vueJs源码解读0-1
vue源码解读-1在github上下载到源码的后在src的目录下也即是该所有分块的源文件的地址所在的地方,使用webstrom在file–>Settings–>languages&Frameworks中选择javascript使用ECMAScript61.index.jsimport Vue from ‘./instance/vue’import installGlobal
vue源码解读-1
在github上下载到源码的后在src的目录下也即是该所有分块的源文件的地址所在的地方,使用webstrom在file–>Settings–>languages&Frameworks中选择javascript使用ECMAScript6
1. index.js
import Vue from ‘./instance/vue’
import installGlobalAPI from ‘./global-api’
import { inBrowser, devtools } from ‘./util/index’
import config from ‘./config’
import export
使用了四个import,导入了所需要的模块。ES6的模块通过export命令显式的指定输出的代码,输入的时候也采用静态命令的形式。模块之间的依赖关系在编译的时候就确定了
- 一个模块也即是一个独立的文件
- 使用export规定模块对外的接口
- 使用import输入其他模块提供的功能
- export可以输出变量函数或类;export输出语句为动态绑定的(如下面的例子);基本写法在所定义的变量函数或类的前面加入export(如:export function a(){ …….}; export var s=’RankBill’) 或者在末尾使用export{a,s ,..}统一的输出;
export var foo='test'
setTimeout(()=>foo='TEST',500)//test TEST
5.import表示导入输出的变量函数或类。import {……} from ‘dst’: dst表示从哪个模块中导入也即是文件名 可以写为 ‘./dst.js’或 ‘./dst’(./表示当前目录下); 整体加载模块的写法为:import * as rank from ‘./dst’ 表示加载dst中所有输出的 整体重命名为rank 或使用module:module rank from ‘./dst’
使用import的时候,变量名或函数名称一定要与export中的对应,用户则必须了解输出的那些属性或方法
6.export default可以指定模块的默认输出(默认的也即是只有一个)使用export default …..相对应的是 import everyName from ”此时不需要使用{ }; export default functionName 会以匿名函数的形式导出,意味着import可以用任何名称 (export default为匿名函数的时候显然符合规定 )
export default function a(){.....}
//function a(){...} export default a
import a from '**'
export function a(){...}
import {a} from '***'
export default function(){.....} //匿名
import name from '....'
ES6输出的是值的只读的引用,区别于commonJs输出的值的拷贝;commonJs是加载时执行,es6只生成一个指向该模块的动态引用
—> import Vue from ‘./instance/vue’(instance/vue.js)
此时进入instance/下的vue 可以看到 export default Vue
‘instance/vue’
function Vue (options) {
this._init(options)
}
1.这个Vue是一个正规正矩的函数的声明的写法(此时涉及函数声明的提升,也即是在代码执行前会先读取函数的声明 ;同理变量的提升)
function fa() {
console.info(“whahaha”)
}
(function () {
if (false) {
function fa() {
console.info(“shuangwaiwai”)
}
}
fa();
}()); //shuangwaiwai
函数的声明会在当前的作用域内提升,相当于预先在该作用域顶部声明了该函数变量的提升:
var tmp=”Beijing”
fucntion rk(){
console.info(tmp)
if(){
var tmp=”yeh”
}
}
rk()// undefined
此时相当于 在rk(rk.name)会在顶部声明var tmp;
2.可以看出this指向调用Vue的作用上下文
在进入其他模块前我们翻译下这段注释:
/**
* The exposed Vue constructor.
*
* API conventions: (API 惯例)
* - public API methods/properties are prefixed with$
* (公共API或属性前加 ‘$’)
* - internal methods/properties are prefixed with_
* (内部调用方法或属性前加‘_’)
* - non-prefixed properties are assumed to be proxied user
* data.(没有任何标示前缀的属性,看作为被代理的用户数据)
*
* @constructor
* @param {Object} [options]
* @public
*/
部分注释不明白的地方在后续会逐步的明朗开来,接下来进入的仍然是instance/vue.js中的其他的部分
// install internals
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
miscMixin(Vue)// install instance APIs
dataAPI(Vue)
domAPI(Vue)
eventsAPI(Vue)
lifecycleAPI(Vue)
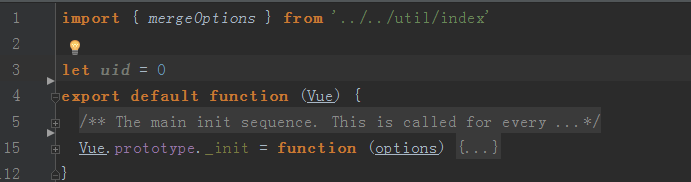
—>initMixin(Vue) (instance/internal/init.js)
1.显然使用到了匿名函数的export default参数也即是Vue
2.导入了util/index中的mergeOptions函数(下文中会有介绍)
3.let的使用
let
let的使用最为块级作用域的福音,ES6引入了let用来声明变量,其作用范围只在let所在的代码块中有效;不存在变量的提升在块级的范围内使用到了let命令 则其声明的变量绑定在该区域之内,任何在未声明之前进行的赋值都会报错
任何在let变量之前,改变量均不可用,语法上暂时性死区(TDZ)z{
tmp=”df”
let tmp
} //error
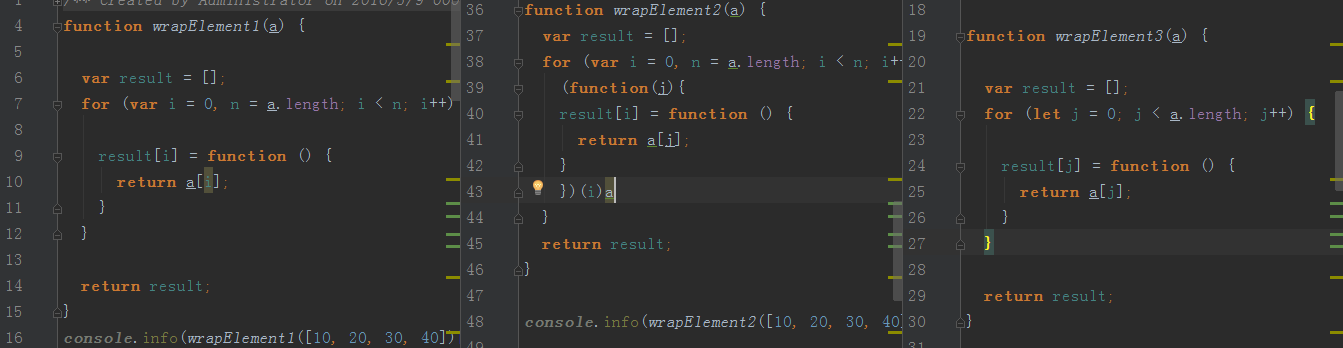
一个例子说明let用法的好处
一种为错误写法后两种为IIFE与用let的写法
对当前出入的Vue添加原型方法_init,c传入参数为options
options = options || {} //options为空则为{} 否则为options
this.$el = null
this.$parent = options.parent
this.$root = this.$parent? this.$parent.$root : this
this.$children = []
this.$refs = {} // child vm references
this.$els = {} // element references
this._watchers = [] // all watchers as an array
this._directives = [] // all directives
$的表示public-api ; _ 开头的表示internal-api,初始化后此时的this也即是指向Vue,为初始化为undefined;options也即是在初始化的时候进行new Vue({…}) 中,下面以具体的实例子讲解大家会更加明白些
在控制台中输出options 与this
随后在Vue上挂在了很多的属性
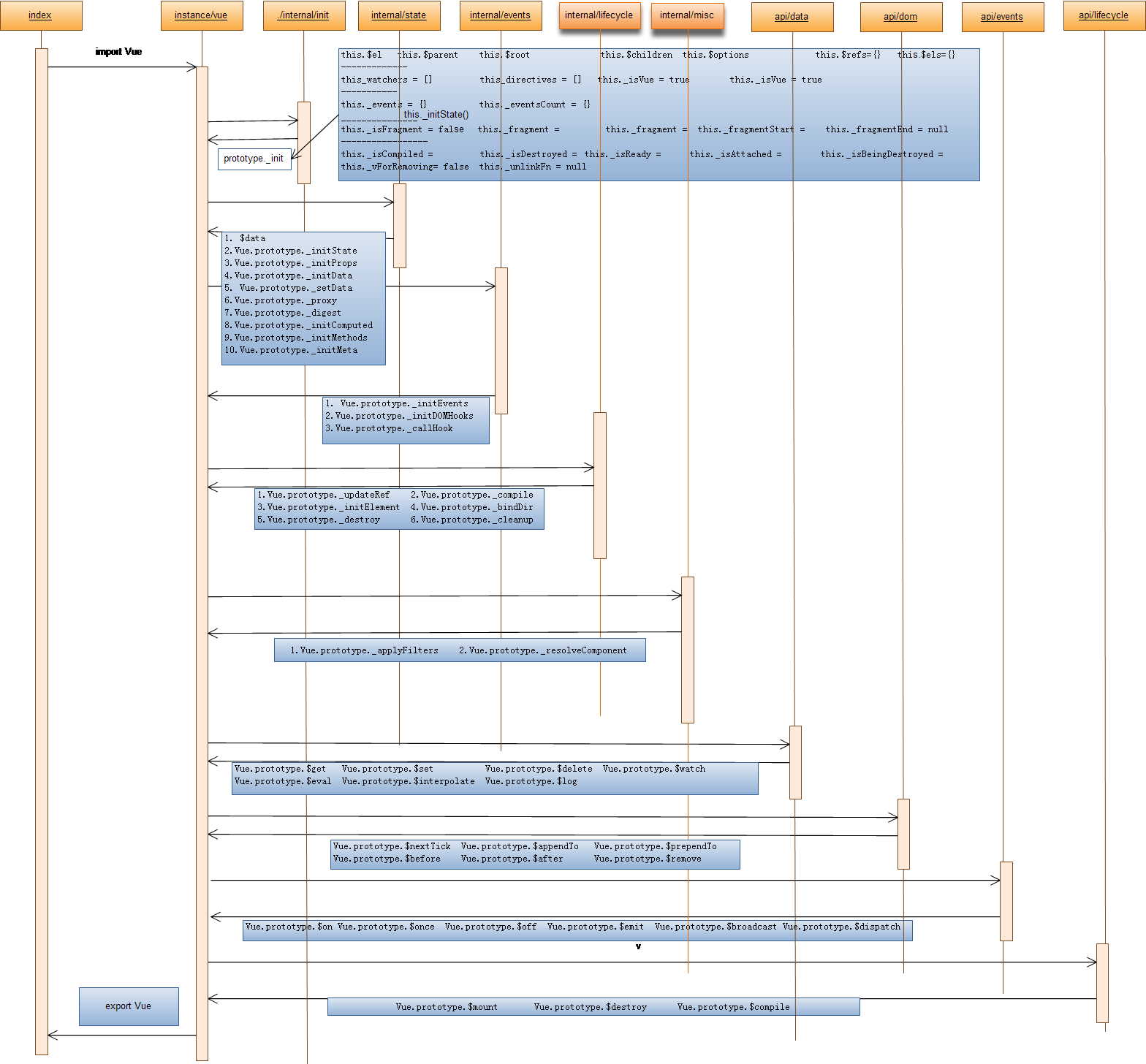
八大实例属性
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| this.$el | |
| this.$parent | |
| this.$root | |
| this.$children | |
| this.$options | |
| this.$refs={} | child vm references |
| this.$els={} | element references |
| 与后面的$state共同构成了八大实例属性 |
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| this._watchers = [] | child vm references |
| this._directives = [] | all directives |
| this._isVue = true | a flag to avoid this being observed |
| this._isVue = true | a flag to avoid this being observed |
event
| 属性名 | – |
|---|---|
| this._events = {} | registered callbacks |
| this._eventsCount = {} | for $broadcast optimization |
fragment
| 属性名 | – |
|---|---|
| this._isFragment = false | registered callbacks |
| this._fragment = | @type {DocumentFragment} |
| this._fragment = | {DocumentFragment} |
| this._fragmentStart = | @type {Text|Comment} |
| this._fragmentEnd = null | @type {Text|Comment} |
lifecycle state
| 属性名 | – |
|---|---|
| this._isCompiled = | |
| this._isDestroyed = | |
| this._isReady = | |
| this._isAttached = | |
| this._isBeingDestroyed = | |
| this._vForRemoving = false | |
| this._unlinkFn = null |
紧接着为Vue install internals与 install instance APIs
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
miscMixin(Vue)dataAPI(Vue)
domAPI(Vue)
eventsAPI(Vue)
lifecycleAPI(Vue)
(下表_为internal ,$为public)
| initMixin(Vue) | Vue.prototype._init |
| stateMixin(Vue) | 1. $data |
| 2.Vue.prototype._initState | |
| 3.Vue.prototype._initProps | |
| 4.Vue.prototype._initData | |
| 5. Vue.prototype._setData | |
| 6.Vue.prototype._proxy | |
| 7.Vue.prototype._digest | |
| 8.Vue.prototype._initComputed | |
| 9.Vue.prototype._initMethods | |
| 10.Vue.prototype._initMeta | |
| eventsMin(Vue) | 1. Vue.prototype._initEvents |
| 2.Vue.prototype._initDOMHooks | |
| 3.Vue.prototype._callHook | |
| lifecycleMixin(Vue) | 1.Vue.prototype._updateRef |
| 2.Vue.prototype._compile | |
| 3.Vue.prototype._initElement | |
| 4.Vue.prototype._bindDir | |
| 5.Vue.prototype._destroy | |
| 6.Vue.prototype._cleanup | |
| miscMixin(Vue) | 1.Vue.prototype._applyFilters |
| 2.Vue.prototype._resolveComponent |
instance api:
7个数据类实例api
| – | |
|---|---|
| dataAPI(Vue) | Vue.prototype.$get |
| 7个数据类api | Vue.prototype.$set |
| Vue.prototype.$delete | |
| Vue.prototype.$watch | |
| Vue.prototype.$eval | |
| Vue.prototype.$interpolate | |
| Vue.prototype.$log | |
6个DOM操作api
| – | |
|---|---|
| domAPI(Vue) | Vue.prototype.$nextTick |
| DOM操作 | Vue.prototype.$appendTo |
| Vue.prototype.$prependTo | |
| Vue.prototype.$before | |
| Vue.prototype.$after | |
| Vue.prototype.$remove | |
6个事件类操作的api
| – | |
|---|---|
| eventsAPI(Vue) | Vue.prototype.$on |
| 事件类 | Vue.prototype.$once |
| Vue.prototype.$off | |
| Vue.prototype.$emit | |
| Vue.prototype.$broadcast | |
| Vue.prototype.$dispatch | |
3个生命周期类api
| – | |
|---|---|
| lifecycleAPI(vue) | Vue.prototype.$mount |
| 生命周期类 | Vue.prototype.$destroy |
| Vue.prototype.$compile |
我们在通过类似的图来准确的说明从index.js到现在的情况
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容










所有评论(0)