linux用c语言获取系统启动时长
思路是通过读取/proc/uptime获得系统启动时长。使用命令cat /proc/uptime通过man proc可以看到如下的信息:/proc/uptime:This file contains two numbers: the uptime of the system (seconds), and the amount of time spent in idle process
·
思路是通过读取/proc/uptime获得系统启动时长。
使用命令cat /proc/uptime 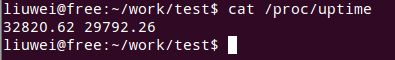
通过man proc可以看到如下的信息:
/proc/uptime:This file contains two numbers: the uptime of the system (seconds), and the amount of time spent in idle process (seconds).
第一个是系统的启动时长,第二个是系统的空闲时间。两个的单位都是秒。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct timeval timeget(void)
{
struct timeval now;
unsigned char timestr[60] = {0};
unsigned char uptimestr[30] = {0};
unsigned char * dotaddr;
unsigned long second;
char error = 0;
FILE * timefile = NULL;
timefile = fopen("/proc/uptime", "r");
if(!timefile)
{
printf("[%s:line:%d] error opening '/proc/uptime'",__FILE__,__LINE__);
error = 1;
goto out;
}
if( (fread(timestr, sizeof(char), 60, timefile)) == 0 )
{
printf("[%s:line:%d] read '/proc/uptime' error",__FILE__,__LINE__);
error = 1;
goto out;
}
dotaddr = strchr(timestr, '.');
if((dotaddr - timestr + 2) < 30)
memcpy(uptimestr, timestr, dotaddr - timestr + 2);
else
{
printf("[%s:line:%d] uptime string is too long",__FILE__,__LINE__);
error = 1;
goto out;
}
uptimestr[dotaddr - timestr + 2] = '\0';
out:
if(error)
{
now.tv_sec = 0;
now.tv_usec = 0;
}
else
{
now.tv_sec = atol(uptimestr);
now.tv_usec = 0;
}
fclose(timefile);
return now;
}
int main()
{
struct timeval uptime;
uptime = timeget();
printf("uptime = %lu\n", uptime.tv_sec);
return 0;
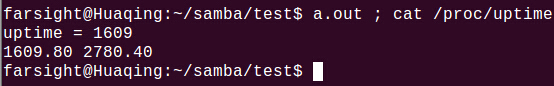
}运行结果:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容









所有评论(0)