android 导入数据库,Android导入数据库
一. 创建数据库建立Android项目用Navicat Premium建立所需数据库若数据过多可以先在Excel中录入再进行导入 二.将现有数据库导入到Android里面在Android的res文件夹下建立raw文件直接将数据库粘贴到raw下然后建立一个java项目代码如下public class DBOpenHelper {private final int BUFFER_SIZE=400000
一. 创建数据库建立Android项目
用Navicat Premium建立所需数据库若数据过多可以先在Excel中录入再进行导入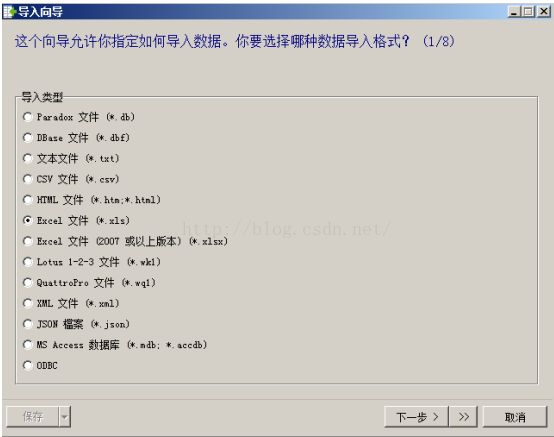
二.将现有数据库导入到Android里面
在Android的res文件夹下建立raw文件直接将数据库粘贴到raw下
然后建立一个java项目代码如下
public class DBOpenHelper {
private final int BUFFER_SIZE=400000;//缓冲区大小
public static final String DB_NAME="idioms.db"; //保存的数据库文件名
public static final String PACKAGE_NAME="com.example.happyidiom";//应用的包名
public static final String DB_PATH="/data"
+Environment.getDataDirectory().getAbsolutePath()+"/"
+PACKAGE_NAME+"/databases";//在手机里存放数据库的位置
private Context context;
public DBOpenHelper(Context context){
this.context=context;
}
public SQLiteDatabase openDatabase(){
try{
File myDataPath=new File(DB_PATH);
if(!myDataPath.exists()){
myDataPath.mkdirs();//如果没有这个数据库则创建
}
String dbfile=myDataPath+"/"+DB_NAME;
if(!(new File(dbfile).exists())){//判断数据库文件是否存在,若不存在直接导入,
//否则直接打开数据库
InputStream is=context.getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.idioms);
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(dbfile);
byte[] buffer=new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int count=0;
while((count=is.read(buffer))>0){
fos.write(buffer, 0,count);
}
fos.close();
is.close();
}
SQLiteDatabase db=SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(dbfile, null);
return db;
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
Log.e("Database","File not found");
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e){
Log.e("Database","IO exception");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
然后编写测试类
public class DBOpenHelperTest extends AndroidTestCase{
public void testDBCopy(){
DBOpenHelper dBOpenHelper=new DBOpenHelper(getContext());
dBOpenHelper.openDatabase();
}
}
然后在项目上右击后选择run as ——>Android Junit Test
出现以下两张图视为成功
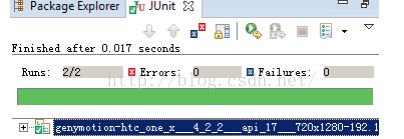
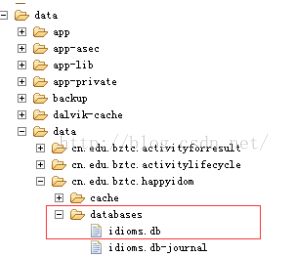
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容









所有评论(0)