Mac os下快速从终端进入Finder & 从Finder进入终端
一、从终端进入Finder Open .# wangji @ wangjideMBP in ~/Documents/study/test_git2 on git:master o [19:09:07]$ lsa.txt# wangji @ wangjideMBP in ~/Documents/study/test_git2 on git:master o [19:09:11]$ ope...
一键AI生成摘要,助你高效阅读
问答
·
一、从终端进入Finder Open .
# wangji @ wangjideMBP in ~/Documents/study/test_git2 on git:master o [19:09:07]
$ ls
a.txt
# wangji @ wangjideMBP in ~/Documents/study/test_git2 on git:master o [19:09:11]
$ open .
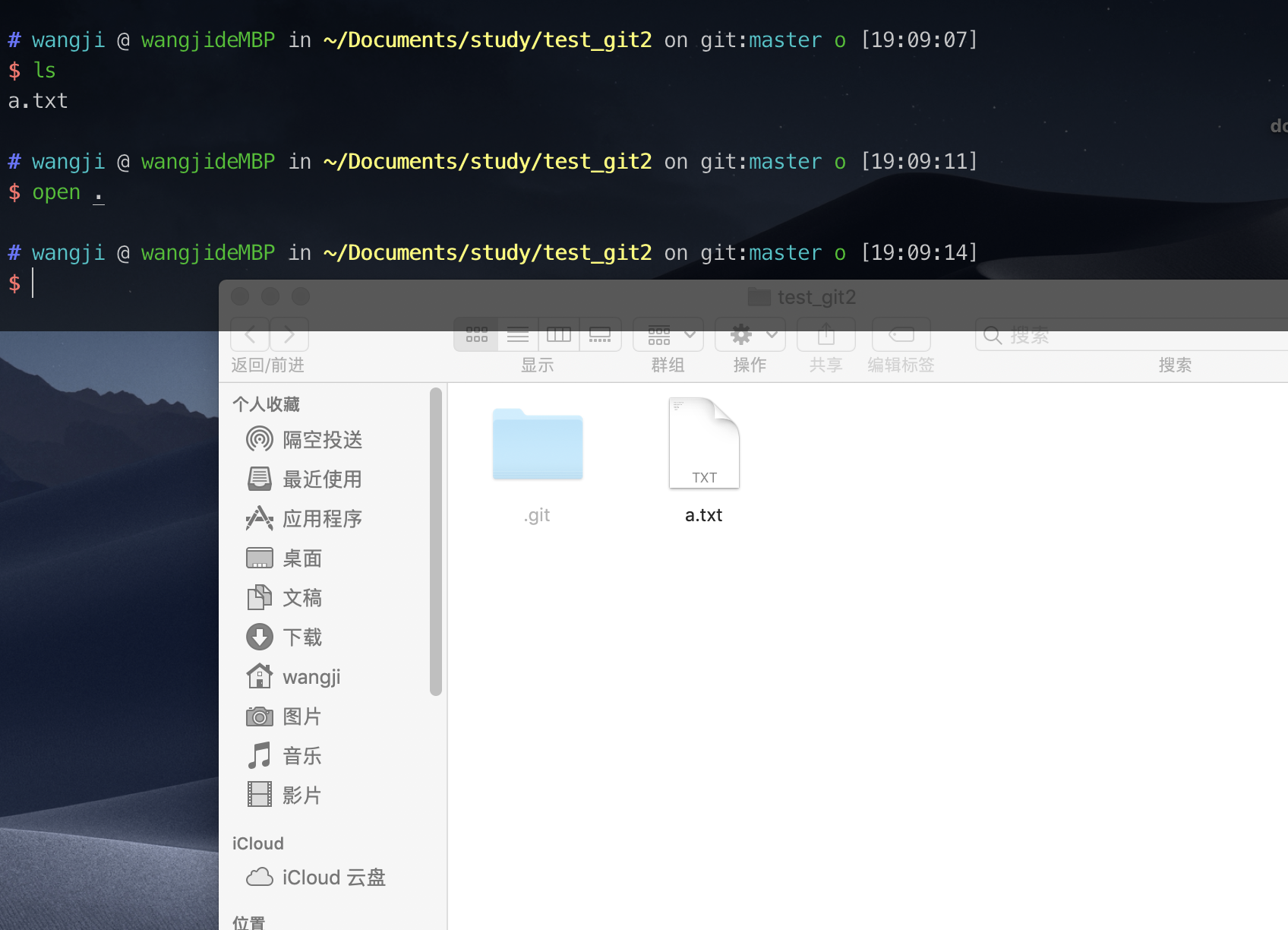
- open 超级好用
打开chrome 并打开网址,知道这两个命令就行啦!
$ open -a Google\ Chrome http://fanyi.baidu.com
OPEN(1) BSD General Commands Manual OPEN(1)
NAME
open -- open files and directories
SYNOPSIS
open [-e] [-t] [-f] [-F] [-W] [-R] [-n] [-g] [-j] [-h] [-s sdk] [-b bundle_identifier] [-a application] file ... [--args arg1 ...]
DESCRIPTION
The open command opens a file (or a directory or URL), just as if you had double-clicked the file's icon. If no application name is specified, the
default application as determined via LaunchServices is used to open the specified files.
If the file is in the form of a URL, the file will be opened as a URL.
You can specify one or more file names (or pathnames), which are interpreted relative to the shell or Terminal window's current working directory. For
example, the following command would open all Word files in the current working directory:
open *.doc
Opened applications inherit environment variables just as if you had launched the application directly through its full path. This behavior was also
present in Tiger.
The options are as follows:
-a application
Specifies the application to use for opening the file
-b bundle_indentifier
Specifies the bundle identifier for the application to use when opening the file
-e Causes the file to be opened with /Applications/TextEdit
-t Causes the file to be opened with the default text editor, as determined via LaunchServices
-f Reads input from standard input and opens the results in the default text editor. End input by sending EOF character (type Control-D). Also useful
for piping output to open and having it open in the default text editor.
-F Opens the application "fresh," that is, without restoring windows. Saved persistent state is lost, except for Untitled documents.
-W Causes open to wait until the applications it opens (or that were already open) have exited. Use with the -n flag to allow open to function as an
appropriate app for the $EDITOR environment variable.
-R Reveals the file(s) in the Finder instead of opening them.
-n Open a new instance of the application(s) even if one is already running.
-g Do not bring the application to the foreground.
-j Launches the app hidden.
-h Searches header locations for a header whose name matches the given string and then opens it. Pass a full header name (such as NSView.h) for
increased performance.
-s For -h, partial or full SDK name to use; if supplied, only SDKs whose names contain the argument value are searched. Otherwise the highest versioned
SDK in each platform is used.
--args
All remaining arguments are passed to the opened application in the argv parameter to main(). These arguments are not opened or interpreted by the
open tool.
EXAMPLES
"open '/Volumes/Macintosh HD/foo.txt'" opens the document in the default application for its type (as determined by LaunchServices).
"open '/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Applications/'" opens that directory in the Finder.
"open -a /Applications/TextEdit.app '/Volumes/Macintosh HD/foo.txt'" opens the document in the application specified (in this case, TextEdit).
"open -b com.apple.TextEdit '/Volumes/Macintosh HD/foo.txt'" opens the document in the application specified (in this case, TextEdit).
"open -e '/Volumes/Macintosh HD/foo.txt'" opens the document in TextEdit.
"ls | open -f" writes the output of the 'ls' command to a file in /tmp and opens the file in the default text editor (as determined by LaunchServices).
"open http://www.apple.com/" opens the URL in the default browser.
"open 'file://localhost/Volumes/Macintosh HD/foo.txt'" opens the document in the default application for its type (as determined by LaunchServices).
"open 'file://localhost/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Applications/'" opens that directory in the Finder.
"open -h NSView" lists headers whose names contain NSView and allows you to choose which ones to open.
"open -h NSView.h" immediately opens NSView.h.
"open -h NSView -s OSX10.12" lists headers whose names contain NSView in the MacOSX 10.12 SDK and allows you to choose which ones to open.
HISTORY
First appeared in NextStep.
macOS April 14, 2017 macOS
(END)
二、从Finder进入终端
方法1、在finder中拖动文件夹到终端
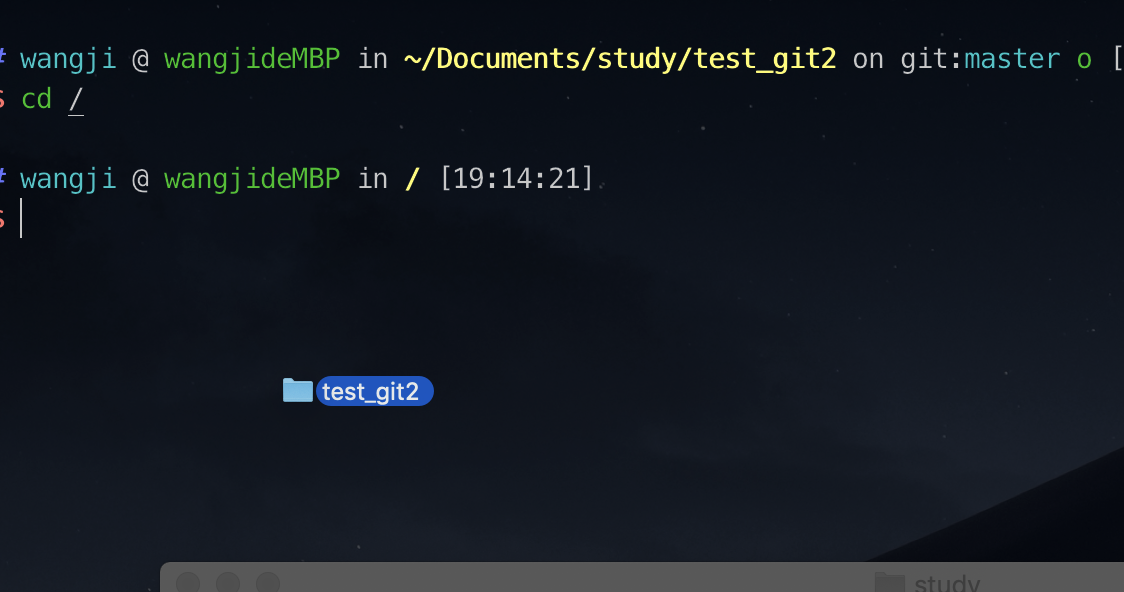
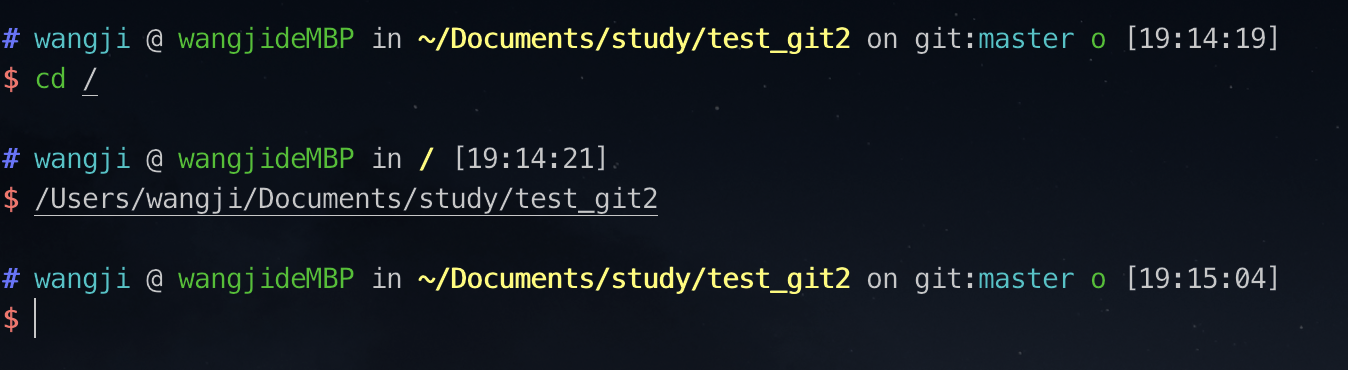
方法2、finder中服务偏好设置
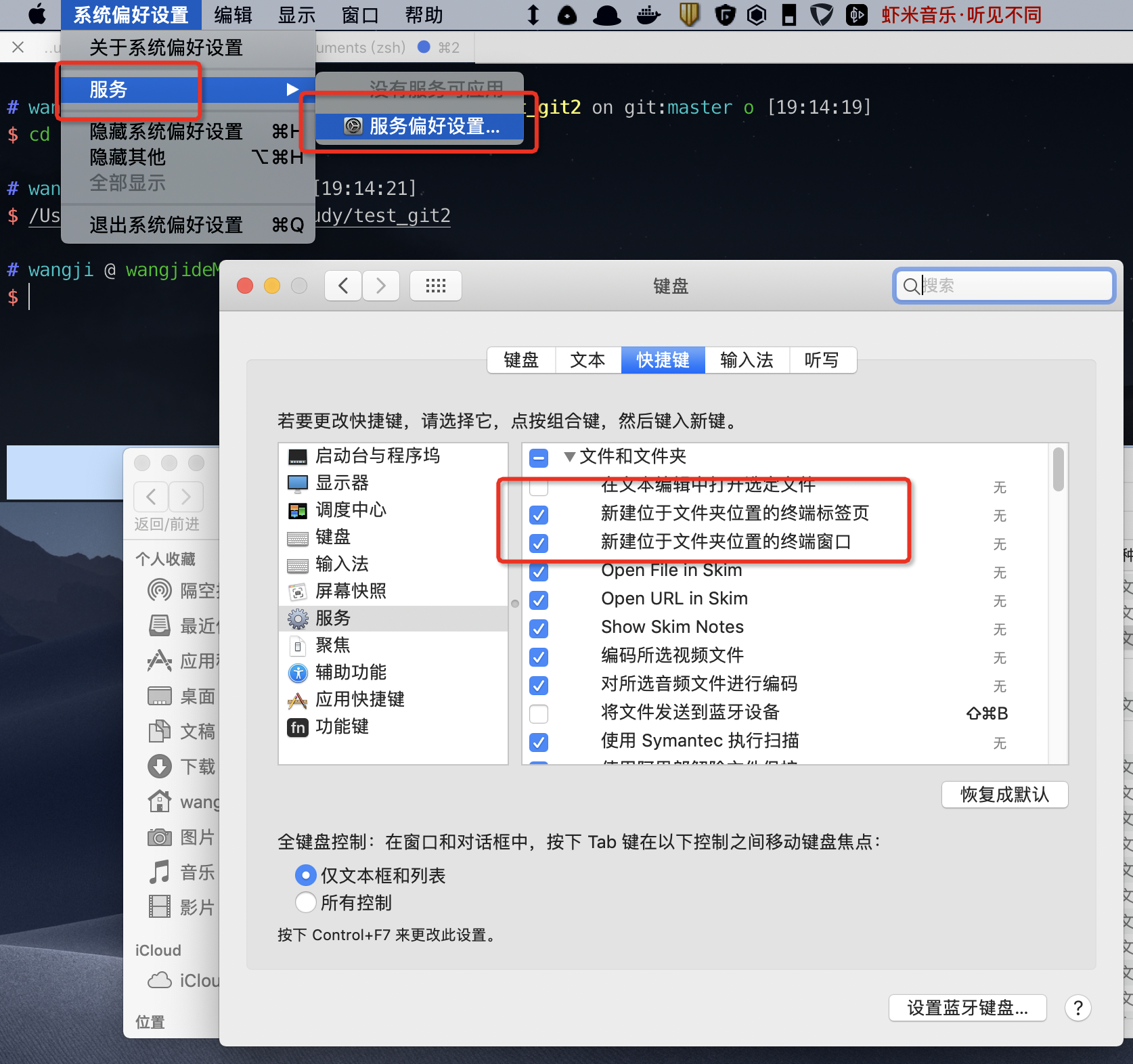
在finder中点击文件夹右键打开服务:就可以选择啦
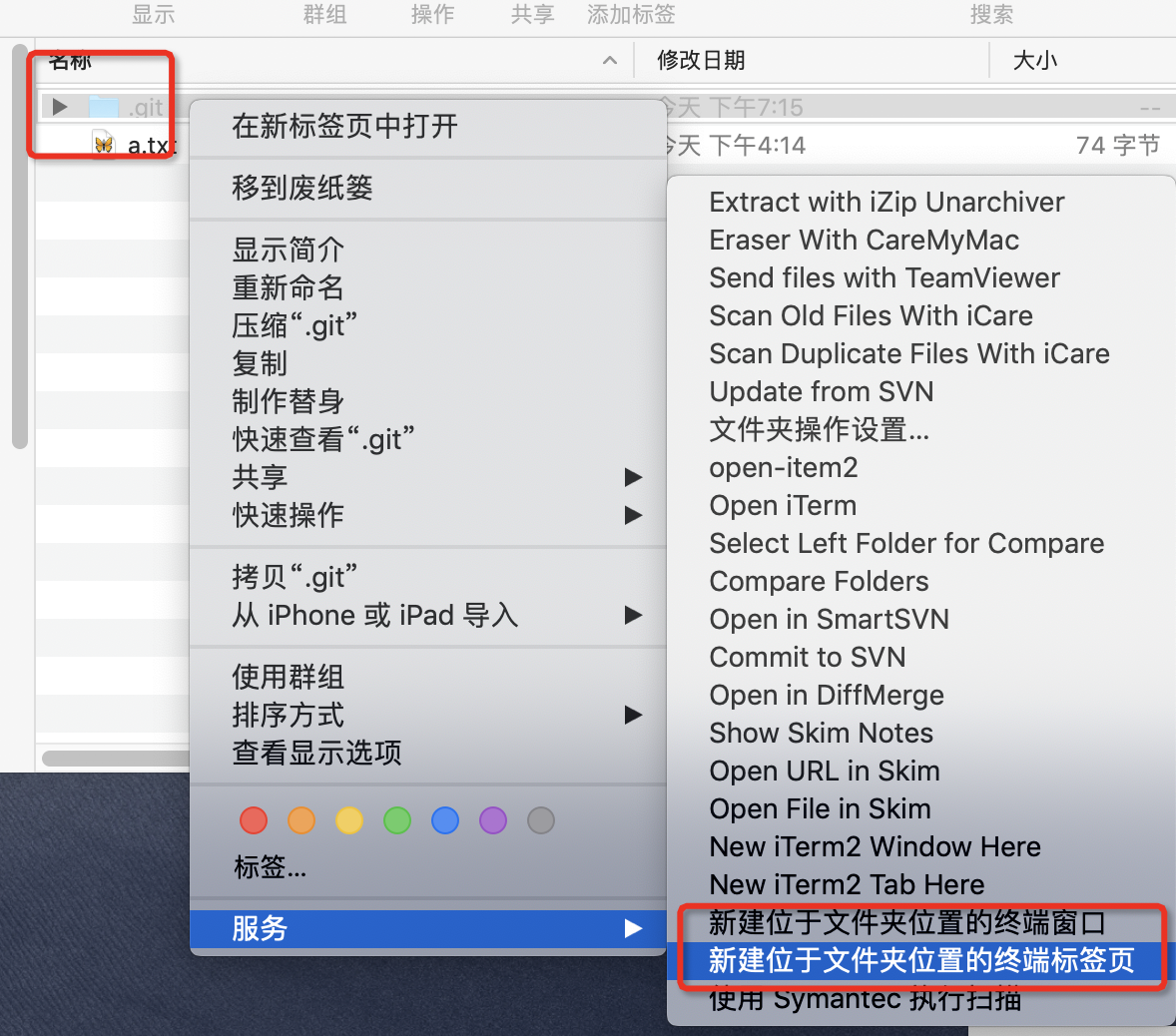
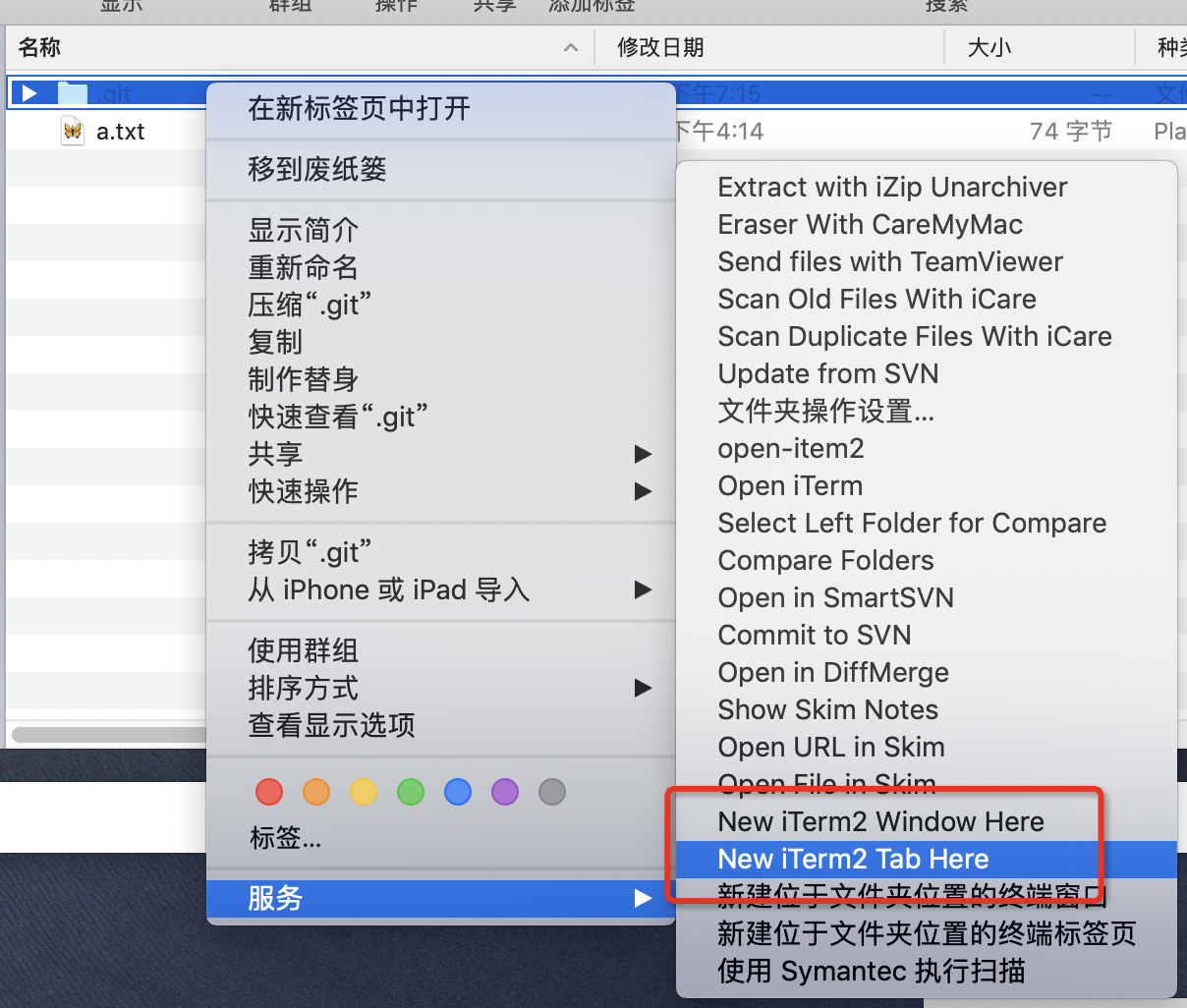
方法3、ITerm2终端自带(推荐)和上面的类似,不过这个可以针对文件,不止文件夹
方法4、iterm2-finder-tools 的 workflow
# wangji @ wangjideMBP in ~/Documents/study [19:27:18] C:129
$ git clone https://github.com/peterldowns/iterm2-finder-tools.git find-tools
Cloning into 'find-tools'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 206, done.
remote: Total 206 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 206
Receiving objects: 100% (206/206), 2.62 MiB | 921.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (87/87), done.
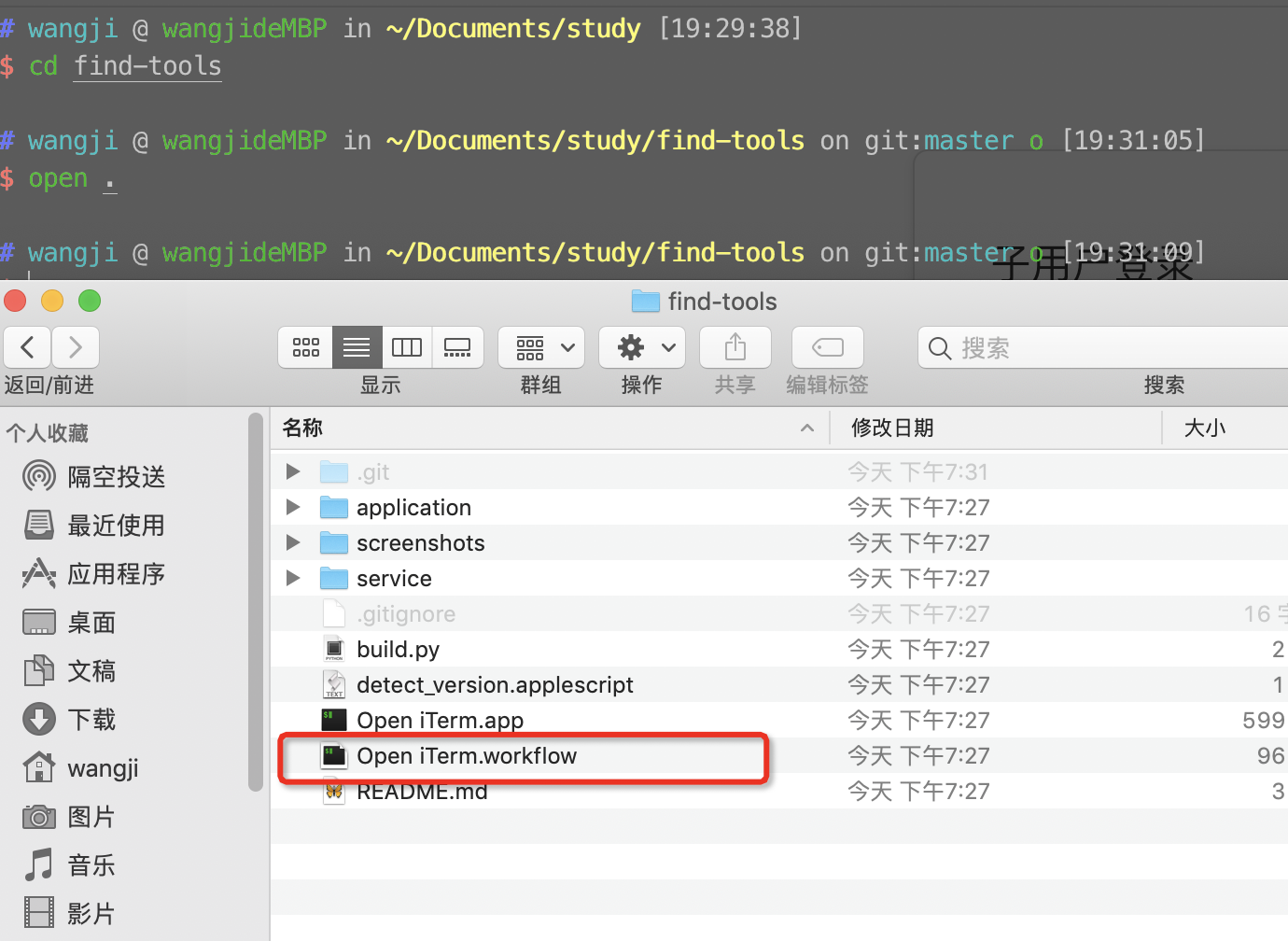
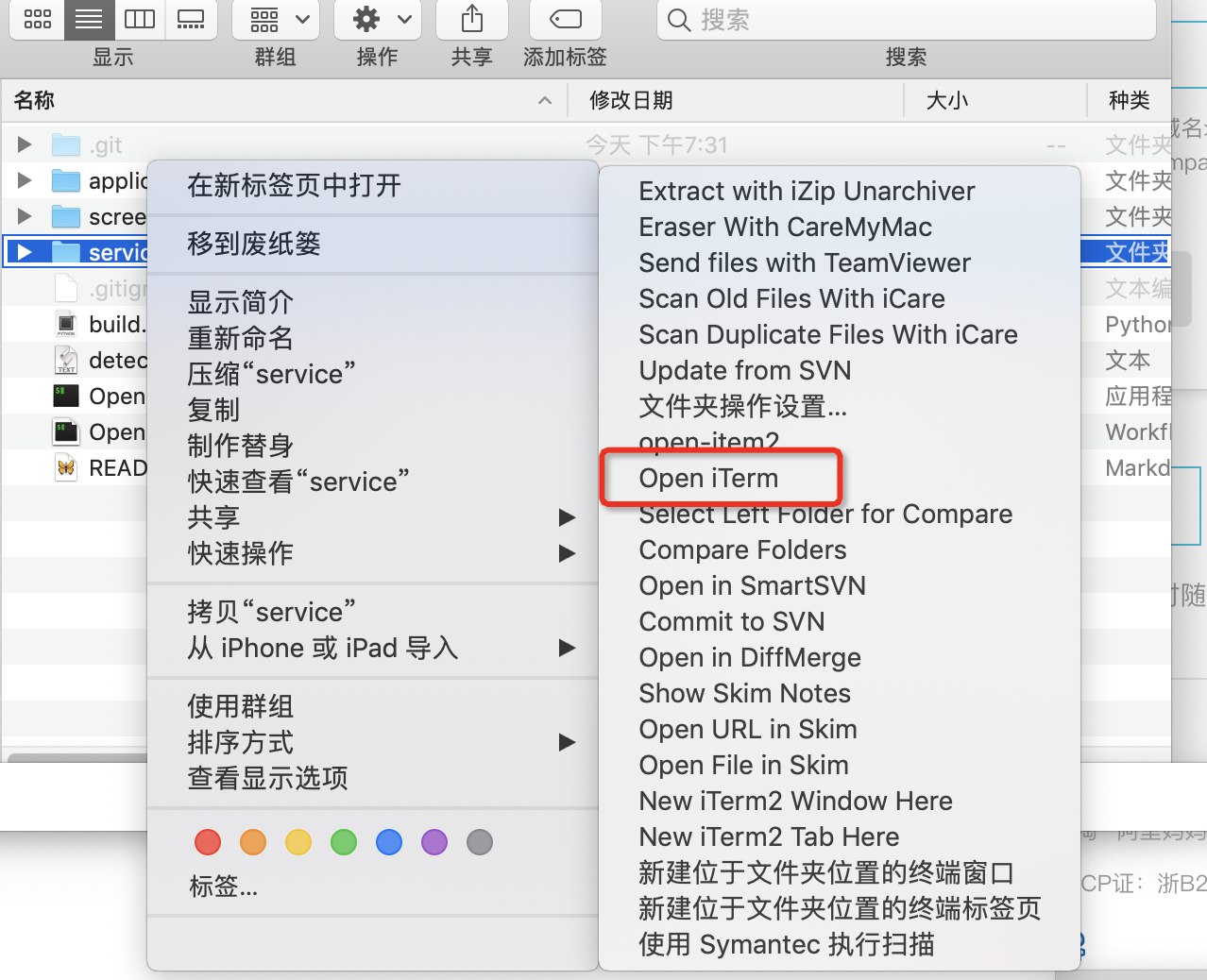
双击 Open iTerm.workflow 并且 单击 安装
这个的效果和上面的一样的,只是针对文件夹有效!
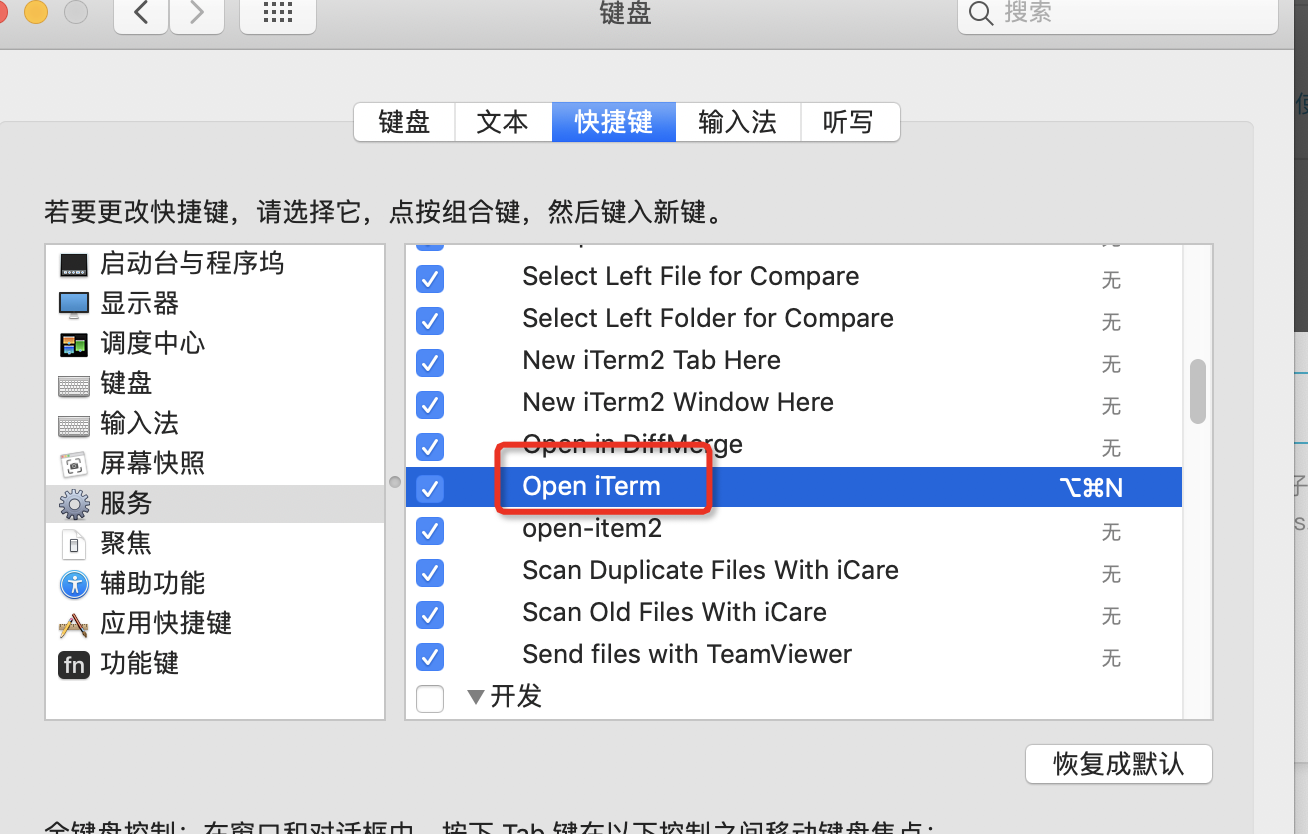
PS.若未找到Open iTerm ,请在 系统设置->键盘->快捷键->服务->文件和文件夹 中查看 Open iTerm 一栏是否打钩。这里还可以设置快捷键哦!上面的几个方法都是一样的这种操作!
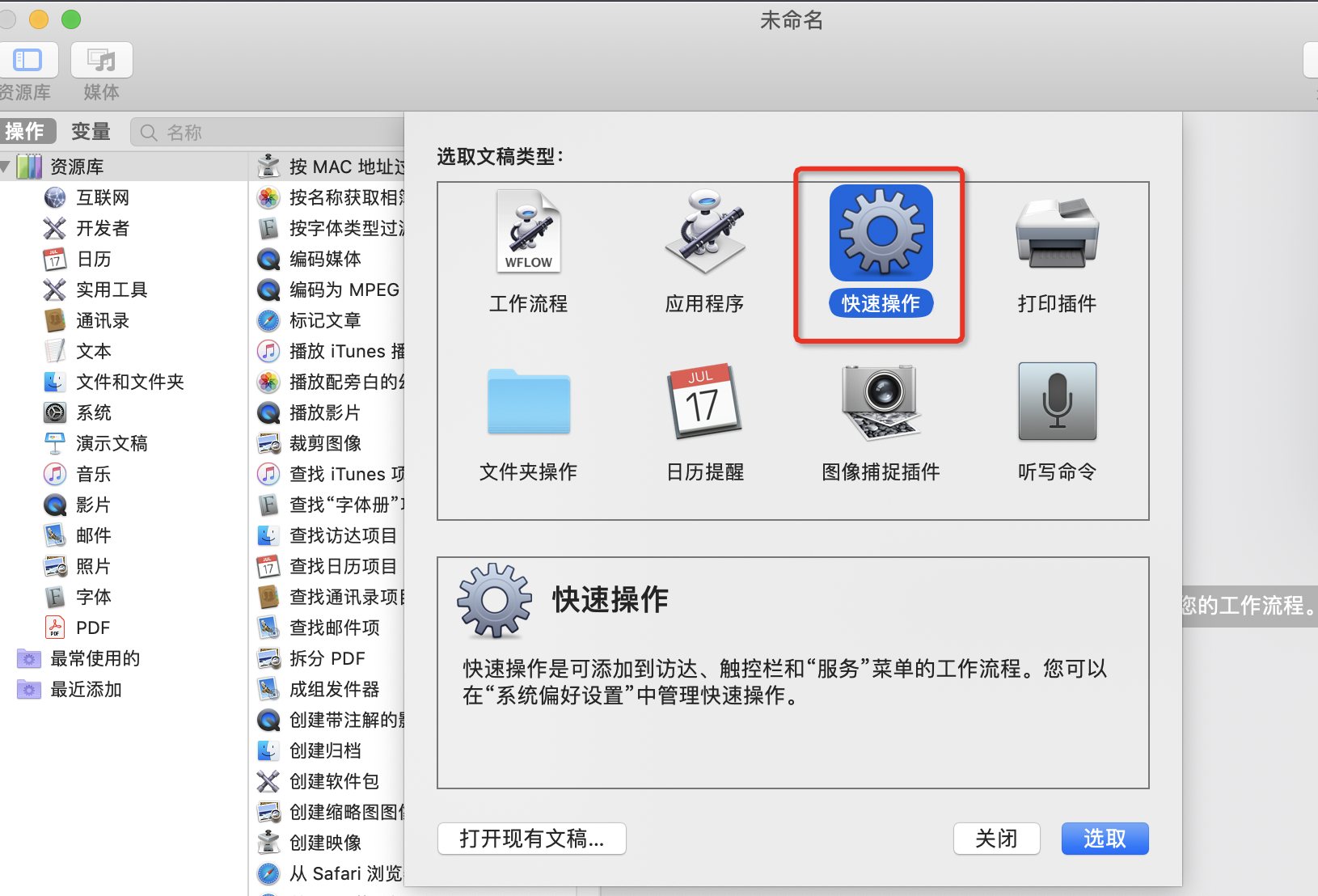
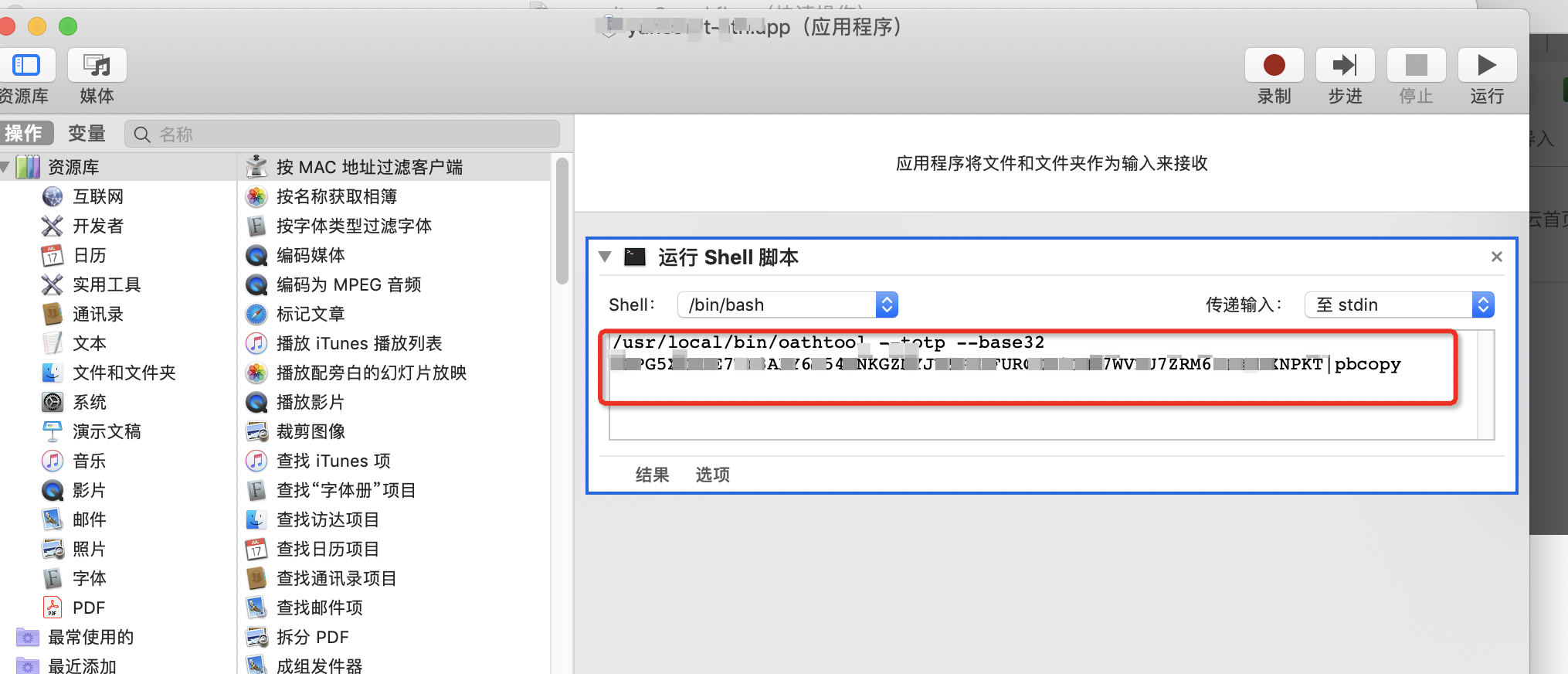
方法5、Mac automator 自定义workflow处理
- 玩转Mac:[1]右键在终端快速打开文件夹路径
- 玩转Automator – 增强Finder功能
- automator来解决mac terminal终端快速连接链接
反正这个功能很强大哈哈,可以自定义一些功能的处理
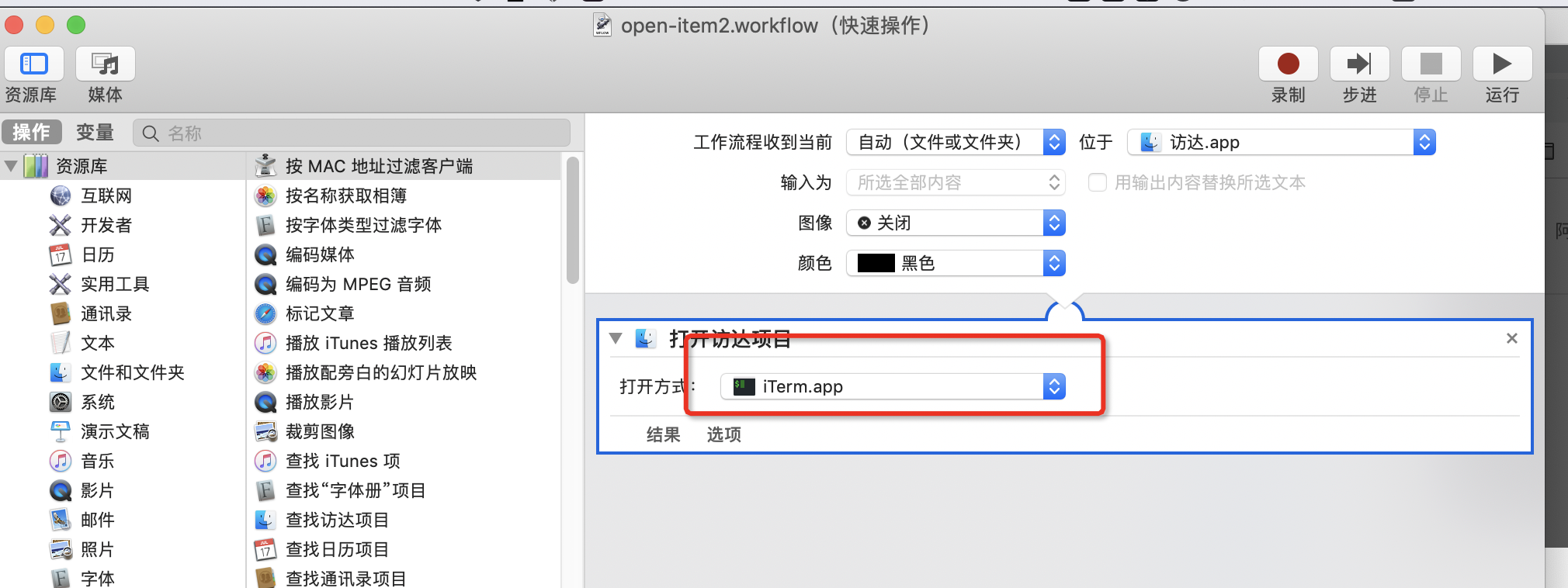
然后就可以和第一个一样的操作啦!
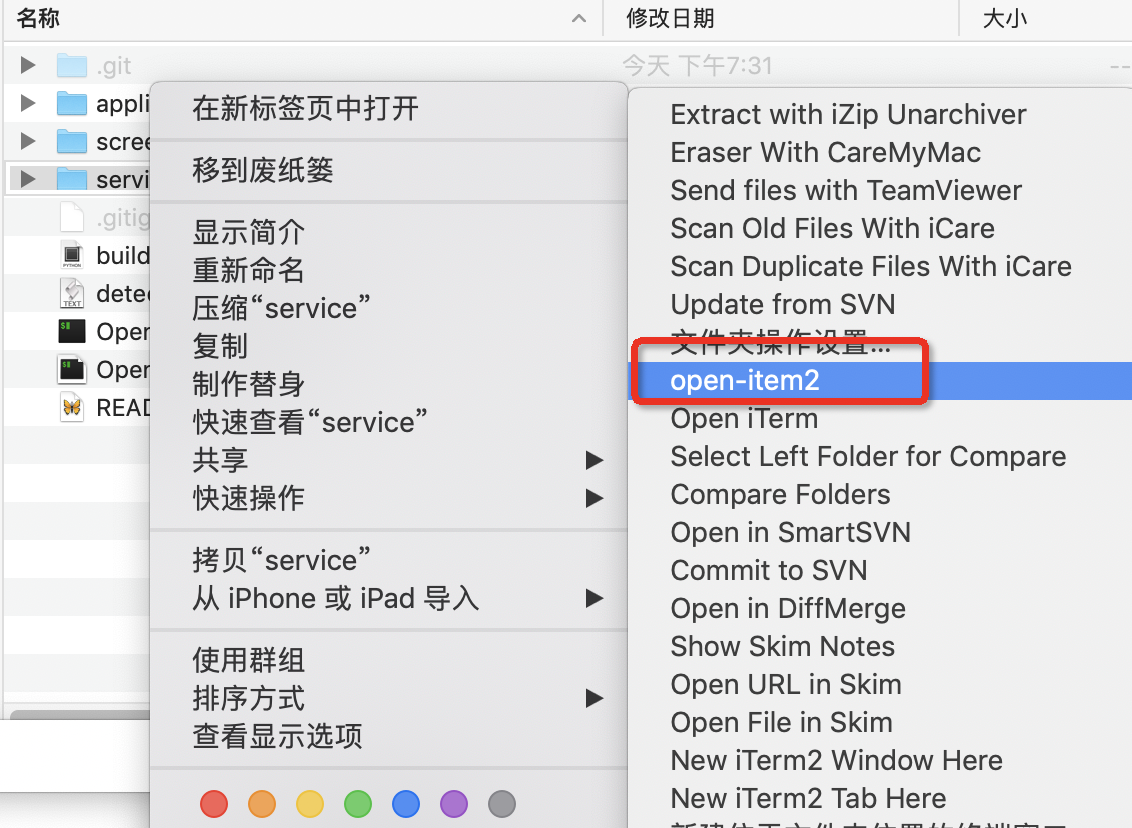
之前定义过一个应用程序,将脚本生成的数字信息复制到剪切板中哈哈
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容










所有评论(0)