Linux C小项目 —— 实现自己的myshell
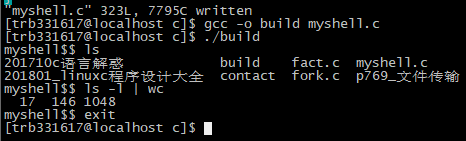
简单的shell,其功能有:解释执行命令,支持输入输出重定向,支持管道,后台运行程序支持的命令格式: 单个命令:如 ls 带1到多个参数的命令:如ls -l /tmp 带一个输出重定向或输入重定向或管道的命令:如ls -l > a, wc -c < a, ls -l / | wc -c 后台运行符&可加在以
·
简单的shell,其功能有:解释执行命令,支持输入输出重定向,支持管道,后台运行程序
支持的命令格式:
单个命令:如 ls
带1到多个参数的命令:如ls -l /tmp
带一个输出重定向或输入重定向或管道的命令:如ls -l > a, wc -c < a, ls -l / | wc -c
后台运行符&可加在以上各个命令的最后面,如ls &
输入exit或logout退出myshell
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h> // exit
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <fcntl.h> // O_RDWR
5 #include <dirent.h> // DIR, struct dirent
6
7 #define BUFFSIZE 64
8
9 #define normal 0 // 一般的命令
10 #define out_redirect 1 // 输出重定向
11 #define in_redirect 2 // 输入重定向
12 #define have_pipe 3 // 命令中有管道
13
14 void print_prompt(); // 打印提示符
15 void get_input(char *); // 读取用户输入的命令
16 // 二维数组作为函数参数,第1维长度可以不指定,但必须指定第2维长度
17 // 也可使用指向含8个元素一维数组的指针,char (*a)[8]
18 void explain_input(char *, int *, char (*a)[8]); // 解析输入的命令
19 void do_cmd(int, char a[][8]); // 执行命令
20 int find_command(char *); // 查找命令中的可执行程序
21
22 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
23 {
24 char buf[BUFFSIZE];
25 char arglist[10][8];
26 int argcount;
27
28 while(1)
29 {
30 memset(buf, 0, BUFFSIZE);
31 print_prompt(); // 打印提示符
32 get_input(buf); // 读取用户输入
33 if(strcmp(buf, "exit")==0 || strcmp(buf, "logout")==0)
34 break;
35 int i;
36 for(i=0; i<10; i++) // 初始化存放命令及其参数的数组
37 arglist[i][0] = '\0';
38 argcount = 0; // 计数,命令中词汇数量
39 explain_input(buf, &argcount, arglist); // 解析命令
40 do_cmd(argcount, arglist); // 执行命令
41 }
42 return 0;
43 }
44
45 void print_prompt()
46 {
47 printf("myshell$$ ");
48 // fflush(stdout); // fflush 冲洗stdout
49 }
50
51 void get_input(char *buf)
52 {
53 fgets(buf, BUFFSIZE, stdin); // fgets
54 int len = strlen(buf); // 计入换行符\n,不计入结束符\0
55 if(len >= BUFFSIZE)
56 {
57 printf("ERROR: command is too long !\n");
58 exit(-1);
59 }
60 buf[len-1] = '\0'; // 去除读入的换行符
61 }
62
63 // 解析buf中的命令,结果存入arglist中,命令及其参数个数为argcount
64 // 如,"ls -l"命令,则arglist[0]、arglist[1]分别为ls、-l
65 void explain_input(char *buf, int *argcount, char arglist[][8])
66 {
67 char *p = buf;
68
69 // 将用户输入的整串字符串拆分为一个个单词
70 // 存入二维数组的每一行中
71 while(*p != '\0')
72 {
73 if(*p == ' ')
74 p++;
75 else
76 {
77 char *q = p;
78 int len = 0; // 单词长度
79 while((*q!=' ') && (*q!='\0'))
80 {
81 q++; len++;
82 }
83 // 将当前拆解的单词存入二维数组中的一行
84 strncpy(arglist[*argcount], p, len+1);
85 arglist[*argcount][len] = '\0';
86 (*argcount)++;
87 p = q;
88 }
89 }
90 }
91
92 //
93 void do_cmd(int argcount, char arglist[10][8])
94 {
95 // 指针数组,每个元素指向二维数组中的一行
96 // arg存放所有命令及其参数,argnext存放管道符后的命令
97 char *arg[argcount+1], *argnext[argcount+1];
98 int i, flag = 0, how = 0, background = 0;
99 char *file;
100 pid_t pid;
101
102 // 提取命令
103 for(i=0; i<argcount; i++)
104 arg[i] = arglist[i];
105 arg[argcount] = NULL;
106
107 // 查看命令行是否有后台运行符
108 for(i=0; i<argcount; i++)
109 {
110 if(strncmp(arg[i], "&", 1) == 0) // strncmp
111 { // 后台运行符必须在命令的末尾,否则命令格式错误
112 if(i == argcount-1)
113 {
114 background = 1;
115 arg[argcount-1] = NULL;
116 break;
117 }
118 else
119 {
120 printf("ERROR: wrong command about backgrount\n");
121 return;
122 }
123 }
124 }
125
126 for(i=0; arg[i]!=NULL; i++)
127 {
128 if(strcmp(arg[i], ">") == 0)
129 {
130 flag++;
131 how = out_redirect;
132 if(arg[i+1] == NULL) // 输出重定向符在最后面
133 flag++; // 使flag大于1,告知命令格式错误
134 }
135 if(strcmp(arg[i], "<") == 0)
136 {
137 flag++;
138 how = in_redirect;
139 if(i == 0) // 输入重定向符在最前面
140 flag++;
141 }
142 if(strcmp(arg[i], "|") == 0)
143 {
144 flag++;
145 how = have_pipe;
146 if(arg[i+1] == NULL) // 管道符在最后面
147 flag++;
148 if(i == 0) // 管道符在最前面
149 flag++;
150 }
151 }
152 // flag大于1,说明同时含有>,<,|中的两个或以上,本程序不支持
153 // 或者命令格式错误
154 if(flag > 1)
155 {
156 printf("ERROR: wrong command about >,<,|\n");
157 return;
158 }
159
160 if(how == out_redirect) // 命令中只含有一个输出重定向符
161 {
162 for(i=0; arg[i]!=NULL; i++)
163 if(strcmp(arg[i], ">") == 0)
164 {
165 file = arg[i+1]; // 获取输出重定向的文件名
166 arg[i] = NULL;
167 }
168 }
169
170 if(how == in_redirect) // 命令中只含有一个输入重定向符
171 {
172 for(i=0; arg[i] != NULL; i++)
173 if(strcmp(arg[i], "<") == 0)
174 {
175 file = arg[i+1];
176 arg[i] = NULL;
177 }
178 }
179
180 if(how == have_pipe) // 命令中只含有一个管道符号
181 {
182 for(i=0; arg[i]!=NULL; i++)
183 if(strcmp(arg[i], "|") == 0)
184 {
185 arg[i] = NULL;
186 i++;
187 int j = 0;
188 // 将管道符后面的命令存入argnext中
189 while(arg[i] != NULL)
190 {
191 argnext[j++] = arg[i++];
192 }
193 argnext[j] = NULL;
194 break;
195 }
196 }
197
198 pid = fork(); // 创建子进程
199 if(pid < 0)
200 {
201 perror("fork failure");
202 return;
203 }
204
205 switch(how)
206 {
207 case 0: // 一般命令
208 if(pid==0) // 子进程执行用户输入的命令
209 {
210 if(!find_command(arg[0])) // 判断命令是否可执行
211 {
212 printf("%s: command not found\n", arg[0]);
213 exit(0);
214 }
215 execvp(arg[0], arg); // execvp 开始执行命令
216 exit(0);
217 }
218 break;
219 case 1: // 命令中含有输出重定向符
220 if(pid == 0)
221 {
222 if(!find_command(arg[0]))
223 {
224 printf("%s: command not found\n", arg[0]);
225 exit(0);
226 }
227 // 打开或新建输出重定向的文件
228 int fd = open(file, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
229 // 将标准输出复制到打开的文件描述符,即用文件描述符替换标准输出
230 dup2(fd, 1); // dup2(int oldfd, int newfd)
231 execvp(arg[0], arg); // execvp
232 exit(0);
233 }
234 break;
235 case 2: // 命令中含有输入重定向符
236 if(pid == 0)
237 {
238 if(!find_command(arg[0]))
239 {
240 printf("%s: command not found\n", arg[0]);
241 exit(0);
242 }
243 int fd = open(file, O_RDONLY);
244 dup2(fd, 0);
245 execvp(arg[0], arg);
246 exit(0);
247 }
248 break;
249 case 3: // 命令中含有管道符
250 if(pid == 0) // 子进程
251 {
252 pid_t pid2;
253 int fd2;
254 if((pid2=fork()) < 0) // 当前子进程中在新建一个子进程
255 {
256 perror("fork2 failure");
257 return;
258 }
259 if(pid2 == 0) // 新建的子进程执行管道符前面的命令
260 {
261 if(!find_command(arg[0]))
262 {
263 printf("%s: command not found\n", arg[0]);
264 exit(0);
265 }
266 // 将管道符前的命令执行结果存入fd2中
267 fd2 = open("/tmp/youdontknowfile",
268 O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
269 dup2(fd2, 1); // 重定向标准输出
270 execvp(arg[0], arg);
271 exit(0);
272 }
273 waitpid(pid2, NULL, 0); // 等待管道符前的命令执行返回
274 if(!find_command(argnext[0]))
275 {
276 printf("%s: command not found\n", argnext[0]);
277 exit(0);
278 }
279 fd2 = open("/tmp/youdontknowfile", O_RDONLY);
280 dup2(fd2, 0); // 将fd2定义为标准输入
281 execvp(argnext[0], argnext); // 执行管道符后面的命令
282 exit(0);
283 }
284 //remove("/tmp/youdontknowfile");
285 //unlink("/tmp/youdontknowfile");
286 break;
287 default:
288 break;
289 }
290 // 命令中有后台运行符,则父进程直接返回,不等待子进程返回
291 if(background == 1)
292 {
293 printf("[process id %d]\n", pid);
294 return;
295 }
296 waitpid(pid, NULL, 0); // waitpid 父进程等待子进程返回
297 }
298
299 // 判断命令是否可执行,是否有对应的可执行文件
300 int find_command(char *command)
301 {
302 DIR *dir;
303 struct dirent *ptr;
304 char *path[] = {"./", "/bin", "/usr/bin", NULL};
305 // 当输入命令"./build"时,将build命令与目录中的build文件进行匹配
306 if(strncmp(command, "./", 2) == 0)
307 command = command + 2;
308 int i = 0;
309 while(path[i] != NULL)
310 {
311 if((dir=opendir(path[i])) == NULL) // 打开目录
312 printf("cannot open /bin\n");
313 while((ptr=readdir(dir)) != NULL) // 读取目录中的文件列表
314 if(strcmp(ptr->d_name, command) == 0)
315 {
316 closedir(dir);
317 return 1;
318 }
319 closedir(dir);
320 i++;
321 }
322 return 0;
323 }更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)