RDS is one of AWS's core products as a managed database service that handles your data storage and workloads, it provides numerous capabilities that a relational database has with the simplicity that managed infrastructure offers.
As for 2019, you don’t have to scale up the storage capacity of your rds database because it will be added automatically, meaning that you will never have to worry about running out of database storage. however, you still need to scale up your instance type manually if you need more computing power (this is called vertical scaling).
In this article, we will be creating RDS horizontal scaling using the RDS Autoscaling policy. This feature is present in an rds cluster, not in the actual individual instance so you need to create the cluster first and then apply the policy.
Keep in mind that:
- the RDS autoscaling policy is not a service but a feature that has rules that automatically add or remove rds instances based on that rules.
- Remember to use your cluster endpoint to access the database instead of the individual database endpoint so that the DB load is divided equally between cluster instances instead of just one instance.
- An RDS cluster consists of one writer instance which is usually the largest instance and one or more readers that handles read operations from users.
- When an instance fails or becomes unreachable, another instance will take its place. if the writer failed, the existing reader with the largest instance size will take its place. If a reader fails, the Autoscaling Policy will add another reader according to the minimum number of instances in the rules.
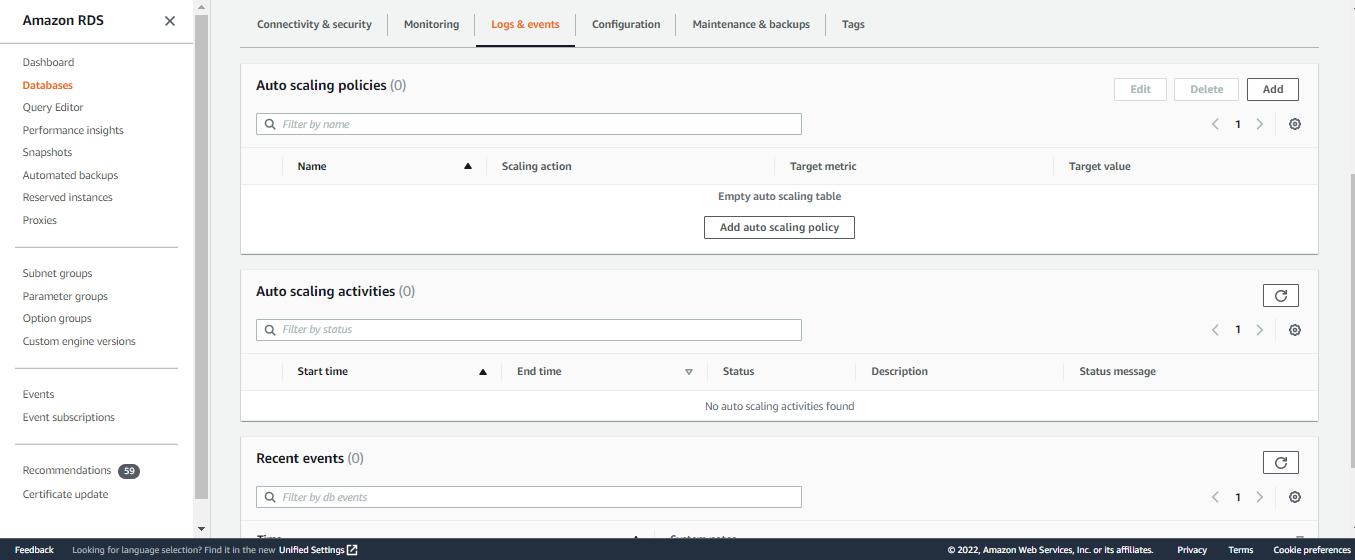
First, Choose the rds cluster that we want to use. if you haven’t you can create one using this instruction. the click on Logs & Events. then Click on add or add auto-scaling policy.
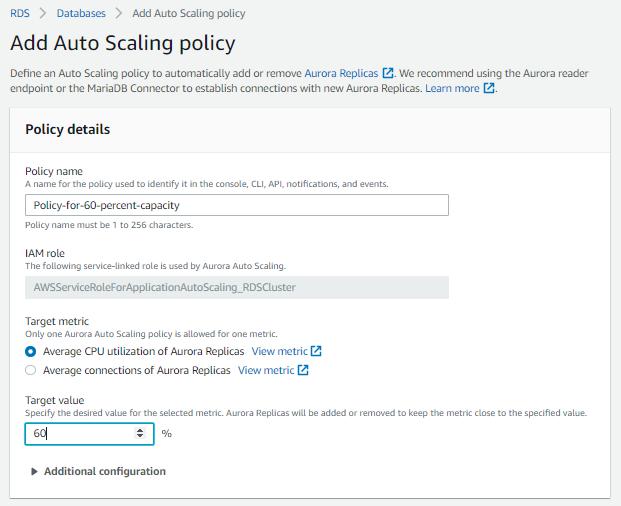
Next, fill out the Policy name whatever you like, then decide which target metric to use. in this case, I use the average CPU utilization because it is good for starter dev or prod projects where the query isn’t optimized and the number of connections was small. you can change it to average connections when the query is optimized and small but your user base grows exponentially larger.
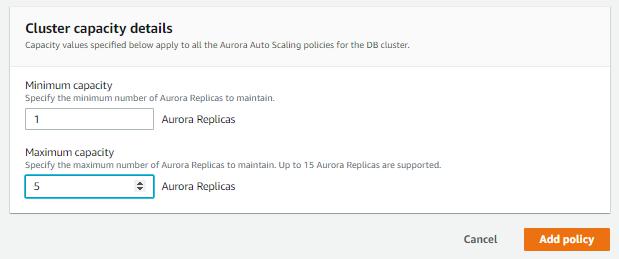
Scroll down, then decide how many replicas you need, replica refers to the number of readers you want in the cluster beside the main writer instance. this can keep my cost low which will only create one reader besides the already existing writer, then set the limit for a maximum number of reader to avoid overbudget. then click add policy.
this will create the policy for us.
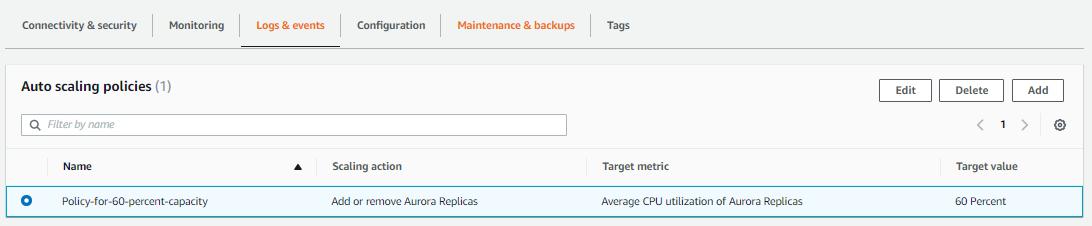
when an instance in the cluster exceeds 60% CPU utilization, the policy will create an additional reader instance with a cool down for each policy trigger. these new instances will be connected to the cluster rds endpoint and any incoming request will be load balanced between all of them.
Thank you for reading. I see you soon!








 已为社区贡献23584条内容
已为社区贡献23584条内容

所有评论(0)