vue.js进阶之组件
因为之前的项目用了vue,但是是边学边用,很多细节都不熟悉,比如vue-router,之前也写过vue+browserify构建大型应用。这次写一个vue最强大的功能,就是vue的组件。首先推荐一个博客,真的写得非常好,当然官方API也写得很好。http://www.cnblogs.com/keepfool/p/5625583.htmlvue组件基本步骤这个图也是盗用这个博客的,所以先声明一
因为之前的项目用了vue,但是是边学边用,很多细节都不熟悉,比如vue-router,之前也写过vue+browserify构建大型应用。这次写一个vue最强大的功能,就是vue的组件。
首先推荐一个博客,真的写得非常好,当然官方API也写得很好。
http://www.cnblogs.com/keepfool/p/5625583.html
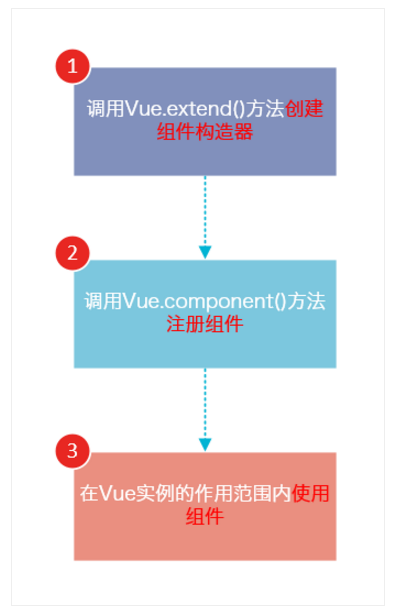
vue组件基本步骤
这个图也是盗用这个博客的,所以先声明一下,我算是转载吧,哈哈。
步骤:
1 、创建组件构造器
2、 注册组件
3、在Vue实例中使用组件
一个小小的demo来说明一下,这个就是官方的例子:
<div id="example">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>// 定义
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
})
// 注册
Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)
// 创建根实例
new Vue({
el: '#example'
})<div id="example">
<div>A custom component!</div>
</div>理解
- Vue.extend()是Vue构造器的扩展,调用Vue.extend()创建的是一个组件构造器。
- Vue.extend()构造器有一个选项对象,选项对象的template属性用于定义组件要渲染的HTML。
- 使用Vue.component()注册组件时,需要提供2个参数,第1个参数时组件的标签,第2个参数是组件构造器。
- 组件应该挂载到某个Vue实例下,否则它不会生效。
属性值的传递
组件实例的作用域是孤立的。这意味着不能并且不应该在子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据。可以使用 props 把数据传给子组件。
Vue.component('child', {
// 声明 props
props: ['message'],
// 就像 data 一样,prop 可以用在模板内
// 同样也可以在 vm 实例中像 “this.message” 这样使用
template: '<span>{{ message }}</span>'
})<child message="hello!"></child>官网的例子。
然而如何绑定到style和id呢?
data和props
1、data
使用组件Components时,大多数选项可以被传入到 Vue 构造器中,有一个例外: data 必须是函数。因为如果不是函数的,声明多个组件的时候,他们共享的就是同一个data,这样就会乱掉。如果通过函数返回,那么每个组件维持自己的data作用域。该data属性只在其component中可见。
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component>
</my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="showMsg">Show Message</button>
</div>
</template>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../dist/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'This is a Component!' //Vue中component的data必须通过function() return
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg);
}
}
}
}
})
</script>Component其他感觉和之前用的Vue没什么区别。
也可以有methods方法,有data,多了props
2、关于组件的作用域
template不是标准的HTML元素,浏览器是不理解这个元素的。
这里还可以看到template
那么Vue是如何让浏览器理解template标签的呢:
感觉必须是挂载在Vue中,通过Vue解析出这个标签成为浏览器可以理解的元素。
就像下面这段代码,必须新new 一个Vue,Vue使用myComponent作为components,然后在Vue绑定的app中,这个component就会被解析成浏览器可以阅读的语言。
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'This is a Component!' //Vue中component的data必须通过function() return
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg);
}
}
}
}
})并且vue实例和component的作用域是独立的
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{
display:true //vue实例的display
},
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'This is a Component!',
display: false //component中的display
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg);
}
}
}
}
}) <div id="app">
<my-component v-show="display">
</my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<div>
<h2 v-show="display">{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="showMsg">Show Message</button>
</div>
</template>运行结果:

h2被隐藏了,
但是my-component没有被隐藏。
也就是说:父组件模板的内容在父组件作用域内编译;子组件模板的内容在子组件作用域内编译
那么父子组件如何进行通信呢?
答案是props
3、父组件和子组件通信
官网的一张图
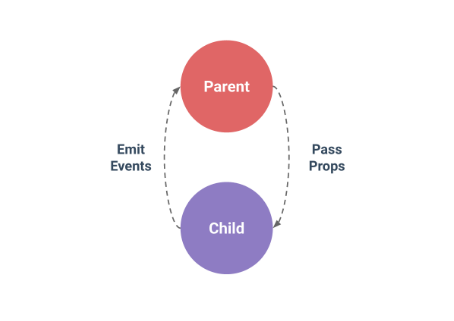
父组件通过* props* 向下传递数据给子组件,子组件通过 events 给父组件发送消息。看看它们是怎么工作的。
a. 父元素向子元素通信:props
还是刚刚的例子,我们在component中添加了props
例子1:静态props
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{
display:true
},
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
props:['parentmsg'], //声明props
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'This is a Component!',
display: false //Vue中component的data必须通过function() return
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg);
}
}
}
}
})我们在template中加了一个p,这个p引用父元素的msg,另外说一声Vue中属性绑定这个不识别大小写
<my-component v-show="display" parentMsg="ParentMsg">在浏览器看到就是
<my-component v-show="display" parentmsg="ParentMsg">所以即使你声明了props:[‘parentMsg’]也显示不出来。我的代码是这样
后来看到官方的解释是这样的:
HTML 特性不区分大小写。当使用非字符串模版时,prop的名字形式会从 camelCase 转为
kebab-case(短横线隔开)
<div id="app">
<my-component v-show="display" parentmsg="ParentMsg">
</my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<div>
<h2 v-show="display">{{msg}}</h2>
<p>{{parentmsg}}</p>
<button @click="showMsg">Show Message</button>
</div>
</template>运行结果
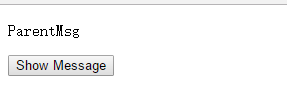
这里就是父元素的ParentMsg传递给了component
例子2:动态props
感觉神奇之处就在这里,用v-bind把刚刚的props绑定起来
<input type="" name="" v-model="ParentMsg">
<my-component v-show="display" v-bind:parentmsg="ParentMsg">
</my-component>
</div>这样ParentMsg就根据输入框中的ParentMsg动态变化了。
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{
display:true,
ParentMsg:"Hello This is Parent"
},
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
props:['parentmsg'],
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'This is a Component!',
display: false //Vue中component的data必须通过function() return
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg);
}
}
}
}
})prop 是单向绑定的:当父组件的属性变化时,将传导给子组件,但是不会反过来。这是为了防止子组件无意修改了父组件的状态——这会让应用的数据流难以理解。
另外,每次父组件更新时,子组件的所有 prop 都会更新为最新值。这意味着你不应该在子组件内部改变 prop 。如果你这么做了,Vue 会在控制台给出警告。
通常有两种改变 prop 的情况:
prop 作为初始值传入,子组件之后只是将它的初始值作为本地数据的初始值使用;
prop 作为需要被转变的原始值传入。
<div id="app">
<input type="" name="" v-model="ParentMsg">
<my-component v-show="display" v-bind:parentmsg="ParentMsg">
</my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<div>
<h2 v-show="display">{{msg}}</h2>
<p>{{parentmsg}}</p>
<p>{{childprops}}</p>
<button @click="showMsg">Show Message</button>
</div>
</template>new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{
display:true,
ParentMsg:"Hello This is Parent"
},
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
props:['parentmsg'],
data: function() {
return {
msg: 'This is a Component!',
childprops:"child:"+this.parentmsg, //可以在data中获取props,并生成新的data
display: false //Vue中component的data必须通过function() return
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg);
}
}
}
}
})a. 子元素向父元素传递信息:自定义事件
我们知道,父组件是使用 props 传递数据给子组件,但如果子组件要把数据传递回去,应该怎样做?那就是自定义事件!
使用 $on(eventName) 监听事件
使用 $emit(eventName) 触发事件 <button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>Vue.component('button-counter', {
template: '<button v-on:click="increment">{{counter}}</button>',
data: function() {
return {
counter: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment: function() {
alert("increment")
this.counter += 1;
this.$emit('increment');
}
}
})new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
display: true,
ParentMsg: "Hello This is Parent",
total: 0
},
methods: {
incrementTotal: function() {
alert("incrementTotal")
this.total += 1;
}
},
})先运行increment,再运行incrementTotal
感觉这两句是非常重要的:
v-on:increment="incrementTotal"
this.$emit('increment');分析,button上面绑定了v-on:click=”increment”,当点击按钮触发increment事件,当increment函数执行完毕,触发incrementTotal函数。全在于 this.$emit(‘increment’); 不然执行完毕increment就完毕了。
官网的例子:
<div id="counter-event-example">
<p>{{ total }}</p>
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
</div>Vue.component('button-counter', {
template: '<button v-on:click="increment">{{ counter }}</button>',
data: function () {
return {
counter: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment: function () {
this.counter += 1
this.$emit('increment')
}
},
})
new Vue({
el: '#counter-event-example',
data: {
total: 0
},
methods: {
incrementTotal: function () {
this.total += 1
}
}
})
这样点击任意一个button都会调用 incrementTotal。
input v-model="something">其实v-model仅仅是一颗语法糖
<input v-bind:value="something" v-on:input="something = $event.target.value">
所以要让组件的 v-model 生效,它必须:
1.接受一个 value 属性
2. 在有新的 value 时触发 input 事件
<div id="app2">
<currency-input label="Price" v-model="price"></currency-input>
<currency-input label="Shipping" v-model="shipping"></currency-input>
<currency-input label="Handling" v-model="handling"></currency-input>
<currency-input label="Discount" v-model="discount"></currency-input>
<p>Total: ${{ total }}</p>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<div>
<h2 v-show="display">{{msg}}</h2>
<p>{{parentmsg}}</p>
<p>{{childprops}}</p>
<button @click="showMsg">Show Message</button>
</div>
</template>Vue.component('currency-input', {
template: '\
<div>\
<label v-if="label">{{ label }}</label>\
$\
<input\
ref="input"\
v-bind:value="value"\
v-on:input="updateValue($event.target.value)"\
v-on:focus="selectAll"\
>\
</div>\
',
props: {
value: {
// type: Number,
default: 0
},
label: {
// type: String,
default: ''
}
},
methods: {
updateValue: function (value) {
this.$emit('input', value) //触发input事件
},
selectAll: function (event) {
setTimeout(function () {
event.target.select()
}, 0)
}
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#app2',
data: {
price: 0,
shipping: 0,
handling: 0,
discount: 0
},
computed: {
total: function () {
return ((
this.price * 100 +
this.shipping * 100 +
this.handling * 100 -
this.discount * 100
) / 100).toFixed(2)
}
}
})使用slot
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容







所有评论(0)