PID控制算法及arduino应用(电机调速和位置控制)
介绍及公式pid算法用于简单的控制非常方便,因此我们常常把pid控制做成固定的库,方便我们调用。库文件说明:这里的库程序,我是基于esp32开发板写的,其他开发板类似,主要区别就是获取当前时间戳不一样。其余的算法是一样的。如果你想移植到其他平台,只需要修改获取时间戳的函数即可。时间戳单位是微秒。位置式pid.h#define PID_H#include "time_utils.h"#include
目录
导航贴:平衡小车的控制算法(PID,LQR,MPC)及arduino程序导航贴_Allen953的博客-CSDN博客
介绍及公式
如果哪里写的不对,欢迎批评指正。QQ:953598974
pid算法用于简单的控制非常方便,它常用于底层的控制。
因此我们常常把pid控制做成固定的库,方便调用。

库文件
说明:这里的库程序,是基于esp32开发板写的,其他开发板类似,主要区别就是获取当前时间戳不一样。其余的算法是一样的。如果你想移植到其他平台,只需要修改获取时间戳的函数即可。时间戳单位是微秒。
esp32位置式
positionPid.h
#define PID_H
#include "time_utils.h"
#include "foc_utils.h"
/**
* PID controller class
*/
class PIDController
{
public:
/**
*
* @param P - Proportional gain
* @param I - Integral gain
* @param D - Derivative gain
* @param ramp - Maximum speed of change of the output value
* @param limit - Maximum output value
*/
PIDController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit);
~PIDController() = default;
float operator() (float error);
float P; //!< Proportional gain
float I; //!< Integral gain
float D; //!< Derivative gain
float output_ramp; //!< Maximum speed of change of the output value
float limit; //!< Maximum output value
protected:
float integral_prev; //!< last integral component value
float error_prev; //!< last tracking error value
unsigned long timestamp_prev; //!< Last execution timestamp
float output_prev; //!< last pid output value
};
positionPid.cpp
#include "pid.h"
PIDController::PIDController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit)
: P(P)
, I(I)
, D(D)
, output_ramp(ramp) // output derivative limit [volts/second]
, limit(limit) // output supply limit [volts]
, integral_prev(0.0)
, error_prev(0.0)
, output_prev(0.0)
{
timestamp_prev = _micros();
}
// PID controller function
float PIDController::operator() (float error){
// 计算上次调用到现在的时间Ts(秒)
unsigned long timestamp_now = _micros();
float Ts = (timestamp_now - timestamp_prev) * 1e-6;
// 快速修复异常 (micros overflow),如果溢出或者出现其他异常,则Ts=0.001ms
if(Ts <= 0 || Ts > 0.5) Ts = 1e-3;
// u(s) = (P + I/s + Ds)e(s) //计算输入函数u(s)
// Discrete implementations //分元素计算
// proportional part //比例项
// u_p = P *e(k) //u_p = P * e(k)
float proportional = P * error;
// Tustin transform of the integral part //积分项的双线性变换
// u_ik = u_ik_1 + I*Ts*(ek + ek _1)/2 //u_ik = u_ik_1 + I*Ts*(ek + ek _1)/2
float integral = integral_prev + I*Ts*(error + error_prev)*0.5;
// antiwindup - limit the output
integral = _constrain(integral, -limit, limit);
// Discrete derivation
// u_dk = D(ek - ek_1)/Ts //微分项,除以Ts,是在求微分
float derivative = D*(error - error_prev)/Ts;
// sum all the components
float output = proportional + integral + derivative;
// antiwindup - limit the output variable
output = _constrain(output, -limit, limit);
// if output ramp defined //这里解决超调问题。
if(output_ramp > 0){
// limit the acceleration by ramping the output
float output_rate = (output - output_prev)/Ts;
if (output_rate > output_ramp)
output = output_prev + output_ramp*Ts;
else if (output_rate < -output_ramp)
output = output_prev - output_ramp*Ts;
}
// saving for the next pass
integral_prev = integral;
output_prev = output;
error_prev = error;
timestamp_prev = timestamp_now;
return output;
}
arduino uno位置式
positionPid.h
#include <Arduino.h>
#define PID_H
/**
* PID controller class
*/
class PosPidController
{
public:
/**
*
* @param P - Proportional gain
* @param I - Integral gain
* @param D - Derivative gain
* @param ramp - Maximum speed of change of the output value
* @param limit - Maximum output value
*/
PosPidController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit);
~PosPidController() = default;
float operator() (float error);
float P; //!< Proportional gain
float I; //!< Integral gain
float D; //!< Derivative gain
float output_ramp; //!< Maximum speed of change of the output value
float limit; //!< Maximum output value
protected:
float integral_prev; //!< last integral component value
float error_prev; //!< last tracking error value
unsigned long timestamp_prev; //!< Last execution timestamp
float output_prev; //!< last pid output value
};positionPid.cpp
#include "positionPid.h"
PosPidController::PosPidController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit)
: P(P)
, I(I)
, D(D)
, output_ramp(ramp) // output derivative limit [volts/second]
, limit(limit) // output supply limit [volts]
, integral_prev(0.0)
, error_prev(0.0)
, output_prev(0.0)
{
timestamp_prev = millis();
}
// PID controller function
float PosPidController::operator() (float error){
// 计算上次调用到现在的时间Ts(秒)
unsigned long timestamp_now = millis();
float Ts = (timestamp_now - timestamp_prev) * 1e-3;
// 快速修复异常 (micros overflow),如果溢出或者出现其他异常,则Ts=0.001ms
if(Ts <= 0 || Ts > 0.5) Ts = 1e-3;
// u(s) = (P + I/s + Ds)e(s) //计算输入函数u(s)
// Discrete implementations //分元素计算
// proportional part //比例项
// u_p = P *e(k) //u_p = P * e(k)
float proportional = P * error;
// Tustin transform of the integral part //积分项的双线性变换
// u_ik = u_ik_1 + I*Ts*(ek + ek _1)/2 //u_ik = u_ik_1 + I*Ts*(ek + ek _1)/2
float integral = integral_prev + I*Ts*(error + error_prev)*0.5;
// antiwindup - limit the output
integral = constrain(integral, -limit, limit);
// Discrete derivation
// u_dk = D(ek - ek_1)/Ts //微分项,除以Ts,是在求微分
float derivative = D*(error - error_prev)/Ts;
// sum all the components
float output = proportional + integral + derivative;
// antiwindup - limit the output variable
output = constrain(output, -limit, limit);
// if output ramp defined //这里解决超调问题。
if(output_ramp > 0){
// limit the acceleration by ramping the output
float output_rate = (output - output_prev)/Ts;
if (output_rate > output_ramp)
output = output_prev + output_ramp*Ts;
else if (output_rate < -output_ramp)
output = output_prev - output_ramp*Ts;
}
// saving for the next pass
integral_prev = integral;
output_prev = output;
error_prev = error;
timestamp_prev = timestamp_now;
return output;
}增量式
pid.h
#define PID_H
#include "time_utils.h"
#include "foc_utils.h"
/**
* PID controller class
*/
class PIDController
{
public:
/**
*
* @param P - Proportional gain
* @param I - Integral gain
* @param D - Derivative gain
* @param ramp - Maximum speed of change of the output value
* @param limit - Maximum output value
*/
PIDController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit);
~PIDController() = default;
float operator() (float error);
float P; //!< 比例增益
float I; //!< 积分增益
float D; //!< 微分增益
float output_ramp; //!< 输出值最大变化率
float limit; //!< 输出限制(最大输出绝对值)
protected:
float error_prev; //!< k-1时刻误差
float error_prev1; //!< k-2时刻误差
unsigned long timestamp_prev; //!< 上次执行计算时的时间戳
float output_prev; //!< k-1时刻输出
float output; //
};pid.cpp
#include "pid.h"
PIDController::PIDController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit)
: P(P)
, I(I)
, D(D)
, output_ramp(ramp) // output derivative limit [volts/second]
, limit(limit) // 输出限制(常用pwm分辨率)
, error_prev(0.0)
, output_prev(0.0)
, output(0.0)
{
timestamp_prev = _micros();
}
// PID controller function
float PIDController::operator() (float error){
// 计算上次调用到现在的时间Ts(秒)
unsigned long timestamp_now = _micros();
float Ts = (timestamp_now - timestamp_prev) * 1e-6;
// 快速修复异常 (micros overflow),如果溢出或者出现其他异常,则Ts=0.001ms
if(Ts <= 0 || Ts > 0.5) Ts = 1e-3;
// 计算输出函数u(s)
// u(k) = u(k-1) + Kp * (e(k)-e(k-1)) + Ki * Ts * (e(k)+e(k-1))/2 + Kd * (e(k)-2*e(k-1)+e(k-2))/Ts
// 分别计算
// 比例项: u_p = P * (e(k)-e(k-1))
float proportional = P * (error - error_prev);
// 积分项: u_ik = I * Ts * (e(k)+e(k-1))/2
float integral = I * Ts * (error + error_prev)*0.5;
// 微分项: u_dk = D * (e(k)-2*e(k-1)+e(k-1))/Ts
float derivative = D * (error - 2 * error_prev + error_prev1)/Ts;
// 各部分加和
output += proportional + integral + derivative;
// antiwindup - limit the output variable
output = _constrain(output, -limit, limit);
// if output ramp defined //这里解决超调问题。
if(output_ramp > 0){
// limit the acceleration by ramping the output
float output_rate = (output - output_prev)/Ts;
if (output_rate > output_ramp)
output = output_prev + output_ramp*Ts;
else if (output_rate < -output_ramp)
output = output_prev - output_ramp*Ts;
}
// 存储数据以便下次调用
output_prev = output;
error_prev1 = error_prev;
error_prev = error;
timestamp_prev = timestamp_now;
return output;
}用法
程序用起来比较简单。
1.把库文件放进自己的工程
2.在主程序中包含pid库文件
3.新建pid控制器并初始化pid参数
PIDController pidv{2.8, 8.0, 0.01, 50000.0, 255.0}; //单纯速度环4.计算error
自己计算一下error,比如我期望电机转速为5r/s,现在通过编码器检测到电机实际速度为3r/s。则error=5-3=2r/s.
5.调用pid控制器计算输出
通过下面一行代码,把误差放进去,pid控制器就会自己计算出来输出。
output = pidv(error);6.将输出施加到系统
比如我是pid调速的,输入的是有效电压(通过调节pwm占空比调节),输出的是速度。
那么我们拿到pid控制器输出的数值,作为系统的输入,也就是pwm占空比施加到系统即可。
实验
位置环
(1)参数,P=2.0,RAMP=50000,LIMIT=255,周期=20ms
![]()
![]()
效果
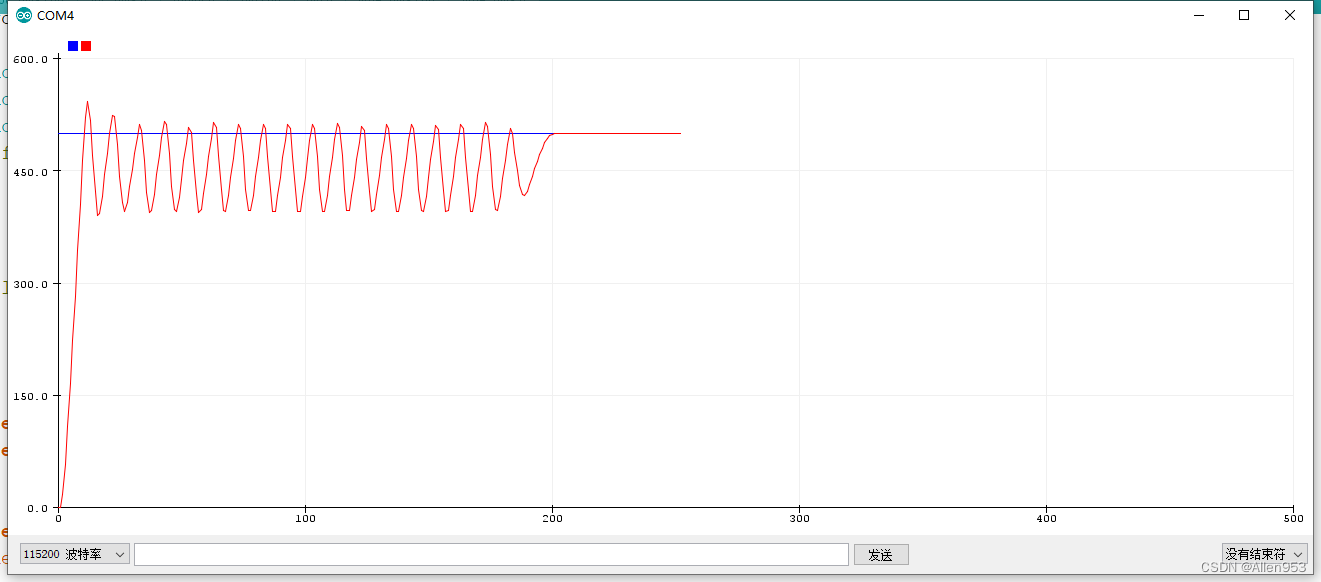
首先增大P而其余参数不变
![]()
![]()
效果
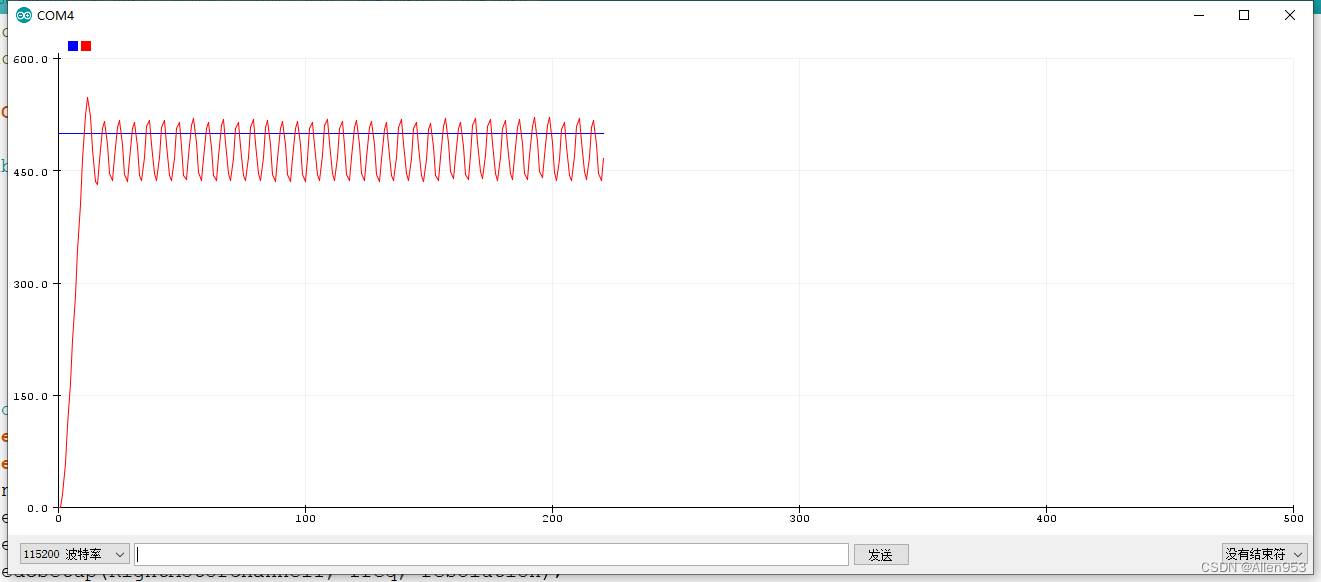
震荡频率增加了,因为P变大,响应变快了,所以震荡频率增加了,但震荡幅度降低了。
再继续增大P。
![]()
![]()
效果
可以看到频率和振幅基本没变。
现在再增大P就没啥用了,现在我们降低周期,加快响应速度。
![]()
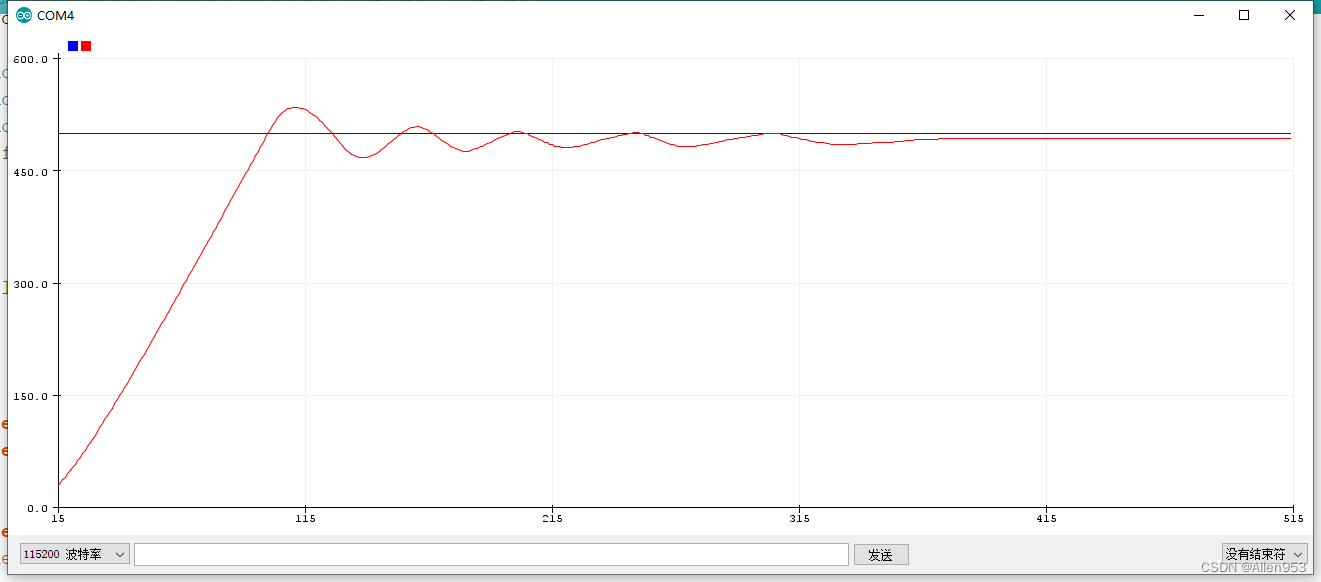
现在周期5ms,这样系统响应速度增加了。
然后我们可以看到系统快速响应过去,经过几次震荡之后稳定了下来,虽然有稳态误差,但系统总算稳定了下来。
得出结论:增加响应速度有利于抑制震荡,使得系统稳定下来。
我们再增加P看看是否响应会更快
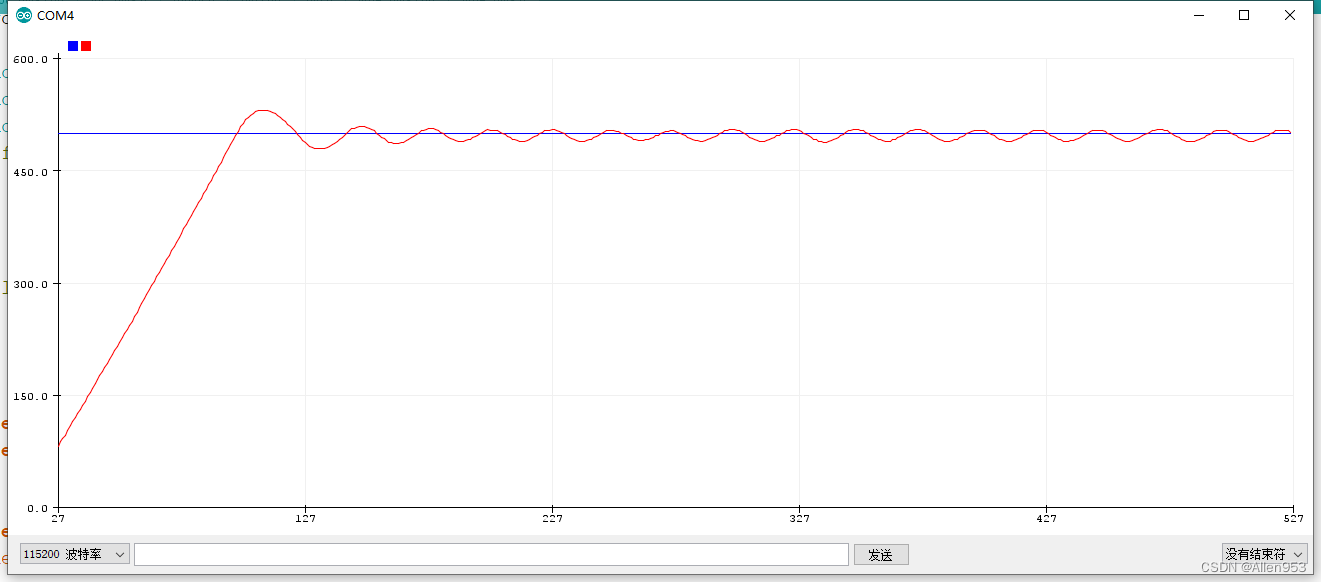
现在系统震荡了起来,响应速度变化不大,因为系统在追踪期望值的时候,已经用了最大速度去跑,因此响应速度无法再提升了,除非输入还能加大(增加电池电压)。
那么我们为了抑制震荡,再次降低延迟,提高系统响应速度。
参数![]()
效果

从上图可以发现,当我们取消延迟, 系统响应很快,但是还是有震荡。这时我们降低一点P值。
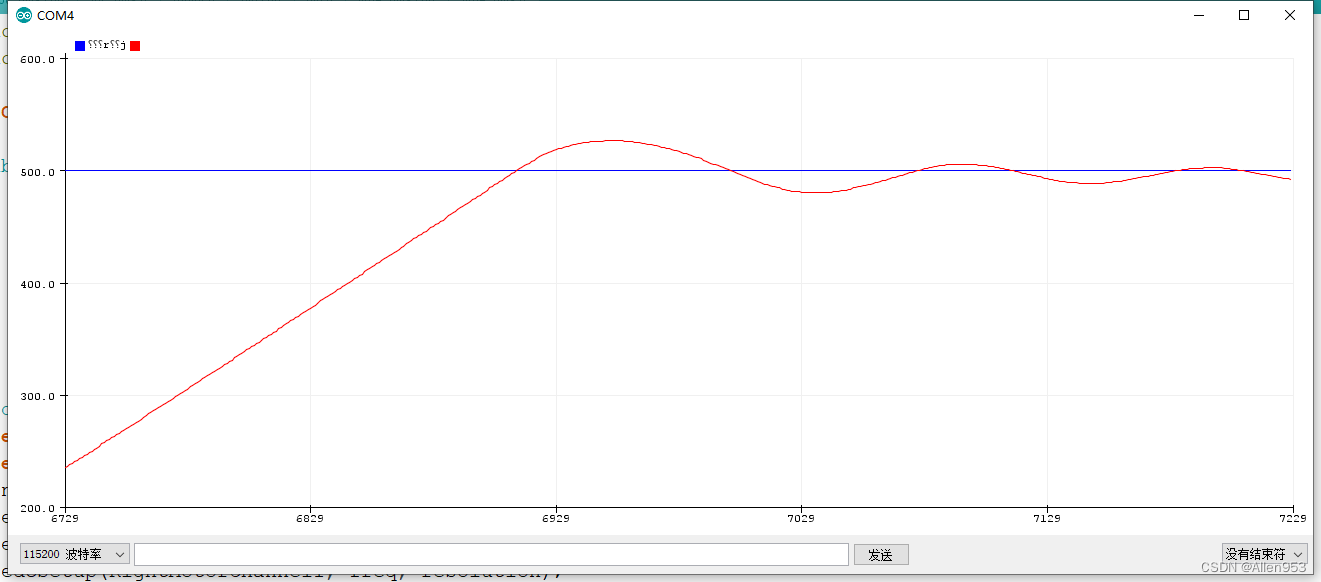
还是有过多的震荡,我们继续降低P值,使得系统在一两个震荡下稳定下来,
由于无法提高响应速度了,现在只能通过降低P值来抑制震荡。
当我们调的系统既能快速响应,又能在一两个震荡周期内稳定下来,就达到目的了。
接下来我们就可以专注于消除稳态误差了,开始调I。
I我们设为0.005,D我们设为0.5
![]()
这时效果如下,系统响应很快,而且没什么稳态误差,但是系统总是震荡几下才稳定。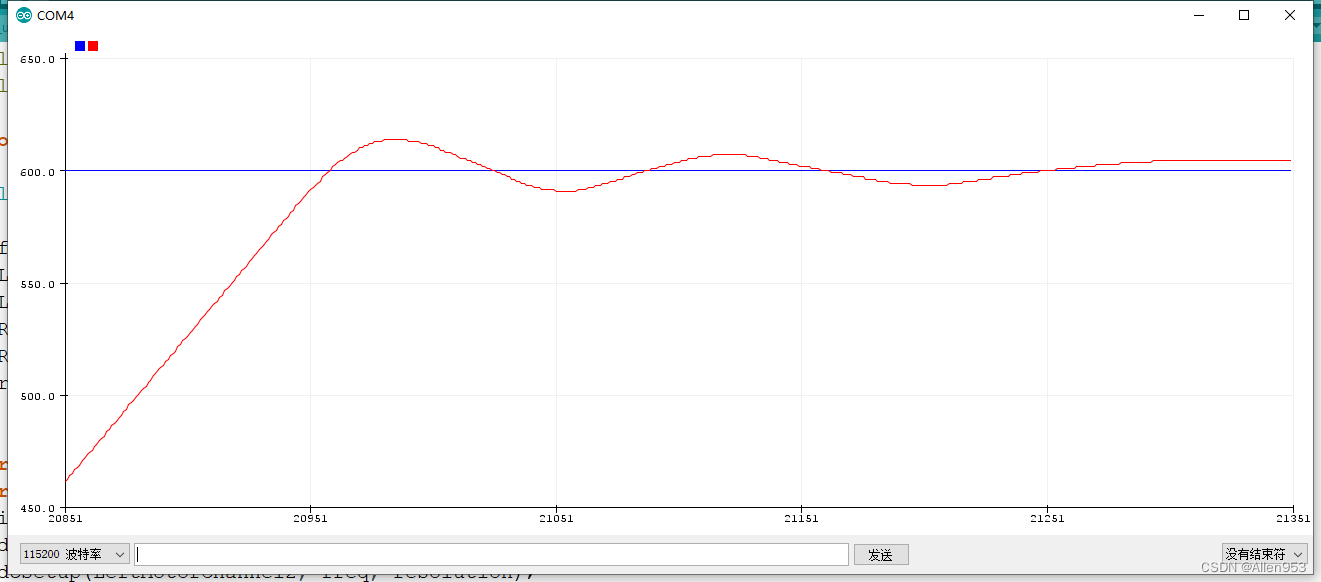
我们想让系统尽快稳定减少震荡
所以我们减少一下P,把P设为20
![]()
这时效果如下,非常理想了,当我们给定目标,系统快速逼近,有一次超调之后再拉回来,接着超调再拉回,结果稳定下来,速度非常快,只震荡一次就稳定。
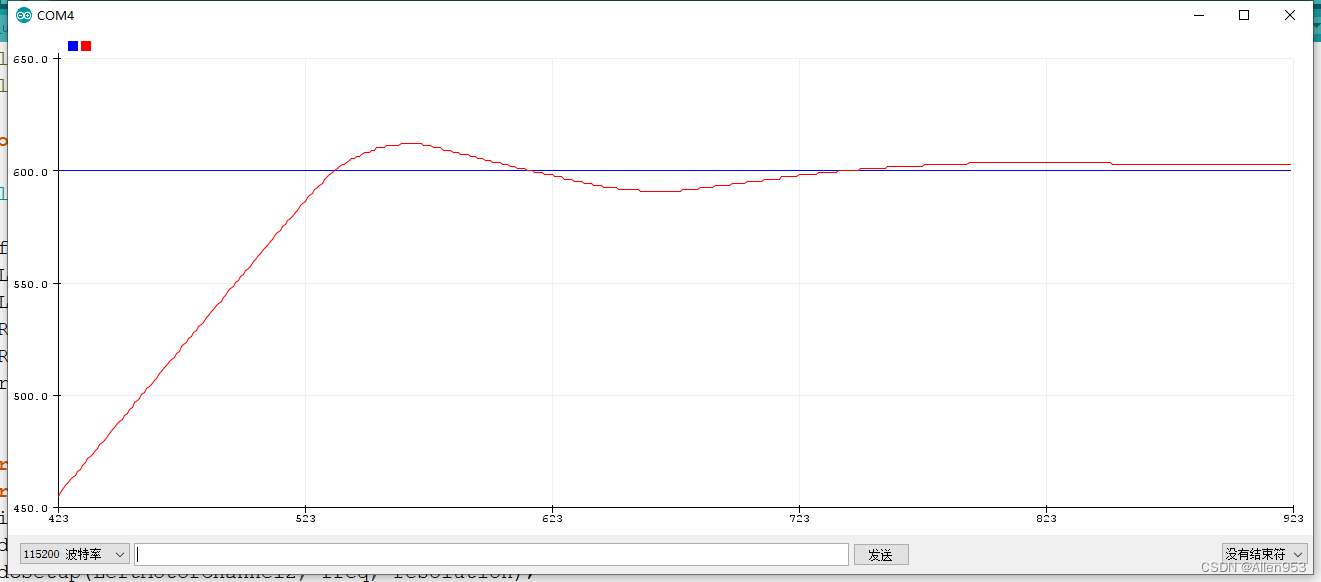
但是,由于当误差比较小的时候,比如误差为5,这个时候pid输出为100左右,这个pwm输入电机的时候,通常电机由于自身阻尼比较大启动不了。深圳当误差为8时,才进行响应。我们希望系统能在小误差下进行响应。
因此我们还把P值调回来,把P还改回30,这时我们增加D的大小,理论上来讲也可以使得系统更快的稳定。
参数
![]()
效果:
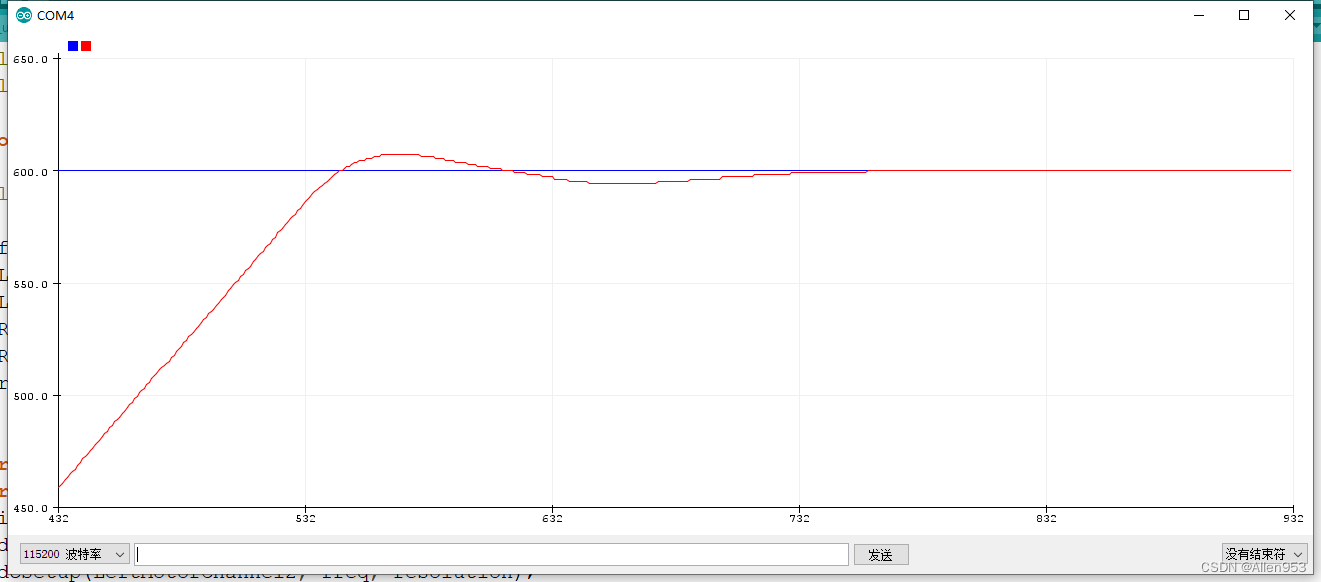
通过上图我们可以看到,一样使得系统只在一个震荡回合内稳定了下来。
结论:如果想减少震荡次数使得系统稳定下来,一个可以减少P,另一个可以增大D。
减少P无疑会使得系统对误差不敏感(小误差系统不响应),而这时就要增大D了。
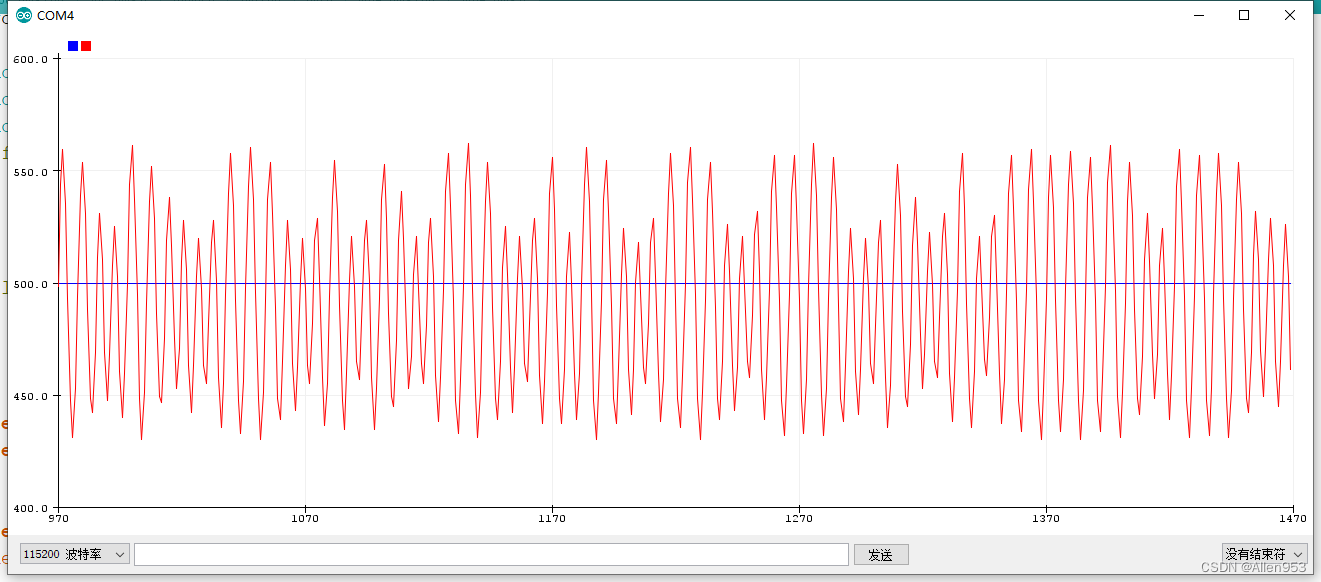
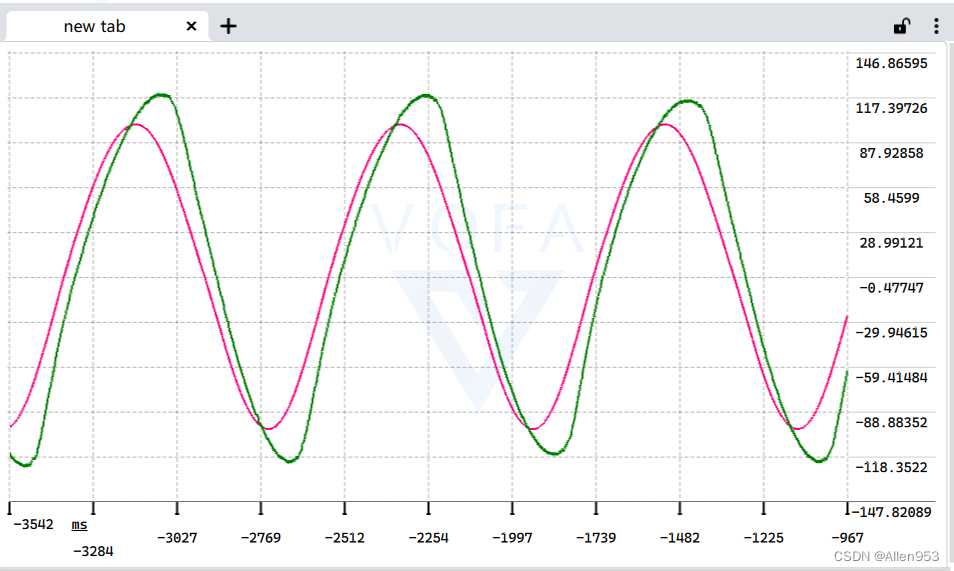
速度环
正弦速度跟踪
![]()
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容









所有评论(0)