人工智能-爬山法解决八数码问题-python源码
问题描述:在一个3*3的方棋盘上放置着1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8八个数码,每个数码占一格,且有一个空格。这些数码可以在棋盘上移动,其移动规则是:与空格相邻的数码方格可以移入空格。现在的问题是:对于指定的初始棋局和目标棋局,给出数码的移动序列。该问题称八数码难题或者重排九宫问题。八数码问题的解决流程如下图所示:算法源代码为:import copyimport numpy as npimport
·
问题描述:
在一个3*3的方棋盘上放置着1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8八个数码,每个数码占一格,且有一个空格。这些数码可以在棋盘上移动,其移动规则是:与空格相邻的数码方格可以移入空格。现在的问题是:对于指定的初始棋局和目标棋局,给出数码的移动序列。该问题称八数码难题或者重排九宫问题。
八数码问题的解决流程如下图所示:
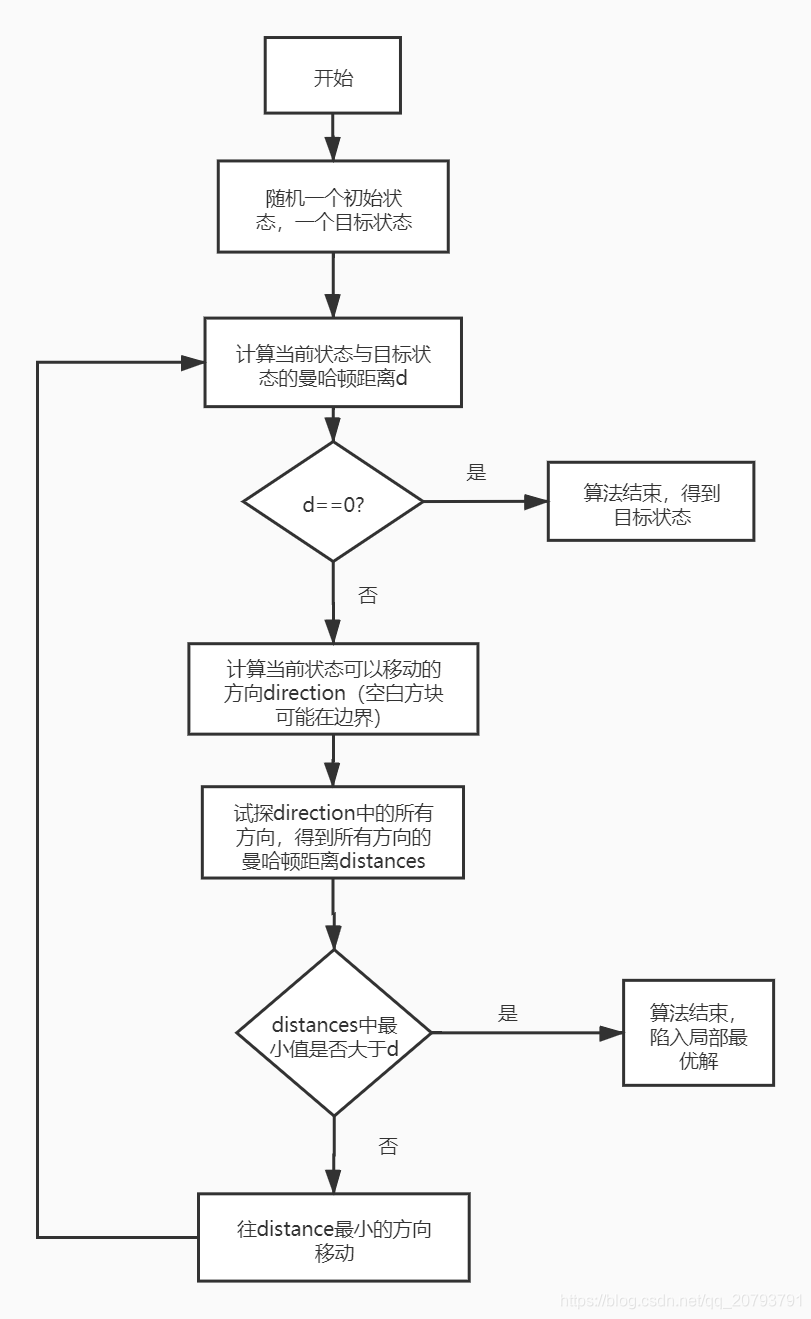
算法源代码为:
import copy
import numpy as np
import random
import time
import math
# 爬山法解决八皇后问题
# 八数码初始化函数,返回一个初始状态和一个目标状态,这里0代表八数码中的空格
def init():
init_state = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
target_state = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
np.random.shuffle(init_state)
np.random.shuffle(target_state)
init_state = np.reshape(init_state, (3, 3))
target_state = np.reshape(target_state, (3, 3))
return init_state, target_state
# 计算当前状态和目标状态下的曼哈顿距离
def compute_manhattan_distance(init_state, target_state):
total_distance = 0
for i in range(1, 9):
(init_row, init_column) = np.where(init_state == i)
(target_row, target_column) = np.where(target_state == i)
total_distance += abs(target_row - init_row) + abs(target_column - init_column)
return int(total_distance)
# 计算接下来所有可能的行动带来的曼哈顿距离
def compute_manhattan_distance_all(init_state, target_state):
distances = {}
coord_cache = {}
# 获取空白方块的坐标
zero_row, zero_column = np.where(init_state == 0)
# 计算空白方块尝试往四个方向移动后产生状态的曼哈顿距离
if zero_row - 1 >= 0: # 如果空白方块在最上边则不能往上移,下面同理
up_row, up_column = zero_row - 1, zero_column
coord_cache["up"] = [up_row, up_column]
if zero_row + 1 <= 2:
down_row, down_column = zero_row + 1, zero_column
coord_cache["down"] = [down_row, down_column]
if zero_column - 1 >= 0:
left_row, left_column = zero_row, zero_column - 1
coord_cache["left"] = [left_row, left_column]
if zero_column + 1 <= 2:
right_row, right_column = zero_row, zero_column + 1
coord_cache["right"] = [right_row, right_column]
for i in coord_cache.keys(): # 移动到所有可以移动的方向,然后计算移动之后的曼哈顿距离以便接下来的贪心选择计算
temp = init_state.copy()
temp[zero_row, zero_column] = temp[coord_cache[i][0], coord_cache[i][1]]
temp[coord_cache[i][0], coord_cache[i][1]] = 0
distances[i] = compute_manhattan_distance(temp, target_state)
return distances
# 得到distances中曼哈顿距离最小的方向
def minimal_manhattan_distance(distances):
temp = copy.deepcopy(distances)
minimal_value = 1000
for i in temp.keys():
if distances[i] < minimal_value:
minimal_value = distances[i]
return minimal_value
# 根据得到的曼哈顿距离进行下一步移动
def next_move(init_state, distances):
current_state = init_state.copy()
zero_row, zero_column = np.where(current_state == 0)
# 获取移动的方向
minimal_value = 1000
key = ""
for i in distances.keys():
if distances[i] < minimal_value:
minimal_value = distances[i]
key = i
if key == "up": # 空格向上移动,下面同理
print("向上移动")
up_row, up_column = zero_row - 1, zero_column
temp = current_state[up_row, up_column]
current_state[zero_row, zero_column] = temp
current_state[up_row, up_column] = 0
if key == "down":
print("向下移动")
down_row, down_column = zero_row + 1, zero_column
temp = current_state[down_row, down_column]
current_state[zero_row, zero_column] = temp
current_state[down_row, down_column] = 0
if key == "left":
print("向左移动")
left_row, left_column = zero_row, zero_column - 1
temp = current_state[left_row, left_column]
current_state[zero_row, zero_column] = temp
current_state[left_row, left_column] = 0
if key == "right":
print("向右移动")
right_row, right_column = zero_row, zero_column + 1
temp = current_state[right_row, right_column]
current_state[zero_row, zero_column] = temp
current_state[right_row, right_column] = 0
return current_state
# 爬山算法
def climbing_algorithm():
init_state, target_state = init()
print("初始状态为:\n", init_state)
print("目标状态为:\n", target_state)
while True:
current_manhattan_distance = compute_manhattan_distance(init_state, target_state) # 计算当前状态与目标状态的曼哈顿距离
print("当前状态距离目标的曼哈顿距离为:", current_manhattan_distance)
if current_manhattan_distance == 0: # 当前状态就是目标状态,算法结束
return True
distances = compute_manhattan_distance_all(init_state, target_state) # 计算空白方块所有可以移动的方向和对应的曼哈顿值
print("distances:", distances)
print("distances里面的最小值为:", minimal_manhattan_distance(distances))
if current_manhattan_distance <= minimal_manhattan_distance(distances):
return False # 即接下来无论如何移动的曼哈顿距离都大于目前的,则陷入了局部最优解
init_state = next_move(init_state, distances)
print("移动后的新状态为:\n", init_state)
def climbing_algorithm_test(num):
tic = time.time()
success_case = 0
fail_case = 0
for i in range(num):
print("第{0}个例子启动".format(i))
if climbing_algorithm():
success_case += 1
print("第{0}个例子成功找到最优解".format(i))
else:
fail_case += 1
print("第{0}个例子失败".format(i))
toc = time.time()
print("{0}个例子中成功解决的例子为:{1}".format(num, success_case))
print("{0}个例子成功解决的百分比为:{1}".format(num, success_case / num))
print("{0}个例子中失败的例子为:{1}".format(num, fail_case))
print("{0}个例子失败的百分比为:{1}".format(num, fail_case / num))
print("{0}运行算法所需的时间为:{1}秒".format(num, toc - tic))
climbing_algorithm_test(10000)
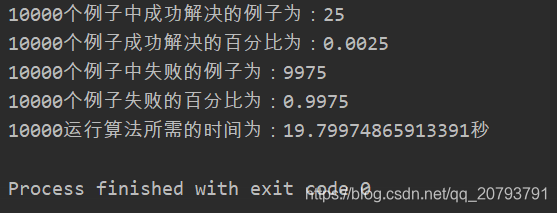
测试结果为:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)