Android Fragment详解
一、什么是Fragment?Fragment:是Android3.0开始新增的概念,意为碎片。Fragment是依赖于Activity的,不能独立存在的。二、为什么要有Fragment?Android运行在各种各样的设备中,有小屏幕的手机,还有大屏幕的平板,电视等。同样的界面在手机上显示可能很好看,在大屏幕的平板上就未必了,手机的界面放在平板上可能会有过分被拉长、控件间距过大等情况。针...
一、什么是Fragment?
Fragment:是Android3.0开始新增的概念,意为碎片。Fragment是依赖于Activity的,不能独立存在的。
二、为什么要有Fragment?
Android运行在各种各样的设备中,有小屏幕的手机,还有大屏幕的平板,电视等。同样的界面在手机上显示可能很好看,在大屏幕的平板上就未必了,手机的界面放在平板上可能会有过分被拉长、控件间距过大等情况。针对屏幕尺寸的差距,Fragment的出现能做到一个App可以同时适应手机和平板。这就是为什么要有Fragment的原因。
三、Fragment的特点
Fragment是一种可以嵌入在Activity当中的UI片段
用来组建Activity界面的局部模块, 也可以说一个Actiivty界面可以由多个Fragment组成
其行为与Activity很相似, 有自己对应的布局(包含具体的View), 它有自己的生命周期,接收自己的输入事件,并且可以从运行中的activity中添加或移除
一个fragment必须总是嵌入在一个activity中,同时fragment的生命周期受activity的影响
本质上会产生一个FrameLayout,它加载的布局为其子布局
优势:
-
模块化:我们不必把所有代码全部写在Activity中,而是把代码写在各自的Fragment中。
-
可重用:多个Activity可以重用一个Fragment。
-
可适配:根据硬件的屏幕尺寸、屏幕方向,能够方便地实现不同的布局,这样用户体验更好。
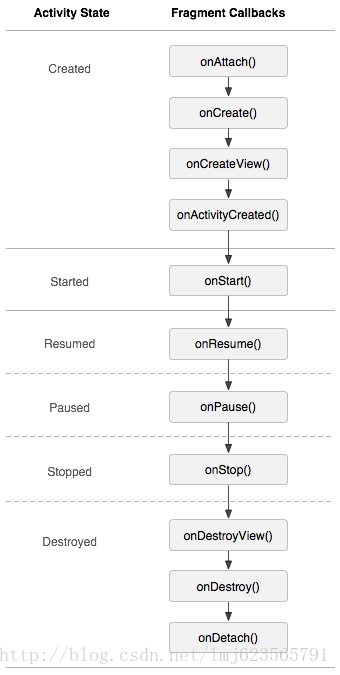
三、Fragment的生命周期
Fragment的生命周期和Activity类似,但比Activity的生命周期复杂一些,基本的生命周期方法如下图:
-
onAttach():Fragment和Activity相关联时调用。可以通过该方法获取Activity引用,还可以通过getArguments()获取参数。
-
onCreate():Fragment被创建时调用。
-
onCreateView():创建Fragment的布局。
-
onActivityCreated():当Activity完成onCreate()时调用。
-
onStart():当Fragment可见时调用。
-
onResume():当Fragment可见且可交互时调用。
-
onPause():当Fragment不可交互但可见时调用。
-
onStop():当Fragment不可见时调用。
-
onDestroyView():当Fragment的UI从视图结构中移除时调用。
-
onDestroy():销毁Fragment时调用。
-
onDetach():当Fragment和Activity解除关联时调用。
fragment生命周期解析:
当一个fragment被创建的时候,需调用以下生命周期方法:onAttach(), onCreate(), onCreateView(), onActivityCreated()
当这个fragment对用户可见的时候,需调用:onStart() ,onResume()
当这个fragment进入后台模式需调用:onPause(),onStop()
当这个fragment被销毁或者是持有它的Activity被销毁了,调用:onPause() ,onStop(), onDestroyView(), onDestroy() onDetach()
四、将fragment添加到Activity的两种方式
静态注册:以<fragment>标签的形式添加到Activity的布局当中。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.wcystart.wcystart.FragmentActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/first_fragment"
android:name="com.example.wcystart.wcystart.FirstFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/second_fragment"
android:name="com.example.wcystart.wcystart.SecondFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>动态注册:通过java代码将fragment添加到已存在的宿主Activity中
重点讲解的是动态添加、删除、替换fragment
动态添加fragment常用的类:
FragmentManager:用来管理Activity中的fragment,app包中使用getFragmentManager() v4包中getSupportFragmentManager
FragmentTransaction:事务,用来添加,移除,替换fragment,FragmentTransaction transaction = fm.benginTransatcion();//开启一个事务
transaction.add() :往Activity中添加一个Fragment
transaction.remove() :从Activity中移除一个Fragment,如果被移除的Fragment没有添加到回退栈,这个Fragment实例将会被销毁。
transaction.replace():使用另一个Fragment替换当前的,实际上就是remove()然后add()的合体~
transaction.hide():隐藏当前的Fragment,仅仅是设为不可见,并不会销毁
transaction.show():显示之前隐藏的Fragment
transaction.commit():提交一个事务
detach():会将view从UI中移除,和remove()不同,此时fragment的状态依然由FragmentManager维护。
注意:在用fragment的时候,可能会经常遇到这样Activity状态不一致:State loss这样的错误。主要是因为:commit方法一定要在Activity.onSaveInstance()之前调用。
上述,基本是操作Fragment的所有的方式了,在一个事务开启到提交可以进行多个的添加、移除、替换等操作。
值得注意的是:如果你喜欢使用Fragment,一定要清楚这些方法,哪个会销毁视图,哪个会销毁实例,哪个仅仅只是隐藏,这样才能更好的使用它们。
attach():重建view视图,附加到UI上并显示。
a、比如:我在FragmentA中的EditText填了一些数据,当切换到FragmentB时,如果希望会到A还能看到数据,则适合你的就是hide和show;也就是说,希望保留用户操作的面板,你可以使用hide和show,当然了不要使劲在那new实例,进行下非null判断。
b、再比如:我不希望保留用户操作,你可以使用remove(),然后add();或者使用replace()这个和remove,add是相同的效果。
c、remove和detach有一点细微的区别,在不考虑回退栈的情况下,remove会销毁整个Fragment实例,而detach则只是销毁其视图结构,实例并不会被销毁。那么二者怎么取舍使用呢?如果你的当前Activity一直存在,那么在不希望保留用户操作的时候,你可以优先使用detach。
动态注册代码示例:
Activity布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/ll_linera"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.wcystart.wcystart.AddFragmentActivity">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/frameLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"></FrameLayout>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/rg_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_home"
style="@style/MainButtonStyle"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/home_button_selector"
android:text="首页" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_community"
style="@style/MainButtonStyle"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/community_button_selector"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:text="发现" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_message"
style="@style/MainButtonStyle"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/message_button_selector"
android:text="消息" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_me"
style="@style/MainButtonStyle"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/me_button_selector"
android:text="我的" />
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>MainButtonStyle:
<style name="MainButtonStyle">
<!-- Customize your theme here. -->
<item name="android:layout_width">0dp</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">1</item>
<item name="android:button">@null</item>
<!-- <item name="android:drawablePadding">3dp</item>-->
<item name="android:textColor">@drawable/bottom_button_text_selector</item>
<item name="android:textSize">10sp</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center</item>
</style>bottom_button_text_selector:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:color="#535353" android:state_checked="false"></item>
<item android:color="#ff4040" android:state_checked="true"></item>
</selector>android:drawableTop="@drawable/home_button_selector"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_checked="false" android:drawable="@mipmap/index"></item>
<item android:state_checked="true" android:drawable="@mipmap/index1"></item>
</selector>示例首页Fragment其他都一样:
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate( R.layout.fragment_home, null);
return view;
}
}<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="fragment.HomeFragment">
<!-- TODO: Update blank fragment layout -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="首页" />
</FrameLayout>在Activity中动态添加,隐藏fragment。
public class AddFragmentActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private FrameLayout mFrameLayout;
private RadioGroup mRg;
private RadioButton mRbHome;
private RadioButton mRbCommunity;
private RadioButton mRbMessage;
private RadioButton mRbMe;
private List<Fragment> mFragments = new ArrayList<>();
private HomeFragment homeFragment;
private CommunityFragment communityFragment;
private MessageFragment messageFragment;
private MeFragment meFragment;
private FragmentManager mSupportFragmentManager;
private FragmentTransaction mTransaction;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment);
mFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.frameLayout);
mRg = findViewById(R.id.rg_main);
mRbHome = findViewById(R.id.rb_home);
mRbCommunity = findViewById(R.id.rb_community);
mRbMessage = findViewById(R.id.rb_message);
mRbMe = findViewById(R.id.rb_me);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
mSupportFragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//设置默认选中首页
mRg.check(R.id.rb_home);
homeFragment = new HomeFragment();
mFragments.add(homeFragment);
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, true);
mRg.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
switch (checkedId) {
case R.id.rb_home: //首页
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, false);
break;
case R.id.rb_community: //发现
if (communityFragment == null) {
communityFragment = new CommunityFragment();
mFragments.add(communityFragment);
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, false);
}
break;
case R.id.rb_message: //信息
if (messageFragment == null) {
messageFragment = new MessageFragment();
mFragments.add(messageFragment);
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, false);
}
break;
case R.id.rb_me: //我的
if (meFragment == null) {
meFragment = new MeFragment();
mFragments.add(meFragment);
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, false);
}
break;
}
}
});
}
private void hideOthersFragment(Fragment showFragment, boolean add) {
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
if (add) {
mTransaction.add(R.id.frameLayout, showFragment);
}
for (Fragment fragment : mFragments) {
if (showFragment.equals(fragment)) {
mTransaction.show(fragment);
} else {
mTransaction.hide(fragment);
}
}
mTransaction.commit();
}五、Fragment通信
1.Fragment与Fragment的通信
不同的fragment,他们之间的通信要依靠ativity来完成。我们可以把他看成Fragment->Activity->Fragment,因为两个乃至多个fragment是依附于同一个activity,所以完全可以通过把值传递到共同依附的Activity,然后通过Bundle传给另一个fragment。
简单方式一:先调用findFragmentById()方法根据id获得fragment的对象,然后调用fragment中的方法进行赋值.
manager.findFragmentById(); //根据ID来找到对应的Fragment实例,主要用在静态添加fragment的布局中,因为静态添加的fragment才会有ID
manager.findFragmentByTag();//根据TAG找到对应的Fragment实例,主要用于在动态添加的fragment中,根据TAG来找到fragment实例
manager.getFragments();//获取所有被ADD进Activity中的Fragment
直接在一个Fragment中调用另外一个Fragment的公开方法,前提是要先拿到另外一个Fragment的实例。
一般情况下,我们都是动态添加Fragment的,所以通过在add每个Fragment的时候,给每个Fragment设置个tag。
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private FragmentManager manager;
private FragmentTransaction transaction;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
/*获取manager*/
manager = this.getSupportFragmentManager();
/*创建事物*/
transaction = manager.beginTransaction();
/*创建leftFragment*/
LeftFragment leftFragment = new LeftFragment();
/*创建RightFragment*/
RightFragment rightFragment = new RightFragment();
/*通过事物把两个fragment分别添加到对应的容器中*/
transaction.add(R.id.left, leftFragment, "left");
transaction.add(R.id.right, rightFragment, "right");
/*提交事物*/
transaction.commit();
}
}在Activity创建的时候,添加上所有的fragment,并为每个fragment设置tag,这样才会在每个fragment中通过
findFragmentByTag()时,不会出现空指针。public class LeftFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvHome;
private Button mBtn;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, null);
mTvHome = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_home);
mBtn = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_home);
initView();
return view;
}
private void initView() {
Bundle bundle = this.getArguments();
String home = bundle.getString("home");
mTvHome.setText(home);
mBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
RightFragment rightFragment = (RightFragment) getActivity().getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("right");
if (rightFragment == null) return;
rightFragment .setTextView("right !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
}
});
}
}
public class RightFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvCommunity;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_community, null);
mTvCommunity=view.findViewById(R.id.tv_community);
initView();
return view;
}
private void initView() {
Bundle bundle = this.getArguments();
String community = bundle.getString("community");
mTvCommunity.setText(community);
}
public void setTextView(String str){
mTvCommunity.setText(str);
}
}这种方式是两个fragment直接通信的。(不推荐使用)
简单方式二:通过接口回调的方法实现另个fragment之间的通信
举例,比如点击MessageFragment的Buton按钮,给CommunityFragment中的TextView传递数据。
我们就需要在MessageFragment中定义接口,并定义回调的方法,该方法的参数中传一个String的字符串。接着让附属Activity实现这个接口,并重写回调方法,也就得到到传过来的数据,然后通过findFragmentByTag()的方法获取要传给的CommunityFragment的实例。
在CommunityFragment中定义一个方法用来接收这个数据,然后用对象直接调用这个方法将参数传递给这个方法,就可以了。
①在MessageFragment中定义接口,并定义回调的方法,该方法的参数中传一个String的字符串
public class MessageFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvMessage;
MessageListener mListener;
@Override
public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//创建接口的子类对象
//获取当前Fragment所属的Activity,因为Activity实现了MessageListener接口,所以是MessageListener的子类
mListener= (MessageListener) getActivity();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_message, null);
mTvMessage = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_message);
initView();
mListener.sendMessage("来自:MessageFragment的消息");
return view;
}
private void initView() {
Bundle arguments = this.getArguments();
String message = arguments.getString("message");
mTvMessage.setText(message);
}
public interface MessageListener {
void sendMessage(String message);
}
}
②
public class AddFragmentActivity extends FragmentActivity implements MessageFragment.MessageListener{
private FrameLayout mFrameLayout;
private RadioGroup mRg;
private RadioButton mRbHome;
private RadioButton mRbCommunity;
private RadioButton mRbMessage;
private RadioButton mRbMe;
private List<Fragment> mFragments = new ArrayList<>();
private HomeFragment homeFragment;
private CommunityFragment communityFragment;
private MessageFragment messageFragment;
private MeFragment meFragment;
private FragmentManager mSupportFragmentManager;
private FragmentTransaction mTransaction;
private TextView mTvMain;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment);
mFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.frameLayout);
mRg = findViewById(R.id.rg_main);
mRbHome = findViewById(R.id.rb_home);
mRbCommunity = findViewById(R.id.rb_community);
mRbMessage = findViewById(R.id.rb_message);
mRbMe = findViewById(R.id.rb_me);
mTvMain=findViewById(R.id.tv_main);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
mSupportFragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//设置默认选中首页
mRg.check(R.id.rb_home);
homeFragment = new HomeFragment();
//创建Bundle对象,并存储数据
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("home","Home");
homeFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(homeFragment);
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, true,"homefragment");
mRg.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
switch (checkedId) {
case R.id.rb_home: //首页
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, false,"homefragment");
break;
case R.id.rb_community: //发现
if (communityFragment == null) {
communityFragment = new CommunityFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("community","Community");
communityFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(communityFragment);
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, true,"communityfragment");
} else {
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, false,"communityfragment");
}
communityFragment.sendMessage(new ICommuntyCallBack() {
@Override
public void getMessageFromCommunty(String community) {
mTvMain.setText(community);
}
});
break;
case R.id.rb_message: //信息
if (messageFragment == null) {
messageFragment = new MessageFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("message","Message");
messageFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(messageFragment);
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, true,"messagefragment");
} else {
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, false,"messagefragment");
}
break;
case R.id.rb_me: //我的
if (meFragment == null) {
meFragment = new MeFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("me","Me");
meFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(meFragment);
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, true,"mefragment");
} else {
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, false,"mefragment");
}
meFragment.sendMessage(new IMeCallBack() {
@Override
public void getMessageFromMe(String me) {
mTvMain.setText(me);
}
});
break;
}
}
});
}
private void hideOthersFragment(Fragment showFragment, boolean add,String tag) {
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
if (add) {
mTransaction.add(R.id.frameLayout, showFragment,tag);
}
for (Fragment fragment : mFragments) {
if (showFragment.equals(fragment)) {
mTransaction.show(fragment);
} else {
mTransaction.hide(fragment);
}
}
mTransaction.commit();
}
@Override
public void sendMessage(String message) {
mTvMain.setText(message);
CommunityFragment communityfragment = (CommunityFragment)
mSupportFragmentManager.findFragmentByTag("communityfragment");
communityfragment.setTextView(message);
}
③在CommunityFragment中定义一个方法用来接收数据
public class CommunityFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvCommunity;
public static final String TAG = "CommunityFragment";
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_community, null);
mTvCommunity = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_community);
initView();
return view;
}
private void initView() {
Bundle bundle = this.getArguments();
String community = bundle.getString("community");
// mTvCommunity.setText(community);
}
public void setTextView(String str) {
//System.out.println("来自HomeFragment传过来的消息" + str + "//");
// mTvCommunity.setText(str);
//if (str == null) return;
mTvCommunity.setText(str);
}
}这样就实现了两个fragment之间的通信。
方式三:使用EventBus
EventBus:使用方便,但其使用的是反射原理,会有稍微的延迟,并且他人维护不方便;
static静态变量:使用方便,但是,每个static变量都会占用一块内存区,Android系统分配给每个App的内存是有限的(63M),过多很容易造成App内存溢出;
广播Broadcast Receiver:Android的广播是有限制的,除了系统的广播外,其他的广播尽量少用。另外,广播会有延迟;
接口:接口是我们常用的Fragment之间的通讯方式,通过一个主Activity作为通讯桥梁(谷歌官方声明:两个Fragment之间永远不要直接通讯),实现两个Fragment之间的通讯。
接口的方式是我们推荐的,但是,传统的接口方式会造成一些问题,如果主Activity实现了多个Fragment的通讯回调接口,那我们需要implements很多的接口,类中还要实现一大堆接口的方法,显得有点繁琐。
怎样解决这样的问题,参考链接:万能Interface实现Fragment之间的通讯
2.Activity与Fragment之间的通信
包括:①Activity如何传递数据到Fragment?
采用Bundle方式:
在activity中建一个bundle,把要传的值存入bundle,然后通过fragment的setArguments(bundle)传到fragment,在fragment中,用getArguments接收。eg:就动态添加fragment的例子,在添加每个fragment之前,使用Bundle传输数据给每个fragment。
Activity传输数据:
private void initView() {
mSupportFragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//设置默认选中首页
mRg.check(R.id.rb_home);
homeFragment = new HomeFragment();
//创建Bundle对象,并存储数据
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("home","Home");
homeFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(homeFragment);
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, true);
mRg.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
switch (checkedId) {
case R.id.rb_home: //首页
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, false);
break;
case R.id.rb_community: //发现
if (communityFragment == null) {
communityFragment = new CommunityFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("community","Community");
communityFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(communityFragment);
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, false);
}
break;
case R.id.rb_message: //信息
if (messageFragment == null) {
messageFragment = new MessageFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("message","Message");
messageFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(messageFragment);
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, false);
}
break;
case R.id.rb_me: //我的
if (meFragment == null) {
meFragment = new MeFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("me","Me");
meFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(meFragment);
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, false);
}
break;
}
}
});
}fragment中接收数据:
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvHome;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, null);
mTvHome = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_home);
initView();
return view;
}
private void initView() {
Bundle bundle = this.getArguments();
String home = bundle.getString("home");
mTvHome.setText(home);
}
}效果图:

②Fragment如何传递数据到Activity?
采用接口回调方式。
首先定义一个接口:
/**
* Created by ${wcystart}
* date:on 2019/1/22
* description: HomeFragment中通过接口回调的方式向Activity传输数据
*/
public interface IHomeCallBack {
void getMessageFromHomeFragment(String home);
}
接着在Fragment中设置接口回调的方法:
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvHome;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, null);
mTvHome = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_home);
initView();
return view;
}
private void initView() {
Bundle bundle = this.getArguments();
String home = bundle.getString("home");
mTvHome.setText(home);
}
//设置接口回调方法
public void sendMessage(IHomeCallBack iHomeCallBack){
iHomeCallBack.getMessageFromHomeFragment("我是来自HomeFragment的消息");
}
}最后在Activity中回调:
public class AddFragmentActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private FrameLayout mFrameLayout;
private RadioGroup mRg;
private RadioButton mRbHome;
private RadioButton mRbCommunity;
private RadioButton mRbMessage;
private RadioButton mRbMe;
private List<Fragment> mFragments = new ArrayList<>();
private HomeFragment homeFragment;
private CommunityFragment communityFragment;
private MessageFragment messageFragment;
private MeFragment meFragment;
private FragmentManager mSupportFragmentManager;
private FragmentTransaction mTransaction;
private TextView mTvMain;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment);
mFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.frameLayout);
mRg = findViewById(R.id.rg_main);
mRbHome = findViewById(R.id.rb_home);
mRbCommunity = findViewById(R.id.rb_community);
mRbMessage = findViewById(R.id.rb_message);
mRbMe = findViewById(R.id.rb_me);
mTvMain=findViewById(R.id.tv_main);
initView();
initData();
}
private void initData() {
homeFragment.sendMessage(new IHomeCallBack() {
@Override
public void getMessageFromHomeFragment(String home) {
mTvMain.setText(home);
}
});
}
private void initView() {
mSupportFragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//设置默认选中首页
mRg.check(R.id.rb_home);
homeFragment = new HomeFragment();
//创建Bundle对象,并存储数据
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("home","Home");
homeFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(homeFragment);
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, true);
mRg.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
switch (checkedId) {
case R.id.rb_home: //首页
hideOthersFragment(homeFragment, false);
break;
case R.id.rb_community: //发现
if (communityFragment == null) {
communityFragment = new CommunityFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("community","Community");
communityFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(communityFragment);
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(communityFragment, false);
}
communityFragment.sendMessage(new ICommuntyCallBack() {
@Override
public void getMessageFromCommunty(String community) {
mTvMain.setText(community);
}
});
break;
case R.id.rb_message: //信息
if (messageFragment == null) {
messageFragment = new MessageFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("message","Message");
messageFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(messageFragment);
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(messageFragment, false);
}
messageFragment.sendMessage(new IMessageCallBack() {
@Override
public void getMessageFromMessage(String message) {
mTvMain.setText(message);
}
});
break;
case R.id.rb_me: //我的
if (meFragment == null) {
meFragment = new MeFragment();
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("me","Me");
meFragment.setArguments(bundle);
mFragments.add(meFragment);
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, true);
} else {
hideOthersFragment(meFragment, false);
}
meFragment.sendMessage(new IMeCallBack() {
@Override
public void getMessageFromMe(String me) {
mTvMain.setText(me);
}
});
break;
}
}
});
}
private void hideOthersFragment(Fragment showFragment, boolean add) {
mTransaction = mSupportFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
if (add) {
mTransaction.add(R.id.frameLayout, showFragment);
}
for (Fragment fragment : mFragments) {
if (showFragment.equals(fragment)) {
mTransaction.show(fragment);
} else {
mTransaction.hide(fragment);
}
}
mTransaction.commit();
}
}实现效果图:

接口的回调还可以这么写:
public class MessageFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView mTvMessage;
MessageListener mListener;
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
//创建接口的子类对象
//获取当前Fragment所属的Activity,因为Activity实现了MessageListener接口,所以是MessageListener的子类
mListener= (MessageListener)context;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container,
@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_message, null);
mTvMessage = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_message);
mListener.sendMessage("来自:MessageFragment的消息");
return view;
}
public interface MessageListener {
void sendMessage(String message);
}
}然后让Fragment依附的activity实现这个接口,然后重写sendMessage()方法,这样我们就可以把数据传过来了。
这种方案应该是既能达到Fragment复用,又能达到很好的可维护性,并且性能也是杠杠的,所以说推荐使用。
至此,Fragment与Activity通信的方式就完成了。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)