【Spring MVC】Spring MVC启动过程源码分析
Spring MVC启动时,Spring容器和Spring MVC组件的启动过程源码分析
一、Servlet开场
servlet现在已经算是很基础的内容了,如果还没有看过、分析过servlet的源码,可能就要out了。
servlet的生命周期通过三个方法init、service、destory来构建,这些方法不用你调用,servlet容器会自动调用。servlet接口里面定义了这些规范,但是在接口实现的抽象类——无协议通用的GenericServelt——中有一些小改动,重载了一个不包含参数的init方法,并且建议你在开发自己的servlet的时候,重写这个不包含参数的方法,GenericServlet是Servlet接口的抽象子类,他并没有实现service方法,而是将这个抽象方法的实现放到子类中完成;再看下一层实现了HTTP协议的子类HttpServlet,他实现了这个public的service方法,但是还重载了一个protected的service方法。
到这里,Spring MVC启动过程中很多有意思的东西就可以渐渐浮出水面了,Spring MVC的启动,依靠DispatcherServelt,这货继承了HttpServlet。
1. 关于运行:如果根据jsp/servlet的开发规范来看,他应该重写protected service模板方法中给出的doXxx方法,否则调用抛出异常,但是用过Spring MVC之后,你发现并不是这样的,那么在HttpServlet中public service转调protected service的逻辑必然被重写了(没有必要重写public service的逻辑,public service将无协议转成了HTTP协议),至于为什么重写的是protected的service方法而不是public的,回顾重写的规则再看看Spring MVC servlet层级中的FramworkServlet源码,两相验证即可;
2. 关于启动:使用Spring MVC,只需要配置DispatcherServlet即可,可以不需要再配置Spring web包中的ContextLoaderListner(配置或不配置都可以,Spring MVC源码逻辑中有相关部分的体现,源码会在后续分析中给出),那么Spring容器在哪里启动呢?这一切必然和Spring MVC重写GenericServlet无参的init方法有关;
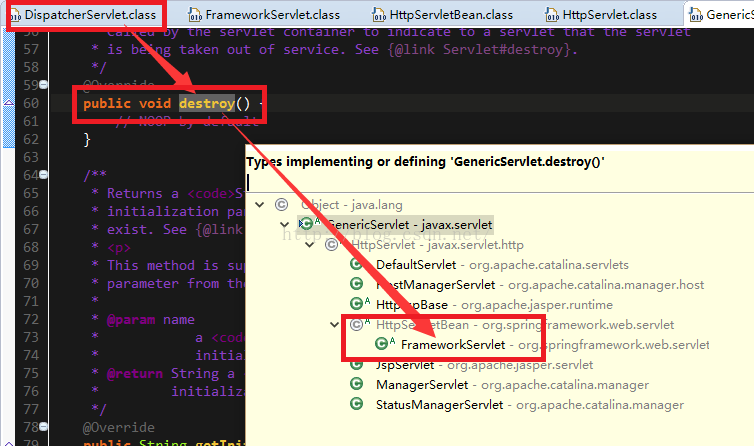
3. 关于销毁:通过Spring web包的ContextLoaderListener将Spring接入web,可以知道当容器销毁的时候需要将Spring的东西从servlet容器中清理掉,既然Spring MVC可以不配置ContextLoaderListner,那么必然要在destory方法中做些什么来释放资源等等;
DispatcherServlet终究还是一个servlet,因此以servlet的视角来审视他再合理不过了。
二、启动过程
1. 铺垫
a. 当servlet实例被创建以后,servlet容器会首先调用其init方法;
b. Spring MVC中servlet的继承体系:DispatcherServlet extends FramworkServlet extends HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet extends GenericServlet implements Servlet;
2. 启动过程简要分析
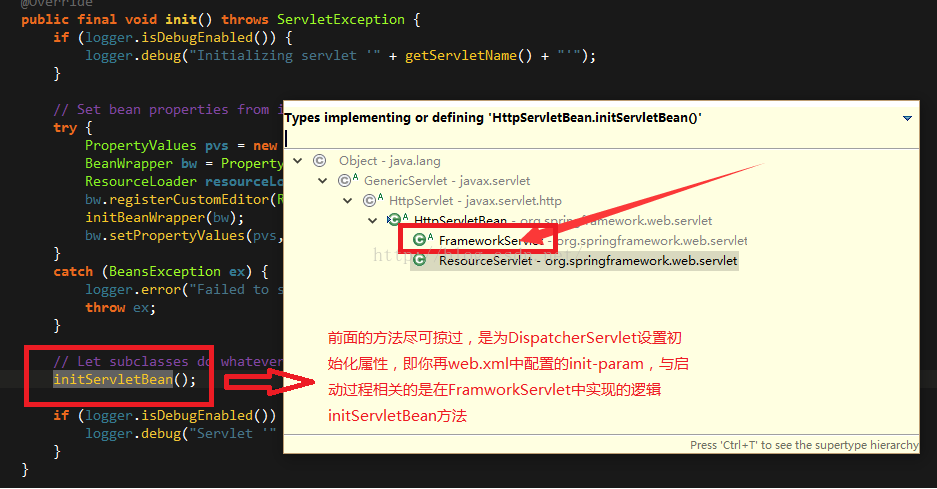
转到HttpServletBean中,查看init方法。
到FraworkServlet中才渐渐接近容器启动的核心方法,其实从servlet的取名就能看出,FramworkServlet类,包含了整个框架的启动逻辑。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 1-------------
// 如果配置了ContextLoaderListener,这里就能够拿到XmlWebApplicationContext的实例
// 也就表明,Spring容器随着ServletContext的启动已经启动过了
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
// 2-------------
// 对于属性webApplicationContext为不为null,我尝试追了一下源码,启动中这个属性应该是位null的
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 3-------------
// 从WebApplicationContextUtils工具类获取applicationcontext,和方法第一句代码一样
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
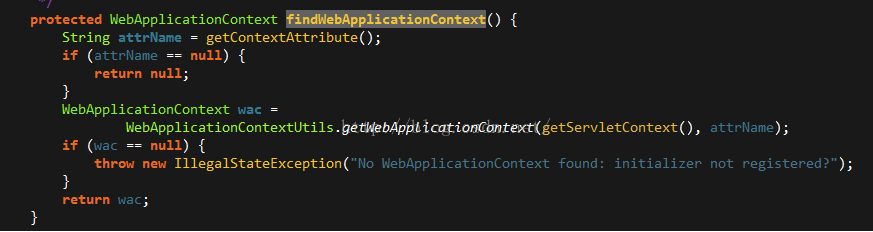
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 4-------------
// 上述找了一轮,没找到,那么就要开始创建了
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// 5-------------
// 到这里,才是Spring MVC的初始化过程,此时会跳转到DispatcherServlet来进行
// 处理器映射器、处理器适配器、试图解析器等等Spring MVC组件都是在这里完成初始化
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
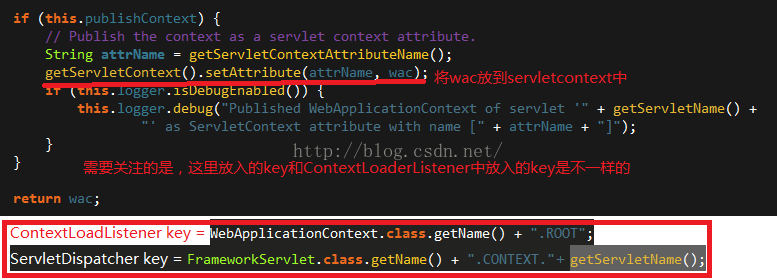
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}第一步,正如之前所说,Spring通过Spring-web包接入web,实际上是配置ContextLoaderListener来使得Spring容器随着web容器的启动而启动,而使用Spring MVC之后,是否还需要配置ContextLoaderListener呢?
对于Spring接入web的源码和原理分析,建议先看一看,也是一个很有意思的过程,参看点击打开链接和点击打开链接。
对于是否需要配置ContextLoaderListener,实际上配不配都可以,配置的话关联一下能用,不配置的话第四步会创建,两种方式实现的差异在于如果没有配置ContextLoadlistener,那么就在第四步中创建一个用;如果配置了ContextLoaderListener,那么就用ContextLoaderListener方式创建出来的ApplicationContext。当然,这是在一般情况下,也就是FrameworkServlet的属性this.webApplicationContext没有被注入的情况下。要追踪this.webApplication是否被注入,从对象初始化的角度来追查,在web.xml中配置的DispatcherServlet的创建,用的是默认的构造器(自己写个类继承一下然后配置可验证),也就是说在大多数场景下this.webApplicationContext不会在构造的时候被注入。实际上这一段的逻辑我自己也没有完全走通,代码做什么很简单,但是为什么这么做的逻辑没有看明白。通过以下列表来罗列可能出现的情形并追踪,可以知道配置与否对系统造成的影响(一般场景是第二和第四列的内容)。
| 是否配置ContextLoaderListener | 是否注入this.webApplictcationContext | 此时DispatcherServlet中ApplicationContext的情况 |
| 是,则rootContext有值 | 是,则wac有值 | rootContext成为wac的parent |
| 是,则rootContext有值 | 否,wac=null | rootContext成为wac的parent |
| 否,rootContext=null | 是,则wac有值 | 使用wac |
| 否,rootContext=null | 否,wac=null | 创建并使用wac |
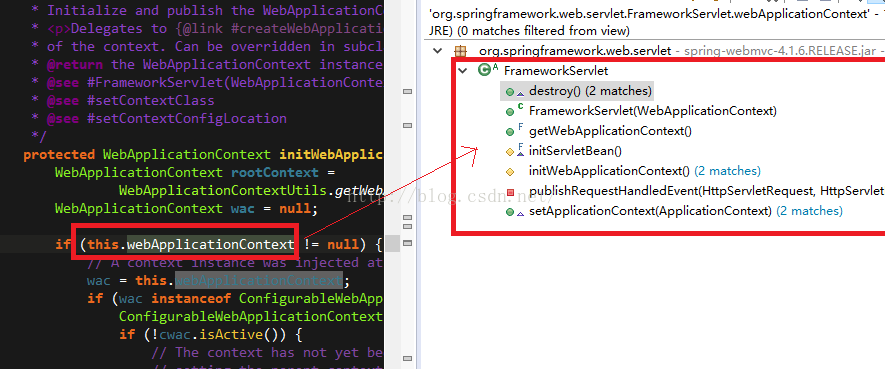
第二步,判断WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext是否为null,不为null,则会在做一些设置之后重启容器,wac.refresh()。实际上,通过配置DispatcherServlet来看,使用的是DispatcherServlet默认构造方法,是不需要传递参数,改构造功能方法中默认super(),调用FrameworkServlet的默认构造方法,改默认构造不会实例化这个属性,因此,这个属性还是为null。参看下图,整个FramworkServlet中使用到该属性的代码。
无论是否配置ContextLoaderListener,都不会通过set方法或构造函数注入该属性,因此第二步的逻辑似乎永远不会被执行,我也没想到相关的场景能触发这一段逻辑的执行,没想明白这一段逻辑的触发,有大神能解答,感激不敬。
关于这一段逻辑,和ContextLoaderListener中极度相似,简直就是copy and paste,只是我没能找到触发的场景,即this.webApplicationContext不为null。
第三步,这一部的逻辑和第一部一个造型,都是从WebApplicationContextUtils中获取wac,和第二步的关系承上启下。
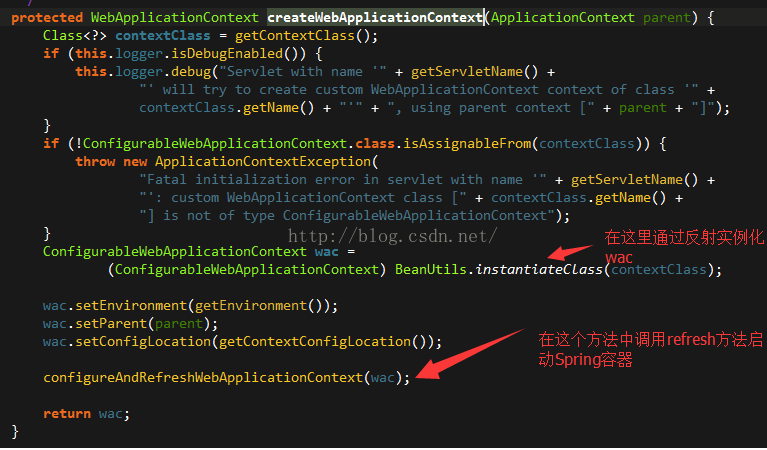
第四步,正常情况会走这一步的,这段代码的逻辑是这样的,wac=createWebApplicationContext(null);,FramworkServlet中对象初始化的时候,就完成了contextClass=XmlWebApplicationContext.class,除非你在web.xml中配置DispatcherServlet时另行平直了contextClass,否则默认会通过反射来实例化XmlWebApplicationContext实例,然后再现实的调用refresh方法启动Spring容器。
进入configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法,第一感觉就是粘贴复制,和ContextLoaderListener的代码一毛一样,最主要的是显式的调用了refresh来启动或刷新Spring容器。
第五步,这一步,才是所谓的Spring MVC的主要逻辑,跳转到DispatcherServlet中执行。
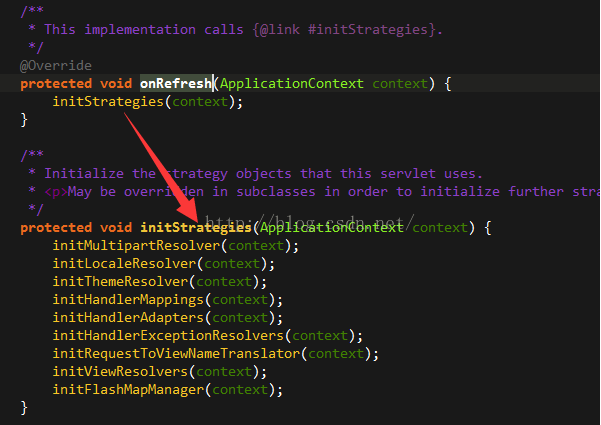
这里就是正式的初始化Spring MVC的各个组件,在此之前,DispatcherServlet有一个静态代码块,加载了Spring MVC中组件的初始化策略,也就是在initStrategies方法中,除了initMultipartResolver没有默认策略之外,其他八个都有默认的初始化策略,而对于initMultipartResolver,需要显示的配置对应的bean来支持文件上传。
Spring MVC默认的初始化策略,即DispatcherServlet.properties的内容。
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager到这里,基本已经能用了,但是还有最后一步,就是要将创建出来的XmlWebApplicationContext放置到全应用都可以访问的地方,即ServletContext,但是这里存放的key和ContextLoadListener中存放的key是不一样的,因此如果没有配置ContextLoaderListener方式启动Servlet容器,那么通过WebApplicationContextUtils是拿不到东西的,但是可以直接从ServletContext中获取。
三、销毁
销毁方法最终调用applicationcontext的close逻辑进行Spring容器的销毁,这里就不再介绍了。
四、补充
如何拿到ApplicationContext对象。
方式一:如果只配置了DispatcherServlet,则可以先获取ServletContext,然后通过key=FrameworkServlet.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX+"DispatcherServlet在web.xml在配置的名字";
方式二:如果既配置了ContextLoaderListener,又配置了DispatcherServlet,表现层的ApplicationContext通过方式一可以获取,业务层的ApplicationContext(即表现层Context的parent),可以通过WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());获取;
方式三:request.getAttribute(DispatcherServelt.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);,不过该方法只能获取表现层的,获取到ApplicationContext之后,也可以获取业务层的parent;
附注:
本文如有错漏,烦请不吝指正,谢谢!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容










所有评论(0)