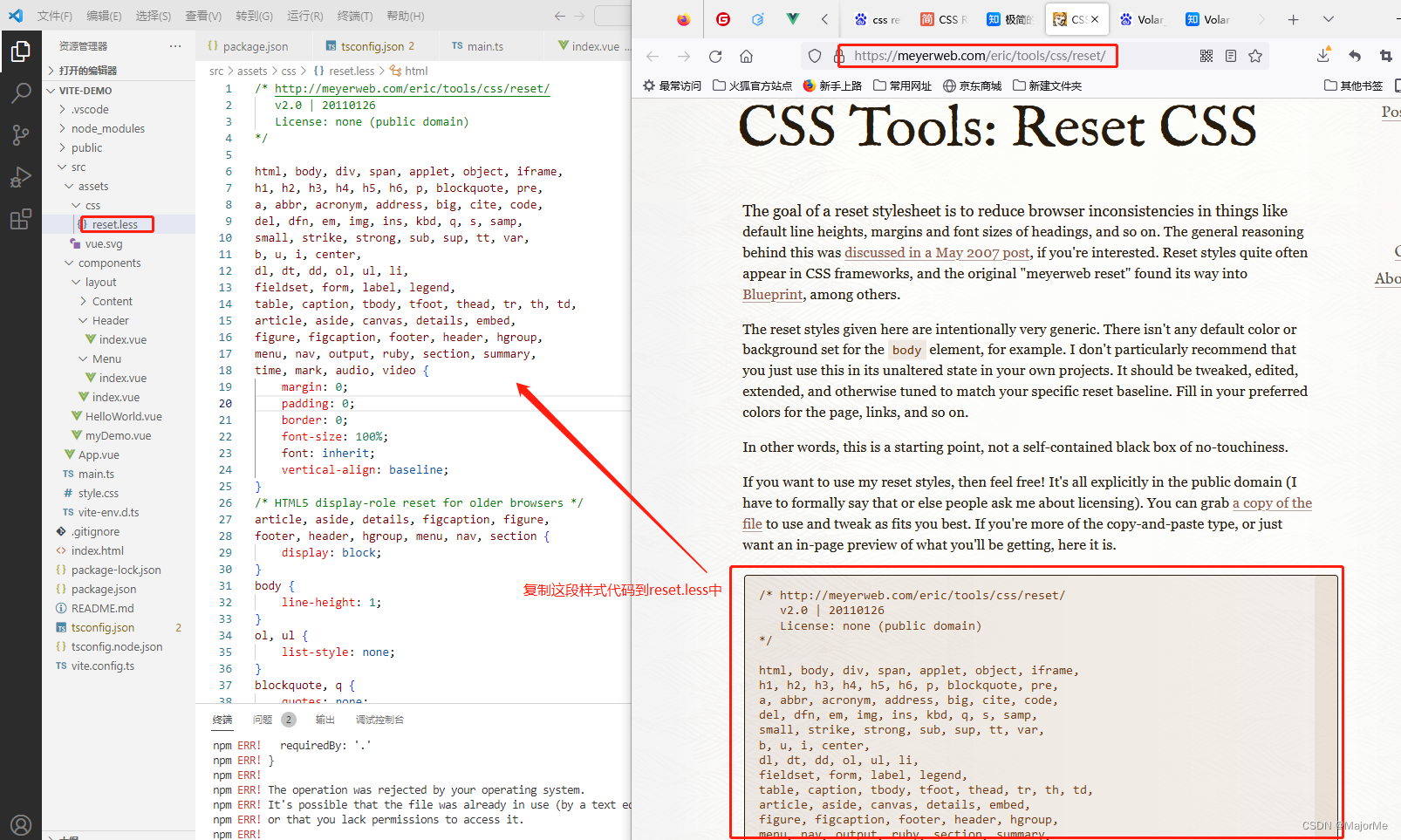 然后修改一下,初始化html,body,#app外层样式:
然后修改一下,初始化html,body,#app外层样式: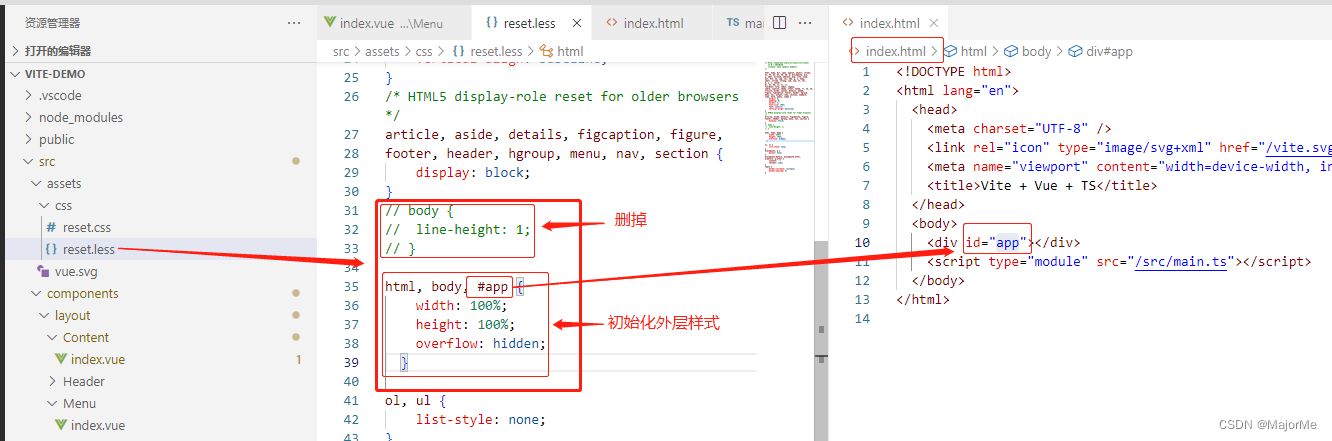
接下来在src\main.ts文件中全局进入: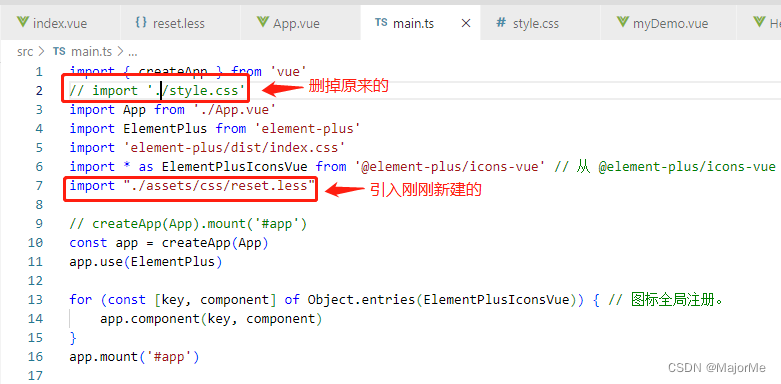
3)layout页面构建
layout包括:Menu、Header、Content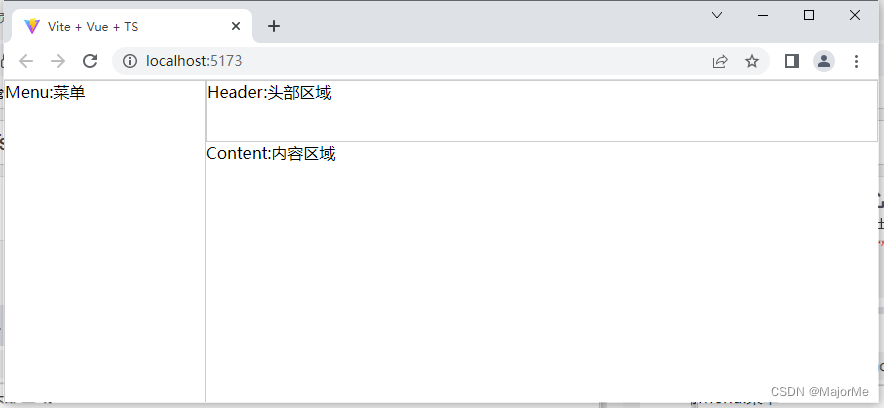 如图创建相应文件夹和文件:
如图创建相应文件夹和文件: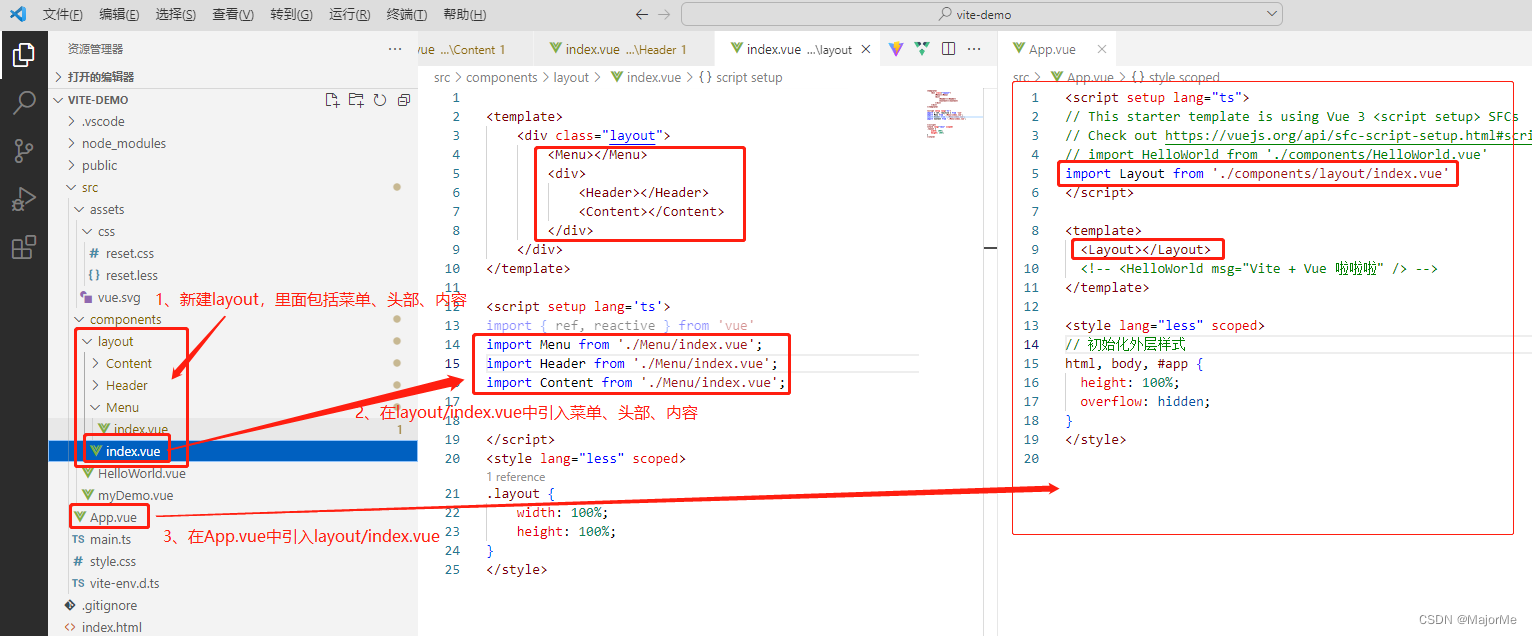
4)scoped的作用
隔离样式: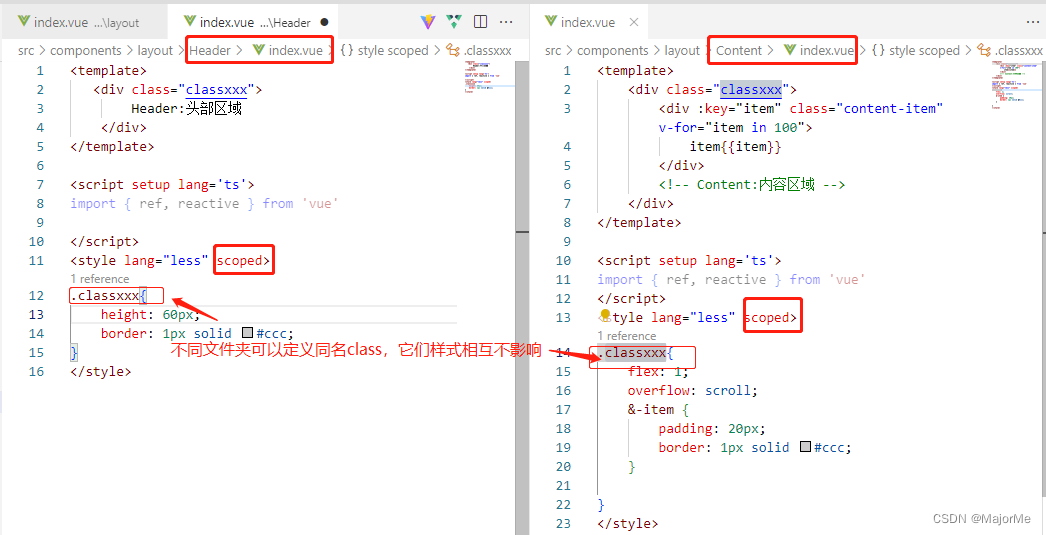 渲染页面的标签会出现 data-v-xxx 属性隔离样式:
渲染页面的标签会出现 data-v-xxx 属性隔离样式: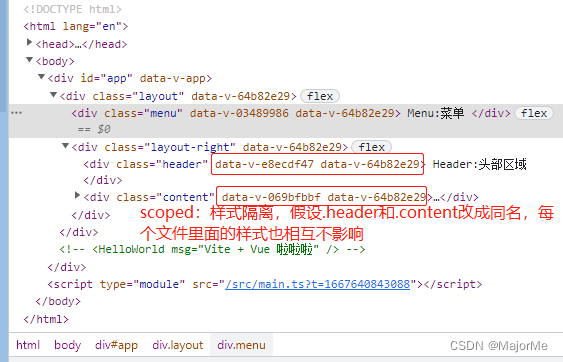
5)vue3的一些css新特性
<style>
// deep选择器 一般用于修改组件库里的组件的样式
/deep/ .el_input_inner {
border: 1px solod pink;
}
// 或者
:deep(.el_input_inner) {
border: 1px solod pink;
}
// 插槽选择器:sloted
:sloted(.className) {
color:blue;
}
// 全局选择器:global
:global(.className) {
color:pink;
// 动态css绑定v-bine
.className {
color: v-bine(colorVal); // 假设 let colorVal = ref('pink')
// 或
color: v-bine('obj.colorVal'); // 假设 let obj = ref({colorVal: 'pink'})
}
</style>
6)其他
二、vue3基础使用学习
1、模板语法&vue指令
v- 开头都是vue 的指令
v-text 用来显示文本
v-html 用来展示富文本
v-if 用来控制元素的显示隐藏(切换真假DOM)
v-else-if 表示 v-if 的“else if 块”。可以链式调用
v-else v-if条件收尾语句
v-show 用来控制元素的显示隐藏(display none block Css切换)
v-on 简写@ 用来给元素添加事件
v-bind 简写: 用来绑定元素的属性Attr
v-model 双向绑定
v-for 用来遍历元素
v-on修饰符
2、Vue核心虚拟Dom和 diff 算法(了解)
3、ref和reactive
1) vue2和vue3的双向绑定值定义区别
- vue2:
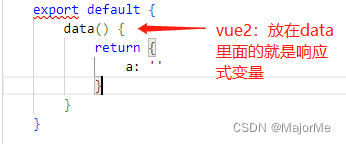
- vue3:使用ref或者reactive包裹,或者自定义customRef
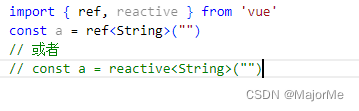
2)ref
- ref接受一个内部值并返回一个响应式且可变的 ref 对象。ref 对象仅有一个 .value property,指向该内部值。
- 使用案例
<template>
<div>啦啦a:{{a}}</div>
<button @click="change">变变变</button>
<form>
<input />
</form>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, isRef } from 'vue'
const a = ref("我是a") // 对象
const change = () => {
a.value = "a变身" // 赋值的时候需要.value赋值,否则直接a=xxx会报错
}
</script>
3)reactive
-
ref用来绑定复杂的数据类型 例如对象、数组, 若绑定普通变量类型会报错。
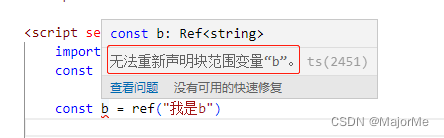
-
使用案例
<template>
<div>啦啦b:{{b.val}}</div>
<button @click="change">变变变</button>
<form>
<input />
</form>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, isRef } from 'vue'
const b = reactive({
val: "我是b"
})
const change = () => {
b.val = "b变身"
}
</script>
- 特别注意:reactive声明的对象和数组,再次赋值不能直接整个赋值,整个赋值页面不会更新。
// 假设
const arr = reactive([]);
const obj= reactive({});
const res = [1,2,3]
const res2 = {a:'1', b: '2'}
直接赋值,即使打印生效,页面也不会更新:
// arr = res // 不可以
// arr.concat(res) // 不可以
// obj = res2 // 不可以
原因: vue3使用proxy,arr= newArr让arr失去了响应性,所以对于对象和数组都不能直接整个赋值:
如何解决?
数组:用push
res.forEach(e => { // 可以
arr.push(e);
});
arr.push(...[1, 2, 3]) // 可以
};
对象:改用ref定义
const obj= ref({});
obj.value = {...res2 } // 可以
其他方法:用reactive封装一层,然后使用toRefs解构(待验证)
<script setup lang='ts'>
const state = reactive({
arr: [],
obj:{}
});
state.arr = [1, 2, 3]
state.obj={...res2}
const { form,obj} = toRefs(state)
4)shallowRef、shallowReactive
只能对浅层的数据,如果是深层的数据只会改变值(打印的是改变的值),不会改变视图(页面不会刷新)
4、toRef、toRefs、toRaw
- toRef、toRefs
注意: 只能解构响应式对象的值
<template>
<div>name:{{name}}</div>
<div>age:{{age}}</div>
<div>num:{{num}}</div>
<button @click="change">变变变</button>
<form>
<input />
</form>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, toRef, toRefs, reactive, isRef } from 'vue'
const myInfo = ref({ // 或者 reactive
name: 'zz',
age: 18,
num: 520
})
// toRef只能解构响应式对象的值,对普通对象(如const myInfo={name:'zz', age: 18, num: 520})则行不通
const { name, age } = toRefs(myInfo.value) // toRefs: 若myInfo使用reactive定义,则这里解构改为 const { name, age } = toRefs(myInfo)
const num = toRef(myInfo.value, "num") // toRef:若myInfo使用reactive定义,则这里解构改为 const num = toRef(myInfo, "num")
const change = () => {
name.value = 'zx'
age.value = 3
num.value = 1314
console.log("name:",name)
}
</script>
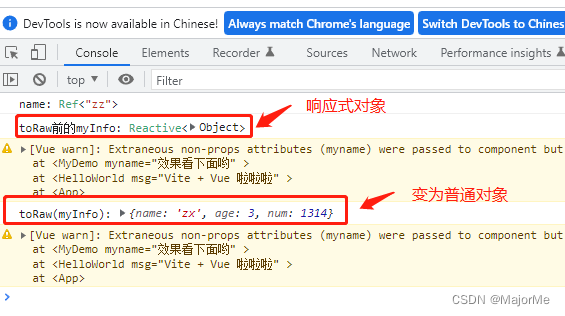
- toRaw
把响应式的对象转为普通对象
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, toRef, toRefs, reactive, isRef, toRaw } from 'vue'
let myInfo = reactive({
name: 'zz',
age: 18,
num: 520
})
const { name, age } = toRefs(myInfo)
const num = toRef(myInfo, "num")
console.log("name:",name)
console.log("toRaw前的myInfo:",myInfo)
const change = () => {
name.value = 'zx'
age.value = 3
num.value = 1314
// myInfo = toRaw(myInfo)
console.log("toRaw(myInfo):", toRaw(myInfo))
}
</script>
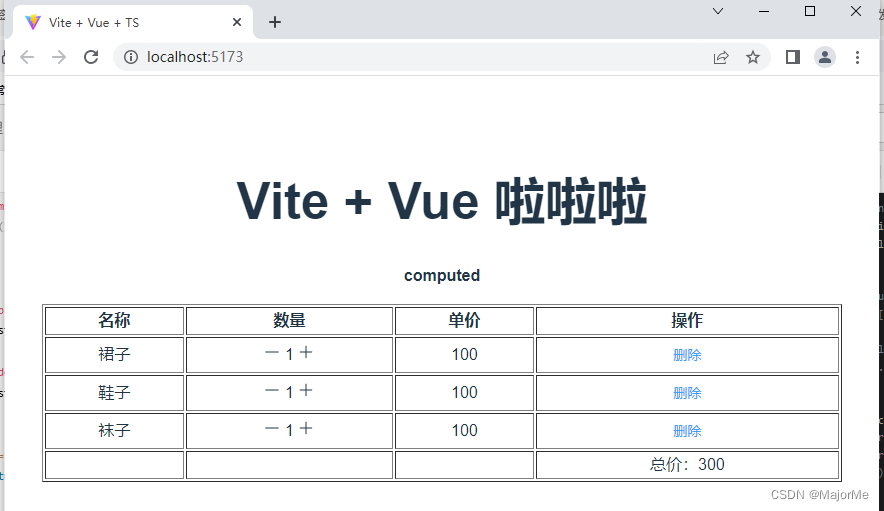
5、computed计算属性
计算属性就是当依赖的属性的值发生变化的时候,才会触发他的更改,如果依赖的值,不发生变化的时候,使用的是缓存中的属性值。
案例:
<template>
<p style="font-weight: bold;">computed</p>
<div>
<table border style="width:800px;text-align: center;">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>名称</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr :key="'item' + index" v-for="(item, index) in list">
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>
<el-icon class="point" @click="minus(index)"><Minus /></el-icon>
{{item.num}}
<el-icon class="point" @click="plus(index)"><Plus /></el-icon>
</td>
<td>
{{item.num * item.price}}
</td>
<td>
<ElButton
type="primary"
text
@click="delet(index)"
>删除</ElButton
>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td>总价:{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, computed } from 'vue'
import { ElButton } from 'element-plus'
type goodInfo = {
name: string,
num: number,
price: number
}
let total = ref<number>(0)
const list = reactive<goodInfo[]>(
[
{
name: '裙子',
num: 1,
price: 100
}, {
name: '鞋子',
num: 1,
price: 100
}, {
name: '袜子',
num: 1,
price: 100
}
]
)
const minus = (index:number) => {
if(list[index].num > 0) {
list[index].num = list[index].num - 1
}
}
const plus = (index:number) => {
list[index].num = list[index].num + 1
}
const delet = (index:number) => {
list.splice(index, 1)
}
total = computed<number>(() => {
return list.reduce((prev, next) => {
return prev + (next.num*next.price)
}, 0)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.point {
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
6、watch监听
watch 需要侦听特定的数据源,并在单独的回调函数中执行副作用
watch第一个参数监听源
watch第二个参数回调函数cb(newVal,oldVal)
watch第三个参数一个options配置项是一个对象{
immediate:true //是否立即调用一次
deep:true //是否开启深度监听
- 监听普通类型
<template>
<p style="font-weight: bold;">computed</p>
<div>
<el-input style="margin: 10px 0" v-model="input1"/>
<el-input style="margin: 10px 0" v-model="input2"/>
<el-input style="margin: 10px 0" v-model="input3"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, computed, watch } from 'vue'
import { ElInput } from 'element-plus'
let input1 = ref('111')
let input2 = ref('222')
let input3 = ref('333')
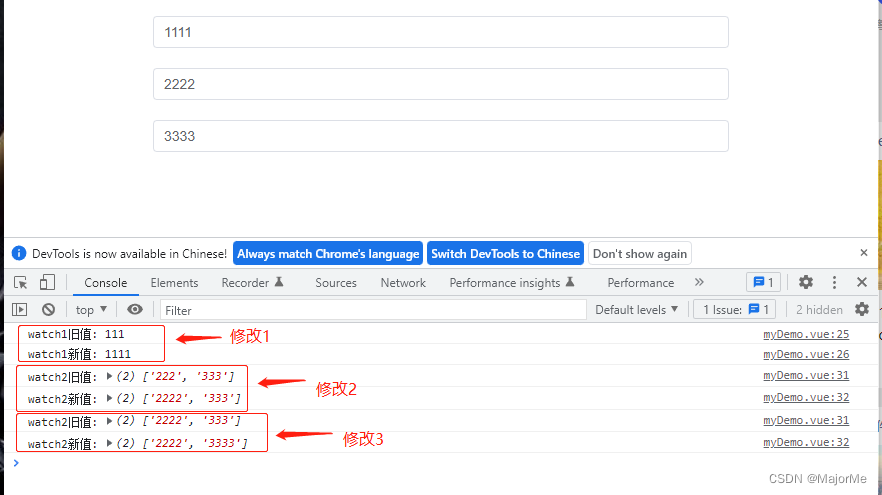
watch(input1, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch1旧值:', oldValue)
console.log('watch1新值:', newValue)
})
// 监听多个数据, watch的第一个参数要用数组形式
watch([input2, input3], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch2旧值:', oldValue)
console.log('watch2新值:', newValue)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
依次修改三个值,监听打印如下:
- 监听深层对象
<template>
<p style="font-weight: bold;">computed</p>
<div>
<el-input v-model="obj.level1.level2.level3"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, computed, watch } from 'vue'
import { ElInput } from 'element-plus'
let obj = ref({ // ref改为reactive,则watch函数不需要设置deep参数,始终可以深度监听
level1: {
level2: {
level3: 'qmz'
}
}
})
watch(
obj,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch1旧值:', oldValue)
console.log('watch1新值:', newValue)
},
{ deep: true }
)
</script>
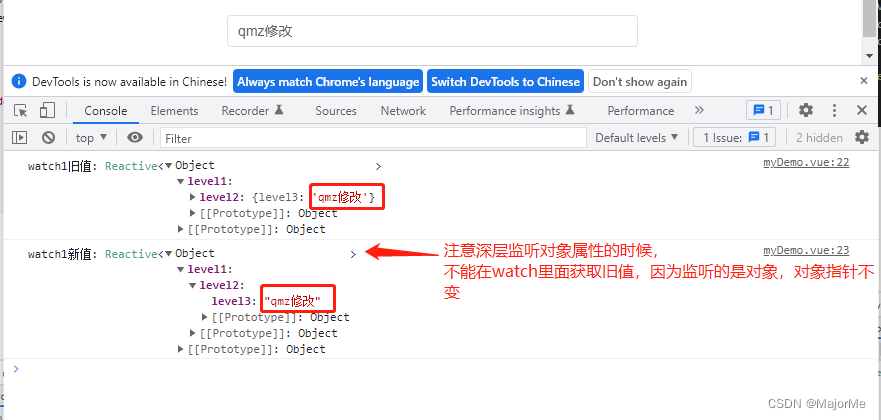
- 监听reactive 单一值
import { ref, watch ,reactive} from 'vue'
let message = reactive({
val1:"",
val2:""
})
watch(()=>message.name, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('新值----', newValue);
console.log('旧值----', oldValue);
})
7、watchEffect高级监听
watchEffect相当于将watch 的依赖源和回调函数合并,当任何你有用到的响应式依赖更新时,该回调函数便会重新执行。不同于
watch,watchEffect 的回调函数会被立即执行(即 { immediate: true })
- 非惰性(立即执行)
<script setup lang="ts">
import { watchEffect } from 'vue'
watchEffect(() => {
console.log('不管有没有监听对象,渲染页面或者刷新页面,都会立即执行')
}
)
</script>
- 不需要传递你要侦听的内容,自动会感知代码依赖(就是watchEffect内用到了哪个响应式变量,就监听哪个变量)
<template>
<p style="font-weight: bold;">watchEffect</p>
<div>
<el-input v-model="inputVal.value"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, computed, watchEffect } from 'vue'
import { ElInput } from 'element-plus'
let inputVal = reactive({
value: '1'
})
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("inputVal.value:", inputVal.value) // 用到inputVal.value,只要它变化了,自动监听到
}
)
</script>
- watchEffect的副作用
副作用就是执行某种操作,如对外部可变数据或变量的修改,外部接口的调用等。watchEffect的回调函数就是一个副作用函数,因为我们使用watchEffect就是侦听到依赖的变化后执行某些操作。
- 清除副作用应用
在触发监听之前会调用一个函数可以处理你的逻辑,例如:
1)节流防抖
// 节流防抖
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, reactive, computed, watchEffect } from 'vue'
import { ElInput } from 'element-plus'
const id = ref(13)
watchEffect(onInvalidate => {
// 异步请求
const token = performAsyncOperation(id.value)
// 如果id频繁改变,会触发失效函数,取消之前的接口请求
onInvalidate(() => {
// id has changed or watcher is stopped.
// invalidate previously pending async operation
token.cancel()
})
})
const performAsyncOperation = (id) => {
// 这是一个请求接口操作(异步操作)
}
</script>
2)定时器注册和销毁
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, watchEffect, onMounted } from 'vue'
import { ElInput } from 'element-plus'
// 定时器注册和销毁
watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
const timer = setInterval(()=> {
// ...
}, 1000)
onInvalidate(() => clearInterval(timer))
})
</script>
3)dom的监听和取消监听
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, watchEffect, onMounted } from 'vue'
import { ElInput } from 'element-plus'
const handleClick = () => {
// ...
}
// dom的监听和取消监听
onMounted(()=>{
watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
document.querySelector('.btn').addEventListener('click', handleClick, false)
onInvalidate(() => document.querySelector('.btn').removeEventListener('click', handleClick))
})
)}
</script>
- 停止监听
<template>
<div style="margin: 10px 0">
<el-input v-model="inputVal1"/>
</div>
<el-button type="primary" @click="stop" >停止监听</el-button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, watchEffect, onMounted } from 'vue'
import { ElInput, ElButton } from 'element-plus'
let inputVal1 = ref('111')
const stop = watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
console.log('inputVal1:', inputVal1)
})
</script>
- 副作用刷新时机 flush (一般使用post)
| pre | sync | post | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 刷新时机 | 组件更新前执行 | 强制效果始终同步触发 | 组件更新后执行 |
8、生命周期
9、父子组件传参
1)父组件给子组件接收传参
// ts特有
type Props = {
title: string,
menus: string[],
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
title: '默认title',
menus: () => [] // 注意:指针类型数据,要用函数返回默认值
})
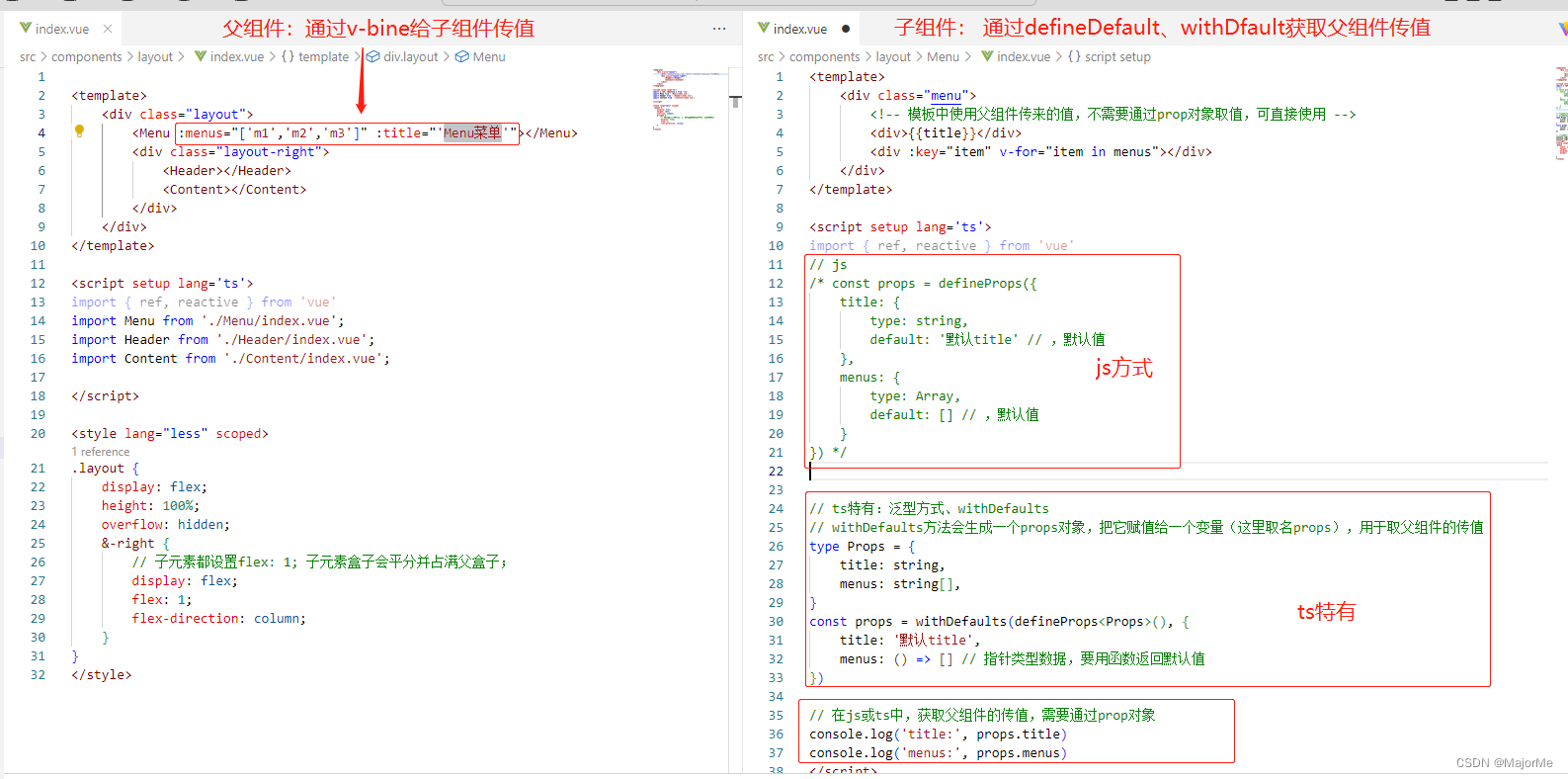
2)子组件给父组件抛出事件
// 抛出事件
// const emit = defineEmits(['click1', 'click2']) // js方式
const emit = defineEmits<{ // ts特有方式
(e: 'click1', id: string): void
(e: 'click2', value: string): void
}>()
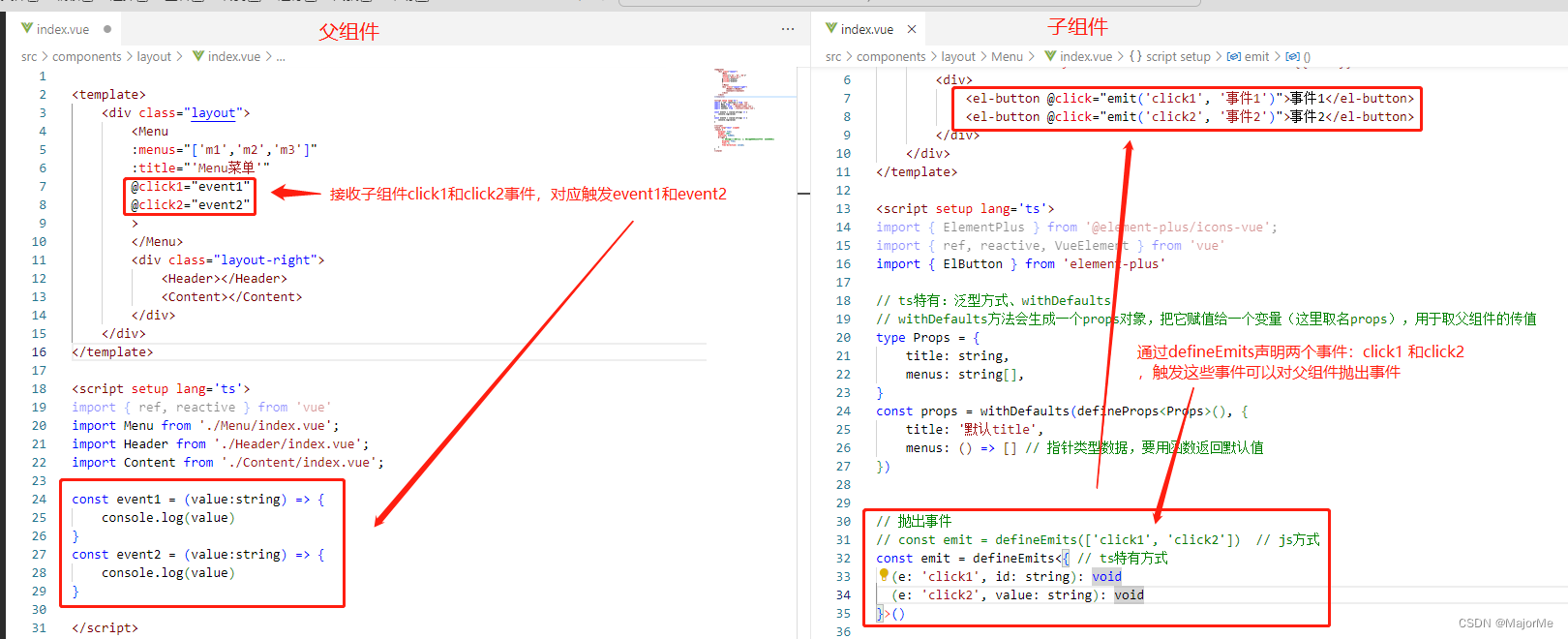
3)给父组件暴露子组件内部属性
defineExpose 使用 script setup 的组件是默认关闭的,也即通过模板 ref 或者 $parent
链获取到的组件的公开实例,不会暴露任何在 <script setup中声明的绑定,组件中明确要暴露出去的属性,使用 defineExpose
// 子组件
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive} from 'vue'
const id = ref<string>('123')
const name = reactive({name1: 'n1'})
const func = () => {
console.log('使用defineExpose声明后,父组件可以调用func函数')
}
defineExpose({ // 暴露出去
id,
name,
func
})
</script>
用.value获取值:
// 父组件
<template>
<Menu ref="MenuRef" />
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive, watchEffect } from 'vue'
import Menu from './Menu/index.vue';
const MenuRef = ref() // 给MenuRef初始化为空,渲染后会自动获取到子组件内部属性
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("MenuRef:", MenuRef) // 第一次执行打印为undefined
if(MenuRef) {
console.log("MenuRef.value:", MenuRef.value)
console.log("MenuRef.value?.id:", MenuRef.value?.id)
console.log("MenuRef.value?.name.name1:", MenuRef.value?.name.name1)
MenuRef.value?.func()
}
})
</script>
在watchEffect方法中打印: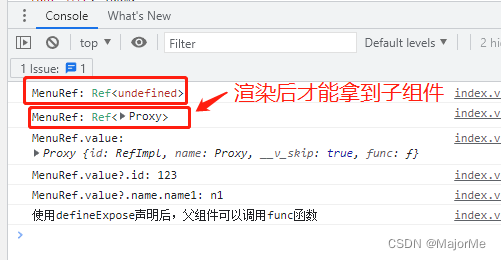
10、全局组件注册
在假设你设计了一个组件Xxx.vue,则在main.ts中全局导入和注册:
import Xxx from 'component/xxx/xxx.vue'
// 注册后,在需要的地方直接使用,不用单独import
app.component('Xxx', Xxx)
例如icon全局注册:
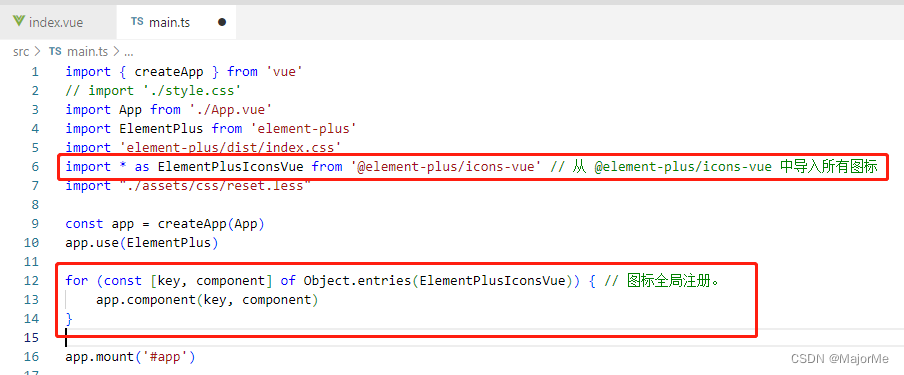
11、动态组件
动态组件是让多个组件使用同一个挂载点,并动态切换。
import A from './A.vue'
import B from './B.vue'
使用内置标签实现,通过is绑定要渲染的组件
<component :is="A"></component>
案例:切换组件
<template>
<div class="one">
<div class="content">
<div
v-for="item in tabsList"
:key="item.name"
:class="[current.name === item.name ? 'tabActive':'', 'tab']"
@click="changeTab(item)"
>
{{item.name}}
</div>
<component :is="current.comName ?? ''"></component>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ElementPlus } from '@element-plus/icons-vue';
import { ref, reactive, markRaw, toRaw, toRefs } from 'vue'
import A from './A.vue';
import B from './B.vue';
import C from './C.vue';
type Tab = {
name: string,
comName: any
}
// type Com = Pick<Tab, 'comName'> // 从一个已知的类型中,取出子集,作为一个新的类型返回。 相当于type Com = {comName: any}
// markRaw 跳过代理,避免出现警告
const tabsList = reactive<Tab[]>([
{
name: '我是A组件',
comName: markRaw(A)
},{
name: '我是B组件',
comName: markRaw(B)
},{
name: '我是C组件',
comName: markRaw(C)
}
])
const state = reactive({
current: {}
})
// 初始化展示组件
state.current = tabsList[0] // 第一个组件
const { current } = toRefs(state) // 神奇:这个方式解构,后面切换组件,直接state.current = item,页面引用的current也可以直接更新
console.log('初始current:', current)
// 切换组件
const changeTab = (item:Tab) => {
state.current = item
console.log('切换组件current:', current)
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.one{
margin-top: 20px;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #fff;
color: #000;
.content {
.tab{
border: 1px solid #ccc;
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
padding: 2px 10px;
}
.tabActive{
color: aquamarine;
}
}
}
</style>
效果:
12、插槽
匿名插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽、动态插槽
具体使用看下面案例注解:
// 子组件A.vue 内定义插槽
<template>
<div class="one">
<!-- 匿名插槽 -->
<header class="header">
<slot></slot>
</header>
<!-- 具名插槽 name= -->
<main class="main">
slot1
<slot name="slot1"></slot>
</main>
<!-- 作用域插槽 :data=传参 -->
<footer class="footer">
slot2
<slot name="slot2" :data="'我出现在slot2插槽'"></slot>
</footer>
<!-- 动态插槽 :name=[插槽名变量] -->
<div class="dynamic">
动态插槽
<slot name="slot3"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.one{
color: azure;
.header{
height: 100px;
width: 100%;
background: rgb(236, 255, 192);
text-align: center;
}
.main{
height: 100px;
width: 100%;
background: pink;
text-align: center;
}
.footer{
height: 100px;
width: 100%;
background: rgb(195, 245, 247);
text-align: center;
}
.dynamic{
height: 100px;
width: 100%;
background: rgb(247, 195, 224);
text-align: center;
}
}
</style>
// 父组件
<template>
<div class="one">
<div class="content">
<!-- 组件A包括插槽模板内容 -->
<A>
<!-- 默认插槽模板: v-slot 或简写 #default -->
<template v-slot>
<div>我出现在默认插槽</div>
</template>
<!-- 具名插槽模板: v-slot:插槽名 或者简写 #插槽名 -->
<template v-slot:slot1>
<div>我出现在slot1插槽</div>
</template>
<!-- 作用域插槽模板,获取插槽传来的参数 v-slot="{ data }" 或者简写 #插槽名="{ data }" -->
<template #slot2="{ data }">
<div>{{data}}</div>
</template>
<!-- 动态插槽模板,#[插槽名] -->
<template #[slotName]>
<div>我出现在插槽{{slotName}}</div>
</template>
</A>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive, markRaw, toRaw, toRefs } from 'vue'
import A from './A.vue'; // 引入子组件A
const slotName = ref('slot3')
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.one{
margin-top: 20px;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
效果:
13、异步组件(涉及性能优化)
小案例:进入页面,3秒完成请求,请求过程展示loading,解决浏览页面出现白屏问题。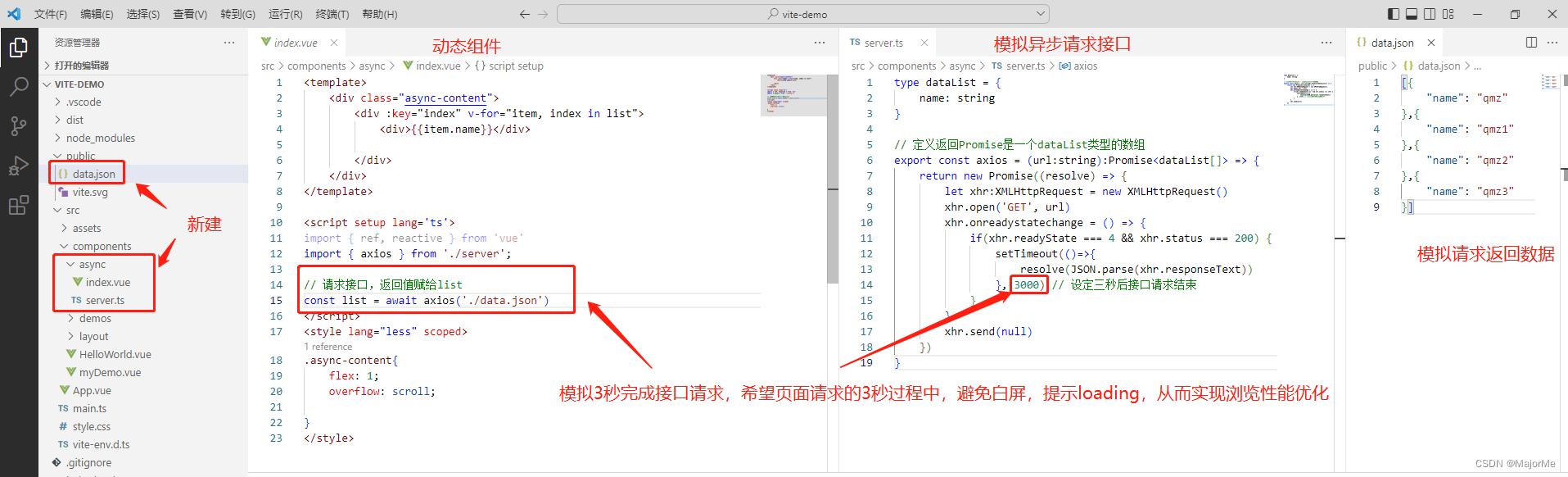
已下父组件引入异步组件,配合Suspense 使用,解决加载过程白屏尴尬
注意引入异步组件要使用 defineAsyncComponent 方法
// 父组件
<template>
<div class="content">
<Suspense>
<!-- 加载完毕,使用默认插槽default -->
<template #default>
<A></A>
</template>
<!-- 加载过程中,使用插槽fallback -->
<template #fallback>
<div>loading...</div>
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive, defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue'
const A = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('../../async/index.vue')) // 异步组件需要defineAsyncComponent引入
</script>
效果展示:
3秒完成加载,过程loading展示
使用异步组件实现分包:
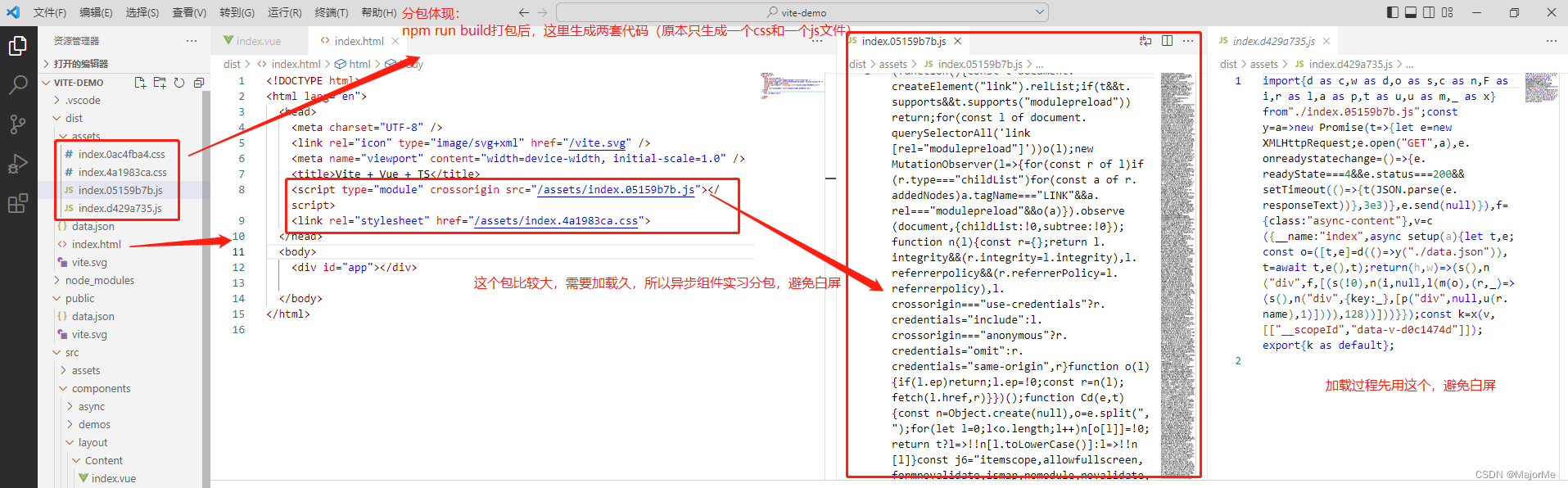
14、Teleport传送组件
Teleport属于Vue 3.0新特性,能够将模板渲染至指定DOM节点,不受父级style、v-show等属性影响,但data、prop数据依旧能够共用。
// 小弹窗相对参考框居中定位
{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -100px;
margin-left: -100px;
position: absolute;
background-color: rgb(233, 135, 152);
}
</style>
父组件: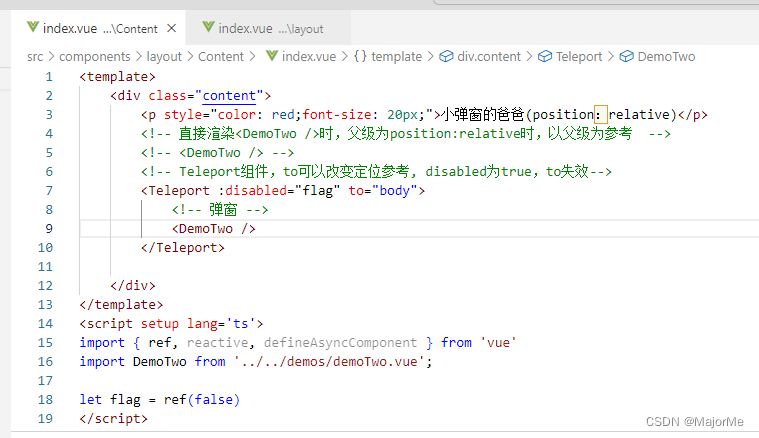
使用传送组件前: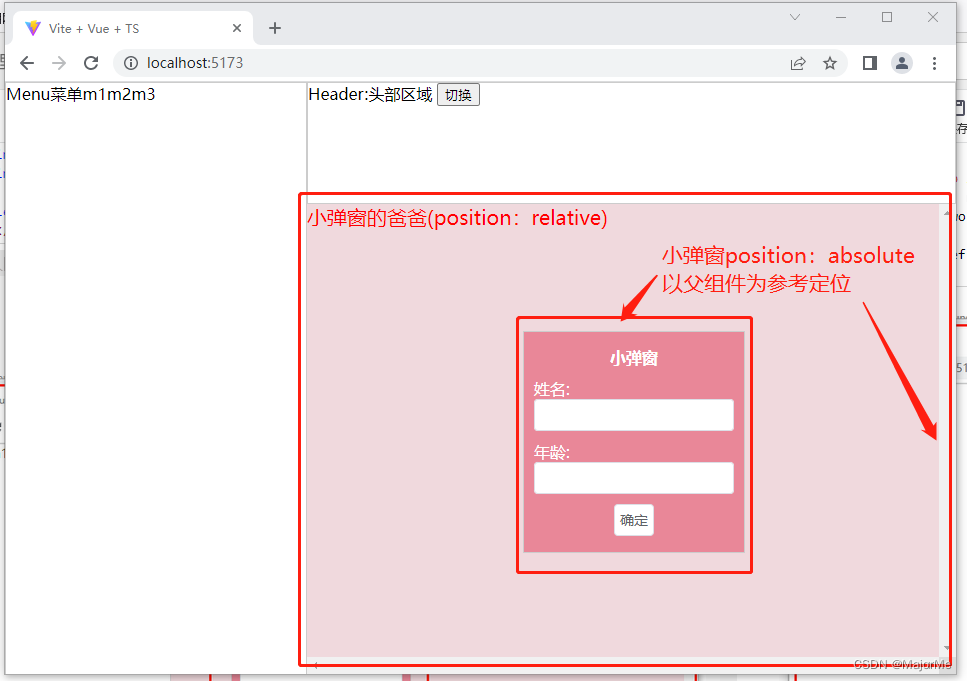 把小弹窗传送给body后:
把小弹窗传送给body后:
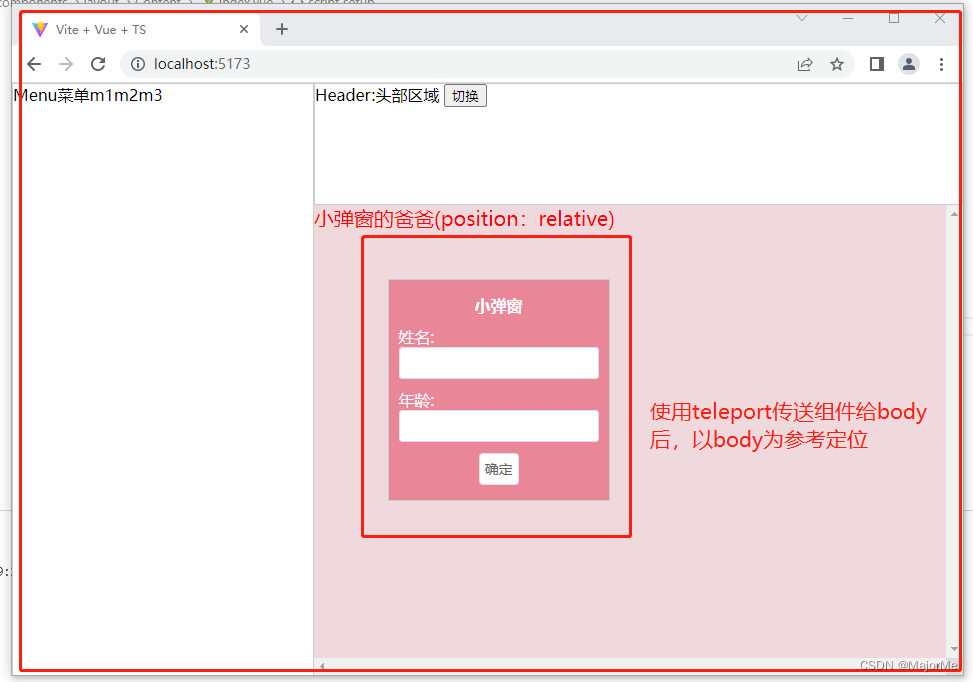
15、keep-alive缓存组件
keep-alive内置组件用于缓存组件,再次切入时不需要重新渲染,并且保留切出前状态。
开启keep-alive 生命周期:
初次进入时: onMounted> onActivated
退出后:触发deactivated
再次进入:触发 onActivated
- 使用方式:
<!-- 基本 -->
<keep-alive>
<component :is="view"></component>
</keep-alive>
<!-- 多个条件判断的子组件 -->
<keep-alive>
<comp-a v-if="a > 1"></comp-a>
<comp-b v-else></comp-b>
</keep-alive>
- include 和 exclude属性
include 和 exclude 允许组件有条件地缓存。二者都可以用逗号分隔字符串、正则表达式或一个数组来表示:
<keep-alive :include="" :exclude="" :max=""></keep-alive>
16、依赖注入Provide / Inject
有一些深度嵌套的组件,而深层的子组件只需要父组件的部分内容。在这种情况下,如果仍然将 prop 沿着组件链逐级传递下去,可能会很麻烦。
例如:当父组件有很多数据需要分发给其子代组件的时候, 就可以使用provide和inject。
// 父组件或者爷爷组件...
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { provide, ref } from 'vue'
import A from './components/A.vue'
let flag = ref<number>(1)
provide('flag', flag)
</script>
// 子组件
<template>
<div>
<button @click="change">change flag </button>
<div>{{ flag }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { inject, Ref, ref } from 'vue'
const flag = inject<Ref<number>>('flag', ref(1))
// 子组件可以修改注入变量
const change = () => {
flag.value = 2
}
</script>
17、兄弟组件传参
- 方法一:以父组件为桥梁
假设one、two为兄弟组件,要实现one组件给two组件传参(flag)
// 父组件
<template>
<div class="parent">
<one @on-click="click1" />
<two :flag="flag" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import one from './demoOne.vue';
import two from './demoTwo.vue';
let flag = ref(false)
const click1 = (param:boolean) => {
console.log('组件one传来参数--param:', param)
flag.value = f
}
</script>
// 子组件 one
<template>
<div class="one">
<el-button @click="clikOne">改变flag值</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, defineEmits } from 'vue'
import { ElButton } from 'element-plus'
let flag = ref<boolean>(false)
const emit = defineEmits<{ // 定义派发事件
(e: 'on-click', flag: boolean):void
}>()
const clikOne = () => {
flag.value = !flag.value
emit('on-click', flag.value) // 给父组件派发事件,并传参flag
}
</script>
// 子组件 two
<template>
<div class="two">
flag:{{props.flag}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, defineProps, withDefaults } from 'vue'
type Props = {
flag: boolean
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(),{
flag: true
})
</script>
- 方法二:封装一个订阅工具Bus
新建一个文件,如Bus.ts
// Bus.ts
type BusClass = {
emit: (name: string) => void
on: (name: string, callback:Function) => void
}
type ParamsKey = string | number | symbol
type List = {
[key: ParamsKey]: Array<Function>
}
class Bus implements BusClass {
list: List
constructor() {
this.list = {}
}
emit(name:string,...args:Array<any>) {
let eventName: Array<Function> = this.list[name]
eventName.forEach(fn => {
fn.apply(this, args)
})
}
on(name:string, callback:Function) {
let fn: Array<Function> = this.list[name] || []
fn.push(callback)
this.list[name] = fn
}
}
export default new Bus
使用方法: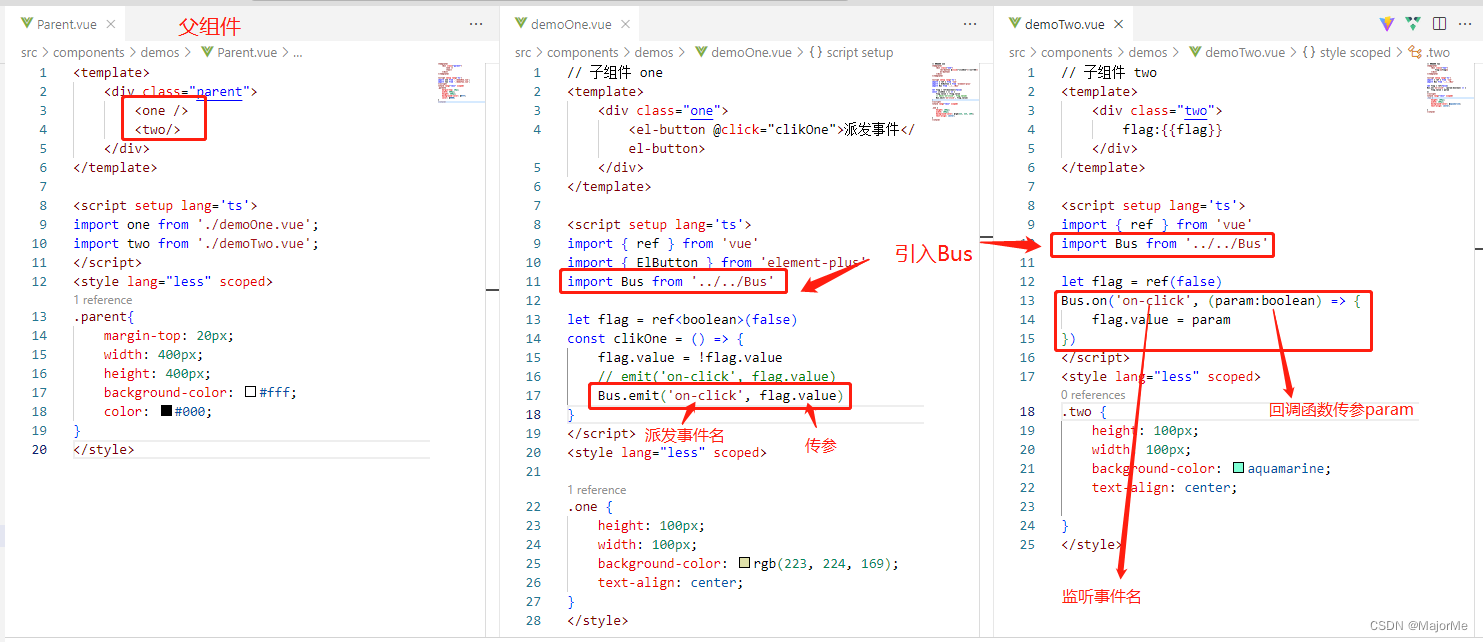 - 方法三:使用库mitt
- 方法三:使用库mitt
- 安装
npm install mitt -S
- 在main.ts 中注册挂载到全局
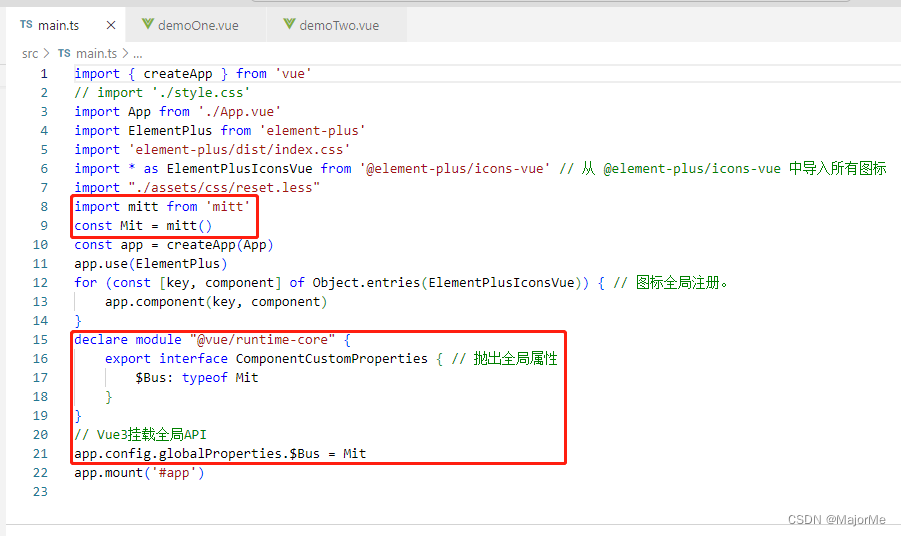
import mitt from 'mitt'
const Mit = mitt()
declare module "@vue/runtime-core" {
export interface ComponentCustomProperties {
$Bus: typeof Mit
}
}
app.config.globalProperties.$Bus = Mit
18、tsx组件
tsx是混合了ts和html的写法
1、在项目根目录下安装插件
npm install @vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx -D
2、vite.config.ts 配置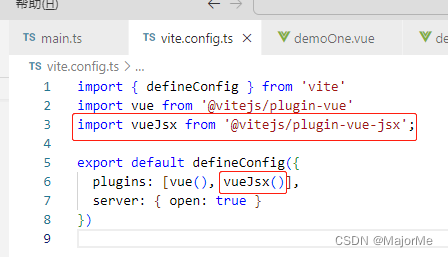
import vueJsx from '@vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue(), vueJsx()],
server: { open: true }
})
3、tsconfig.json 配置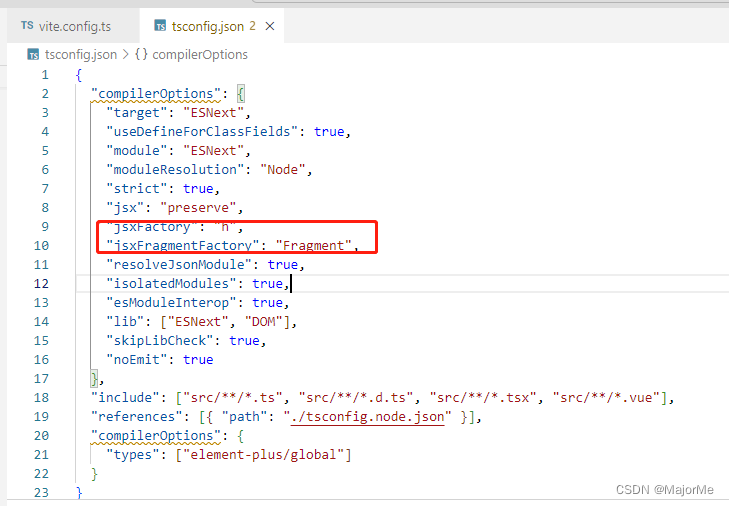
"jsxFactory": "h",
"jsxFragmentFactory": "Fragment",
4、具体使用方法看注释
/* :
1、html模板绑定变量:单括号格式<div>{xxx}</div>
2、支持v-model、v-show、v-bine 也是单括号格式绑定,ref变量需要.value获取
3、v-if、v-for不支持,具体和react同
4、v-on绑定事件 同react 如onClick={xxx}
5、Props 函数组件第一个参数接收
6、Emit 函数组件第一个参数提供
*/
// tsxDemo.tsx
import { ref } from 'vue'
import { ElInput, ElButton } from 'element-plus'
type Props = {
name: string,
arr: Array<string>
}
let inputVal = ref<string>('')
let showInputVal = ref<boolean>(true)
const tsxDemo = (props:Props, ctx:any) => {
console.log('props:', props)
return (
<div>
{/* v-model */}
<ElInput v-model={inputVal.value} type="text" />
{/* v-show */}
<div v-show={showInputVal.value}>
不能说的秘密:
</div>
{/* v-bine:直接=赋值 */}
<div innerHTML={inputVal.value}></div>
{/* v-if(tsx不支持,要用表达式形式) */}
{
showInputVal.value ? <div>喜欢</div> : <div>不喜欢</div>
}
{/* props、v-for(tsx不支持,要使用map循环) */}
{
props.arr.map((item, index) => {
return <div key={index}>{item}</div>
})
}
<ElButton onClick={click1.bind(this,ctx)}>test</ElButton>
</div>
)
}
const click1 = (ctx:any) => {
ctx.emit('testClick', 'tsx的emit测试')
}
export default tsxDemo
// 父组件 引用tsxDemo组件
<template>
<div class="parent">
<tsxDemo name="'qmz'" :arr="arr" @testClick="testClick" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
import tsxDemo from './tsxDemo';
const arr = reactive<string[]>(['水蜜桃', '香蕉', '芒果', '橘子', '黑布林'])
const testClick = (param:string) => {
console.log(param)
}
</script>
19、v-model
v-model 是 props 和 emit组合而成的语法糖。
defineProps<{
modelValue: boolean, // modelValue是默认变量名, 和绑定格式v-model="xxx"匹配
xxx: string // 自定义变量名,绑定格式v-model:xxx= "xxx"
}>()
// defineEmits格式是约定的, 1、默认v-model对应:'update:modelValue', 2、自定义v-model对应:'update:自定义变量名'
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue', 'update:xxx'])
const functionXXX = () => {
emit('update:modelValue', '变量值')
emit('update:xxx', '变量值')
}
案例:
// 子组件 定义v-model和父组件响应
<template>
<div v-if="modelValue" class="two">
<p style="color:pink">子组件</p>
<div style="margin-top:20px">
<input @input="inputChange" v-model="inputValue" type="text" />
</div>
<div style="margin-top:20px">
<ElButton type="primary" style="margin: auto;" @click="handleClose">关闭</ElButton>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
defineProps<{
modelValue: boolean, // modelValue是默认变量名, 和绑定格式v-model="xxx"匹配
inputValue: string // 自定义变量名,绑定格式v-model:inputValue = "xxx"
}>()
// defineEmits格式是约定的, 1、默认v-model对应:'update:modelValue', 2、自定义v-model对应:'update:自定义变量名'
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue', 'update:inputValue'])
const handleClose = () => {
emit('update:modelValue', false)
}
const inputChange = (e:Event) => {
const target = e.target as HTMLInputElement
console.log()
emit('update:inputValue', target.value)
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.two {
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid pink;
margin-top: 10px;
height: 110px;
width: 250px;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
// 父组件
<template>
<div class="parent">
<p style="color:red">v-model</p>
<div style="margin-top:20px">
<span style="margin-right:20px">input值:{{inputVal}}</span>
<ElButton type="primary" @click="visible=!visible">{{visible? '关闭' : '修改'}}</ElButton>
</div>
<DemoTwo v-model="visible" v-model:inputValue="inputVal"></DemoTwo>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
import DemoTwo from './demoTwo.vue';
let visible = ref<boolean>(true)
let inputVal = ref<string>('')
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.parent{
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
width: 30%;
height: 50%;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid red;
color: #000;
}
</style>
效果:
20、自定义指令
vue3钩子函数:
created 元素初始化的时候
beforeMount 指令绑定到元素后/渲染前 调用
mounted 指令绑定的子组件渲染完成时调用
beforeUpdate 元素被更新之前调用
update 这个周期方法被移除 改用updated
beforeUnmount 在元素被移除前调用
unmounted 指令被移除后调用 只调用一次
简单案例:
<template>
<div class="one">
<div>
请输入颜色值:<input v-model="color" type="text" />
</div>
<DemoTwo v-set-color="{ background: color }"></DemoTwo>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import DemoTwo from './demoTwo.vue'
import { ref, Directive, DirectiveBinding } from 'vue' // 引入Directive, DirectiveBinding
let color = ref<string>('')
type Dir = {
background: string
}
// el拿到指令绑定的组件dom,binding拿到指令的绑定值
const vSetColor: Directive = (el: HTMLElement, binding: DirectiveBinding<Dir>) => {
el.style.background = binding.value.background
}
</script>
<style>
.one {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
// 子组件 DemoTwo
<template>
<div class="two" />
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.two {
margin-top:10px;
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid pink;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
}
</style>

21、自定义hook
Vue3 的 hook函数 可以帮助我们提高代码的复用性, 让我们能在不同的组件中都利用。
安装:npm i @vueuse/core
使用小案例:
<template>
<div class="one">
<div>
<input ref="target" v-model="color" type="text" />
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
// 安装后直接从'@vueuse/core'引入就可以使用了
import { useFocus } from '@vueuse/core'
const target = ref()
const { focused } = useFocus(target)
// 监听target(也就是input)的foucus状态
watch(focused, (focused) => {
if (focused)
console.log('input element has been focused')
else console.log('input element has lost focus')
})
</script>
- 自定义hooks
demo:把图片转成的canvas地址
// 定义hooks
import { onMounted } from 'vue'
type Options = {
el: string
}
export default function (options: Options): Promise<{imgUrl: string}> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
onMounted(() => {
let img:HTMLImageElement = document.querySelector(options.el) as HTMLImageElement
console.log('img:', img)
img.onload = () => {
resolve({
imgUrl: drawCanvasImg(img)
})
}
})
const drawCanvasImg = (el:HTMLImageElement) => {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas')
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
canvas.width = el.width
canvas.height = el.height
ctx?.drawImage(el,0,0,canvas.width, canvas.height)
return canvas.toDataURL('image/png')
}
})
}
// 使用上面定义hooks
<template>
<div class="one">
<img id="img" width="200" height="200" src="../../assets/imgs/1.jpeg" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang='ts'>
import canvasUrl from '../../hooks/canvasUrl' // 引入hooks
canvasUrl({el: '#img'}).then(res => {
console.log('res.imgUrl:', res.imgUrl)
})
</script>
22、定义全局函数和全局变量
声明并暴露全局属性
declare module “@vue/runtime-core” {
export interface ComponentCustomProperties {
属性名1: 属性类型,
属性名2: 属性类型,
…
} }
定义全局属性
app.config.globalProperties.属性名1 = 函数或变量值
app.config.globalProperties.属性名2 = 函数或变量值
…
案例:
// 配置 main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
type Filter = {
format1: <T>(str:T) => string
format2: <T>(str:T) => string
}
// 声明全局属性
declare module "@vue/runtime-core" {
export interface ComponentCustomProperties { // 抛出全局属性
$filters: Filter,
$xxx: string
}
}
// 定义全局对象$filters,里面包含format1、format2函数,它们接收泛型参数,给传参拼上前缀“啦啦啦-”和“啦啦啦-”后返回字符串
app.config.globalProperties.$filters = {
format1 <T>(str:T):string {
return `啦啦啦-${str}`
},
format2 <T>(str:T):string {
return `哈哈哈-${str}`
}
}
// 定义全局变量$xxx
app.config.globalProperties.$xxx = '我是一个字符串全局变量值'
app.mount('#app')
直接在组件里使用:
<template>
<div class="one">
<div>$xxx: {{$xxx}}</div>
<div>format1: {{$filters.format1('qmz')}}</div>
<div>format2: {{$filters.format2('qmz')}}</div>
</div>
</template>
效果: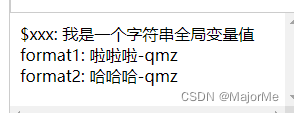
23、
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)