Windows对异常的处理
异常处理异常产生后,首先是要记录异常信息(异常的类型、异常发生的位置等),然后要寻找异常的处理函数,称为异常的分发,最后找到异常处理函数并调用,称为异常处理。异常的分类cpu产生的异常执行指令时检测到的错误,除0,GP,无效指令Machine Check Exceptions, 总线错误,ECC错误,Cache错误预先埋伏的,int 3,调试异常程序产生RaiseException,Win32 A
·
异常处理
异常产生后,首先是要记录异常信息(异常的类型、异常发生的位置等),然后要寻找异常的处理函数,称为异常的分发,最后找到异常处理函数并调用,称为异常处理。
异常的分类
cpu产生的异常
- 执行指令时检测到的错误,除0,GP,无效指令
- Machine Check Exceptions, 总线错误,ECC错误,Cache错误
- 预先埋伏的,int 3,调试异常
程序产生
- RaiseException,Win32 API
- C++,throw Exception,编译器会翻译为对RaiseException的调用
异常的产生
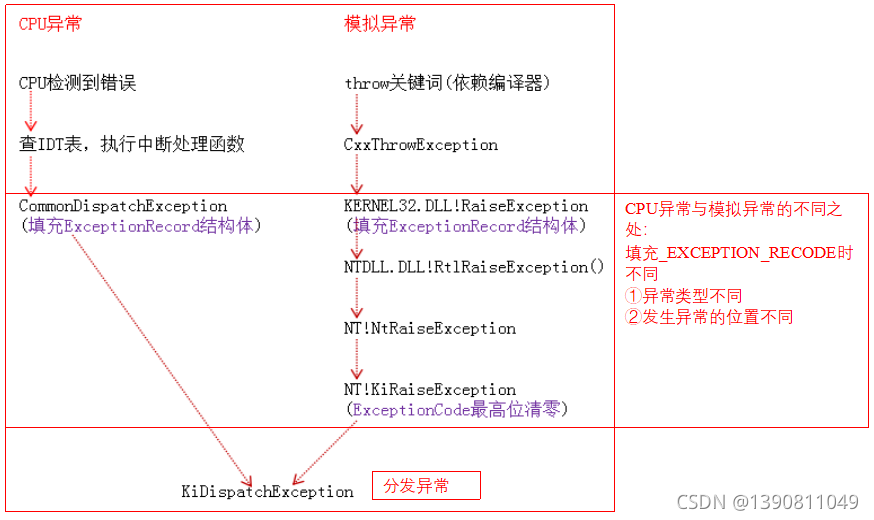
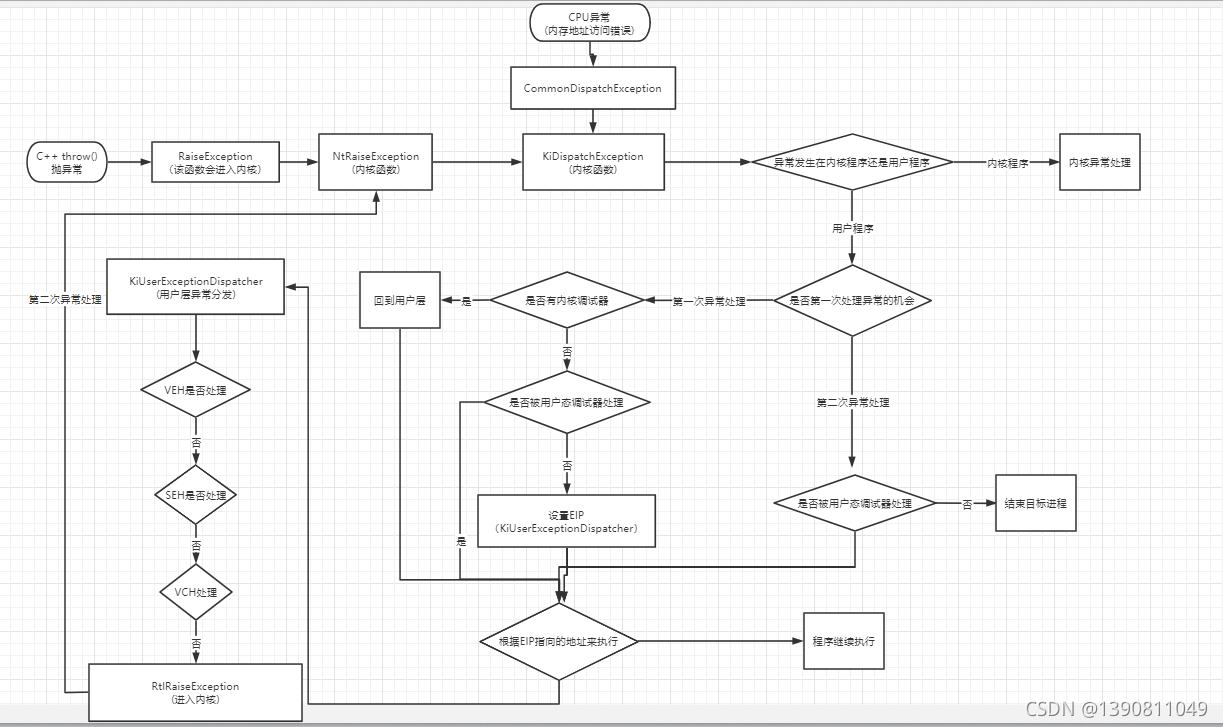
异常的分发
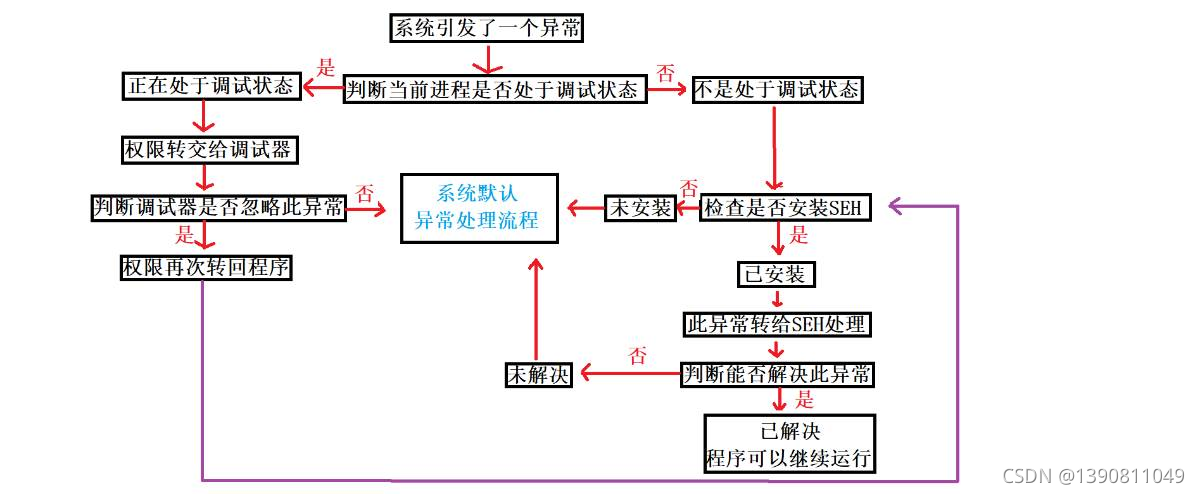
KiDispatchException
// 异常派发函数
// 派发一个异常到适当的模式
// 如果中断发生前 处于内核模式,将直接处理该异常,否则把异常信息包装抛出到用户模式(涉及跨级别的内存拷贝)
VOID
KiDispatchException(
IN PEXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord, // 异常记录的指针
IN PKEXCEPTION_FRAME ExceptionFrame, // 指向异常帧,在 NT386 模式下 该指针为 NULL
IN PKTRAP_FRAME TrapFrame, // 指向陷阱帧
IN KPROCESSOR_MODE PreviousMode, // 前一个模式, 在中断发生之前系统所处的模式
IN BOOLEAN FirstChance // 是否是第一次机会异常
{
CONTEXT ContextFrame;
EXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord1, ExceptionRecord2;
LONG Length;
ULONG UserStack1;
ULONG UserStack2;
// 增加异常派发计数
KeGetCurrentPrcb()->KeExceptionDispatchCount += 1;
// 设置上下文帧需要记录的内容标志
// SS:SP, CS:IP, FLAGS, BP
// AX, BX, CX, DX, SI, DI
// DS, ES, FS, GS
// DB 0-3,6,7
ContextFrame.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_FULL | CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS;
// 如果之前处于用户程序,且处于调试模式,需要对 ContextFrame 进行包装
if ((PreviousMode == UserMode) || KdDebuggerEnabled) {
// 为了处理一些特殊情况 (80387处理器 的npx支持) 而特别需要加上的标志
ContextFrame.ContextFlags |= CONTEXT_FLOATING_POINT;
if (KeI386XMMIPresent) {
ContextFrame.ContextFlags |= CONTEXT_EXTENDED_REGISTERS;
}
}
// 根据所设置的标志位从 陷阱帧中取出相应的寄存器数据 加入 上下文帧
// 注意 这里并未使用异常帧
KeContextFromKframes(TrapFrame, ExceptionFrame, &ContextFrame);
switch (ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode) {
case STATUS_BREAKPOINT: // 如果是 int 3 造成的异常,eip需要减一之后传递给用户层
ContextFrame.Eip--;
break;
// 应用层无效的访问或访问越界
case KI_EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION:
ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode = STATUS_ACCESS_VIOLATION;
if (PreviousMode == UserMode) {
if (KiCheckForAtlThunk(ExceptionRecord, &ContextFrame) != FALSE) {
goto Handled1;
}
if ((SharedUserData->ProcessorFeatures[PF_NX_ENABLED] == TRUE) &&
(ExceptionRecord->ExceptionInformation[0] == EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_FAULT)) {
if (((KeFeatureBits & KF_GLOBAL_32BIT_EXECUTE) != 0) ||
(PsGetCurrentProcess()->Pcb.Flags.ExecuteEnable != 0) ||
(((KeFeatureBits & KF_GLOBAL_32BIT_NOEXECUTE) == 0) &&
(PsGetCurrentProcess()->Pcb.Flags.ExecuteDisable == 0))) {
ExceptionRecord->ExceptionInformation[0] = 0;
}
}
}
break;
}
ASSERT((
!((PreviousMode == KernelMode) &&
(ContextFrame.EFlags & EFLAGS_V86_MASK))
));
// 当之前的模式处于内核模式
if (PreviousMode == KernelMode) {
//
// 首先判断 内核调试器是否存在,如果内核调试器存在,给予内核调试第一轮处理机会
// 如果内核调试器处理异常,将继续运行。
// 如果内核调试器不能处理,交给异常的处理框架处理。
// 如果框架能处理则继续运行。
// 如果处理框架也不能处理,给予内核调试器第二次处理机会,如果不能处理 KeBugCheck,给个蓝脸
if (FirstChance == TRUE) {
if ((KiDebugRoutine != NULL) &&
(((KiDebugRoutine)(TrapFrame,
ExceptionFrame,
ExceptionRecord,
&ContextFrame,
PreviousMode,
FALSE)) != FALSE)) {
goto Handled1;
}
// Kernel debugger didn't handle exception. 所以 实际上 异常处理框架只有一次处理机会
if (RtlDispatchException(ExceptionRecord, &ContextFrame) == TRUE) {
goto Handled1;
}
}
// 第二次机会处理异常
if ((KiDebugRoutine != NULL) &&
(((KiDebugRoutine)(TrapFrame,
ExceptionFrame,
ExceptionRecord,
&ContextFrame,
PreviousMode,
TRUE)) != FALSE)) {
goto Handled1;
}
KeBugCheckEx(
KERNEL_MODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED,
ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode,
(ULONG)ExceptionRecord->ExceptionAddress,
(ULONG)TrapFrame,
0);
}
else {
// 如果当前处于用户模式
// 如果这是第一次处理机会且当前进程存在调试端口,发送消息到调试端口并等待回应。
// 如果调试器处理异常,继续执行。
//
// 如果不存在调试器,则拷贝异常信息到用户栈,交由用户层的异常处理框架处理。
// 如果处理框架能够处理,则继续执行。
// 如果是调用的 NtRaiseException 自行抛出的异常且不接收第一次处理机会
// 那么它将在第二次调用的时候才有机会处理
// 如果这是第二次机会,并且当前进程存在调试端口,还是优先发往调试端口
// 否则则发往子系统端口,如果子系统端口不能处理,结束进程
if (FirstChance == TRUE) {
//
// 第一次处理异常的机会
//
// 优先交给内核调试器处理
if ((KiDebugRoutine != NULL) &&
((PsGetCurrentProcess()->DebugPort == NULL &&
!KdIgnoreUmExceptions) ||
(KdIsThisAKdTrap(ExceptionRecord, &ContextFrame, UserMode)))) {
//
// 将错误分发给内核调试器
//
if ((((KiDebugRoutine)(TrapFrame,
ExceptionFrame,
ExceptionRecord,
&ContextFrame,
PreviousMode,
FALSE)) != FALSE)) {
goto Handled1;
}
}
// 发往调试端口和异常端口(子系统端口)
if (DbgkForwardException(ExceptionRecord, TRUE, FALSE)) {
goto Handled2;
}
//
// Transfer exception information to the user stack, transition
// to user mode, and attempt to dispatch the exception to a frame
// based handler.
ExceptionRecord1.ExceptionCode = 0; // satisfy no_opt compilation
// 拷贝异常信息到用户栈上
repeat:
try {
//
// If the SS segment is not 32 bit flat, there is no point
// to dispatch exception to frame based exception handler.
//
if (TrapFrame->HardwareSegSs != (KGDT_R3_DATA | RPL_MASK) ||
TrapFrame->EFlags & EFLAGS_V86_MASK) {
ExceptionRecord2.ExceptionCode = STATUS_ACCESS_VIOLATION;
ExceptionRecord2.ExceptionFlags = 0;
ExceptionRecord2.NumberParameters = 0;
ExRaiseException(&ExceptionRecord2);
}
//
// Compute length of context record and new aligned user stack
// pointer.
//
UserStack1 = (ContextFrame.Esp & ~CONTEXT_ROUND) - CONTEXT_ALIGNED_SIZE;
//
// Probe user stack area for writability and then transfer the
// context record to the user stack.
//
ProbeForWrite((PCHAR)UserStack1, CONTEXT_ALIGNED_SIZE, CONTEXT_ALIGN);
RtlCopyMemory((PULONG)UserStack1, &ContextFrame, sizeof(CONTEXT));
//
// Compute length of exception record and new aligned stack
// address.
//
Length = (sizeof(EXCEPTION_RECORD) - (EXCEPTION_MAXIMUM_PARAMETERS -
ExceptionRecord->NumberParameters) * sizeof(ULONG) + 3) &
(~3);
UserStack2 = UserStack1 - Length;
//
// Probe user stack area for writeability and then transfer the
// context record to the user stack area.
// N.B. The probing length is Length+8 because there are two
// arguments need to be pushed to user stack later.
//
ProbeForWrite((PCHAR)(UserStack2 - 8), Length + 8, sizeof(ULONG));
RtlCopyMemory((PULONG)UserStack2, ExceptionRecord, Length);
//
// Push address of exception record, context record to the
// user stack. They are the two parameters required by
// _KiUserExceptionDispatch.
//
*(PULONG)(UserStack2 - sizeof(ULONG)) = UserStack1;
*(PULONG)(UserStack2 - 2 * sizeof(ULONG)) = UserStack2;
//
// Set new stack pointer to the trap frame.
//
KiSegSsToTrapFrame(TrapFrame, KGDT_R3_DATA);
KiEspToTrapFrame(TrapFrame, (UserStack2 - sizeof(ULONG) * 2));
//
// Force correct R3 selectors into TrapFrame.
//
TrapFrame->SegCs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_CODE, PreviousMode);
TrapFrame->SegDs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_DATA, PreviousMode);
TrapFrame->SegEs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_DATA, PreviousMode);
TrapFrame->SegFs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_TEB, PreviousMode);
TrapFrame->SegGs = 0;
//
// Set the address of the exception routine that will call the
// exception dispatcher and then return to the trap handler.
// The trap handler will restore the exception and trap frame
// context and continue execution in the routine that will
// call the exception dispatcher.
//
TrapFrame->Eip = (ULONG)KeUserExceptionDispatcher;
return;
} except(KiCopyInformation(&ExceptionRecord1,
(GetExceptionInformation())->ExceptionRecord)) {
//
// If the exception is a stack overflow, then attempt
// to raise the stack overflow exception. Otherwise,
// the user's stack is not accessible, or is misaligned,
// and second chance processing is performed.
//
if (ExceptionRecord1.ExceptionCode == STATUS_STACK_OVERFLOW) {
ExceptionRecord1.ExceptionAddress = ExceptionRecord->ExceptionAddress;
RtlCopyMemory((PVOID)ExceptionRecord,
&ExceptionRecord1, sizeof(EXCEPTION_RECORD));
goto repeat;
}
}
}
//
// This is the second chance to handle the exception.
//
if (DbgkForwardException(ExceptionRecord, TRUE, TRUE)) {
goto Handled2;
}
else if (DbgkForwardException(ExceptionRecord, FALSE, TRUE)) {
goto Handled2;
}
else {
ZwTerminateProcess(NtCurrentProcess(), ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode);
KeBugCheckEx(
KERNEL_MODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED,
ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode,
(ULONG)ExceptionRecord->ExceptionAddress,
(ULONG)TrapFrame,
0);
}
}
//
// Move machine state from context frame to trap and exception frames and
// then return to continue execution with the restored state.
//
Handled1:
// 还原上下文到陷阱帧
KeContextToKframes(TrapFrame, ExceptionFrame, &ContextFrame,
ContextFrame.ContextFlags, PreviousMode);
//
// Exception was handled by the debugger or the associated subsystem
// and state was modified, if necessary, using the get state and set
// state capabilities. Therefore the context frame does not need to
// be transferred to the trap and exception frames.
//
Handled2:
return;
}
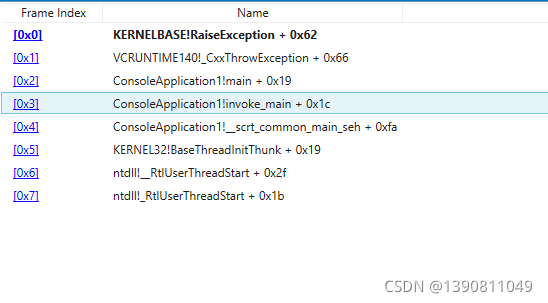
throw
int main()
{
throw 1;
return 0;
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)