Vivado IP核调用——FIFO
FIFO(first-in-first-out),可作为以先入先出顺序存取数据的数据缓存器。读写时钟或存取速率不同时,需要一个数据缓存器作为桥梁进行存—取两端的数据传输,常用异步FIFO完成该任务。与BRAM的区别在于,FIFO无地址线,可以简单地实现缓冲数据的先入先出顺序传输,无需按地址存取数据。FIFO内存取的数据不由地址指向,而是由自动变化的读指针和写指针指向要读或写的下一个数据。
一、FIFO的相关概念、作用
1.概念
FIFO(first-in-first-out),可作为以先入先出顺序存取数据的数据缓存器。读写时钟或存取速率不同时,需要一个数据缓存器作为桥梁进行存—取两端的数据传输,常用异步FIFO完成该任务。与BRAM的区别在于,FIFO无地址线,可以简单地实现缓冲数据的先入先出顺序传输,无需按地址存取数据。FIFO内存取的数据不由地址指向,而是由自动变化的读指针和写指针指向要读或写的下一个数据。
2.原理
写指针等于读指针时,写满或读空。读指针追上写指针:读空;写指针追上读指针:写满
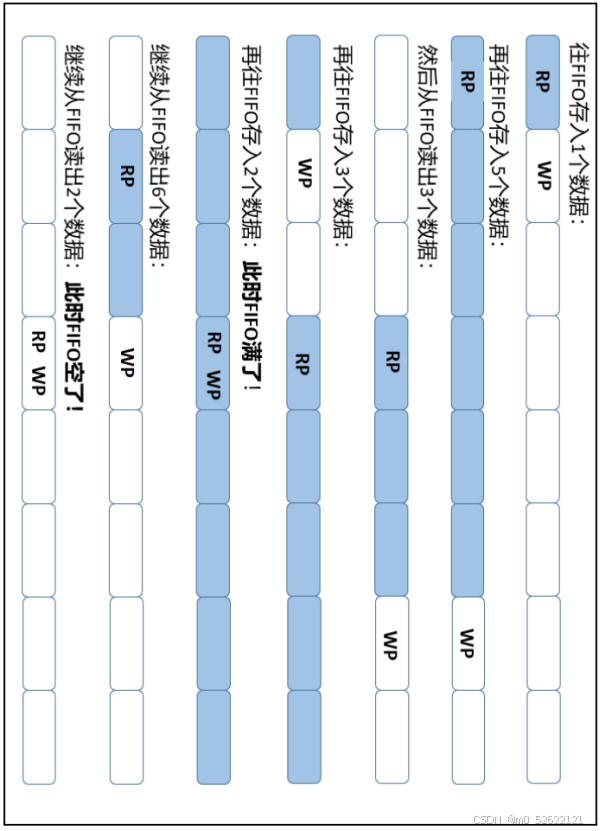
(从别处拿来的一张图,个人习惯,从右往左做井状图看其变化)
3.常见应用
数据缓存、协议处理、串并转换、跨时钟域数据处理
4.FIFO分类
(1)同步FIFO(Independent Clock FIFO)
读写时钟相同。
简单判断满空:可以简单用一个额外的计数器实现判断满空:WP移动向下一写入位置时,计数器+1;RP移动向下一读出数据时,计数器-1;计数=FIFO深度时,写满,计数=0时,读空。
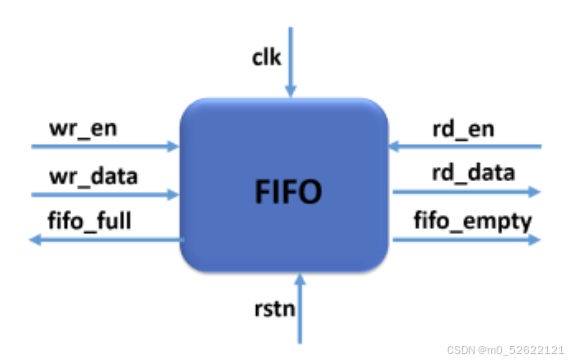
| 信号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| clk | 系统时钟 |
| rstn | 系统复位信号 |
| wr_en | 写使能端 |
| wr_data | FIFO写数据 |
| fifo_full | FIFO的满标志位 |
| rd_en | 读使能端 |
| rd_data | FIFO读数据 |
| fifo_empty | FIFO的空标志位 |
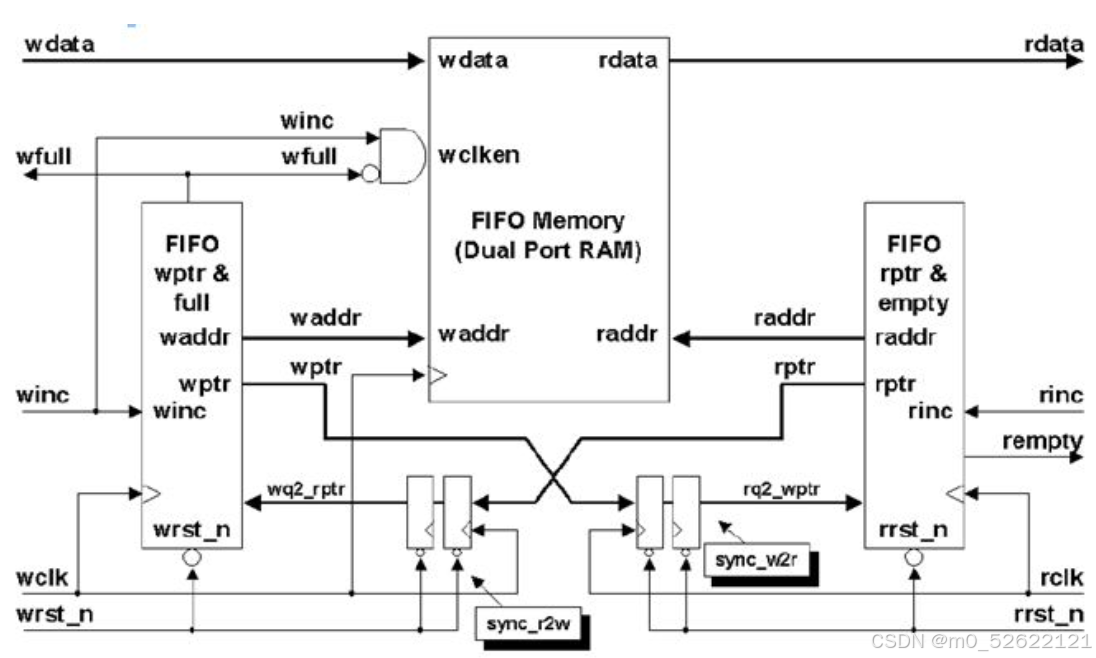
(2)异步FIFO(Common Clock FIFO)
读写时钟不同。
跨时钟域处理判断满空:需要将写地址指针放入读时钟域(以读端clk为标准对写端地址指针采样),将其与读地址指针比较判断是否读空;将读地址指针放入写时钟域(以写端clk为标准对读端地址指针采样),将其与写地址比较判断是否写满。
跨时钟域处理可能产生亚稳态,一般有两种方法减少亚稳态:打两拍和使用格雷码表示地址指针,这里不进行深入讨论。
二、FIFO IP核(FIFO Generator)
这里只对比较主要的可定制选项进行说明。
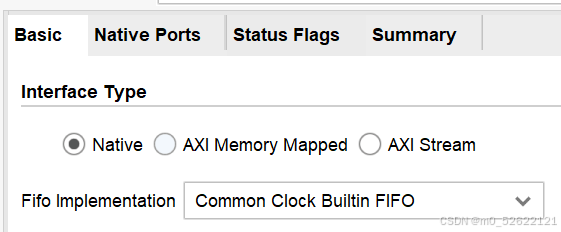
Interface Type
调用FIFO IP核时可在Basic中选择下面3种Interface Type,本文目前暂时只讨论Native类型。各Interface Type可定制选项差别较大,但均有同步、异步FIFO的选项。
Ⅰ.Native Type
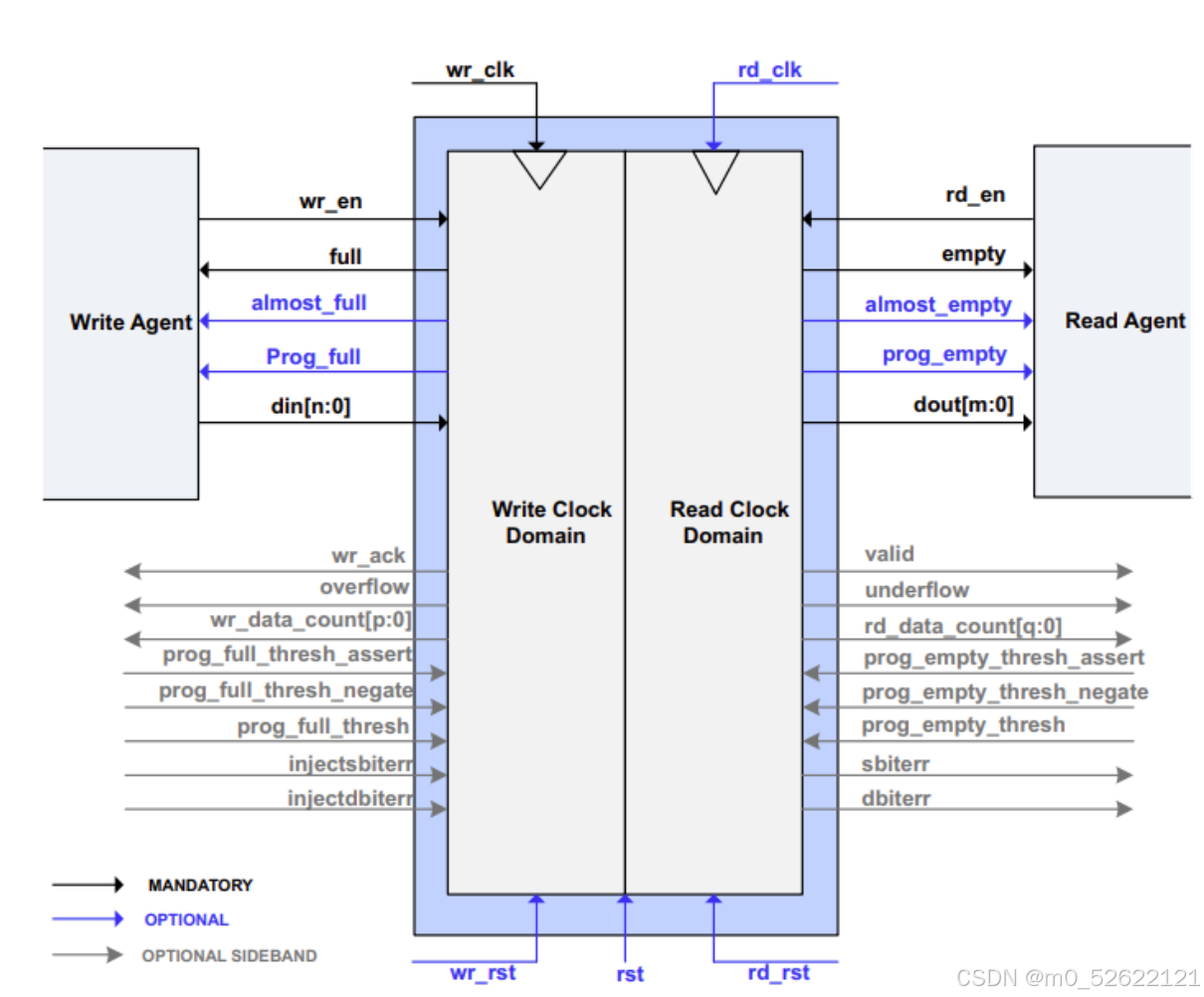
1.各ports 说明
在介绍各Interface Type下,IP核的不同选项前,最好先了解其端口。下面进行端口介绍,免去对部分不重要的IP选项的繁琐介绍。
基本信号 |
注 |
||
| rst | 输入 | 异步复位信号,能初始化所有的内部指针和输出寄存器。 | |
| wr_clk | 输入 | 写时钟 | |
| rd_clk | 输入 | 读时钟 | |
| din[a:0] | 输入 | 单次clk写入的的a位宽数据 | |
| wr_en | 输入 | 写入使能 | |
| rd_en | 输入 | 读出使能 |
读失能时,dout保持输出寄存器上存的上一输出值 |
| dout [b:0] | 输出 | 单次clk输出的b位宽数据 | |
写相关握手信号 |
注 : 受写时钟控制 |
||
| full | 输出 | 满标志:生效时说明FIFO满了,此时写操作可以直接忽视 | 已经写不下了 |
| almost_full | 输出 | 将满信号:生效时说明FIFO只能最多再允许一个写操作 | 下一周期写不下了 |
| wr_ack | 输出 | 写确认:生效时说明上个周期数据写入成功 | 上一周期写进去了 |
|
overflow |
输出 | 溢出信号:表示上个周期的写请求被拒绝,因为FIFO已经满了 | 上一周期没写进去,溢出了 |
读相关握手信号 |
注 受读时钟控制 |
||
| empty | 输出 | 空标志:生效时说明FIFP空了,此时读操作直接忽视 | 已经读不出了 |
| almost_empty | 输出 | 将空信号:生效时说明FIFO只剩下最后一个数据可以读 | 下一周期读不出了 |
| valid | 输出 | 有效信号:生效时表示输出总线上的数据有效,上个周期数据读取成功 | 上一周期读出来了 |
| underflow | 输出 | 下溢出:表示上一个周期的读操作被拒绝,因为FIFO是空的 | 上一周期没读出来,下溢了(此时dout保持输出寄存器存的上一输出值) |
rst相关信号 |
注 | ||
| wr_rst_busy | 输出 | 生效时表示整个写时钟域被rst了,处于复位状态 | 写时钟域目前复位状态,不要看此时的时序 |
| rd_rst_busy | 输出 | 生效时表示整个读时钟域被rst了,处于复位状态 | 读时钟域目前复位状态,不要看此时的时序 |
可编程满空阈值以及对应握手信号 |
注 |
||
| prog_full | 输出 |
可编程满信号:在生成FIFO IP核前通过选项设置一个阈值来判断FIFO还有多少空间,该信号在FIFO剩余空间大于等于某阈值时=1。 |
满握手信号, 可提前设定阈值,也可动态设定阈值 |
|
prog_full_thresh |
输入 | 可编程满阈值:输入可编程满信号的阈值,可动态调控 | 使/失能满握手信号的动态阈值 |
|
prog_full_thresh_assert |
输入 | 可编程阈值生效信号:输入可编程满信号的上阈值,可动态设置,与prog_full_thresh_negate一同用于替代仅有一个阈值的prog_full_thresh | 使能满握手信号的动态上阈值 |
|
prog_full_thresh_negate |
输入 | 可编程阈值失效信号:输入可编程满信号的下阈值,可动态设置,与prog_full_thresh_assert一同用于替代仅有一个阈值的prog_full_thresh | 失能满握手信号的动态下阈值 |
| prog_empty | 输出 | 可编程空:在生成FIFO IP核前通过选项设置,该信号在FIFO中已写入的数据数小于等于某阈值时=1。 |
空握手信号, 可提前设定阈值,也可动态设定阈值 |
|
prog_empty_thresh |
输入 | 可编程空阈值:输入可编程满信号的阈值,可动态调控,用于替代不可动态调控的prog_empty | 使/失能空握手信号的动态阈值 |
|
prog_empty_thresh_assert |
输入 | 可编程空阈值生效:输入可编程空信号的下阈值,可动态设置,与prog_empty_thresh_negate一同用于替代仅有一个阈值的prog_empty_thresh | 失能空握手信号的动态上阈值 |
|
prog_empty_thresh_negate |
输入 |
可编程空阈值失效:输入可编程空信号的上阈值,可动态设置,与prog_empty_thresh_negate一同用于替代仅有一个阈值的prog_empty_thresh |
使能空握手信号的动态下阈值 |
计数器信号 |
注 |
||
| wr_data_count[d:0] | 输出 |
写数据计数:显示FIFO中目前写进了多少个字。 例外情况是,当一个写操作发生在wr_clk/ clk的上升缘时,该写操作将只反映在下一个上升时钟边缘的wr_data_count上。如果D小于log2(FIFO depth)-1,总线通过删除最不重要的位而被截断。 这条总线在UltraScale系类,通过一个common clock Block RAM-based 实现的(还要用上了Asymmetric Port Width端口)FIFO里也有效。 |
1.该字的位宽和din字的位宽一样,与dout字位宽不一定相同。不考虑位宽差,代表的数据量其实和读数据计数相同。 2.受写时钟域控制。 3.写入字增加其数值,读出字也会减少其数值。 4.读出的字位宽小于该字时,依然视作减少一个该字。 5.在某时钟沿时开始写入一个字,则读写数据计数在未完成字的完全写入前都不变。比如:在上升沿开始最后一个字写入时,写满,full立即拉高,但读写数据计数在该字所有bit位都写入后才+1为满计数。 |
|
rd_data_count [c:0] |
输出 | 读数据计数:显示FIFO中目前可以读多少个字。 这条总线在UltraScale系类,通过一个common clock Block RAM-based 实现的(还要用上了Asymmetric Port Width端口)FIFO里也有效。 |
1.该字的位宽和dout字的位宽一样,与din字位宽不一定相同。不考虑位宽差,代表的数据量其实和写数据计数相同。 2.受读时钟域控制。 3.写入字也会增加其数值,读出字减少其数值。 4.写入的字位宽小于该字时,不视作增加一个该字。 5.在某时钟沿时开始读出一个字,则读写数据计数在未完成字的完全读出前都不变。比如:在上升沿开始最后一个字读出时,读空,empty立即拉高,但写数据计数在该字所有bit位都读出后才+1为空计数。 |
ECC相关信号 |
|||
|
injectsbiterr |
输入 | 使用ECC的时候插入一位错误 | |
|
injectdbiterr |
输入 | 使用ECC的时候插入两位错误 | |
|
sbiterr |
输出 | 单位错误:表示ECC解码器检测到并修复了块RAM或内置的FIFO宏上的单位错误。 | |
|
dbiterr |
输出 | 双位错误:表示ECC解码器在块RAM或内置的FIFO宏上检测到双位错误,并且FIFO核心中的数据已损坏。 | |
2.FIFO Implementation
可选择使用的FIFO类型,基本只会用到BRAM或DRAM模式,前者是使用FPGA内部固定缓存资源,后者是使用LUT等逻辑资源搭建的FIFO功能。当BRAM资源紧张的时候,合理利用后者可以减轻BRAM负担。各类型FIFO支持的选项如下表。
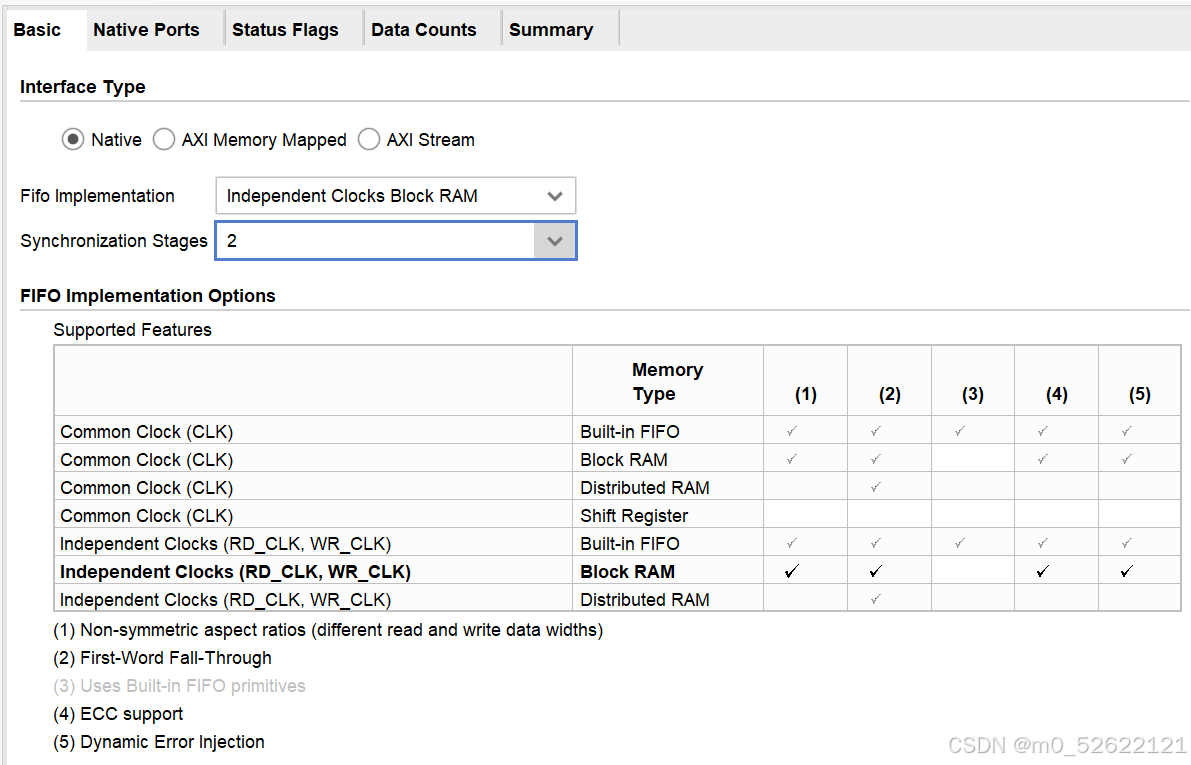
(1)Non-symmetric aspect ratios指读写数据位宽不同,成一定比例,即非对称读写位宽;(之后在说明Port的选项时将介绍)
(2)First-word Fall-Through指前显模式读操作,提前将第一个要读取的数据放在输出寄存器dout上;(一般不用,用标准读操作即可)
(3)Uses Built-in FIFO Primitives指使用内置的FIFO单元,从而可以通过在宽度和深度上级联内置 FIFO 来创建大型 FIFO;
本文将以异步BRAM FIFO(Independent Clocks Block RAM FIFO)为例进行说明。
★注:当选择异步FIFO时,会出现Synchronization stages —— 同步级数的选项,此选项的意思是,当FIFO中写入数据后,empty信号并不会立刻拉低,因为写入数据是基于写时钟的,而empty信号是基于读时钟的,要多拍寄存器才能去掉跨时钟亚稳态。
如果Synchronization stages设定为2,则意味着empty会在FIFO中写入数据成功后的2个读时钟周期后拉低。
3.Ports
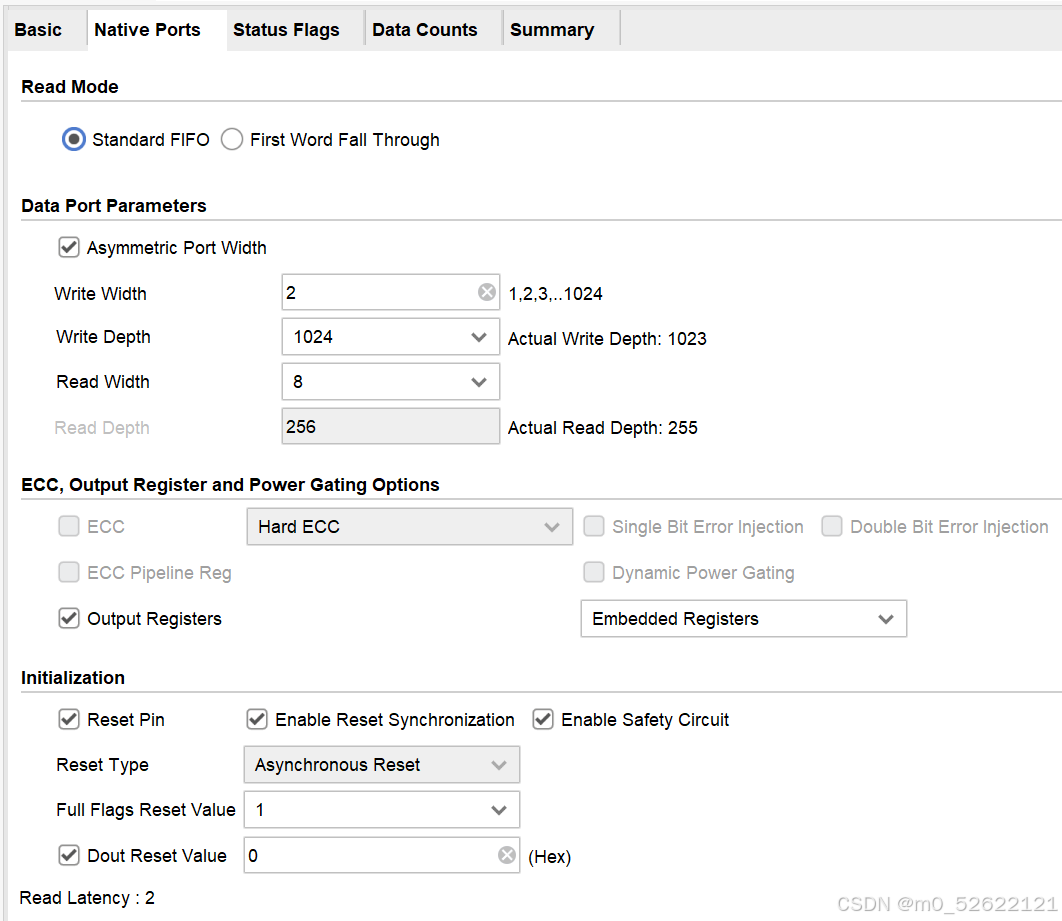
(1)读操作Read Mode:Standard FIFO和First-word Fall-Through,一般使用标准读操作模式Standard FIFO
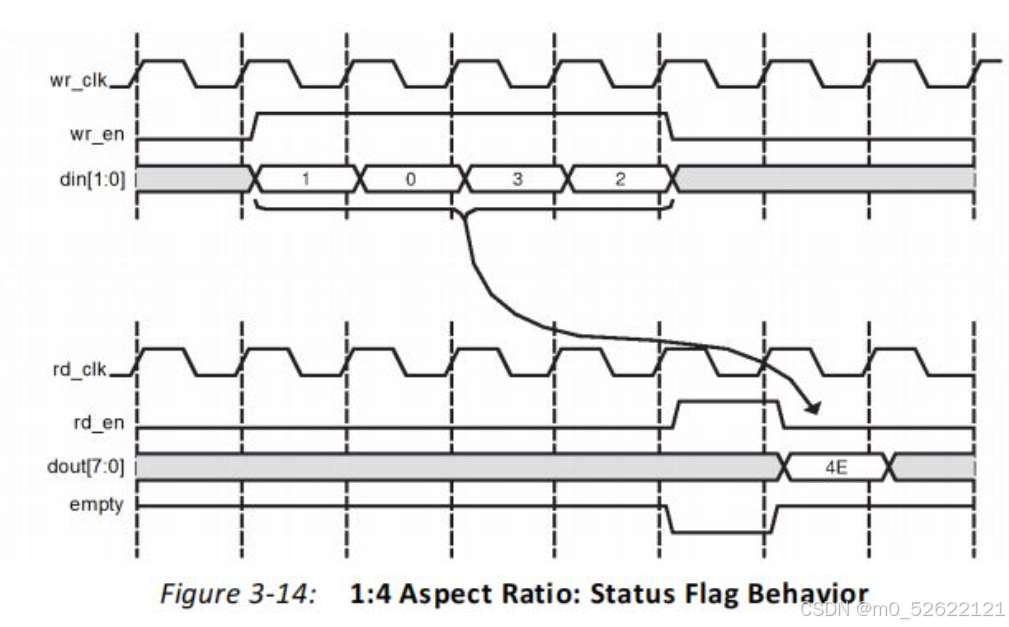
(2)读写的数据参数Data Port Parameters:可选择非对称读写位宽Asymmetric Port Width,实现串并转换、位宽转换等效果。Vivado可以自动根据读写位宽判断FIFO深度。下面以为读写位宽4:1、1:4的情况和时序分别介绍读位宽>写位宽和写位宽>读位宽情况:
a.读写位宽4:1
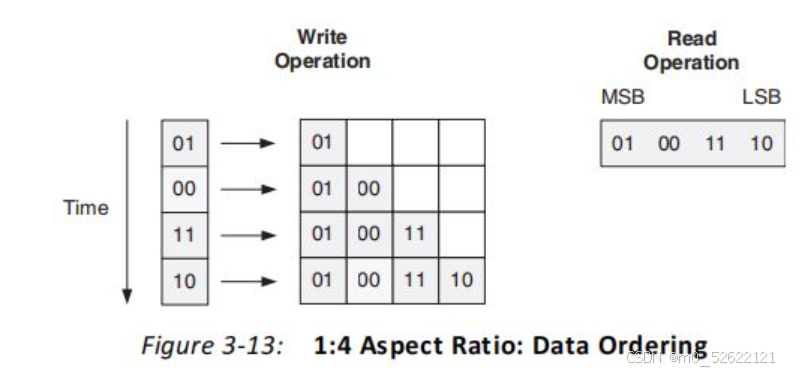
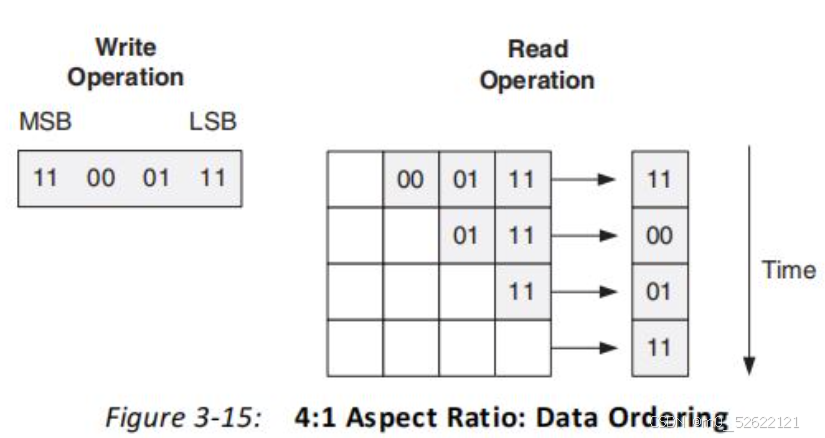
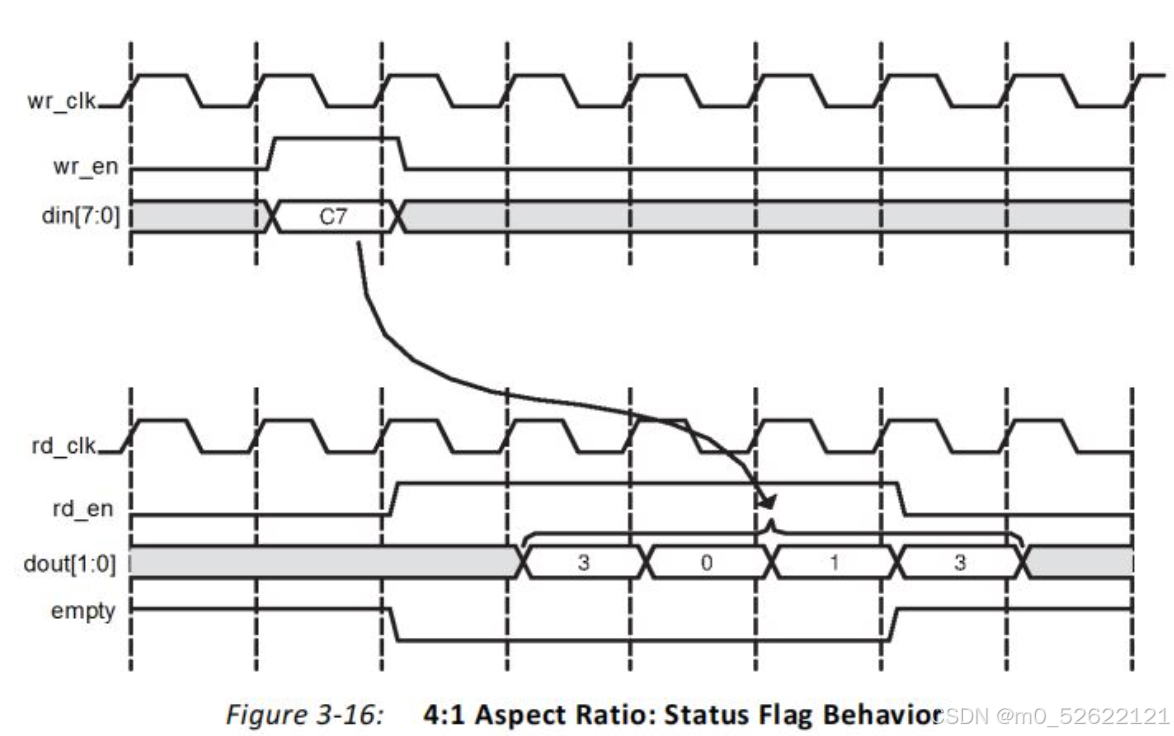
b.读写位宽1:4
4.Status Flags
这里可选各个握手信号,详细含义可参考1.ports说明
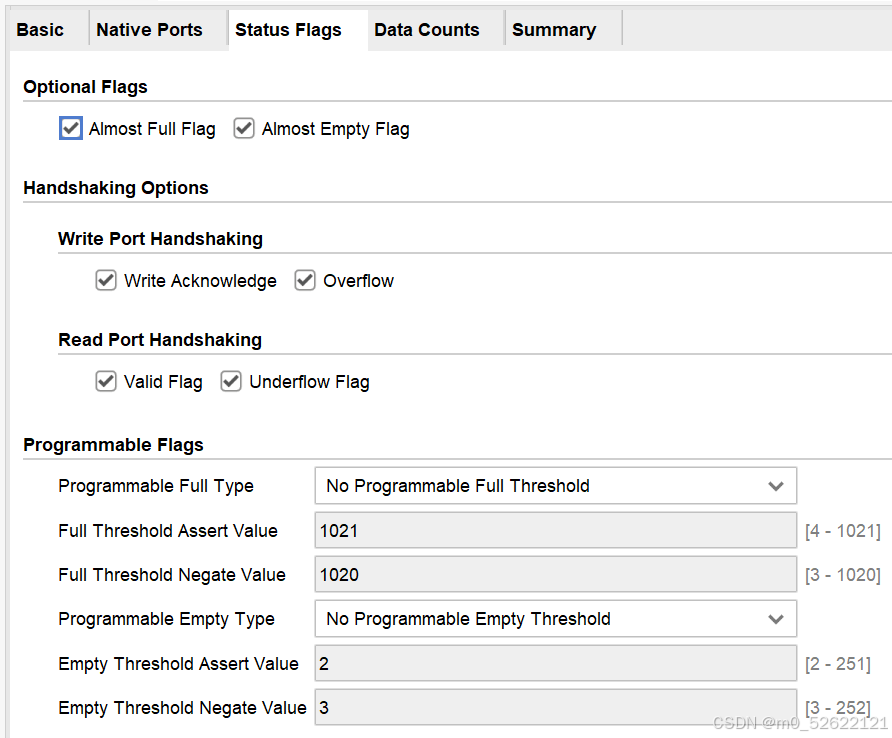

对Programma Flags的额外说明:
Full与Empty均可选5个Programmable Type
①No Programmable Threshold Constant:不设置可编程满/空信号;
②Single Programmable Threshold Constant:在选项中设置一个固定的满/空阈值常数;
③Multiple Programmable Threshold Constant:在选项中设置两个固定的满/空阈值常数,一个上阈值,一个下阈值;
④Single Programmable Threshold Input Port:允许一个输入信号作为一个可动态调控的满/空阈值;
⑤Multiple Programmable Threshold Constant:允许两个输入信号分别作为可动态调控的满/空阈值的上、下阈值;
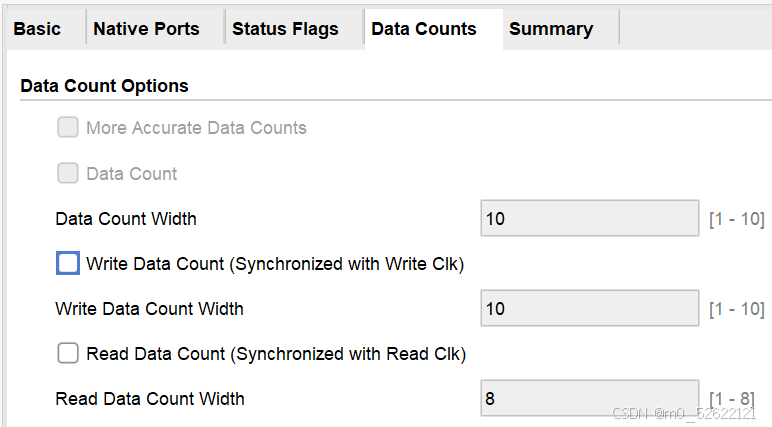
5.Data Counts
增加读or写计数器并设计其计数位宽,输出的write_data_count直接显示目前FIFO中写入的字,read_data_count直接显示目前FIFO中可读出的字。参考1.ports说明。
三、FIFO IP核的调用和仿真
这里只调用异步FIFO
Ⅰ.Native Type
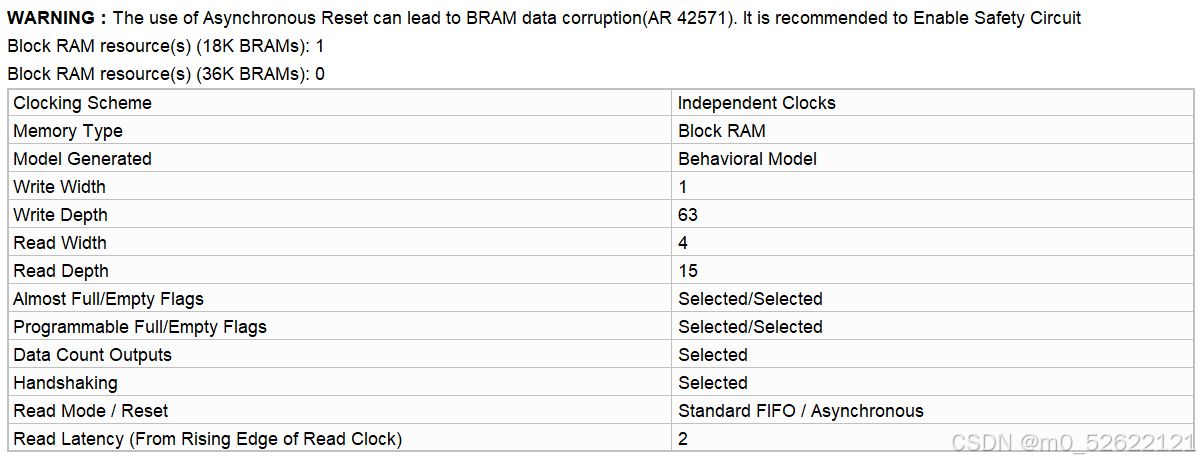
调用FIFO的summary:
顶层文件:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module fifo_test(
input rst,
input wr_clk,
input rd_clk,
input [0:0] din,
input wr_en,
input rd_en,
input [3 : 0] prog_empty_thresh_assert,
input [3 : 0] prog_empty_thresh_negate,
input [5 : 0] prog_full_thresh_assert,
input [5 : 0] prog_full_thresh_negate,
output [3: 0] dout,
output full,
output almost_full,
output wr_ack,
output overflow,
output empty,
output almost_empty,
output valid,
output underflow,
output [3: 0] rd_data_count,
output [5: 0] wr_data_count,
output prog_full,
output prog_empty,
output wr_rst_busy,
output rd_rst_busy
);
fifo_generator_1 fifo_inst1 (
.rst(rst), // input wire rst
.wr_clk(wr_clk), // input wire wr_clk
.rd_clk(rd_clk), // input wire rd_clk
.din(din), // input wire [0 : 0] din
.wr_en(wr_en), // input wire wr_en
.rd_en(rd_en), // input wire rd_en
.prog_empty_thresh_assert(prog_empty_thresh_assert), // input wire [3 : 0] prog_empty_thresh_assert
.prog_empty_thresh_negate(prog_empty_thresh_negate), // input wire [3 : 0] prog_empty_thresh_negate
.prog_full_thresh_assert(prog_full_thresh_assert), // input wire [5 : 0] prog_full_thresh_assert
.prog_full_thresh_negate(prog_full_thresh_negate), // input wire [5 : 0] prog_full_thresh_negate
.dout(dout), // output wire [3 : 0] dout
.full(full), // output wire full
.almost_full(almost_full), // output wire almost_full
.wr_ack(wr_ack), // output wire wr_ack
.overflow(overflow), // output wire overflow
.empty(empty), // output wire empty
.almost_empty(almost_empty), // output wire almost_empty
.valid(valid), // output wire valid
.underflow(underflow), // output wire underflow
.rd_data_count(rd_data_count), // output wire [3 : 0] rd_data_count
.wr_data_count(wr_data_count), // output wire [5 : 0] wr_data_count
.prog_full(prog_full), // output wire prog_full
.prog_empty(prog_empty), // output wire prog_empty
.wr_rst_busy(wr_rst_busy), // output wire wr_rst_busy
.rd_rst_busy(rd_rst_busy) // output wire rd_rst_busy
);
endmodule
testbench:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module fifo_test_tb();
reg rst;
reg wr_clk;
reg rd_clk;
reg [0:0] din;
reg wr_en;
reg rd_en;
reg [3 : 0] prog_empty_thresh_assert;
reg [3 : 0] prog_empty_thresh_negate;
reg [5 : 0] prog_full_thresh_assert;
reg [5 : 0] prog_full_thresh_negate;
wire [3:0] dout;
wire full;
wire almost_full;
wire wr_ack;
wire overflow;
wire empty;
wire almost_empty;
wire valid;
wire underflow;
wire [3 : 0] rd_data_count;
wire [5 : 0] wr_data_count;
wire prog_full;
wire prog_empty;
wire wr_rst_busy;
wire rd_rst_busy;fifo_test fifo_test_1(
.rst(rst),
.wr_clk(wr_clk),
.rd_clk(rd_clk),
.din(din),
.wr_en(wr_en),
.rd_en(rd_en),
.prog_empty_thresh_assert(prog_empty_thresh_assert),
.prog_empty_thresh_negate(prog_empty_thresh_negate),
.prog_full_thresh_assert(prog_full_thresh_assert),
.prog_full_thresh_negate(prog_full_thresh_negate),
.dout(dout),
.full(full),
.almost_full(almost_full),
.wr_ack(wr_ack),
.overflow(overflow),
.empty(empty),
.almost_empty(almost_empty),
.valid(valid),
.underflow(underflow),
.rd_data_count(rd_data_count),
.wr_data_count(wr_data_count),
.prog_full(prog_full),
.prog_empty(prog_empty),
.wr_rst_busy(wr_rst_busy),
.rd_rst_busy(rd_rst_busy)
);always begin //读写时钟翻转
#5 wr_clk<=~wr_clk;
#7 rd_clk<=~rd_clk;
endinitial begin //设定控制信号初始值,规定结束时间
din <= 0;
wr_clk <= 0;
rd_clk <= 0;
rst <= 1;
wr_en <= 0;
rd_en <= 0;
prog_empty_thresh_assert <= 61;
prog_empty_thresh_negate <= 60;
prog_full_thresh_assert <= 2;
prog_full_thresh_negate <= 3;
#5000 $finish;
endinitial begin //实现读写使能信号和重置信号的变化、din的变化
#5;
repeat(150) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 0; end //深度为63,75次1位输入1'b1,溢出FIFO
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 0; end
repeat(200) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 1; end //约71次4位输出4'b1111,下溢FIFO
repeat(20) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 1; end //同时允许读写信号
#5 rst <= 1'b1; //rst清空fifo
#5 rst <= 1'b0;
repeat(40) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 0;end //20次1位输入1'b1
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 0;end //读写失能时din尝试写入1'b1
repeat(12) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 1;end //4次4位输出4'b1111,FIFO中仍有数据repeat(40) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 0;end //20次1位输入1'b0
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 0;end
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 1;end //写失能,din尝试写入1'b1,读使能,3次4位输出4'b1111,FIFO中仍有数据
repeat(20) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 1;end //10次1位输入1'b0,同时7次4位输出4'b1111 ,FIFO中仍有数据
#5 rst <= 1'b1; //rst清空fifo
#5 rst <= 1'b0;
repeat(40) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 0;end //20次1位输入1'b0
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 0;end //读写失能时din尝试写入1'b0
repeat(12) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 1;end //4次4位输出4'b0000,FIFO中仍有数据repeat(40) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 0;end //20次1位输入1'b1
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 0;end
repeat(10) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 0;rd_en <= 1;end //写失能,din尝试写入1'b0,读使能,3次4位输出4'b????,FIFO中仍有数据
repeat(20) #5 begin din <= 0;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 1;end //10次1位输入1'b0,同时7次4位输出4'b??? ,FIFO中仍有数据
repeat(800)#5 begin din <= 1;wr_en <= 1;rd_en <= 0;end //造成溢出
end
initial begin //阈值信号的设定、重置信号的发送
#10 rst = 0;
prog_empty_thresh_assert <= 4;
prog_empty_thresh_negate <= 5;
prog_full_thresh_assert <= 55;
prog_full_thresh_negate <= 54;
#200 prog_empty_thresh_assert <= 10;
prog_empty_thresh_negate <= 15;
prog_full_thresh_assert <= 63;
prog_full_thresh_negate <= 60;
#200 prog_empty_thresh_assert <= 10;
prog_empty_thresh_negate <= 11;
prog_full_thresh_assert <= 40;
prog_full_thresh_negate <= 30;
#200 prog_empty_thresh_assert <= 2;
prog_empty_thresh_negate <= 3;
prog_full_thresh_assert <= 61;
prog_full_thresh_negate <= 60;
end
endmodule
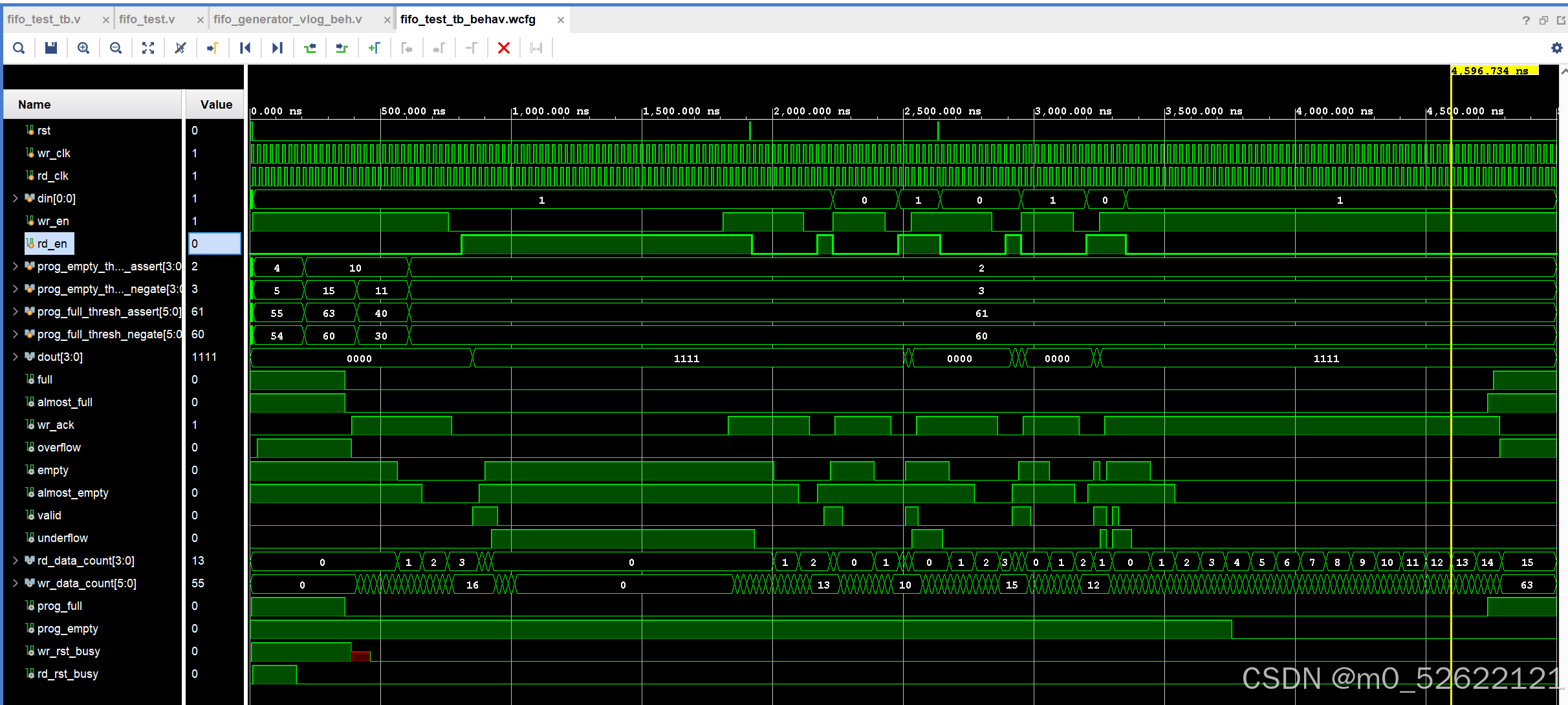
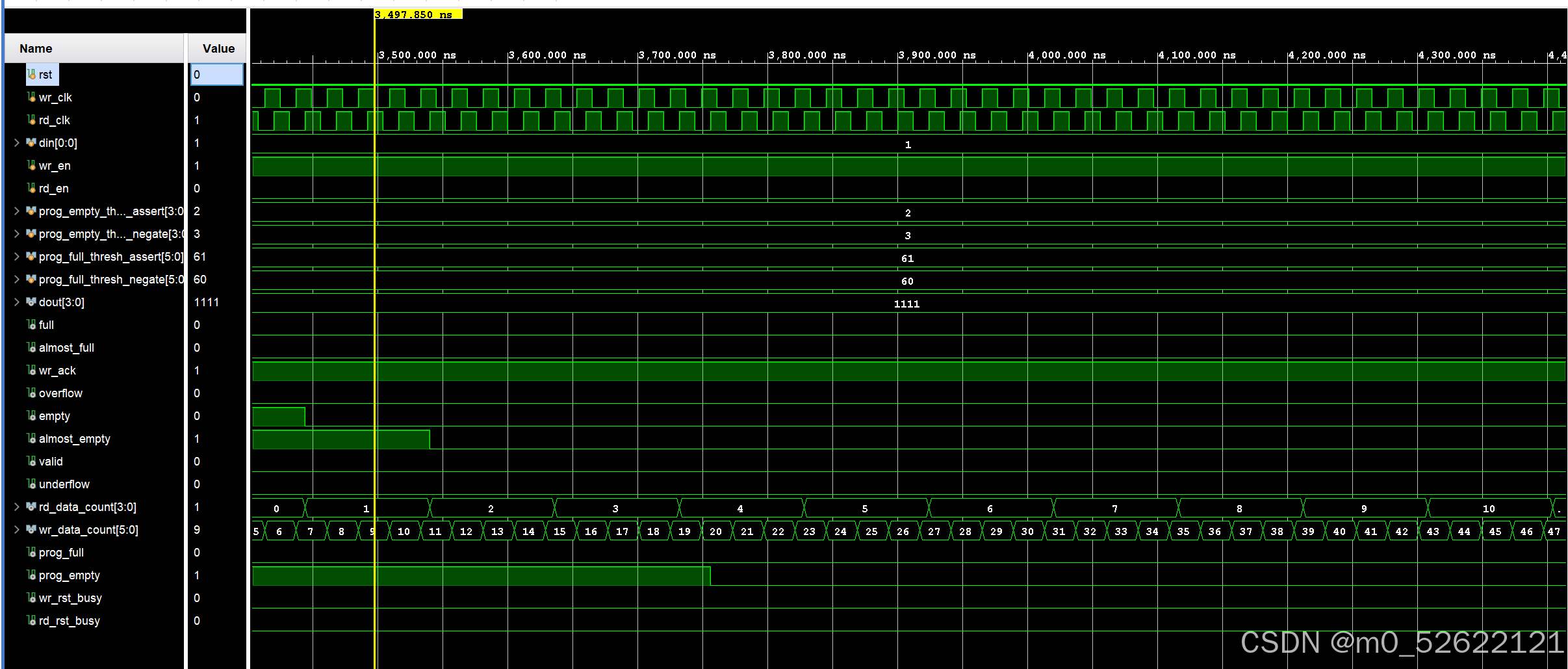
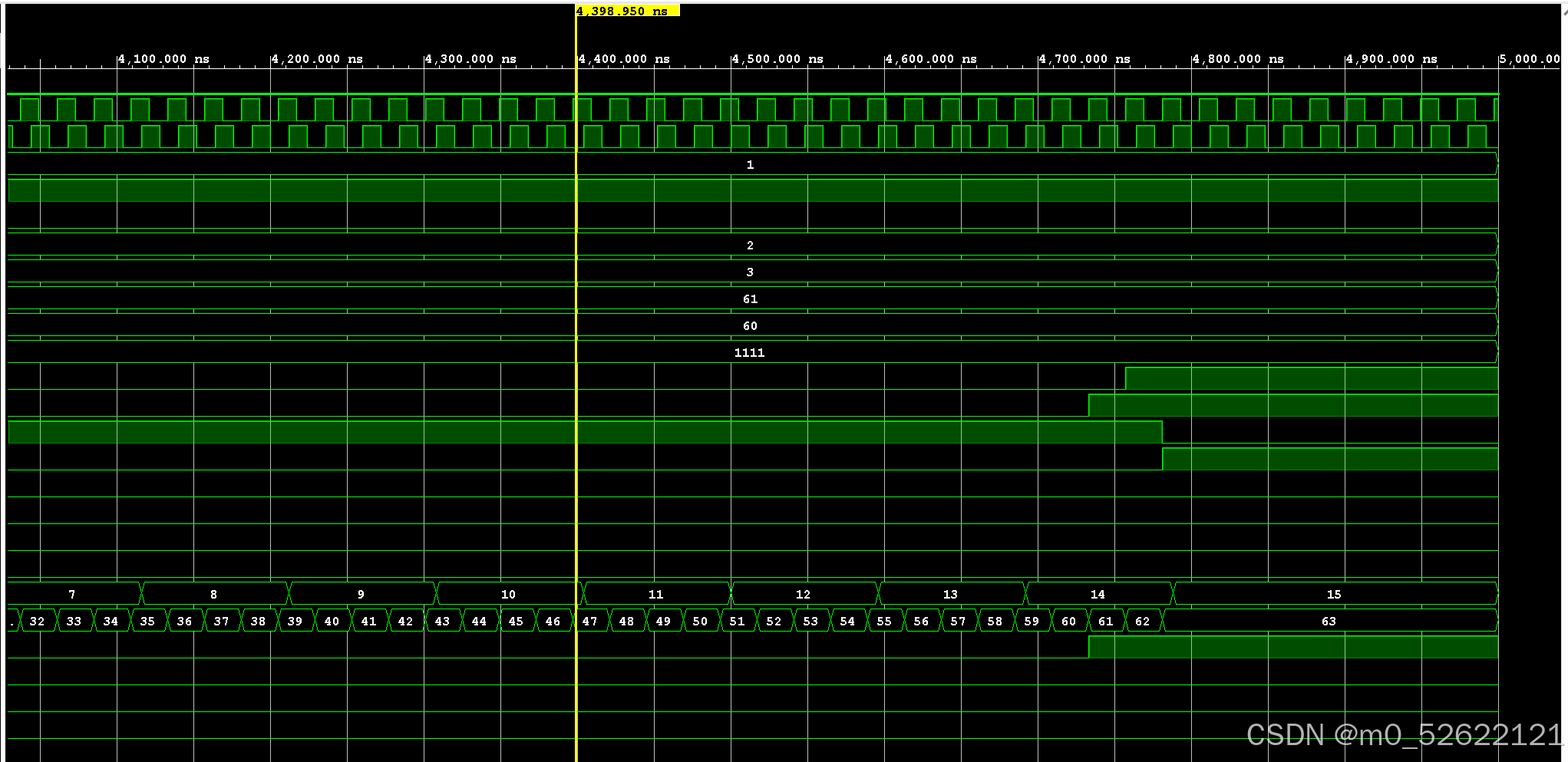
仿真结果:
· 全图
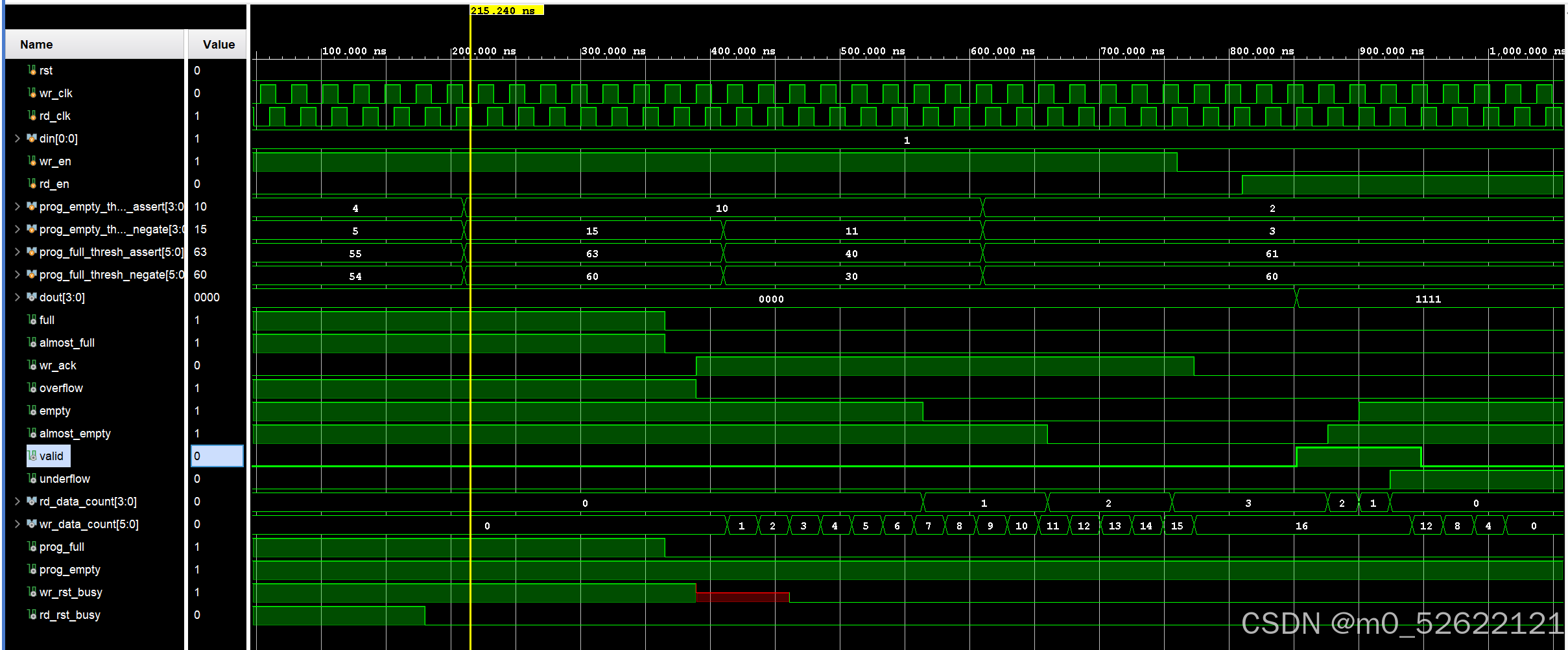
· 0~1000.00ns
· 1700.00ns~2600.00ns
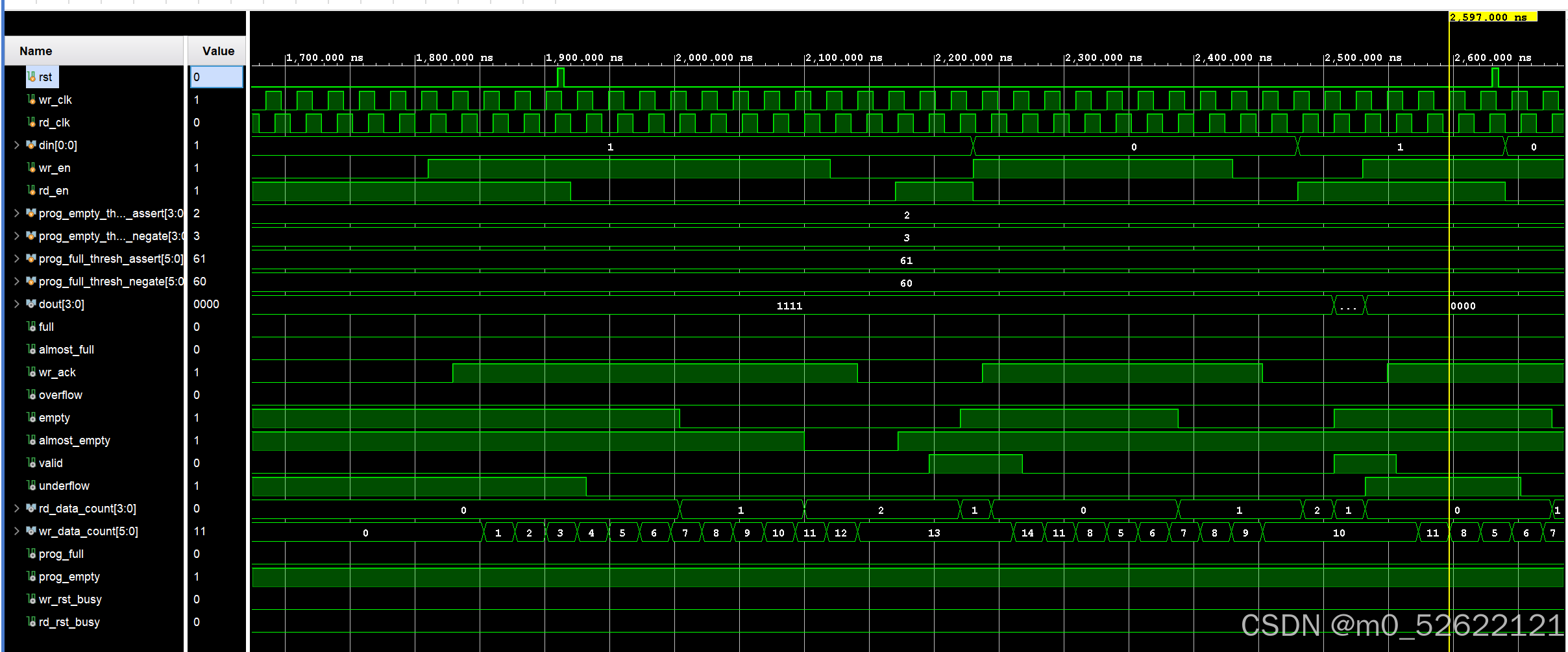
放大后的2500.00ns~2600.00ns
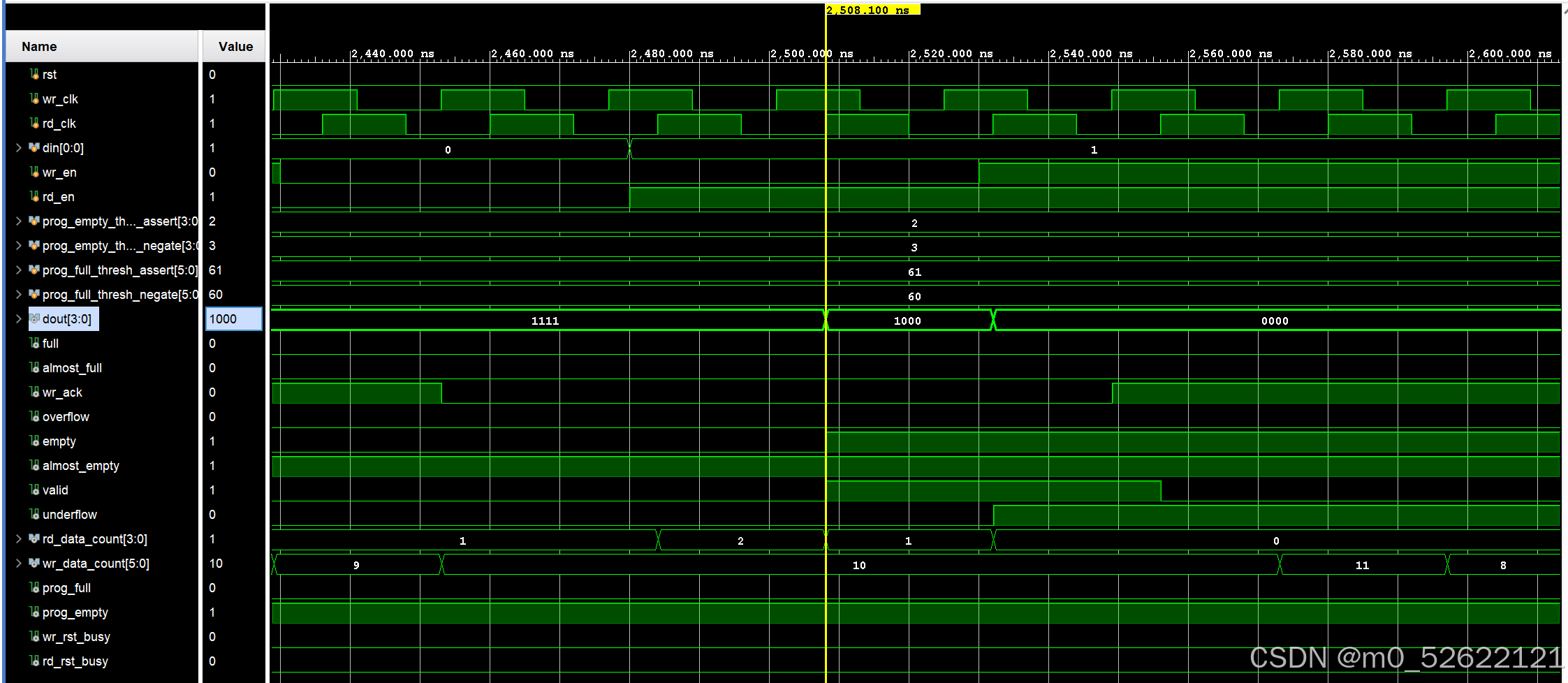
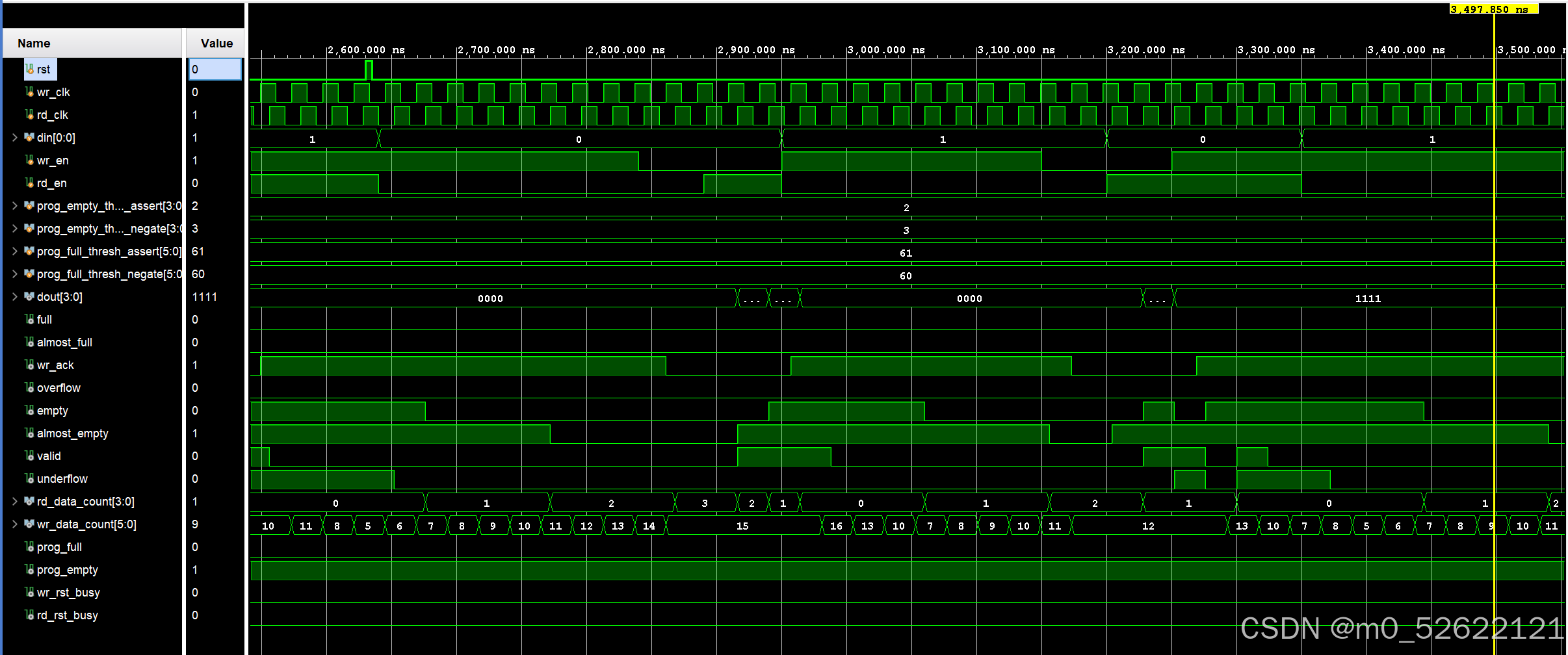
· 2600.00ns~3500.00ns
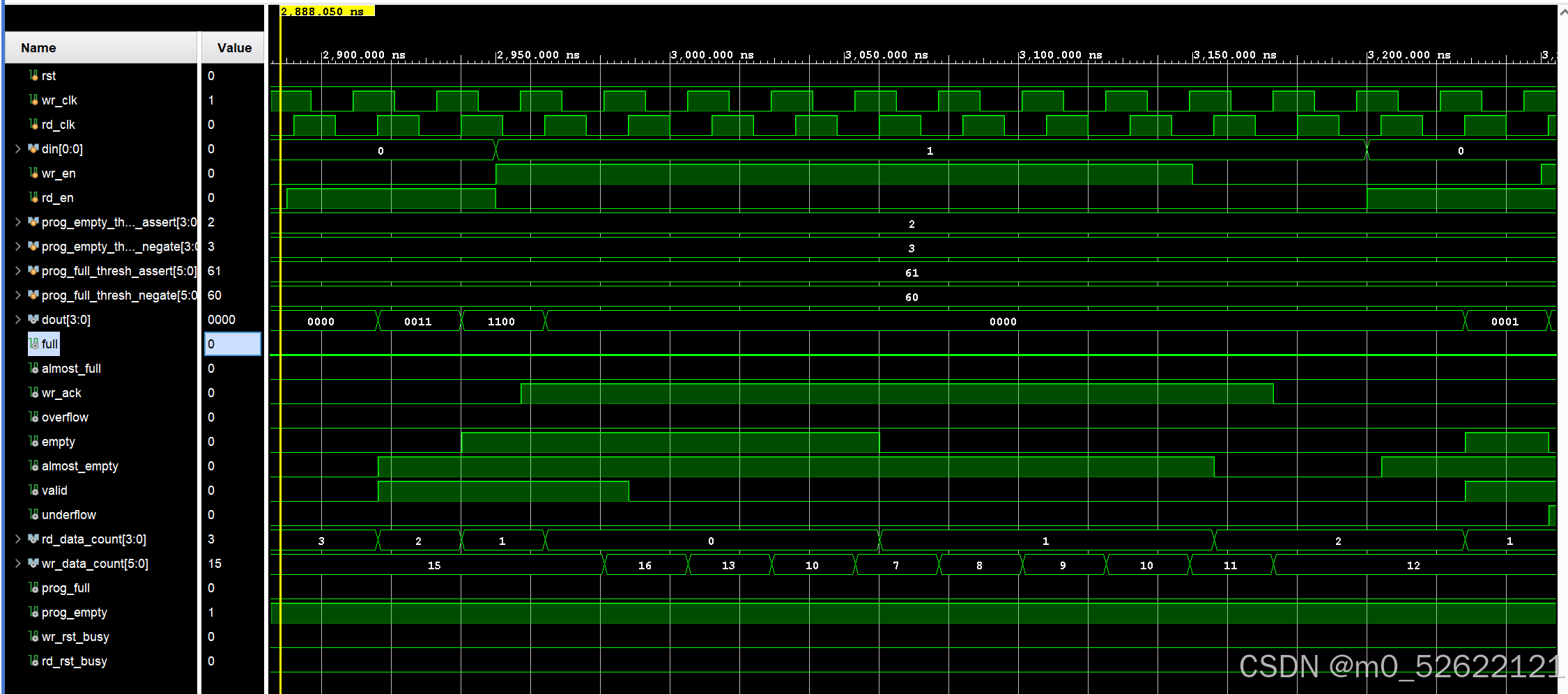
放大后的2900.00ns~3300.00ns
· 3500.00ns~4400.00ns
· 4400.00ns~5000.00ns
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)